What to do if baby burns mouth on food
How to treat a burn on the roof of the mouth
Burning the roof of the mouth is a common problem. Some natural remedies for minor burns include yogurt, milk, aloe vera gel, and honey. Severe burns may require medical treatment.
In this article, we look at some natural remedies for burns on the roof of the mouth. We also describe how to help prevent burns in the mouth and when to contact a doctor.
A person’s mouth contains delicate tissues that are susceptible to burns. Consuming hot foods or drinks can scald the roof of the mouth and cause superficial burns, also known as first degree burns.
First degree burns are the most minor form of burn and often do not require medical treatment. They commonly occur when a heat source damages the top layer of a person’s skin. Sun exposure and electrical currents are also common causes of first degree burns.
Burns can damage tissue and kill skin cells. As the roof of the mouth heals, the dead cells will fall away and reveal new cells underneath. New skin can be tender initially, though it will quickly toughen up. A first degree burn takes around 1 week to heal.
If a person has a first degree burn, they can typically treat it at home. Taking immediate steps can limit the damage, and natural remedies can promote healing and help prevent infection.
Cool water
Taking immediate action after burning the roof of the mouth can curb the extent of the damage. Immediately cooling the area can help prevent the burn from affecting the inner layers of the skin.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that anyone who experiences a burn submerges the area in cold water for at least 10 minutes.
When the burn is in the mouth, a person can fill their mouth with cold water. When the water is no longer cool, spit it out and replace it. People should avoid using ice to soothe a burn, as it can stick to the skin and cause further pain and damage.
Yogurt or milk
Milk proteins can assist in wound healing, according to a 2021 review. However, many studies assessing their efficacy used concentrated topical solutions rather than applying pure milk.
However, many studies assessing their efficacy used concentrated topical solutions rather than applying pure milk.
People may still find eating some cool natural yogurt or drinking a glass of milk may help ease the discomfort of a mouth burn.
Aloe vera
The topical application of aloe vera can help treat various wounds, including burns. Plant compounds in aloe vera can reduce inflammation and discomfort, retain skin moisture, and promote healing responses.
However, the consumption of aloe vera can lower blood sugar. This means oral application may not be suitable for some people, such those with diabetes.
Honey
Honey can help a burn on the roof of the mouth to heal. Gently coating the burn with honey keeps it moist, which can help with healing.
Some research suggests that honey has antimicrobial properties. This means that it may kill harmful organisms or slow their growth, helping prevent infection and speed up the healing process.
Saltwater rinse
One of the skin’s essential jobs is to be a barrier against infection. Damage to the skin, such as burns, can make it vulnerable to infection.
Damage to the skin, such as burns, can make it vulnerable to infection.
Washing wounds with a saline or saltwater solution is an effective way to clean wounds at home. To clean burns to the roof of the mouth, a person can rinse their mouth with a saltwater solution.
A person can make a saltwater mouth rinse at home by:
- warming some water
- stirring in a one-quarter teaspoon of table salt
- swishing the mixture around the mouth then spitting it out
Learn more about saltwater rinses here.
Look after the skin
As the skin heals, the area may be delicate and sore. Minimizing interference with the wound or the new skin forming beneath it can help the natural healing process.
Some simple steps to protect the healing skin include:
- being gentle when brushing the teeth
- refraining from wearing a mouth guard until the area has healed
- avoiding picking at loose skin
- avoiding hot drinks until the burn heals
Doctors classify burns by the amount of damage they cause. More severe burns affect deeper layers of skin, while minor burns cause only superficial damage.
More severe burns affect deeper layers of skin, while minor burns cause only superficial damage.
- First degree burn: This type of burn affects the uppermost skin layer, the epidermis.
- Second degree burn: This type of burn damages the epidermis and the lower layer of skin, the dermis.
- Third degree burn: This type of burns destroys the epidermis and dermis. It also damages subcutaneous tissue, a layer of fat, connective tissue, and blood vessels beneath the skin.
The following table details common burn symptoms by degree.
| Burn degree | Tissue damage | Pain | Swelling | Blisters | Nerve damage | Blood vessel damage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| first | x | x | x | |||
| second | x | x | x | x | ||
| third | x | x | x | x | x | x |
Learn more about the different types of burn here.
If a child burns the roof of their mouth, their parent or caregiver should provide immediate treatment as they would to themselves.
For first degree burns, helping the child soothe the area with cool water and providing paracetamol and ibuprofen may help reduce pain.
If a parent or caregiver suspects second or third degree burns, they should seek emergency assistance immediately.
Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) can cause a burning sensation without heat damage.
There are two types of BMS.
Primary BMS
Primary BMS occurs without an underlying medical condition or outside causes. It may be the result of nerve damage in the mouth.
Secondary BMS
A person may experience a burning sensation in their mouth as a side effect of another condition or medication. This is secondary BMS.
Causes of secondary BMS include:
- allergies
- depression
- difficulty maintaining oral hygiene
- acid reflux
- infection
- nutritional deficiencies
Learn more about burning mouth syndrome here.
A person can treat most burns on the roof of the mouth at home. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help reduce inflammation and pain.
An individual may have a first, second, or third degree burn. People with second or third degree burns should seek urgent medical attention.
A person may also need treatment if the wound becomes infected. Signs of infection include:
- fever
- discoloration around the burn
- swelling around the wound that does not go away
- lasting pain
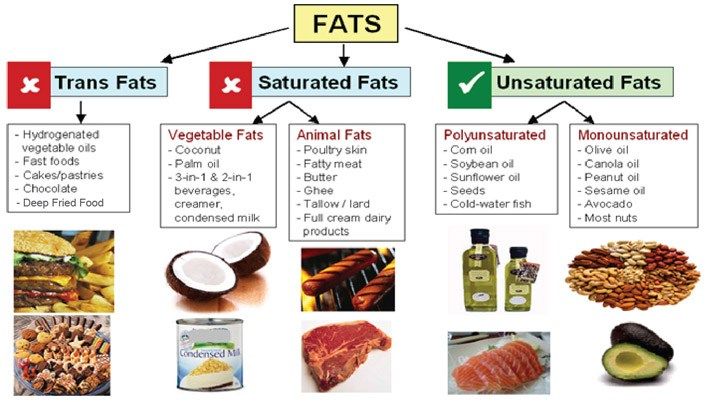
Being aware of foods that hold heat for long periods can help prevent burns. Oils, fats, and liquids can reach and hold very high temperatures.
Waiting until foods and drinks have cooled can help prevent burns on the roof of the mouth.
Parents and caregivers may wish to test the temperature of food before giving it to a child. They could also teach children to do the same, and to gently blow on their food to cool it before eating.
Hot foods and drinks can cause burns to the roof of the mouth. These are often superficial, and a person can typically treat them with home remedies. These include soothing with cool water, applying honey or aloe vera to the affected area, and rinsing with a saline solution.
These are often superficial, and a person can typically treat them with home remedies. These include soothing with cool water, applying honey or aloe vera to the affected area, and rinsing with a saline solution.
People should seek medical assistance if their burn causes significant pain, blisters, or becomes infected.
My Baby Burned His Tongue, Now What? Pediatricians Explain
Life
Shutterstock
by Abi Berwager Schreier
My kid’s favorite food is a big pile of steamed green beans, for which I’m thankful. A couple of weeks ago, I apparently didn’t cool them off enough before putting said beans on his tray. He of course dove right in and grabbed a huge handful and shoved them in his mouth. His eyes got so wide and he spit them all over the tray and started bouncing up and down. I have never felt like more of a jerk in my entire life. My baby burned his tongue, and now what? I felt like the worst mom on the planet and was also slightly concerned he would no longer consider green beans his favorite food since they betrayed him.
My baby burned his tongue, and now what? I felt like the worst mom on the planet and was also slightly concerned he would no longer consider green beans his favorite food since they betrayed him.
I asked Dr. Robert Hamilton, a pediatrician at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica, California, and author of 7 Secrets of the Newborn, what to do when your baby burns their tongue. He tells Romper in an email interview, "Comfort your child in your arms. Every child will cry out in pain, and a good start in alleviating the trauma of a burned tongue is a loving and empathetic embrace from a parent." Next, Hamilton suggests giving your child a cool drink as soon as possible, and if they're not old enough to choke, allow them to suck on ice chips. Dr. Gina Posner, a pediatrician at MemorialCare Orange Coast Medical Center in Fountain Valley, California, says for a baby, "milk and formula can help soothe a burned tongue. Popsicles will work too depending on the age of the baby — I would say 7 or 8 months or older. You can also use the mesh sacks and put some ice in them and let the baby suck on that."
You can also use the mesh sacks and put some ice in them and let the baby suck on that."
For slightly older children who burn their tongue, Hamilton says, "Have your child swish the tongue with a diluted salt water solution (1/8 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of water), and avoid giving them any more overly warm hot foods or drinks." Worst-case scenario, you can always give your child liquid Tylenol and/or Motrin (Advil) to alleviate pain or even use Chloraseptic spray, which has a numbing, analgesic, on the tissue and will help mollify pain, he adds.
As for when you need to seek medical attention, Posner says, "If the burn looks deep, seek medical attention immediately. The good news is that tongues typically heal very quickly, but if you are ever worried, don’t hesitate to have the baby be seen by a pediatrician."
To avoid this situation, Posner suggests always testing your baby's food manually before giving it to them. "Hard boiled eggs, or anything thick for that matter, can get very hot, so always open it and let it cool down before feeding your baby. Another food that can be deceptively hot is melted cheese."
Another food that can be deceptively hot is melted cheese."
So make sure you test and retest all the food you give your baby before they shove it in their mouths. And luckily, they'll just need some additional cuddles, something cold, and maybe a popsicle to make them feel better. Always check with your pediatrician if you're really worried, or if they don't seem to find relief from what you're doing at home. P.S. you're not the worst mom ever.
The child is burned. What to do? | Nutrilak
Published: 01/16/2023
Reading time: 6 min
460
Distinguish burns thermal, chemical, radiation (radiation), electrical (in case of electrical injury).
In the home, burns are common as a result of exposure to high temperatures. Various objects can serve as heat carriers: food, water (including steam), open fire and heating objects (batteries, stoves, irons, etc.).
The most common burns are children under 5 years of age, so it is important to observe safety precautions when handling fire and its sources at home in order to prevent children from coming into contact with them.
In case of burns, not only the skin and mucous membranes, but also the underlying tissues can be damaged. The area and depth of the lesion determine the severity of the damage.
Burns are classified according to degrees:
| Degree | Damaged structures | Damage description | Recovery period | Consequences (tissue defects) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 degree | only superficial layers of skin and mucous membranes | redness | 2-3 days | no |
| | | thin-walled vials with clear contents | up to 10 days | temporary depigmentation |
| Grade 2 | Deeper layers are also involved, derivatives of the skin | blisters have thick walls and opaque contents, dead tissue is visible | 18-21 days | depigmentation and scars |
| Grade 3 | all layers of the skin and underlying tissues (fat, muscle, bone) | eschar, very deep wounds, tissue severely damaged | long | depigmentation, scars and cicatricial deformities |
Fortunately, 80% of burns are superficial and do not require hospitalization.
Basic principles of first aid for thermal injuries:
- Interrupt exposure to heat source
- Reduce pain by cooling with water (at least 15 minutes)
Baby burned with formula
This happens in two cases: heating the finished formula in a microwave oven (when heating is uneven) and violation of the formula preparation technology using too hot water (above 45C).
This is important!
If the child quickly calmed down and did not refuse the mixture of water offered to him, then there is no reason for great concern and seeking medical help.
If, after contact with formula, the child is difficult to calm down, there is a hoarse voice, coughing or vomiting, immediately call an emergency room or go to the hospital yourself.
A specific feature of mixture burns is the localization of lesions: the palate, the root of the tongue and the pharynx. This complicates the diagnosis and limits our ability to provide assistance at home: rinsing and applications are excluded, sprays and aerosols are contraindicated. In addition, due to early age, there is a risk of developing mucosal edema with a further violation of the airway. Therefore, seek medical help immediately!
In addition, due to early age, there is a risk of developing mucosal edema with a further violation of the airway. Therefore, seek medical help immediately!
First aid - cool (not icy) water, offer it. But the probability of refusal of the child from any bottles is high. Therefore, try to calm the baby, because the pain syndrome is very pronounced. Breathing cool moist air will ease the suffering of the baby; weather conditions, a humidifier and a nebulizer can help.
If you have a nebulizer and an inhaled corticosteroid (such as budesonide) in your first aid kit, you can inhale with a mask before the emergency arrives or on the way to the hospital. The drug will help relieve swelling and reduce the pain component.
The child was burned by tea
When a child already knows how to drink from a cup, there are frequent cases of “attacks” on “adult” hot drinks (tea, coffee, etc.). In such cases, the mucous membrane of the lips, tongue, possibly gums and hard palate are damaged.
The main help is cool water. Ice, snow and ice water can only aggravate tissue damage. Rinsing with cool water will distract the child and help reduce the pain component. Local anesthetics with lidocaine (spray, kamistad, kalgel, lident baby, dentinox, dinexan) will also help in this.
The child knocked over soup or boiling water on himself
When a child reaches for a dish with hot liquids or, pulling the tablecloth, knocks over the scalding contents on himself, the “blow” falls on his hands, face, chest, head.
First, remove the soaked clothing (break contact with the hot source). If the clothes stick to the skin, in no case try to tear it off, just cut it off along the edge.
Second, rinse affected areas with cool running water (to relieve pain). For burns to the head and torso, you can put the child in a cool shower, but such cooling of the body should last no more than 10 minutes if the child is less than a year old, and 20 minutes if older.
If the burn is superficial, without blisters, redness can be treated with wound healing agents only in the form of sprays, for example, panthenol, livian, olasol. To protect against friction and scratching, apply a clean cloth (lint-free), sterile or special gel dressing.
If blisters appear with clear contents, do not open them and protect them from the baby's hands by applying a clean bandage.
Child burned on a stove
Due to significantly high temperatures, burns from contact with hot objects or open flames cause some of the most serious skin lesions (2-3 degrees), especially when they are grasped with a hand.
Cold is the main helper. Place the affected area under cool running water or immerse in a bath of cool water. For a deep defect, seek medical attention.
The child was burned by water in the bath
The depth and degree of injury from contact with hot water in the bath depends on the area of skin contact with it.
The main aid is cool water.
Since burn injuries have their own characteristics of the course, hospitalization of children and adults with such injuries is carried out only in specialized centers and departments. Treatment of deep and extensive injuries is time consuming and has a long recovery period.
This is important!
All family members with small children should be careful when handling fire, heaters and hot liquids. The main goal of first aid for burns is to reduce pain. Cool water works best for this. It is acceptable to use painkillers (strictly according to the age and manufacturer's instructions) and antihistamines (if the child is prone to allergic reactions).
If the damage is superficial, then relief comes quickly and the child calms down, redness disappears within a few days.
Seek medical attention if:
- The burn is located deep in the mouth, face, neck, groin, perineum, feet and hands;
- There was hoarseness, coughing, vomiting;
- There are blisters with opaque contents, especially if they break open;
- Clothes stuck to the body;
- There is deep tissue involvement;
- Damaged area larger than one palm of the child;
- edema appeared around the burn;
- The child's crying and restlessness does not go away within 20 minutes.

Prevention is always cheaper than cure. Be carefull. Create a safe home for the child.
Share on Vkontakte Share on Odnoklassniki
Contents of the article
- Child burned with formula
- Child burned with tea
- The child burned himself on the stove
- The child was scalded by water in the bathroom
Products from article
Nutrilak Premium 2 1050g
Nutrilak Premium 1 1050g
From 0 to 6 months
Nutrilak Premium 3 dry milk drink for children 600g
Older than 12 months
May be interesting
- Why does the baby hiccup?
- A newborn baby is crying. Why?
- The child was poisoned.
 What to do?
What to do? - How to understand that the child is cold
Burning Mouth Syndrome: How to Extinguish the Flame
Burning Mouth Syndrome, Glossodynia, Glossopyrosis, Flaming Mouth Syndrome - these and many more names for this condition show how acute this problem is, how difficult it is to find a complete description for it. And, as practice shows, the search for causes and treatment also cause certain difficulties [1].
Glossodynia — what it is
Burning mouth syndrome, or glossodynia, is discomfort and even pain in the mouth, on the tongue, gums, mucous membranes, which are accompanied by a feeling that the mouth has been scalded with boiling water or medicine. This condition may be accompanied by dry mouth (xerostomia), loss of taste or smell. Sometimes people with burning sensation in the mouth and tongue complain that they can't feel anything - not even the temperature of the food [1].
This condition develops suddenly, but may begin as a small tingling sensation in a limited area of the mouth, and then spread further or worsen only in the same area. The symptoms of this condition are described by subjective complaints, they can be combined or single:
The symptoms of this condition are described by subjective complaints, they can be combined or single:
- sensation of burnt mucosa, burning pain. Most often, burning of the oral cavity is felt on the tongue, especially along its front edge and sides, as well as on the lips, on the inside of the cheeks, in the throat or throughout the mouth;
- feeling of tightness, burning and dryness of the mucosa in the mouth, from severe to episodic;
- change in taste, up to the complete loss of this sensation;
- the appearance of an unusual taste in food and drink, such as bitterness, metallic;
- decrease or loss of smell;
- Feeling that sensitivity in the mouth has disappeared, as if the mouth is frozen [2].
Symptoms of burning of the oral mucosa can manifest themselves in different ways throughout the day for several days and even months. Sometimes they begin at a certain time of the day, for example, after waking up, and by the end of the day they decrease or, conversely, intensify in order to quietly disappear and return again in the morning. The subjective characteristics of pain in burning mouth syndrome can vary significantly. In people with similar diseases and other life factors and conditions, the symptoms of this condition, their intensity, duration and prevalence can vary greatly [2].
The subjective characteristics of pain in burning mouth syndrome can vary significantly. In people with similar diseases and other life factors and conditions, the symptoms of this condition, their intensity, duration and prevalence can vary greatly [2].
Special mention should be made of the great social and personal significance of glossopyrosis. The fact is that sensations in this state can affect the quality of life in all its aspects: nutrition, sleep, rest and restoration of physical strength, communication, reactions to some stimuli. Those suffering from constant pain cannot sleep, have a rest, they have difficulties with eating and communicating. In an attempt to find the source of the problem, somehow eliminate it, they begin to pay a lot of attention to this condition. So, many note that with the advent of glossopyrosis, spots formed in their mouths, papillae enlarged, or the tongue began to look unusual. As practical observations have shown, in 50% or more cases, such changes are actually normal, in no way associated with burning mouth syndrome, and a person had them before, he just did not notice them [2].
This is very important for diagnosis, because the appearance of some real clinical signs, obvious manifestations of trouble may indicate that the burning mouth syndrome did not arise by itself, it is not idiopathic, but there are some problems, prerequisites for its occurrence [3].
Causes of burning mouth syndrome
This condition may be associated with some general somatic or dental disease, or may occur on its own. As a rule, burning mouth syndrome refers to exactly the condition in which its source is unknown. It occurs spontaneously, and the patient cannot point to the cause or starting point of the complaint.
There are several theories for the development of this pathology, but none of them has been proven yet. The researchers of this problem as a theory of the origin of the syndrome made several assumptions. One of the most common is the theory of sex hormone deficiency, since complaints of chronic burning of the tongue are often made by women in pre- or postmenopause. True, when checking studies in this area, reliable statistical significance was not established, but, nevertheless, as a theory, this reason is supported by many practitioners [3].
True, when checking studies in this area, reliable statistical significance was not established, but, nevertheless, as a theory, this reason is supported by many practitioners [3].
“Women were more common among patients with flaming mouth syndrome. According to some studies, there were 10.3 times more women with complaints typical of this condition than men. PIMU [1]
There is an assumption that some autoimmune processes, especially those that occur in the elderly and senile age, can also be background for the occurrence of burning mouth syndrome [2].
It is possible that this disease occurs in people with neurological or mental disorders, depression. But this is also not a leading theory, since there are studies indicating that it was not depression that led to the onset of the syndrome, but, on the contrary, burning mouth syndrome became one of the causes of the development of a depressive episode. The same range of causes of burning in the mouth includes carcinophobia, especially in people who have quit smoking and are afraid of developing cancer of the lip or tongue, as well as in people with fear of household transmission of STDs [2].
Can lead to injury syndrome, including those not noticed by a person, associated with his habits, congenital or due to pathologies with malocclusion, anomalies of teeth. Some researchers note that individual changes in the sensitivity and density of the oral mucosa can lead to the development of glossopyrosis. A correlation was noted between mental lability and increased sensitivity of taste buds: in such people, the incidence of burning mouth syndrome was higher. In general, an approximate list of conditions and diseases in which the syndrome may appear is quite wide [3].
- In women, estrogen or progesterone deficiency.
- Autoimmune pathology.
- Neurological disorders, PTSD.
- Psychiatric disorders.
- Chronic irritation of the oral cavity, eg by malformed dentures.
- Sensory defects.
Diseases that may cause burning in the mouth:
- Anemia.

- Parkinson's disease.
- Deficiency of B vitamins, zinc.
- Neuropathy.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Taking medicines.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2.
- Sjögren's syndrome with xerostomia.
- Candidiasis of the oral mucosa, esophagus.
- Herpes.
- Fissures of the tongue.
- Allergy, including contact.
- Hiatus hernia.
- HIV.
- Myeloma.
- Oncological diseases [3].
What to do in case of burning mouth syndrome
The syndrome is etiologically and diagnostically complex, there is no treatment protocol for it and there is no possibility to develop treatment protocols. In each case, the approach and search for the reasons why it burns in the mouth will be individual. Therefore, if there is a burning sensation in the mouth, you need to contact your dentist, who, based on the results of the examination and assessment of the history, will give further recommendations for treatment.
If glossopyrosis is idiopathic, that is, the causes of its occurrence are not found, then drugs and methods will be selected to help alleviate or eliminate the symptoms. As possible treatment options, antidepressants, antipsychotics, tranquilizers, drugs that stimulate salivation, moisturizers can be prescribed. The doctor can connect the methods of physiotherapy - from rinsing to electrophoresis. Psychotherapy, taking dietary supplements may be effective. In the case of secondary burning mouth syndrome, it is necessary to diagnose and treat the disease against which the syndrome developed [4, 5].
Medical expert: Oleg Sergeevich Shchekin
The date of the last update: July 21, 2021
List of sources
- Saperkin N.V., Tiunova N.V. V., Sergeeva A.V. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of the "flaming mouth" syndrome at the regional level // Medical Almanac. 2017. No. 4 (49). URL: https://cyberleninka.
 ru/article/n/kliniko-epidemiologicheskaya-harakteristika-sindroma-pylayuschego-rta-na-regionalnom-urovne (date of access: 02.10.2020).
ru/article/n/kliniko-epidemiologicheskaya-harakteristika-sindroma-pylayuschego-rta-na-regionalnom-urovne (date of access: 02.10.2020). - Brad W. Neville; Douglas D. Damm; Carl M. Allen; Jerry E. Bouquot (2002). Oral & maxillofacial pathology (2. ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 752–753
- Mikhailova E. S., Kulik I. V., Katkovnik N. V. Somatic status and psycho-emotional state of patients with burning sensation in the oral cavity after orthopedic treatment // Russian Family Doctor. 2006. No. 2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/somaticheskiy-status-i-psihoemotsionalnoe-sostoyanie-bolnyh-s-sindromom-zhzheniya-v-polosti-rta-voznikshim-posle-ortopedicheskogo (date accessed: 10/14/2020).
- Vasenev E. E., Alekhanova I. F., Popova A. N., Krainov S. V. Effectiveness of drug treatment of patients with stomalgia // Problems of Dentistry. 2018. No. 3. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/effektivnost-medikamentoznogo-lecheniya-bolnyh-stomalgiey (date of access: 10/14/2020).