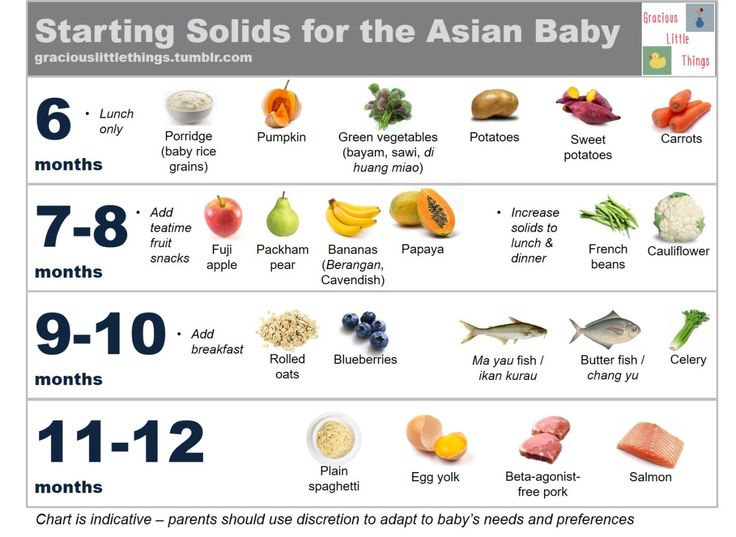
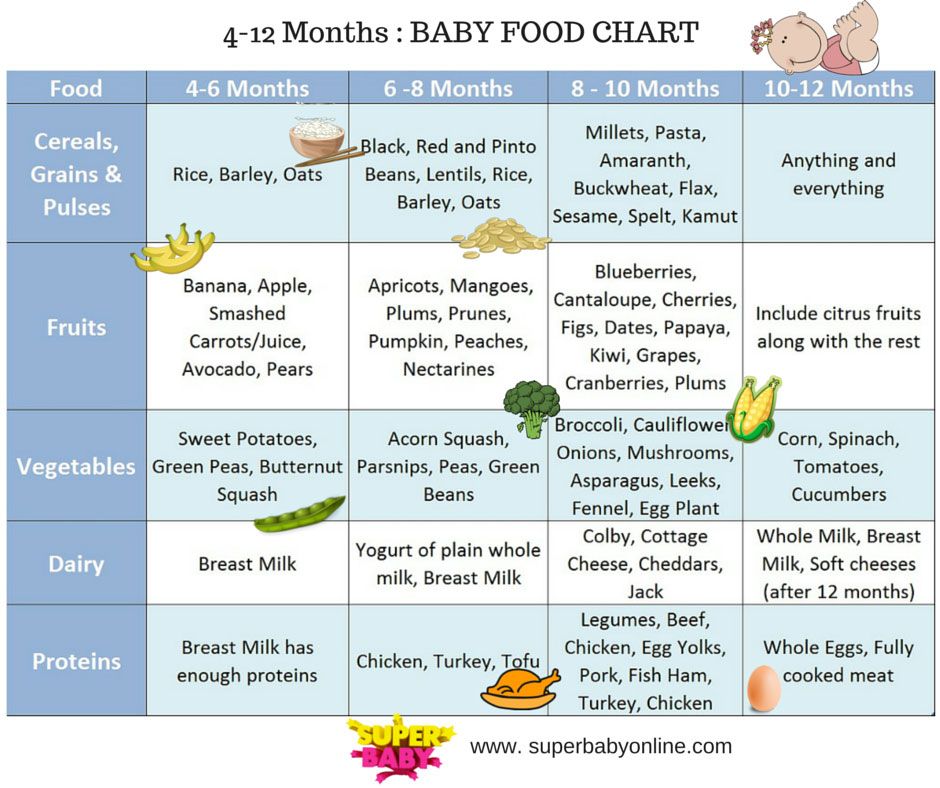
When should i feed my baby more formula
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day. Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough. If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings. They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique. No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Breast milk and formula: what do they have in common?
1 Cribb VL et al. Contribution of inappropriate complementary foods to the salt intake of 8-month-old infants. Eur J Clin Nutr . 2012;66(1):104. - Cribb V.L. et al., "Effects of inappropriate complementary foods on salt intake in 8-month-old infants". Yur J Clean Nutr. 2012;66(1):104.
2 Lönnerdal B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am J Clin Nutr . 2003;77(6):1537 S -1543 S - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
2003;77(6):1537 S -1543 S - Lönnerdahl B., "Biologically active proteins of breast milk". F Pediatrician Child Health. 2013;49 Suppl 1:1-7.
3 Savino F et al. Breast milk hormones and their protective effect on obesity. Int J Pediatric Endocrinol. nine0004 2009;2009:327505. - Savino F. et al., "What role do breast milk hormones play in protecting against obesity." Int J Pediatrician Endocrinol. 2009;2009:327505.
4 Hassiotou F, Hartmann PE. At the Dawn of a New Discovery: The Potential of Breast Milk Stem Cells. Adv Nutr . 2014;5(6):770-778. - Hassiot F, Hartmann PI, "On the threshold of a new discovery: the potential of breast milk stem cells." Adv Nutr. 2014;5(6):770-778.
5 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology . - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
- Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
6 Pannaraj PS et al. nine0004 Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(7):647-654. - Pannaraj P.S. et al., "Bacterial communities in breast milk and their association with the emergence and development of the neonatal gut microbiome". JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
7 Bode L. Human milk oligosaccharides: every baby needs a sugar mama.Glycobiology. nine0004 2012;22(9):1147-1162. - Bode L., "Oligosaccharides in breast milk: a sweet mother for every baby." Glycobiology (Glycobiology). 2012;22(9):1147-1162.
8 Deoni SC et al. Breastfeeding and early white matter development: A cross-sectional study.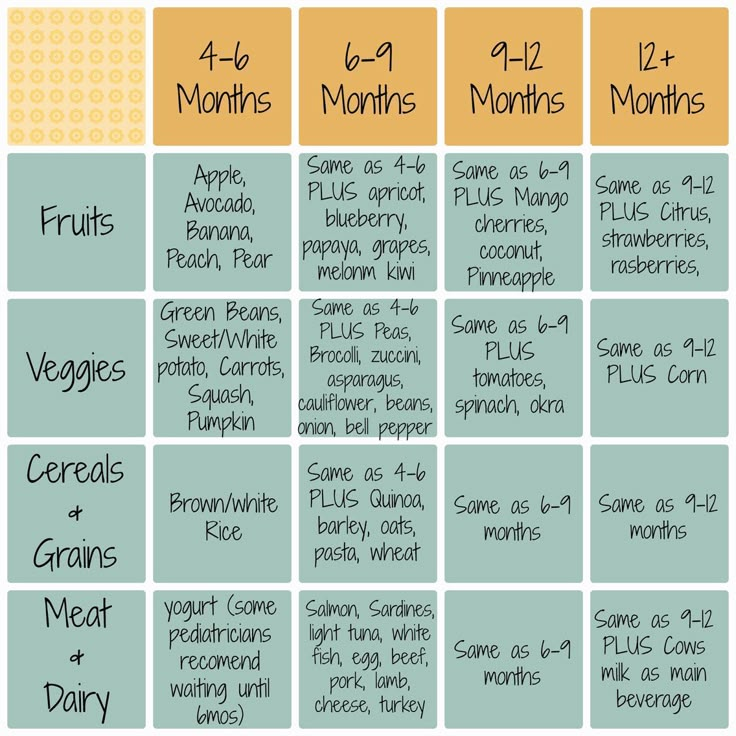 neuroimage. 2013;82:77-86. - Deoni S.S. et al., Breastfeeding and early white matter development: a cross-sectional study. Neuroimaging. 2013;82:77-86. nine0004
neuroimage. 2013;82:77-86. - Deoni S.S. et al., Breastfeeding and early white matter development: a cross-sectional study. Neuroimaging. 2013;82:77-86. nine0004
9 Birch E et al. Breast-feeding and optimal visual development. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993;30(1):33-38. - Birch, I. et al., "Breastfeeding and Optimum Vision Development." J Pediatrician Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993;30(1):33-38.
10 Sánchez CL et al. The possible role of human milk nucleotides as sleep inducers. Nutr Neurosci . 2009;12(1):2-8. - Sanchez S.L. et al., "Nucleotides in breast milk may help the baby fall asleep." nine0004 Nutr Neurosai. 2009;12(1):2-8.
11 Moukarzel S, Bode L. Human Milk Oligosaccharides and the Preterm Infant: A Journey in Sickness and in Health. Clin Perinatol. 2017;44(1):193-207. - Mukarzel S., Bode L., "Breast milk oligosaccharides and the full-term baby: a path to illness and health. " Klin Perinatol (Clinical perinatology). 2017;44(1):193-207.
" Klin Perinatol (Clinical perinatology). 2017;44(1):193-207.
12 Beck KL et al. Comparative Proteomics of Human and Macaque Milk Reveals Species-Specific Nutrition during Postnatal Development. J Proteome Res . 2015;14(5):2143-2157. - Beck K.L. et al., "Comparative proteomics of human and macaque milk demonstrates species-specific nutrition during postnatal development." G Proteome Res. 2015;14(5):2143-2157.
13 Michaelsen KF, Greer FR. Protein needs early in life and long-term health. Am J Clin Nutr . 2014;99(3):718 S -722 S . - Mikaelsen KF, Greer FR, Protein requirements early in life and long-term health. Am J Clean Nutr. 2014;99(3):718S-722S.
14 Howie PW et al. Positive effect of breastfeeding against infection. BMJ .1990;300(6716):11-16. — Howie PW, "Breastfeeding as a defense against infectious diseases." nine0004 BMJ. 1990;300(6716):11-16.
BMJ .1990;300(6716):11-16. — Howie PW, "Breastfeeding as a defense against infectious diseases." nine0004 BMJ. 1990;300(6716):11-16.
15 Duijts L et al. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in infancy. Pediatrics , 2010;126(1): e 18-25. - Duitz L. et al., "Prolonged exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in the first year of life." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2010;126(1):e18-25.
16 Ladomenou F et al. nine0004 Protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding against infections during infancy: a prospective study. Arch Dis Child . 2010;95(12):1004-1008. - Ladomenu, F. et al., "The effect of exclusive breastfeeding on infection protection in infancy: a prospective study." Arch Dis Child. 2010;95(12):1004-1008.
17 Vennemann MM et al. Does breastfeeding reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome?. Pediatrics . 2009;123(3): e 406- e 410. - Wennemann M.M. et al., "Does Breastfeeding Reduce the Risk of Sudden Infant Death?" Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2009;123(3):e406-e410.
Pediatrics . 2009;123(3): e 406- e 410. - Wennemann M.M. et al., "Does Breastfeeding Reduce the Risk of Sudden Infant Death?" Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2009;123(3):e406-e410.
18 Straub N et al. Economic impact of breast-feeding-associated improvements of childhood cognitive development, based on data from the ALSPAC. Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6. - Straub N. et al., "Economic Impact of Breastfeeding-Associated Cognitive Child Development (ALSPAC)". Br J Nutr . 2016;1-6.
19 Heikkilä K et al. Breast feeding and child behavior in the Millennium Cohort Study. Arch Dis Child . 2011;96(7):635-642 - Heikkila K. et al., "Breastfeeding and Child Behavior in a Millennial Cohort Study". nine0004 Arch Dis Child. 2011;96(7):635-642.
20 Singhal A et al. Infant nutrition and stereoacuity at age 4–6 y. Am J Clin Nutr , 2007;85(1):152-159. - Singhal A. et al., Nutrition in infancy and stereoscopic visual acuity at 4-6 years of age. Am F Clean Nutr. 2007;85(1):152-159.
21 Peres KG et al. nine0004 Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
22 Horta B et al. Long - term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr . 2015;104(467):30-37. - Horta B.L. et al., "Long-term effects of breastfeeding and their impact on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis." Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):30-37.
2015;104(467):30-37. - Horta B.L. et al., "Long-term effects of breastfeeding and their impact on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis." Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):30-37.
23 Lund-Blix NA. Infant feeding in relation to islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible children: the MIDIA Study. Diabetes Care . 2015;38(2):257-263. - Lund-Blix N.A. et al., "Breastfeeding in the context of isolated autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes in genetically predisposed children: the MIDIA study ". Diabitis Care. 2015;38(2):257-263.
24 Amitay EL, Keinan-Boker L. Breastfeeding and Childhood Leukemia Incidence: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. JAMA Pediatr . 2015;169(6): e 151025. - Amitai I.L., Keinan-Bocker L., "Breastfeeding and incidence of childhood leukemia: a meta-analysis and systematic review. " JAMA Pediatrician. 2015;169(6):e151025.
" JAMA Pediatrician. 2015;169(6):e151025.
25 Bener A et al. Does continued breastfeeding reduce the risk for childhood leukemia and lymphomas? Minerva Pediatr. 2008;60(2):155-161. - Bener A. et al., "Does long-term breastfeeding reduce the risk of leukemia and lymphoma in a child?". nine0004 Minerva Pediatric. 2008;60(2):155-161.
26 Dewey KG. Energy and protein requirements during lactation. Annu Rev Nutr . 1997;17:19-36. - Dewey K. J., "Energy and Protein Requirements During Lactation". Anna Rev Nutr. 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36.
27 Victoria CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. nine0004 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects. Lancet (Lancet). 2016;387(10017):475-490.
28 Jordan SJ et al. Breastfeeding and Endometrial Cancer Risk: An Analysis From the Epidemiology of Endometrial Cancer Consortium. Obstet Gynecol . 2017;129(6):1059-1067. — Jordan S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of endometrial cancer: an analysis of epidemiological data from the Endometrial Cancer Consortium". nine0004 Obstet Ginecol (Obstetrics and Gynecology). 2017;129(6):1059-1067.
29 Li DP et al. Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev . 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. nine0004 Asia Pas G Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
30 Peters SAE et al. Breastfeeding and the Risk of Maternal Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women. J Am Heart Assoc . 2017;6(6). - Peters S.A. et al., "Breastfeeding and Maternal Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women". nine0004 J Am Hart Assoc. 2017;6(6):e006081.
J Am Heart Assoc . 2017;6(6). - Peters S.A. et al., "Breastfeeding and Maternal Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Prospective Study of 300,000 Chinese Women". nine0004 J Am Hart Assoc. 2017;6(6):e006081.
31 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet ; 2011 Jan 20 — Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer, January 20, 2011 [cited April 4, 2018]
32 Doan T et al. Breast-feeding increases sleep duration of new parents. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs . 2007;21(3):200-206. - Dawn T. et al., "Breastfeeding increases parental sleep duration." G Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2007;21(3):200-206.
33 Menella JA et al. Prenatal and postnatal flavor learning by human infants. Pediatrics . 2001;107(6): E 88. - Menella J.A. et al., Prenatal and Postnatal Taste and Smell Recognition in Children. Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2001;107(6):e88.
Pediatrics . 2001;107(6): E 88. - Menella J.A. et al., Prenatal and Postnatal Taste and Smell Recognition in Children. Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2001;107(6):e88.
34 Forestell CA, Mennella JA. Early determinants of fruit and vegetable acceptance. Pediatrics . 2007;120(6):1247-1254. - Forestell S.A., Mennella J.A., "The First Signs of Readiness to Taste Fruits and Vegetables." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2007;120(6):1247-1254. nine0004
Breastfeeding after 1 month: what to expect
Do you know when breast milk production stabilizes? And how does the frequency and duration of feedings change as the baby grows? You will find answers to these questions in our recommendations for breastfeeding after the first month.
Share this information
Congratulations: You made it through the first month of breastfeeding. Your breast milk has reached full maturity 1 , its production stabilizes and it leaks almost or not at all from the chest. Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding. nine0021
Don't worry, it's not getting less milk, it's just that your breasts are better able to produce and store it now. 2 At the age of six weeks, your baby will begin to please you with his charming toothless smiles, and by two months you will already have 500-600 feedings behind you. With a favorable development of events, problems with latch on by this point will already be resolved, and you can simply enjoy the convenience and benefits of breastfeeding. nine0021
When is the frequency of breastfeeding reduced?
The "normal" feeding frequency for babies aged one to six months varies considerably, with some needing four times a day, others asking to be breastfed 13 times a day. 3
“From the age of one month, the amount of milk a baby consumes per feed increases so that he can go without food for longer,” explains Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding, “A baby’s stomach grows, so he eat more at one time. In addition, mature milk allows him to stay full longer. ” nine0021
” nine0021
Feeding can last from 12 minutes to one hour -
the habits of babies vary so much! 3 But if the child is gaining weight and falls within this range, there is no reason to worry.
What is most surprising, no matter how often the baby eats, he consumes approximately the same amount of milk per day - both at one month and at six, when it is time to start complementary foods with solid food. 4
“However, sometimes the baby eats more and sometimes less, especially when he is unwell. It’s better to just listen to his needs,” explains Katie. nine0021
Is breast milk enough for the first six months?
Yes. Breast milk contains everything a baby needs for the first 90,593 six months of life—exclusively breastfed babies don't even need to drink more water! 5 Until about six months of age, the child's digestive system is simply not adapted to the digestion of solid food, and he will be able to drink cow's milk only after a year.
In addition, breastfeeding during this period prepares the child for further development. It strengthens the muscles of the mouth, develops the jaw and helps straighten the teeth 6.7 . All this will come in handy when the baby begins to eat and talk. And because what you eat and drink affects how your breast milk tastes, your baby discovers new tastes even before he starts eating solid foods. 8
In addition, when your baby is sick, your body produces breast milk that is
rich in antibodies that help fight infection. 9 In other words, milk continues to protect the baby for many months as it grows and becomes more active. nine0021
Breastfeeding is also very comfortable once you get used to it. Claudia, a mother of two from the UK, notes: “No need to sterilize a mountain of bottles, prepare formula, carry it all with you, warm it up - in general, breastfeeding turned out to be very convenient, especially when my babies grew up and we began to leave the house more often. ".
".
At what age does a breastfed baby start sleeping through the night?
Waking up at night is normal for babies. Most babies between the ages of one and six months consume a fifth of their daily milk requirement at night, so nighttime feedings should not be neglected if you want your baby to get the required amount of calories. nine0579 3
"It really depends on what you mean by 'sleep through the night,'" says Cathy. "And it's better than waking up every two hours anyway! I have met infants who, starting at six weeks old, fell asleep at 19:00 and woke up at 7:00, but most continue to wake up frequently at night after this age. All children are different."
In Wales, a study of more than 700 babies found that almost 80% of children aged 6 to 12 months wake up at least once a night, and 25% of them wake up three times or more. And it did not depend on what type of feeding the child is on - breastfeeding or artificial. nine0579 10
And if nighttime awakenings are unavoidable anyway, breastfeeding is at least comfortable! Maina, a mother of two from Australia, agrees: “You can even take a nap while feeding in the middle of the night - both the body and the baby do their job on autopilot. No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
No need to plan, measure, sterilize anything - ready-made food at the right temperature is right in your chest. I think it's ideal."
My child wakes up more often. Perhaps he is hungry?
Around four months of age, a baby's sleep pattern changes as he, like an adult, develops deep and light sleep phases. Because of this, he may wake up more often at night. “At four months, sleep is more of a problem than feeding,” Cathy admits. “It can be exhausting, but try to adapt and be patient.” nine0021
Some call this " a four-month sleep regression ", but "progress" is more appropriate here. From the outside it may look like a step back, but in fact the child is approaching an important stage of development. He learns quickly, begins to become aware of the world around him, his perception is sharpened and, perhaps, there is anxiety about being separated from his mother. Crying when waking up and being able to eat milk while cuddling up to your mother’s breast is a way for a baby to calm down. nine0579 11-13
nine0579 11-13
Resist the urge to "supplement" your baby with formula or start solid foods early
in an attempt to improve his sleep. Breast milk contains
hormones that make you sleepy and help you both relax
. Studies show that breastfeeding mothers actually sleep longer at night than formula- or formula-fed mothers
. 14
How does teething affect breastfeeding?
Teething usually begins around four months of age. When a baby has gum pain, he becomes restless, throws his chest and cries. All this, of course, is unpleasant.
However, breastfeeding can be an excellent sedative.
Studies have shown that babies who are breastfed
during the vaccination period cry less and forget pain more quickly. 15 Breastfeeding during teething can have the same calming effect. nine0021
An unpleasant side effect may be the child's attempts to try out his new teeth on the mother's breast. “Sometimes children flirt and bite their mother’s nipples. This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
This can be felt in advance by how the behavior of the child changes when feeding: before biting, he removes his tongue, explains Cathy, “Usually this is not a problem and only happens a couple of times. It is enough to stop feeding, affectionately say that biting is not good, and the baby will soon leave this fun.
How to continue breastfeeding if you have to be separated from your baby? nine0585
It happens that during the first six months, when the baby is still fully breastfed, the mother needs to be away for several hours - or even longer if she has to go to work or go away on business for a couple of days.
But this does not mean that you should stop breastfeeding. You can still feed your baby healthy breast milk - just express it and have someone give it to your baby when you're away. Here's Katie's advice:
“Start expressing milk in a couple of days, in small batches, 40-60 ml at a time. So you will have the necessary supply for the time of your absence, but at the same time the amount of milk produced will remain the same. nine0021
nine0021
If you have to return to work, check with your employer about your daily schedule. Many mothers breastfeed their babies in the morning, evening and night, and pump milk at lunchtime to relieve discomfort and create a reserve for the next day.
This usually turns out to be much easier than you might think, and today many companies have the conditions for this, notes Cathy, “Breast pumps make it easy to solve this problem.”
Natalie, mother from the USA, shares her experience: “I feed Dylan as soon as he wakes up, and sometimes again before leaving for work, in order to maintain milk production and not lose contact with the child. At work, I pump twice the next day (in my absence, he eats two bottles of breast milk), and after work I rush home for the evening feed. I don't pump on the weekends - we resume regular breastfeeding." nine0021
Is it possible to continue breastfeeding after the introduction of solid foods?
When your baby begins to show interest in food and can sit up on his own - usually around six months of age - it's time to start solid foods. However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
However, it is not necessary to stop breastfeeding, Cathy explains: “A baby’s iron stores during pregnancy are depleted by six months, so he needs additional sources of this element.
Start complementary foods with solid foods, but remember that breast milk remains a more important source of calories and nutrients until the baby is eight to nine months old. By this time, he will be eating much more solid food, but he will still need to breastfeed four to five times a day. By 12 months, the frequency of feeding may be two to six times a day. All babies are different, and many of them at this age are still getting half their daily calorie intake from breast milk.” nine0021
Don't forget that breastmilk can be added to solid foods such as cereals and purees so that the baby can taste the familiar taste. If possible, use milk expressed just before feeding (not thawed) and add just before serving to keep bacteria and nutrients alive. 16
You may be pressured by others to stop breastfeeding when your baby is six months old, but the longer you breastfeed or pump, the better for you and your baby. nine0021
nine0021
How long can I continue breastfeeding?
“The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding along with solid foods until at least two years of age because it plays an important role in supporting immunity,” says Cathy. feels bad".
At eight months, the baby sometimes breastfeeds four times a day, but by the age of one, the frequency of feedings can be reduced to two times a day. You yourself will understand which feeding regimen is more suitable for you and your baby. For example, Jane, a mother of two from the US, breastfed until the age of two: “I breastfed when I was at home - in the evenings and on weekends, when the children wanted to be close to me,” says Jane, “It helped a lot when they were sick . Breastfeeding has become my favorite form of comfort." nine0021
“When my son got a little older and bolder, he still often asked me to breastfeed him – as if to calm down and gain strength,” recalls Amy, mother of two children from Canada, “When he happened to hit or skin his knee , breastfeeding was a wonderful way to comfort him. ”
”
If your baby is over a year old and you are still breastfeeding, people around you will probably tell you that this way he will never wean. But if children are not pressured, they usually refuse to breastfeed themselves between the ages of two and four. nine0579 17
“I didn’t intend to breastfeed for so long, but as a result, I still breastfeed my four-year-old daughter and 22-month-old son,” says Suzanne, mother of two from the UK, “I breastfeed my youngest before and after work, and in I express milk on business trips. The eldest daughter likes to breastfeed a little before bed or when she is upset - this is a great way to make contact. When I get tired of it, I remind myself what great benefit and comfort it brings them. I now plan to pursue a baby-initiated end breastfeeding strategy — let them decide when to stop.” nine0021
For more information on what to expect and lots of tips and tricks, see our guide Breastfeeding Problems After the First Month.
Literature
1 Ballard O, Morrow AL. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am . 2013;60(1):49-74. - Ballard O., Morrow A.L., "Composition of breast milk: nutrients and biologically active factors." nine0004 Pediatrician Clean North Am. 2013;60(1):49-74.
2 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-21. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol and Neonatal Nurse. 2012;41(1):114-121. nine0004
3 Kent J.C. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
4 Kent JC et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breast Med . 2013;8(4):401-407. - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns between 1 and 6 months of lactation. Brest Med. 2013;8(4):401-407.
5 Almroth S, Bidinger PD. No need for water supplementation for exclusively breast-fed infants under hot and arid conditions. Trans 9 Trop Med Hyg Hyg 1990;84(4):602-604. - Elmroth S., Bidinger P.D., "No need for supplementation of exclusively breastfed infants in hot, dry conditions." Trans R Sots Trop Med Hyg. 1990;84(4):602-604.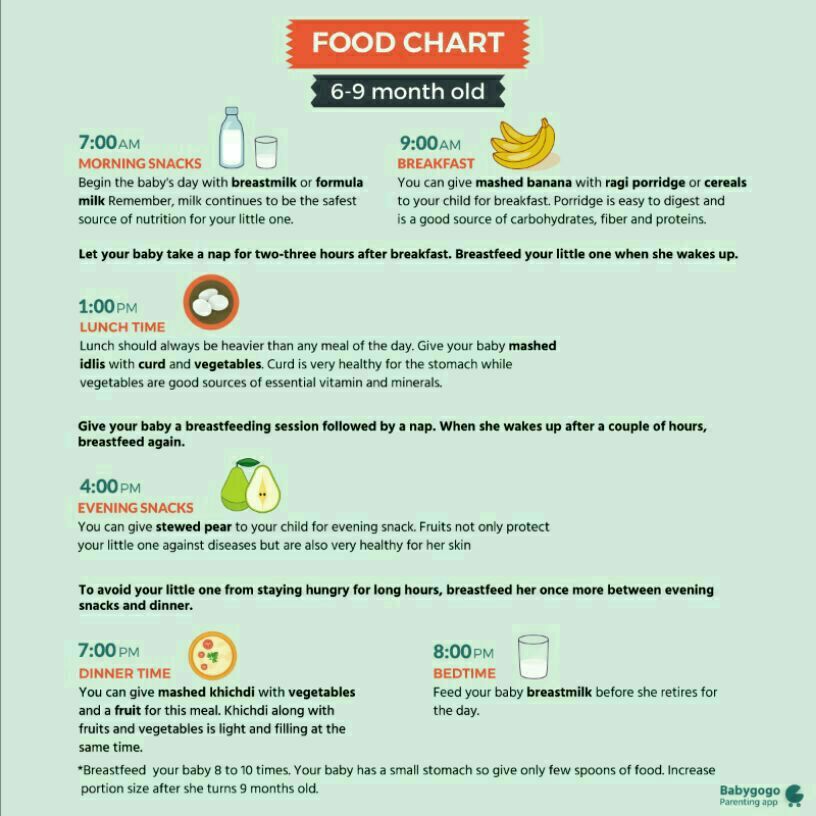
6 Victora CG et al . Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects. Lancet (Lancet). 2016;387(10017):475-490.
7 Peres KG et al. Effect of breastfeeding on malocclusions: a systematic review and meta - analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104( S 467):54-61. - Perez K.G. et al., "The impact of breastfeeding on malocclusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Akta Pediatr. 2015;104(S467):54-61.
8 Mennella JA, Beauchamp GK. Maternal diet alters the sensory qualities of human milk and the nursling's behavior. Pediatrics. 1991;88(4):737-744. - Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition affects the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." nine0004 Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
- Mennella, JA, Beauchamp, GK, "Maternal nutrition affects the organoleptic properties of breast milk and infant behavior." nine0004 Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 1991;88(4):737-744.
9 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4).
10 Brown A, Harries V. Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
2015;10(5):246-252.
11 Infant sleep information source. [Internet]. Normal Infant Sleep Development; December 2017 [cited 2018 Feb] - All about baby sleep. [Internet] "The development of normal sleep in a child", December 2017 [cited February 2018]. nine0004
12 Baby sleep science. [Internet]. The-Four-Month-Sleep-Regression-What-is-it-and-What-can-be-Done-About-it. March 2014 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - The Science of Baby Sleep. [Internet], "Four-month sleep regression: what it is and what to do about it." March 2014 [cited February 2018].
13 The Myth Of Baby Sleep Regressions – What’s Really Happening To Your Baby’s Sleep? [Internet]. Pinky Mckay ; December 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - "The Myth of Baby Sleep Regression - What's Really Happening to Your Baby?" [Internet]. Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
Pinky McKay, December 2017 [cited February 2018].
14 Kendall - Tackett K Al 9000 . The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. Clinical Lactation . 2011;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
15) Harrison D et al. Breastfeeding for procedural pain in infants beyond the neonatal period. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2014;10. — Harrison D. et al., "Breastfeeding for Relief of Medical Pain in the Neonatal Period." Cochrane Database of System Rev. 2014;10:CD11248
16 Czank C et al.