When to start baby food for breastfed babies
Breastfeeding FAQs: Solids and Supplementing (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about about introducing formula, solids, and more.
Is it OK to Give My Baby Breast Milk and Formula?
Breast milk is the best nutritional choice for babies. But in some cases, breastfeeding (or exclusive breastfeeding) isn’t possible or an option. What’s best for your baby's health and happiness is, in large part, whatever works for your family. So if you need to supplement, your baby will be fine and healthy, especially if it means less stress for you.
Babies who need supplementation may do well with a supplemental nursing system. This is when moms place a small tube by their nipple that delivers pumped milk or formula while a baby is breastfeeding.
Babies also can get pumped milk or formula by bottle. But it’s a good idea to wait until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3-4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
If I Give My Baby Formula, How Do I Start?
If you're using formula because you're not producing the amount of milk your baby needs, nurse first. Then, give any pumped milk you have and make up the difference with formula as needed.
If you're stopping a breastfeeding session or are weaning from breastfeeding altogether, begin to replace breastfeeding with bottle feeds. As you do this, pump to reduce uncomfortable engorgement. Engorgement is when your breasts overfill with milk and other fluids and get painful, swollen, warm, or hard. This can lead to problems with plugged ducts (when the ducts won’t drain well or at all) or a breast condition called mastitis.
When you reduce the number of nursing sessions, your milk supply will decrease. Your body will adapt to produce just enough milk to fit your new feeding schedule.
How Might a Diet With Formula Affect My Baby?
Starting your breastfed baby on formula can cause some change in the frequency, color, and consistency of your baby’s poop. Be sure to talk your doctor, though, if your baby has trouble pooping.
If your baby refuses formula alone, you can try mixing some of your pumped breast milk with it to help the baby get used to the new taste.
Is it OK for Me to Give My Baby the First Bottle?
If possible, have someone else give the first bottle. This is because babies can smell their mothers and they're used to receiving breast milk from mom, not a bottle. So try to have someone else — like a caregiver or partner — give the first bottle.
Also consider being out of the house or out of sight when your baby takes that first bottle, since your little one will wonder why you're not doing the feeding as usual. Depending on how your baby takes to the bottle, you might need to keep doing this until your baby gets used to bottle feeding.
If your baby has a hard time adjusting to this new form of feeding, be patient and keep trying. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Does My Breastfed Baby Need Supplements?
Breast milk contains many vitamins and minerals. But it’s a good idea to give a daily supplement for some nutrients that may be lacking. It all depends on your baby’s age.
Here are some guidelines:
- Vitamin D. Breastfed babies need to take a daily vitamin D supplement. Vitamin D is added to infant formulas. Vitamin D is made by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight, but it is not safe for infants under 6 months to be in direct sunlight. (After 6 months, use sunscreen when in the sun to protect your baby’s sensitive skin).
- Iron. Iron is a mineral found in breastmilk during the first 4 months of life. After that, babies need an iron supplement until they begin eating enough iron-rich foods (such as cereals or meats) when they’re around 6 months old.
 If your baby gets a mix of breast milk and iron-fortified formula, talk to your doctor about whether your little one needs a supplement. After they start on solids, some babies still need iron supplements if they don’t eat enough iron-rich foods. You doctor can tell you if your baby is getting enough iron.
If your baby gets a mix of breast milk and iron-fortified formula, talk to your doctor about whether your little one needs a supplement. After they start on solids, some babies still need iron supplements if they don’t eat enough iron-rich foods. You doctor can tell you if your baby is getting enough iron. - Fluoride. Babies younger than 6 months do not need a fluoride supplement. After your baby is 6 months old, you can start supplementing with fluoride if your water supply lacks fluoride. Well water, bottled water, tap water in some communities, and ready-to-feed formulas do not have fluoride.
It’s important to find out if your water supply has fluoride in it. You can ask your doctor, dentist, or local water utility agency if the water in your community is fluoridated. Giving a child too much fluoride can cause white marks on the teeth, so there is no need to give a fluoride supplement if your child gets enough fluoride from water.
When Should I Introduce Solid Foods?
The best time to introduce solid foods is when your baby has the skills needed to eat, usually between 4 and 6 months of age. This is when your baby:
This is when your baby:
- has good head and neck control
- can sit up
- has lost the tongue-thrust reflex (which causes babies to push food out of the mouth)
- has the motor skills needed to transfer food to the back of the mouth to swallow
- shows an interest in food (by watching others eat, reaching for food, or opening the mouth as food approaches)
By this age, babies usually weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it.
Wait until your baby is at least 4 months old and shows these signs of readiness before starting solids. Many babies exclusively breastfeed until 6 months of age, which is perfectly healthy.
Babies who start solid foods before 4 months are at a higher risk for obesity and other problems later on. They also aren't coordinated enough to safely swallow solid foods and may choke on the food or inhale it into their lungs.
How Should I Start Solids?
When the time is right, start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Rice cereal has traditionally been the first food for babies, but you can start with any you prefer. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Never add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
Rice cereal has traditionally been the first food for babies, but you can start with any you prefer. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Never add cereal to a baby's bottle unless your doctor recommends it.
Another good first option is an iron-rich puréed meat. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon.
At this stage, solids should be fed after a nursing session, not before. That way, your baby fills up on breast milk, which should be your baby's main source of nutrition until age 1.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce others, such as puréed fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, or yogurt. Wait a few days between introducing new foods to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
Experts recommend introducing common food allergens to babies when they're 4–6 months old. This includes babies with a family history of food allergies. In the past, they thought that babies should not get such foods (like eggs, peanuts, and fish) until after the first birthday. But recent studies suggest that waiting that long could make a baby more likely to develop food allergies.
But recent studies suggest that waiting that long could make a baby more likely to develop food allergies.
Offer these foods to your baby as soon as your little one starts eating solids. Make sure they're served in forms that your baby can easily swallow. You can try a small amount of peanut butter mixed into fruit purée or yogurt, for example, or soft scrambled eggs.
When Can I Give My Baby Water?
In their first few months, babies usually don't need extra water. Breast milk and formula supply all the fluids that your baby needs. On very hot days, most babies do well with extra feedings.
When your baby starts eating solid foods, you can offer a few ounces of water between feedings, but don't force it.
What About Juice?
Fruit juices are not recommended for babies. Juice offers no health benefits, even to older children. Juice can fill them up (leaving little room for more nutritious foods), promote obesity, cause diarrhea, and even put a baby at risk for cavities when teeth start coming in.
Starting Solid Food - La Leche League GB
Human milk is the perfect first food
Introducing your baby to other foods is a big milestone, and can be fun too. The simplest approach is to continue your usual breastfeeding pattern and let your baby join you at family mealtimes. Your baby will be able to learn about new foods gradually and in their own time.
Signs of readiness for complementary foods
Babies begin eating solid foods according to their own unique timetables, just as they will walk and talk when they are ready. Readiness to try new foods is just another developmental step and it isn’t necessary to do anything special.
Babies show signs of readiness for complementary foods (to complement their milk intake) around the middle of the first year.
Although previous research suggested that signs of readiness for starting solids were related to developmental changes which happen at around 4 months, recent research indicates the following signs of readiness:1
Fact: Ability to sit up well when supported
Once your baby can sit up well when supported (for at least a few minutes) let them join you at family mealtimes and allow them to pick up food.
Fact: Loss of the tongue thrust reflex
Babies who have not yet lost their tongue thrust reflex will push food out of their mouth with their tongue. The tongue thrust reflex is a sign that they are not developmentally ready for solid food.
Fact: Ability to pick up food, put it in their mouth and chew
A baby who is able to reach out and grab a piece of food, then bring it to their mouth and chew it is generally ready for solids. Research indicates that the ideal time to start solid food in terms of oral-motor developmental readiness is between six and eight months. As with other developmental stages, babies learn to chew when they are ready, not because solid food has been introduced by six months.
Myth: Breastfeeding more often
Your baby may ask to breastfeed more, yet still not be ready for solid food. They may just be unwell, having a growth spurt, teething, or reacting to stress. Offering your baby both breasts during each feed may be all that is needed.
Myth: Waking at night
Waking at night is normal and common behaviour and is not a sign that a baby is ready to start other foods even if they have previously slept for longer periods.
Myth: Watching you eat
Babies are interested in and want to copy what they see around them, so watching others eat does not necessarily mean they are ready to start eating solid foods.
Why follow your baby’s cues?
Human milk is the most important food in your baby’s diet during their first year, providing them with most of the calories and fluids they need, as well as a wide range of nutrients. Allowing solids to replace breastmilk too quickly may lead to undernutrition, imbalance of nutrients, or poor weight gain. Breastfeeding continues to be a valuable source of nutrition and calories if your baby is unwell or teething, and doesn’t want to eat solid food.
Breastfeeding provides your baby with antibodies, other immune factors, stem cells, and many other components unique to breastmilk. Breastfeeding alongside introducing solids helps to prevent harmful bacteria, such as E.coli, growing in your baby’s gut. Replacing your milk with solid food too early reduces the level of protection they receive.
Breastfeeding alongside introducing solids helps to prevent harmful bacteria, such as E.coli, growing in your baby’s gut. Replacing your milk with solid food too early reduces the level of protection they receive.
Developmental readiness inside and out
Your baby’s digestive system gradually matures during the first six months. Introducing solids when your baby is developmentally ready means they will be able to eat and digest these new foods.
Preterm babies, babies with special needs or developmental delay may not be ready for solids until later than six months. Following their readiness signs will help you know when to offer solids. Speak to your baby’s healthcare team regarding their individual nutritional needs.
Carry on breastfeeding
Starting solid food is a new experience for your baby and is about taste, texture and learning new skills, not about replacing your milk. Babies are more likely to try something new if they aren’t too hungry – they may refuse solids when they really want to breastfeed. Remember that your baby isn’t likely to eat very much to start with.
Remember that your baby isn’t likely to eat very much to start with.
You may feel pressured into limiting breastfeeds so that your baby will take more solid food, but this can have the opposite effect. If your baby is happy and content after a breastfeed they may be more open to the idea of trying some new foods.
Breastmilk gradually and gently introduces babies to the foods their mother eats because traces of those appear in her milk. This provides a variety of flavour experiences in a natural way, helping prepare the baby for the foods they will eat at the family table. Babies will want to eat whatever food is on the table, so this is a good opportunity to review the whole family’s diet.
First tastes
Baby–led weaning
The principle behind baby-led weaning is that babies will instinctively start to feed themselves when they are developmentally ready, given the opportunity. The skills to feed themselves and readiness of their body to process food occur naturally and do not need to be taught.
Babies who are in control of feeding themselves (in contrast with spoon feeding) will only be able to pick up food, put it in their mouth and chew it when they are developmentally ready. This approach also lets babies determine which foods and how much they want to eat: they will naturally progress at their own pace and reduce breastfeeds when they are ready.
Allowing babies to join in with family mealtimes will expose them to a wide variety of different foods, enable them to copy how other children and adults eat, and help make eating a pleasant experience, encouraging a positive lifelong relationship with food. A baby who is allowed free choice of good, nutritious foods tends to balance their own diet.
For more information on baby-led weaning, see book Baby-led Weaning: The Essential Guide (2019).
How to present food – shapes and sizes
Babies love to use their hands, so offer foods that they can easily hold and put into their mouth. Until they have developed a pincer grip, babies can’t pick up small pieces of food. Offer sticks or pieces of food the shape/size of an adult’s finger. Most 6-month-old babies will be able to pick up the piece, hold it in their fist and gnaw the end sticking out of their fist.
Offer sticks or pieces of food the shape/size of an adult’s finger. Most 6-month-old babies will be able to pick up the piece, hold it in their fist and gnaw the end sticking out of their fist.
Softer foods can be spread on unsalted oat cakes, rice cakes or crackers, or dipped into with a suitable piece of food so your baby can manage by themselves. For tastes of soup, yoghurt or porridge, offer your baby a spoon with a small amount of food on, or let them dip their fingers in and lick off the food.
Different tastes and textures
It is important to offer your baby a wide variety of different foods as this will expose them to a range of tastes and textures. The ability to explore the different taste, texture,colour and smell of food may help babies to have a healthier relationship with food.
Aim to offer tastes of a wide variety of foods in as close to their natural state as possible. Given access to a range of food groups, your baby will show you what they need. If they don’t want a certain food, try something else, but do offer it again.
If they don’t want a certain food, try something else, but do offer it again.
You don’t need to purée foods or even mash them. Puréeing often requires liquid to be added, diluting the nutritional content. Solid (un-mashed) food aids development of chewing skills, which babies don’t get from sucking puréed food. Early exposure to different textures can also prevent a baby refusing to eat lumpy food later on.
Gagging and choking
Gagging happens when food triggers a baby’s gag reflex and the food is pushed forwards to prevent it from blocking the airway. A baby gagging will usually be calm and breathing normally. Gagging is a natural protective mechanism to prevent choking and usually doesn’t need any intervention.
Choking happens when a baby’s airway is (fully or partially) blocked and they can’t breathe. A baby choking will be coughing or silent (unable to make any noise), not breathing, and their face or lips may change colour.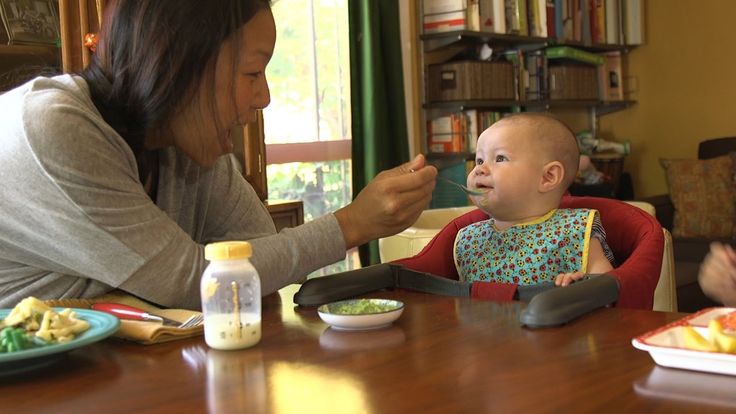 Choking is an emergency and they may need first aid to clear the blockage.
Choking is an emergency and they may need first aid to clear the blockage.
Babies are less likely to choke on food if they are sitting upright and feeding themself. Research shows baby-led weaning is not associated with an increased risk of choking.2
Certain foods are a choking risk for children under three years of age and should be avoided, including whole grapes, whole cherry tomatoes, popcorn, large amounts of peanut butter and any food that could break off in large chunks, such as raw carrot, hard apple or celery sticks. Nuts are a choking risk up to five years of age.
At first, you may want to check your baby’s mouth for unswallowed food after a meal, including their cheeks and palate. Never leave your baby alone with food or when they are eating.
Plan for a little mess!
Solid foods are another part of the world your baby is exploring and they will do this as much by touch and smell as by taste. This can be messy, but is an important learning experience for them. To make cleaning up easier, roll up their sleeves, use a bib or apron and put a clean plastic cloth on the floor so you can safely re-offer dropped foods.
To make cleaning up easier, roll up their sleeves, use a bib or apron and put a clean plastic cloth on the floor so you can safely re-offer dropped foods.
Natural appetite control
It is normal for your baby’s appetite to go up and down over the course of days, weeks and months. Don’t worry. Just offer more of any food they ask for and stop when they don’t want any more. There is no need to ‘top them up’ with a spoon if they haven’t eaten much at a meal. Allowing a baby to feed themselves and take their time over a meal helps them to tune in to their feelings of fullness and to stop eating, which is important throughout their life.
If your baby refuses food, they are not rejecting you or your efforts. They may simply not be hungry. If they are ill or teething, unrestricted breastfeeding will ensure they receive good nutrition and will comfort them until they feel well and interested again.
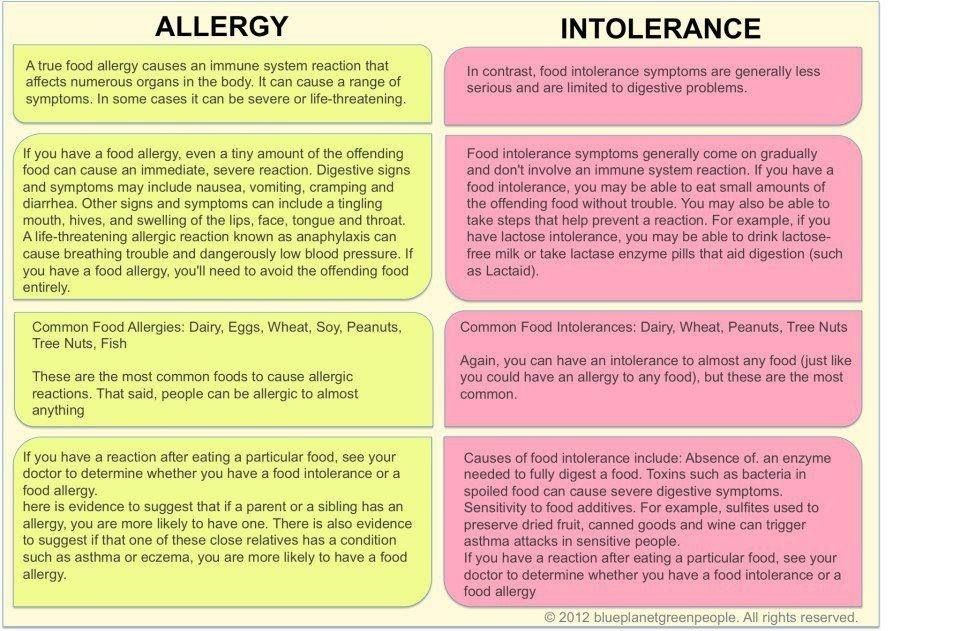
Allergy & Food Intolerance
Common allergens
The most common allergens (in order of incidence) are:
- Milk and other dairy products such as butter, yoghurt, cheese, whey, casein, caseinate, lactose
- Egg
- Peanut and tree nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, cashews, etc.
 )
) - Soy
- Wheat
- Fish and Shellfish: crustaceans (e.g. crab, lobster, crayfish, shrimp, prawn), molluscs (e.g. mussels, oysters, squid)
- Sesame seeds (in tahini and hummus)
- Lupin/lentils (including chickpeas which are in hummus)
- Fenugreek (closely related to peanuts)
- Celery and celeriac
- Mustard
Introducing peanut and egg
Peanut and hen’s egg are common allergens for babies. Current guidance recommends that foods containing peanut or hen’s egg need not be differentiated from other solid foods and can be introduced from around 6 months along with other foods.
The deliberate exclusion of peanut or hen’s egg beyond 6 to 12 months of age may increase the risk of allergy to the same foods. Once introduced, and where tolerated, these foods should continue to be part of your child’s usual diet. If initial exposure is not continued as part of your child’s usual diet, then this may increase the risk of sensitisation and subsequent food allergy. 3
3
Eczema
If your baby has eczema, suspected food allergy, or a family history of food allergy you may wish to seek medical advice before introducing allergenic foods. If eczema is well-controlled (i.e. mild or cleared), it is easier to assess your baby’s tolerance to new foods.
Offer allergenic foods in very small amounts and watch carefully for any symptoms of an allergic reaction. If eczema becomes difficult to manage after food introduction, stop the allergen and seek medical advice.
Allergic reactions and symptoms to watch for
In very rare cases allergy can cause a severe life-threatening reaction called anaphylactic shock. If your baby has a severe and immediate allergic reaction, which may include swelling of the lips, tongue, eyes or face, seek emergency medical care.
Food sensitivity reactions can include eczema, nettle rash (urticaria), a sore bottom, wheezing, asthma, colic, vomiting, constipation and diarrhoea. If a food causes a mild reaction, talk to your health visitor or doctor about whether you should continue to give it. For further information, see Allergies & Food Intolerances.
If a food causes a mild reaction, talk to your health visitor or doctor about whether you should continue to give it. For further information, see Allergies & Food Intolerances.
Nutrition Requirements
Vitamins and minerals
The UK Department of Health recommend that all babies be given supplements including vitamins A, C and D from 6 months, and a vitamin D supplement from birth for breastfed babies and those receiving less than 500ml of formula per day.4
Iron
A healthy full-term baby has sufficient iron stores at birth, and delayed cord clamping helps to increase a baby’s iron levels. Iron is present in human milk and bioavailable to the baby, which is sufficient for the first 6 months of a baby’s life. Introduce iron rich foods from six months such as meat, poultry, fish, egg, pulses/legumes (e.g. chickpeas and lentils) and fortified cereals.
Vitamin D
This is produced when our bodies are exposed to sufficient sunlight. Wearing clothes and suncream to protect against skin cancer limits how much vitamin D we can produce. Vitamin D supplements are particularly important for babies who have limited exposure to sunlight and for babies with darker skin colour living in the UK. Breastmilk doesn’t contain high levels of vitamin D as, in the past, babies would absorb most of their vitamin D from exposure to sunlight.
Wearing clothes and suncream to protect against skin cancer limits how much vitamin D we can produce. Vitamin D supplements are particularly important for babies who have limited exposure to sunlight and for babies with darker skin colour living in the UK. Breastmilk doesn’t contain high levels of vitamin D as, in the past, babies would absorb most of their vitamin D from exposure to sunlight.
Vitamin B12
This is found in animal protein. Your baby may need vitamin B12 supplements if you eat a strict vegetarian or vegan diet.5
Nutritional needs of preterm babies
A premature baby does not have a good iron store at birth. If your baby was born before 34 weeks, they may already be receiving iron, zinc and vitamin supplements. Your preterm baby’s healthcare team will be able to give more specific guidance regarding their individual nutritional needs.
Good First Foods
Offering your baby a wide variety of foods in as close to their natural state as possible will ensure they receive a range of nutrients. Highly processed, low-fat or ready-prepared adult foods are not suitable for babies. You don’t need to buy ready-prepared baby food. These foods are expensive, often come in over-large portions and may contain added ingredients your baby doesn’t need. If you choose to buy convenience foods, check labels carefully.
Highly processed, low-fat or ready-prepared adult foods are not suitable for babies. You don’t need to buy ready-prepared baby food. These foods are expensive, often come in over-large portions and may contain added ingredients your baby doesn’t need. If you choose to buy convenience foods, check labels carefully.
To preserve nutrients as much as possible, bake, steam or cook foods in water. Take out a small portion for your baby before adding any salt or sugar to the rest. Allow it to cool to a suitable temperature. Offering finger foods avoids the need to add extras your baby may not be ready for, such as milk or butter.
Note: Some foods can trigger allergic reactions in some babies. See further down this article for more information.
| Food | Serving Suggestion | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables (e.g. carrot, pea, sweet potato, potato) | Cook lightly to soften if needed. Give sticks or adult finger-sized pieces.  | Remove skin if needed. Avoid small chunks of raw hard vegetables, such as carrots, which could cause choking. |
| Fruit (e.g. apple, banana, avocado) | Give your baby a whole fruit or large piece to hold. | Remove skin and stones if needed. Small chunks can cause choking |
| Poultry (e.g. chicken) Meat | Give large pieces of lean cooked meat, moisten with meat juices. | Make sure to remove any bones and gristle. |
| Fish | Poach in a little water (no salt) or oven bake. | Check carefully for bones. Fish can be allergenic so introduce it with caution. Don’t introduce shellfish, smoked fish or pickled fish until your baby is over 12 months. |
| Rice cakes Oat cakes Crackers | Spread soft foods on, or use them for dipping. | Plain, unsalted rice cakes, oat cakes and crackers are useful alternatives to rusks. |
| Beans Lentils | Cooked beans and lentils can be mashed to make a spread or dip.  | Cook all beans and lentils thoroughly. |
| Dried fruit | Cut up larger fruits such as apricots. Apricots and prunes can be cooked in a small amount of water to make a nutritious spread. | Although rich in nutrients, dried fruit can stick to teeth and if given frequently can cause tooth decay even if you clean your baby’s teeth regularly. |
| Wholegrain cereals such as oats, corn (maize) and wheat | Can be cooked with water, without salt, sugar or sweetener. Choose unsweetened breakfast cereals. | Most cereals contain a protein called gluten, a potential sensitizer, so avoid mixed-grain cereals until you know your baby can tolerate each one individually. |
| Bread Pasta Rice | Bread and pasta are easy finger foods. Serve pasta plain, with butter or grated cheese. | Avoid pasta made with eggs until you know your baby can tolerate egg. |
| Cottage cheese, yoghurt, fromage frais, butter, unprocessed cheese | Your baby can use a spoon or their fingers.  Useful with cooked vegetables. Grate cheese or serve slices. Useful with cooked vegetables. Grate cheese or serve slices. | Use unsalted butter. |
| Eggs | Can be served scrambled, boiled, poached, in an omelette, etc. | If lion-stamped, egg can be served raw. Otherwise, cook until both white and yolk are solid. |
| Nuts and seeds (e.g. peanut butter, tahini) | Should be spread thinly. Only use smooth varieties. | Never give whole nuts or seeds until 5 years of age. Crunchy nut butter varieties can cause choking. |
Foods to avoid
Salt can overload a baby’s system and too much can cause kidney failure. Highly salted foods may foster a taste for salty foods. Avoid and minimize the use of processed foods, packet mixes, crisps, savoury snacks, gravy and condiments such as ketchup, yeast extract, mustard and brown sauce. When buying convenience foods look for low salt versions, including tinned beans and vegetables canned only in water.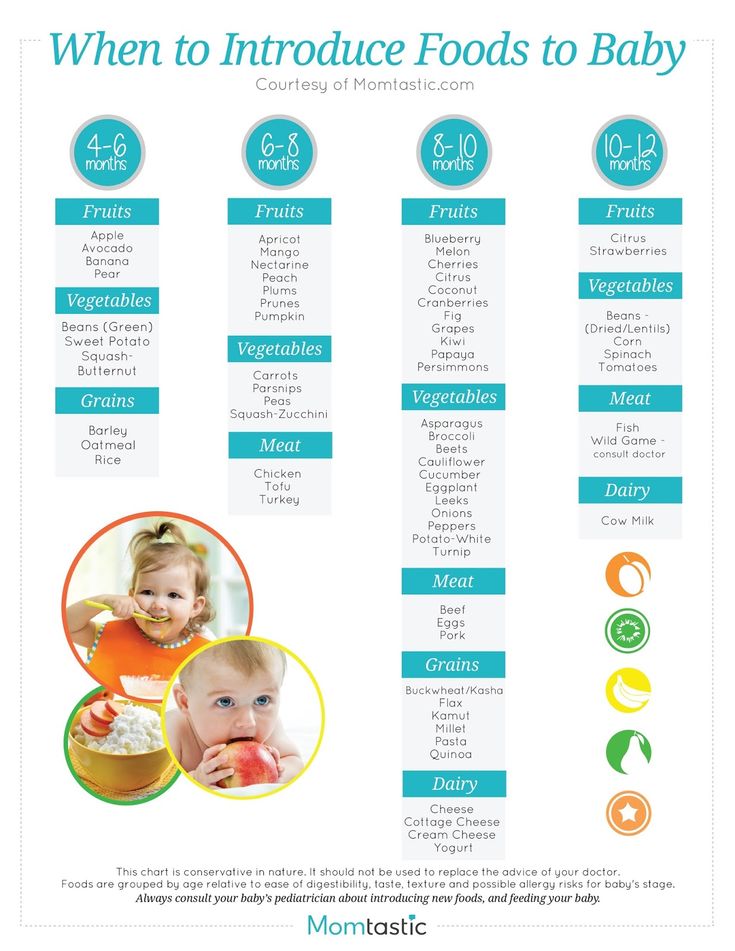
White sugar contains virtually no nutrients and is a major factor in tooth decay. When checking food labels watch for other names for sugars – such as glucose, dextrose, sucrose, corn syrup and fructose. Molasses, maple syrup and honey are also almost pure sugar and can displace healthy nutritious foods. Many processed foods which are advertised for babies have high sugar content and should be avoided, including teething biscuits and baby rusks.
Honey may contain botulism spores and should not be given to babies younger than one year.
Teething biscuits are often high in sugar. Your baby can teethe using anything hard and safe to chew on, including unsalted rice cakes or crusty bread.
Artificial sweeteners are present in many processed foods and drinks aimed at babies and children, including juice drinks, ready meals and jars, and snack foods. Children who eat food with artificial sweeteners may be more likely to develop a ‘sweet tooth’ and a preference for sweet food in later life.
Children who eat food with artificial sweeteners may be more likely to develop a ‘sweet tooth’ and a preference for sweet food in later life.
Artificial flavourings and food colouring are unnecessary chemicals.
Foods high in saturated fats. While babies need fats in their diet, foods containing unnecessary saturated fats, such as fried foods, should be offered only in moderation.
Very hot spicy food. Many babies like spicy food, but very hot spices, especially chillies, may be unpleasant for a baby.
Shark, swordfish and marlin all contain high levels of mercury.
Drinks
Water, human milk and formula are the only recommended drinks until 1 year old.
At mealtimes offer some plain tap water in a baby-sized (shot glass size) cup. You don’t need to use bottles or spouted cups but, if you do, a free flow cup is better than one with a non-spill valve on which a baby needs to bite to get the drink to flow.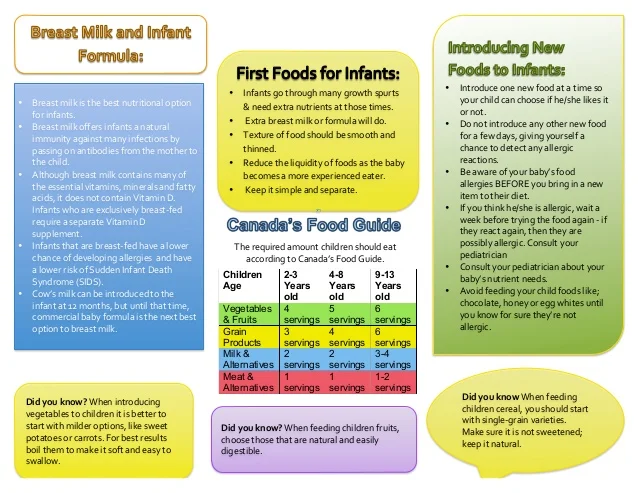
Avoid juices, sugary drinks and those with artificial sweeteners. Even unsweetened juices contain natural fruit sugars and acids that can damage teeth. They can leave no room for nutritious foods and it can be hard to limit them once you start them.
Avoid giving bottled water, which may have high mineral levels, and drinks that contain caffeine. This includes fizzy and other soft drinks, tea and coffee.
Can I offer cow’s milk as a drink?
Cow’s milk is not suitable as a drink until after 12 months. Instead offer water, human milk or formula. However, you can use cow’s milk when cooking for your baby, for example in porridge and sauces. Other dairy products can be offered to your baby as a food e.g. cheese, yogurt, cream.
After 1 year of age, cow’s milk can be given as a drink. Follow-on and toddler formulas are not necessary.
Further Reading
The Womanly Art of Breastfeeding. LLLI. London: Pinter & Martin, 2010.
My Child Won’t Eat. González, C. MD. London: Pinter & Martin, 2020.
Baby-Led Weaning The Essential Guide. Rapley, G. & Murkett, T. Experiment, 2019.
Why Starting Solids Matters. Brown, A. Pinter & Martin, 2017.
Starting Solids DVD. LLLGB, 2007.
How Weaning Happens. Bengson, D. Schaumburg, IL: LLLI, 1999.
LLLGB articles (and Leaflets & Information Sheets available from our LLLGB Shop)
Allergy and Food Intolerance
Amazing Milk
Thinking of Weaning?
Still Nursing
Toddlers and Food
Online Information
First Steps Nutrition Trust firststepsnutrition.org/ eating-well-infants-new-mums
NHS: Your baby’s first solid foods
Start 4 life nhs.uk/start4life/weaning/safe-weaning
Unicef unicef.org/nutrition
GP Infant Feeding Network gpifn.org.uk/introducing-solids/
References
1Why Starting Solids Matters. Brown, A. Pinter & Martin, 2017.
2LLLGB: Baby-led weaning and choking
3Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition. Feeding in the First Year of Life, July 2018:
4NHS: Vitamins for Children
5NHS: Vegetarian and vegan diets Q&A
how to choose and what kind of baby food is better?
The ideal "baby food" for an infant is breast milk. However, not all mothers can breastfeed their baby, usually this is due to the health of the mother or child. It happens that the woman herself has a serious condition after childbirth and in the early postoperative period, reduced lactation or diseases in which breastfeeding is contraindicated. In such cases, the baby is given formula milk - this is the only alternative to mother's milk. Subsequently, at four to seven months, complementary foods should be introduced into the child's diet, regardless of whether he is breastfed or artificial. The mother is faced with the task of choosing the right baby food for complementary foods.
In this article, we will talk about what foods for babies are and how to choose the best baby food.
Legislation under "baby food" means food products that meet the physiological needs of the body of a child under 14 years of age. And nutrition for young children is food intended for children from birth to three years[1]. It is necessary to make a diet taking into account the age of the baby and the characteristics of his physical condition.
The Union of Pediatricians of Russia created the National Program for feeding children in the first year of life and the National Program for optimizing the nutrition of children from one to three years old [2]. They describe recommendations regarding what formula to feed the baby from birth, how to introduce complementary foods and expand the baby's diet. These programs provide detailed information on what nutrients and nutrients should be included in the diet of children of different ages.
First you need to figure out what kind of baby food is [3]. Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Products for toddlers can be divided into two categories:
Infant formula. There are for children from birth to six months (formula 1 mixtures, or initial), from six months to a year (formula 2) and from a year (formula 3). The composition of such baby food is adapted, that is, as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
- In the initial mixtures, the amount of protein is reduced to 1.2-1.5 g / 100 ml - in accordance with the composition of breast milk. They also changed the fat and mineral profile. The initial mixtures are enriched with such an essential amino acid as taurine, and micronutrients, probiotics, vitamins.
- After six months, the baby's need for protein increases, mother's milk changes its composition. And babies on artificial feeding begin to be fed with a more nutritious mixture of formula 2. Taurine is no longer always needed: the body of a baby aged from six months to a year is able to synthesize this amino acid itself.
 Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished.
Meanwhile, the content of iron, calcium, zinc increases compared to the initial mixtures, because by this age the child's reserves of minerals received from the mother during pregnancy are depleted, and they need to be replenished. - A child's diet changes after one year - he is already able to eat a variety of solid foods. However, it is advisable to continue to feed him with a mixture, though already formula 3. Pediatricians recommend it as a source of vitamins and minerals that the baby can easily absorb.
Complementary foods As we have already noted, it is introduced when the baby is four to seven months old. This interval is called the "critical window" and is considered optimal for the initiation of complementary foods for several reasons:
- The baby needs a wider range of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients. In addition, his baby's digestive system is already ready to accept more solid and complex foods than mother's milk or infant formula.

- At this age, the child develops an interest in food, and it is necessary to offer him the right foods to develop his taste.
- During this period, the risk of developing a food allergy to a new product is lower.
- Timely introduction of complementary foods prevents the risk of micronutrient deficiencies and iron deficiency anemia.
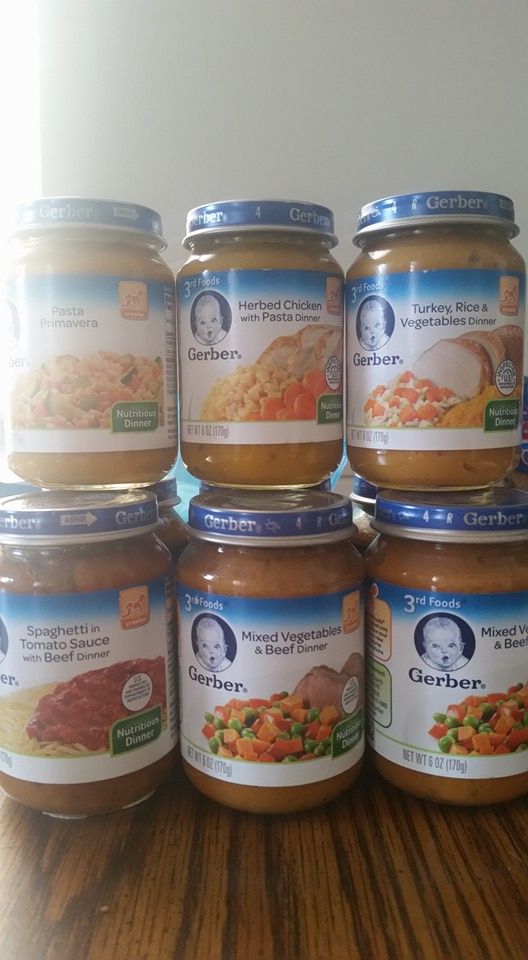
Usually the first food is vegetable puree or monocomponent gluten-free cereals, dairy or dairy-free. Over time, cereals containing gluten, supplements from fruits and berries, and also consisting of several cereals are added. A six-month-old child can already be given several types of vegetables and cereals. Also, at about six months, they begin to give meat puree, then fruit, and from eight months - fish. A child from seven months is allowed the yolk.
From the age of 12 months, complementary foods already make up the majority of your baby's diet. At this age, it is especially important to diversify the child's diet: he can be given soups with small pieces of vegetables, meat, fish and cereals.
Information
During the first feeding, the baby's eating habits are laid, and it depends on the parents how correct they will be. Often, mothers introduce fruit juices into complementary foods too early. And because babies have an innate preference for sweet tastes, they can become naughty and stop eating the unsweetened foods they need, especially vegetables. Unhealthy taste habits are formed, which can later provoke obesity.
Domestic doctors are concerned about such irrational nutrition of young children - due to the wrong approach to nutrition, many babies experience a deficiency of vitamins and an excess of fast carbohydrates.
How to choose baby foods
Finding the right foods for your baby is not an easy task. Store shelves are bursting with boxes, jars and bottles, and manufacturers write on every second package that the baby will be healthy, strong and cheerful after feeding. Of course, the baby will receive the necessary substances, no matter what product his parents choose, because all the production of baby food is strictly controlled by the state. By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
By the way, Russia has some of the most stringent requirements for the quality of baby food in the world.
However, products for children differ in their properties. It is necessary to select food so that by the end of the first year of life the baby has actively developed chewing skills and an interest in independence, and the diet of complementary foods is reasonably varied.
For children from one to three years of age, the diet should be even more varied. It is important that the child receives daily something new from the main food groups: dairy, vegetables and fruits, meat and fish, cereals, butter and vegetable oil. Of course, the baby's diet should be expanded taking into account his state of health.
When organizing the nutrition of a child from the moment of introduction of complementary foods and up to three years, a mother needs not only to know what can be fed, but also to consider what foods should not be included in the diet. Among the prohibited products for children under three years of age:
- any mushrooms, vegetables and fruits in a marinade;
- pickles, preserves in tomato sauce;
- commercial juice concentrates, carbonated drinks, coffee and strong tea;
- various condiments - mustard, ketchup, hot sauces, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise;
- products containing flavors, industrial colors, including chewing gum;
- margarine and refractory fats - lamb, pork;
- chocolates, sweets and other sweets.

To choose the right baby food, you need to know exactly what you should pay attention to and what you don't need to worry about.
When choosing mixtures, it is important to check:
- Absence of palm oil. Formula manufacturers may use palm oil (more specifically palm extract) because, like breast milk, it is rich in palmitic acid. However, in human milk, palmitic acid is in the beta position, while in palm oil it is in the alpha position. Such alpha-palmitic acid can interfere with the absorption of calcium and fats and is generally less well absorbed by the child's body. This can negatively affect the work of the intestines, lead to constipation, regurgitation. Milk fat is better suited for baby food as a source of palmitic acid[4][5].
- Protein ratio. Breast milk protein is primarily whey proteins and casein. A child needs both types of protein, while proteins are easily digested, which cannot be said about casein.
 If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool.
If baby food contains a lot of casein, it stays longer in the digestive tract, which can cause problems with the baby's stool. - The presence of additional functional elements in the composition - lutein, nucleotides, pre- and probiotics. The task of lutein is to protect vision from ultraviolet rays. Nucleotides are low molecular weight compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bifidobacteria in the intestines. And pre- and probiotics in the composition of infant formulas help to establish comfortable digestion.
When choosing complementary foods, pay attention to:
- Age appropriate. It is important that in the diet of a child under three years of age who receives complementary foods, special children's products predominate - in their composition the components are selected taking into account the age-related needs of the baby's body. It is impossible at an early age to transfer children to "adult" foods like pickles, smoked foods, fast food, and so on.

- Fortified products. It is important that the composition contains vitamins and minerals. The National Child Nutrition Optimization Program recommends choosing complementary foods that contain elements designed to prevent anemia, rickets, and vitamin deficiencies.
- For a varied diet. The menu for a baby up to six months is quite monotonous. But as they grow older, the baby needs more various nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals.
- For the individual reaction of the baby. If the child is already receiving complementary foods, then it is worth introducing a new product only after the previous one has been fully introduced. If the baby is allergic to the product, then it should be administered carefully, carefully checking the reaction of the body.
Ingredient safety testing is optional. Of course, the content of any "chemistry" in the product for feeding a child, whether it be a mixture or complementary foods, is unacceptable. There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
There is no need to worry about this: baby food is carefully checked. If it is registered on the territory of the Customs Union and hit the shelves, then it complies with SanPiN 2.3.2.1940-05 and there will be no "prohibited" components in its composition. Also, contrary to popular misconception, in Russia it is forbidden to use GMOs in children's products.
Note
Baby food in jars (usually mashed potatoes) has a short shelf life after opening because it does not contain preservatives. However, before the jar is opened, the products can stand for quite a long time on the shelves of stores or in the refrigerator at home. This is possible thanks to a special production technology, sterilization and vacuum packaging. If a soft pop is heard when opening the jar, this is a good sign: the puree is not spoiled. But products in jars with swollen lids or a protruding bottom should not be used: microorganisms already multiply in such food, it is not suitable for food.
Features of the choice of dairy products
It is necessary to choose dairy products for babies, following the doctor's recommendations. The specialist will take into account the health of the baby, especially if he is allergic to cow protein. In Russia, such an allergy occurs in 30–40% of children [6]. Such a reaction may occur due to hereditary predisposition and immaturity of the body. But most often, allergies go away when the child grows up.
Goat milk baby food may be a suitable option for young children with a predisposition to allergies. Its protein is perceived by the body better than cow's: alpha-s1-casein, contained in large quantities in cow's milk, makes a product based on it difficult to digest - food stagnates in the baby's gastrointestinal tract, motor skills are disturbed, as a result, allergies often occur. In goat milk, as in breast milk, there is practically no alpha-s1-casein [7]. Therefore, goat's milk, and hence the mixture based on it, are better absorbed.
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, other dairy products will appear in the baby's diet. Unadapted fermented milk drinks, such as kefir, yogurt, biolact, can be introduced into the diet from eight months and in an amount not exceeding 200 ml. Also during this period, it is recommended to give cottage cheese - no more than 50 g per day, but according to indications, it can also be prescribed from the age of six months. Whole milk cannot be used as the main food, and it is advised to introduce it into the diet of babies no earlier than a year (in the amount of 100-150 ml per day) [8]. As mentioned above, it must be adapted infant milk or formula 3 formula.
To choose the best baby food, it is necessary to take into account the health of the baby, his tastes, as well as individual reactions of the body. Therefore, before going to the store, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will not only tell you which baby food to choose, but also give recommendations on how to make the child's diet balanced and healthy.
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its administration is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc. ). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can we wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start introducing complementary foods to a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.
The first complementary foods can be vegetable puree or porridge, it is better to give fruit puree to the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, and before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually “dilute” this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up on your plan and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children with food allergies are introduced to complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens. From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started to receive complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml | |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Breast milk supplement or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI  :
:
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk