What not to feed a 6 month old baby
Foods to avoid giving babies and young children
Salt
Babies should not eat much salt, as it's not good for their kidneys.
Do not add salt to your baby's food or cooking water, and do not use stock cubes or gravy, as they're often high in salt.
Remember this when you're cooking for the family if you plan to give the same food to your baby.
Avoid salty foods like:
- bacon
- sausages
- chips with added salt
- crackers
- crisps
- ready meals
- takeaways
Sugar
Your baby does not need sugar.
By avoiding sugary snacks and drinks (including fruit juice and other fruit drinks), you'll help prevent tooth decay.
Saturated fat
Do not give your child too many foods that are high in saturated fat, such as crisps, biscuits and cakes.
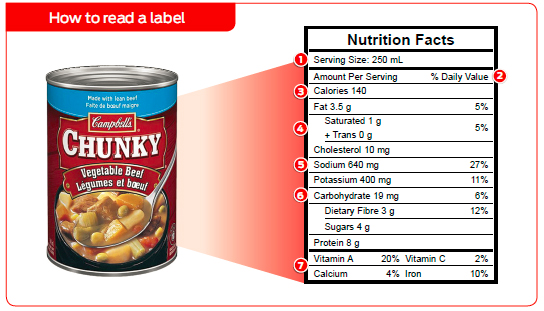
Checking the nutrition labels can help you choose foods that are lower in saturated fat.
See more on food labels.
Honey
Occasionally, honey contains bacteria that can produce toxins in a baby's intestines, leading to infant botulism, which is a very serious illness.
Do not give your child honey until they're over 1 year old. Honey is a sugar, so avoiding it will also help prevent tooth decay.
Whole nuts and peanuts
Whole nuts and peanuts should not be given to children under 5 years old, as they can choke on them.
You can give your baby nuts and peanuts from around 6 months old, as long as they're crushed, ground or a smooth nut or peanut butter.
If there's a history of food allergies or other allergies in your family, talk to your GP or health visitor before introducing nuts and peanuts.
See more on food allergies in babies and young children.
Some cheeses
Cheese can form part of a healthy, balanced diet for babies and young children, and provides calcium, protein and vitamins.
Babies can eat pasteurised full-fat cheese from 6 months old. This includes hard cheeses, such as mild cheddar cheese, cottage cheese and cream cheese.
Babies and young children should not eat mould-ripened soft cheeses, such as brie or camembert, or ripened goats' milk cheese and soft blue-veined cheese, such as roquefort. There's a higher risk that these cheeses might carry a bacteria called listeria.
There's a higher risk that these cheeses might carry a bacteria called listeria.
Many cheeses are made from unpasteurised milk. It's better to avoid these because of the risk of listeria.
You can check labels on cheeses to make sure they're made from pasteurised milk.
But these cheeses can be used as part of a cooked recipe as listeria is killed by cooking. Baked brie, for example, is a safer option.
Raw and lightly cooked eggs
Babies can have eggs from around 6 months.
If the eggs are hens' eggs and they have a red lion stamped on them, or you see a red lion with the words "British Lion Quality" on the box, it's fine for your baby to have them raw (for example, in homemade mayonnaise) or lightly cooked.
Hens' eggs that do not have the red lion mark should be cooked until both the white and yolk are solid. So should duck, goose or quail eggs.
So should duck, goose or quail eggs.
Avoid raw eggs, including uncooked cake mixture, homemade ice creams, homemade mayonnaise, or desserts that contain uncooked egg that you cannot confirm are red lion stamped.
Rice drinks
Children under 5 years old should not have rice drinks as a substitute for breast milk or infant formula (or cows' milk after 1 year old) as they may contain too much arsenic.
Arsenic is found naturally in the environment and can find its way into our food and water.
Rice tends to take up more arsenic than other grains, but this does not mean that you or your baby cannot eat rice.
In the UK, there are maximum levels of inorganic arsenic allowed in rice and rice products, and even stricter levels are set for foods intended for young children.
Do not worry if your child has already had rice drinks. There's no immediate risk to them, but it's best to switch to a different kind of milk.
There's no immediate risk to them, but it's best to switch to a different kind of milk.
Raw jelly cubes
Raw jelly cubes can be a choking hazard for babies and young children.
If you're making jelly from raw jelly cubes, make sure you always follow the manufacturers' instructions.
Raw shellfish
Raw or lightly cooked shellfish, such as mussels, clams and oysters, can increase the risk of food poisoning, so it's best not to give it to babies.
Shark, swordfish and marlin
Do not give your baby shark, swordfish or marlin. The amount of mercury in these fish can affect the development of a baby's nervous system.
Further information
For more information and advice about babies and food, see:
- food allergies in babies and young children
- your baby's first solid foods
- baby and toddler meal ideas
Your baby's first solid foods
When to start introducing solid foods
Introducing your baby to solid foods, sometimes called complementary feeding or weaning, should start when your baby is around 6 months old.
At the beginning, how much your baby eats is less important than getting them used to the idea of eating.
They'll still be getting most of their energy and nutrients from breast milk or first infant formula.
Giving your baby a variety of foods, alongside breast or formula milk, from around 6 months of age will help set your child up for a lifetime of healthier eating.
Gradually, you'll be able to increase the amount and variety of food your baby eats until they can eat the same foods as the rest of the family, in smaller portions.
If your baby was born prematurely, ask your health visitor or GP for advice on when to start introducing solid foods.
Why wait until around 6 months to introduce solids?
It’s a good idea to wait until around 6 months before introducing solid foods because:
- breast milk or first infant formula provide the energy and nutrients your baby needs until they're around 6 months old (with the exception of vitamin D in some cases)
- if you're breastfeeding, feeding only breast milk up to around 6 months of age will help protect your baby against illness and infections
- waiting until around 6 months gives your baby time to develop so they can cope fully with solid foods – this includes solid foods made into purées, cereals and baby rice added to milk
- your baby will be more able to feed themselves
- your baby will be better at moving food around their mouth, chewing and swallowing it – this may mean they'll be able to progress to a range of tastes and textures (such as mashed, lumpy and finger foods) more quickly, and may not need smooth, blended foods at all
Signs your baby is ready for solid foods
There are 3 clear signs which, when they appear together from around 6 months of age, show your baby is ready for their first solid foods alongside breast milk or first infant formula.
They'll be able to:
- stay in a sitting position and hold their head steady
- co-ordinate their eyes, hands and mouth so they can look at the food, pick it up and put it in their mouth by themselves
- swallow food (rather than spit it back out)
The following behaviours can be mistaken by parents as signs that their baby is ready for solid foods:
- chewing their fists
- waking up in the night (more than usual)
- wanting extra milk feeds
These are all normal behaviours for babies and not necessarily a sign that they're hungry or ready to start solid food.
Starting solid foods will not make your baby any more likely to sleep through the night. Sometimes a little extra milk will help until they're ready for solid foods.
Get tips to help your baby sleep well
How to start solid foods
In the beginning your baby will only need a small amount of food before their usual milk feed.
Do not worry about how much they eat. The most important thing is getting them used to new tastes and textures, and learning how to move solid foods around their mouths and how to swallow them.
They'll still be getting most of their energy and nutrients from breast milk or infant formula.
There are some foods to avoid giving to your baby. For example, do not add sugar or salt (including stock cubes and gravy) to your baby's food or cooking water.
Babies should not eat salty foods as it's not good for their kidneys, and sugar can cause tooth decay.
Tips to get your baby off to a good start with solid foods:
- Eating is a whole new skill.
 Some babies learn to accept new foods and textures more quickly than others. Keep trying, and give your baby lots of encouragement and praise.
Some babies learn to accept new foods and textures more quickly than others. Keep trying, and give your baby lots of encouragement and praise. - Allow plenty of time, especially at first.
- Go at your baby's pace and let them show you when they're hungry or full. Stop when your baby shows signs that they've had enough. This could be firmly closing their mouth or turning their head away. If you're using a spoon, wait for your baby to open their mouth before you offer the food. Do not force your baby to eat. Wait until the next time if they're not interested this time.
- Be patient and keep offering a variety of foods, even the ones they do not seem to like. It may take 10 tries or more for your baby to get used to new foods, flavours and textures. There will be days when they eat more, some when they eat less, and then days when they reject everything. Do not worry, this is perfectly normal.
- Let your baby enjoy touching and holding the food.
 Allow them to feed themselves, using their fingers, as soon as they show an interest. If you're using a spoon, your baby may like to hold it or another spoon to try feeding themselves.
Allow them to feed themselves, using their fingers, as soon as they show an interest. If you're using a spoon, your baby may like to hold it or another spoon to try feeding themselves. - Keep distractions to a minimum during mealtimes and avoid sitting your baby in front of the television, phone or tablet.
- Show them how you eat. Babies copy their parents and other children. Sit down together for family mealtimes as much as possible.
Texture progression
Once you've started introducing solid foods from around 6 months of age, try to move your baby on from puréed or blended foods to mashed, lumpy or finger foods as soon as they can manage them.
This helps them learn how to chew, move solid food around their mouth and swallow.
Some babies like to start with mashed, lumpy or finger foods.
Other babies need a little longer to get used to new textures, so may prefer smooth or blended foods on a spoon at first.
Just keep offering them lumpy textures and they'll eventually get used to it.
Safety and hygiene
When introducing your baby to solid foods, it's important to take extra care to not put them at risk.
Key food safety and hygiene advice:
- always wash your hands before preparing food and keep surfaces clean
- cool hot food and test it before giving it to your baby
- wash and peel fruit and raw vegetables
- avoid hard foods like whole nuts, or raw carrot or apple
- remove hard pips and stones from fruits, and bones from meat or fish
- cut small, round foods, like grapes and cherry tomatoes, into small pieces
- eggs produced under the British Lion Code of Practice (stamped with the red lion) are considered very low risk for salmonella and safe for babies to eat partially cooked
Always stay with your baby when they're eating in case they start to choke.
Choking is different from gagging. Your baby may gag when you introduce solid foods.
This is because they're learning how to deal with solid foods and regulate the amount of food they can manage to chew and swallow at one time.
If your baby is gagging:
- their eyes may water
- they might push their tongue forward (or out of their mouth)
- they might retch to bring the food forward in their mouth or vomit
Equipment checklist
- High chair. Your baby needs to be sitting safely in an upright position (so they can swallow properly). Always use a securely fitted safety harness in a high chair. Never leave babies unattended on raised surfaces.
- Plastic or pelican bibs. It's going to be messy at first!
- Soft weaning spoons are gentler on your baby's gums.

- Small plastic bowl. You may find it useful to get a special weaning bowl with a suction base to keep the bowl in place.
- First cup. Introduce a cup from around 6 months and offer sips of water with meals. Using an open cup or a free-flow cup without a valve will help your baby learn to sip and is better for their teeth.
- A messy mat or newspaper sheets under the high chair to catch most of the mess.
- Plastic containers and ice cube trays can be helpful for batch cooking and freezing small portions.
Find out more:
- tips to help your baby enjoy new foods
- children's food: safety and hygiene
- foods to avoid giving babies and young children
- how to stop a child from choking
- baby and toddler safety
Feeding your baby: from 0 to 6 months
Breast milk is the best food your baby can have during their first 6 months of life.
It's free, always available and at the perfect temperature, and is tailor-made for your baby.
First infant formula is the only suitable alternative if you do not breastfeed or choose to supplement breast milk.
Other milks or milk substitutes, including cows' milk, should not be introduced as a main drink until 12 months of age.
"Follow-on" formula is not suitable for babies under 6 months, and you do not need to introduce it after 6 months.
Babies do not need baby rice to help them move to solid foods or sleep better.
When using a bottle, do not put anything (such as sugar or cereals) in it other than breast milk or infant formula.
Vitamins for babies
It's recommended that breastfed babies are given a daily supplement containing 8.5 to 10 micrograms (µg) of vitamin D from birth, whether or not you're taking a supplement containing vitamin D yourself.
Babies having 500mls (about a pint) or more of formula a day should not be given vitamin supplements.
This is because formula is fortified with vitamin D and other nutrients.
All children aged 6 months to 5 years should be given vitamin supplements containing vitamins A, C and D every day.
Find out more:
- benefits of breastfeeding
- how to make up baby formula
- vitamins for children
Feeding your baby: from around 6 months
When they first start having solid foods, babies do not need 3 meals a day. Babies have tiny tummies, so start by offering them small amounts of food (just a few pieces, or teaspoons of food).
Pick a time that suits you both, when you do not feel rushed and your baby is not too tired.
Start offering them food before their usual milk feed as they might not be interested if they're full, but do not wait until your baby is too hungry.
Allow plenty of time and let your baby go at their own pace.
Keep offering different foods, even foods your baby has already rejected.
It can take 10 tries or more before your baby will accept a new food or texture, particularly as they get older.
Your baby will still be getting most of their energy and nutrients from breast milk or first infant formula.
Breast milk or infant formula should be their main drink during the first year. Do not give them whole cows' (or goats' or sheep's) milk as a drink until they're 1 year old.
You can continue breastfeeding for as long as you both want.
Introduce a cup from around 6 months and offer sips of water with meals. Using an open cup or a free-flow cup without a valve will help your baby learn to sip and is better for their teeth.
Using an open cup or a free-flow cup without a valve will help your baby learn to sip and is better for their teeth.
First foods
You might want to start with single vegetables and fruits.
Try mashed or soft cooked sticks of parsnip, broccoli, potato, yam, sweet potato, carrot, apple or pear.
Include vegetables that are not sweet, such as broccoli, cauliflower and spinach.
This will help your baby get used to a range of flavours (rather than just the sweeter ones, like carrots and sweet potato) and might help prevent them being fussy eaters as they grow up.
Make sure any cooked food has cooled right down before offering it to your baby.
Foods containing allergens (such as peanuts, hens' eggs, gluten and fish) can be introduced from around 6 months of age, 1 at a time and in small amounts so you can spot any reaction.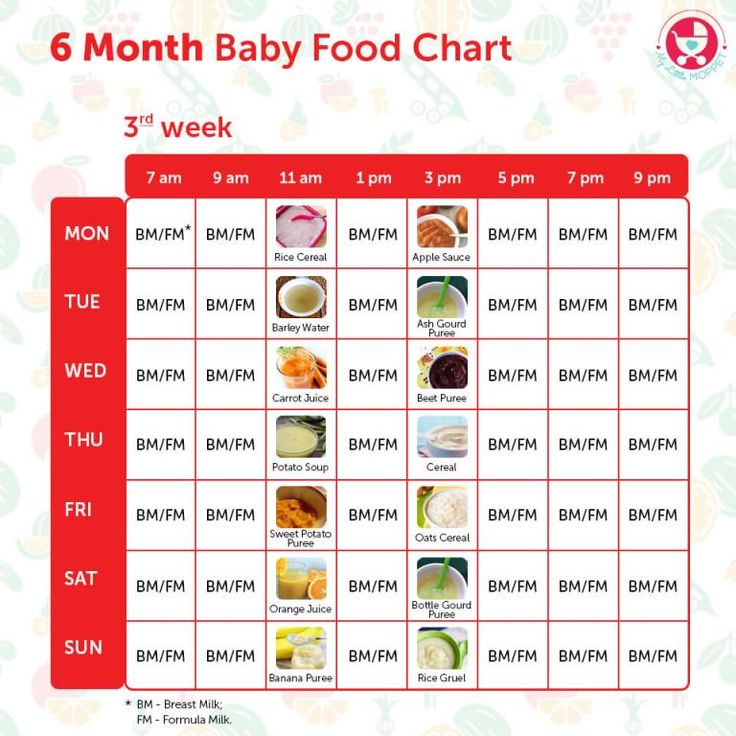
Cows' milk can be used in cooking or mixed with food from around 6 months of age, but should not be given as a drink until your baby is 1 year old.
Full-fat dairy products, such as pasteurised cheese and plain yoghurt or fromage frais, can be given from around 6 months of age. Choose products with no added sugar.
Remember, babies do not need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water).
Finger foods
As soon as your baby starts solid foods, encourage them to be involved in mealtimes and have fun touching, holding and exploring food.
Let them feed themselves with their fingers when they want to. This helps develop fine motor skills and hand-eye co-ordination.
Your baby can show you how much they want to eat, and it gets them familiar with different types and textures of food.
Offering your baby finger foods at each meal is a good way to help them learn to self-feed.
Finger food is food that's cut up into pieces big enough for your baby to hold in their fist with a bit sticking out.
Pieces about the size of your own finger work well.
Start off with finger foods that break up easily in their mouth and are long enough for them to grip.
Avoid hard food, such as whole nuts or raw carrots and apples, to reduce the risk of choking.
Examples of finger foods include:
- soft cooked vegetables, such as carrot, broccoli, cauliflower, parsnip, butternut squash
- fruit (soft, or cooked without adding sugar), such as apple, pear, peach, melon, banana
- grabbable bits of avocado
- cooked starchy foods, such as potato, sweet potato, cassava, pasta, noodles, chapatti, rice
- pulses, such as beans and lentils
- fish without bones
- hardboiled eggs
- meat without bones, such as chicken and lamb
- sticks of pasteurised full-fat hard cheese (choose lower salt options)
Baby-led weaning
Baby-led weaning means giving your baby only finger foods and letting them feed themselves from the start instead of feeding them puréed or mashed food on a spoon.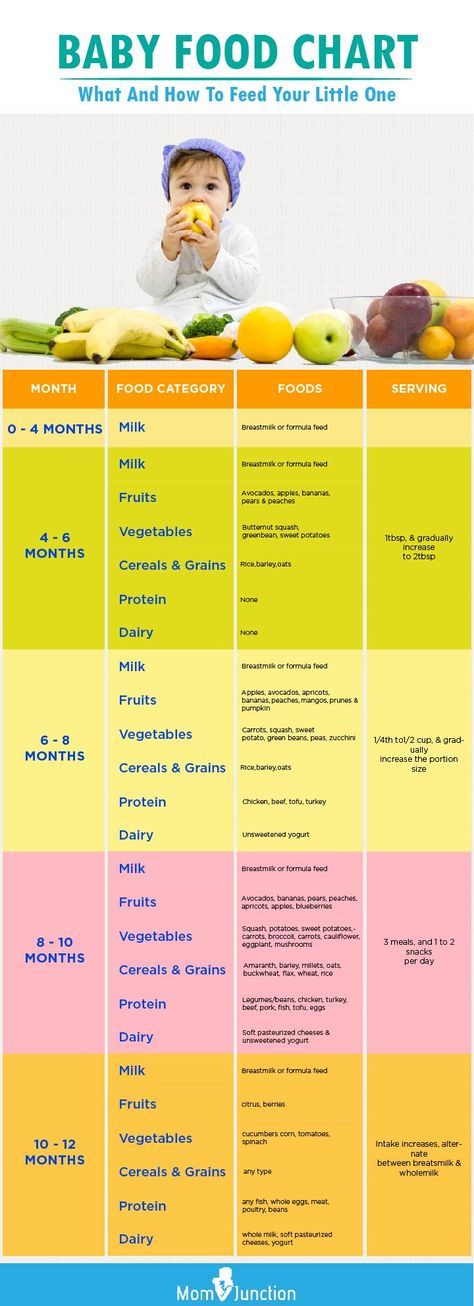
Some parents prefer baby-led weaning to spoon feeding, while others do a combination of both.
There's no right or wrong way. The most important thing is that your baby eats a wide variety of food and gets all the nutrients they need.
There's no more risk of choking when a baby feeds themselves than when they're fed with a spoon.
Find out more:
- help your baby enjoy new foods
- drinks and cups for babies and young children
- food allergies in babies and young children
- foods to avoid giving babies and young children
Feeding your baby: from 7 to 9 months
From about 7 months, your baby will gradually move towards eating 3 meals a day (breakfast, lunch and tea), in addition to their usual milk feeds, which may be around 4 a day (for example, on waking, after lunch, after tea and before bed).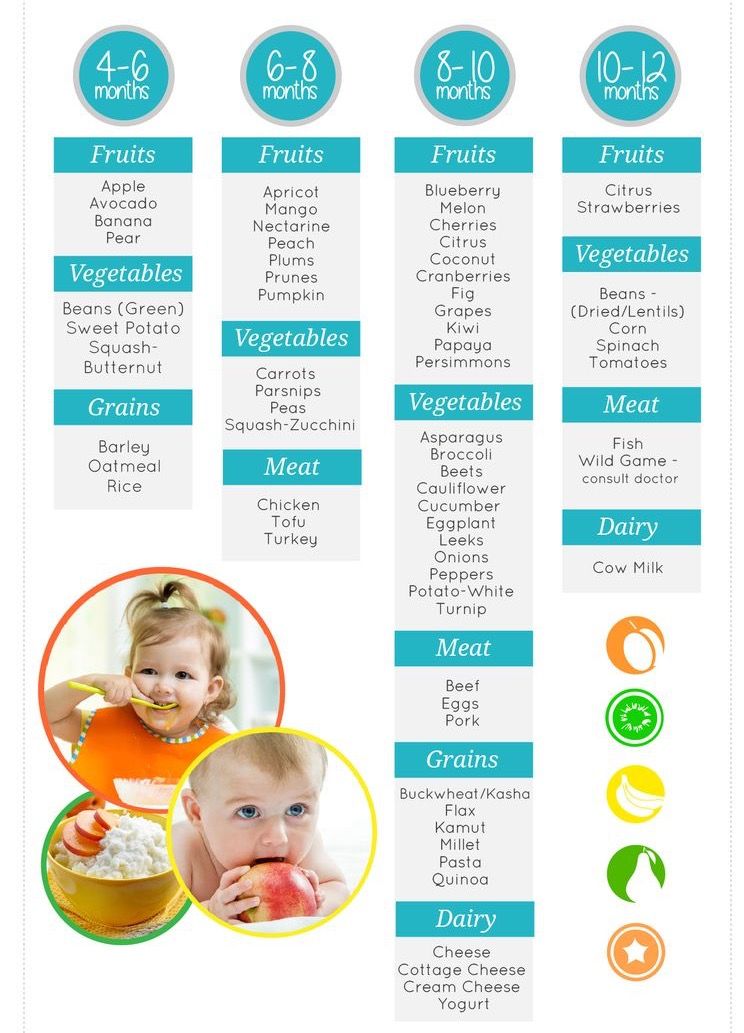
As your baby eats more solid foods, they may want less milk at each feed or even drop a milk feed altogether.
If you're breastfeeding, your baby will adapt their feeds according to how much food they're having.
As a guide, formula-fed babies may need around 600ml of milk a day.
Gradually increase the amount and variety of food your baby is offered to ensure they get the energy and nutrients they need.
Try to include food that contains iron, such as meat, fish, fortified breakfast cereals, dark green vegetables, beans and lentils, at each meal.
Your baby's diet should consist of a variety of the following:
- fruit and vegetables, including ones with bitter flavours, such as broccoli, cauliflower, spinach and cabbage
- potatoes, bread, rice, pasta and other starchy foods
- beans, pulses, fish, eggs, meat and other non-dairy sources of protein
- pasteurised full-fat dairy products, such as plain yoghurt and cheese (choose lower salt options)
As your baby becomes a more confident eater, remember to offer them more mashed, lumpy and finger foods.
Providing finger foods as part of each meal helps encourage infants to feed themselves, develop hand and eye co-ordination, and learn to bite off, chew and swallow pieces of soft food.
Remember, babies do not need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water).
Feeding your baby: from 10 to 12 months
From about 10 months, your baby should now be having 3 meals a day (breakfast, lunch and tea), in addition to their usual milk feeds.
Around this age, your baby may have about 3 milk feeds a day (for instance, after breakfast, after lunch and before bed).
Breastfed babies will adapt their milk consumption as their food intake changes.
As a guide, babies fed infant formula will drink about 400ml daily.
Remember that formula-fed babies should take a vitamin D supplement if they're having less than 500ml of formula a day.
All breastfed babies should take a vitamin D supplement.
By now, your baby should be enjoying a wide range of tastes and textures.
They should be able to manage a wider range of finger foods, and be able to pick up small pieces of food and move them to their mouth. They'll use a cup with more confidence.
Lunches and teas can include a main course, and a fruit or unsweetened dairy-based dessert, to move eating patterns closer to those of children over 1 year.
As your baby grows, eating together as a family encourages them to develop good eating habits.
Remember, babies do not need salt or sugar added to their food (or cooking water).
Feeding your baby: from 12 months
From 12 months, your child will be eating 3 meals a day containing a variety of different foods, including:
- a minimum of 4 servings a day of starchy food, such as potatoes, bread and rice
- a minimum of 4 servings a day of fruit and vegetables
- a minimum of 350ml milk or 2 servings of dairy products (or alternatives)
- a minimum of 1 serving a day of protein from animal sources (meat, fish and eggs) or 2 from vegetable sources (dhal, beans, chickpeas and lentils)
Your child may also need 2 healthy snacks in between meals.
Go for things like:
- fresh fruits, such as apple, banana or small pieces of soft, ripe, peeled pear or peach
- cooked or raw vegetable, such as broccoli florets, carrot sticks or cucumber sticks
- pasteurised plain full-fat yoghurt
- sticks of cheese (choose a lower salt option)
- toast, pitta or chapatti fingers
- unsalted and unsweetened rice or corn cakes
The World Health Organization recommends that all babies are breastfed for up to 2 years or longer.
You can keep breastfeeding for as long as it suits you both, but your child will need less breast milk to make room for more foods.
Once your child is 12 months old, infant formula is not needed and toddler milks, growing-up milks and goodnight milks are also unnecessary.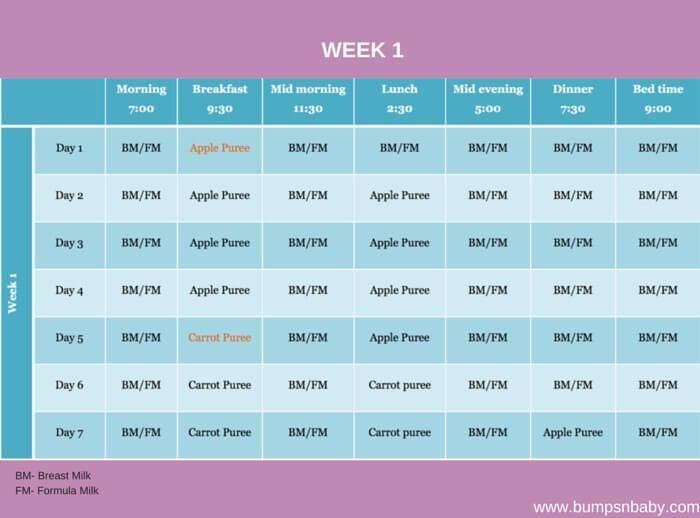
Your baby can now drink whole cows' milk. Choose full-fat dairy products, as children under 2 years old need the vitamins and extra energy found in them.
From 2 years old, if they're a good eater and growing well, they can have semi-skimmed milk.
From 5 years old, 1% fat and skimmed milk is OK.
You can give your child unsweetened calcium-fortified milk alternatives, such as soya, oat or almond drinks, from the age of 1 as part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Children under 5 years old should not be given rice drinks because of the levels of arsenic in these products.
Find out more:
- what to feed young children
- foods to avoid giving babies and young children
- drinks and cups for babies and young children
- vitamins for children
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
For information and advice you can trust, sign up for weekly Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails.
diet for a 6-month-old baby with breast and artificial feeding, an approximate menu for a week in the table, a diet for a day
Published: 02/10/2021
Reading time: 4 min.
Number of reads: 222293
Author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences, allergist-immunologist
Changes in a child in the first year of life are very rapid, and each month is not like another. The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different.
Content: Hide
- The first feeding of 6 months
- The start of complementary foods in 4-5 months
- The second half of life
- for a week for a child at 6 months
The first lure of 6 months
If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
However, the rate of expansion of the child's diet in this situation will be accelerated. Before the 8th month of life, it is necessary to introduce all basic food groups into the baby’s menu, since in the second half of the year the need for additional intake of nutrients and micronutrients is very high. Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
Complementary feeding starts at 4-5 months
In today's life, the nutrition of a nursing mother, unfortunately, is not always complete. Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions.
If a child is bottle-fed, then by the 4th month of life, the baby will not have enough adapted formula alone, and in this group of children, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods usually shifts a month earlier than in breast-fed babies. Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture.
Fruit puree and juice can be another possible complementary food for children under 6 months of age without allergy symptoms. In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month.
In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month.
Second six months of life
Children over 6 months of age can supplement their diet with cereals containing gluten. First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
From the age of 6 months, the baby's diet is expanded with such important products as meat and cottage cheese. These products are a source of high-quality protein, fats, and are also rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and phosphorus. Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals).
To enrich the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids in the second half of the year, the menu includes vegetable oil in the amount of 3–5 grams per day, which can be added to the complementary food dish. The volume of each feeding is approximately 150-170 ml, and the child can already stand up to 3.5 hours between meals.
In the table below, we offer a menu of 6 months for a week for a child who started receiving complementary foods at the age of 4-5 months, and by the time the second half of life begins, dairy-free gluten-free cereals, vegetable and fruit purees have already been introduced into his diet.
1st day
| Meeting | menu | ml/g |
| Breast milk/mixture | 150 | 50 |
| Lunch (12.30) | Vegetable soup with beef, olive oil | 100/30/3 | 9 9006 900 66 9 |
Afternoon snack (16.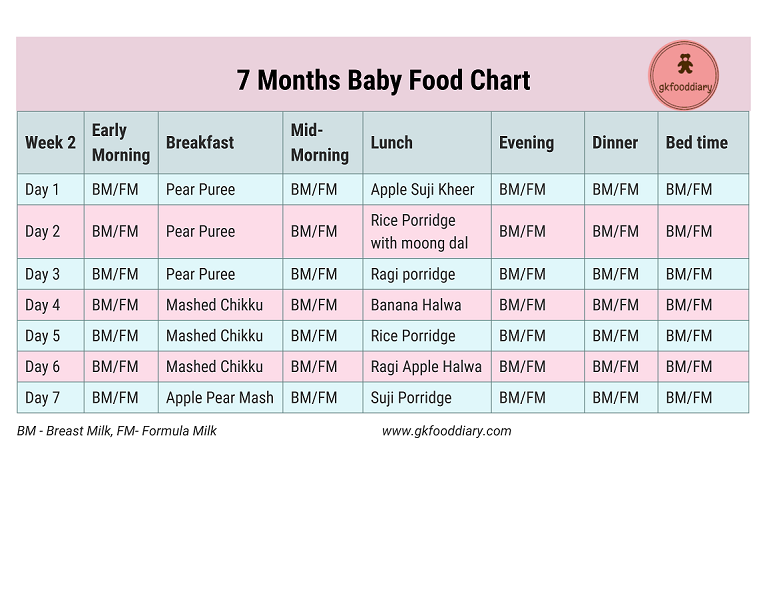 00) 00) | Plum puree with cottage cheese | 60/40 |
| Breast milk/formula | 60 066 | |
| Lunch (12.30) | soup puree made of cauliflower and broccoli, olive oil | 80/3 |
| souffle from meat of rabbits | ||
| Afternoon snack (16.00) | Milk porridge “Delicious afternoon snack with Bebi Premium biscuits and pears” | 100 | 9007 1
| food intake | menu | ml/g |
| Early morning | breast milk/mixture | 150 | COMLACE (09) cherry Bebi Premium» | 100 |
| 0065 Breast milk/mixture | 150 | |
| children's soluble cookies "BEBIKI" Classic | ||
| Bebi Premium Kids Instant Herbal Tea | 50 | |
| Bedtime 065 Breast milk/formula | 150 | |
Rate the article
(Number of votes: 23, average 4. 8)
8)
Share with friends:
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food.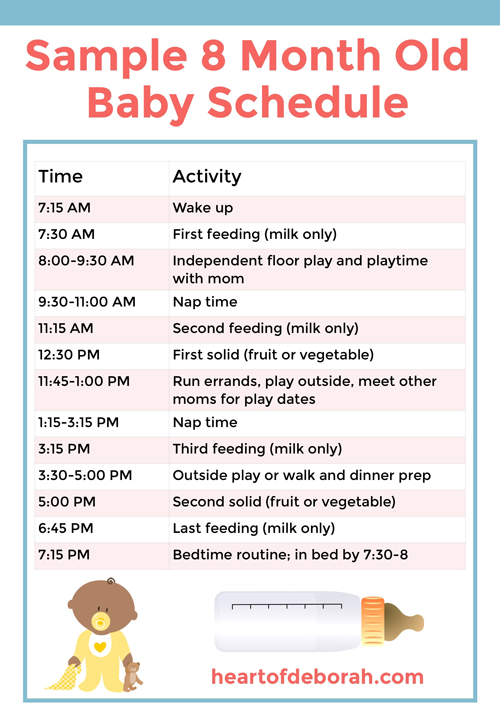 And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary food is introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.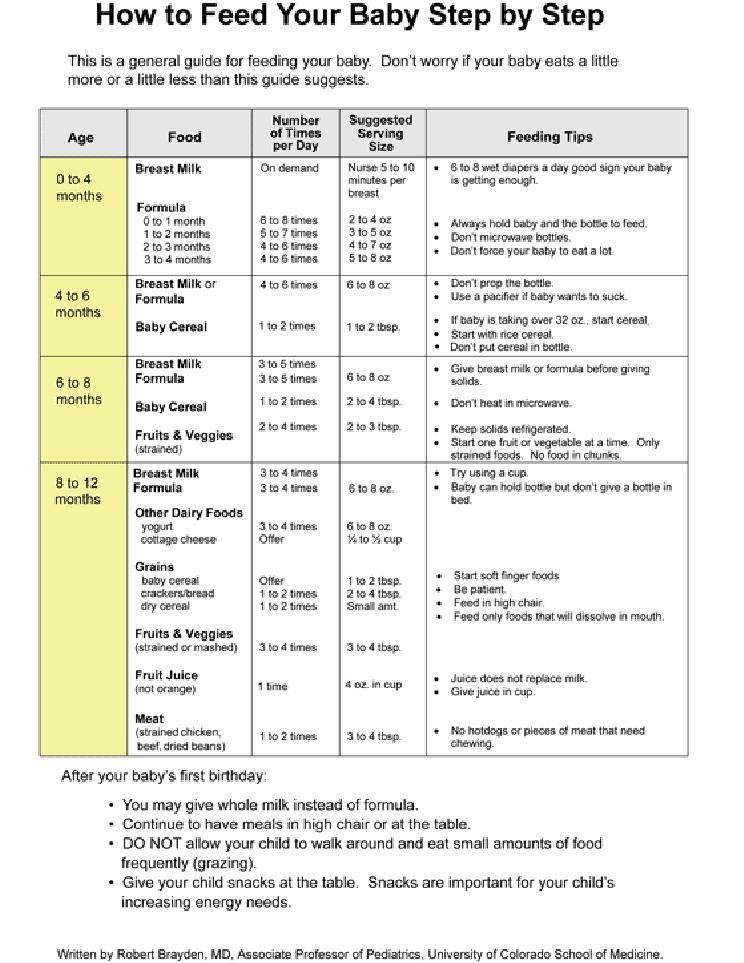
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- new products are not introduced in the event of acute illnesses, and before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually "dilute" this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml | |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.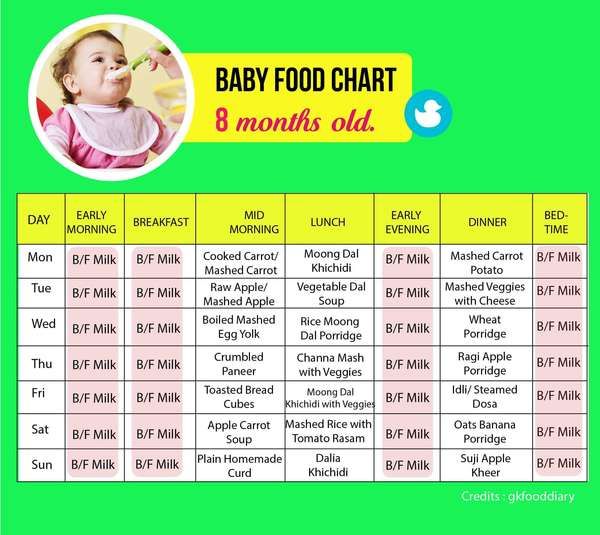
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI 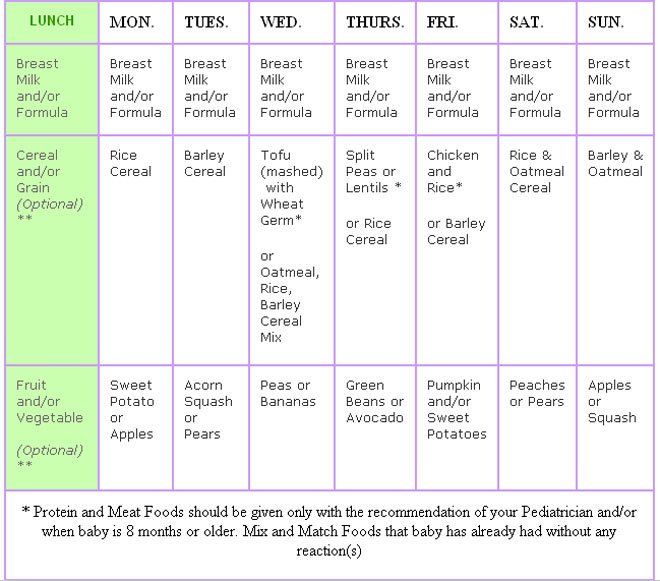
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk