When do baby bunnies start eating food
Diet for Young/Baby Rabbits
Rabbit House > Rabbit Diet & Nutrition >
What you feed you rabbit has a big impact on their health and well-being. Feeding the correct diet to a young rabbit will support their growth and help them form good eating habits, which in turn will help avoid many diet related issues in adulthood.
Although young rabbits eat the same types of foods as adults, we need to take into account the different nutritional needs of their growing bodies and the extra sensitivity of their developing digestive system.
Baby rabbits' diet
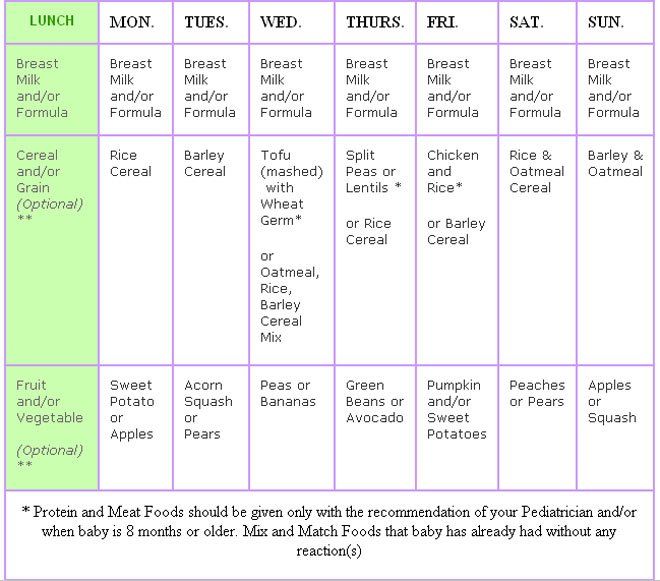
Like all mammals rabbit's initial diet is their mother's milk, which they'll continue to drink until 6-8 weeks old. They first start nibbling on solids (usually hay from around the nest) between 2-3 weeks and by 3-4 they'll be eating the same foods as their mum (plus milk).
As rabbits are weaning between 6-8 weeks their digestive system is adjusting from milk to adult solids, which is a particularly sensitive time and why rabbits should stay with their mother for a minimum of 8 weeks. If your rabbit is younger than 8 weeks: one, never get a rabbit from that source again they shouldn't be selling them, and two, you'll need to be particularly careful about your bunny's diet and try to avoid any changes.
Consistency
One of the key points in feeding any young rabbit is consistency. Baby's digestive systems are much more sensitive to changes in food and they are more susceptible to digestive related problems and can go downhill more quickly if they do get sick. Moving home is already a stressful time for a young rabbit so it is best to avoid changes to food at the same time.
When you get a rabbit you should ask exactly what food your baby has been eating and make sure you get a supply of the same brand food to start you off. In most cases it will do less harm to continue temporarily with a bad diet e.g. low quality pellets or mix, rather than make a sudden change to a 'good' diet.
If you don't know what your rabbit was fed prior to you getting it or you can't get hold of a supply then the safest option is to start with just hay and water. You can then introduce the other components to their diet gradually.
You can then introduce the other components to their diet gradually.
Ideal diet for young rabbits
The diet of young rabbits and adults is very similar. Hay is the most important component and this is supplemented with dry food (pellets) and fresh foods. There are a few extra considerations for young rabbits though.
Hay
Like adults, hay should play an important role in young rabbit's diet. Grass hay (e.g. meadow or timothy) is the one food you should introduce from the start, even if your rabbit isn't already eating it. This is the gentlest food on the gut and will provide the fibre needed for the digestive process to function.
Young rabbits can also have alfalfa, which looks a bit like chopped up hay but is made from lucerne rather than grass. It is higher in calcium and protein than grass hay, which is ideal for growing rabbits but too rich for adults.
If you are feeding alfalfa it's a good idea to feed it mixed with grass hay. This stops your rabbits getting so hooked on alfalfa that it's difficult to make the transition to grass hay when they reach adulthood. You should phase out alfalfa at around 4-5 months old.
You should phase out alfalfa at around 4-5 months old.
Learn more about types of hay here
Dry Food
Baby rabbits have higher protein requirements to support their growth, so whilst an adult requires dry food around 12-14% protein, for a baby rabbit around 16% protein is ideal. Many manufactures offer junior versions of their foods specifically formulated with this in mind.
The most popular brands in the UK are Supreme and Burgess. Allen & Page is only available in large bags, aimed at breeders rather than people feeding one or two bunnies. Oxbow is also a good brand and very popular in the US, it's more expensive in the UK as it's imported.
| Brand | Fibre | Protein | Ingredients | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supreme Science Selective Junior Rabbit | 19% | 17% | Alfalfa, wheat, soybean hulls... | £3.13 for 1.5kg (£2.09 / kg) |
| Burgess Excel - Junior and Dwarf | 17% | 16% | Grass, Oat Bran, Wheat. .. .. |
£8.50 for 2kg (£4.25 per kg) |
| Allen & Page Breeder Grower | 18% | 15% | Grass meal wheatfeed, oat feed, nutritionally improved straw... | £16 for 20kg (80p/kg) |
| Oxbow Essentials/Bunny Basics - Young Rabbit Food | 22-25% | 15% | Alfalfa Meal, Soybean Hulls, Wheat Middlings... | £11.55 for 2.25kg (£5.13 per kg) |
It's also possible to meet young rabbit's protein needs simply by feeding a larger portion of adult pellets, but it's important to ensure they don't eat fill up on pellets and avoid hay.
Should I feed unlimited pellets?
It's suggested in some books that young rabbits be given unlimited access to pellets but doing this can create issues later on.
As with people, good habits are often formed when young, and it is very important for your rabbit's future health that they get into the habit of eating lots of hay. It's much more difficult to introduce hay to an adult that has not grown up eating it. Pellets are extremely tasty and rabbits often prefer them to hay, so having unlimited pellets available can mean young rabbits eat little or no hay, a habit that can cause dental problems and make them more prone to digestive issues.
It's much more difficult to introduce hay to an adult that has not grown up eating it. Pellets are extremely tasty and rabbits often prefer them to hay, so having unlimited pellets available can mean young rabbits eat little or no hay, a habit that can cause dental problems and make them more prone to digestive issues.
Pellets were designed for commercial breeders to make rabbits grow quickly, but in this situation little attention was given to the long term health or lifespan. Remember, wild rabbits grow up just fine on a diet exclusively plant material. Unlimited pellets are not necessary to rabbit's development.
For these reasons, it's a good idea to restrict pellets to a certain extent even in young rabbits, although they can have more than an adult.
How much dry food?
It's difficult to give an exact quantity because it will depend on the nutritional content of the pellets (high or low protein), your individual rabbit's growth, what other foods they are eating (e. g. alfalfa) and their activity levels. I also know though, it's difficult to estimate, particularly if you're a first time owner so as a rough guide 25g per 1kg of expected adult weight for high protein pellets and a little more if you are feeding adult pellets. You can split the feed into two so they are spread out over the day/night.
g. alfalfa) and their activity levels. I also know though, it's difficult to estimate, particularly if you're a first time owner so as a rough guide 25g per 1kg of expected adult weight for high protein pellets and a little more if you are feeding adult pellets. You can split the feed into two so they are spread out over the day/night.
With this as a basis you can observe your rabbit and adjust if necessary. If your rabbit is active and healthy looking, and eating lots of hay you have it about right. If they are not eating much hay or produce soft droppings then reduce the quantity.
Changing dry food
Changes to dry food brands or varieties need to be done gradually over 7-10 days, by gradually reducing the amount of old food and increasing the new. If you have enough of the old food, it's a good idea to allow your rabbit to settle in before making a change, even if the old food isn't great quality.
If you don't have any of the old food, then just gradually introduce the new food over the same period, gradually building up the quantity over 7-10 days. Your rabbit will top up on hay in the interim.
Your rabbit will top up on hay in the interim.
Fresh Foods
When can a baby rabbit have fresh foods?
If you read some old books you might find it suggested that rabbits are not given any fresh foods until they are 6 months old. This is an over simplified approach that came about because people would buy young rabbits, often at an age when they should still be with their mum, take them home and feed them things like carrot or lettuce, and then find that they become ill with digestive problems. Telling people not to give any fresh foods was easy to remember and helped bypass these issues.
However, providing you follow a few simple rules, it's fine to introduce fresh foods to young rabbits.
If a rabbit's mother was fed fresh foods whilst she was raising the litter, your baby will have been nibbling those too and it's fine to continue providing these same foods. The key is to ask what your rabbit is used to and continue that - consistency.
If your rabbit has not access to fresh foods before, then allow them to settle in before introducing new foods so you aren't making lots of changes at an already stressful time. Twelve weeks or two weeks after you've got your bunny, whichever is later, is a good guide. If your rabbit has had any digestive issues then hold off a little longer.
Twelve weeks or two weeks after you've got your bunny, whichever is later, is a good guide. If your rabbit has had any digestive issues then hold off a little longer.
Introducing fresh foods
New fresh foods need to be introduced slowly so your rabbit's gut bacteria can adapt to processing the new food. It's a good idea to introduce one type of food at a time, then if your rabbit is sensitive to one type it's easy to identify and avoid in future.
If you find your rabbit's droppings change from their normal solid round pellets, this is a sign that you may be going too fast or that particular food doesn't agree with them. Stopping the fresh foods for a few days should return them to normal.
What fresh foods for a baby rabbit?
Leafy greens, except lettuce, are best for rabbits for example dandelion leaves, carrot tops, kale, spinach, spring greens, raspberry/blackberry leaves and herbs such as parsley and basil. For young rabbits first introduction to greens it's best to avoid fruits, though these can be introduced as treats later.
Start with small pieces e.g. 2" square as a test as build up the amount and variety gradually.
Problems
Keep an eye on your rabbit's droppings, changes in these are generally the first sign that you've gone a little fast with introducing new foods. The most common problem is excess cecotropes - the type of dropping that rabbits usually eat. They are soft and can end up stick the fur or squidged on the floor. They are usually resolved by cutting out fresh foods and reducing dry food for a couple of days so your rabbit eats plenty of hay.
If your rabbit stops producing droppings, refuses food or has watery droppings seek immediate veterinary advice. Young rabbits are very fragile and can become very sick in a matter of hours.
Transitioning to an Adult Diet
Rabbit's grow most rapidly in the first three months of life. At four months you should begin reducing pellets, and if you are feeding a higher protein pellets changing over to adult pellets. If you've fed alfalfa, it's also time to start decreasing this in favour of grass hay. Your rabbit should be on an adult ration by 6-7 months old. Giant breed rabbits mature more slowly and do more growing than small ones so you may want to delay by a month for breeds like Giants and French Lops. Rabbit's will continue to growing at a much slower rate for a few more months, filling out rather than getting larger.
Your rabbit should be on an adult ration by 6-7 months old. Giant breed rabbits mature more slowly and do more growing than small ones so you may want to delay by a month for breeds like Giants and French Lops. Rabbit's will continue to growing at a much slower rate for a few more months, filling out rather than getting larger.
What To Feed Baby Rabbits — Rabbit Care Tips
The first six months of a rabbit’s life are pivotal to their long-term health. At this key stage of their development, a rabbit is constantly growing. Their diet needs to reflect this fact. Ensuring that your baby rabbit is sufficiently nourished will mean healthy bones and muscle mass into adulthood.
Hay and water are essential foods. Baby rabbits need more protein, so give them pellets and alfalfa hay. Your rabbit should be weaned. If not, use kitten or goat milk to imitate their mother’s milk.
Make sure that you get a baby rabbit into good eating habits. It’s tempting to overfeed young rabbits, but this can lead to obesity in later life. When their growth spurts subside, your rabbit needs less protein and more fiber. We will explain what the optimal diet plan for a baby rabbit is. You should also read our comprehensive guide to caring for baby rabbits.
When their growth spurts subside, your rabbit needs less protein and more fiber. We will explain what the optimal diet plan for a baby rabbit is. You should also read our comprehensive guide to caring for baby rabbits.
New owners are sometimes surprised to learn what baby rabbits eat. Excessive carrots and iceberg lettuce can cause health issues. Instead, domesticated rabbits mainly sustain themselves on hay.
This replicates the experience of wild bunnies, which graze on grass all day. It would be impossible to provide a pet rabbit with enough grass to sustain itself. Hay is a substitute, and pet rabbits munch on it throughout the day.
In addition to hay, rabbits enjoy fresh fruit and vegetables and specialist pellets. The former must be offered sparingly. Too many vegetables can cause a stomach upset.
Pellets are also optional once a rabbit reaches adulthood. Pellets are critical for young and baby rabbits, as they provide a range of vitamins and nutrients. They’re also calorific. Pellets must be reduced in quantity as the rabbit gets older. Don’t panic if your rabbit has stopped eating pellets.
They’re also calorific. Pellets must be reduced in quantity as the rabbit gets older. Don’t panic if your rabbit has stopped eating pellets.
Hydration is also just as important to a rabbit. Bunnies must always have access to fresh water. You can provide this in a bowl, or a bottle that’s attached to their hutch.
What to Feed Pet Rabbits
The three core elements of a rabbit’s diet are pellets, hay, and fresh vegetables. If we were to draw a diagram of a bunny’s needs, hay would be at the base as the most critical.
This is because a rabbit’s digestive tract is engineered to process the fiber found in grass. There are several different types of hay available, each with slightly different qualities.
- Grass Hay (aka Meadow Hay or Timothy Hay). This is the most popular hay feed among rabbit owners. This hay is fresh grass that has been cut and dried out. This means that it replicates a wild rabbit’s diet.
- Oat Hay.
 This hay is made up of oat grass, which is harvested before blooming. Once the oat blooms, this hay no longer contains any nutritional value for a rabbit. It can be used as bedding, though.
This hay is made up of oat grass, which is harvested before blooming. Once the oat blooms, this hay no longer contains any nutritional value for a rabbit. It can be used as bedding, though. - Alfalfa Hay. This is a little different; it’s a legume, rather than grass. Alfalfa hay is usually fed to larger animals. It contains more protein and calcium than other hays, so it leads to weight gain.
Pellets are considered to be an essential part of a rabbit’s diet. Many claim that pellets are unnecessary for adult rabbits though, and are just empty calories.
If your rabbit is looking overweight, pellets should be sacrificed. Adult rabbits can happily sustain themselves on hay alone. Pellets are essential for helping a young rabbit grow, though.
These should always be kept as a treat, especially fruit. Rabbits love sweet tastes, so they enjoy berries, raisins, parsnips, and carrots. Their bodies are not designed to process carbs, though.
A rabbit can enjoy a tablespoon of fresh fruit and vegetables for every 2 lbs. of their body weight.
Again, an overweight rabbit should not receive any fruit and veg for a while. Rabbits do not necessarily need these to flourish. They’ll get all the vitamins they need from hay.
Baby Rabbit Feeding Guide
Young bunnies need to eat more, as they are continually growing. Baby rabbits also use food to stay warm ahead of the first shedding of their fur. Here’s some info on when baby rabbits get fur.
The diet of baby rabbits adjusts steadily as they grow. They’ll start eating solid hay at around 2 weeks of age. This will be supplemented by milk from their mother, though. By the time they reach 4 weeks, baby rabbits eat pellets and hay.
Feed alfalfa hay to a baby rabbit. The protein and calcium found within will help them grow strong muscles and bones. Also mix in some standard hay, though. This will make the transition easier when your rabbit reaches adulthood.
You should also ensure that you pick up pellets designed especially for young rabbits. These will provide everything that a growing bunny needs.
Whatever you decide to feed your baby rabbit, keep it consistent. Any bunny is sensitive to changes in diet, but young rabbits are especially so. Don’t chop and change unless it’s strictly necessary.
Baby Rabbit Food List
Before you even bring your rabbit home, you should pull together a shopping list. Healthy food for baby rabbits is pivotal, so don’t make any best guesses after their arrival.
You’ll need to buy hay in advance. Prioritize alfalfa hay, but get some traditional meadow hay too. Your bunny cannot eat alfalfa hay forever, so don’t let them get too attached to the taste.
You’ll also need pellets. Have a chat with a clerk in your local pet store, and get the ideal pellets for your bunny. There will be numerous options, tailored to different life stages.
Avoid the temptation to buy a huge bag of pellets. You may be told that baby rabbits can eat unlimited pellets. Pellets can grow moldy quite quickly. Smaller bags are preferred.
You may be told that baby rabbits can eat unlimited pellets. Pellets can grow moldy quite quickly. Smaller bags are preferred.
Pellets
It’s advisable to make pellets part of your baby rabbit’s meal plan. These will help your young bunny grow up happy and healthy. Both quality and quantity should be carefully managed, though.
Tread carefully around claims that baby rabbits can eat unlimited pellets. In theory, this is correct. The ever-growing body of a bunny will cope with the calories consumed while they’re so young.
All the same, this is teaching your bunny bad habits. They’ll grow accustomed to having a constant supply of pellets. If you remove this option as an adult, they’ll grow distressed. It’s better to teach a young rabbit to enjoy hay early.
Also, ensure that you pick up the highest quality pellets possible. They should make up at least 22% fiber. Protein should not amount to more than 14%. Avoid anything with more than 1% calcium, as this can be harmful.
Don’t be tempted by muesli-based pellets. These will be tastier, as they contain nuts and seeds. A baby rabbit will pick out the nutrient-deficient fun ingredients, and ignore the rest.
Hay
Alfalfa hay is ideal for baby rabbits. For the first months of their life, a rabbit will enjoy the protein in this hay. As pellets also contain alfalfa, your baby bunny will be in good health.
Even though alfalfa hay is good for baby rabbits, it shouldn’t be all they have. Aim for a ratio of around 60:40, mixing alfalfa with traditional grass hay. This will make the eventual transition to meadow hay only less jarring.
Another thing to remember is that your rabbit’s hutch will be filled with hay. They’ll sleep on it, and generally surround themselves with the substance. This also means that your rabbit will pee and poop in their hay.
As baby bunnies have immature brains and bladders, they take a while to be litter trained. This needs to be handled with care. Urine can turn hay moldy, and moldy hay is toxic to rabbits. Clean their hutch regularly.
Urine can turn hay moldy, and moldy hay is toxic to rabbits. Clean their hutch regularly.
It’s vital that your baby rabbit sees hay as a source of pleasure. Get them into the habit of grazing on hay as early as possible. Incorporate it into playtime, and exercise.
Fresh Fruit and Vegetables
In the past, popular opinion dictated that baby rabbits should not be fed fresh food. This is because young bunnies have particularly sensitive digestive tracts. The truth is, fresh fruit and vegetables are fine in moderation.
The misconception that fresh vegetables are dangerous to baby bunnies arose through a lack of education. Feeding a rabbit of any age-inappropriate vegetables will cause stomach upsets. A bunny needs time to adjust to dietary changes.
When bringing home a baby rabbit, learn what fresh food their mother enjoyed. Once the bunny reached 4 weeks of age, they would have nibbled on these vegetables too. Their stomachs will be able to cope with them in small doses.
Fresh vegetables will also help a young rabbit manage the size of their teeth. Rabbit teeth never stop growing. By crunching on tough, solid vegetables, they’ll be filed down.
Fruit is best avoided in baby rabbits, unless used as training treats. Offer small amounts of vegetable as a treat, once your bunny has eaten sufficient hay.
Should I Give a Baby Rabbit Meat?
Meat must be avoided. While baby bunnies need protein, they don’t need meat. They’ll suffer from an excess of protein, and experience stomach upsets as a result.
Your rabbit may develop a taste for meat. A little won’t kill them, but it will make them uncomfortable. A rabbit’s digestion is engineered to process fiber, not protein. The older they get, the more problematic this will become.
Rabbits are herbivores. They do not want or need to eat meat. Babies are no exception to this rule.
Can Baby Rabbits Drink Water?
Baby rabbits can drink water. It should be actively encouraged.
Rabbits will start to hydrate from their mother’s water source at around 3 weeks old. As baby bunnies eat more dry food, water becomes particularly important. They need to hydrate regularly to stay healthy.
It’s vital to learn how your baby rabbit enjoys drinking. Some bunnies find water bottles fun. Others would rather lap from a bowl. Encourage your pet to drink in whatever way they prefer.
If you use a bowl, ensure that it’s heavy and shallow. Baby rabbits are playful and curious. They will splash around in water if they can. This can turn their hay moldy, and wet rabbits suffer a drop in body temperature.
Can Baby Rabbits Drink Cow Milk?
Baby rabbits drink milk from their mother’s until they’re 8 weeks old. A bunny should never be separated from their mother before this. If you’re offered a rabbit younger than 8 weeks by a breeder, walk away.
If you must provide a rabbit with milk, don’t use cow milk. This is too dense in calcium. The closest equivalent is kitten milk. Warm goat milk will be suitable in a pinch.
The closest equivalent is kitten milk. Warm goat milk will be suitable in a pinch.
Rabbit milk contains more calories than kitten milk, though. As a result, mix in a tablespoon of sugar-free heavy cream. Baby bunnies should be fed milk twice a day.
Also, don’t forget that baby rabbits are not sustained on milk alone. Once they reach 2 weeks, they also need water and solids. Failing to provide these will leave a rabbit malnourished.
How Can I Tell if My Baby Rabbit’s Diet is Healthy?
Young rabbits need to nap regularly, but they’ll be energetic in between. If your young rabbit is lethargic, it may be due to dietary deficiency.
Another way to check on a rabbit’s condition is their droppings. Rabbit poop is a fine way to assess your bunny’s digestive health. Rabbit’s produce two types of poop:
- Pellets, which will be littered throughout their cage.
- Cecotropes, which are bunches of fecal matter that the rabbit eats.
A healthy poop pellet will be light brown, and will crumble when picked up. If your rabbit’s feces pellets are dark, it suggests they’re eating too much protein.
If your rabbit’s feces pellets are dark, it suggests they’re eating too much protein.
Diarrhea in a baby rabbit is a medical emergency. This condition can be fatal in hours. Administer the first aid suggested by the University of Miami, and make an urgent vet appointment.
My Baby Rabbit Eats Too Fast
This is nothing to worry about. Even if it leads to hiccups, these will pass in a short period of time.
The main reason that baby rabbits eat quickly is food insecurity. Until they get into a strict routine, bunnies worry about when they’ll be fed. They’ll guzzle food in case they don’t receive any more.
Rabbits that share a hutch are particularly likely to eat fast. They’ll be worried that another, older bunny will eat their share otherwise.
Also, remember that baby rabbits are always growing. This means that they’ll be hungry pretty much constantly. Once they establish a routine, they’ll calm down.
My Baby Rabbit is Not Feeding
If your baby rabbit is refusing to eat, it’s essential to find out why. A rabbit not eating at any age is worrying. This goes double when the bunny is young.
A rabbit not eating at any age is worrying. This goes double when the bunny is young.
A young rabbit eating less as they reach adulthood is not as concerning. As they grow older, rabbits need fewer calories. They may take to eating more hay than pellets. This is a good thing. Don’t let them eat too much alfalfa hay, though.
You should also check that your bunny is not just being stubborn. If you have changed their diet, they may be holding out for a favorite. This needs to be managed carefully.
Baby rabbits need to eat, but if you cave too quickly, you’re setting a dangerous precedent. They’ll refuse to eat anything that doesn’t like into adulthood.
Move the bowl around in the first instance. If a rabbit feels a draught, it will put them off eating. Food that’s too close to a preferred elimination spot will also deter a bunny from eating. Rabbit pee has an overpowering smell.
Also, ensure that your baby rabbit is not anxious. Being separated from their mother and siblings can be distressing. Offer plenty of TLC and a welcoming home environment to help your bunny settle.
Offer plenty of TLC and a welcoming home environment to help your bunny settle.
Spaying or neutering young rabbits also leads to behavioral changes. Your bunny may temporarily lose their appetite. This should pass quickly. Observe them, and take action is necessary.
Alternative Food for Baby Rabbits
If your baby rabbit is refusing to eat, you’ll need to offer the formula. This is often easier said than done. Seek professional help to ensure your bunny is sufficiently nourished.
Use kitten or goat milk if you cannot source rabbit-specific milk. Zooh Corner recommends feeding milk at the following quantities, at least twice a day. If your rabbit will not eat hay or pellets, they’ll need more:
- 1 – 2 Weeks of Age – 10 – 15 cubic cm
- 2 – 3 Weeks of Age – 15 – 30 cubic cm
- 3 – 8 Weeks of Age – 30 cubic cm
You can pick up a syringe to provide this milk from a pet store. Many baby rabbits will not take to this, though. Bunny-savvy suppliers will stock a product called the Miracle Nipple. This imitates the nursing experience.
Many baby rabbits will not take to this, though. Bunny-savvy suppliers will stock a product called the Miracle Nipple. This imitates the nursing experience.
This is not a permanent solution, though. You must learn why your rabbit is not eating, and resolve the issue.
Feeding a baby rabbit is largely similar to nourishing an adult equivalent. Young bunnies eat more, and show more interest in pellets.
What’s most important is that you get your rabbit into good habits surrounding food. Like any animal, a rabbit’s formative experiences will play a significant role in their adult persona.
Help a rabbit eat appropriately while they’re young, and they’ll reach adulthood in a healthy condition. From there, you can enjoy a long and happy relationship.
When baby rabbits start eating on their own
Expert opinion
Dobryshev Sergey Anatolyevich
Professional rabbit breeder and hare breeder with 30 years of experience
Up to 12 babies are born in one litter. They are born completely helpless, and need the care of their mother. However, the length of stay in the nest is limited. The development of rabbits occurs at a rapid pace. After some time, their body will require the transition from mother's milk to independent food. The new breadwinner for them is the farmer, who makes a gradual transition to a new diet.
They are born completely helpless, and need the care of their mother. However, the length of stay in the nest is limited. The development of rabbits occurs at a rapid pace. After some time, their body will require the transition from mother's milk to independent food. The new breadwinner for them is the farmer, who makes a gradual transition to a new diet.
Contents
- All the most interesting things about newborn rabbits
- Development of young rabbits after birth
- Development of young rabbits by stages
- Basic manipulations with newborn rabbits after birth
- After how many days do the young rabbits leave the nest?
- Why do baby rabbits leave the nest prematurely?
- What to do if the rabbits come out early?
Everything you need to know about newborn rabbits
It can be assumed that when the rabbits were born, the hardest part was left behind. Now they will be taken care of first by the mother, and then by the farmer, helping them grow up.![]() Newborns are born defenseless, bald, blind, deaf. Their eyes are closed, they are guided by the smell of their mother.
Newborns are born defenseless, bald, blind, deaf. Their eyes are closed, they are guided by the smell of their mother.
A caring female immediately after birth begins to lick her cubs, as her instinct tells her. It is good for newborns, calms them down after stress and stimulates the start of the protective action of the immune system. A kind of massage starts the work of a still weak intestine.
The temperature in the cage must be at least 20°C, which must be monitored by the breeder. The necessary temperature regime is also provided by down, with which the still pregnant female carefully lines the mother liquor. Babies huddle together to keep warm. Wool in rabbits appears in 5-7 days, but quickly acquires density.
In the first month, their life depends on the availability of sufficient milk from the mother. Therefore, special attention should be paid to it. It is necessary to give an increased amount of food, and always fresh, and constant access to clean water. The diet should be dominated by juicy food with lots of greens. Vitamins must be added to food. You should also protect the nursing mother from infections. Taking care of the female, the breeder automatically takes care of the newborns.
The diet should be dominated by juicy food with lots of greens. Vitamins must be added to food. You should also protect the nursing mother from infections. Taking care of the female, the breeder automatically takes care of the newborns.
In addition, after birth, he must remove the stillborn from the cage, isolate the sick and weakened. Before this procedure, you should wash your hands with laundry soap. This is necessary so as not to leave a smell on the babies that can alert the female. It is advisable to transplant the rabbit into another cage during the examination, since mothers react nervously if they start touching her babies.
Development of baby rabbits after birth
From the first weeks of life, babies intensively acquire new opportunities. Rabbits begin to open their eyes 10-12 days after birth. Before that, they use their sense of smell for orientation. Young animals are becoming more and more independent. But, since their diet is still mother's milk, the rabbit needs to continue to provide decent care.
Development of baby rabbits by stages
Small and defenseless at birth, baby rabbits are stable at three months. Before that, they go through the following stages:
- First week. A coat is formed. An intensive weight gain begins, which after seven days doubles.
- Fourth week. With open eyes, kids begin to explore the world around them with curiosity.
- Two months. The grown-up rabbits are separated from their mother in a separate housing for young animals.
Replanting is very stressful and should be done with all precautions. New food is introduced gradually. It should contain all the necessary substances, vitamins and mineral supplements. The flora in the intestines is still weak, which can cause disturbances, so the quality must be high.
Basic handling of newborn rabbits after birth
It is recommended by experienced farmers to have minimal contact with newborns so that the alert female does not abandon the entire litter. As long as they are close to their mother, no additional care is required. Small animals depend only on the well-being of the female and the degree of her responsibility for her maternal duties. The main role of the breeder during this period is to maintain a normal temperature.
As long as they are close to their mother, no additional care is required. Small animals depend only on the well-being of the female and the degree of her responsibility for her maternal duties. The main role of the breeder during this period is to maintain a normal temperature.
Over time, the animals will have to leave their nest, but for now they can only make small trips. Tired babies quickly come back. In order for them to finally leave their first home, the breeder needs to create the necessary conditions.
After how many days do the rabbits leave the nest?
The average time the young rabbits stay in the nest, necessary for them to become strong enough, is about 20 days. A sufficient period of adaptation is the key to health. Even in one brood there are rabbits with character traits. The most daring and inquisitive are the first to make reconnaissance at the age of three weeks. Leaving earlier than this period may provoke aggression.
Too long stay of the brood in the nest pampers the young and there is no development of qualities that will help to withstand the difficulties of independent life. When the rabbits leave the nest, it is time for the first feeding, consisting of grated carrots. Gradually, they become more confident and stay outside the mother liquor for a longer time. This serves as a signal to gradually expand the diet and begin to accustom to adulthood.
When the rabbits leave the nest, it is time for the first feeding, consisting of grated carrots. Gradually, they become more confident and stay outside the mother liquor for a longer time. This serves as a signal to gradually expand the diet and begin to accustom to adulthood.
In addition to mother's milk, small animals are able to eat on their own:
- hay;
- vegetables;
- small pieces of root vegetables;
- grain.
Expert opinion
Dobryshev Sergey Anatolyevich
Professional rabbit breeder and hare breeder with 30 years of experience
Complementary foods should be introduced gradually. Delicious new food serves as motivation for the moment when the rabbits leave the nest.
It must be remembered that getting into them adult food intended for a rabbit can harm a fragile body. Therefore, feeding of young animals should be carried out in the mother liquor, where they can already move. Be sure to ensure that there is constant access to fresh water. Feed should be given 4-5 times a day with an interval at night.
After 40 days after birth, small rodents are able to completely switch to adult food with a high content of vitamins and minerals. Therefore, the final jigging of healthy rabbits with strong immunity is carried out for 40-45 days. It is recommended to carry it out within a few days. They start with the two strongest strong men, and after a couple of days they put out a few more. Individuals with aggressive behavior are isolated from the rest. This method is gentle for the whole family. It should be sympathetic to the increased shyness of small animals and carry out their weaning carefully and with clean hands.
Why do baby rabbits leave the nest prematurely?
The normal length of stay in the nest is three weeks. If babies begin to strive for freedom earlier, then this does not indicate their independence. The most likely cause is malnutrition. A rabbit may not have enough milk for everyone or its quality cannot be called good. After fruitless attempts, the cubs will begin to search for food outside of their nest.
After fruitless attempts, the cubs will begin to search for food outside of their nest.
Lack or insufficient milk supply may be due to physiological causes or postpartum stress, especially when there are large numbers of stillborn and sick babies. The diet of a nursing female and the conditions of her maintenance should be reviewed. It is easy enough to check lactation: the nipples should look swollen. When stroking and lightly pressing, milk should be released. On the nipples, the absence of inflammation is necessary. The skin around them should not be overgrown with hair so that access to food is convenient.
What to do if the rabbits come out early?
Malnutrition can be identified by the appearance of babies. When everything is in order, their tummies are round, but the formation of wrinkles indicates malnutrition and dehydration. This is indicated by restless behavior and squeaking. To verify your guesses, the rabbits should be weighed. If the weight for their age is insufficient, then you will have to start feeding them with milk mixtures. To maintain the level of sugar in the body, you can give a drop of jam, jam or molasses.
To maintain the level of sugar in the body, you can give a drop of jam, jam or molasses.
For feeding use a mixture of the following composition:
- 250 grams of milk;
- chicken yolk;
- a couple of drops of vitamins;
- a little sweet.
Feeding is done with a pipette. After the kids are full, you should lightly massage their lower tummy. This will help expel the excrement. Stimulation of the activity of the mammary glands is facilitated by oxytocin, which must be administered by a veterinarian.
Another way to solve the problem is to transfer to another lactating female. In order for her to calmly accept them, you should first remove the smell of fluff, sawdust, and hay that is alien to her. If lactation is normal and there is enough food, then you should not take the initiative, take the rabbits or start feeding them.
When do rabbits leave the nest and after how many days do newborn rabbits open their eyes and start eating themselves
The birth of baby rabbits is a very exciting moment, especially if this is the first addition to your household.
Those who have just started breeding rabbits have many questions. Namely: when the rabbits leave the nest, at what age do they become independent and can they be touched after birth? We will talk about all this in our article.
Contents
- 1 Development after birth
- 1.1 When do the eyes open?
- 1.2 When do they leave the nest?
- 1.3 When do they start eating on their own?
- 2 Can I touch babies with my hands?
- 3 Photogallery
- 4 Video "Cub Handling Rules"
- 4.1 Related Articles
Development after birth
A newborn rabbit is a blind and bald, defenseless creature. The average weight of babies after birth is 70 grams. As soon as the female has brooded, she begins to lick the cubs. This "massage" is very useful, as it triggers the immune defense and stimulates the first bowel movement. The eyes of newborns are closed, the cubs react only to the smell of the mother, they sleep, cuddling up to each other.
The fluff in the nest serves as a heater for the crumbs. The rabbits' own thin and sparse hair will appear only after 5-7 days, but it will quickly become thick. Their development at the age of up to a month depends entirely on the female's milk production, feeding regularity, and room temperature. By the time mole rats begin to see, their weight increases by 3 times.
When do they open their eyes?
It is especially interesting for novice rabbit breeders when a newborn rabbit opens its eyes and after how many days it can fully see. Usually the eyes of rabbits open at 10-12 days. Up to this point, their behavior is based solely on the instincts and care of the rabbit. We can say that up to 18-20 days the survival rate of cubs is 99% depends on the female and 1% on who looks after the rabbits.
When do they leave the nest?
Rabbit, having opened his eyes, begins to be interested in the world around him and develops very quickly. 16-20 days after birth, the rabbits become crowded in the walls of the mother liquor. When the young begin to crawl out into that part of the cage where the rabbit lives, you can remove the partition of the mother liquor. At this age, rabbits are quite large, their weight becomes 10 times more than it was after birth.
16-20 days after birth, the rabbits become crowded in the walls of the mother liquor. When the young begin to crawl out into that part of the cage where the rabbit lives, you can remove the partition of the mother liquor. At this age, rabbits are quite large, their weight becomes 10 times more than it was after birth.
It also happens that there is an earlier release of cubs, but this is not the norm. This behavior should immediately catch your eye, because it usually indicates a lack of food. Check how much the babies weigh, and if the weight is not normal, supplement them with formula milk. After the babies left the nest, the uterine compartment must be disinfected.
When do they start eating on their own?
Young rabbits grow quite intensively and already after leaving the nest they are interested in adult food. Babies start eating on their own on the 20th day of life. Some rabbits can eat on their own as early as 16 days, but this food should be soft, not coarse. If you want the crumbs to start eating everything as soon as possible, you can accustom them to carrots, giving them grated. They also give fine hay and crushed grain after steaming.
If you want the crumbs to start eating everything as soon as possible, you can accustom them to carrots, giving them grated. They also give fine hay and crushed grain after steaming.
Can I touch babies with my hands?
There is a lot of information on this issue and some facts are contradictory. Inexperienced rabbit breeders mistakenly believe that after the birth of the rabbits in the nest, you can’t touch them, supposedly the female will leave them. This is not true. Inspection of the nesting part can and even should be carried out no later than two days after birth. This examination reveals the total number of pups and the number of stillborns.
Dead rabbits are removed from the nest, you can immediately put the rabbit alive in the same amount, if there are refuseniks. If the babies are "frozen" from low temperature, but alive, they are moved to a warm place. When you go to inspect the nest, move the rabbit to another cage for a while, and then inspect the newborns.