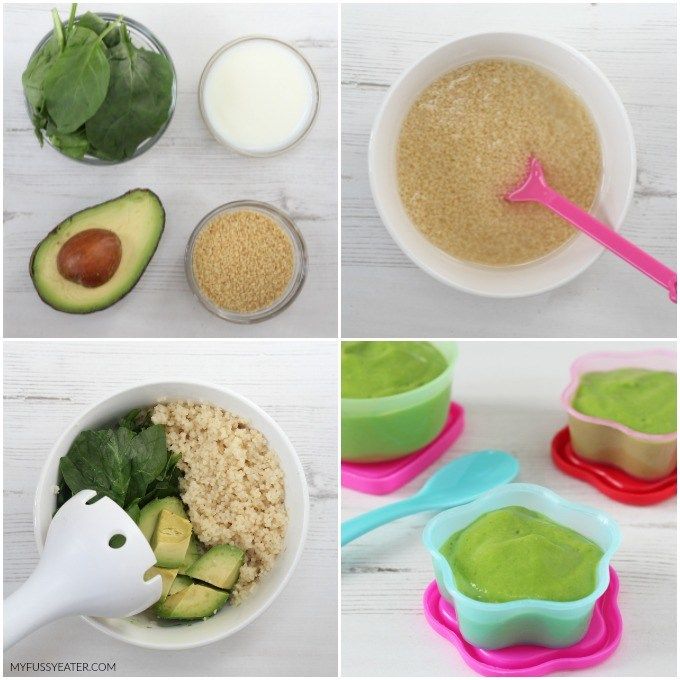
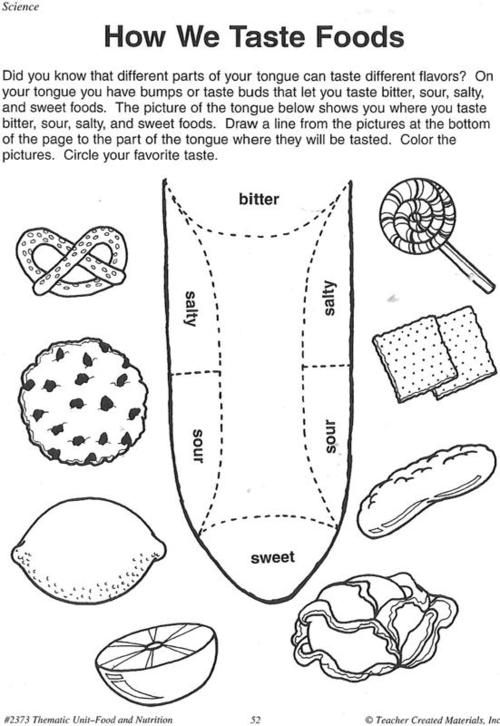
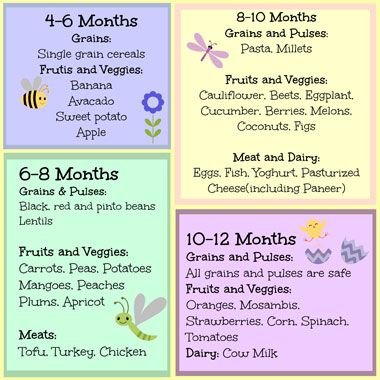
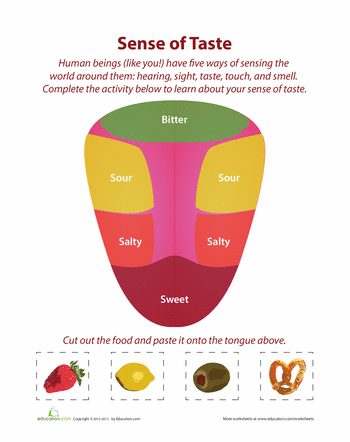
When can i let my baby taste food
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday.
 It can cause botulism in babies.
It can cause botulism in babies. - unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.

- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods. (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
- After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
In Baby's 'First Bite,' A Chance To Shape A Child's Taste : The Salt : NPR
Heard on Fresh Air
Food writer Bee Wilson says that babies are most open to trying new flavors between the ages of 4 and 7 months. Duane Ellison/iStock hide caption
toggle caption
Duane Ellison/iStock
Food writer Bee Wilson says that babies are most open to trying new flavors between the ages of 4 and 7 months.
Duane Ellison/iStock
Food writer Bee Wilson has a message of hope for parents struggling to get their children to eat their veggies: "As parents, we have a far greater power than we think we have to form children's tastes," Wilson tells Fresh Air's Terry Gross.
In her new book, First Bite, Wilson examines how genetics, culture, memory and early feeding patterns contribute to our food preferences. She says that a child's palate can be formed even before birth. And this insight can be helpful for parents who want their children to eat well and healthfully.
Wilson is also the author of Consider the Fork: A History of How We Cook and Eat. Charlotte Griffiths/Basic Books hide caption
toggle caption
Charlotte Griffiths/Basic Books
Wilson is also the author of Consider the Fork: A History of How We Cook and Eat.
Charlotte Griffiths/Basic Books
"One of the main things we know about taste is that liking is a consequence of familiarity, so the things that our mothers eat, even before we're born, affect the way we'll respond to those flavors when we later encounter them because they seem familiar," Wilson says.
A mother of three, Wilson notes that babies are most open to trying new flavors between the ages of 4 and 7 months. But, Wilson adds, even if parents miss introducing a food during the so-called "flavor window," all hope is not lost.
"It's not that the flavor window then flips shut ... and we can never learn to love bitter green vegetables. Humans can learn to love new flavors at any age," Wilson says. "One of the amazing things about our relationship with food is how malleable it is, how plastic it is. But we don't usually as adults give ourselves an opportunity to change."
Interview Highlights
On the "flavor window" that occurs between 4 and 7 months
Researchers I've spoken to [about] the question of how you get children to be less picky eaters [and] how you get them to try more different vegetables say that the World Health Organization advice, which currently says you should keep them on an exclusive milk diet up to 6 months, is wrong. It's not that a child necessarily needs any nutrition besides milk before 6 months, it's that you're missing an opportunity to introduce them to all of these flavors which they would likely accept at this age. Then, having accepted them, they would seem familiar when they encounter them again as toddlers.
It's not that a child necessarily needs any nutrition besides milk before 6 months, it's that you're missing an opportunity to introduce them to all of these flavors which they would likely accept at this age. Then, having accepted them, they would seem familiar when they encounter them again as toddlers.
On how our palates are formed while we're still in the womb
[Our palate is] formed [before breast-feeding] — it's formed when our mothers are expecting us. There have been remarkable studies done showing that if someone eats a lot of garlic when they're pregnant, their amniotic fluid will taste and smell garlicky. So imagine swimming around in that for 9 months. ... That baby will grow up to love garlic. ... It feels like home, it tastes like home. One of the main things we know about taste is that liking is a consequence of familiarity. So the things that our mothers eat, even before we're born, affect the way we'll respond to those flavors when we later encounter them because they seem familiar.
The flavor of milk is then hugely important as well. With mothers who breast-feed, there was a study done showing that if they drank a lot of carrot juice, when those babies first tasted solid food, they preferred cereal that was flavored with carrot juice. So the flavor of carrots goes into the [breast milk], the babies experience it, and then they have all of these wonderful, positive feelings about carrot. This is getting replicated many, many times. In most cases it's not something like carrot or broccoli. There have been studies done with rats who are fed on a junk food diet and their babies gravitate towards junk food rat chow.
On how store-bought formula can also affect taste long-term
Breast milk has varied flavors, whereas formula milk has a single flavor, depending on which brand you pick. But even with formula-fed babies there are some interesting things that have come out of scientific experiments. There's a type of formula called hydrolysate, which is designed for babies who can't tolerate regular cow's milk, and to adults it has a really offensive, horrible, hay-like, musty aroma. But to the babies who've been reared on it, it's like nectar. One study showed that these children, when they were older, when they're aged 4, gravitated towards sour flavors. So it was if they were imprinted with the flavor of this nasty formula milk. But, again, it's a really useful case of how powerful these early tastes can be. As parents, we have a far greater power than we think we have to form children's tastes.
But to the babies who've been reared on it, it's like nectar. One study showed that these children, when they were older, when they're aged 4, gravitated towards sour flavors. So it was if they were imprinted with the flavor of this nasty formula milk. But, again, it's a really useful case of how powerful these early tastes can be. As parents, we have a far greater power than we think we have to form children's tastes.
On how we are hard-wired to love sweetness
All human beings are hard-wired to love sweetness. This is a cross-cultural phenomenon — it's been seen in babies in every continent of the world, that they smile if you offer them a little taste of something sweet. Equally, we all are born with a mild aversion to bitterness. And curiously, with salt, we have no feelings at all about salt when we're born. And then [by age] 4 months we get switched onto it and develop a salt preference, and nobody really knows why that's true. But with the sweetness thing — so, we're hard-wired to love sweetness. Many people have interpreted this to mean that we're doomed to grow up and love junk food. ... All of our specific tastes for particular flavors are learned. As omnivores, this has to be the case because human beings are forced to eat in such different food environments. So the fact that we love sweetness as a baby doesn't mean that we're going to love nothing but chocolate; we could get that sweetness in the form of corn on the cob, or caramelized fennel. All of our flavor preferences are ones that we learn over the course of a lifetime. The trouble is that most of us don't see it that way.
Many people have interpreted this to mean that we're doomed to grow up and love junk food. ... All of our specific tastes for particular flavors are learned. As omnivores, this has to be the case because human beings are forced to eat in such different food environments. So the fact that we love sweetness as a baby doesn't mean that we're going to love nothing but chocolate; we could get that sweetness in the form of corn on the cob, or caramelized fennel. All of our flavor preferences are ones that we learn over the course of a lifetime. The trouble is that most of us don't see it that way.
On how children's food has changed since World War II
If you look to previous generations, before the second world war, and indeed afterwards a bit, there was a nursery food mentality. So the idea was it was safest to give children foods that they didn't actually like, which were very plain but very nourishing. Then, in the postwar years, partly fueled by a transformation of the food supply, much greater industrialization, we went to a completely opposite view of what children's food should be. It was that it should be sweet and palatable and designed to make children smile. We all know that the kid's breakfast cereals are the ones which are highest in sugar in the whole of the cereal aisle. And it's really curious that we should've swung in this way from one extreme to another — from food which was nourishing but unpleasant, to food which was too pleasant and deeply un-nourishing. The ideal way to feed children would be somewhere in the middle. And actually, the ideal way to feed children would be to give them food that's not that dissimilar from an adult diet.
It was that it should be sweet and palatable and designed to make children smile. We all know that the kid's breakfast cereals are the ones which are highest in sugar in the whole of the cereal aisle. And it's really curious that we should've swung in this way from one extreme to another — from food which was nourishing but unpleasant, to food which was too pleasant and deeply un-nourishing. The ideal way to feed children would be somewhere in the middle. And actually, the ideal way to feed children would be to give them food that's not that dissimilar from an adult diet.
On authoritative, authoritarian and indulgent styles of feeding
An authoritative feeder would place high demands on the child to eat well. In other words, you wouldn't be stocking your house with loads of junk food. You'd make sure there were nutritious, home-cooked meals on the table, but equally you would be highly responsive to the child and their needs, and you would be respectful when they say "no. " ... On the one hand, there are authoritarian forms of feeding. ... Force-feeding would be an extreme example, but also just any form of saying, "I demand that you eat this." ... "I want a clean plate." ... That style of feeding ... creates an unpleasant atmosphere at the dinner table, but, interestingly, research shows it also seems to result in children who are actually less responsive to their own hunger cues, so they're more likely to end up overweight, paradoxically. The parent who thinks that they're doing the right thing by insisting that you finish this nourishing meal is not allowing the child to develop their own skills, their own judgment about when they stop and when they start eating.
" ... On the one hand, there are authoritarian forms of feeding. ... Force-feeding would be an extreme example, but also just any form of saying, "I demand that you eat this." ... "I want a clean plate." ... That style of feeding ... creates an unpleasant atmosphere at the dinner table, but, interestingly, research shows it also seems to result in children who are actually less responsive to their own hunger cues, so they're more likely to end up overweight, paradoxically. The parent who thinks that they're doing the right thing by insisting that you finish this nourishing meal is not allowing the child to develop their own skills, their own judgment about when they stop and when they start eating.
The other style of parenting, or feeding, would be indulgent. And there are signs that this is becoming one of the most common ways of feeding a child, and as with so much of what we do as parents, it comes with the most loving intentions. To feed a child in an indulgent way would be to be highly responsive to them as a person, what they love, what they seem to need, the foods they crave, the foods they demand, but the indulgent style would place no demands on them to eat well, or fewer demands. There'd be no sense of, "Are you really hungry?" There'd be no sense of, "Well, I only want you to have these foods because they're the ones that'll do you good." Again, there are studies done showing indulgent parenting is strongly correlated with higher child obesity. ...
There'd be no sense of, "Are you really hungry?" There'd be no sense of, "Well, I only want you to have these foods because they're the ones that'll do you good." Again, there are studies done showing indulgent parenting is strongly correlated with higher child obesity. ...
Food and love are so bound up, it's sometimes hard to see where the sugar ends and the love begins.
Bee Wilson
It's such a wonderful feeling to see the treat disappear and to see the happy face. Feeding, no less than eating, is a learned behavior, and we learn to feed through our parents, who probably themselves rewarded us with food. Food and love are so bound up, it's sometimes hard to see where the sugar ends and the love begins.
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to mixed or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary food is introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually “dilute” this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. The materials were prepared by the staff of the Healthy and Sick Child Nutrition Laboratory of the National Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of Russia and are based on the recommendations given in the National Program for Optimizing the Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation, approved at the XV Congress of Pediatricians of Russia (02.2009d.) Main page / Meals / 0.5-3 year old child Breakfast Snacks Lunch and dinner The most important child nutrition keywords: There are many ways to offer fruits and vegetables to your child: There are many different uses for fruits and vegetables. Fruits and vegetables do not have to be eaten fresh or boiled, they can be discreetly added to various dishes: Get your child used to a variety of simple salads, such as carrot or kale salad. But to get the child used to different tastes, try other salads, for example, a salad of sauerkraut, pumpkin, onions (bulb and green). Children grow in periods, which means that there may be times when the child eats too little, and there are times when he eats more. Many young children go to nursery from about 1.5 years old. This means that often on weekdays the child eats out three times - breakfast and lunch, as well as dinner. According to how much time the child spends in kindergarten, how many times and what he eats, it is necessary to form the child's home meals. The body needs to be regularly provided with the necessary amount of energy, so it is important to stick to daily meals. Keep up to date with the weekly menu in kindergarten, make different options for homemade dinners or weekend lunches. In Estonia, food regulations have been developed in pre-school child care institutions, which are regulated by an order of the Minister of Social Affairs. It is not so easy for children under one year old, even under 2 years old, to find the right food if you are not eating at home. Meals offered to children often include too much salt or sugar. Children's meals may appeal to children (often due to their high fat, sugar and/or salt content), but their nutritional value is often very low. Instead of children's meals, it is better to choose a regular dish or soup and ask for it to be prepared with as little salt as possible. The food offered in fast food places is generally not suitable for children under 3 years old (and in fact, adults). I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VMS
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk
0.5-3 year old child – Tarkvanem ‹ Meals – Tarkvanem
Lateral navigation
Children under the age of 3 (actually people of any age) do not need sweet or salty snacks, soft drinks, highly processed and/or high sugar and salt foods. In addition to the protective properties of breast milk, depending on the mother's diet, the milk tastes slightly different each time, which further helps the baby to accept different tastes when forming eating habits.
In addition to the protective properties of breast milk, depending on the mother's diet, the milk tastes slightly different each time, which further helps the baby to accept different tastes when forming eating habits. 
Meals
The baby's belly is small, so they need to eat more often and in smaller portions. At the same time, in terms of dental health, you should not eat more than 5 times a day. That is, 3 main meals and 1-2 small snacks are ideal.


All children are different, just like adults. Every child has favorite foods, as well as those that they do not like at all. Knowing the preferences of children, the child can slowly teach him to eat those foods that he usually does not eat. To do this, you can hang on the refrigerator a list of products that the child must consume during the day. In this case, it is convenient to track the choice of products and teach the child healthy eating. 
 Habits formed in childhood often influence the choices we make later in life. Some children are quite selective in terms of what he eats and what not; It is important that you, as a parent, be an example to your child and encourage and support healthy eating habits.
Habits formed in childhood often influence the choices we make later in life. Some children are quite selective in terms of what he eats and what not; It is important that you, as a parent, be an example to your child and encourage and support healthy eating habits. 
 Enjoy each other's company while eating.
Enjoy each other's company while eating.
 Why not offer fruit on a skewer (melon, pear, watermelon, grapes).
Why not offer fruit on a skewer (melon, pear, watermelon, grapes).  A child who does not want to eat raw carrots will gladly eat them boiled in vegetable stew.
A child who does not want to eat raw carrots will gladly eat them boiled in vegetable stew.

 If parents still feel that the child may not be getting all the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities, from time to time blood tests can be done by a doctor to check the health.
If parents still feel that the child may not be getting all the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities, from time to time blood tests can be done by a doctor to check the health.
 Clean water should always be available to quench thirst. You can drink up to two glasses of juice per week. If necessary, dilute the juice yourself, do not buy nectars, juice drinks and syrups in the store, not to mention soft drinks. While vitamin-fortified water is thought to help you get enough vitamins, one 750 ml bottle actually contains about 40 grams of sugar, which is about the daily dose of sweets for an adult. A varied, balanced, and regular diet (including cereals, fruits and vegetables, and other food groups) ensures adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, as well as energy, and reduces the desire to eat something sweet.
Clean water should always be available to quench thirst. You can drink up to two glasses of juice per week. If necessary, dilute the juice yourself, do not buy nectars, juice drinks and syrups in the store, not to mention soft drinks. While vitamin-fortified water is thought to help you get enough vitamins, one 750 ml bottle actually contains about 40 grams of sugar, which is about the daily dose of sweets for an adult. A varied, balanced, and regular diet (including cereals, fruits and vegetables, and other food groups) ensures adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, as well as energy, and reduces the desire to eat something sweet.
 At the same time, it is absolutely possible to feed a 2-3-year-old child if he is indiscriminately offered sweets, chocolate, cookies, pastries, soft drinks, etc.
At the same time, it is absolutely possible to feed a 2-3-year-old child if he is indiscriminately offered sweets, chocolate, cookies, pastries, soft drinks, etc.  The more different tastes and dishes you introduce your child to from an early age, the easier it will be for him to get used to food in kindergarten.
The more different tastes and dishes you introduce your child to from an early age, the easier it will be for him to get used to food in kindergarten.