What to feed baby hamsters
How To Feed Baby Hamsters
Have a pregnant hamster? Not sure what to feed her or the babies? These tips will help guide you to the best hamster diet during these life stages.
What Do Pregnant Or Mother Hamsters Eat?
Mother hamsters need extra protein while they are pregnant or nursing. Feed them boiled egg, bits of cooked unseasoned chicken or beef, mealworms (usually available at high-end pet stores) and fruits or vegetables rich in vitamins A (natural A is good) and E.
Broccoli, sweet apple (as opposed to sour green apple), cantaloupe, and peas are all good fruit and vegetable choices for your hamster.
During pregnancy the restriction on sunflower seeds may be safely lifted; let the hamster eat as much as she can. Pregnant hamsters need the extra folic acid and vitamins as well as the fats and proteins that sunflower seeds provide, which is why mother hamsters can eat more. Protein needs for a hamster increase 60 percent during pregnancy. Nursing 14 to 28 pups in a litter can sap a mother hamster’s reserves; she’ll be able to use the fat in the seeds to keep from losing weight.
Always provide plenty of hamster food for a nursing mother hamster. She’ll need the food both physically and emotionally. Having plenty of resources to draw from makes a mother hamster feel secure and less stressed, which gives the hamster pups the best chance of survival. Hamster babies continue to nurse for almost three weeks after birth.
Feeding Baby Hamsters
Baby hamsters are usually well cared for by their mothers, but you can offer a few foods to help the hamster pups along. Baby hamsters will likely benefit from wheat germ cereal early in their development, so sprinkle a little close to the nest. Also small seeds such as millet are good for hamster pups, even those younger than 10 days old. Place a whole sprig of millet in the cage as an extra treat for the mother. This gives her something interesting to do, because she will need to gather the seeds off the stem.
Sometimes you will need to feed a hamster pup if the mother dies or rejects it. This will be a full-time job. Pups less than 8 days old have a poor survival rate, but you should still try. It can be rewarding to nurse a young hamster to adulthood. Saving a motherless hamster pup involves more than just feeding it, but our focus is nutrition.
Pups less than 8 days old have a poor survival rate, but you should still try. It can be rewarding to nurse a young hamster to adulthood. Saving a motherless hamster pup involves more than just feeding it, but our focus is nutrition.
Feed a pup evaporated milk mixed in a 50/50 solution with water. Warm the solution to 90 degrees Fahrenheit before feeding it to the baby hamster. Administer the solution via syringe or feeding wick (available at most pet stores). You may also use puppy or kitten formula. The volume to feed varies with the type of hamster.
Feeding Baby Dwarf Hamsters
For a dwarf hamster less than 2 weeks old, start at 2 drops every half-hour around the clock. Increase this to 3 drops every half-hour as it approaches 2 weeks of age. When the hamster pup reaches 2 weeks of age, increase the volume to 1/2 milliliter every hour. While nursing on this formula also provide wheat germ, small seeds and something fresh such as broccoli.
Hamsters continue to nurse for up to 3 weeks in extreme cases. This doesn’t mean that the hamsters won’t eat solid foods. Hamster pups start using their teeth at about 5 days old on smaller seeds. If you provide wheat germ by sprinkling it close to the nest, small hamster pups will lick at it.
This doesn’t mean that the hamsters won’t eat solid foods. Hamster pups start using their teeth at about 5 days old on smaller seeds. If you provide wheat germ by sprinkling it close to the nest, small hamster pups will lick at it.
During the third week you should see hamster pups eating from the bowl of solid foods. You can breathe easy after three weeks and start weaning them from the milk. To wean a hamster, just reduce the amount of milk given by half for a day or two and then stop all milk by the next day.
Feeding Baby Syrian Hamsters
For a Syrian hamster or other full-sized species of hamster, increase the amount of milk offered. Start with 1 milliliter 12 times a day around the clock until the hamster pups are 2 weeks old. After 2 weeks, feed them 2 milliliters 8 times a day. Provide the hamster pups with wheat germ, small seeds and something fresh while feeding the formula.
Around 3 weeks of age, you should see the hamster pups start to eat solid food. When you see this, gradually wean them off the formula. If you watch hamster pups carefully you’ll notice that they eat droppings from adult hamsters. This is normal and quite necessary. The droppings contain bacteria that the hamster pups need to help them break down and digest the mostly cellulose foods they eat. This is true for orphan hamsters as well. If you are a surrogate parent, remember to place droppings from an adult hamster near the nest so the pups you are nursing can benefit.
When you see this, gradually wean them off the formula. If you watch hamster pups carefully you’ll notice that they eat droppings from adult hamsters. This is normal and quite necessary. The droppings contain bacteria that the hamster pups need to help them break down and digest the mostly cellulose foods they eat. This is true for orphan hamsters as well. If you are a surrogate parent, remember to place droppings from an adult hamster near the nest so the pups you are nursing can benefit.
By: Doran Jones
Excerpt from the Popular Critters Series magabook Hamsters with permission from its publisher, BowTie magazines, a division of BowTie Inc.
Share:
When Can Baby Hamsters Start Eating Hamster Food?
By Naomi Millburni Jupiterimages/liquidlibrary/Getty Images
Newborn hamsters of all types begin their existences in highly dependent states, lacking both vision and fur. Despite this powerless start in life, a hamster's development is extremely fast, and before you know it, the little rodents are completely weaned and heartily chowing down on commercial hamster formula.
Hamster Food
Wee hamsters typically start taking in solid, dry hamster foods when they're about 10 days old. This is when the weaning process commences. As with many other animals, weaning entails the gradual transition from exclusive nursing with the mama hamster to eating only "normal" foods."
Completion of Weaning
Although baby hamsters start eating hamster foods when they're just days old, they still continue to nurse with their mothers for a little while longer. Dwarf hamsters -- like Chinese and Campbell's hammies -- typically are all through with weaning once they get to roughly 3 weeks old. The process doesn't move as fast with Syrian hamsters, however. Many Syrian hamster youngsters wait to be fully weaned for almost a month. Typical weaning age for Syrian hamsters is between 26 and 28 days old.
Pellets
Before you give baby hamsters their earliest servings of hamster food, make a point to immerse the pellets in water beforehand. By doing this, you give the food a smooth and soggy feel, and therefore make it easier for the little guys to eat them initially. Note that putting these pellets on the floor of their living space offers the young hamsters easy access, too.
Note that putting these pellets on the floor of their living space offers the young hamsters easy access, too.
Water
Baby hamsters also need to have clean water always available to them. Once they're old enough to eat hamster food, they need to be regularly drinking water, too. When setting up the bottled water in the hamsters' cage, make sure that the wee ones can comfortably get to the bottles' tubes. Make sure too that the tubes don't touch the hamsters' sleeping area. Clean water is vital for young and adult hamsters alike.
General Hamster Feeding Information
When planning your hamster's mature meal plan, look not only at commercial hamster foods but also at produce. Discuss with your veterinarian supplementing your hamster's diet with small and controlled amounts of fresh produce, both vegetables and fruits. Never offer your hamster any specific vegetables or fruits unless you're 100 percent sure that they're hamster-safe. Seek your vet's OK before introducing anything new into your pet's menu. Also ask about suitable commercial treats that are made for hamsters.
Also ask about suitable commercial treats that are made for hamsters.
References
- The Humane Society of the United States: Hamster Feeding
- Hilltop Animal Hospital: Care of Pet Hamsters
- Hunt's Veterinary Clinics: Hamsters
- Purdue University College of Veterinary Medicine: Care of Hamsters
- Caddy Veterinary Practice: Hamsters
- SPCA Singapore: Hamsters
- Florida Atlantic University Veterinary Services: Hamster Hideout
- Marlborough Bird & Animal Hospital: Gerbils and Hamsters
- SmallAnimalChannel.com: All About Baby Hamsters
Photo Credits
How to make a diet for a hamster
Proper nutrition is important not only for humans. Your pet must receive all the necessary nutrients - this is the only way to avoid problems with the health of the hamster.
When compiling a diet, the following points must be taken into account:
- age of the animal;
- temperament, habits;
- general health.

For a better understanding of the principle of selecting healthy feed and diet, it is useful to study the habits of rodents in the wild. These animals drink little liquids and always make “stocks of food”.
Feed the hamster twice a day, and the main portion is given in the evening. If a hamster is trying to bury food in a secluded place in the cage, he should not be allowed to do this. Feed can spoil and become the cause of various diseases. It is better to reduce the amount of food. The diet should be balanced, of high quality. It is best to buy feed in specialized stores. nine0003
The best diet for rodents is a grain mixture and green fodder - this is what they eat in nature. Seeds of wheat, oats, corn are suitable as grain. You can feed hamsters watermelon, pumpkin, sunflower seeds, beans, peas. Infrequently, but you can give walnuts, pine nuts, cashews, peanuts.
Leaves of plantain, dandelion, clover are suitable as green fodder. Rodents like beetroot, carrot tops, lettuce leaves. In winter, hamsters are fed hay from forbs. Branches of linden, maple, willow, apple, pear, birch, as well as branches of shrubs (rose hips, raspberries, black currants) are ideal for grinding teeth. Leaves and branches should be collected away from roads, it is best to do this during trips to nature. nine0003
In winter, hamsters are fed hay from forbs. Branches of linden, maple, willow, apple, pear, birch, as well as branches of shrubs (rose hips, raspberries, black currants) are ideal for grinding teeth. Leaves and branches should be collected away from roads, it is best to do this during trips to nature. nine0003
In the diet of hamsters, you can add fruits and vegetables. Pieces of dried apples, pears, various berries are a delicacy for rodents. They also love carrots, beets, zucchini, cucumbers, pumpkins, potatoes. Fresh, you can feed slices of banana, apricot, pears, peaches.
The diet of domestic hamsters in small quantities should contain protein foods. It is recommended to give rodents a little cottage cheese, a boiled egg, milk, and once a week - a small piece of boiled meat. Many hamsters like small insects - ants, worms, grasshoppers, beetles, locusts. It is best to buy such "live" food in pet stores. You should also give the hamster vitamins and mineral supplements (drops, tablets . ..), they are mixed with fresh feed. nine0003
..), they are mixed with fresh feed. nine0003
Fresh food is given in the morning, grain in the evening feeding. Strongly not recommended for rodents: products from the table, sweets, fatty dairy products, mushrooms, exotic fruits. It is forbidden to give cabbage, sorrel, onion, garlic.
Good quality budget cat food
More details
Which cat food should I choose?
More details
Sphynx feeding features
More details
English Angora rabbit - useful and cute pet
Read more
What to feed a hamster - Reserve
Peculiarities of feeding a hamster: what can and cannot be given to a pet
Hamsters, like any other pets, need the most varied diet. However, this does not mean that a small rodent can be fed to everyone. The health and longevity of the animal depends on how properly selected and healthy the food of the animal will be. In order for the pet’s table to be complete, you need to know which foods are allowed to be included in its diet, and which are prohibited.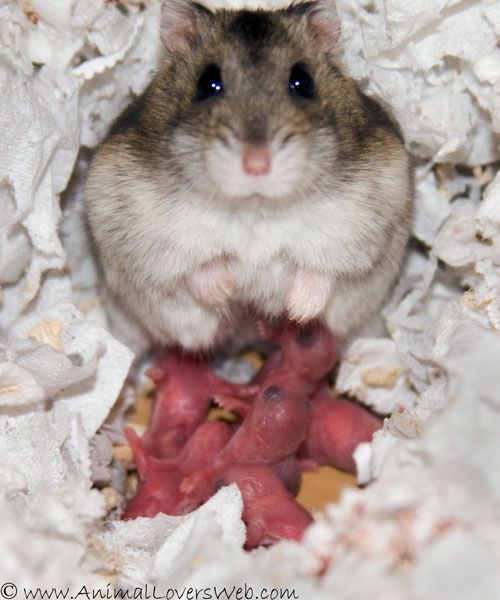 nine0003
nine0003
Basic and additional components of hamster nutrition
The basis of the diet of indoor hamsters is dry grain food and succulent food. The main component is grain: wheat, oats, corn and other cereals, which are presented in the optimal ratio in "store" mixes for hamsters. Ready-made feeds consisting of grains, granules, flakes, as a rule, are very nutritious and balanced in terms of the amount of vitamins and other important substances. Give them to the animals daily.
A hamster's diet must contain juicy food: vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs. From vegetable crops, this rodent can be given carrots, beets, pumpkins, turnips, including boiled ones, zucchini, cucumbers, tomatoes, bell peppers, radishes. From fruits - apples, pears, apricots and peaches, and from berries - grapes, currants, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, cherry pulp. Fresh vegetation is very useful for hamsters: lettuce, dandelion leaves, plantain and clover, dill, parsley, beet leaves. In winter, greens for hamsters will replace hay, oat or wheat sprouts. nine0003
In winter, greens for hamsters will replace hay, oat or wheat sprouts. nine0003
Occasionally offer your pet nuts (any but Brazil nuts and almonds), seeds (sunflower, pumpkin, melon, watermelon), legumes (dried beans and peas). Nuts and seeds are usually included in ready-made feed mixtures, so these treats should be served to the hamster in small quantities.
Hamsters eat dried fruits with great pleasure, they can be treated with various dried fruits, except for prunes: raisins, dried apricots, apples, pears, banana chips. nine0003
As a protein supplement, give your pet foods from the following list approximately two to three times a week, alternating between them: low-fat kefir, cottage cheese or yogurt without sugar and flavorings, boiled chicken meat without salt and spices, boiled chicken or quail egg flour or earthworms purchased at a pet store, dried gammarus and dried insects.
In the diet of sick, debilitated and elderly animals, as well as young animals, cereals on the water, baby food: dairy-free cereals, vegetable and meat purees without salt, sugar, gluten and starch should be introduced.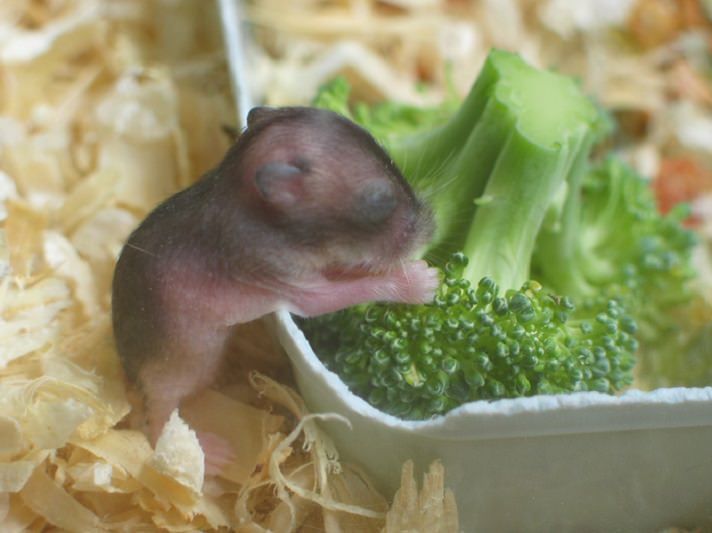 In addition, aged hamsters are given ground grains and nuts, mashed vegetables. nine0003
In addition, aged hamsters are given ground grains and nuts, mashed vegetables. nine0003
In a rodent’s cage for grinding teeth, there must be a mineral stone or branches of deciduous and fruit trees that grow best outside the city: birch, poplar, hazel, beech, maple, apple, pear, cherry and others. The branches, before giving the animal, should be boiled for an hour and a half and dried. You can also find ready-made twig sets at pet stores.
Do not abuse special treats for hamsters in the form of cereal sticks and bars, crackers, biscuits, drops. Occasionally, a pet can be pampered with simple drying or home-cooked popcorn without salt, sugar and other additives. nine0003
What not to feed a hamster Food from our table is absolutely not suitable for hamsters! The body of these animals does not tolerate sweet, salty, fatty, fried foods, as well as canned and smoked foods, spices. Do not offer your hamster expired grain mixtures, as well as food created for other rodents and ornamental birds!
The list of prohibited products includes potatoes, including peel and eyes, cabbage, onion, garlic, sorrel, mint, milk and fatty dairy products (sour cream, cream, yogurt), butter, pasta, including dry, and also dry breakfasts and muesli. Cheese and bread cause great harm to hamster health: they cause severe constipation, which can lead to the death of the animal. Watermelon, citrus fruits, exotic fruits (kiwi, persimmon, pineapple, pomegranate, avocado and others), mushrooms, acorns, red beans, branches of coniferous trees, apricot pits, peaches, plums, cherries are contraindicated for hamsters. You can not pamper your pet with honey, goats and other sweets, fruit juices, sausages and sausages. nine0003
Cheese and bread cause great harm to hamster health: they cause severe constipation, which can lead to the death of the animal. Watermelon, citrus fruits, exotic fruits (kiwi, persimmon, pineapple, pomegranate, avocado and others), mushrooms, acorns, red beans, branches of coniferous trees, apricot pits, peaches, plums, cherries are contraindicated for hamsters. You can not pamper your pet with honey, goats and other sweets, fruit juices, sausages and sausages. nine0003
There is nothing critical if you once gave your hamster any of the above. A single use of junk food is unlikely to cause irreparable damage to the animal's body, the main thing is not to give the forbidden product again.
Feeding tips for hamsters
A hamster's diet depends on its age, lifestyle, habits, nutritional needs, and season.
When choosing ready-made food, pay attention to the ratio of its components, the amount of proteins and carbohydrates. It is better to refuse mixtures with a large volume of seeds or nuts: the animal will choose them, leaving more valuable ingredients intact.