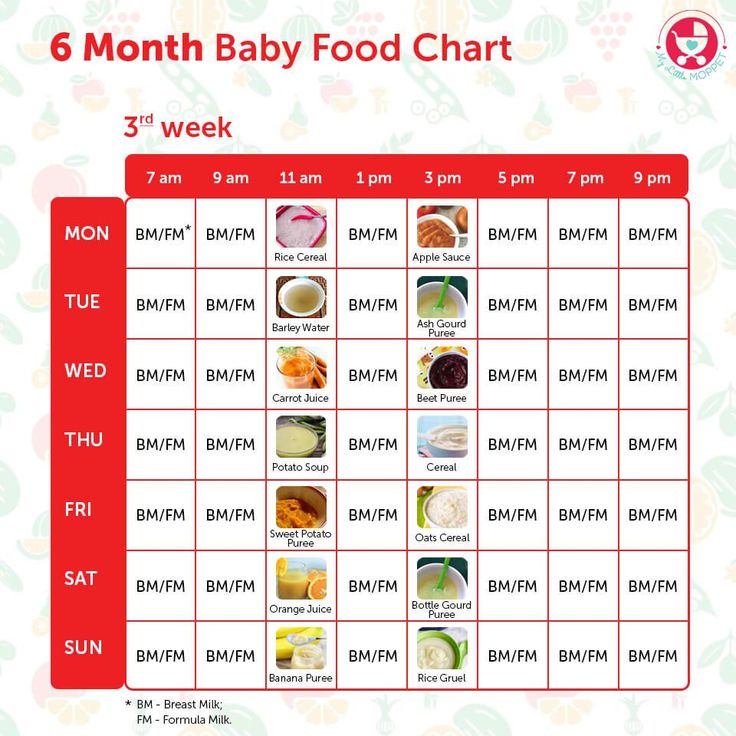
When to feed your baby cereal
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
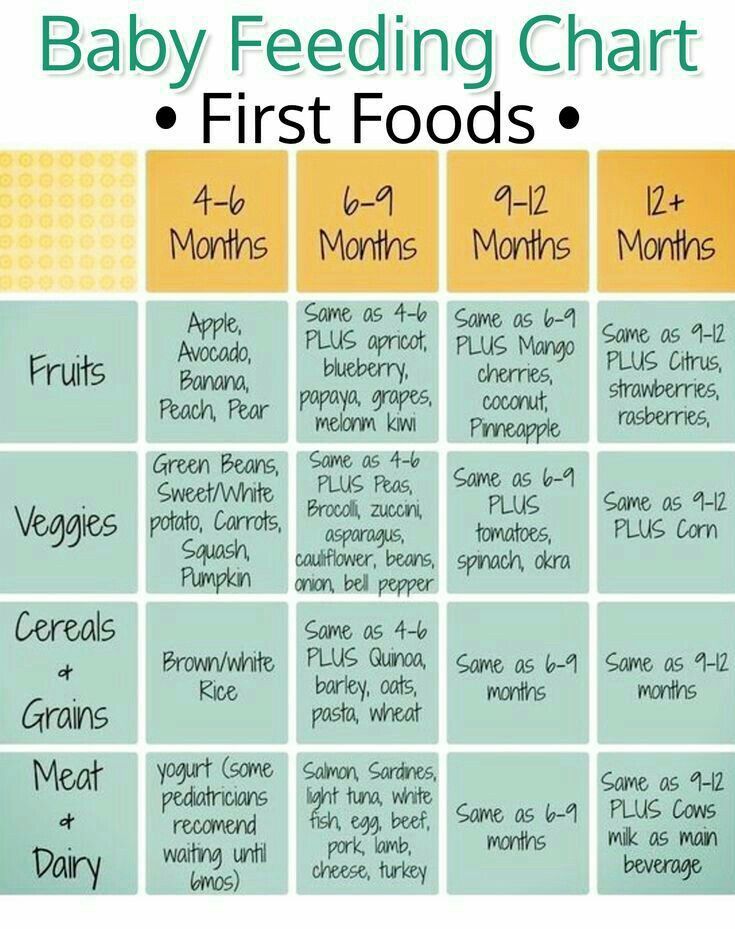
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.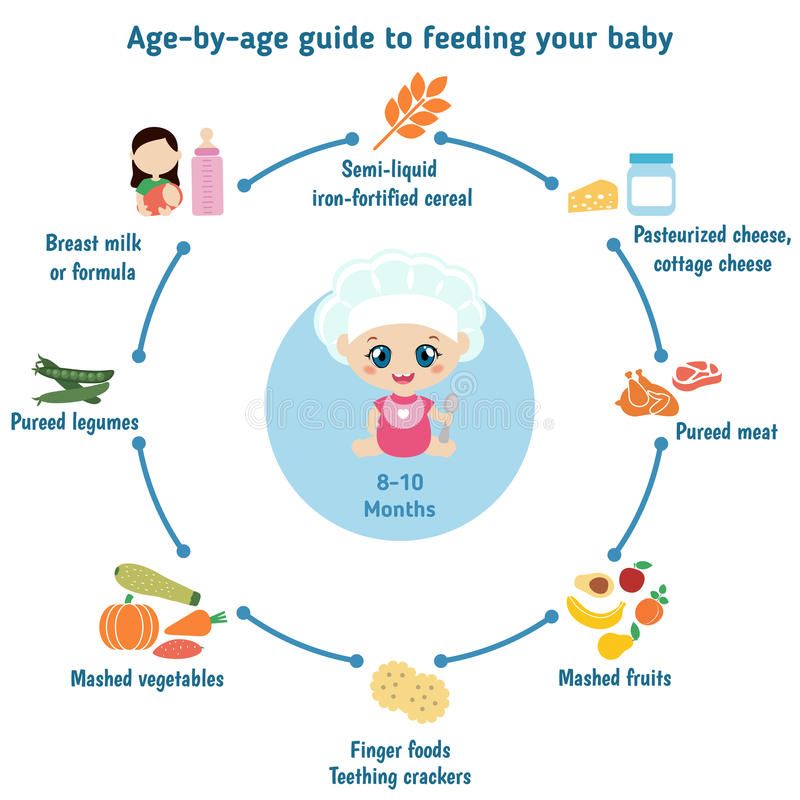
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
When Can My Baby Start Eating Solid Foods? (for Parents)
en español: ¿Cuándo puede empezar a comer alimentos sólidos mi bebé?
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Gavin, MD
A friend just started giving her 3-month-old applesauce and rice cereal. My son is just 2 weeks younger than hers, and I am wondering if I should be introducing solids soon too. When should I start?
– Taylor
Doctors recommend waiting until a baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Starting before 4 months is not recommended.
At about 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — such as iron and zinc — that solid foods provide. It’s also the right time to introduce your infant to new tastes and textures.
Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but don't start until your baby is at least 4 months old.
How do you know it’s the right time to start solid foods? Here are some signs that babies are ready:
- They have good head and neck control and sit up in a high chair.
- They're interested in foods. For example, they may watch others eat, reach for food, and open their mouths when food approaches.

- They don’t push food out of their mouths, which is a natural tongue reflex that disappears when they’re between 4–6 months old.
- They weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it.
Talk to your doctor about the right time to start solid foods.
How Should I Start Solids?
When the time is right, you can start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal or other food to a baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain. Let your baby practice eating from a spoon and learn to stop when full.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce others, such as puréed meat, fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, or yogurt. Try one food at a time and wait a few days before trying something else new to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
When starting your baby on solids, avoid:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy drinks before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Also, do not give fruit juices to infants younger than 12 months old.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
Share:
/content/kidshealth/misc/medicalcodes/parents/articles/solid-foods
norm, how many times a day, color
So many experiences are connected with how a newborn baby "walks big". Mom is worried about the frequency of the stool, its color, consistency. So how do you determine if the crumbs are all right with digestion? Perhaps he needs help?
Many mothers know that it is very important to monitor the baby's stool, and during the examination, the pediatrician is always interested in how the baby walks in a big way. This information is one of the most important points in diagnosing the health of the crumbs. Unfortunately, quite often mothers mistakenly interpret the completely natural and safe states of the baby. And because of these mistakes, they can start unnecessary treatment and worry about the baby for no good reason. So let's figure out how a baby's chair should look like and when to worry and when not.
This information is one of the most important points in diagnosing the health of the crumbs. Unfortunately, quite often mothers mistakenly interpret the completely natural and safe states of the baby. And because of these mistakes, they can start unnecessary treatment and worry about the baby for no good reason. So let's figure out how a baby's chair should look like and when to worry and when not.
Immediately after childbirth
When the baby is in the mother's tummy, he receives all the necessary substances and trace elements through the umbilical cord. The digestive system of the crumbs does not work, but his stomach is not empty. The baby sucks his fingers, opens his mouth and thus swallows a small amount of amniotic fluid. When the baby is born, this substance will be in his intestines and will gradually come out as the baby is attached to the chest and his digestive system begins to work.
So, the first stool of the baby is meconium: dark, plasticine-like feces. So the baby recovers the first day or two. Sometimes it gives him discomfort: the baby worries, cries, pushes, before he manages to go big. However, this is not always the case - many children recover easily, only slightly pushing.
So the baby recovers the first day or two. Sometimes it gives him discomfort: the baby worries, cries, pushes, before he manages to go big. However, this is not always the case - many children recover easily, only slightly pushing.
If everything is in order with the baby, he was put to the breast in time and fed on demand, then his stool gradually changes. On the third or fifth day, the baby has the so-called "transitional stool", partly consisting of meconium, which is still in the gastrointestinal tract, partly from digested colostrum and milk. As a rule, streaks appear first in the meconium mass, then the feces gradually turn yellow. By the end of the first week, the baby's stool usually acquires the features of a normal infant: yellow, rather liquid.
When should you worry? If the baby did not go down in a big way in the first two days, it is necessary to consult a doctor. There are children with individual characteristics who will continue to do this less often than most babies. However, the cause of the stool retention should be determined by the doctor. If the crumbs have some kind of problem with intestinal patency, help will be needed immediately, but you should not diagnose your baby without a doctor.
However, the cause of the stool retention should be determined by the doctor. If the crumbs have some kind of problem with intestinal patency, help will be needed immediately, but you should not diagnose your baby without a doctor.
We are at home
On the third or fifth day, the mother receives milk, and the baby has a fairly stable stool by the end of the first week. The literature sometimes says that the stool of newborns is "creamy", and this confuses mothers, who begin to suspect that something is not right with the crumbs. In reality, the stool of a healthy baby is liquid and not always homogeneous. The normal color of feces is yellow and its shades. You may notice lumps, a little mucus - it's not scary. Do not be afraid if the baby's feces have a greenish tint for up to three months due to the immaturity of the liver enzyme systems and the characteristics of bilirubin metabolism, such a condition has the right to be and also does not require treatment.
Many mothers sometimes worry that the baby's stool "suddenly" becomes watery and the baby walks in a big way with abundant gas, a sharp sound. Doctors in this case often suspect lactase deficiency. In reality, things usually go like this. In the period from 3 weeks to a month and a half, the baby has frequent growth spurts, so at certain moments the baby literally “hangs on the chest” to help the mother produce more milk. Within a day or a few, the baby needs to breastfeed more often and longer than before, and the mother begins to suspect that there is not enough milk. As a result, she often begins to shift the baby from one breast to another, and the baby receives mostly "forward" milk, which comes at the beginning of feeding from each breast. This milk is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, the baby is actively growing from it, however, the stool is liquid and gassy because of this milk (sometimes the “result” looks frothy if the baby is held over a pot or basin when he needs to clear out, and the mother can observe the consistency chair). In this situation, there is no need to panic - just the baby does not need to be constantly shifted from one breast to another, fearing that he is starving.
Doctors in this case often suspect lactase deficiency. In reality, things usually go like this. In the period from 3 weeks to a month and a half, the baby has frequent growth spurts, so at certain moments the baby literally “hangs on the chest” to help the mother produce more milk. Within a day or a few, the baby needs to breastfeed more often and longer than before, and the mother begins to suspect that there is not enough milk. As a result, she often begins to shift the baby from one breast to another, and the baby receives mostly "forward" milk, which comes at the beginning of feeding from each breast. This milk is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, the baby is actively growing from it, however, the stool is liquid and gassy because of this milk (sometimes the “result” looks frothy if the baby is held over a pot or basin when he needs to clear out, and the mother can observe the consistency chair). In this situation, there is no need to panic - just the baby does not need to be constantly shifted from one breast to another, fearing that he is starving. Give the baby the opportunity to get "hind" milk, rich in fats, which will not cause flatulence and stay longer in the intestines.
Give the baby the opportunity to get "hind" milk, rich in fats, which will not cause flatulence and stay longer in the intestines.
In this situation (when the baby suddenly begins to clearly suck more milk), the mother may feel insecure and start drinking lactic teas. From this, more carbohydrates again begin to flow into her milk and the baby's stool becomes more liquid and with gases.
Similar problems due to "front" milk occur in the case of improper attachment to the breast, as a result of which the baby swallows the air and interrupts feeding itself, or simply cannot get "hind" milk. The best way out in this situation is to consult with a breastfeeding specialist to correct the application technique and stop panicking that the baby "does not have enough milk."
In short, don't worry if your baby has problems with this type of stool. Of course, the flora of his intestines is unstable, it is just beginning to be established - it takes at least three to four months.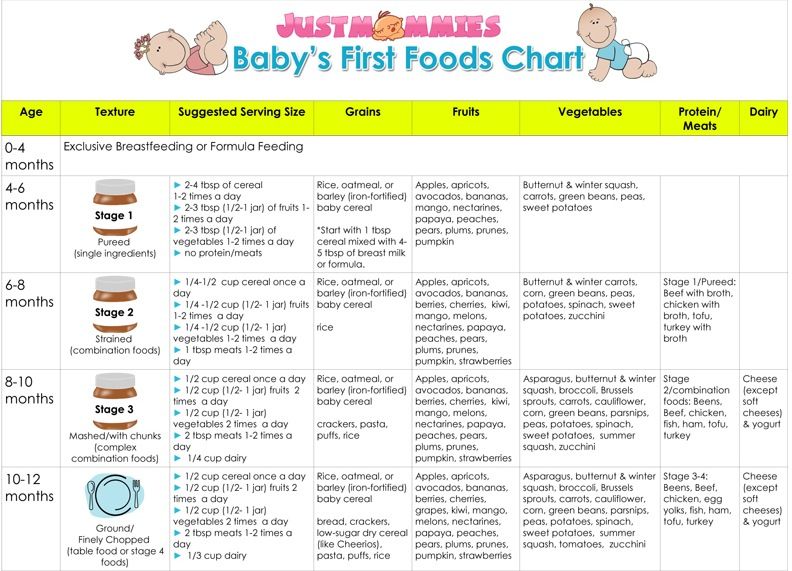 Your task is simply to feed the baby on demand and correctly and not to rush to treat him for imaginary diseases.
Your task is simply to feed the baby on demand and correctly and not to rush to treat him for imaginary diseases.
Delayed stool
Mothers worry not only about the appearance of the stool, but also because of its periodicity. How often should the baby "do things"? Normally, the baby walks in a big way several times a day, usually after feeding. However, in some children, the norm may be a chair and once a day, and even once every few days. Typically, these children have an anatomically weak anterior abdominal wall and intestinal motility. Such a periodicity of the stool can be considered the norm, if the baby still walks more regularly, the stool is of normal consistency and, in general, the baby is cheerful and cheerful and does not suffer from colic. It's not worth worrying. However, if the baby is allergic, then you need to do everything possible so that he goes to the toilet at least once a day. Atopic dermatitis is much more severe if the baby does not empty the intestines often enough - consult a doctor about this.
Babies also have physiological delays in stool at the age of one and a half to five months. Here it is important to monitor the condition of the baby. If he experiences discomfort, you should consult a doctor. Children can hold back their stools for psychological reasons, just as adults sometimes cannot go to the toilet if they are nervous. Do not panic because of a one-time problem, but if the problem persists or recurs, consult your doctor.
However, in babies there are not just "delays" of the stool, but also real constipation. Constipation is called not only when the baby does not go to the toilet at all, but also feces "peas", overdried, when a bowel movement is difficult. What could be the reason?
Regular constipation is usually caused by improper feeding of the crumbs. However, this condition can also occur if the mother does everything right, but she has her own health problems, for example, with the thyroid gland. Medications can also be the cause of constipation.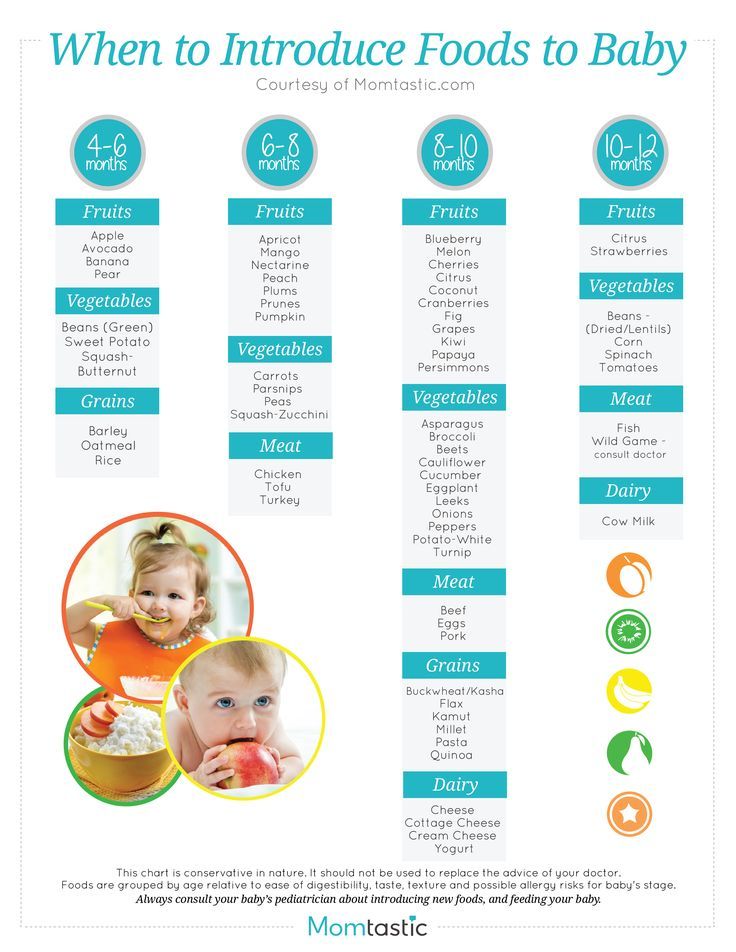 For example, intestinal weakness is provoked by all kinds of sedative mixtures and drugs, which are often prescribed to children by neurologists at an early age. Even cough medicines or tooth gels can cause constipation. In any case, the doctor should deal with this. You should not give your baby medicines and laxatives on your own, or act on it mechanically with an enema or gas tube. It is better to discuss with the doctor the issues of feeding, drug treatment and the lifestyle of the baby - so you can understand the problem.
For example, intestinal weakness is provoked by all kinds of sedative mixtures and drugs, which are often prescribed to children by neurologists at an early age. Even cough medicines or tooth gels can cause constipation. In any case, the doctor should deal with this. You should not give your baby medicines and laxatives on your own, or act on it mechanically with an enema or gas tube. It is better to discuss with the doctor the issues of feeding, drug treatment and the lifestyle of the baby - so you can understand the problem.
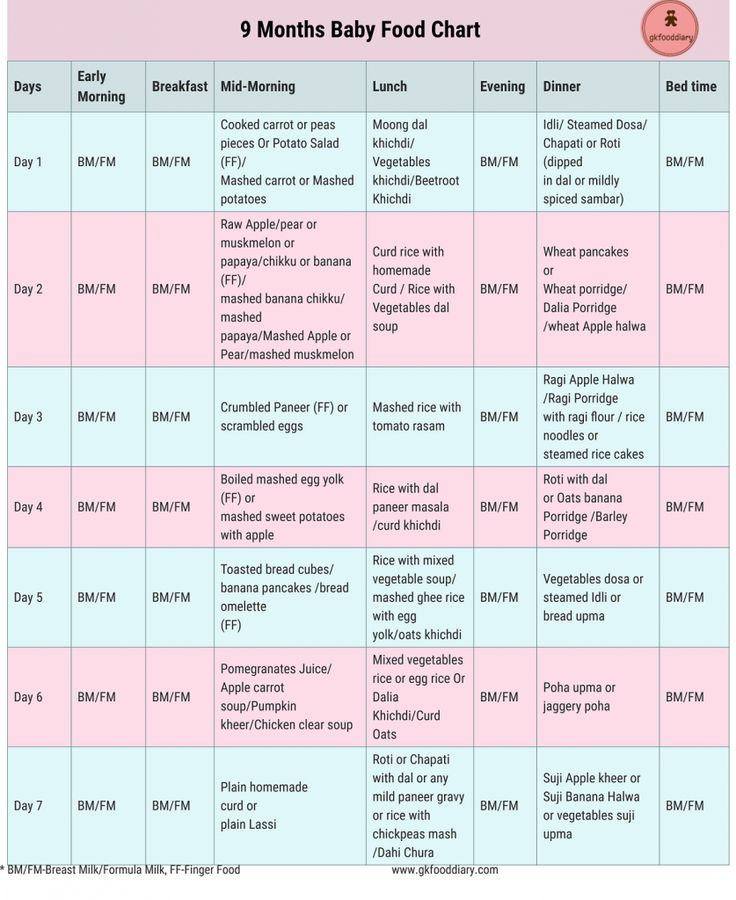
Weaning time
Of course, when you start to introduce complementary foods, the baby's stool pattern changes. First of all, you need to remember that the task of the first complementary foods (at 5, 6 months) is not to feed, but to help adapt to new tastes, to new food. Give the baby complementary foods in the amount of "lick" and only gradually move on to doses "with a marigold" or "half a teaspoon". Recall that you need to introduce one product into the diet of crumbs so that you can understand how and what the baby reacts to. Quite often, as soon as we give the baby “with a fingernail” some food, it is not digested - we find the product in the feces almost in its original form. Within one or two days, this is normal, the baby’s body has not figured out the new component in the stomach, but if this continues on the third day, the product must be removed from the diet, since it is obvious that the baby is not yet ready to accept it. You need to take a break for a week or two, without offering the baby anything but the breast, then try again with another product.
Quite often, as soon as we give the baby “with a fingernail” some food, it is not digested - we find the product in the feces almost in its original form. Within one or two days, this is normal, the baby’s body has not figured out the new component in the stomach, but if this continues on the third day, the product must be removed from the diet, since it is obvious that the baby is not yet ready to accept it. You need to take a break for a week or two, without offering the baby anything but the breast, then try again with another product.
The baby's body can also react more violently, for example, with loose stools and abdominal pain, and sometimes with allergies. In this case, you also need to cancel the product and keep the baby breastfed so that the gastrointestinal tract calms down.
When you introduce protein to your baby, he may react with constipation. To avoid this, you need to remember simple rules. Proteins require more liquid, so if this is your baby's first food (for example, cottage cheese), give him more breast milk. If you started introducing proteins when the baby is already drinking liquid, provide him with a drink. Do not worry about the fact that the introduction of new products has to be postponed - nothing terrible will happen to the baby. And be especially calm about the opinion that at 6-7 months the child needs to be given meat products so that he grows well. Not all children are able to absorb such a protein; for many, even a homogenized meat product at this age will lead to constipation and overload the kidneys. Let the baby eat breast milk for a longer time and receive vegetables and fruits as complementary foods - this way you will avoid many problems with the stool.
If you started introducing proteins when the baby is already drinking liquid, provide him with a drink. Do not worry about the fact that the introduction of new products has to be postponed - nothing terrible will happen to the baby. And be especially calm about the opinion that at 6-7 months the child needs to be given meat products so that he grows well. Not all children are able to absorb such a protein; for many, even a homogenized meat product at this age will lead to constipation and overload the kidneys. Let the baby eat breast milk for a longer time and receive vegetables and fruits as complementary foods - this way you will avoid many problems with the stool.
In general, mothers' concern about baby's stool is quite justified: after all, this is an important diagnostic symptom that allows you to understand a lot about the baby's condition. However, it must be remembered that not all situations require intervention, and most problems can be solved simply by correcting feeding mistakes. Do not rush to treat the baby and resort to medication, start with a diet.
Do not rush to treat the baby and resort to medication, start with a diet.
Text: Anna Babina
Consultant: Olga Ivanovna Tkach, pediatrician, Center for Traditional Obstetrics
what not to feed a child on a permanent basis
Vika Vishnyakova
nutritionist
Author profile .
And if we want a child to be healthy and develop normally, then it is better to buy products from the shelves of children's stores, and in restaurants and cafes choose food from the children's menu. But in most cases, it's all just marketing.
We understand that it can be difficult to feed a child broccoli and healthy white fish, and if he only asks for corn flakes for breakfast, then it is easier for him to give them and avoid tantrums. This does not make you a bad parent.
I'll tell you why "baby" products can be dangerous.
Go see a doctor
Our articles are written with love for evidence-based medicine. We refer to authoritative sources and go to doctors with a good reputation for comments. But remember: the responsibility for your health lies with you and your doctor. We don't write prescriptions, we make recommendations. Relying on our point of view or not is up to you.
We refer to authoritative sources and go to doctors with a good reputation for comments. But remember: the responsibility for your health lies with you and your doctor. We don't write prescriptions, we make recommendations. Relying on our point of view or not is up to you.
Cereals and corn flakes
Even if cereals contain iron, make the child smart and active, do not overdo it.
Breakfast products advertised for children contain 3 times more sugar than those advertised for adults: Spanish study
They are actually high in sugar and low in nutrients. This can lead to an unbalanced menu, when there are few macro and microelements important for the development and maintenance of health, and a lot of calories, sugar and salt.
For example, a 30-gram serving of Nestlé breakfast cereal contains about 14 g of sugar. Most often, we do not measure portions with the help of scales, but pour "by eye" - there can be more sugar. For a preschooler, this amount of sugar is the daily norm.
This limit includes all added sugars in any form and with any name. Corn syrup, dextrose, coconut sugar, honey, Jerusalem artichoke syrup and agave nectar are also free sugars that WHO recommends limiting in the diet.
How to calculate sugar in foods: 61 sugars
Allowable amount of free sugars in a child's diet
| Age | How much sugar can you have per day |
|---|---|
| 4-6 years | 19 g or 5 teaspoons |
| 7-10 years | 24 g or 6 teaspoons |
| over 11 years old | 30 g or 7 teaspoons |
Age
How much sugar is possible per day
4-6 years
19 g, or 5 teaspoons
7-10 years
24 g, or 6 teaspoons
older
30 g or 7 teaspoons
The WHO and the American Heart Association recommend eliminating all added sugar up to 2 years and the UK Department of Health up to 4 years.
Breakfast alone can contain a daily amount of sugar, but in addition to breakfast, there are other meals, inconspicuous snacks, desserts and juice. It turns out to be an overkill.
If you regularly exceed the sugar norm, this can lead to unpleasant consequences:
- overweight;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- caries;
- nutrients will be less absorbed.
And the passion for sugar changes the perception of tastes: the usual kiwi or peach seems not sweet enough, and sugary biscuits are just right. This can force other foods out of the diet.
All the health benefits of breakfast cereals are in the flour from which the balls or pillows are made. That is, ordinary cereals were cleaned of the shell - the most valuable element of the grain, ground into flour, added sugar in several forms, butter, starch and additional ingredients to improve taste and texture.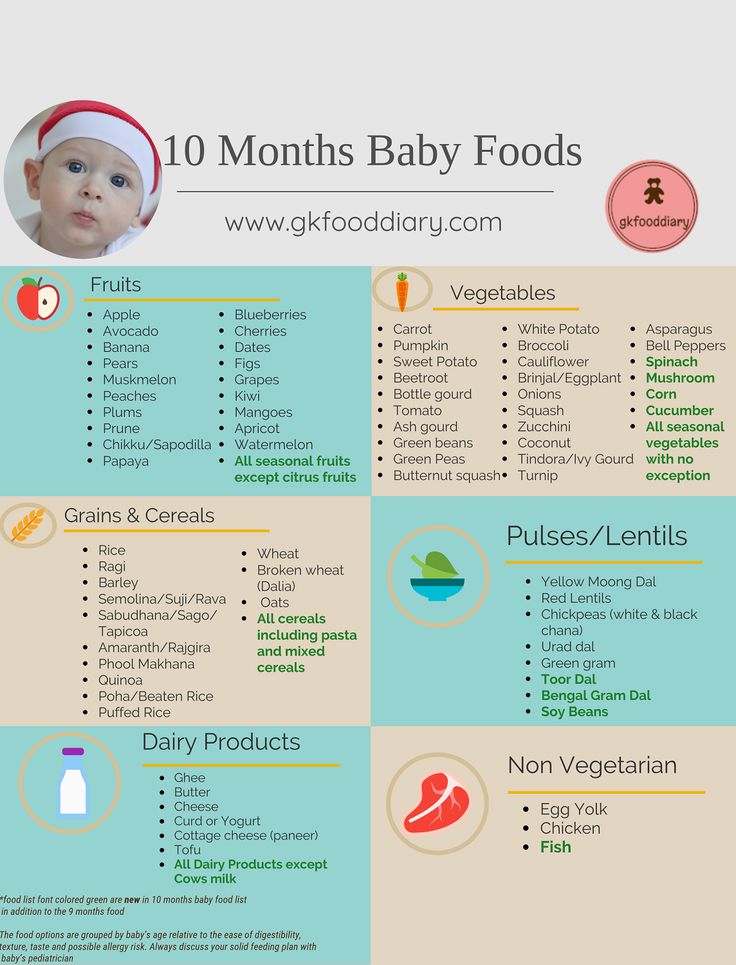 To compensate for the loss of vitamins and trace elements that were removed along with the grain shell, the product can be enriched with vitamins and minerals. But this is not always done.
To compensate for the loss of vitamins and trace elements that were removed along with the grain shell, the product can be enriched with vitamins and minerals. But this is not always done.
/list/norm-menu/
The main thing is variety: a ready-made menu for the average Russian
If we gave children ordinary cereals, then there would be more fiber - food for beneficial bacteria in the intestines, the very vitamin B with which the manufacturer promised to increase the ingenuity of consumers, others important trace elements and there would be no added sugar.
Juices
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia notes that juices contain few vitamins and minerals, but a lot of sugar, so they should not be offered before 12 months. The habit of drinking juices can increase the risk of tooth decay and obesity.
The WHO, European and American Societies of Pediatrics do not recommend giving free sugars to children under 2 years of age. And juice is one of their forms. If fiber is removed from the product, but only juice or its concentrate is left, then the product goes into the section of free sugars - “free” from fiber. That is, any juice - even marked "without sugar" - is still a variant of sugar.
And juice is one of their forms. If fiber is removed from the product, but only juice or its concentrate is left, then the product goes into the section of free sugars - “free” from fiber. That is, any juice - even marked "without sugar" - is still a variant of sugar.
Whole fruits should not be limited in the diet: it is almost impossible to get an excess of sugars from them, but from juices it is easy. For example, it takes me four oranges to make a glass of freshly squeezed juice. A child will drink such a glass in one minute and ask for more. But if I cut these four oranges, he will manage two at best. At the same time, the child will receive fiber, vitamins, minerals and a bonus in the form of training the jaw apparatus.
A glass of freshly squeezed juice may be in the diet of a child over 7 years of age. Until this age, pediatric organizations recommend giving juices occasionally and diluting with water in a ratio of 1:1.
Unicef - what to feed a baby up to 1 year old
A package of baby juice can contain up to 6 tablespoons of free sugars, absolutely no fiber and a dubious amount of vitamins, because almost all of them are destroyed during the production process. And a whole apple contains 5 g of fiber - that's 20% of the daily value for adults, 9mg magnesium and 0 g free sugars.
And a whole apple contains 5 g of fiber - that's 20% of the daily value for adults, 9mg magnesium and 0 g free sugars.
Juice consumption is associated with excess weight: Harvard Medical School
Dairy products for children
By itself, milk, kefir and fermented baked milk are essential foods in the diet. From them, children get calcium, protein, various microelements, and from fermented milk products they also get beneficial bacteria.
But now, baby dairy products are not always a good option, despite the labels "from 6 months" on the packages. The point here is not in the milk itself and its derivatives, but again in exceeding the safe norms of sugar with the regular use of such products.
Nutrition for children aged 1-3 years: guidelines from the Union of Pediatricians of Russia
Dairy guidelines: American Pediatric Association
WHO recommends 2-3 servings of dairy products per day: each serving is the size of a child's fist. For example, it can be 100 ml of kefir or a jar of non-drinkable yogurt 120 g.
But if you put 1-3 teaspoons of sugar in each of them, as manufacturers of children's yogurts do, you get a search for the norm of sugars with all the ensuing consequences for health . In addition, we can form the wrong taste preferences: after the “strawberry flavored” option, ordinary fermented baked milk may seem insipid to the child and he will refuse it. Therefore, it will be more useful to give ryazhenka without additives and put a couple of berries in it for taste.
"Children's menu" in restaurants and cafes
Most often, the children's menu offers french fries, sausages, nuggets and dumplings. It seems that this is a variant of a normal lunch for children.
Almost all of these products are ultra-processed. That is, those in which there are almost no nutrients, but there are a large number of flavor enhancers and preservatives: salt, sugar and fats. Yes, they affect our receptors and such food seems tasty, but there is very little nutritional value in it.
There is a connection between the regular consumption of ultra-processed food and lipid metabolism disorders in children. In the future, this can lead to atherosclerosis and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. And also to an imbalance in nutrition, metabolic disorders and obesity.
Study on the association of frequent consumption of fast food and obesity in children
Scientific review on the impact of fast food on children's health
Ultra-processed foods can be included in the diet of adults and children, but as a supplement to a basic balanced diet, not as a substitute for it.
If you feed this food daily, then the children form the idea that this is a normal food option. Then why eat broccoli and shrimp on another day? Food with an adequate level of nutritional value can be forced out of the diet, and this is fraught with a deficiency of essential substances.
Therefore, when looking at the menu with your child, it is important to draw his attention to the fact that nuggets and fries are more of an addition to the main course, and if you need to satisfy your hunger, then it is better to choose alternatives with a higher nutritional value. And be prepared for the question "If this is not children's food, then why is it on the children's menu?".
/list/free-for-kids/
Going to a cafe with your family and not going broke: 7 Moscow restaurants with a free children's menu child, because it is sold in a pharmacy. It is also much healthier than candy because it contains iron. The same applies to ascorbic acid in dragee format: vitamin C in a "candy" package is just a godsend for parents who want to strengthen their child's immunity.
A 50g hematogen bar contains about 5g of iron and 30-40g of sugar. For comparison: the same amount of iron in 25 g of stewed liver, 30 g of sesame seeds, 12 tablespoons of boiled lentils or 150 g of beef steak. Moreover, these products do not contain added sugar.
Moreover, these products do not contain added sugar.
One dragee of ascorbic acid weighing 2.9 g contains 2.8 g of sugar, and ascorbic acid itself is only 25 mg - 112 times less than sugar. The same amount can be obtained from 50 g of bell pepper or half a kiwi.
If you do not live in conditions of total food shortage, then the child does not need either hematogen or ascorbic acid. They may be optional, as a dessert, but not as a necessary means to maintain health.
/list/healthy-eating-myths/
No Sugar or Carbs: 6 Healthy Eating Myths
Bottom Line
- Baby food is not a set of products with cartoon characters on the packaging and the inscription “from 6 months”.
- Children's diet is the usual food groups: vegetables, fruits, cereals, dairy products, sources of protein and a moderate amount of fat, among which unsaturated is preferred. Minimum salt, moderate amount of sugar.
- Products targeted at children often contain too many free sugars, but this is not always clear from just looking at the front of the package.