When do babies start eating regular food
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
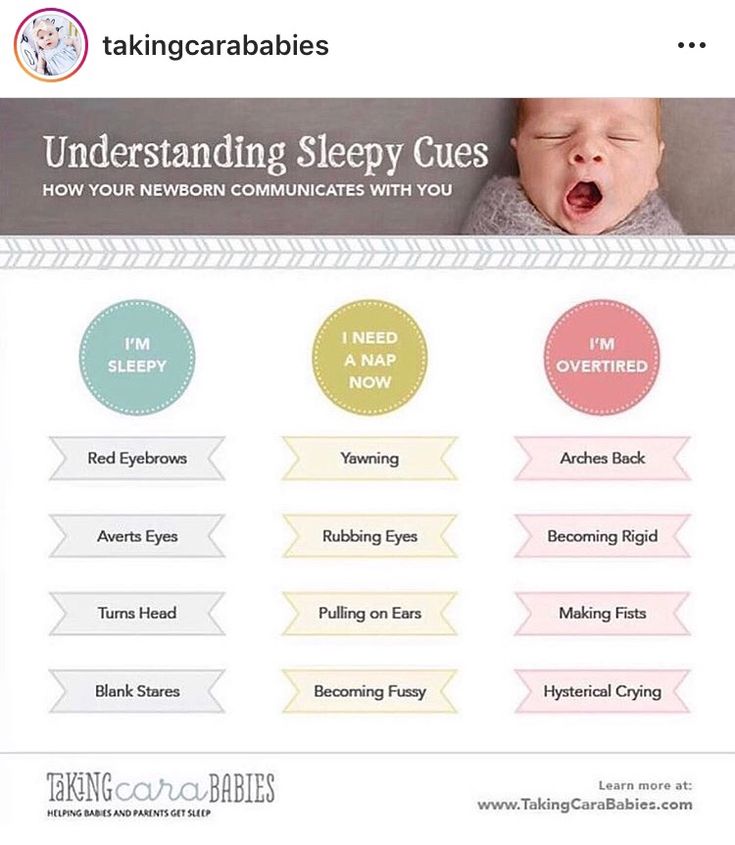
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
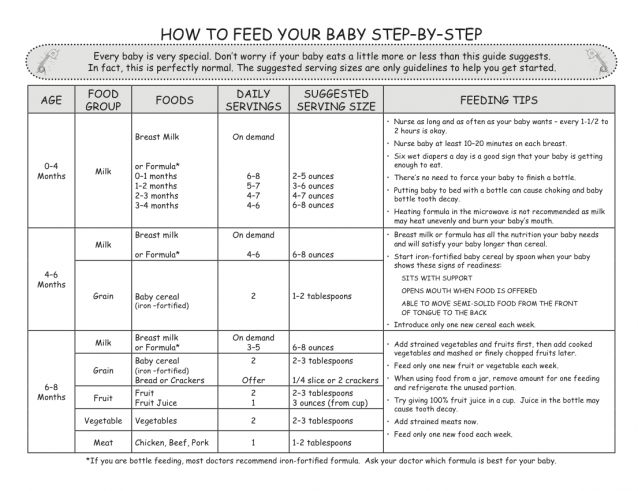
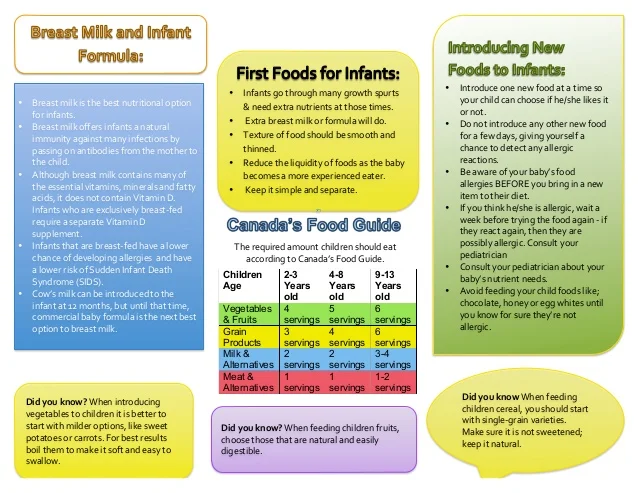
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Solids, Finger Foods, and More
Written by Gina Shaw
In this Article
- Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
- Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
- Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
- Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
- Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
- Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
- Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
- Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
There are many milestones that need to be achieved when a baby is ready to start to eat solid foods. Here are some of the big ones.
Here are some of the big ones.
Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
Most pediatricians, and the American Academy of Pediatrics, recommend introducing solid foods to babies when they are between ages 4 and 6 months. That’s when they start to lose the “tongue-thrust reflex” or extrusion reflex, which is important for sucking the breast or bottle when they are younger, but interferes with feeding. Babies at this point can also lift their heads up independently and hold their necks high.
If your baby is around this age, can sit up well with support, and shows interest in the foods they see you eating, it’s probably a good time to venture into feeding your baby solid food. If your baby is exclusively breastfed, it is recommended that you wait until they are 6 months to start solids.
Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
“Chunking up” babies’ food is a process -- obviously, they shouldn’t go straight from rice cereal to raisin bran. But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
Introduce new textures slowly. Good starters are mashed bananas or mashed avocados. You can also use the “staged” store-bought baby foods -- going from the smooth puree of stage 1 to the slightly thicker stage 2 and then the chunkier stage 3 by around 9 months of age. (Babies don’t necessarily have to have a lot of teeth to handle more texture in their foods -- they can often gum soft foods very well!)
Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
When babies are ready to eat solid foods, they can sit upright with support and hold up their head and neck. They're capable of sitting in a high chair! That's a serious milestone, but you'll need to follow these safety rules: Always buckle a baby into their chair for safety, even if they are unable to get out with the tray in place. As they get older and become more active, they may be able to squirm out. It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
Babies between ages 7 and 11 months usually tell you they’re ready to eat more grown-up foods by trying to grab them from you. Almost any food that is healthy and nutritious and has a soft texture makes a good finger food, if it’s cut small enough: diced pasta; small pieces of well-cooked vegetables such as carrots, peas, or zucchini; and pea-sized bites of chicken or soft meat. Small, unsweetened round cereals and cereal puffs are also a good choice. Avoid feeding your baby grapes, hot dogs (even cut up), nuts, and hard candy, as they are choking hazards.
At first babies “rake” food into their hand, but soon they develop the “pincer grasp” that allows them to pick up small objects between thumb and forefinger. At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
Almost as soon as babies adjust to being fed with a spoon, they'll want to hold and grab the spoon themselves and put it in their mouths. That doesn't mean they're graceful, of course.
Most babies don’t learn to use a spoon effectively until after their first birthday, but let a younger baby who’s interested give it a whirl for practice. Try giving them a soft-tipped spoon to hold while you feed them with another. They can get used to holding the spoon themselves and will also be distracted from grabbing yours.
When you think they are ready to actually navigate the spoon into their mouth, try thicker, stickier foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or cottage cheese. Another tip: Put some cream cheese on the spoon and then a few pieces of O-shaped cereal on top. The cream cheese won’t fly everywhere, and the baby can get the experience of actually getting the cereal into their mouth.
Expect a mess! Use a plastic or other waterproof bib, and put a mat under the high chair to make cleanup easier.
Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
Some pediatricians still recommend waiting until children are at least age 1 before offering them certain foods that are considered highly allergenic, like eggs or fish. But current research doesn’t demonstrate any benefit to waiting past a certain age to introduce these foods, unless you have a significant family history of food allergies or other reasons to believe your baby may be predisposed to them.
There is no evidence that introducing highly allergenic foods to children under age 1 makes them any more likely to be allergic to them, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now says it’s fine to give these foods before the baby's first birthday. Many pediatricians are still very cautious about shellfish and peanuts, however, because allergic reactions to these foods can be particularly dangerous.
Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
Babies don't need water during their first 6 months of life. They get all the water they need from breast milk or baby formula. Babies under age 6 months should not be given any water at all, because it’s easy to fill up their tiny stomachs -- and they should be filling up on the nutrients they receive from the milk to grow. Once they start eating mostly solid foods, around age 9 months, they can start water with meals using a sippy cup.
If your older baby shows an interest in water that you’re drinking, there’s no harm in letting them have a few sips. Just don’t let it replace the nutritious breast milk or formula they should be getting.
Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
Mastering eating with utensils is a long process. Most babies do not become really skilled at it until they are well past their first birthday. Encourage your child to practice safely, and again, be prepared for a little mess. (How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
(How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
0.5-3 year old child - Tarkvanem ‹ Food - Tarkvanem
Main page / Food / 0.5 - 3 year old child
Lateral navigation
- An infant between the ages of 6 months and a year must begin to receive complementary foods in addition to breast milk in order to cover the need for energy and all nutrients.
- Gradually, as the child grows, you can switch to regular food (prepared from unprocessed raw materials, without the addition of salt and sugar).
- Babies over 1 year of age can continue to receive breast milk in addition to complementary foods or normal foods, but by 2 years of age, the baby should mostly switch to regular food. In addition to the protective properties of breast milk, depending on the mother's diet, the milk tastes slightly different each time, which further helps the baby to accept different tastes when forming eating habits.

- When choosing complementary foods and regular meals, it is important to ensure that there is a variety of meals on offer. Both when breastfeeding, and when switching to complementary foods and regular food, babies can experience colic or allergies. Therefore (including during breastfeeding) those foods should be avoided or used with caution, in relation to which the mother herself or the father of the child was sensitive in childhood or remains sensitive in adulthood.
- For children over 2 years of age, the recommendations for nutrition and food selection are similar to adults, but in absolute terms, the recommended amounts are smaller.
- Remember not to teach your child to drink juice, let alone sugary drinks.
Meals
The baby's belly is small, so they need to eat more often and in smaller portions. At the same time, in terms of dental health, you should not eat more than 5 times a day. That is, 3 main meals and 1-2 small snacks are ideal.
At the same time, in terms of dental health, you should not eat more than 5 times a day. That is, 3 main meals and 1-2 small snacks are ideal. Breakfast
- Breakfast is the most important meal of the day - it provides the body with energy so that the child can play and learn new skills.
- If the child is already on a regular diet, porridge is the best choice for breakfast. Make it with a variety of grains, mixed grains, or whole grains. Porridge can be cooked with milk, water or a mixture of both (for children under the age of one who do not receive breast milk, with a subsequent milk formula). Milk mixtures cannot be boiled, so they are always added to food at the end of cooking. Do not add salt and sugar. Instead, flavor your porridge with a variety of fruits and vegetables (e.g. banana, peach, carrot).
- Egg dishes work well, but try to add vegetables to them too.
- For a young child, the best drink is milk (breast milk, formula milk) or water.
- You can give your child a few glasses of juice a week, but it's best to have it as a snack to make breakfast more energizing. Always prefer whole fruits to juices.
- On Sunday mornings, for example, pancakes can be offered. We repeat, cook them without adding salt and sugar, but add either immediately to the dough, or then berries-fruits.
- If the child attends kindergarten, weekday breakfasts should be adapted according to whether the child eats breakfast in the garden and what time he eats it. Breakfast does not need to be eaten immediately after waking up, but it is useful to have breakfast within an hour.
Snacks
- Snacking is important on infants and young children's menus because a young child can only eat a small amount of food at a time. Snacking gives him energy and various important nutrients needed for development and growth.
- Snacks should be as unprocessed as possible (eg, fresh or dry fruits and berries, vegetables, bread, juice, oatmeal, sandwiches, unflavored yogurt, also cottage cheese for children older than one year).

- Candy, crackers, cookies, soft drinks, juice drinks, ice cream, etc., are not good snacks. Even one candy or cookie between meals can ruin a child's appetite for the whole day.
- Do not give your child food as a prize or consolation, or if the child is bored.
Lunch and dinner
- Lunch and dinner can be heavy especially lunch. Soups and a slice of bread with soup go very well, as well as a dessert using a minimum amount of sugar, or even a small second.
- The smaller the child, the more it is necessary to use stewing-cooking in the preparation of his food. Perfect for a variety of casseroles. Since children want to see what ingredients food is made of, teaching a child to eat mixed dishes from infancy can hide vegetables in them that children do not really like.
- For dinner, a hearty vegetable salad is suitable, to which you can add an egg, cheese, fish, meat, homemade cheese or something else.
 If the child eats properly in the garden, the food offered at home should not be very energy intensive. Dinner can be a specific time that the family spends together where they can talk about the events of the day and be together. Here you can discuss the menu for the next day, as well as prepare for the weekend.
If the child eats properly in the garden, the food offered at home should not be very energy intensive. Dinner can be a specific time that the family spends together where they can talk about the events of the day and be together. Here you can discuss the menu for the next day, as well as prepare for the weekend.
- A child should be taught to eat right and healthy from an early age. Habits formed in childhood often influence the choices we make later in life. Some children are quite selective in terms of what he eats and what not; It is important that you, as a parent, be an example to your child and encourage and support healthy eating habits.

- Breast milk tastes sweet, so most babies have a natural craving for anything sweet. At the same time, a child who received breast milk is more even about new tastes, because through breast milk he felt different tastes and it is easier to offer him new dishes.
- Sometimes a child may refuse certain foods, it may take up to 15 attempts before the child gets used to a new food. Be consistent in your decisions, feed your child with all the products necessary for his development, do not give up even when the child refuses for the first time or the first time. If the child actually completely refuses to eat something, change this product to something similar. The most important thing is not to give up. If you are breastfeeding your baby often enough at the same time, there is no need to worry about the baby, even if it takes several months to introduce new foods along with breast milk.
- Young children in their food preferences are guided by two main factors - whether they are familiar with food and the taste of food (sweetness).
 For children under 4 years old, the most important thing is that the child knows what kind of food it is. Therefore, new products must be introduced carefully and in small quantities, leading by example. Getting used to new foods takes time. If you do it carefully and in a playful way, the children will be very interested. The more natural flowers will be presented on the plate, the more beautiful and appetizing the dish will be, the more it will contain various essential nutrients.
For children under 4 years old, the most important thing is that the child knows what kind of food it is. Therefore, new products must be introduced carefully and in small quantities, leading by example. Getting used to new foods takes time. If you do it carefully and in a playful way, the children will be very interested. The more natural flowers will be presented on the plate, the more beautiful and appetizing the dish will be, the more it will contain various essential nutrients. - When eating, the child's mood and environment are important (for example, whether the TV is playing or there are guests), as well as whether the child is hungry.
- For eating, it is imperative to set aside time to enjoy food. When eating together with the family, the child will eat faster, the example of parents is important from early childhood. Enjoy each other's company while eating.
- Appearance and correct food temperature are important for a child. The child will eat with great appetite if he sees what ingredients the food was prepared from.
 Try different foods and cook them in different ways to ensure food variety and availability of different nutrients.
Try different foods and cook them in different ways to ensure food variety and availability of different nutrients. - Teach your child to choose foods from different food groups so that he understands the diversity of food. Give your child the opportunity to choose their own food from suitable foods: this or that fruit, various grains, various vegetables, etc. Teach children to eat plenty of vegetables from an early age. To quench your thirst, offer water, not juice.
- A child should never be scared about food. Food is not a means of punishment or reward. Do not force the child to eat, rather attract. If you force a child to eat, it greatly affects the psyche and behavior of the child and can leave a negative imprint on his entire subsequent life.
The most important child nutrition keywords:
- example
- communal meal
- availability of suitable food
- explanatory work
- time
- choice and decision making
- When a baby is born (recommended already during the mother's pregnancy), it is the last time to review the eating habits of the whole family.
- An example is one of the factors that will begin to shape the nutrition of a young child.
- A child's eating habits are also shaped by what choice of food is available to the family (including the child), how meals are organized at home, etc. First of all, they will begin to influence a child over a year old.
- Many children aged 2-3 are already in nursery or kindergarten, and often spend time at home only in the evenings or on weekends. These meals should form a conscious choice. Children can discuss with children and direct their nutritional wishes.
There are many ways to offer fruits and vegetables to your child:
- The child likes to eat with fingers, sticks, matches. Why ban it?
- As a snack before dinner, after coming home from kindergarten or while watching TV, offer your child instead of chips carrot slices, apple slices, etc.
- Children love sliced carrots, paprika, cucumbers and pieces of cauliflower with dipping sauce on the birthday table.
 Why not offer fruit on a skewer (melon, pear, watermelon, grapes).
Why not offer fruit on a skewer (melon, pear, watermelon, grapes). - If you're in a hurry and don't have time to eat, keep a fruit handy that you can give your child a snack.
- For children, the size of fruit or vegetable pieces and how they are processed may be important. A child may prefer a whole carrot over a grated carrot salad or a stewed carrot dish.
- Young children do not like to chew on large and hard carrots, but they will eat carrots cut into slices with pleasure. It is especially difficult for children to cope with carrots with a hard core.
- If the child does not eat fresh fruits and vegetables at all, then cut them into molds (a month, a heart), maybe you will like it? Why not do it with the kids?
- The child can happily eat a small round sandwich with a face made of vegetable pieces.
- If you are making a salad for children, consider their wishes. As a rule, children like to eat different foods separately.
- A child who does not eat boiled rutabagas or carrots happily eats them raw.
 A child who does not want to eat raw carrots will gladly eat them boiled in vegetable stew.
A child who does not want to eat raw carrots will gladly eat them boiled in vegetable stew.
There are many different uses for fruits and vegetables.
Fruits and vegetables do not have to be eaten fresh or boiled, they can be discreetly added to various dishes:
- soups, vegetable stews, casseroles, wok
- pasta, sauces, cereals, meatballs
- herbs (e.g. dill, parsley) for seasoning dishes
- in pies, cakes, pizzas
- fresh berry sauces for desserts, fruits in jelly and jelly
- in smoothies, milk and juice drinks
Teach your child to enjoy a variety of simple salads, such as carrot or kale salad. But to get the child used to different tastes, try other salads, for example, a salad of sauerkraut, pumpkin, onions (bulb and green).
Children grow in periods, which means that there may be times when the child eats too little, and there are times when he eats more.
- It is useful to ensure that food intake and energy expenditure are balanced.

- If the child is very active, he should eat more.
- If the child seems to be eating too little or too much, keep a food diary - for about a week, write down everything that and how much the child ate and drank.
- If the child has a bowel movement every day, then the amount of food for the child is sufficient, there is no need to worry. Often it turns out that the problem is not in the amount eaten, but in the choice of food. After all, you can get as much energy from a couple of candy cookies as from a good portion of soup. Therefore, it is unreasonable to immediately grab a jar of vitamins and minerals, first of all, nutrition should be reconsidered - sufficient, balanced and varied nutrition will provide the necessary substances. The only exception is vitamin D, which all children should receive as a dietary supplement.
- As long as a varied and balanced diet is available to a child, he grows and develops according to his age, there is no cause for concern.
 If parents still feel that the child may not be getting all the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities, from time to time blood tests can be done by a doctor to check the health.
If parents still feel that the child may not be getting all the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities, from time to time blood tests can be done by a doctor to check the health.
- Ideally, it would be better not to give sweets (sweets, chocolates, cookies, soft drinks, etc.) to children under 3 years of age.
- Candy or biscuits should never be given to children as a consolation, reward or boredom dispersal - on a subconscious level, this may affect his eating habits in the future. This recommendation is quite difficult to follow if the family has older children, but in this case, avoid bringing home sweets (sweets, cookies) and keep them on the table. Instead, put peeled-cut fruits and vegetables on the table.
- To satisfy the desire to eat something sweet, nuts and dried fruits and berries are suitable, but one should not be too zealous with them either. Babies and young children can only be given nuts in a ground or highly ground form, and make sure that children do not have an allergic reaction to them.
 Clean water should always be available to quench thirst. You can drink up to two glasses of juice per week. If necessary, dilute the juice yourself, do not buy nectars, juice drinks and syrups in the store, not to mention soft drinks. While vitamin-fortified water is thought to help you get enough vitamins, one 750 ml bottle actually contains about 40 grams of sugar, which is about the daily dose of sweets for an adult. A varied, balanced, and regular diet (including cereals, fruits and vegetables, and other food groups) ensures adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, as well as energy, and reduces the desire to eat something sweet.
Clean water should always be available to quench thirst. You can drink up to two glasses of juice per week. If necessary, dilute the juice yourself, do not buy nectars, juice drinks and syrups in the store, not to mention soft drinks. While vitamin-fortified water is thought to help you get enough vitamins, one 750 ml bottle actually contains about 40 grams of sugar, which is about the daily dose of sweets for an adult. A varied, balanced, and regular diet (including cereals, fruits and vegetables, and other food groups) ensures adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, as well as energy, and reduces the desire to eat something sweet.
- The risk of being overweight in adulthood is higher in infants who received formula and complementary foods instead of breast milk in infancy.
- It is very likely that an obese child will grow into an obese adult. Fortunately, serious obesity among children aged 0-3 years is very rare and is primarily associated with more serious diseases.
 At the same time, it is absolutely possible to feed a 2-3-year-old child if he is indiscriminately offered sweets, chocolate, cookies, pastries, soft drinks, etc.
At the same time, it is absolutely possible to feed a 2-3-year-old child if he is indiscriminately offered sweets, chocolate, cookies, pastries, soft drinks, etc. - To check whether the child is growing and gaining weight normally, you can look at the growth and weight curve of infants and children, and in case of underweight or overweight, it is imperative to consult a family doctor or pediatrician for further instructions. You can not limit the nutrition of the child, guided by their own ideas.
Many young children go to nursery from about 1.5 years old. This means that often on weekdays the child eats out three times - breakfast and lunch, as well as dinner. According to how much time the child spends in kindergarten, how many times and what he eats, it is necessary to form the child's home meals. The body needs to be regularly provided with the necessary amount of energy, so it is important to stick to daily meals. Keep up to date with the weekly menu in kindergarten, make different options for homemade dinners or weekend lunches. The more different tastes and dishes you introduce your child to from an early age, the easier it will be for him to get used to food in kindergarten.
The more different tastes and dishes you introduce your child to from an early age, the easier it will be for him to get used to food in kindergarten.
In Estonia, food regulations have been developed in pre-school child care institutions, which are regulated by an order of the Minister of Social Affairs.
It is not so easy for children under one year old, even under 2 years old, to find the right food if you are not eating at home. Meals offered to children often include too much salt or sugar. Children's meals may appeal to children (often due to their high fat, sugar and/or salt content), but their nutritional value is often very low. Instead of children's meals, it is better to choose a regular dish or soup and ask for it to be prepared with as little salt as possible. The food offered in fast food places is generally not suitable for children under 3 years old (and in fact, adults).
- When a child turns one year old, the dishes offered on the occasion of his birthday are intended primarily for visiting adults and other children.
- Depending on the age of the children, their age recommendations can be used.
- Food offered to the birthday person must be prepared without salt and sugar. Sweets, soft drinks, potato chips and other products that are very popular at children's birthdays are best removed from the festive table of a child who is one year old, and even 2 and 3 years old.
- Dishes on the festive table of a 2-3-year-old child should have a mild taste with minimal or no added salt and sugar.
- Child-friendly chopped vegetables such as carrots, paprika, cucumber and cauliflower pieces with unflavored yoghurt dipping sauce.
- You can offer fruit on a skewer (melon, pear, watermelon, grapes).
- If desired, you can prepare more dense dishes (salads, homemade pizza, etc.), but they must be prepared from minimally processed raw materials.
- If you offer baked goods, try to find low sugar options (raw sugar, agave syrup, etc. are not good alternatives).
- Always read the label on food packaging! This will help you make a more informed choice.
- The allowable amount of supplements for children is usually less than for adults (the maximum amount is based on the body weight of an adult). Therefore, be careful with colored sweets, drinks, cookies with a long shelf life, desserts and sausages, products containing synthetic sweeteners.
- If the child is old enough to participate in the grocery shopping, let the child choose between suitable foods: one or another fruit, various cereal products, various vegetables, etc.
- Avoid the shelves with sweets, biscuits, soft drinks, etc., so that the child does not have a desire to buy sweets. Ideally, it would be to introduce the child to sweets, etc. in small quantities and rarely, and also as late as possible, and exactly after the third year of life. Unfortunately, this recommendation is difficult to follow if there are older children in the family.
- What to do if the child in the store constantly whines and cries to get what he wants? Read practical tips here.
- Children under 3 years of age should not and should not be given gadgets, especially with meals.
- The child should not be taught to watch TV while eating, as this diverts attention from eating and, in turn, creates poor eating habits in the child. While eating, all attention should be paid to the process of eating.
- Children under 3 are usually very active and need extra energy.
- The principle of a healthy lifestyle is that the amount of energy received from food and the amount of energy expended are in balance.
- All children should be as active as possible from an early age - climbing, crawling, walking, jumping, chasing a ball, playing in the yard. Parents themselves should orient their children to the movement, be an example to them.
- Mobility habits formed in childhood are the basis for adult mobility habits.

- Before eating and preparing food, you and your baby should always be thoroughly washed to prevent possible germs that cause disease from getting into the stomach. If food is interrupted (for example, due to a trip to the toilet), hands should be washed again before continuing to eat.
- Teeth should be taken care of before they erupt. Clean water and a soft brush can clean the gums of a two-month-old baby, and must be continued after the teeth erupt. Toothpaste should be used only when the child can spit it out. Teeth should be brushed in the morning and evening. After eating, you can rinse your mouth with clean water.
- In terms of teeth, there should be no more than 5 food contacts per day (3 main meals, 1-2 snacks), with a gap of at least 3 hours between meals.
-
Download
WORKSHEET: How to give orders to a child?
-
How to make agreements and set boundaries?
Solid food | Tervisliku toitumise informatsioon
From the age of 6 months, in addition to breast milk, the baby needs to be supplemented to provide the necessary amount of energy and nutrients. As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, so that the food is varied . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, so that the food is varied . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
For children over two years of age, the same nutritional recommendations apply as for adults, but the recommended serving sizes are smaller.
Children under three years old (actually, a person of any age) do not need salty or sugary snacks, carbonated drinks, deep fried and/or very sweet and salty foods!
By the sixth month of life, the infant's eating habits and digestive system are mature enough to offer more solid foods in addition to breast milk. Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i.e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it.
Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i.e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it.
Proper complementary foods are food that is hard enough to eat with a spoon, contains all the important types of food (except sweets), is rich in nutrients and does not contain salt or sugar. Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development.
Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development.
Complementary foods for babies by months:
0-6 months
6-8 months
9-11 months
substances can be markedly reduced.
World Health Organization recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for children aged 6-23 months.
| Age (in months) | Frequency of feedings | The portion for 1 feeding | Power consistency |
| 6 | or 2 times 9000 quantity | Finely pounded or pureed | |
| 6-8 | 2-3 feedings per day 9 0325up to 1 DL | Crowned or Pyurated | |
|
| 9000 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 Open per day | 9000 1-1.5 DL DL 9000 1-1.5 DL DL DL 9000 1-1.5 DL DL 9000 1-1.5 DL Dl 9000 1-1.5 DL | Crowned or finely busy |
| -2-23 | 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 snacks | .5 DL 328 |
The recommendations in the table are general and give an idea of how much a child could eat on average, however the exact amount and frequency of feeding may vary from child to child.