When can babies have butter in their food
Butter for Baby: Benefits, Drawbacks, and More
Butter for Baby: Benefits, Drawbacks, and More- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M. D. — By Sarah Garone on April 8, 2021
If we’re honest, we really can’t argue with the catchphrase “Butter makes everything better.” Anyone who’s ever eaten butter dolloped on a baked potato, spread atop a blueberry muffin, or whipped into sweet buttercream frosting can attest to the magical richness of this delicious fat.
But butter isn’t exactly a health food. Its high calorie count and saturated fat content place it in the “sometimes” category of food choices for adults.
Still, while we grown-ups may want to limit our butter intake as part of a balanced diet, do babies need to exercise the same restraint in the face of a flaky croissant or buttery cake? Baby and adult nutritional needs are different — but when it comes to butter, just how different?
Here’s what you need to know about babies and butter.
Aside from the rare possibility of a dairy allergy, butter is safe for babies.
A pure fat, it provides around 100 calories, 11 grams of fat, virtually no protein, and 0 carbohydrates per tablespoon, according to the U. S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Its fat content — which we’ll discuss in a sec — can contribute to baby’s healthy development in several positive ways.
Plus, because of its smooth, creamy texture, butter doesn’t pose a hazard for choking in infants (whew!). As long as it’s spread thin or incorporated into other smooth foods, it should go down quite easily.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) states that you can introduce baby to a wide variety of healthy solids around 6 months of age or when your little one shows signs of readiness.
You don’t have to follow any particular order of which food groups to introduce and when.
While butter might not be among the very first foods you debut on the high chair tray — and you’ll probably want to serve it on something, rather than as a solo pat — kids should be developmentally ready for it at 6 months old and beyond.
Just keep in mind that to spot food allergies or adverse reactions in your child, it’s best to limit your introductions to one new food at a time.
When you’re ready to get started with butter, try serving it with something your child has already sampled.
Believe it or not, butter offers some health benefits for young children, though your baby can be perfectly healthy without eating it, too. And limiting fat intake isn’t recommended for most babies and toddlers, so that shouldn’t be a concern.
Then there’s butter’s satiation factor. Not only does the fat in butter help keep baby bellies full, its high calorie count can be an advantage for kids who need to put on weight (though this is rare in babies). If you’re concerned about your little one’s weight, talk with their doctor about the possible need for extra calories.
Butter is also a surprising source of vitamins. (Who knew?) One tablespoon contains 400 international units of vitamin A, as well as small amounts of vitamin D, vitamin E, vitamin B12, and vitamin K2, according to the USDA.
Finally, the real star of butter’s benefits for babies might be its fat content.
For decades, research (like this 1999 study) has shown the important role fat plays in babies’ neurological development and brain function. Getting enough each day from nutritious sources is a critical piece of the puzzle for infant brain health.
Like anyone else, babies aren’t immune to the delicious charms of butter — so it’s possible that your little one could overdo it on the creamy fat.
According to the AAP, certain conditions may call for cutting back the saturated fat in your child’s diet.
Parents of children with overweight, at risk of overweight, or with a family history of heart disease or high cholesterol should speak with their pediatrician or registered dietitian about the possibility of limiting saturated fats, as in foods like butter.
Another buttery pitfall for little eaters: If too much fat fills up their tummies, they may not have an appetite for other nutritious foods. Keep butter servings moderate to help your child leave room for fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and other building blocks of a balanced, nutritious diet.
Margarine enjoyed a heyday back in the 1970s and 1980s, when the prevailing nutritional wisdom ran that dietary fat was a leading contributor to excess body fat. And it’s true that margarine, made from vegetable oils, contains less fat than butter.
However, the hydrogenation process often used to create margarine produces trans fats, which have been linked to increased risk of health issues like inflammation and heart disease.
To prevent the formation of trans fats, some margarine producers instead use a production method called interesterification, but the health effects of this process are debated.
As for feeding margarine to your baby, just note that any type of margarine is a highly processed food. Processed foods aren’t all bad — and you’re certainly not a bad parent if your kiddo eats them sometimes — but in general, the more whole foods you can offer your child, the better.
Because of all the benefits of fat for infant development, experts give babies a major green light on this macronutrient. Until kids reach the age of 2, the AAP advises not restricting fats in their diet.
Until kids reach the age of 2, the AAP advises not restricting fats in their diet.
In fact, babies and toddlers should get about half their daily calories from fat. Since 1-year-old babies need around 1,000 calories per day, this means 500 calories can come from fats (totaling about 56 grams of fat per day).
Of course, not all these fat grams should come from butter. You might begin with a 1-teaspoon serving of butter for your baby. (And be sure to offer fats from a variety of other nutritious sources, such as nut butter, avocado, olive oil, and fatty fish.)
Much of a baby’s fat intake may come from breast milk, formula, or — if they’re over 1 year old — whole milk.
For such a simple product, butter can come with head-spinning variety. When shopping at your local grocery store, you may wonder which of the numerous butters in the dairy case is best for your baby.
When budget allows, consider opting for organic butter. Not only are organic farming practices more environmentally friendly, they result in foods that may lessen your child’s exposure to potentially harmful pesticides.
Butter made with cream from grass-fed cows’ milk is another great (though sometimes pricey) choice.
Research from 2019 shows that grass feeding may improve the nutrition of cows’ milk, boosting nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid. However, the health benefits aren’t clear.
Butter can make its way into everything from fancy soufflés to long-simmering risottos. If you’re cooking these for your family, there’s no need to leave the butter out of your little one’s portion.
And if your child’s doctor really suggests looking for more ways to add butter to their diet, you can try these simple serving ideas:
- Add a small amount of butter to cooked vegetables (especially those with a bitter flavor, like spinach, broccoli, or Brussels sprouts).
- Make toast points for baby by spreading butter on toasted whole wheat bread, sliced into quarters.
- Use butter as a base in creamy pureed soups like potato, tomato, or cream of mushroom (cooled down to avoid scalding baby’s mouth).

Some foods are tougher than others to introduce to your baby — but your little one isn’t likely to have a hard time accepting butter. (We’re betting there’ll be no need for the “Here comes the airplane” game here.)
In addition to its rich flavor and creamy texture, butter can even provide health benefits for your growing kiddo’s body and brain. Keep portion sizes moderate and let your high chair diner develop a taste for this delicious fat.
Last medically reviewed on April 8, 2021
- Parenthood
- Baby
- 06 Months 1 Year
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Alothman M, et al. (2019). The “grass-fed” milk story: Understanding the impact of pasture feeding on the composition and quality of bovine milk.

ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6723057/ - Butter. (2019).
fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/551488/nutrients - Feeding & nutrition tips: Your 1-year-old. (2020).
healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/toddler/nutrition/Pages/Feeding-and-Nutrition-Your-One-Year-Old.aspx - Infant food and feeding. (n.d.).
aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/HALF-Implementation-Guide/Age-Specific-Content/Pages/Infant-Food-and-Feeding.aspx - Mills CE, et al. (2017). What are interesterified fats and should we be worried about them in our diet?
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5497165/ - Milner JA, et al. (1999). The role of dietary fat in child nutrition and development: Summary of an ASNS Workshop.
academic.oup.com/jn/article/129/11/2094/4721978 - What about fat and cholesterol? (2018).
healthychildren.org/English/healthy-living/nutrition/Pages/What-About-Fat-And-Cholesterol. aspx
aspx
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Apr 8, 2021
Written By
Sarah Garone
Edited By
Jessica Jondle
Medically Reviewed By
Karen Richardson Gill, MD
Copy Edited By
Chris Doka
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D. — By Sarah Garone on April 8, 2021
related stories
Can Babies Eat Pickles?
Can Babies Eat Onions?
Baby Feeding Schedule: A Guide to the First Year
When Can Babies Eat Cheese?
Can Babies Eat Tomatoes?
Read this next
Can Babies Eat Pickles?
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.N., CCRN, CPN
When barbecue season rolls around, pickles can be fair game for babies. Just keep sodium content in mind.
READ MORE
Can Babies Eat Onions?
Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R.
 D.
D.With their savory, aromatic flavor and tons of health benefits, onions can be a healthy, tasty addition for babies.
READ MORE
Baby Feeding Schedule: A Guide to the First Year
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D.
You may have questions about feeding your baby. How much should they eat? How often should they eat? Will they ever be on a schedule? Here is what you…
READ MORE
When Can Babies Eat Cheese?
Medically reviewed by Jillian Kubala, MS, RD
Your baby can eat cheese made from pasteurized milk shortly after it's safe to introduce solids. Here are some benefits — and risks — to know about.
READ MORE
Can Babies Eat Tomatoes?
Medically reviewed by Jillian Kubala, MS, RD
Tomatoes can be nutritious, tasty treats for babies.
 Here's what you need to know about giving them to your little one.
Here's what you need to know about giving them to your little one.READ MORE
The Best Humidifiers for Baby Nurseries
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.N., CCRN, CPN
A humidifier for your baby may help ease the symptoms of a cold or other respiratory illness. Learn more about things to keep in mind when buying a…
READ MORE
Can Babies Drink Goat’s Milk?
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D.
Goat's milk or goat's milk-based formulas may be a healthy option for babies with cow milk sensitivities or for those with other health concerns about…
READ MORE
Kidney Problems in the Premature Baby
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.D.
A baby's kidneys usually mature quickly after birth. Problems balancing the body's fluids, salts, and wastes can occur during the first four to five…
READ MORE
The Best Breast Pumps for 2023
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
Finding the best breast pump for you can be a challenge.
 That's why we've put together this list of options based on experience from moms who have…
That's why we've put together this list of options based on experience from moms who have…READ MORE
Signs and Symptoms of Group B Strep
Medically reviewed by Meredith Goodwin, MD, FAAFP
The symptoms of group B strep disease differ in babies and adults. Learn more about the signs of this condition in newborns and other high risk…
READ MORE
Can Babies Have Butter? - Netmums
Your browser cannot play this video.
BABY
Last modified on Wednesday 7 April 2021
Find out when it's safe to give your baby butter. Plus, get tips on how to serve butter to your little one and information on allergies.
This page contains affiliate links, which means we may earn a small amount of money if a reader clicks through and makes a purchase. All our articles and reviews are written independently by the Netmums editorial team.
The official advice on when babies can eat butter
The NHS says you can introduce butter to your baby's diet from around six months old.
At this age, babies can start to eat meals which include fats such as butter, oils and oil-based spreads. Fats are important for babies and children under the age of two, as they need the energy from it and there are some vitamins that are only found in fats. That's why babies should also have full-fat milks, cheeses and other dairy products.
It's safest to wait until around six months before giving your baby any solid food, because younger babies may not be able to sit up and swallow well.
Once you start serving your baby different solid foods, you can start to add butter to them too. It's recommended that you use a full-fat butter, rather than a low-fat one, as babies need the energy in fats.
How to introduce butter to your baby
With cooked food
You can start off introducing butter to your baby by mixing it in with other foods that your baby has already tried.
If your baby is only eating small amounts or struggling to gain weight, the NHS recommends adding butter to your baby's food in the following ways:
- Add between half and one full teaspoon of butter to two tablespoons of vegetable puree or mashed potato – or anything else your baby likes!
- Cook meats, fish or lentils with butter or oil for your baby, instead of baking or grilling them.
- You can also add a little melted butter to cooked vegetables for your baby, as this boosts calories and can help with absorbing certain vitamins.
If your baby is gaining weight healthily, it's still fine to give them butter, but they may not need as much.
On toast or bread
An easy way to serve butter to your baby is to spread it on some toast or bread.
You can spread butter onto one or two fingers of toast or pitta bread to make a nice finger food for your baby. Your baby will enjoy picking bits of food up and feeding themselves, and it also helps to develop hand-eye coordination.
Butter will also go well on mini rice cakes and crackers, or even on small pieces of enriched breads like croissants, brioches or a Scotch pancake.
For more information on introducing your baby to solid foods, check out our article on getting started with weaning.
Health benefits of butter for babies
Butter is largely made up of fat, but babies need full-fat dairy products as they're a good source of calcium, which helps them build strong bones and teeth (though babies will get more of their fat intake from milk, cheeses and other dairy products).
Butter is also a good source of:
- vitamin A (for a healthy immune system, skin and vision)
- vitamin D (for healthy bones, teeth and muscles)
- vitamin E (for strengthening the immune system and healthy skin and eyes)
- vitamin B12 (for making red blood cells and releasing energy from food)
However, it's important to remember that because babies will only have small amounts of butter in their food, they will be only getting small amounts of these vitamins.
Could my baby have a cow's milk allergy?
Butter is made from cow's milk, which is one of the main food allergens to be aware of.
An allergy to cow's milk, also known as cow's milk protein allergy (CMPA), is one of the most common childhood food allergies. It affects around 7% of babies under the age of one, although most children grow out of it by the time they're five.
If allergies, asthma or eczema run in your family, your child may be more likely to develop an allergy, too. You might want to talk to your GP or health visitor for advice before weaning your baby.
When you first start introducing new food and drink to your child it's a good idea to give them any that can cause an allergy – like cow's milk or butter – in small amounts and one at a time, with several days between them. That way, if your baby does have a reaction, you'll know what caused it.
According to the NHS, the main foods and drinks that can cause an allergy are:
- cow's milk
- eggs
- foods that contain gluten, including wheat, barley and rye
- nuts and peanuts (serve them crushed or ground)
- seeds (serve them crushed or ground)
- soya
- shellfish (don't serve raw or lightly cooked)
- fish
So try to avoid giving any of these other foods at the same time as you give your baby cow's milk or butter for the first time.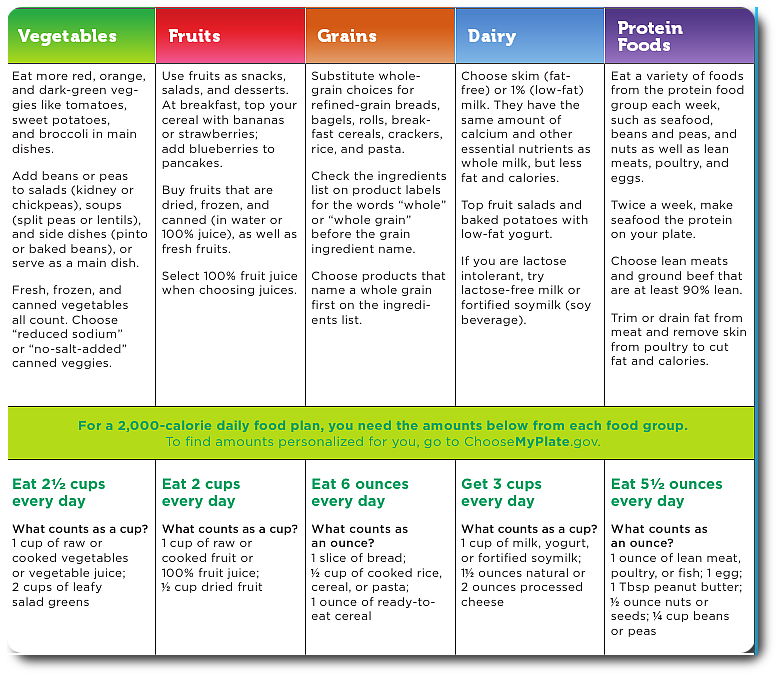
Signs of allergies in babies
If your baby does have a cow's milk allergy, you'll probably notice one or more of the following symptoms:
- eczema that doesn't improve with treatment
- stomach ache, diarrhoea, vomiting, colic or constipation
- a cough
- wheezing and shortness of breath
- itchy throat and tongue
- itchy skin or rash
- swollen lips and throat
- runny or blocked nose
- sore, red and itchy eyes
Lactose intolerance
While lactose intolerance isn't an allergy, it can also cause your baby or child discomfort. Lactose intolerance happens when the body can't digest lactose, the natural sugar found in milk.
This means that butter can also affect lactose intolerant people. However, as butter only contains a low amount of lactose, some lactose intolerant people are able to eat butter without any problems.
The NHS says lactose intolerance can be temporary and may come on for a few days or weeks after a stomach bug.
Symptoms can include wind, stomach pain, diarrhoea and vomiting.
What should I do if I think my baby has an allergy?
If you think your baby may have an allergy, speak to your health visitor or GP. If the reaction is mild, don't cut important foods out of your baby's diet until you've received medical advice, as your baby could miss out on important nutrients.
Less commonly, cow's milk (found in butter) can cause a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening. If your baby has trouble breathing, or loses consciousness, call 999 for an ambulance straight away and tell them that you think it could be anaphylaxis.
Butter recipes for babies
Whether you're including butter in your cooking, mixing it in with your baby's favourite puree, or adding butter to toast, these recipes are suitable for babies:
- Baked sweet potatoes with ginger and lime butter
- Cheesy mash
- Mashed neeps
- Carrot puree for babies
- Broccoli puree for babies
- French toast
Weaning by baby feeding guru Annabel Karmel is a must for every parent's bookshelf and has all the information you need about your baby's first foods. See more details here at Amazon.
See more details here at Amazon.
The Baby-led Weaning Cookbook by Gill Rapley has over 130 recipes that the whole family can enjoy. See more details here at Amazon.
Looking for more tips on feeding your baby? Check out our articles below, or swap tips and meal ideas with other parents in our forum.
Related stories
7 things a nutritionist wishes parents knew about weaning
CHAT: Weaning drop-in clinic
Avoid these common choking hazards for babies and children
Butter for a child: when can you start giving, how much
Tiunova Elena
Published: 11/24/2022
Reading time:
691
What role do these components play?
Butter is a tasty addition to food. Usually the child eats it with pleasure: in porridge, potatoes or on bread. Can children have butter?
You can. If you adhere to the norms of its use, then the oil will benefit the baby.
What is in it?
Butter contains milk fat, vitamins A, D, K, choline, cholesterol *, **.
From choline in the body is obtained:
- acetylcholine, with which the nervous system works,
- phospholipids, which ensure the development of the brain.
Cholesterol is used to create:
- adrenal hormones: eg aldosterone and cortisol. Aldosterone regulates the amount of water and salts in the body. Cortisol is responsible for maintaining energy reserves in the human body;
- cell walls
- bile acids. With their help, vitamins A, D, E are assimilated. When there are a lot of animal fats in food - several times more than the norm - then cholesterol is also harmful.
Milk fat is easy to digest and gives energy to the baby ***.
So do not spoil the porridge with butter: the point is in its quantity and the age of your baby.
At what age can a child have butter?
It is added to porridge from 4-5 months ***.
Children may be allergic to butter: it contains cow's milk proteins in small amounts.
For the first time, give just a little bit of oil, about ¼ - ½ teaspoon. If suspicious symptoms do not appear: rash, diarrhea, itching, swelling around the mouth, then add it to the porridge the next day.
This is important!
The norm of butter for a child in the first year is 3-5 g per day.
Which children should not have butter?
If your baby is over 1 year old, treat him to a butter sandwich for breakfast. The norm of butter for a child older than a year is 10-20 g per day. This means that you can add a little butter to your porridge and side dish every day, but let's have a sandwich every 3 days ***.
Do not give this oil to:
- children who are allergic to cow's milk protein.
 Who can not milk, cottage cheese, kefir and yogurt - butter is also impossible. For them, add vegetable oil to the porridge.
Who can not milk, cottage cheese, kefir and yogurt - butter is also impossible. For them, add vegetable oil to the porridge. - overweight children. Here are the weight guidelines ***.
If there are no contraindications, have your child eat butter in porridge and on sandwiches. Your task is to monitor the consumption rate.
Sources:
* https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/kislomolochnye-produkty-v-pitanii-detey-rannego-vozrasta/viewer
** https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n /primenenie-kislomolochnyh-produktov-v-pitanii-detey-opyt-i-perspektivy
***http://www.pediatr-russia.ru/sites/default/files/nacprog(2019).pdfArticle author
Tiunova Elena
Pediatrician of the highest category, nutritionist, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department of faculty pediatrics and propaedeutics of childhood diseases, Ural State Medical University
About the author
Share on Vkontakte Share on Odnoklassniki
Contents of the article
- What role do these components play?
- Which children should not have butter?
Products from the article
Might be interesting
Butter for a baby: how much and when to start giving - Parents.
 ru
ru About nutrition
- Photo
- Getty Images
At what age can a child be given butter? Usually, this product is introduced to the baby in the interval from 4 to 6 months, when complementary foods are introduced. Often this product is put in cereals, but it can also be seasoned with vegetable dishes. If you buy canned food for your baby, the oil supplement will be superfluous: the required amount of dietary fat is already there.
A valuable product
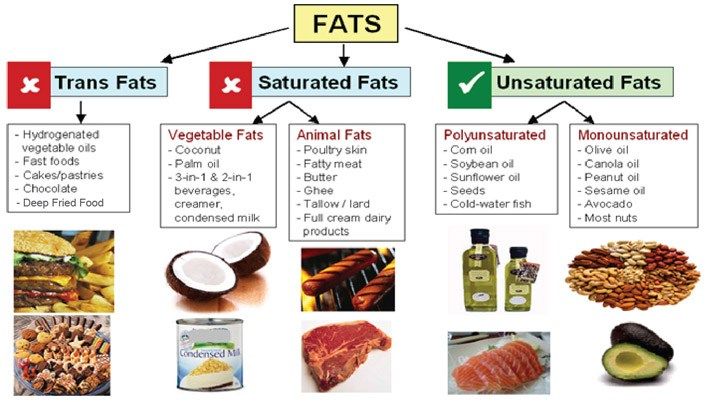
The nutritional value of butter is determined by milk fat, which is needed by the body as a source of energy and fat-soluble vitamins. Although these fats are animal based, they are easily digested and are 98% digestible. In addition, they contain not only saturated, that is, "harmful" components, but also useful ones - monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. These are linolenic, linoleic and arachidonic acids, which are involved in the formation of immunity.
 And, finally, milk fats contain essential vitamins A, E, D, B2. Vitamin A is included in the visual pigment rhodopsin and provides color perception, B2 is needed for hair growth, healthy skin and nails, E affects the reproductive organs, and D contributes to the accumulation of calcium and phosphorus in bone tissue and its strengthening.
And, finally, milk fats contain essential vitamins A, E, D, B2. Vitamin A is included in the visual pigment rhodopsin and provides color perception, B2 is needed for hair growth, healthy skin and nails, E affects the reproductive organs, and D contributes to the accumulation of calcium and phosphorus in bone tissue and its strengthening. At the same time, butter contains quite a lot of cholesterol and calories, so you should not get carried away with this product. An excess of both in the body can lead to a violation of fat metabolism.
Norms of consumption
Like any complementary foods, butter is gradually introduced into the baby's diet. You should start with unsalted or sweet cream. They do not contain lactic acid bacteria that can upset the balance of the intestinal flora of the child. The first serving is 1 g per day. By 6 months, it can be increased to 4 g (for comparison: 5 g of melted butter fits in a teaspoon), and by the year - up to 6 g per day.
 From 1 to 3 years old, the baby can consume 15-20 g of this product daily. It is better to distribute the volume over 3 meals: in the morning put butter in porridge or spread on bread, in the afternoon - put it in a side dish, and in the evening cook any dish on it.
From 1 to 3 years old, the baby can consume 15-20 g of this product daily. It is better to distribute the volume over 3 meals: in the morning put butter in porridge or spread on bread, in the afternoon - put it in a side dish, and in the evening cook any dish on it. - Photo
- Getty Images
Melted version
Melted butter is also very healthy. Since it contains almost no cow's milk proteins and lactose, this product can be given to children with lactase deficiency and intolerance to cow's milk proteins.
Ghee helps digestion, has a beneficial effect on the reproductive system and intelligence. In addition, it improves memory, increases mental abilities and keeps the central nervous system in good shape. When buying it in a store, pay attention to the smell, color and consistency of the product. Good quality butter has a caramel flavor and an amber color and must be soft.
- children who are allergic to cow's milk protein.