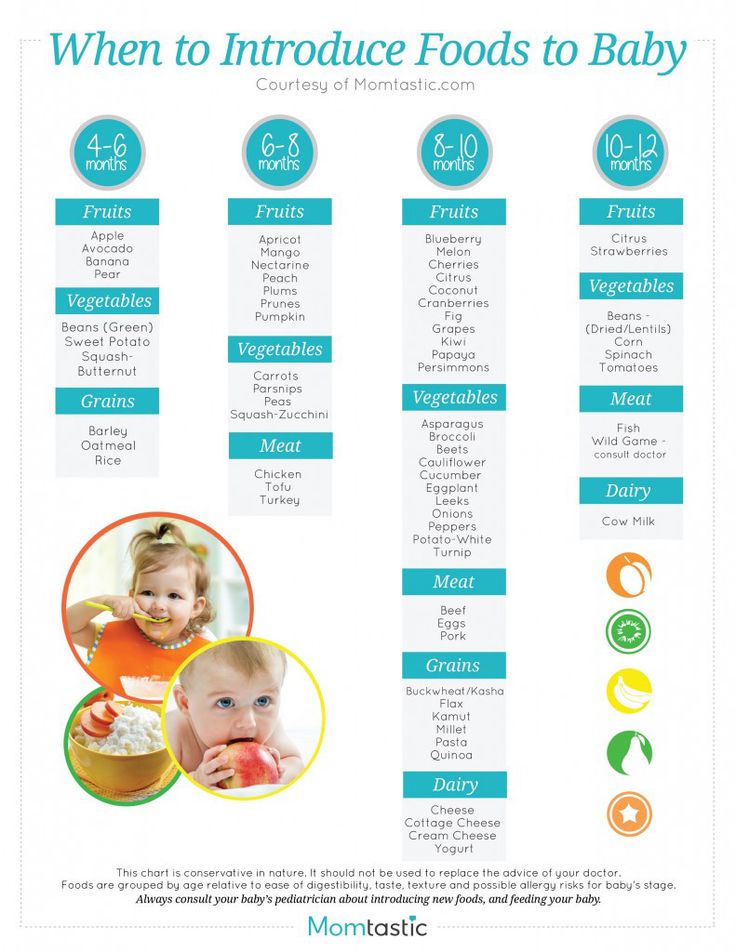
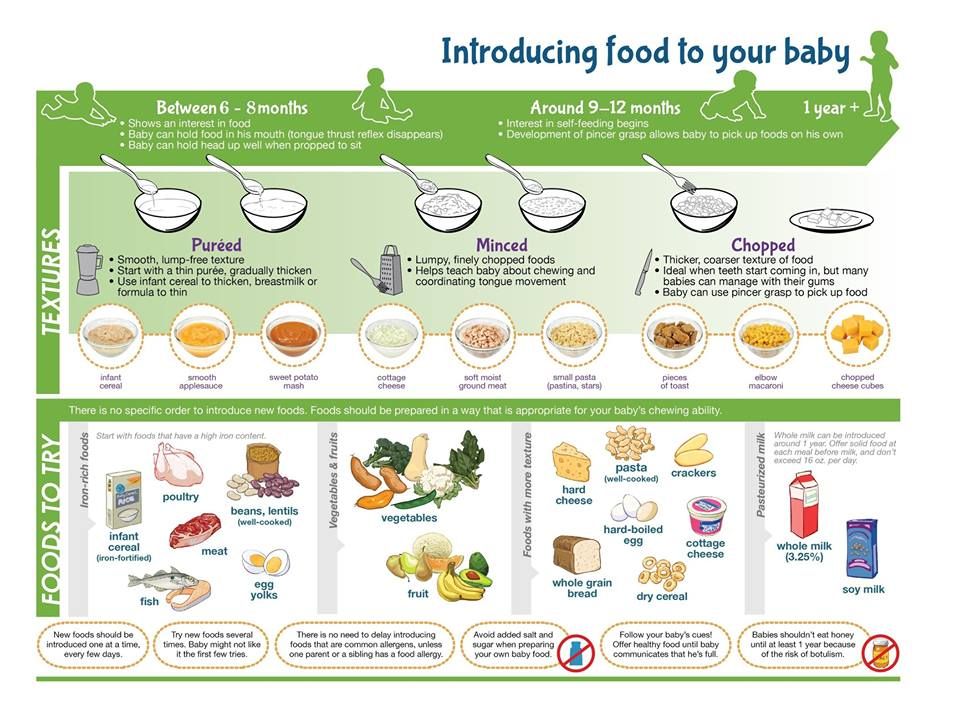
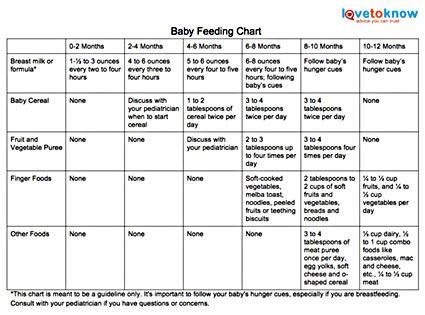
When to start feeding baby fruits and vegetables
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
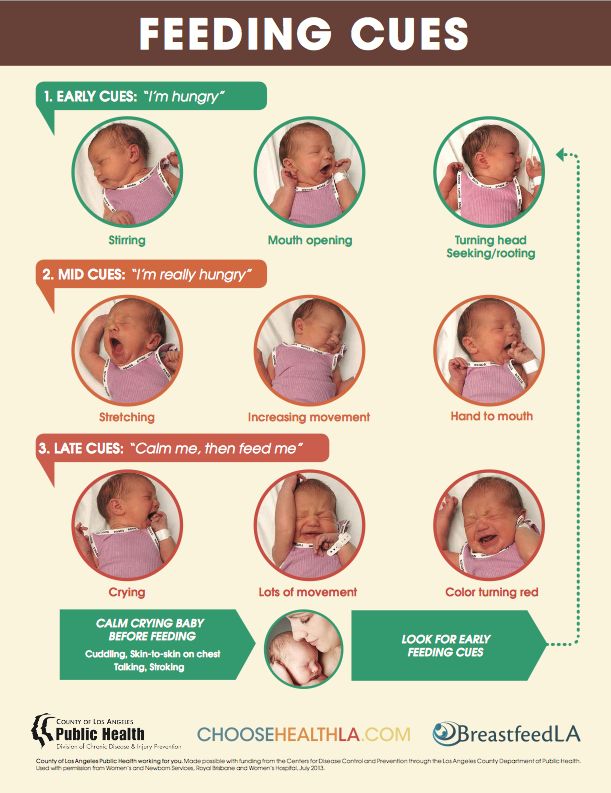
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula.
 It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese. - foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.
- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods.
 (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
(Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.) - After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
Vegetables and fruits for the baby. When and what to give?
Babies grow fast and therefore need a lot of nutrients. By the age of 6 months, usually, the baby receives everything he needs with his mother's milk or formula. But this is only up to 6 months of age, and then, according to WHO recommendations, the child's diet should be supplemented with complementary foods.
The first foods offered to a child at 6 months of age may be cereal, vegetable or fruit puree. nine0003
Regarding the introduction of vegetables and fruits, there are different opinions about what is better to give first: vegetables or fruits.
Vegetables or fruits?
Pediatricians often recommend starting your baby's introduction with mashed vegetables, because fruit is sweeter and some children may then refuse vegetables. In fact, it is very individual. An important argument in favor of vegetables is the fact that fruits are not the main meal and, therefore, they can be offered as a snack, dessert, or added to cereals and sour-milk products. nine0003
nine0003
But vegetable puree is introduced into the baby's diet as a main dish, to which meat will be added later.
To get the most out of new foods, no matter what kind, introduce them to your baby in the right way.
How to choose fruits and vegetables for a baby?
For the first acquaintance, it is advisable to use the vegetables of our climatic zone: zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, pumpkin, potatoes, squash. Give preference to seasonal vegetables. You need to start with one type of vegetable, and only after the child has received each of them separately, you can mix them. nine0003
Pediatricians recommend apples, peaches, apricots, plums as the first fruits.
What is better to choose: mashed potatoes in jars or cook it yourself?
There is no unequivocal opinion on this issue either among doctors or mothers.
Many people find that homemade vegetable or fruit puree is healthier because it retains nutrients, vitamins and minerals better.
Another part of the experts argue that modern growing conditions do not guarantee the safety of fruits and vegetables for young children, as they may contain a large amount of nitrates or pesticides. nine0003
Unfortunately, if vegetables and fruits are not from your own garden and you do not know where and how they were grown and how they were processed, then it is better to give preference to children's vegetable or fruit puree from jars.
Preference is given to industrial purees even when the beginning of acquaintance with vegetables and fruits falls outside the season of vegetables and fruits. If winter and zucchini are only imported, and apples have been stored in vegetable stores for quite a long time, then they are unlikely to be safe for a small child. nine0003
According to modern requirements for baby food products, vegetables and fruits for baby foods of industrial production are grown in special raw materials zones without the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Modern production technologies make it possible to preserve vitamins and minerals as much as possible and provide the necessary consistency, in accordance with the characteristics of the digestive system and chewing apparatus of the baby.
Modern production technologies make it possible to preserve vitamins and minerals as much as possible and provide the necessary consistency, in accordance with the characteristics of the digestive system and chewing apparatus of the baby.
Industrial purees also allow you to choose your baby's favorite vegetable or fruit, regardless of the season. nine0003
If you have your own garden and grow organically, you can confidently prepare vegetable and fruit dishes at home.
How to prepare vegetables and fruits for a baby at home?
When preparing vegetables and fruits, observe the following rules:
- select only good, undamaged, fresh vegetables and fruits
- Wash them thoroughly before cooking
- cook just before feeding your baby. nine0054
For a child of the first year of life, vegetables are boiled or cooked in a double boiler without salt and pepper. Grind with a blender or carefully grind to a homogeneous creamy consistency. If the puree is too thick, you can add a little vegetable broth in which the vegetables were boiled.
If the puree is too thick, you can add a little vegetable broth in which the vegetables were boiled.
Vegetable puree is given warm, the optimum temperature of the puree for feeding is 37 - 38ºС.
Fruit can be given fresh or baked in the oven. But like vegetables, fruits should be chopped and peeled. nine0003
Fruit can be grated on a plastic grater or chopped in a blender. The grater or blender must be poured over with boiling water before preparing the puree!
When the child has 6-8 teeth, you can give a piece of fruit and he will eat it on his own.
Remember not to chase exotic fruits as they can cause an allergic reaction in your baby. Useful substances are better absorbed from fruits that are traditional for our climatic zone.
How many fruits and vegetables does a baby need?
A child can eat only a certain amount of vegetable and fruit puree per day in order to avoid indigestion. This amount depends on the age of the baby.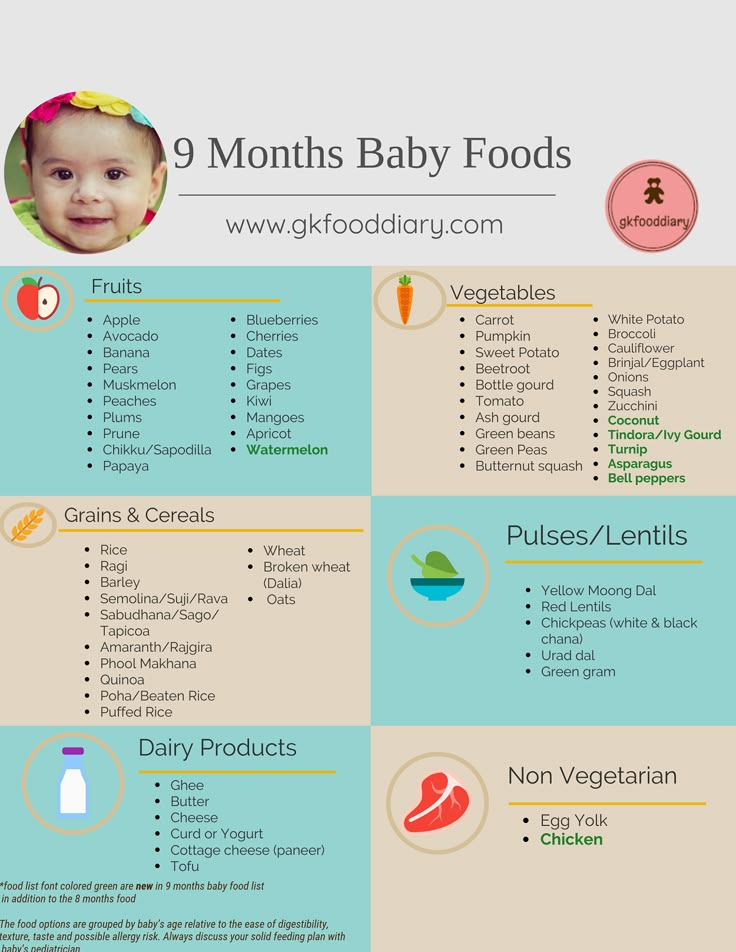
Approximate recommended daily intake of vegetable puree is
50-100g for a 6 month old baby, 150g for a 7 month old baby, 170-180g for a 8-9 month old baby, and from 10 to 12 months the amount of vegetable puree can be increased up to 200 g *. nine0003
Your pediatrician will help you determine the right amount of puree for your baby.
But, regardless of the age of the child, acquaintance with each new product should begin with no more than 1 teaspoon and gradually increase to the recommended age norm!
A child needs 2 times less fruit purees than vegetables.
Children at 6 months can consume 40-50g of fruit puree, at 7-8 months - 50-70g, at 9-12 months - 80-100g *. nine0003
What to combine vegetables and fruits with?
Vegetable and fruit purees are low-protein complementary foods, therefore they are given as an independent dish for no more than 2 weeks, then it is necessary to enrich them with high-protein foods.
Pediatricians recommend combining vegetable puree with meat supplements, thanks to which the baby will receive a rational, easily digestible lunch.
Fruit is good to combine with soft cheese, if it has already been introduced into the baby's diet, or added to milk or dairy-free cereals. nine0003
TM "Malyatko" offers different flavors of vegetable and fruit purees. Our purees are made from vegetables and fruits grown in our own fields in compliance with all the requirements of organic farming.
They are ready to use, so you will have more time to spend with your baby.
Malyatko - the basis of health for life!
*Clinical protocol for the care of a healthy child under 3 years of age
Complementary foods - introduction of fruit puree, fruits and juices into the baby's diet
Historically, fruit juice was recommended by pediatricians as a source of vitamin C, calcium, and other vitamins. The juice is delicious, sweet, children drink it with pleasure, and suddenly it turned out that there are potential risks: the high sugar content in the juice increases calorie intake, overweight and the risk of caries. More recently, about twenty years ago, doctors recommended the introduction of complementary foods, starting with juices and fruits. But now the situation has changed. Children's nutritionists believe that the optimal time for the introduction of juices is 1 year after the child gets used to the main complementary foods: vegetables, cereals, meat, fish, fruits. At the same time, you can find recommendations to give juices from 6 months or after 3 years. Carbohydrates, which are abundant in juice, change the child's appetite, but to get the required amount of vitamins, you need to drink a lot of it, about 1 liter! In addition, they do not give a feeling of satiety and the child may be prone to overeating. nine0003
The juice is delicious, sweet, children drink it with pleasure, and suddenly it turned out that there are potential risks: the high sugar content in the juice increases calorie intake, overweight and the risk of caries. More recently, about twenty years ago, doctors recommended the introduction of complementary foods, starting with juices and fruits. But now the situation has changed. Children's nutritionists believe that the optimal time for the introduction of juices is 1 year after the child gets used to the main complementary foods: vegetables, cereals, meat, fish, fruits. At the same time, you can find recommendations to give juices from 6 months or after 3 years. Carbohydrates, which are abundant in juice, change the child's appetite, but to get the required amount of vitamins, you need to drink a lot of it, about 1 liter! In addition, they do not give a feeling of satiety and the child may be prone to overeating. nine0003
Administering fruit juice American Academy of Pediatrics recommendations: download
- Optimal completely avoid the use of juice in infants up to 6 months;
- AAP and the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry guidelines state that juice should be offered to babies in a cup, not a bottle, and that babies should not go to bed with a bottle in their mouth.
 nine0054
nine0054 - They concluded that long-term exposure of the sugar contained in the juice to the teeth is the main factor influencing dental caries.
- After 1 year, fruit juice can be used as part of a meal or snack. It should not be drunk like water during the day or used as a means to calm an upset child.
- Do not give juices if the child has diarrhea, oral rehydration solutions only.
- The development of perioral rash in some children after feeding freshly squeezed citrus juice is most likely due to the chemical irritant effect of the acid. nine0054
- Diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms that some children experience are most commonly associated with carbohydrate malabsorption.
- Although fruit allergy can develop at an early age, this is rare.
Baby food - fresh juices
Freshly squeezed juices are not recommended for children under one year of age. But there is no strict ban. Juice up to a year is not useful, unlike children older than one year . It contains a lot of fruit acid, which can lead to increased peristalsis and intestinal walls, pain, and digestive disorders. Dilute with water in a ratio of 1:1. And remember, fresh juice retains its maximum amount of vitamins in the first half hour, so do not store juice for later. With a later introduction of juice, their better tolerance is noted. This is due to the maturation of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract and its readiness for the absorption of juice. But even with this, the child may experience pain and bloating, regurgitation, and stool disorders. This is due to the presence of organic acids in juices, which have an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal tract. nine0003
It contains a lot of fruit acid, which can lead to increased peristalsis and intestinal walls, pain, and digestive disorders. Dilute with water in a ratio of 1:1. And remember, fresh juice retains its maximum amount of vitamins in the first half hour, so do not store juice for later. With a later introduction of juice, their better tolerance is noted. This is due to the maturation of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract and its readiness for the absorption of juice. But even with this, the child may experience pain and bloating, regurgitation, and stool disorders. This is due to the presence of organic acids in juices, which have an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal tract. nine0003
How do I start adding juice to my baby?
First, a teaspoonful (about 5 ml) between feedings, observing the baby's reaction. For children under 3 years old, juices are recommended to be diluted with boiled or baby water in a ratio of 1:2. Freshly squeezed juices - up to 7-8 years. The amount of juice: from 1 year to 1.5 years - up to 100 ml, should not be exceeded. At 2 years - 200 ml.
The amount of juice: from 1 year to 1.5 years - up to 100 ml, should not be exceeded. At 2 years - 200 ml.
First, it is better to give the juice of green apples or pears. Juice from plums, apricots, peaches - it is better to give at an older age, they have a slight laxative effect. nine0003
Then you can give a mixture of juices from 2 or 3 fruits. You can give a mixture of cherry, cherry, currant, raspberry juice, orange juice, pineapple, mango, grapefruit and mixtures thereof. It is better to give grape juice from 5-6 years old, there are a lot of carbohydrates.
It must be remembered that:
- Apple, carrot and pear juice - strengthen
- Plum, pumpkin, apricot, peach - weakening
This can be used if there are digestive problems.
If we choose industrial juices - carefully read what is written on the label, there should be no artificial additives, dyes and preservatives. Do not use opened packages. Should I give industrial juices for baby food? Why not? They are made from high quality, proven, specially selected raw materials, production is strictly controlled, they have balanced compositions and optimal taste. Until the age of 3, buy juices for your child only marked “baby food” on the package. nine0003
Do not use opened packages. Should I give industrial juices for baby food? Why not? They are made from high quality, proven, specially selected raw materials, production is strictly controlled, they have balanced compositions and optimal taste. Until the age of 3, buy juices for your child only marked “baby food” on the package. nine0003
Introduction of fruit and fruit puree - European recommendations
If your young child has already tasted vegetables and accepted them, it's time for fruit. The season is always for them, but the best is in autumn, when the most delicious apples, pears and plums appear. Fresh fruits from all over the world are available in stores all year round, but it's worth starting with seasonal, locally grown ones. And these are: apricots, raspberries, apples, pears, plums. They contain not only vitamins, dietary fiber, but also minerals, including valuable microelements, which should be present in the child during the expansion of the diet. nine0003
nine0003
Fruit is usually recommended from 6-7 months of age. Complementary foods often begin with fruit or vegetable purees. But it is better to start with vegetables. Fruit puree tastes better, is sweeter, and the child may then eat vegetables worse. But vegetable puree will not affect the baby's desire to eat fruit dishes. Therefore, more often pediatricians are advised to give fruit dishes after the introduction of vegetables and cereals. Start complementary foods with fruits in the form of mashed apples or bananas or pears. Then you can add fruits that grow in your area of \u200b\u200bresidence. Then you can include fruit and fruit and vegetable mixtures. nine0003
Fashionable but exotic fruits or with strong flavors - strawberries, mangoes, kiwis, currants - should be introduced later. But there is no strict ban.
Fruit puree should be started with 1 teaspoon in the morning, increasing to 100 g over 2 weeks.
Homemade or factory made? As you wish, subject to the basic hygiene rules of cooking. If you have time, make your own fruit puree. Plums, apricots, banana can be mashed in a mortar or blender. Grate apples and pears on a fine plastic grater. For the first time, the apple can be boiled, then it will be soft. Pour the prunes with boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. nine0009 Do not add sugar!
If you have time, make your own fruit puree. Plums, apricots, banana can be mashed in a mortar or blender. Grate apples and pears on a fine plastic grater. For the first time, the apple can be boiled, then it will be soft. Pour the prunes with boiling water and leave for 15 minutes. nine0009 Do not add sugar!
Homemade fruit puree - don't forget about hygiene
Pour boiling water over a grater, preferably a plastic one or a blender, wash and peel the fruit.
Gradually make the fruit puree coarser.
Start with liquid puree, at 8 months - finely ground puree, at 10 months of age. - puree from larger particles.
When the child has 6-8 teeth, you can give pieces of fruit and he will eat them on his own. nine0003
Properties of various fruit purees
- Banana puree is a good source of trace elements: magnesium and potassium, calcium, iron and phosphorus.
 Bananas rarely cause allergic reactions
Bananas rarely cause allergic reactions - Prune puree can act as a mild laxative that increases intestinal motility. Contains potassium, vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin).
- Blueberry puree contains a tannin - tannin, contains pectin, which has a disinfectant and anti-inflammatory effect, contains a large amount of provitamin A - beta-carotene, which is good for vision, manganese. In addition, blueberries are low allergenic. Apricots are an excellent source of potassium, carotene, vitamin C and pectin.
Advice from the Nyankovskikh Healthy Child University
- Fruits are sweet and can be used instead of sweets. nine0054
- Fruits should be included in the child's diet as the second food group after vegetables. They can be given quite early, when the baby is four months old (between 17 and 26 weeks of age).
- Initially it can be a mousse (or puree from a jar) and then an apple scraper with a spoon.