When can a baby start eating soft food
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Solids, Finger Foods, and More
Written by Gina Shaw
In this Article
- Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
- Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
- Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
- Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
- Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
- Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
- Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
- Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
There are many milestones that need to be achieved when a baby is ready to start to eat solid foods. Here are some of the big ones.
Here are some of the big ones.
Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
Most pediatricians, and the American Academy of Pediatrics, recommend introducing solid foods to babies when they are between ages 4 and 6 months. That’s when they start to lose the “tongue-thrust reflex” or extrusion reflex, which is important for sucking the breast or bottle when they are younger, but interferes with feeding. Babies at this point can also lift their heads up independently and hold their necks high.
If your baby is around this age, can sit up well with support, and shows interest in the foods they see you eating, it’s probably a good time to venture into feeding your baby solid food. If your baby is exclusively breastfed, it is recommended that you wait until they are 6 months to start solids.
Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
“Chunking up” babies’ food is a process -- obviously, they shouldn’t go straight from rice cereal to raisin bran. But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
Introduce new textures slowly. Good starters are mashed bananas or mashed avocados. You can also use the “staged” store-bought baby foods -- going from the smooth puree of stage 1 to the slightly thicker stage 2 and then the chunkier stage 3 by around 9 months of age. (Babies don’t necessarily have to have a lot of teeth to handle more texture in their foods -- they can often gum soft foods very well!)
Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
When babies are ready to eat solid foods, they can sit upright with support and hold up their head and neck. They're capable of sitting in a high chair! That's a serious milestone, but you'll need to follow these safety rules: Always buckle a baby into their chair for safety, even if they are unable to get out with the tray in place. As they get older and become more active, they may be able to squirm out.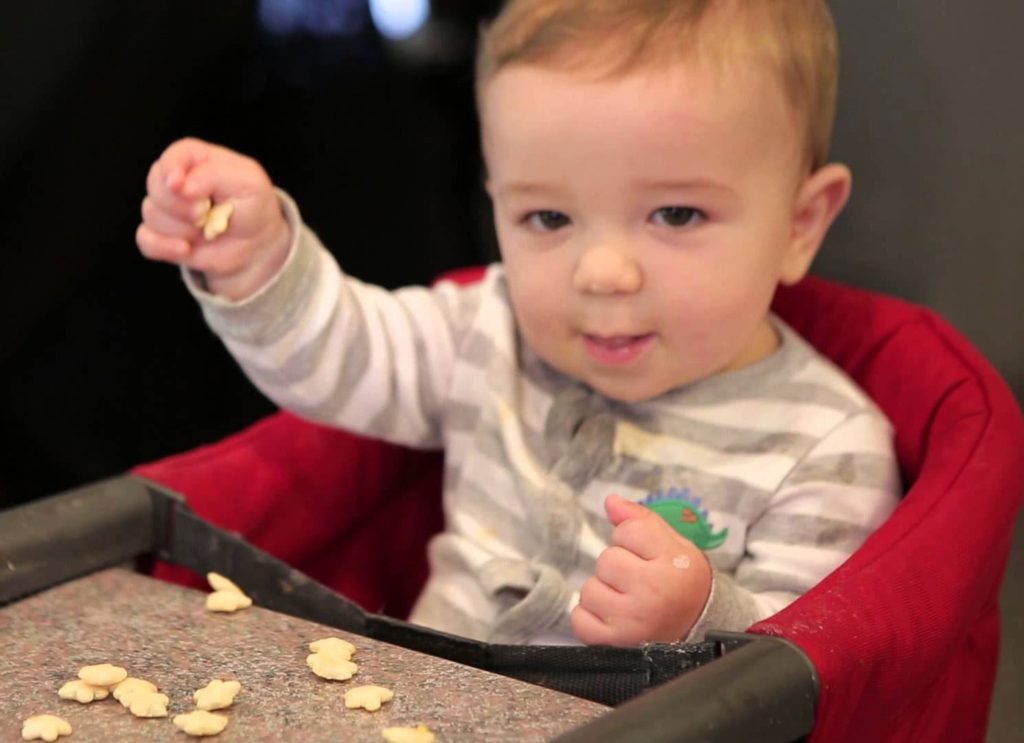 It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
Babies between ages 7 and 11 months usually tell you they’re ready to eat more grown-up foods by trying to grab them from you. Almost any food that is healthy and nutritious and has a soft texture makes a good finger food, if it’s cut small enough: diced pasta; small pieces of well-cooked vegetables such as carrots, peas, or zucchini; and pea-sized bites of chicken or soft meat. Small, unsweetened round cereals and cereal puffs are also a good choice. Avoid feeding your baby grapes, hot dogs (even cut up), nuts, and hard candy, as they are choking hazards.
At first babies “rake” food into their hand, but soon they develop the “pincer grasp” that allows them to pick up small objects between thumb and forefinger. At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
Almost as soon as babies adjust to being fed with a spoon, they'll want to hold and grab the spoon themselves and put it in their mouths. That doesn't mean they're graceful, of course.
Most babies don’t learn to use a spoon effectively until after their first birthday, but let a younger baby who’s interested give it a whirl for practice. Try giving them a soft-tipped spoon to hold while you feed them with another. They can get used to holding the spoon themselves and will also be distracted from grabbing yours.
When you think they are ready to actually navigate the spoon into their mouth, try thicker, stickier foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or cottage cheese. Another tip: Put some cream cheese on the spoon and then a few pieces of O-shaped cereal on top. The cream cheese won’t fly everywhere, and the baby can get the experience of actually getting the cereal into their mouth.
Expect a mess! Use a plastic or other waterproof bib, and put a mat under the high chair to make cleanup easier.
Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
Some pediatricians still recommend waiting until children are at least age 1 before offering them certain foods that are considered highly allergenic, like eggs or fish. But current research doesn’t demonstrate any benefit to waiting past a certain age to introduce these foods, unless you have a significant family history of food allergies or other reasons to believe your baby may be predisposed to them.
There is no evidence that introducing highly allergenic foods to children under age 1 makes them any more likely to be allergic to them, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now says it’s fine to give these foods before the baby's first birthday. Many pediatricians are still very cautious about shellfish and peanuts, however, because allergic reactions to these foods can be particularly dangerous.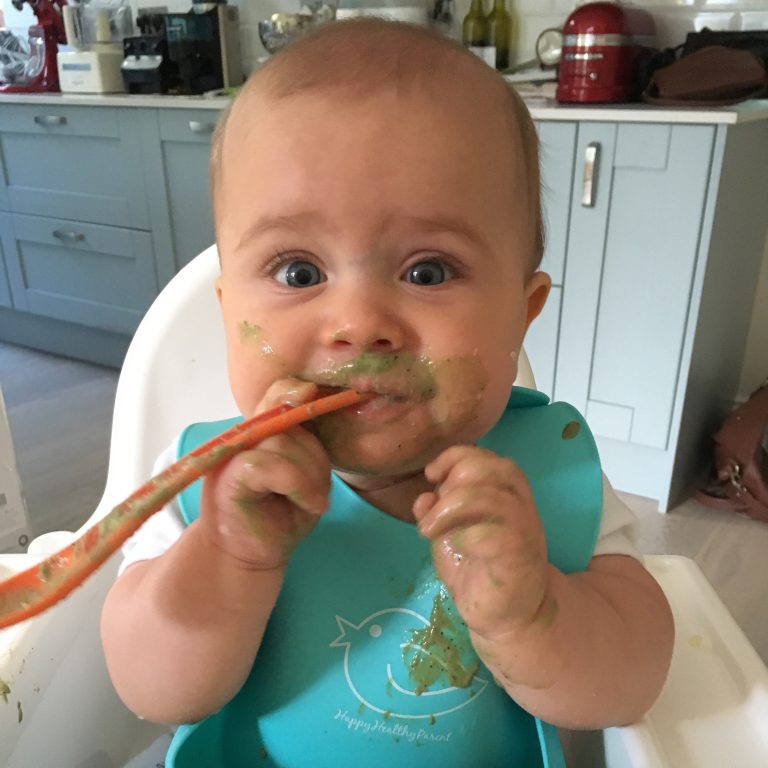
Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
Babies don't need water during their first 6 months of life. They get all the water they need from breast milk or baby formula. Babies under age 6 months should not be given any water at all, because it’s easy to fill up their tiny stomachs -- and they should be filling up on the nutrients they receive from the milk to grow. Once they start eating mostly solid foods, around age 9 months, they can start water with meals using a sippy cup.
If your older baby shows an interest in water that you’re drinking, there’s no harm in letting them have a few sips. Just don’t let it replace the nutritious breast milk or formula they should be getting.
Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
Mastering eating with utensils is a long process. Most babies do not become really skilled at it until they are well past their first birthday. Encourage your child to practice safely, and again, be prepared for a little mess. (How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
(How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
How to transition your baby from mashed potatoes to regular food
The introduction of solid food with pieces improves satiety and teaches the baby to chew, prepares him for the transition to a common table and trains speech skills. We are discussing how to transfer a child to solid food with puree and at the same time not provoke a refusal to eat, which can lead to health problems, with a pediatrician, medical consultant of the SMART-MAMA project, Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino.
— Polina Aleksandrovna, why do they start with pureed food for the first meal?
- Classic complementary foods are introduced around 6 months or earlier. At this age, it is quite difficult for babies to coordinate the work of all the muscles of the oral cavity and chew hard pieces. Other than breast milk or formula, the baby has not tried anything yet. Therefore, if you give him hard pieces right away, he may not figure out what to do with them. In addition, for good absorption and easier swallowing, of course, pureed food is more suitable - cereals or mashed potatoes.
Therefore, if you give him hard pieces right away, he may not figure out what to do with them. In addition, for good absorption and easier swallowing, of course, pureed food is more suitable - cereals or mashed potatoes.
If, for some reason, a child begins to receive complementary foods at 7-8 months (that is, later than the recommended 4-6 months), it is acceptable to introduce products with very soft and small pieces, similar to mashed potatoes. Even if a child swallows such a piece without chewing, it will happen without discomfort and does not threaten to refuse food with pieces in the future.
— What should be the consistency of food in the first year of a baby's life?
- At the stage of introducing the first or second complementary foods, the nutritional consistency is required to be homogeneous, that is, completely homogeneous, without pieces, veins of vegetables or cereal flakes. As the baby matures, he is already able to eat vegetables mashed with a fork. Gradually, the pieces may become harder and larger. However, even if the baby eats pieces, this does not mean that homogeneous foods should be immediately excluded when learning to chew. He can get both.
Gradually, the pieces may become harder and larger. However, even if the baby eats pieces, this does not mean that homogeneous foods should be immediately excluded when learning to chew. He can get both.
— Why is solid food obligatory for children under one year old?
- It is necessary to transfer a child to solid food only because he will not eat homogeneous purees and cereals all his life. And as soon as the physiological ability to chew appears, the baby begins to chew soft food, even if he does not yet have teeth. If the baby remains on homogeneous food and does not learn to chew, then it will be difficult for him to switch to other foods, he will not want to eat in a new way.
When chewing, the oral apparatus develops: jaws, muscles, teeth. The skill of chewing is closely related not only to the maxillofacial system and food processing, but also to the formation of bite and the development of speech in a child.
— When should a child be taken to a common table with hard pieces?
- This happens differently for all children, but on average about 7-8 months. At the same time, solid pieces do not mean those products that need to be gnawed, but precisely what is different from homogeneous food.
At the same time, solid pieces do not mean those products that need to be gnawed, but precisely what is different from homogeneous food.
All changes in the child's diet are introduced gradually. Imagine if he suddenly bites off a large piece that he cannot chew and starts swallowing - as a result, there is a risk of severe choking and choking. Or, at best, experience discomfort, so you don’t want to try this product again. In order not to provoke such situations, all transitions in a child's life must be carried out very smoothly.
— How do parents know when a child is ready for solid food?
— Apart from the age and positive reaction of the child to the proposed product, there are no other signs. Even teeth will not be a readiness factor for solid foods. But if parents delay the introduction of solid pieces and a child at 9-10 months old is not yet familiar with them, then he will not want to eat this and will demand mashed potatoes.
Constant choking on food, spitting up, restlessness of the baby are adverse reactions to the introduction of solid food.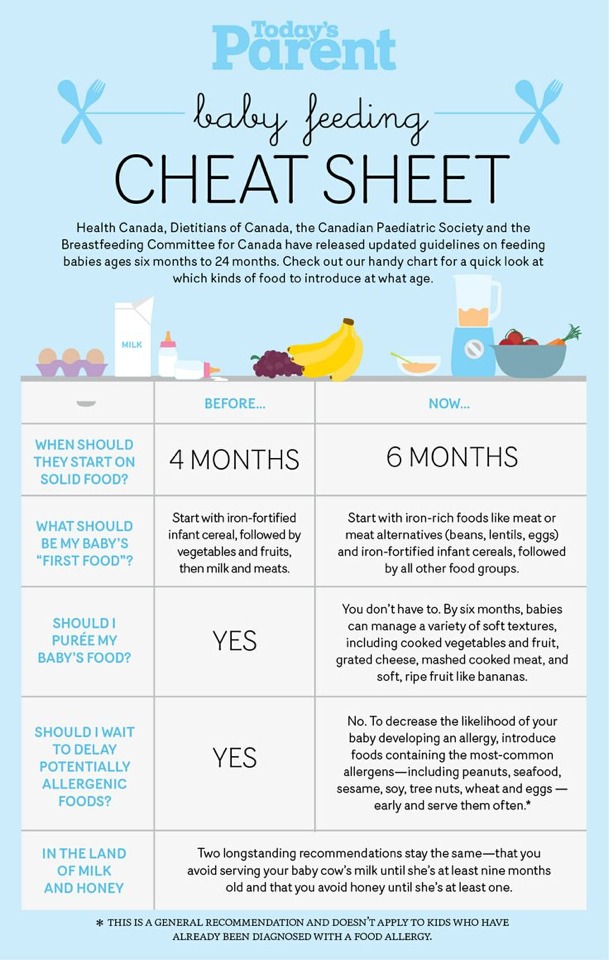 It makes sense to consult a pediatrician.
It makes sense to consult a pediatrician.
Remaining undigested food in the stool may be normal and should not be a concern for parents. In order for food to begin to be fully absorbed, the body needs time to adapt to complementary foods. It is important to monitor the condition of the baby.
— How to transfer a child to a common table if he refuses solid food?
- Unfamiliar and "unpleasant" foods should be offered at the start of feeding while the baby is still hungry. If the baby starts breakfast or lunch with his favorite dish, then, having been a little full and realizing that he got what he wanted, he, of course, will refuse other food.
It is necessary to interest the child in literally all suitable ways:
- demonstrate interest in the product by example, praise its taste;
- offer "baby" food from your own plate;
- put food on a pretty children's plate;
- beautifully decorate food on a plate, make “pictures”;
- praise for the eaten pieces.
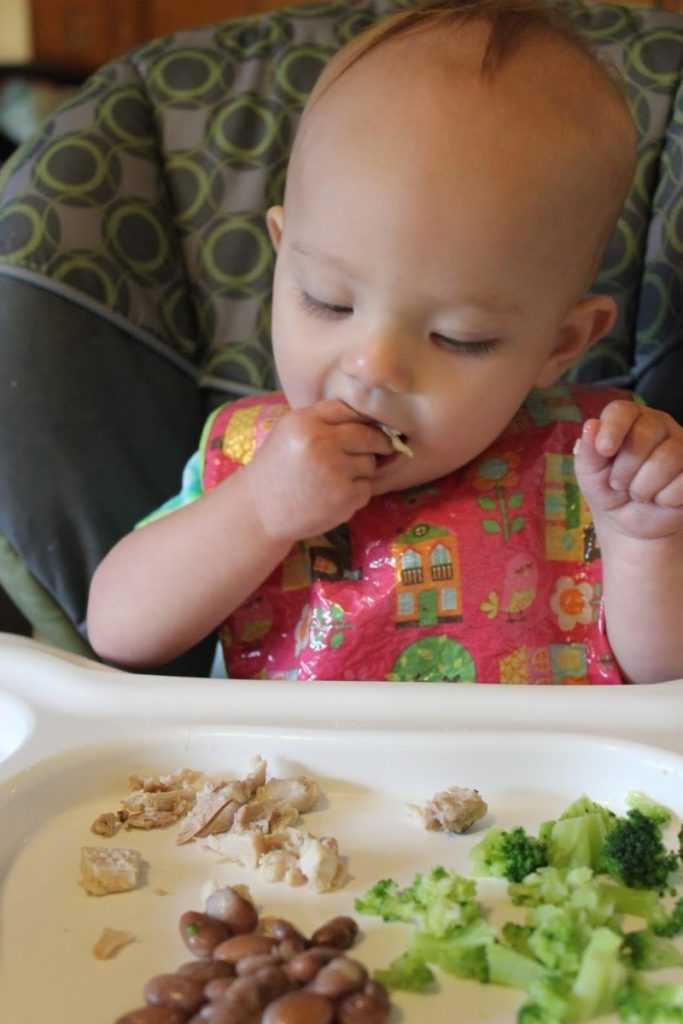

All this does not distract from the process of eating, like cartoons, and does not disguise eating as a game. The food will be interesting for the child, and he will get pleasure and satisfaction from what he eats.
Praise from parents is especially important for babies over one year old. For the sake of keeping the parents happy, the child is sometimes ready to do something that he does not like.
— What food to offer first and what does the child's menu depend on?
- This can be any food, and not necessarily new dishes. But you need to gradually change the density and hardness of food, the size of the pieces. To help in getting to know the pieces, but not with chewing, a nibbler can. Let not all children love it, but this accessory is important for the safety of the child: with it, the baby will not swallow too large a piece and will not choke.
How to start introducing solid food
| Products | Familiar products, but no longer homogeneous, but of a different consistency - you just need to mash the vegetables with a fork, grind them larger, chop a piece on a fork or invite the baby to take the vegetable with his hand and bite off him on his own. |
| Quantity | Look at the child's reaction, his desire and ability. |
| Consistency | The softness of the product should be the same as, for example, a ripe banana, so that when swallowing, even without chewing, the baby does not experience pain, gag reflex and other unpleasant sensations. Subsequently, the food becomes more and more solid. |
| Administration order | One new product is administered over three to four days to monitor the response. Moreover, it should be exactly the same for the same product in both hard and soft form. |
| Piece size | Start with pieces about the size of a pea. You need to pay attention to how the child will chew the boiled "peas" of food. With their softness, there is practically no risk of choking and it is unlikely that a piece will get stuck. |
— How often should there be hard pieces in the diet? A child can eat only homogeneous purees all day, and then all day - only pieces. In addition, food chopped in different ways can be mixed in one dish, but so that the baby understands that in the spoon he has not only mashed potatoes, but also pieces. Then he will count on what he will have to chew. Food should be washed down - WHO recommends the mandatory introduction of water at the start of complementary foods.
In addition, food chopped in different ways can be mixed in one dish, but so that the baby understands that in the spoon he has not only mashed potatoes, but also pieces. Then he will count on what he will have to chew. Food should be washed down - WHO recommends the mandatory introduction of water at the start of complementary foods.
- Rusks, bagels or whole fruits - when can they be introduced?
- Hard crackers and fruits can be in the diet for up to a year, but at a time when the baby still has no or few teeth and he will definitely not bite off, but lick or procrastinate treats. The child rubs boiled potatoes, carrots, broccoli well with gums, but cannot chop solid foods from the adult menu. It is right to give them in pedagogical complementary foods in order to introduce the baby to different tastes.
Be aware that when the incisors appear, the child may bite off a large enough piece that he cannot chew. Therefore, it is better for parents not to take risks if they cannot control the size of the pieces.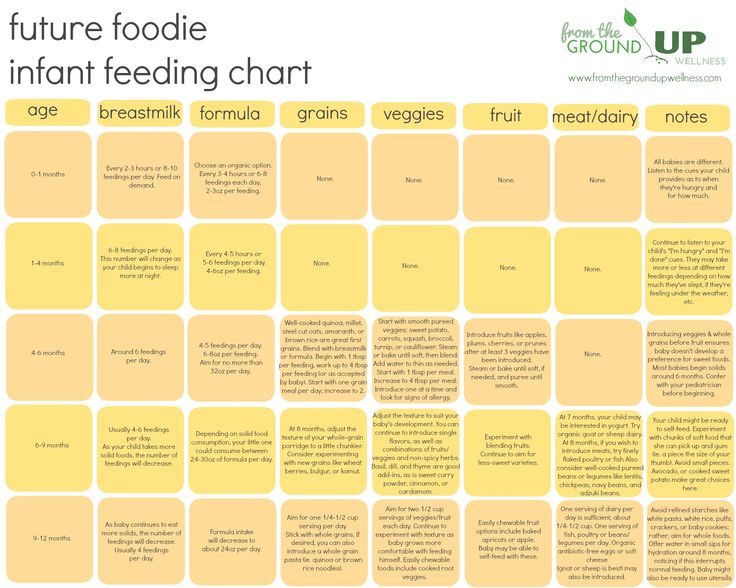 A large unchewed lump of food causes pain and vomiting when it cannot penetrate the esophagus due to its size.
A large unchewed lump of food causes pain and vomiting when it cannot penetrate the esophagus due to its size.
— How to teach a child to chew hard pieces?
- Other than constantly offering to try pieces, there are no special exercises that would help a child learn to chew before the age of one. It's like walking or speaking. Parental example, interest, patience and, of course, the timeliness of introducing pieces into the baby's diet are important.
Complementary foods are recommended to start with homogeneous purees or cereals. After the baby, it is necessary to offer pieces, because without them it will be impossible to acquire the skill of chewing. But it is undesirable to immediately move from homogeneous products to large hard pieces that require intensive chewing. Like other innovations in a child's life, it is desirable to master solid food gradually: from small, soft pieces to progressively denser and harder.
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk.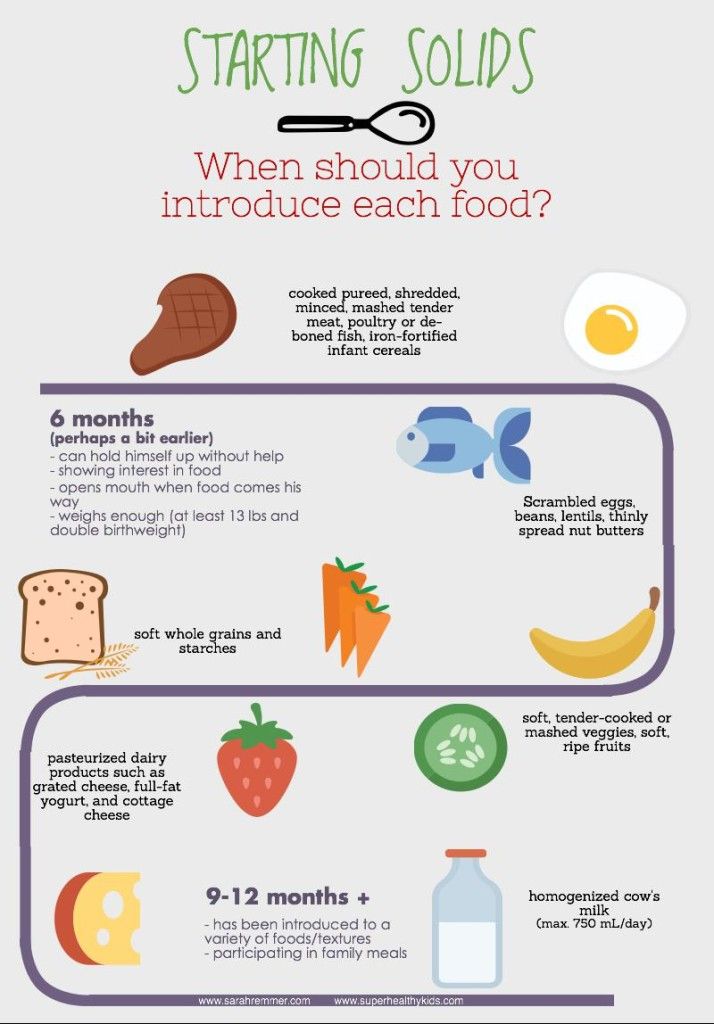 WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby's diet, consult with a specialist.
WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby's diet, consult with a specialist.
Union of Pediatricians of Russia
Introduction of complementary foods
How to introduce complementary foods correctly is one of the most pressing issues that concern parents.
In the first months of life, the main food for the baby is breast milk or an adapted milk formula, however, as the child grows and develops, this becomes insufficient and it is necessary to think about the introduction of complementary foods.
Your baby is over 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines them and reaches for them. The child's emotional reactions have become much richer: he smiles happily at all people, makes various sounds. Perhaps you notice that the child looks into your plate with interest, closely monitors what and how you eat, does this mean that it is time to introduce complementary foods? And where is the best place to start? Let's figure it out!
When should complementary foods be started?
According to the Program for optimizing the feeding of infants in the first year of life in the Russian Federation (2019), the recommended age for the introduction of complementary foods is in the range from 4 to 6 months.
The following points will help determine the readiness of the baby for the introduction of complementary foods:
1. Food interest - you can check its presence as follows: during your meal, give the baby an empty spoon or fork, and if he plays with it, licks it, then there is no food interest yet; but if the child is dissatisfied with the fact that the spoon is empty, food interest has probably appeared. “But how does a child understand that there should be food in a spoon?” Parents often ask. The answer is quite simple: take your baby to the table with you so that he can see how you eat!
2. The child can sit alone or with support. It is unacceptable to feed the child lying down, because he may choke.
3. Extinction of the “pushing out” reflex - when the baby pushes out of the mouth both the offered food and the pacifier, etc.
Why is it not recommended to introduce complementary foods before 4 and after 6 months of life?
Before 4 months of life, the baby is not yet ready to digest food other than breast milk or infant formula. By this age, a number of digestive enzymes mature, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, which reduces the risk of developing allergic reactions, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, which is due to the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”. The introduction of complementary foods after 6 months can cause a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) and lead to a delay in the formation of chewing skills for thick foods. Too late the introduction of a variety of products increases the risk of allergic reactions. Remember that the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is set individually, taking into account the readiness of the child to accept new foods.
By this age, a number of digestive enzymes mature, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, which reduces the risk of developing allergic reactions, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, which is due to the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”. The introduction of complementary foods after 6 months can cause a pronounced deficiency of micronutrients (iron, zinc, etc.) and lead to a delay in the formation of chewing skills for thick foods. Too late the introduction of a variety of products increases the risk of allergic reactions. Remember that the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is set individually, taking into account the readiness of the child to accept new foods.
Complementary feeding guidelines:
1. introduce a new product in the first half of the day to track possible reactions to it;
2. cereals, vegetable / fruit / meat purees should be introduced, starting with monocomponent ones, gradually adding other products of this group;
3.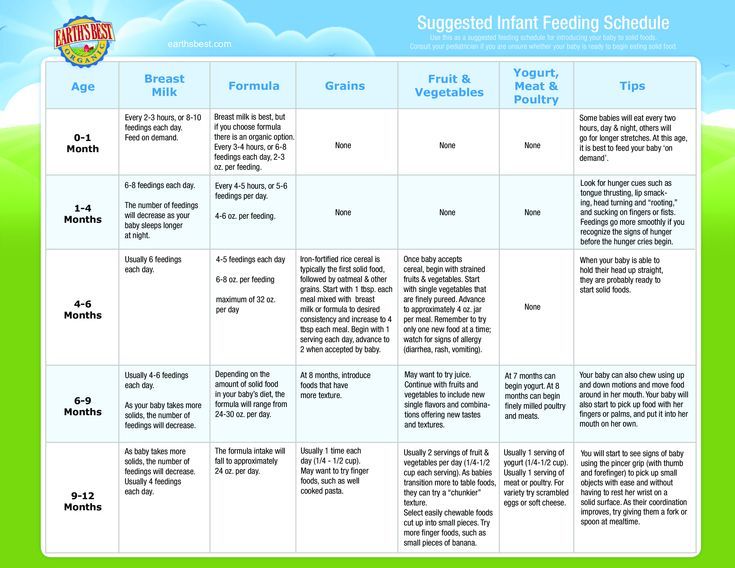 start giving a new product with 1/2 teaspoon, gradually increasing the volume to the age norm within a week;
start giving a new product with 1/2 teaspoon, gradually increasing the volume to the age norm within a week;
4. It is not recommended to introduce new products during acute infectious diseases or at some special moments (moving to another apartment, leaving the city, on vacation, illness of parents, etc.).
What is the best way to start complementary foods?
The first complementary food can be anything. Often parents worry that if the child first tries the fruit, then because of its sweet taste, he will refuse other foods. We hasten to reassure you: breast milk is also sweet, so babies may like sweet fruits / berries more, but this does not mean at all that he will refuse vegetables or cereal. Traditionally, they begin to introduce complementary foods in the form of mashed potatoes, but if the child shows interest in “pieces”, then, observing the safety rules, you can give them. Also, along with the introduction of complementary foods, you can offer the child water.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen. If the baby shows that he is full and no longer wants to eat (for example, leaning back or turning away from food), then you should not continue to force him to feed, because this can lead to eating disorders in the future. Also, do not force the child to eat as much as possible before bedtime in the hope that he will not wake up for nightly feedings.
Traditionally, in our country, complementary foods begin with vegetables or cereals.
Vegetables: zucchini, broccoli, cauliflower, pumpkin, etc. If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in small quantities daily, you can even not once, but 2-3 times, and after a while (7-14 days) the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies his diet, will help form the right taste habits in the child.
As for cereals, it is worth starting with dairy-free gluten-free ones - buckwheat, corn, rice. You can use commercial baby food porridge, which is enriched primarily with iron. In addition, such porridge is already ready to eat, you just need to dilute it with water, which will save you a lot of time.
You can use commercial baby food porridge, which is enriched primarily with iron. In addition, such porridge is already ready to eat, you just need to dilute it with water, which will save you a lot of time.
It is also recommended to add oil to food, for example, vegetable puree to vegetable puree, and butter to porridge.
Of meat products, lean meats, such as mashed turkey or rabbit, are most preferred to start complementary foods. Meat puree contains iron, which is easily absorbed, and adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of this micronutrient from them. Subsequently, the daily use of children's enriched porridge and mashed meat allows you to meet the needs of babies for iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
When introducing fruit purees (apple, pear, peach, prunes, etc.) into your baby's diet, you should pay special attention to the composition of the product - it is important that it does not contain added sugar.
Fish is a source of easily digestible protein and contains a large amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the omega-3 class, as well as vitamins B2, B12, and minerals. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock, sea bass, etc.), salmon can be recommended from red, and pike perch from river.
Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock, sea bass, etc.), salmon can be recommended from red, and pike perch from river.
Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Some foods have added prebiotics, certain vitamins and minerals. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, increases appetite and the absorption of micronutrients.
Recommendations and timing of the introduction of complementary foods for children at risk of developing food allergies and suffering from food allergies are the same as for healthy children. Delayed introduction of highly allergenic foods has previously been recommended to prevent the development of allergic diseases in children at risk. There is now evidence that this practice may lead to an increase rather than a decrease in the incidence of food allergies.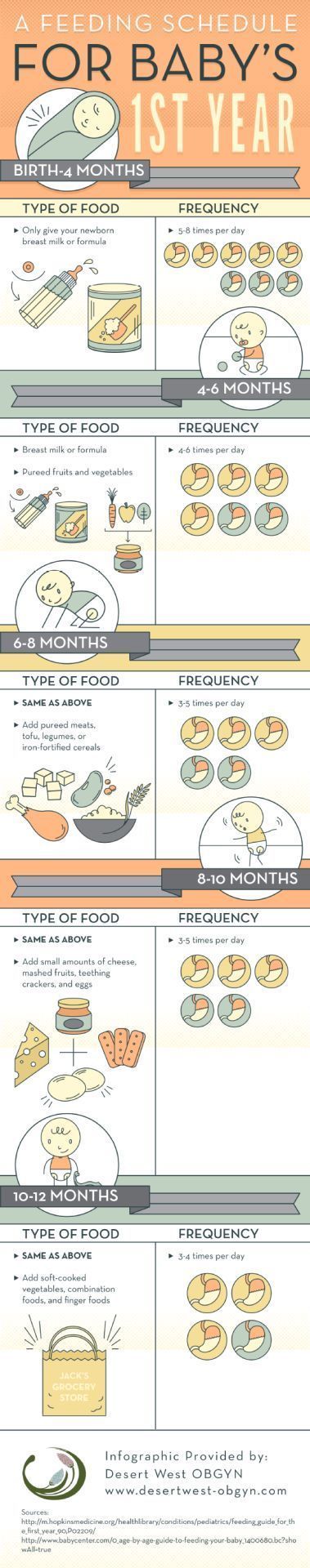 The most common highly allergenic foods include cow's milk, chicken eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish and fish. If a child has a high risk of developing allergies or an existing allergic disease, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician, an allergist-immunologist before introducing highly allergenic products.
The most common highly allergenic foods include cow's milk, chicken eggs, soybeans, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish and fish. If a child has a high risk of developing allergies or an existing allergic disease, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician, an allergist-immunologist before introducing highly allergenic products.
By the age of 8 months, when all the main food groups have already been introduced and your baby is improving his skills to eat on his own, special attention should be paid to the diversity of the composition of dishes and the change in the consistency of food - from puree to finely and coarsely ground. Soft foods cut into small pieces (fruits, vegetables, meat, etc.) are perfect for a little gourmet, which diversifies his diet and will contribute to the formation of chewing skills.
By 9–12 months, most babies have the dexterity to drink from a cup (holding with both hands) and to eat foods prepared for other family members. This behavior needs to be encouraged, but combined with regular feeding to meet energy and nutrient requirements.
It is advisable to use industrial products that are designed specifically for young children after a year.
What should not be given to the baby?
It is not recommended to add salt or sugar to food to enhance the taste.
Drinks that should be avoided include fruit juices, whole cow and goat milk (whole milk is not recommended for children under one year old, and even longer, due to a high risk of developing iron deficiency and increased kidney stress), sweet fruit drinks, compotes and carbonated drinks.
Also, some foods should be excluded from the diet of infants: solid round foods (for example, nuts, grapes, raw carrots, raisins, peas, etc.), due to the fact that the child can choke on them.
It is not recommended to eat products with added sugar, for example, confectionery (marshmallow, marshmallow, marmalade, jam, jam, cookies, waffles, etc.), etc.
You should not give your child the meat of large predatory fish (shark, bigeye tuna, king mackerel, swordfish): these types of fish accumulate more harmful substances than others.
It is forbidden to give honey to children under one year old due to the fact that it may contain spores of Clostridium botulinum bacteria, which in the still immature digestive system of babies are able to multiply, produce toxins directly inside the intestines and, thus, cause infant botulism, which can be fatal. outcome.
Do not give babies raw meat, fish, eggs, caviar, salted fish, soft pickled cheeses because of the risk of intestinal infections.
If you follow all these simple rules, your baby will grow up healthy and happy!
Diets for different ages
References:
1. Methodological recommendations. The program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life in the Russian Federation. [Internet]. - M.: Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2019. [Methodicheskie rekomendaczii. Programma optimizaczii vskarmlivaniya detej pervogo goda zhizni v Rossijskoj Federaczii. [Internet]. – Moscow: Soyuz pediatrov Rossii, 2019.











