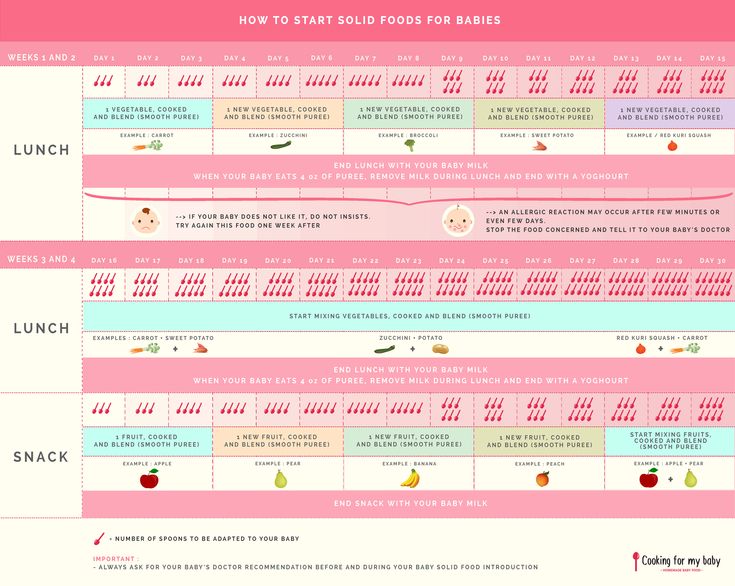
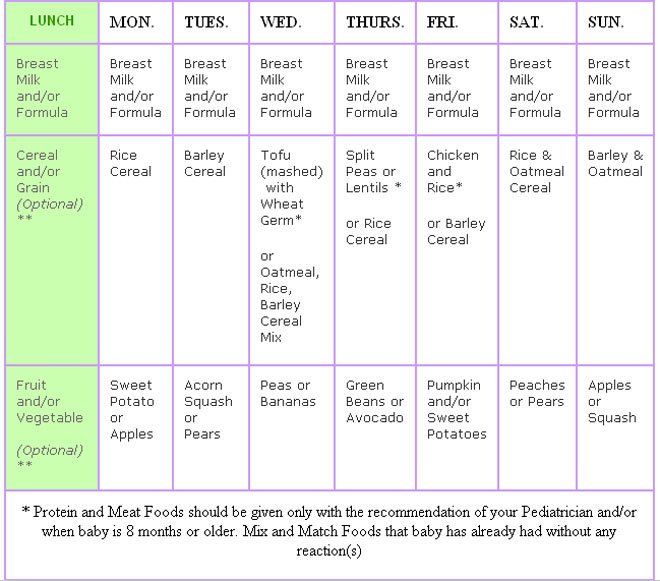
When to feed baby solid foods chart
Baby's first foods: How to introduce solids to your baby
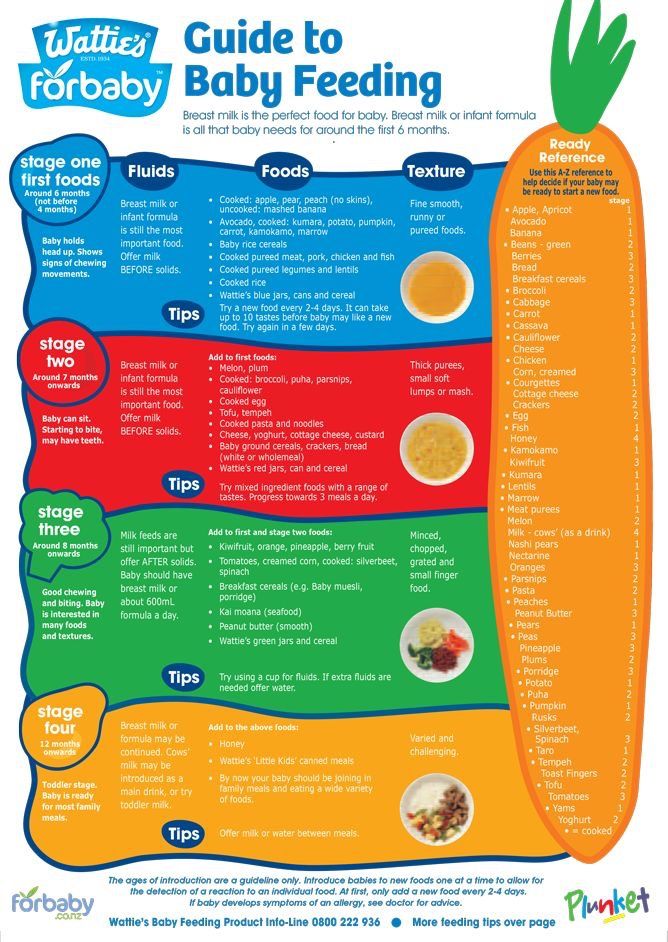
Babies are typically ready to start solids between 4 and 6 months, as long as they're showing signs of readiness, such as being able to sit upright with good head control. Talk to your baby's doctor about which foods to introduce first, particularly if you're concerned about a risk for an allergy. In general, infant cereal and pureed, one-ingredient veggies, fruits, and meats are great first foods. Try spoon-feeding or baby-led weaning, and keep up the breast milk or formula until your baby's first birthday.
When do babies start eating baby food?
It depends. As long as your baby shows signs of readiness, your pediatrician will probably give you the go-ahead to start baby food (also called solid food or solids) any time between 4 and 6 months.
Until then, breast milk or formula provides all the calories and nourishment your baby needs. Infants don't yet have the physical skills to swallow solid foods safely, and their digestive system isn't ready for solids until they're at least 4 months old.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and World Health Organization (WHO) recommend breastfeeding exclusively for the first six months of your baby's life and introducing solids at 6 months old. The AAP advises breastfeeding until age 1 – and longer if you and your baby want to.
Signs your baby is ready for solids
Your baby will give you clear signs when they're ready. Look for:
- Head control. Your baby needs to be able to keep their head in a steady, upright position.
- Sitting well when supported. Your baby needs to be able to sit upright in a baby seat or highchair to swallow well.
- Losing the "extrusion reflex." Your baby's mouth and tongue develop in sync with their digestive system. To start solids, they should be able to move food to the back of their mouth and swallow it, instead of using their tongue to push food out of their mouth.
- Curiosity about food. Your baby may start showing interest in what you're eating, reaching for your food or even opening their mouth if you offer them a spoonful.
Starting solids by 6 months old is important for your baby's oral motor development (the use of their lips, tongue, jaw, teeth, and hard and soft palates). Also, solid foods can provide specific nutrients your baby needs, such as iron and zinc. (These are especially important if your baby has been exclusively breastfed.)
What are the best first baby foods?
Start your baby with any pureed, single-ingredient food. Although it used to be standard for parents to give rice cereal as a first food, that's not necessary. In fact, pediatricians often don't recommend baby rice cereal since it can contain inorganic arsenic, and it's not as nutritious as some other first foods.
Good first baby foods include
- pureed squash
- applesauce
- mashed bananas
- mashed avocado
- pureed peaches
- pureed pears
- pureed meats
- whole-grain, iron-enriched baby cereal such as oatmeal
Advertisement | page continues below
If your baby is breastfed, the AAP suggests meat as a first food because the iron in beef, chicken, and turkey helps to replace iron stores, which start to diminish at about 6 months of age.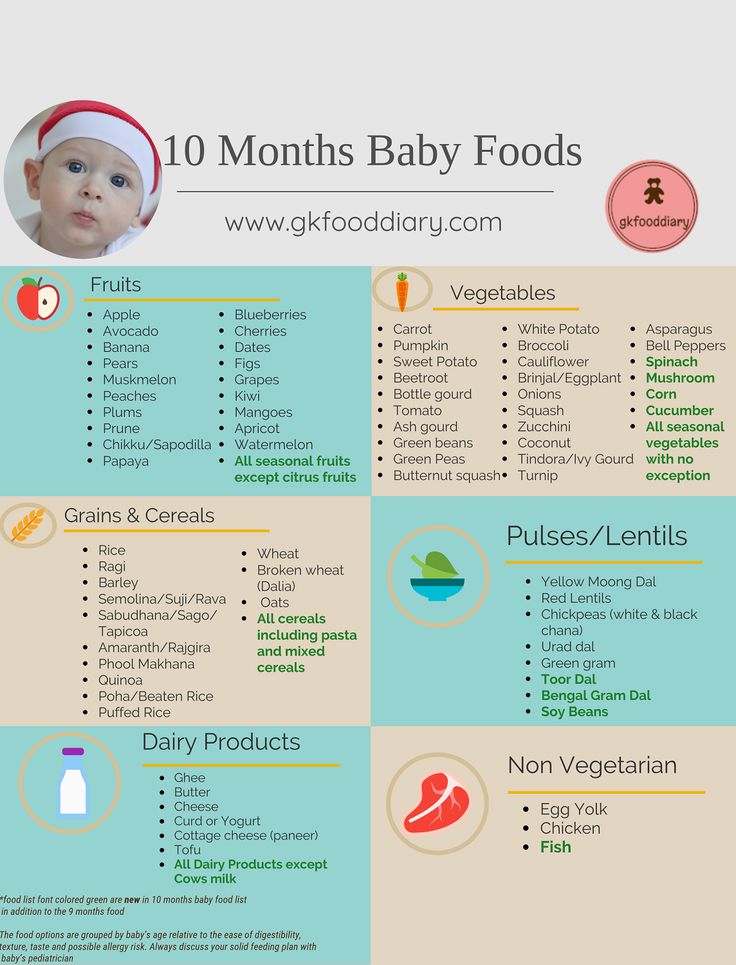
How to introduce solids to your baby
The traditional way to start solids is by spoon-feeding your baby cereal or purees, but some parents use a different method called baby-led weaning. Using this method, you put chunks of soft, developmentally appropriate food on the highchair tray or table and let your baby grab the food and feed themself.
Here's how to start spoon-feeding your baby:
For your first few feedings, start with just 1 or 2 teaspoons of pureed solid food or baby cereal about an hour after nursing or bottle-feeding (so your baby isn't too hungry or full).
Use a soft-tipped plastic spoon to feed your baby to avoid injuring their gums. Put a small amount of food on the tip of the spoon and offer it to them. If your baby doesn't seem very interested, just let them smell the food for now and try again another time.
If you're feeding your baby ready-to-eat jars or pouches of baby food, put some into a small dish and feed them from that. (If you dip the feeding spoon into the jar, it's not a good idea to save the leftovers because bacteria from your baby's mouth will now be in the jar. ) Store leftovers in the fridge and throw away any opened baby food jars or pouches within a day or two of opening them.
) Store leftovers in the fridge and throw away any opened baby food jars or pouches within a day or two of opening them.
If you decide to start with cereal, give your baby 1 to 2 teaspoons of diluted infant cereal. Add breast milk or formula to a tiny pinch of cereal. It will be very runny at first, but as your baby starts to eat more solid foods, you can gradually thicken the consistency by using less liquid.
Begin with one daily feeding in the morning whenever your baby isn't too tired, hungry, or cranky. Your baby may not eat much at first, but give them time to get used to the experience. Don't be surprised if your baby is confused or rejects solid food at first. Some babies need practice keeping food in their mouths and swallowing.
Eventually you can start giving your baby more solid food until they're having a few tablespoons a day, over two feedings. In general, your baby could start with pureed or semi-liquid food, then move on to strained or mashed food, and finally graduate to small pieces of finger foods.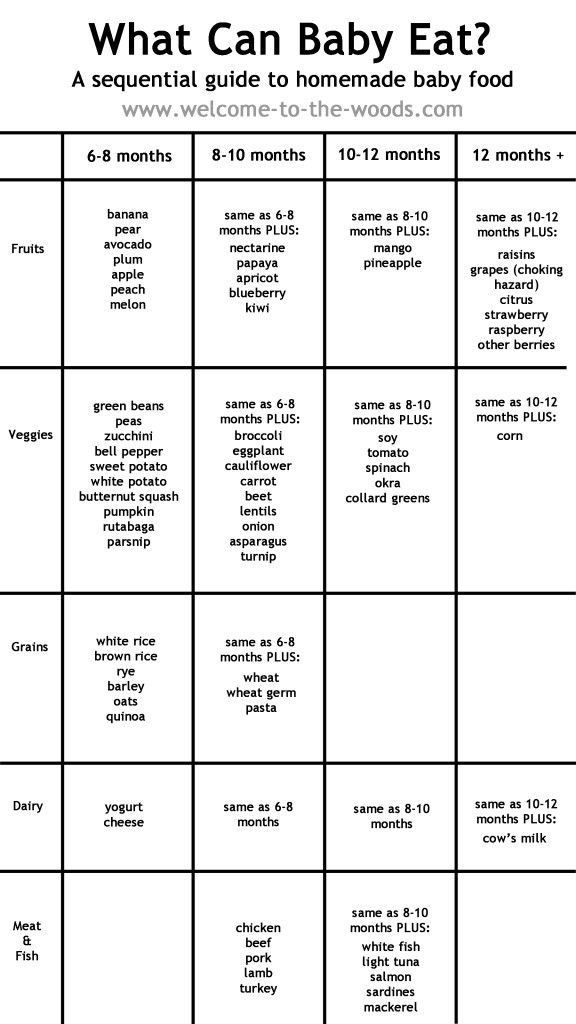
Signs that your baby is full
Your baby's appetite will vary from one feeding to the next, so a strict accounting of how much they've eaten isn't a reliable way to tell when they've had enough. Look for these signs that your baby's probably done:
- They lean back in their chair
- They turn their head away from food
- They start playing with the spoon
- They refuse to open up for the next bite (Sometimes a baby will keep their mouth closed because they haven't finished the first mouthful, so give them time to swallow.)
Food allergies and introducing solids
Experts recommend that you introduce one food at a time to your baby, and wait 3 to 5 days before introducing another food, so you can watch for any allergic reactions. It's also a good idea to write down the foods your baby samples. If they have an adverse reaction, a food log will make it easier to pinpoint the cause.
You don't have to hold off on giving allergenic foods such as eggs, peanut butter, or soy. There's no evidence that waiting to introduce certain foods will help your baby avoid allergies. In fact, there's evidence that the opposite is true.
There's no evidence that waiting to introduce certain foods will help your baby avoid allergies. In fact, there's evidence that the opposite is true.
According to the American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI), incorporating commonly allergenic foods into your baby's diet starting at around 4 to 6 months (and continuing through childhood) may actually help prevent the development of food allergies.
Start with traditional first foods, such as iron-fortified infant cereal, pureed veggies, fruits, and meats. Once you've tried a few of these foods and your baby seems to be tolerating them well, you can introduce more commonly allergenic foods, such as soy, eggs, wheat, fish, and peanut products.
Food manufacturers have products on the market designed to help you incorporate commonly allergenic foods into your child's diet. These stir-in powders and finger foods may contain one commonly allergenic protein or a blend of several.
Special precautions need to be taken with certain babies.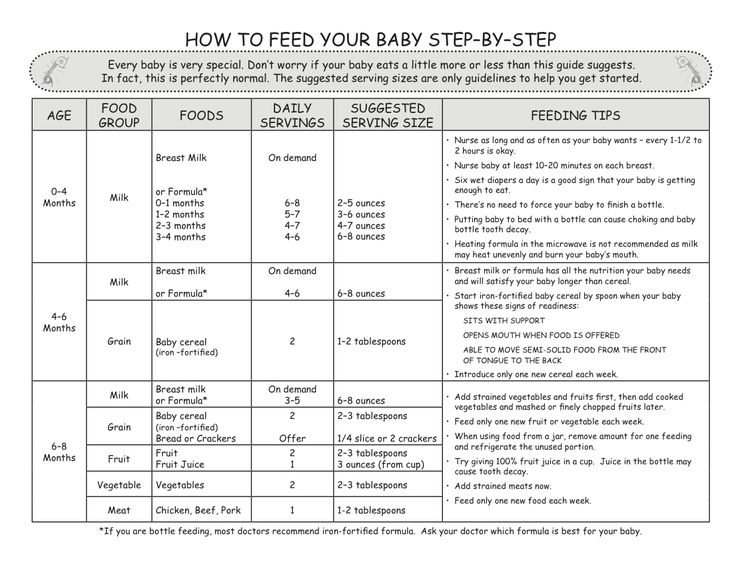 If your child falls into any of the following categories, consult with your baby's doctor or an allergist to create a customized feeding plan before adding solids to your baby's diet:
If your child falls into any of the following categories, consult with your baby's doctor or an allergist to create a customized feeding plan before adding solids to your baby's diet:
- Your baby has a sibling with a peanut allergy.
- Your baby has moderate to severe eczema despite following a doctor's treatment plan.
- Your baby previously had an immediate allergic reaction to a new food or has been diagnosed with a food allergy.
If your baby is allergic to a new food, you'll see signs of a reaction within a few minutes or hours. Most children with food allergies have mild reactions. If you notice a few hives, a new rash, or diarrhea, call your baby's doctor for advice.
If you notice wheezing, difficulty breathing, vomiting, facial swelling (including the tongue and lips), or more than two body systems affected (such as hives and vomiting), your baby may be having a life-threatening reaction called anaphylaxis. Call 911 or your local emergency number immediately.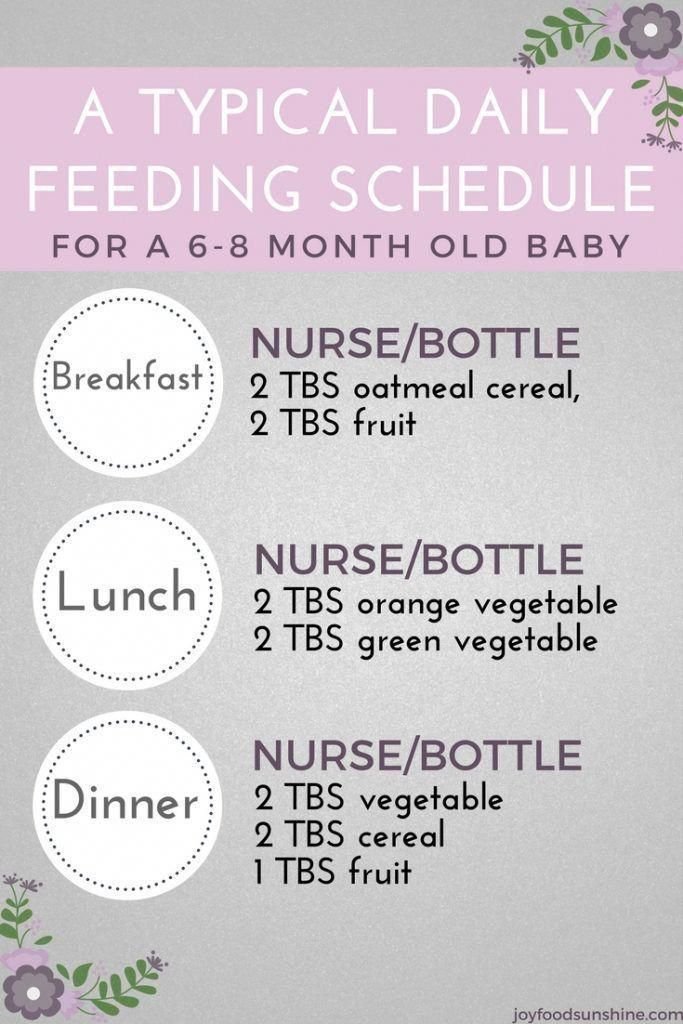
Baby food feeding tips
- Offer fruits or vegetables in any order. Some parents may tell you to start with vegetables instead of fruits so your infant won't develop a taste for sweets. But babies are born with a preference for sweets, so you don't have to worry about introducing sweet or savory foods in any particular order.
- Feed cereal with a spoon only. Unless your baby's doctor asks you to, don't add cereal to a bottle – your baby could choke or end up gaining too much weight.
- Encourage adventurous eating. You don't have to stick with bland and boring. See how to make your own baby food and use spices and seasonings to create delicious baby food flavors.
- Give new foods time. If your baby turns away from a particular food, don't push. Try again in a few days.
- Check for added sugars and too much salt. Check the Nutrition Facts label on canned, frozen, or packaged foods for "Added Sugars.
 " If there's 1 gram or more listed, give your baby something else. Also look at sodium amounts. Babies shouldn't have no more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day.
" If there's 1 gram or more listed, give your baby something else. Also look at sodium amounts. Babies shouldn't have no more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day. - Avoid unsafe foods. Don't give your baby foods that could cause choking, such as whole grapes or popcorn. Babies under 1 can't have honey, cow's milk, or soy milk. Also, unpasteurized juices and undercooked fish, meat, eggs, or poultry could be a source of bacteria.
- Watch for constipation. Your baby's poop sometimes changes when their diet does. Although it's usually temporary, your baby may have constipation after you introduce solids. If you notice that your baby is having less frequent bowel movements, or that their stools have become hard or dry and seem difficult to pass, let their doctor know. Some doctors recommend adding high-fiber fruits such as pears, prunes, and peaches to a baby's diet, or giving a few ounces of prune, apple, or pear juice every day until bowel movements are back to normal.
Also, don't be surprised if your baby's poop changes color and odor when you add solids to their diet. If your baby has been exclusively breastfed up to this point, you'll probably notice a strong odor to their formerly mild-smelling stools as soon as they start eating even tiny amounts of solids. This is normal.
If your baby shies away from new foods, here are a few things you can try:
- Test a range of textures. If your baby doesn't like pear puree, try giving them pieces of very ripe pear instead.
- In a similar vein, try different cooking methods. If your baby doesn't like steamed veggies, try giving them roasted vegetables.
- Serve food at different temperatures. Some babies prefer broccoli cold rather than warm, for example.
- Combine the new food with a familiar favorite. If your baby rejects a new food on its own, mix it in with something you know they like.
- Add a dipping sauce! Try shredded chicken with applesauce, yogurt with baked apple slices, or hummus with well-cooked pieces of carrot.

- Above all, be patient. Sometimes it takes a while for a baby to get used to new flavors and textures, so keep trying and eventually they'll accept the new food.
How many times a day should my baby eat solids?
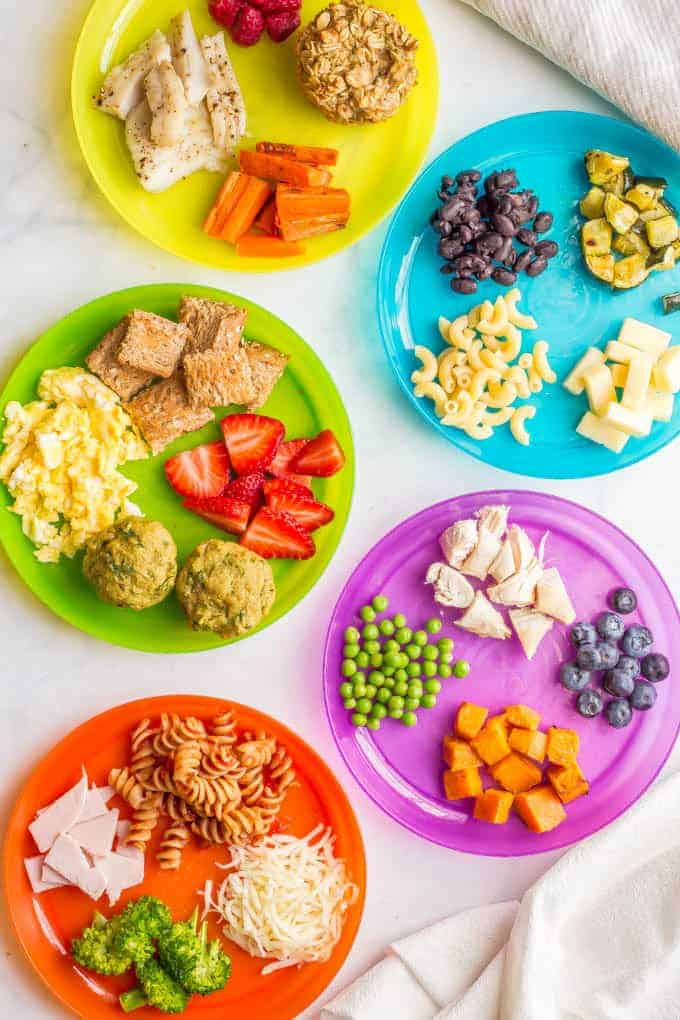
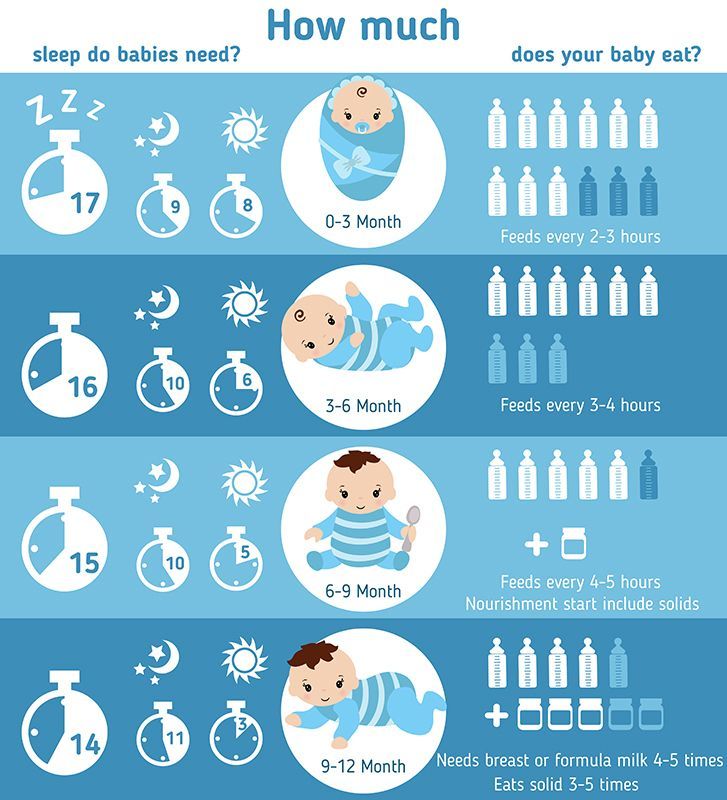
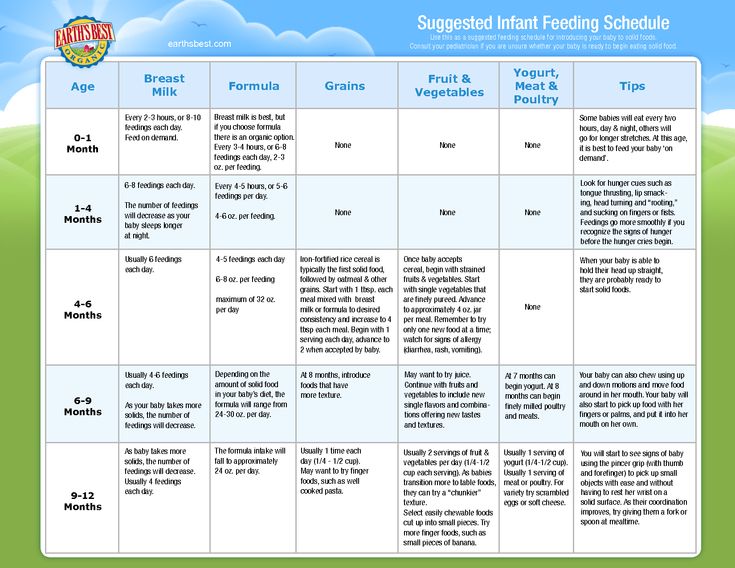
At first your baby will eat solid food just once a day. By around 6 to 7 months, two meals a day is the norm. Starting around 8 to 9 months, they may be eating solid food three times a day plus a snack. A typical day's diet at 8 months might include a combination of:
- Breast milk or iron-fortified formula
- Iron-fortified cereal
- Vegetables
- Fruit
- Small amounts of protein, such as eggs, cheese, yogurt, poultry, lentils, tofu, and meat
- High-allergy foods, if appropriate
See our age-by-age baby feeding guide for more detail on how much to feed your baby and when.
How much breast milk or formula does my baby need after we introduce solids?
Even after your baby starts solids, breast milk or formula will provide the majority of their calories and nutrition until they're 9 months to 1 year old. Breast milk and formula contain important vitamins, iron, and protein in a form that's easy to digest.
Breast milk and formula contain important vitamins, iron, and protein in a form that's easy to digest.
You may notice that as your baby starts to eat more solid foods (around 9 months old), they'll gradually decrease their intake of formula or breast milk. This is normal. Over time, your baby will take fewer bottles with more ounces in each.
Here's how much breast milk or formula babies need after starting solids:
- 4 to 6 months old: 4 to 6 feedings a day (breastfeeding, or bottles with 4 to 6 ounces)
- 6 to 8 months old: 3 to 5 feedings a day (breastfeeding, or bottles with 6 to 8 ounces)
- 8 to 12 months old: 3 to 4 feedings a day (breastfeeding, or bottles with 7 to 8 ounces)
What equipment do I need to introduce solids?
It's helpful to have:
- A highchair
- Baby bowls and plates
- Baby spoons
- Bibs
- A splat mat on the floor
You may also want to introduce your baby to a sippy cup soon after you start solids.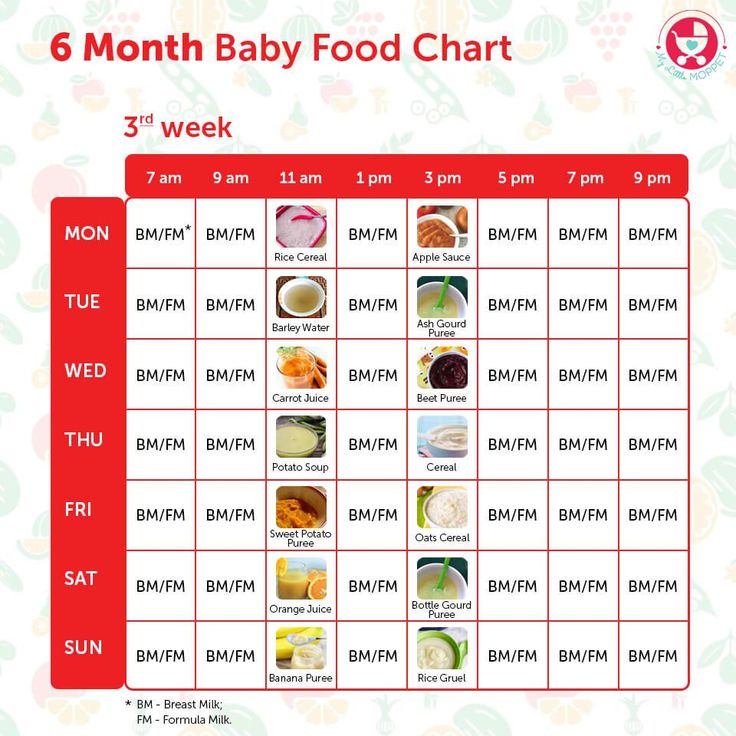
If you're making your own baby food, you'll need:
- A tool to puree the food, like a blender, food processor, or baby food maker
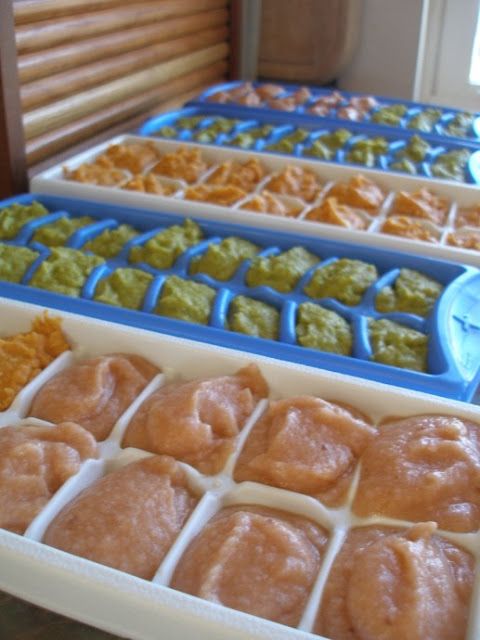
Storage containers for refrigerating and freezing extra portions (Some parents use ice cube trays – or similar devices made just for baby food – to store and freeze individual portions.)
Baby formula feeding chart: How much formula by weight and age
Is your baby getting too much or too little formula? It's an important question that worries many new parents, especially those with newborns. When deciding how much formula to give your baby, it's important to watch their hunger cues as well as looking at guidelines based on age and weight. In general, before they're eating solids, babies need 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.
These guidelines are for babies who are exclusively formula-fed for the first 4 to 6 months, and then fed a combination of formula and solids up to age 1. If your baby is getting a combination of breast milk and formula, talk to their doctor for separate advice.
Your pediatrician can tell you where your baby falls on the growth charts, make sure they're growing steadily on their own growth curve, and help you ensure that they're getting a healthy amount of formula. If you're ever worried about your baby's growth, behavior, or development, talk with their doctor.
How much formula for a newborn
For the first few days, offer your newborn 1 to 2 ounces of formula every 2 or 3 hours. (At first, newborns may only take a half ounce of formula at a time.)
After the first few days, give your newborn 2 to 3 ounces of formula every 3 to 4 hours.
Initially it's best to feed your formula-fed newborn on demand, whenever they show signs that they're hungry. Because your little one can't tell you when they want a bottle, you'll need to learn to read their hunger cues. Crying is often a late sign of hunger, so if you can, try to catch the earlier signs that it's time for a feeding.
Here are some hunger cues to watch for:
- Smacking or licking their lips
- Rooting (moving their jaw, mouth, or head in search of food)
- Putting their hands to their mouth
- Opening their mouth
- Fussiness
- Sucking on things
- Becoming more alert
- Crying
As time passes, your newborn will begin to develop a fairly regular feeding schedule.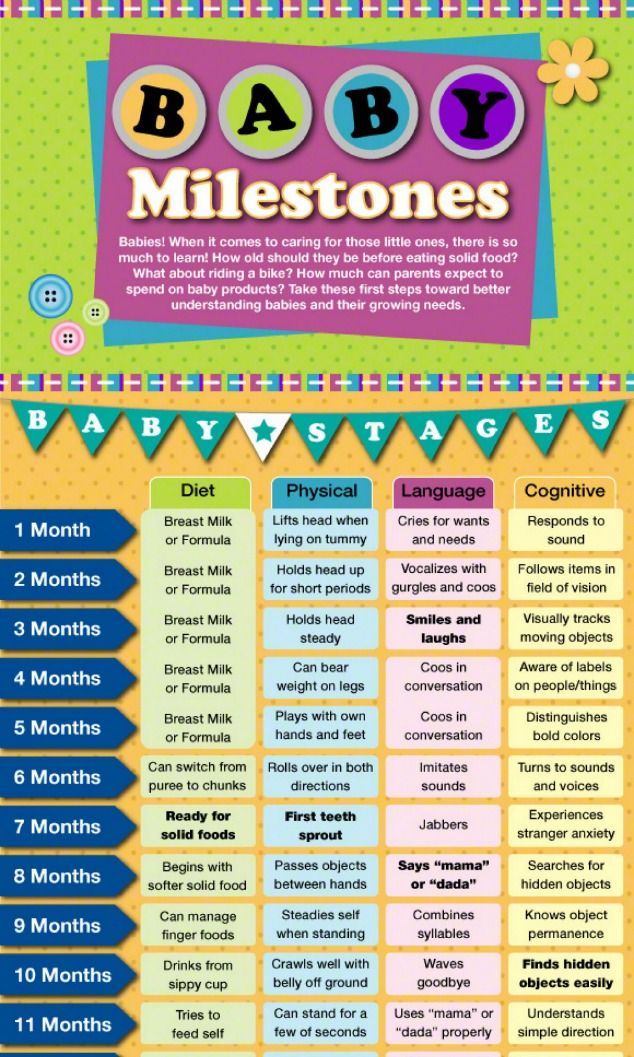 You'll become familiar with their cues and needs, and knowing when and how much to feed them will be much easier.
You'll become familiar with their cues and needs, and knowing when and how much to feed them will be much easier.
Formula feeding chart by weight
During the first 4 to 6 months, when your baby isn't eating solid foods, here's a simple rule of thumb: Offer 2.5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight every 24 hours, with a maximum of about 32 ounces.
Advertisement | page continues below
| Weight | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| 6 pounds | 15 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 7 pounds | 17.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 8 pounds | 20 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 9 pounds | 22.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 10 pounds | 25 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 11 pounds | 27.5 fl oz every 24 hours |
| 12 pounds | 30 fl oz every 24 hours |
These numbers aren't rigid rules. They offer a rough estimate for what your baby may need.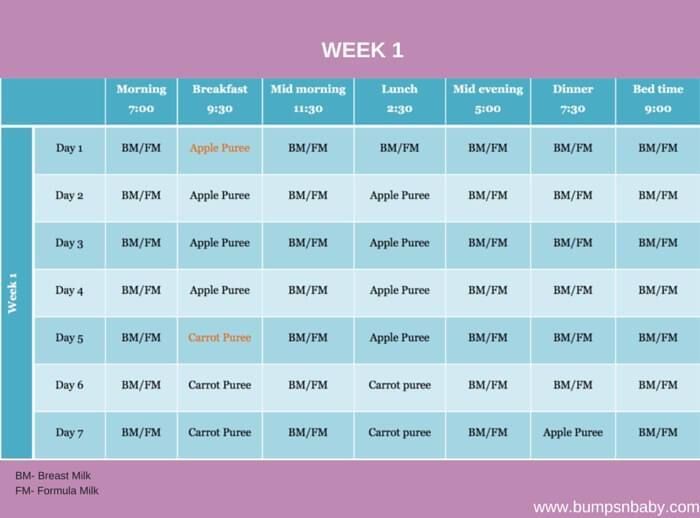 Some babies will grow well while taking less than the recommended amount, while others consistently need more. Your baby's daily feedings will also vary according to their individual needs – in other words, they may want a bit more on some days and a bit less on others.
Some babies will grow well while taking less than the recommended amount, while others consistently need more. Your baby's daily feedings will also vary according to their individual needs – in other words, they may want a bit more on some days and a bit less on others.
Formula feeding chart by age
Here are typical amounts per day based on age:
| Age | Ounces of formula |
|---|---|
| Full-term newborn | 2 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 1 month old | 3 to 4 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 2 month old | 4 to 5 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 3 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle every 3 to 4 hours |
| 4 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 5 month old | 4 to 6 ounces per bottle, 4 to 6 times a day |
| 6 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 4 to 5 times a day |
| 7 month old | 6 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 5 times a day |
From 8 months old until their first birthday, you can expect your baby to have 7 to 8 ounces per bottle, 3 to 4 times a day.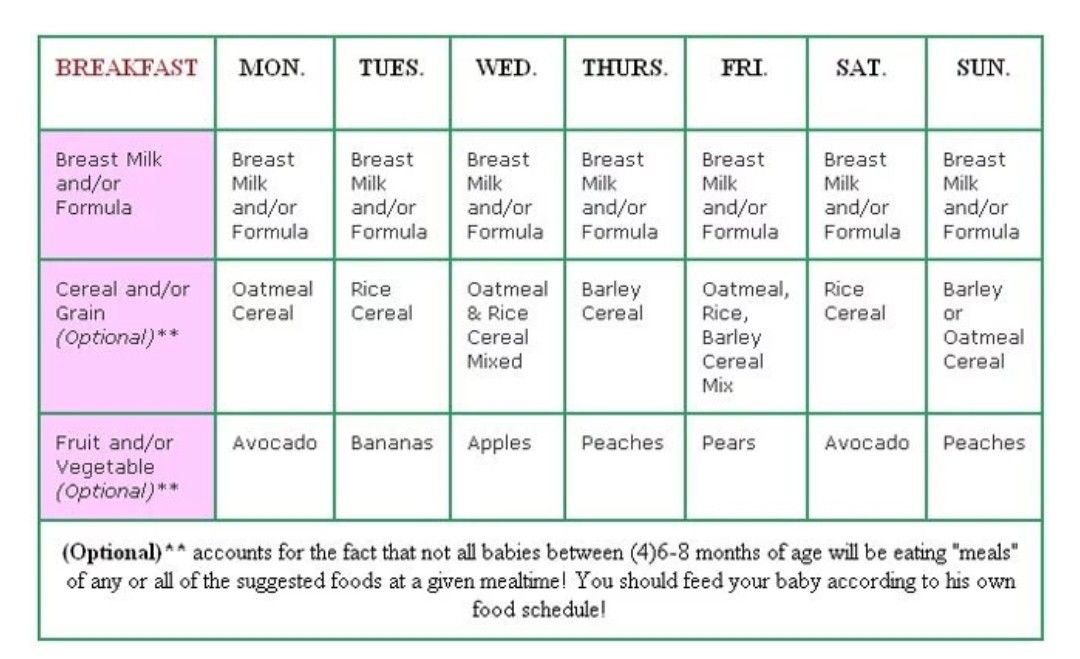
As your baby gets older – and their tummy gets bigger – they'll drink fewer bottles a day with more formula in each. It's important not to overfeed your baby so they'll stay at a healthy weight. Your baby shouldn't have more than 32 ounces of formula in 24 hours.
When they reach their first birthday, they can stop drinking formula and transition to cow's milk in a bottle, sippy cup, straw cup, or open cup. Limit your toddler to 16 to 24 ounces (2 to 2.5 cups) a day of whole milk, so they have room for other healthy foods.
Here are signs that your baby's getting all the formula they need:
- Steady weight gain. They continue to gain weight after their first 10 days and follow a healthy growth curve during their first year. (Most babies lose up to 7 to 10 percent of their birth weight in the first few days and then regain it by the time they're about 2 weeks old.)
- Happy baby. They seem relaxed and satisfied after a feeding.
- Wet diapers. They wet two to three diapers a day in the first few days after birth. Over the next few days, the amount should increase to at least five to six wet diapers a day.
Babies are usually good at eating the amount they need, but bottle-fed babies can drink too much at times. Here are the signs that they're getting too much formula:
- Vomiting after a feeding may be a sign that your baby had too much. (Spitting up is normal, vomiting isn't.)
- Tummy pain after a feeding can also be a sign of overfeeding. If your baby draws up their legs or their tummy seems tense, they may be in pain. (See other possible reasons for stomach pain in babies.)
If your baby seems to want to eat all the time, even after finishing a bottle, talk to your pediatrician. Using a pacifier may help soothe their need to suck.
Formula-feeding tips
- In general, babies eat when they're hungry and stop when they're full, so resist the temptation to encourage your baby to finish each bottle.
Overfeeding during infancy can contribute to obesity later in life.
- Don't respond to your baby's every cry with a bottle. They may be crying because their diaper is wet, they're cold or hot, they need to be burped, or they want to be close to you. (Learn more about why babies cry, and how to soothe them.)
- Your baby may be hungrier than usual during growth spurts. These typically occur 10 to 14 days after birth and around 3 weeks, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months of age.
Read more:
- Formula Feeding Problem Solver
- How to safely store and use formula
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
table of the introduction of the first complementary foods by months, input scheme, the correct menu of the child on the IV, what can be given to the artificial
Contents: Hide
Formula-fed complementary foods
Inexperienced mothers of newborn babies are concerned about many problems: fighting colic, establishing a daily routine, performing hygiene procedures. However, time goes by and acute issues gradually become irrelevant. Inexorably, a new crucial stage is coming - the introduction of the first complementary foods begins. We will tell you how to properly introduce complementary foods with artificial feeding.
Why does a baby need complementary foods
Both natural and bottle-fed babies are usually equally full of energy, active and inquisitive. The introduction of complementary foods allows you to gradually accustom the baby's gastrointestinal tract to new food, as well as give the growing body the vitamins and minerals that it needs at a particular stage of physical development. Also, with its help, you can gradually adapt the baby to the diet of adult family members and then painlessly transfer it to the common table. There are no exact norms and rules for the introduction of complementary foods. It is necessary to focus on the needs of the child and follow the recommendations of the pediatrician.
When can complementary foods be introduced with artificial feeding
Teaching children to adult food should be timely. The fact is that the gastrointestinal tract of an infant at a too early age (for example, 2-3 months) is not able to process certain foods. The mucous membrane of the digestive system is irritated, and this can provoke gastritis and other serious health problems.
IMPORTANT! At what age can you introduce your baby to new products? For children in good health, WHO recommends that complementary foods be introduced at 6 months of age. But for some babies, if there are certain medical indications, the doctor may advise you to do this earlier.
The recommendations do not provide a specific menu for each age, which must be followed. Much depends on the socio-cultural characteristics of different peoples and the individual pace of development of children. In most cases, the timing of the start of complementary foods varies from 4.5 to 6 months. Specialists distinguish the following signs of a child's readiness to try something new, in addition to the usual artificial mixture:
• the baby is not quite full of the mixture and asks to continue the meal;
• his first teeth have already erupted, he tries to chew them, takes and tries to taste food from adult plates;
• if you bring a spoon to the baby, he will begin to examine its contents and want to try it;
• the child sits confidently, can turn his head and control his body;
• The tongue thrust reflex fades so baby can drink water from a spoon without it dripping back out.
It is not necessary that all of the listed features be present at once. If several of them are observed, then it is quite possible to try to introduce the first complementary foods.
Read also: How much does a newborn eat per feeding?
When to delay feeding
It is better to delay feeding if:
• the child is ill;
• less than three days have passed since vaccination;
• the baby is teething, he does not sleep well and is naughty;
• there have been some changes in the family's lifestyle, such as moving to a new home, mother going to work, traveling to another city or country;
• the crumbs have manifestations of allergies, upset of the gastrointestinal tract;
• The weather is too hot outside.
Therefore, complementary foods should only be offered to a child when he is completely healthy, calm and in a good mood.
Basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods
Anna Levadnaya, pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, explains that the principles of introducing complementary foods on natural and artificial feeding are similar: it is recommended to focus on food interest, signs of a child's readiness for introducing complementary foods. The only thing is that with exclusive breastfeeding, it is not recommended to supplement the child with water, while bottle-fed children can be offered water.
Video: 10 rules for complementary foods
Author: pediatrician, Ph.D. Komarovsky E.O.
The rest of the principle is the same: for both breastfeeding and formula-feeding, offer your baby a new food before feeding, and then supplement with breast milk or formula.
In order for new products to bring benefits to the baby on artificial feeding and not harm his health, you should follow a number of simple recommendations.
1. Complementary foods are usually given in the morning before the main formula feeding. This allows you to track the reaction to unfamiliar food during the day and take action if necessary.
2. It is necessary to carefully monitor the cleanliness of children's dishes, pots and blenders. The gastrointestinal tract of an infant is very sensitive to infectious agents.
3. New food is introduced into the baby's diet from a quarter of a teaspoon. If he tolerated the product well, then within a week the portion is brought to one or two tablespoons. Then you should look at the desire of the child and his well-being, and also take into account the recommendations of the pediatrician.
4. The first dishes should be of a liquid consistency, then they are made into a puree, and only closer to a year can you give soft pieces to chew. Pediatricians advise adding butter and vegetable oils to them as vegetables and cereals are introduced into the diet.
5. In order to protect the child's body from pathogens that may be contained in unprocessed food, complementary foods should first be boiled, stewed or baked. The baby is offered slightly warm food: the optimum temperature is 36-37 degrees.
6. It is advisable to try the products immediately from a spoon. If the baby gets used to the bottle, this will slow down the formation of the skill of chewing food and may subsequently affect diction.
7. A food diary can help you reliably identify what your child has an allergic reaction to. It should record everything that the baby ate during the day, in what quantity and at what time. You can also record in a diary whether he liked the new dish or not.
8. Complementary foods should be introduced only from mono-products. Only after making sure that vegetables, cereals, juices, fruits or protein products are well tolerated by the child, you can offer their mixes.
9. The interval between introduced and new complementary foods should be at least a week. Such a period of time will allow the child's body to adapt to the expanded diet and perceive other dishes without unpleasant surprises.
10. If an allergy occurs to any product, it should be immediately removed from the menu and consulted by a pediatrician. It will be possible to return to this complementary food no earlier than in a month.
11. It is desirable that with the introduction of complementary foods, the infant receives a sufficient amount of liquid. It can be both ordinary water and compotes.
12. Do not offer your child foods that are considered highly allergenic as first foods: full-fat cow's milk, citrus fruits, gluten-containing cereals, chicken eggs, etc.
13. Do not force-feed a child, even if you think that he is hungry. A small person has the right to defend his opinion in the choice of dishes.
14. Feed your baby exclusively in a sitting or reclining position to avoid the risk of aspiration. Very convenient for this purpose are special highchairs made of easy-to-clean material.
From 7–8 months, formula-fed mashed or pureed food, such as a banana, can be used as complementary foods. If semi-solid food is not introduced into his diet in time, problems may arise with the intake of solid food in the future: after a year, the child will refuse it completely. From 8–9 months, the child should be offered the so-called finger food: cut soft fruits and vegetables into pieces, such as boiled carrots, potatoes, and offer them to the baby. If you follow this scheme, by the year the child will be ready to eat solid food from the common table, Levadnaya explains.
Complementary Feeding Schedule
We provide a suggested complementary feeding schedule for up to a year to guide you unless advised otherwise by your doctor. As a standard formula-fed babies with normal weight gain are offered products in approximately the following order:
• vegetable puree;
• cereals;
• fruit puree;
• kefir;
• butter and vegetable oil;
• children's biscuits and bread;
• meat puree;
• fish puree.
The earlier introduction of vegetable puree rather than fruit puree is due to the fact that the former has a more insipid taste. Having fallen in love with sweet apples and bananas, the child may subsequently refuse to eat zucchini, pumpkin, etc. However, if the infant is underweight, the doctor may recommend porridge as the first complementary food for him. They are more high-calorie and allow you to gain the missing kilograms faster. Each type of complementary food is described in the table.
| Vegetables | They are usually offered to children in the following order:
Tomatoes, white cabbage and cucumbers are recommended to be included in the menu already after a year. |
| Fruit | Seasonal fruits are recommended. The approximate order of their introduction: apples, pears, peaches, apricots and bananas. If the baby suffers from constipation, you can carefully and with the permission of the pediatrician offer him plums. |
| Kashi | To start complementary foods, choose gluten-free cereals: buckwheat, rice, corn grits. After the child is 8 months old, you can gradually give him a taste of oatmeal, wheat and barley porridge. It is better to refuse semolina altogether, since it contains very few useful substances and at the same time it is very high in calories. Cereals can be ground in a coffee grinder or mashed from ready-made cereals in a blender. |
| Protein products | Fermented milk products do not need to be introduced earlier than 8 months, since only by this time do children begin to produce the enzymes necessary for their processing. From meat, children under one year old should be given rabbit, chicken, turkey and veal. Sea fish is more suitable - hake, cod or flounder. Meat and fish are offered to kids in grated form as part of vegetable dishes and cereals. Cottage cheese can be prepared for the baby yourself. |
IMPORTANT! It is undesirable to add salt, sugar and spices to food for a child. His taste buds are not yet accustomed to strong stimuli, so it is better for him to appreciate the natural taste of the food offered. Soup should be boiled only on vegetable broths, and meat should be added to an already prepared dish. Meat broth may be too heavy for the baby's kidneys.
How to choose complementary foods
The main recommendations for choosing specific foods to start complementary foods are as follows:
1. It is recommended that your baby's diet be based on products grown in the region where he/she lives. If the period of the first feeding falls on the winter, it is advisable to stock up vegetables, fruits and berries from your garden in advance, putting them in the freezer for safekeeping. In the event that this is not possible, you can give preference to ready-made canned mashed potatoes. They undergo mandatory certification confirming the quality.
2. It is advisable not to buy store-bought juices for your child in large quantities. Compotes will be much more useful for him. You can also offer decoctions of dried fruits.
3. If you decide to buy ready-made food for your baby, then pay attention to the label and the release date. The product must be age appropriate and fresh. The composition should not contain salt, sucrose, dextrose and other extraneous additives.
In general, it is worth remembering that the first food offered to a child should be puree-like, not too viscous products, consisting of one ingredient, soft consistency, without added sugar, salt and spices, says Andrey Mosov, head of the expert direction of NP Roskontrol, doctor on nutritional hygiene of children and adolescents. He insists that preference should be given to industrial prepared meals, as such products have been tested and certified. There are no guarantees with mashed homemade vegetables.
Introduction of complementary foods to formula-fed premature babies
The question of the correct introduction of complementary foods to a premature baby should be discussed individually at a pediatrician's appointment. In order for the body to be able to process a new product, organs and systems must be sufficiently mature and prepared. The quality of food digestion largely depends on the production of special enzymes, so you should not be self-motivated in compiling the baby's menu.
The schedule for the introduction of complementary foods will be determined by the presence or absence of anemia, the rate of weight gain, the tendency to allergies, and some other nuances. Formula-fed premature babies are usually advised to start introducing meat and egg yolk earlier. It is advisable to cook porridge on a vegetable broth or mixture, and not on water, since then they will be more nutritious and healthy.
IMPORTANT! However, the course of complementary foods must be monitored by a pediatrician. The doctor monitors the child's reaction to new products, evaluates the dynamics of growth and general physical development. The scheme may change if any deviations from the norm are detected during routine inspections.
Answers to frequently asked questions for mothers
• What foods should not be given to babies under one year old?
It is forbidden to give cow's milk to babies under the age of one, as it can cause allergic reactions and digestive disorders. It is perfectly replaced by adapted mixtures from modern manufacturers. In addition to milk, it is not recommended to include nuts, citrus fruits, exotic fruits and vegetables, red fish and honey in the menu of the crumbs of the first year of life.
• What should I do if my child absolutely does not want to eat complementary foods?
Wait a while and try to offer food again, but don't insist on another refusal. Perhaps the baby did not like the new dish because of the unfamiliar taste. Children are big conservatives and are often wary of change. Be patient, do not rush to introduce complementary foods. Show your child with what appetite you yourself eat from your plate, and then he may have a desire.
• What should I do if my baby has problems with stool while weaning?
If a child has a stool retention of more than three days during the introduction of complementary foods, then we can talk about constipation. In this case, you need to visit a pediatrician, as well as immediately exclude fixing foods from the menu and give more fluids to drink. If the stool has become too frequent (more than 5 times a day), then this may be due to indigestion or an intestinal infection. Be sure to consult your doctor about this.
• What should I do if I have an allergy to complementary foods?
It is advisable to take care of this issue even before the introduction of complementary foods, asking the pediatrician observing the child to prescribe an antihistamine drug that is optimal for his age. You should also carefully fill out the food diary at first. With it, it will be possible to identify a possible allergen and exclude it from the baby's menu, preventing more serious health consequences.
• How do you know if a baby tolerates complementary foods well?
Normal weight and height gain, regular bowel movements, and the absence of allergic skin rashes indicate the successful introduction of complementary foods. If the baby is cheerful, active, he has a good appetite and a good sleep, most likely, this means that you are doing everything right and the selected diet suits him.
However, it is impossible to completely refuse artificial formula when introducing complementary foods, even when the infant eats complementary foods with appetite. His body is not yet ready for a complete change in the type of food and may malfunction. This often manifests itself in the form of allergies, stool disorders or growth retardation. Remember that the baby should enjoy the new food. Only under this condition will he form the correct eating behavior.
#Nutrition for children up to a year #Complementary food
Baby menu at 9 months
6-12 months
Article
5/5 1 reviews
Although breast milk or formula remains the mainstay of an infant's diet at this age, a 9-month-old baby's menu becomes more varied with new complementary foods. The correct diet of the child is the basis of his harmonious development, good health and good mood. But how to organize a diet, what can be given at this age and how much should a child eat at one meal?
8 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
The correct diet for a nine-month-old baby includes 5 meals: a day, the baby receives liquid food twice and thick food three times. This is due to the fact that mashed potatoes and cereals take longer to digest than milk, so they give the baby a longer energy supply. Feeding is usually carried out at intervals of 4 hours. If the baby asks to eat 2-3 hours after liquid food, offer her a baby snack, fruit or vegetable (in small pieces or in the form of a puree).
A 9-month-old baby's daily diet includes many healthy foods and drinks that provide essential nutrients such as vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals. In addition to milk and infant formula, the following products can be given to a child:
- Fruits and vegetables in the form of puree (apple, pear, cauliflower, etc.)
- Fruit juices and compotes without sugar.
- Meat in various forms.
- Fish.
- Kashi from various cereals.
- Chicken or quail egg yolk.
- Children's fresh cottage cheese.
- Children's low-fat kefir.
- Children's cookies, croutons, bread.
Read also: The baby refuses new foods
According to WHO recommendations, by the 9th month, all of the above products should already be on the menu. If something from the food is still unfamiliar to your child, it is recommended to gradually add it to the diet.
Start with smaller portions and see how your child reacts to the new food. If there is no allergic reaction to the product, you can increase the volume and add it to new dishes. New complementary foods are recommended to be introduced at intervals of 5-7 days. An indicative table for one day will help to create an optimal diet for health. It also shows how much formula or milk the baby should eat per day.
* infant formula.
**Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or infant formula given to the baby. Milk porridge is diluted with water.
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with intolerance to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge* | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil < | about 1 tsp | |
| Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 70 g | |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree or pureed soup | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Meat puree (rabbit, turkey) | 50 g | |
| Fruit juice | 70 g | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree | 50 g |
| Vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge | 180 g | |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Meat puree | 50 g | |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with intolerance to cow's milk proteins | 200 ml |
*Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk, or it can be used for children allergic to cow's milk proteins.
** you can eat porridge or vegetables, so you can eat grass - porridge with vegetables.
1st day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Buckwheat porridge with pumpkin, juice |
| Lunch | Pumpkin steam cutlets, veal puree |
| Snack | Rusks or baby biscuits, yoghurt |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
2nd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal, berry juice |
| Lunch | Steamed fish, rice, fruit compote |
| Snack | Vegetable puree |
| Dinner | Vegetable puree |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
3rd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Semolina porridge, quail egg yolk |
| Lunch | Steamed zucchini, boiled veal, apple compote |
| Snack | Pumpkin and apple puree |
| Dinner | Curd casserole with carrots |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
Fourth day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, fruit puree |
| Lunch | Mashed potatoes or turkey meatball soup |
| Snack | Carrot-apple juice |
| Dinner | Kefir |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
5th day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal and apple puree |
| Lunch | Cream soup with chicken and vegetables |
| Snack | Carrot juice |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree, crackers or bread |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
6.
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, half yolk (chicken egg) |
| Lunch | Vegetable soup with chicken breast, juice |
| Snack | Baked apple |
| Dinner | Spinach mashed potatoes |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
Seventh day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Millet porridge, croutons |
| Lunch | Steamed chicken cutlets, vegetable puree |
| Snack | Apple juice |
| Dinner | Curd with fruits |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Parents need to gradually accustom the child to eating solid food, because now he is moving to a new level of development: more teeth appear, so the baby can now chew food. If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
No need to grind fish and potatoes in a blender - just put the food on a plate and mash well with a fork. Meat can be offered in the form of meatballs to develop chewing skills. It can be turkey, rabbit, veal, beef, chicken. The norm of meat for one meal is 60-70 g.
It is quite normal if at first large pieces in a dish cause discontent in a child or even a gag reflex - he will soon get used to it. Sometimes it happens the other way around - the baby willingly tries the pieces, but refuses pureed food. Treat your baby with apple slices, bread, crackers or baby snacks. But the meat is still better to grind thoroughly.
At this age, consumption of mother's milk or adapted formula decreases. There are only two feedings per day - in the morning and in the evening. Everything else is "adult" food. Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Please note that uneaten food (already cooked) must not be stored and reheated. It is also not recommended to add sugar and salt to the dish.
If you give your child ready-made baby puree, we recommend that you do not feed him immediately from a jar, but pour the right amount onto a plate. In this case, the rest can be stored in the refrigerator for another 24 hours.
Find out more: Baby Portion
Pay attention to the quality of food you cook: appearance, smell and expiration date. It is better to use seasonal vegetables and fruits, and shop in trusted places.
Wash food thoroughly under running water before cooking. You can also use special children's products for washing fruits and vegetables.
All products must be brought to full readiness, and then carefully crushed to the desired consistency, so that the baby can comfortably chew small pieces. After eating, wash the dishes with a special detergent.
What is the correct way to feed a 9-month-old baby if he refuses food and does not eat the foods you suggest?
Poor appetite is one of the indicators of a baby's health. The problem may concern the digestive tract, glucose levels, central nervous system. The feeling of hunger appears when the level of sugar in the blood decreases. But for this you need to take breaks between meals. Also, the smell of food affects the appetite - it causes the release of gastric juice.
How to restore your appetite:
- observe the diet;
- develop a delicious menu for a baby at 9 months;
- Serve dishes beautifully and set the table;
- ventilate the room before eating;
- let the baby use cutlery.
See also: The baby does not eat well, how to feed?
In order for the baby to eat willingly, he must be in an excellent mood. Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere.
If the baby refuses to eat or eats very slowly, do not rush or force him to eat. Also, do not force the little one to eat foods that he refuses. Otherwise, in the future, he will have a negative attitude towards the feeding process, refuse to eat any food at all. He can even feel sick and vomit only with one kind of food.
Important
Games and cartoons during meals do not really improve appetite. On the contrary, in this way you only teach the baby to eat without noticing the dishes.
With the help of our tips, you can create a menu for a child at 9 months for every day, which will meet the requirements of a healthy diet and preferences of the baby
1. What should not be given to a child at 9 months?
It is not recommended to give cow's milk until the age of one. It contains too much calcium, which overloads the kidneys, and protein, which is poorly digested.