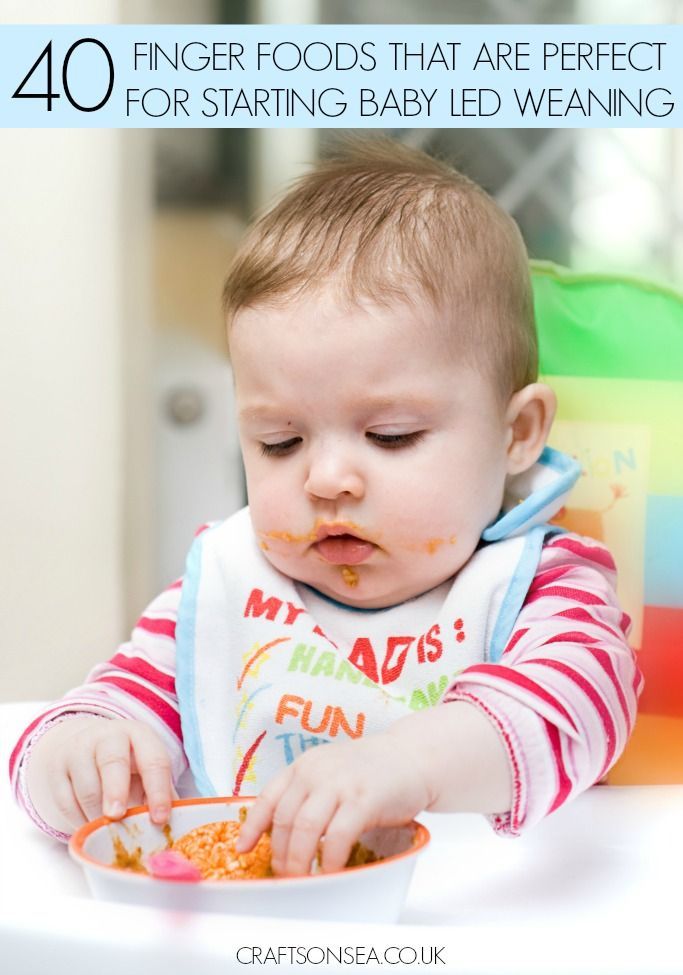
When do you start stage 2 baby foods
What It Is, When to Start, and Options to Try
Accompanying your child through the different stages of learning how to eat real food is an exciting journey. Sometimes, along with the sense of pride — Look, they polished off the whole jar! — you can feel a little confused. How are you supposed to navigate the milestones?
Let’s start at the beginning: What do the stages of baby food mean, anyway?
Rome wasn’t built in a day, and your baby’s digestive system won’t make the leap from liquid to solid in one day either. That’s what the stages of baby food are for — to help your baby manage the mechanics of eating and to make the transition easier on your baby’s digestive system.
Defining the stages across the brands
While the different stages of baby food aren’t standardized (it would make your life easier if they were!), most popular brands more-or-less follow these four stages:
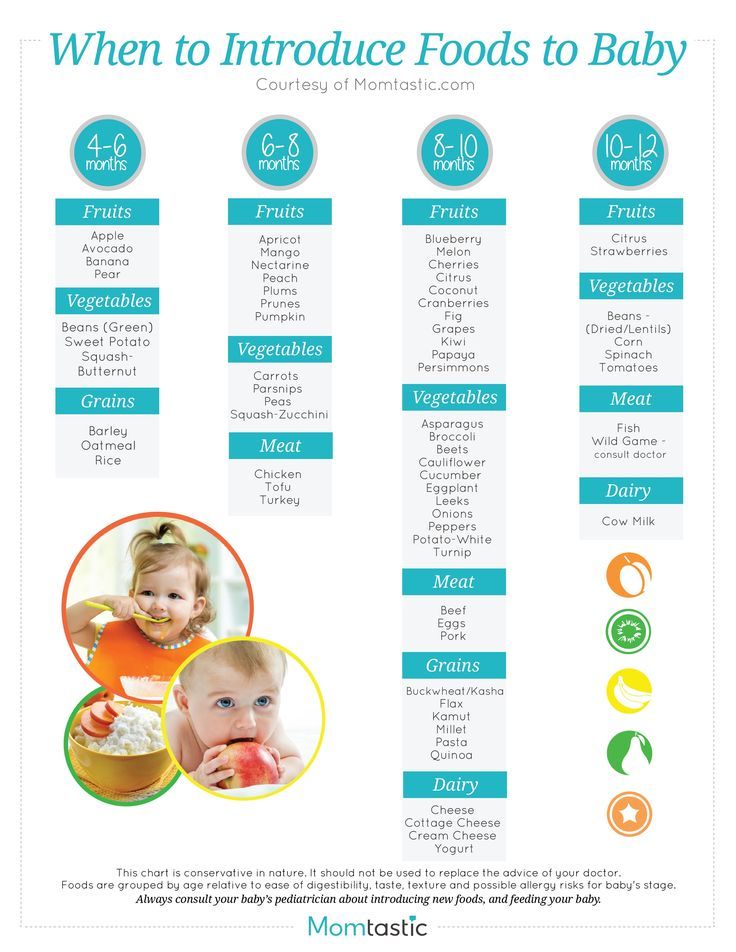
- Stage 1: 4 to 6 months (watery puree of a single ingredient)
- Stage 2: 6 to 9 months (thicker texture that is strained or mashed)
- Stage 3: 10 to 12 months (mush that has soft, chewable, small chunks)
- Stage 4: After 12 months (finger foods and small, soft pieces of foods you share from your own supper)
What is the difference between stage 1 and stage 2 food?
Stage 1 foods are pretty watery. They’re pureed into a smooth paste that can drip off a spoon easily, so stock up on your bibs. These foods are usually made of a single ingredient: oatmeal cereal, apple, carrots. Your baby will start off eating about half a teaspoon of this.
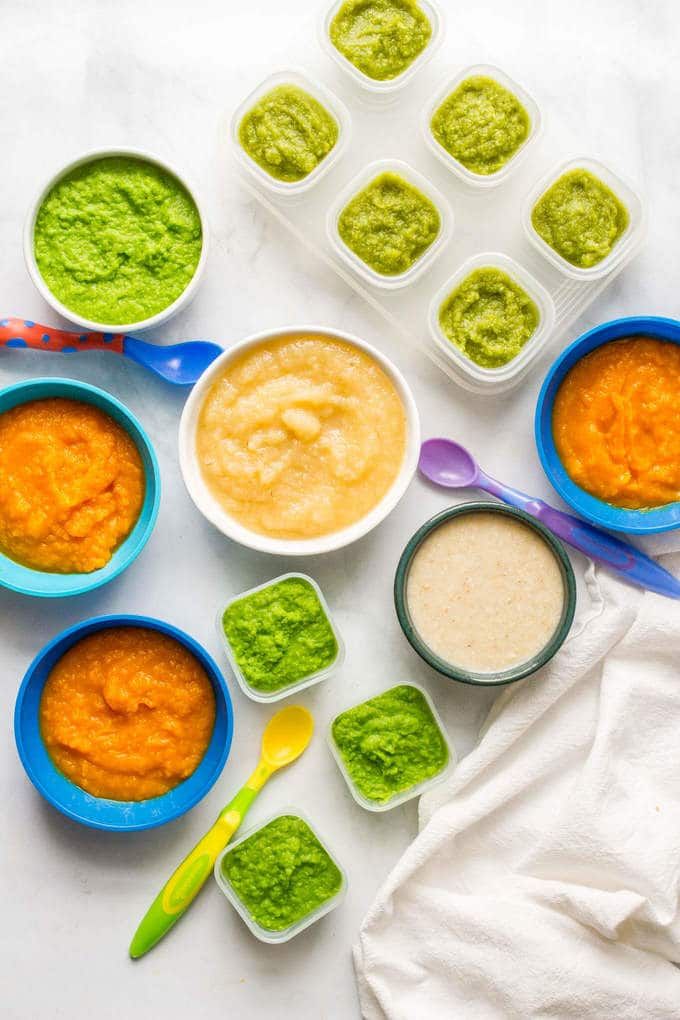
Stage 2 foods get more exciting. These are strained or mashed into a dense paste. They’re made with a combination of foods that can include legumes and even meats or fish. They may combine flavors, like fruit and veggie blends. Your baby’s appetite is growing and you’ll have to keep pace with bigger portions.
At around 6 to 9 months, your baby is probably ready to move on to stage 2 foods. Not every baby will stick to this schedule simply because every child is a world to their own.
Here are some signs that your child is ready to move on:
- Tongue reflex: At around five months, your child will start losing their tongue thrust reflex and won’t immediately push out the food that you try to feed them.
- More please: They’ll easily polish off the stage 1 foods and look hungry for more.
- Variety: They’ll have eaten foods from all the food categories (vegetables, fruits, legumes, grains, meat) and shown no allergy or intolerance.
- Enjoyment: They’re managing spoonfuls of stage 1 foods easily, mouthing and swallowing happily.
At this exciting stage, feel free to give your baby most types of foods. By offering them a wide range of tastes and textures, you’re giving them a foundation for healthy eating habits — as well as making it easier for yourself. Keep in mind the following safety points:
- Choking hazards: Avoid nuts, seeds, and popcorn at this stage. And make sure to slice round foods like grapes and hot dogs lengthwise.
- No honey: Children younger than 12 months should not be given honey because it could lead to a botulism infection.
- No juice: Follow AAP guidelines and stick with breast milk, formula or a little water and steer clear of juices.

- Safe feeding: Always strap your child into their high chair and keep an eye on them while they’re eating.
And if you’re wondering about peanuts, here’s the scoop: A 2017 release from the National Institutes of Health suggests exposing children to peanut-containing foods as early as 4 months old. (Wait till 6 months for children with mild or moderate eczema.)
Surprised? Don’t be. A recent study suggested that Israeli kids rarely suffer from peanut allergies because they’re munching on Bamba, a peanut-based snack, from as early as 3 months. Talk to your doctor about suggested safe ways to incorporate peanut products into your little one’s diet.
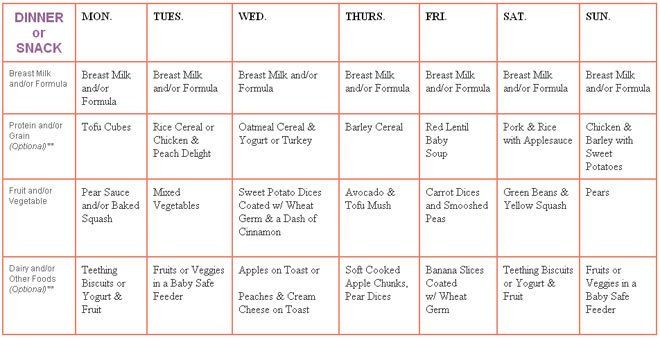
What’s on the menu for stage 2 baby foods? Basically, you can go the store-bought or the homemade route. Or you can mix both depending on how much time you have. It’s up to you and your personal schedule.
Here are tasty ideas for both options.
Store-bought stage 2 baby food
- Plum: These organic blends come in easy-to-transport pouches.
 Try pear, spinach, and pea, or banana and pumpkin.
Try pear, spinach, and pea, or banana and pumpkin. - Beech-Nut: Options are available in jars and pouches. Serve up some apples and bananas or pineapple, pear, and avocado.
- Earth’s Best: Another organic option, in pouches or jars. Try sweet potato, barley, and garbanzo or pasta with tomato and white bean.
- Gerber: A classic, whether served up from plastic tubs, jars, or pouches. Flavor combinations include peach mango and oatmeal or chicken noodle dinner.
Remember to monitor your little one while they’re eating. Pouches are handy, but the caps can be a choking hazard. Glass jars are at risk of breaking, so keep them out of baby’s reach. Your baby should always enjoy snacks and meals with attentive adult supervision.
Homemade stage 2 baby food
Cooking up a storm for your baby’s budding taste buds at this stage doesn’t have to be challenging. Here are a few recipes to get you going. (You can find even more baby food recipes here. )
)
Don’t shy away from spices and herbs: your baby will appreciate the added flavor, and the micronutrients in them will give their immune system a boost.
- Apple, butternut, and carrot: Boil the ingredients until they test soft with a fork. Drain some of the water, but set it aside in case you need to thin the mixture. Sprinkle in a little curry and blend.
- Blueberries and chickpeas: You can cook up your own chickpeas or use a prepared version to save time. Mix equal amounts of blueberries and chickpeas. Blend and add breastmilk, formula, or water to get the right consistency. You can also add in some rice for extra oomph and texture.
- Salmon with roasted zucchini and fennel: Spray the salmon and vegetables with oil and broil for about 15 minutes. Add chopped parsley and blend. You can thin the mixture with breastmilk, formula, or water.
Enjoy this stage with your baby because it won’t be long before they move on to the next stages.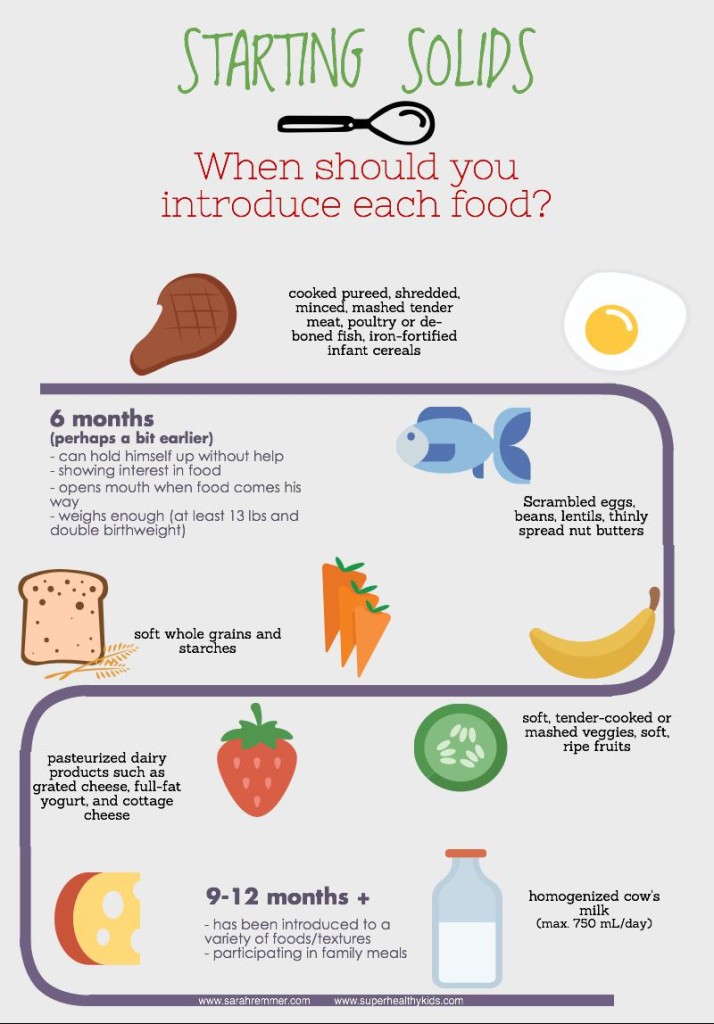 And then, sooner than you think, you may be facing competition for that last slice of caramel-topped cheesecake.
And then, sooner than you think, you may be facing competition for that last slice of caramel-topped cheesecake.
When is a child ready to try a bit more texture?
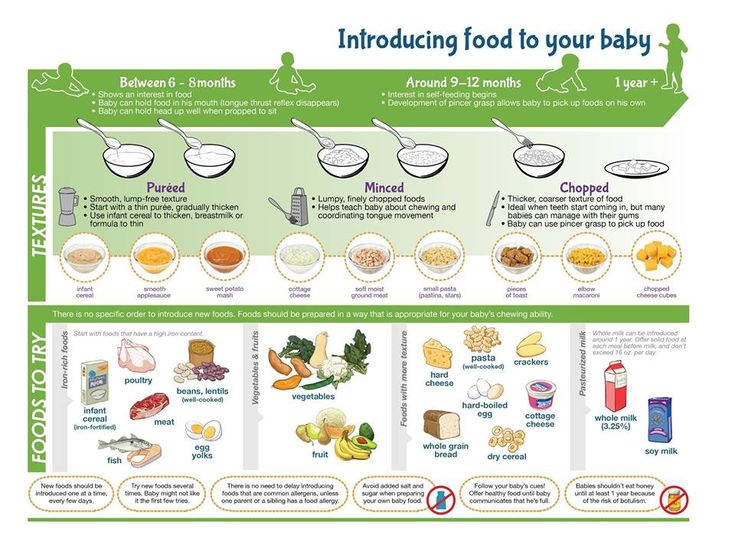
Once your baby has mastered the art of slurping down smooth purees, it may be time to expand their culinary horizons with Stage 2 baby food. Your little gourmand isn’t quite ready to dine on a plate of spaghetti and meatballs just yet, but Stage 2 foods will give them the opportunity to sample new tastes, as well as consistencies.
Think your baby is ready to graduate onto the next stage of baby food? Here, parents and experts weigh in on Stage 2 baby food. Bon appetit!
What is Stage 2 baby food?
While the jarred Stage 2 baby food you find at the store is typically combinations of food (“sweet potato and chicken dinner”), it’s important to keep in mind this stage is more about the consistency of the food.
“While Stage 1 baby food is completely pureed, Stage 2 baby food has a bit more texture to it,” says Dr.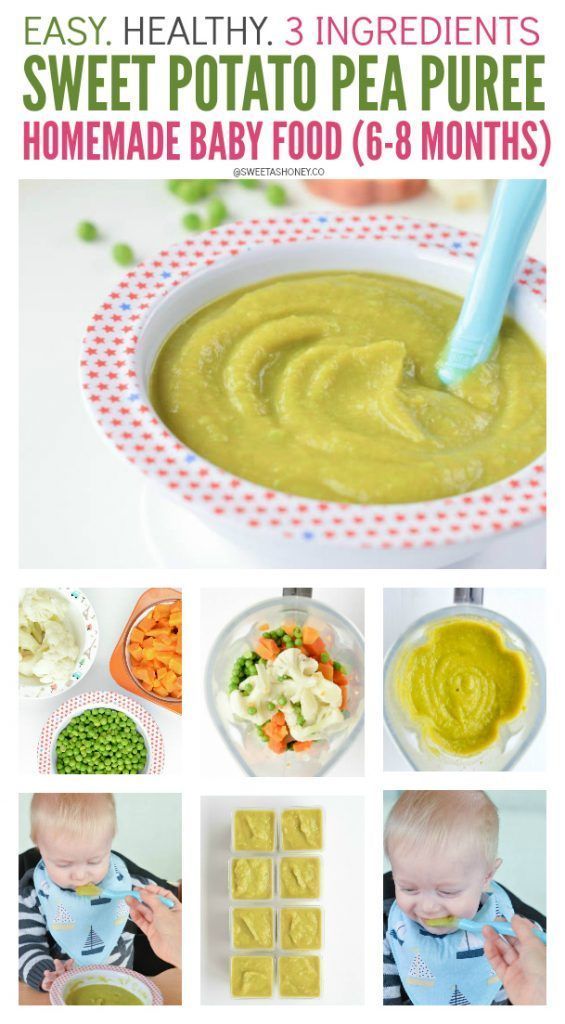 Zulma Laracuente, a pediatrician in Alexandria, Louisiana. “The concept behind slowly transitioning baby from purees to thicker solids is to get them used to chewing and swallowing.”
Zulma Laracuente, a pediatrician in Alexandria, Louisiana. “The concept behind slowly transitioning baby from purees to thicker solids is to get them used to chewing and swallowing.”
Of course, every child develops at their own individual pace, so check with your child’s doctor for baby food recommendations during the first 12 months.
When to start Stage 2 baby food
The Stage 2 baby food age may vary based on when your infant started eating Stage 1 foods. The general age recommendation for Stage 1 baby food is between 4 and 6 months, so taking into consideration how long — and how well — your child has been eating these foods will help you determine if they’re ready to move up. According to Laracuente, babies are usually ready for Stage 2 between 6 and 8 months old — but make sure your little one has honed their Stage 1 skills before making the leap.
“Once your baby has done well with Stage 1 solids and has tried multiple foods, it is safe to advance to Stage 2 baby food,” says Dr.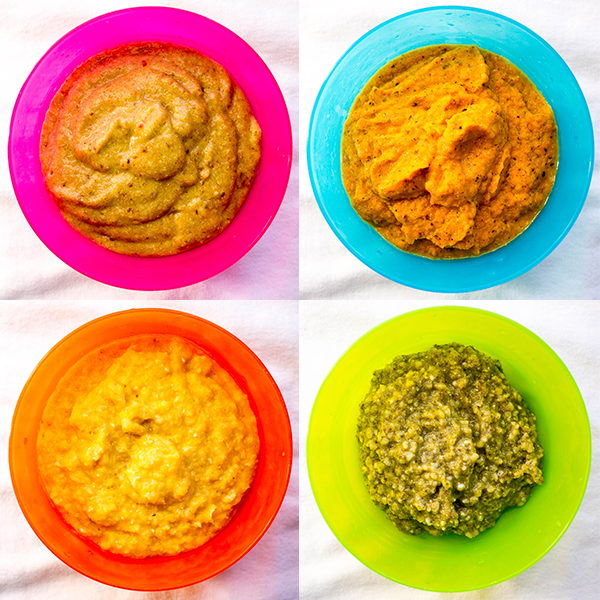 Melanie Custer, a pediatrician at at West Bend Pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin. “These foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices and are thicker in consistency.”
Melanie Custer, a pediatrician at at West Bend Pediatrics at Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin. “These foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices and are thicker in consistency.”
“These foods usually have multiple ingredients, including some spices and are thicker in consistency.”
DR. MELANIE CUSTER, PEDIATRICIAN
Signs baby is ready to start Stage 2 food
How do you know if your baby is nailing it with their Stage 1 foods and ready for the next step? Simply put, they’re eating and swallowing.
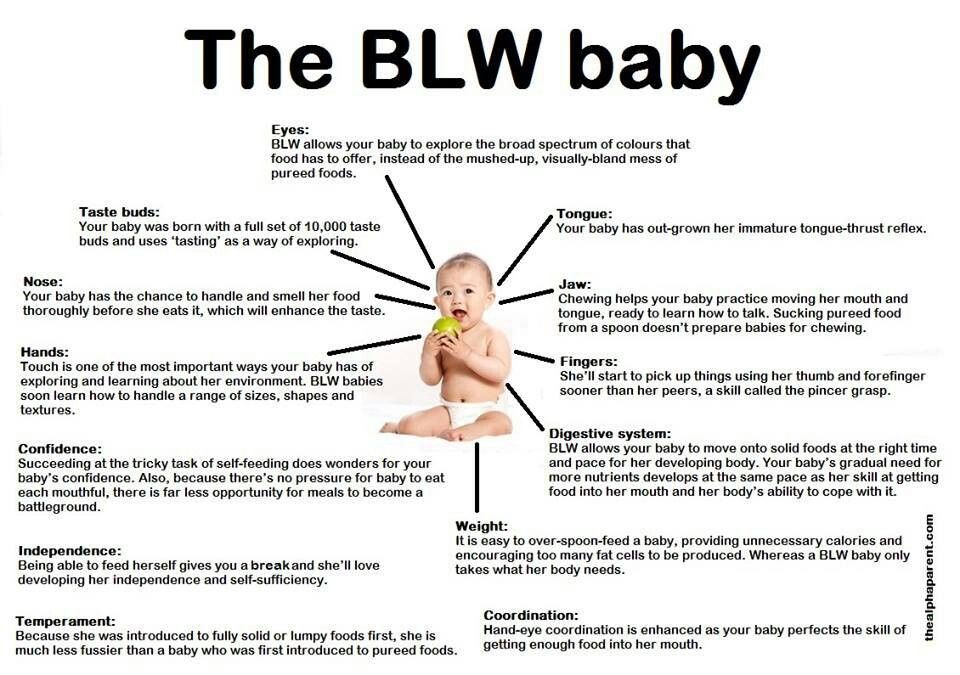
“As your baby’s oral skills develop and improve, you can move on to Stage 2 foods, which are purees with small chunks and texture,” says Jenifer Thompson, R.D., an advanced practice dietician at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
Thompson says in order to move on to Stage 2 foods, babies should be consistently taking the spoon in their mouth when you offer it to them, without spitting or pushing it back out.
“Once my baby was no longer grimacing or letting his food dribble onto his chin, I knew we were ready to move onto Stage 2 foods,” says mom of two Darcy McConnell of Garwood, New Jersey. “I actually have no idea how old he was when we made the switch since I based it off of how well he was eating!”
“I actually have no idea how old he was when we made the switch since I based it off of how well he was eating!”
What Stage 2 baby foods to start with
It’s important to expose your child to a number of foods, most of which are safe at this point.
“By the time they are 7 to 8 months, babies should be eating a variety of foods from different food groups, including cereals, meat and other proteins, yogurt, cheese, vegetables and fruits,” says Thompson.
“Most foods can be prepared for any stage, so long as they’re texturally age-appropriate,” says Dr. Kristen Treegoob, a pediatrician at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. “When we think of Stage 2 baby food, we’re thinking of thicker purees with some mashable bits.”
Experts advise introducing as many different foods as possible during this stage of food development so your baby gets accustomed to them.
“While bananas, applesauce and peaches are good options and most babies like them, as they are naturally sweet, it is also important to try other foods that aren’t as common and popular, such as beets, rhubarb and asparagus, so they develop a taste for them,” says Custer.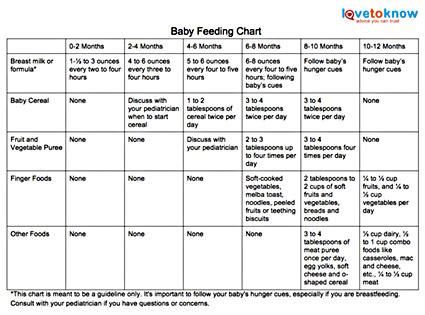
Another thing to keep in mind is that the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) no longer recommends delaying the introduction of allergenic foods, particularly peanuts. While it was once advised to wait until your baby was at least 10 months to introduce peanut-containing foods, the AAP now recommends giving babies with no known egg allergy or eczema, infant-safe forms of peanut between 4 to 6 months old. Babies with mild eczema should wait until at least 6 months, and for babies with severe eczema, speak to their doctor before giving them peanut-containing foods. (To find out if your baby has an egg allergy, they must be tested by their pediatrician.)
Which foods to avoid during Stage 2
Even though your little one is venturing into new food texture territory with Stage 2, you should still avoid giving them chunks and small pieces of food, which can pose a serious risk. (Food may be thicker at Stage 2, but it’s still all about the purees and mashes at this point.)
“Infants may have any food that is texture-appropriate for their developmental feeding stage, but it’s important to stay away from choking hazards, such as whole grapes, nuts and seeds,” says Treegoob.
“Infants may have any food that is texture-appropriate for their developmental feeding stage, but it’s important to stay away from choking hazards, such as whole grapes, nuts and seeds.”
DR. KRISTEN TREEGOOB, PEDIATRICIAN
Also, avoid giving your baby honey — raw or cooked — before the age of 12 months, as it may cause a botulism infection.
And finally, when it comes to your baby’s beverage, steer clear of juice. The AAP recommends parents eschew juice, which has “no nutritional benefits over whole fruit,” until at least 1. “At this point, it’s best to stick with breast milk, formula or the odd bit of water (1 to 2 ounces a day), which is mainly for introducing your baby to the skill of using a sippy cup,” says Thompson.
How to start Stage 2 foods safely
Baby should be sitting in a highchair when eating and never left alone. You’ll still be spooning food into your baby’s mouth at this point, but don’t be afraid to let your little one take a whirl at self-feeding in order to get in some practice using utensils.
“At around 9 months, we started letting our son try his hand at feeding himself in his highchair,” says mom of two Erin Henderson, of Waltham, Massachusetts. “It was a mess, but he obviously enjoyed the learning experience.”
Also, during the latter half of your baby’s Stage 2 stint, they may learn how to grab things with their thumb and forefinger and bring them to their mouth.
“Between 8 and 12 months, babies develop the pincer grasp ability and should be able to pick up small pieces of finger food, such as Cheerios or puffs,” says Thompson.
As your baby grows and hones their eating skills, they’ll cut down a bit on how much breast milk or formula they drink — but keep in mind, that should still be their primary source of nutrients.
“Most infants will naturally start to moderate their breast milk or formula intake once their solid intake increases,” says Treegoob. “Solid food may start to account for a significant source of nutritional intake closer to 7 to 9 months.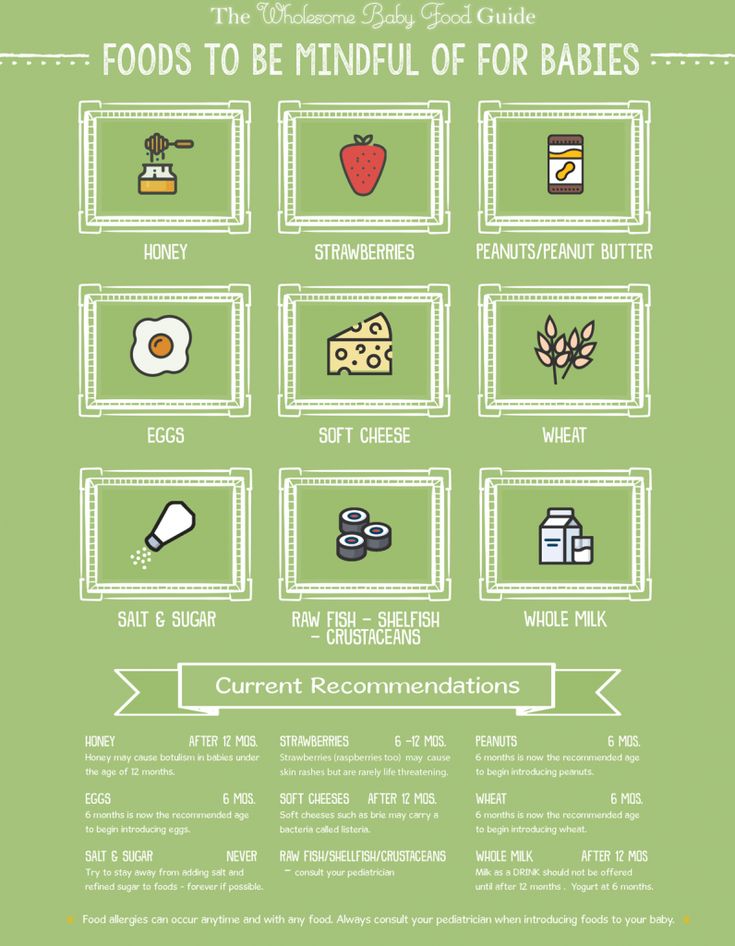 At this time, parents may notice that their baby shows interest in smaller or less frequent bottle or breastfeeds. As long as their weight remains on track and baby is drinking enough milk to stay well-hydrated, there should be no need for concern. Infants typically take somewhere between 24 to 40 ounces of breast milk or formula between 4 to 6 months and 24 to 32 ounces from 6 to 9 months.”
At this time, parents may notice that their baby shows interest in smaller or less frequent bottle or breastfeeds. As long as their weight remains on track and baby is drinking enough milk to stay well-hydrated, there should be no need for concern. Infants typically take somewhere between 24 to 40 ounces of breast milk or formula between 4 to 6 months and 24 to 32 ounces from 6 to 9 months.”
According to the AAP, babies should be eating about 4 ounces of solids (about one small jar of baby food) at each of their meals. And if you’re wondering how long baby food lasts, experts typically recommend 24-48 hours in the fridge or up to 3 months in the freezer.
Lastly, bear in mind that if at first you don’t succeed with a food, try, try again.
“At this age, if babies grimace when taking a bite or shake themselves, it is most often because of a texture issue, not the actual taste,” says Custer. “It is important to keep introducing these foods as it may take a baby up to 15 times to get used to a texture before you can say for sure he/she doesn’t like it.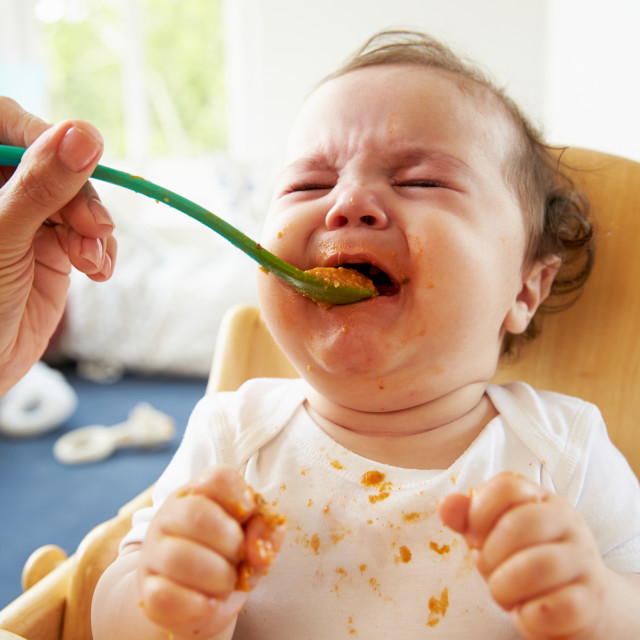 ”
”
Ready for the next stage?
- Stage 3 baby food
Stage 2 baby food: what is it, when to start and what options to try
Contents
- What is stage 2 baby food?
- Identification of stages by brand
- What is the difference between stage one and stage two meals?
- When and how should I start feeding my baby 2nd stage complementary foods?
- What are your baby food options for stage 2?
- Store-bought baby food stage 2.
- Homemade baby food stage 2
- Conclusion
Accompanying your child through the different stages of learning how to eat real food is an exciting journey. Sometimes, along with a sense of pride - - you can feel a little confused. How should you navigate milestones?
What is stage 2 baby food?
Let's start from the beginning: what do the stages of baby food mean?
Rome wasn't built in a day, and your child's digestive system won't jump from liquid to solid in one day either. That's what baby feeding stages are for - to help your baby manage the mechanics of eating and ease the transition to your baby's digestive system.
That's what baby feeding stages are for - to help your baby manage the mechanics of eating and ease the transition to your baby's digestive system.
Defining milestones by brand
Although the different baby food steps are not standardized (if they were, your life would be easier!), most popular brands more or less follow these four steps:
- Step 1: From 4 up to 6 months (single ingredient watery puree)
- Stage 2: 6 to 9 months (thicker texture, strained or puréed)
- Stage 3: 10 to 12 months (porridge with soft chewy small pieces )
- Stage 4: After 12 months (food that you can eat with your fingers and small soft pieces of food that you share with your dinner)
What is the difference between eating the first and second stages?
Stage 1 food is quite watery. They turn into a smooth paste that runs off a spoon easily, so stock up on bibs. These products usually consist of one ingredient: oatmeal, apples, carrots. Your child will start eating about half a teaspoon of this.
These products usually consist of one ingredient: oatmeal, apples, carrots. Your child will start eating about half a teaspoon of this.
Stage 2 food becomes more exciting. They are strained or ground into a thick paste. They are made from a combination of foods that can include legumes and even meat or fish. They can combine flavors, such as fruit and vegetable blends. Your child's appetite is growing and you will have to keep up with larger portions.
When and how should I start feeding my baby 2nd stage complementary foods?
Around 6 to 9 months of age, your baby is probably ready to switch to stage 2 complementary foods. Not every child will stick to this schedule, simply because every child is a separate world.
Here are a few signs that your baby is ready to move on:
- Tongue reflex: At around five months, your baby will begin to lose the tongue thrust reflex and will not immediately push out the food you are trying to feed.

- More Please: They will easily eat the first stage foods and look hungry to eat more.
- Variety: They ate foods from all food categories (vegetables, fruits, legumes, grains, meat) and showed no allergies or intolerances.
- Delight: They easily eat a spoonful of food in stage 1, swallow and swallow with pleasure.
At this exciting stage, feel free to give your child most of the foods. By offering them a wide range of flavors and textures, you give them the foundation for a healthy diet and also make it easier for you. Be aware of the following safety considerations:
- Choking Hazard: Avoid nuts, seeds, and popcorn at this stage. And don't forget to cut round foods like grapes and hot dogs lengthwise.
- No honey: Babies under 12 months old should not be given honey as it can lead to botulism.
- No Juice: Follow AAP guidelines and stick to breast milk, formula or a little water and stay away from juices.

- Safe Feeding: Always fasten your child to a high chair and supervise him while he eats.
And if you're curious about peanuts, here's the scoop: 2017 National Institutes of Health report suggests giving babies peanut-containing foods as early as 4 months of age. (Wait up to 6 months for children with mild to moderate eczema.)
Surprised? Do not be. A recent study showed that Israeli children rarely suffer from peanut allergies because they have been chewing bamba, a peanut-based snack, as early as 3 months old. Talk to your doctor about safe ways to include peanut products in your baby's diet.
What are your baby food options for stage 2?
What is included in the stage 2 baby food menu? Basically, you can go the store or home route. Or you can mix both depending on how much time you have. It depends on you and your personal schedule.
Here are some delicious ideas for both.
Store-bought baby food stage 2.

- Plum: These organic blends come in easy-to-carry bags. Try pear, spinach and peas, or banana and pumpkin.
- Beech-walnut: Available in tins and bags. Serve a few apples and bananas or pineapple, pear and avocado.
- Best in the world: Another organic option, in bags or jars. Try sweet potatoes, barley and chickpeas, or pasta with tomatoes and white beans.
- Gerber: A classic served in plastic jars, jars or bags. Flavor combinations include peach mango and dinner with oatmeal or chicken noodles.
Remember to keep an eye on your baby while he is eating. Bags are convenient, but caps can be a choking hazard. Glass jars can break, so keep them out of the reach of children. Your child should always enjoy snacks and meals under close adult supervision.
Homemade Baby Food Stage 2
Cooking up a storm for your baby's nascent taste buds doesn't have to be a daunting task at this stage. Here are some recipes to help you. (You can find more baby food recipes here.)
Here are some recipes to help you. (You can find more baby food recipes here.)
Don't skimp on spices and herbs: your little one will appreciate the extra flavor and the micronutrients they contain will boost their immune system.
- Apple, walnut and carrot: Cook the ingredients until they are soft when checked with a fork. Drain off some of the water, but set it aside in case you need to dilute the mixture. Sprinkle with a little curry and stir.
- Blueberries and chickpeas: You can make your own chickpeas or use ready-made ones to save time. Mix equal amounts of blueberries and chickpeas. Mix and add breast milk, formula, or water to get the right consistency. You can also add some rice for added appeal and texture.
- Salmon with fried zucchini and fennel: Drizzle salmon and vegetables with oil and roast for about 15 minutes. Add chopped parsley and stir. You can dilute formula with breast milk, formula, or water.

Conclusion
Enjoy this stage with your child because he will soon move on to the next stages. And then, sooner than you think, you may face competition for the last slice of caramel cheesecake.
How to feed a child? Top Books on Baby Nutrition
Which of the modern parents is not concerned about the nutrition of their child? It seems to someone that the baby eats too little, and it seems to someone that he eats enough - but not quite what he needs (or not at all). We receive a lot of information about healthy nutrition, including children's nutrition - but how to understand it and which experts can you definitely trust? We have compiled a list of the most reliable and proven books on healthy eating for children.
1. PRO nutrition for children. Without tears and persuasion”, Alexandra Sitnova
One of the most popular books on baby food in the Russian-speaking world. Written by a nutritionist who has been blogging on Instagram (@pro_appetit) for a long time — Alexandra Sitnova. Written as simply and accessible as possible, perfect for "beginning moms." After all, how many disturbing questions are connected precisely with the nutrition of babies: is he getting enough milk? Is he gaining weight well? Maybe you need to add the mixture? Or is food better? So which product to start with? And when to start feeding from the common table? Alexandra's book was published in the "Doctor Blogger" series, which means that the knowledge and experience of pediatricians, allergists, and scientists were used in its writing.
Written as simply and accessible as possible, perfect for "beginning moms." After all, how many disturbing questions are connected precisely with the nutrition of babies: is he getting enough milk? Is he gaining weight well? Maybe you need to add the mixture? Or is food better? So which product to start with? And when to start feeding from the common table? Alexandra's book was published in the "Doctor Blogger" series, which means that the knowledge and experience of pediatricians, allergists, and scientists were used in its writing.
2. "Baby food in the big city", Regina Doktor
But Regina Doktor is a professional therapist herself, specializing today in nutrition. She wrote 2 wonderful bestsellers: “Healthy Eating in the Big City” and “I DON'T LIKE SWEET”, in which she laid out the basic principles of healthy eating in a very systematic and at the same time fascinating way. The book about baby food is no less informative and useful. It helps to calmly go through all the exciting stages of complementary feeding, to move from stress and not understanding what to do, to the magical realization that you are finally doing everything right. Regina Doctor talks about the ideal preparation for pregnancy, and about the nutrition of the expectant mother (moreover, depending on the trimester), and even about childbirth ... Well, then everything that worries us even more: breastfeeding and artificial feeding, complementary foods, food allergies, intestinal problems, atopic dermatitis. The book also contains exemplary diets for children over one year old - a very useful guide for all conscious parents. We also love Regina's book for lots of cool recipes like zucchini muffins, superhero borscht, and smart and smart roast.
It helps to calmly go through all the exciting stages of complementary feeding, to move from stress and not understanding what to do, to the magical realization that you are finally doing everything right. Regina Doctor talks about the ideal preparation for pregnancy, and about the nutrition of the expectant mother (moreover, depending on the trimester), and even about childbirth ... Well, then everything that worries us even more: breastfeeding and artificial feeding, complementary foods, food allergies, intestinal problems, atopic dermatitis. The book also contains exemplary diets for children over one year old - a very useful guide for all conscious parents. We also love Regina's book for lots of cool recipes like zucchini muffins, superhero borscht, and smart and smart roast.
3. “First soup, then dessert”, Maria Kardakova
A very sincere and inspiring book, mainly dedicated to the nutrition of children from one to 7 years old. Its main message is that it is important not only to form a complete children's diet; it is even more important to instill healthy habits in the child, thanks to which he will consciously eat even when he becomes an adult and moves out from caring parents. To establish a healthy relationship with food, the first complementary foods are very important - Maria will tell you how not to make mistakes at this stage - as well as the psychology of nutrition in the family as a whole. Therefore, in the book you will find a lot of clear recommendations: both on the ratio of products and portion sizes, and on how to color the process of eating with a solid positive. For parents who are just getting into the topic of healthy eating and changing habits to more environmentally friendly ones, this is just a treasure trove of basic knowledge. For further immersion in the topic, you can also look at the author's Instagram profile - @marysstories.
To establish a healthy relationship with food, the first complementary foods are very important - Maria will tell you how not to make mistakes at this stage - as well as the psychology of nutrition in the family as a whole. Therefore, in the book you will find a lot of clear recommendations: both on the ratio of products and portion sizes, and on how to color the process of eating with a solid positive. For parents who are just getting into the topic of healthy eating and changing habits to more environmentally friendly ones, this is just a treasure trove of basic knowledge. For further immersion in the topic, you can also look at the author's Instagram profile - @marysstories.
4. “My child doesn't want to eat. How to turn feeding into pleasure”, Carlos Gonzalez
You frantically calculate grams of squash puree, get nervous, get upset if the baby ate “less than normal” ... you start to persuade, entertain, and then insist ... Familiar? Then read this book and relax. The process of eating should not turn into a battle. Never force a child to eat - never for any reason. Let it be for you a manifestation of love and respect! Dr. González, a father of three and a famous pediatrician from Barcelona, knows what he's talking about.
The process of eating should not turn into a battle. Never force a child to eat - never for any reason. Let it be for you a manifestation of love and respect! Dr. González, a father of three and a famous pediatrician from Barcelona, knows what he's talking about.
5. “Tasty for kids. Learning to cook for the fussy”, Maria Ivanova
From theory to practice. Catch 55 great recipes that even the pickiest kid will love. Maria suggests using healthy ingredients and paying attention to design and presentation - children love it. In the book you will find soups, salads, and cottage cheese dishes (a valuable protein, you remember) ... well, some sweet pastries, sometimes you can! And another nice bonus of the edition is its wonderful design. You will see, your kid will be happy to leaf through the book and choose a recipe for dinner.
6. “Dr. annamama, I have a question. How to feed a child?”, Anna Levadnaya
Another basic book about healthy baby food from a pediatrician, neonatologist and - no less! – Candidate of Medical Sciences Anna Levadnaya (@doctor_annamama). All burning topics are revealed: breast and artificial feeding, weaning, introduction of complementary foods, allergen foods, toddlers, intestinal infections ... The book is perfect for those who are expecting a child or have just become a parent - in order to systematize information from numerous sources and not get confused. Curious questions are also covered, such as the effect of heating in the microwave on food or the need to take vitamins. Little "water", a lot of practical important information - for this we love books written by professional doctors.
All burning topics are revealed: breast and artificial feeding, weaning, introduction of complementary foods, allergen foods, toddlers, intestinal infections ... The book is perfect for those who are expecting a child or have just become a parent - in order to systematize information from numerous sources and not get confused. Curious questions are also covered, such as the effect of heating in the microwave on food or the need to take vitamins. Little "water", a lot of practical important information - for this we love books written by professional doctors.
7. “Love and Broccoli: In Search of Children's Appetite”, Svetlana Kolchik
And in conclusion, a little entertaining, a little instructive book from a journalist and part-time mother of Svetlana Kolchik. Faced with painfully familiar questions like “What should I feed my baby?” and “How to make him friends with food?”, she decided to study how things are with baby food in other countries.