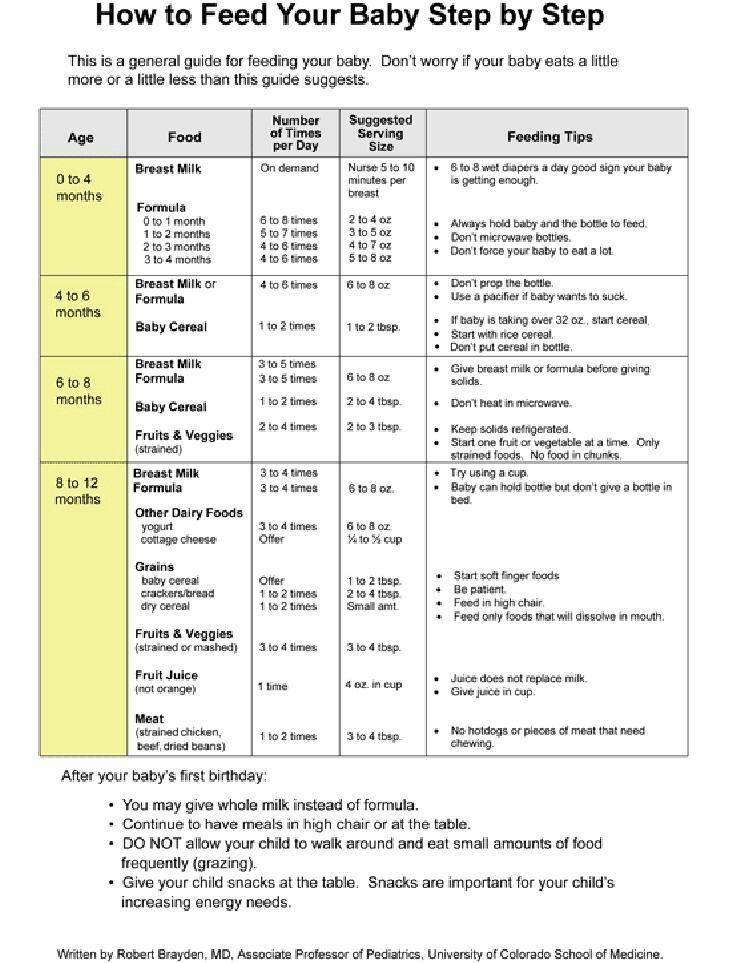
When to start feeding baby more formula
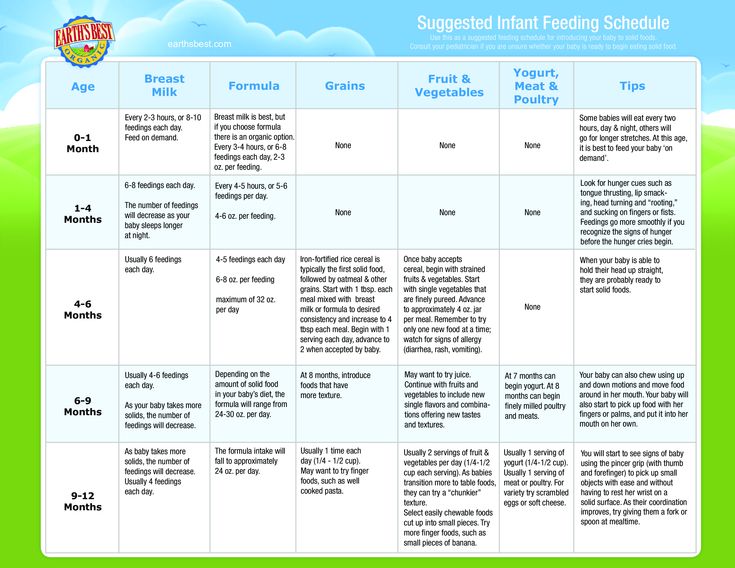
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day. Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough. If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings. They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique.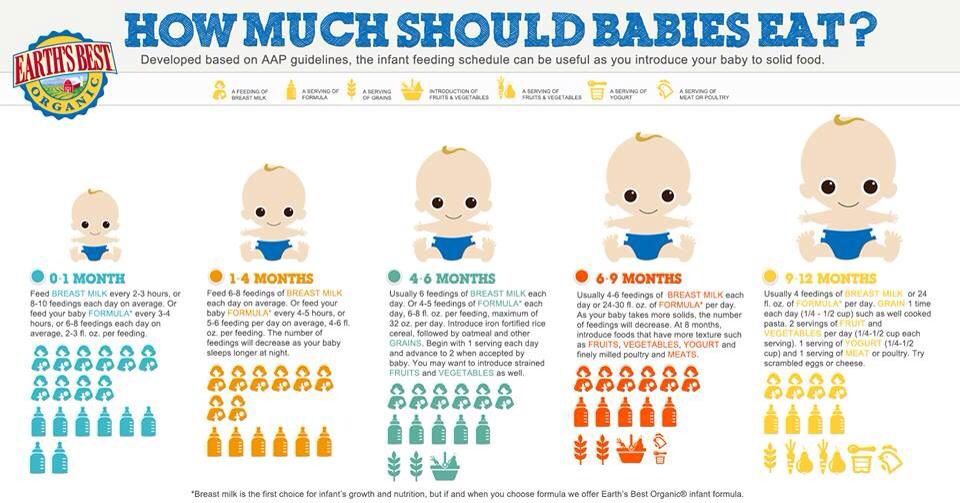 No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Last Updated
- 5/16/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).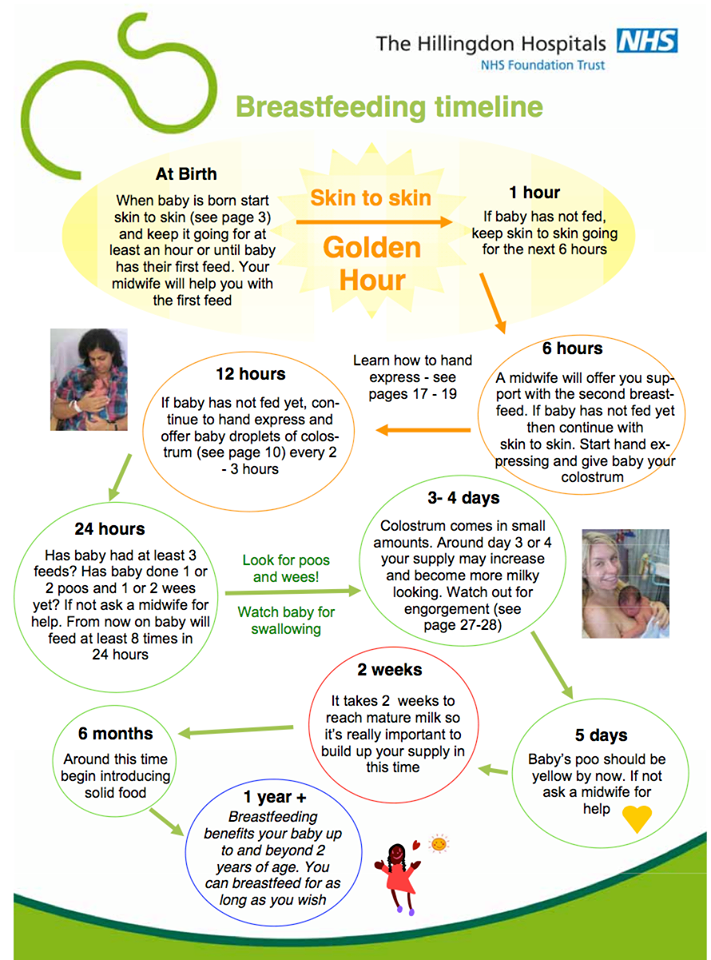
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.
 5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding. - At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.
Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.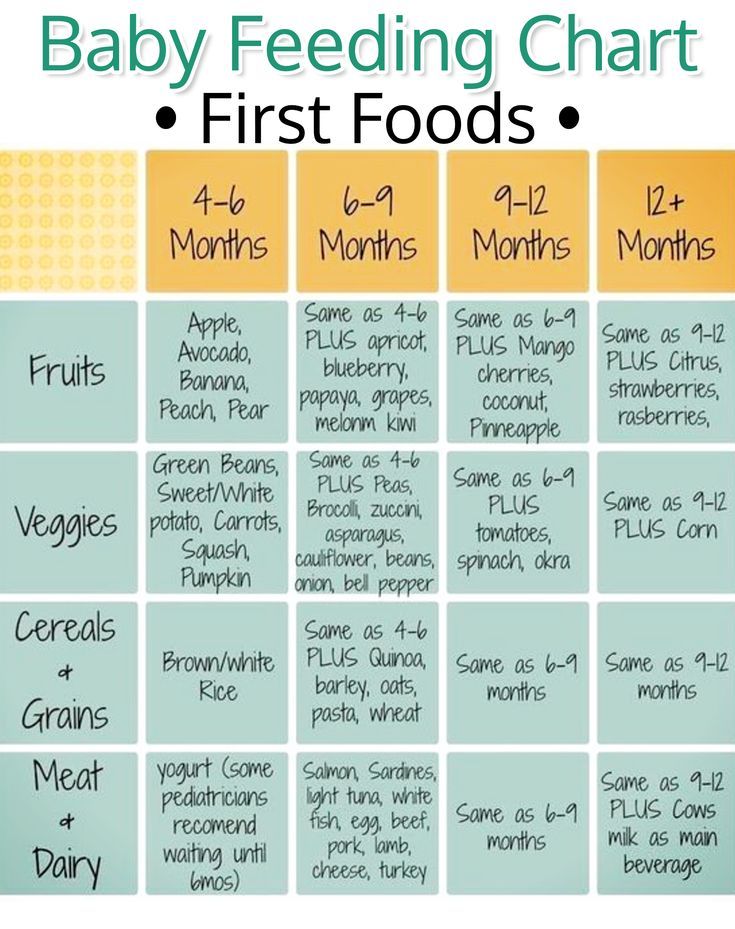
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
feeding rules, types of mixtures, tips for breastfeeding mothers
If breastfeeding is not possible, do not be upset: modern technologies make it possible to achieve maximum compliance of artificial feeding with all healthy nutrition standards. We talk about the basic rules of artificial feeding and common mistakes.
Website editor
Tags:
Health
weight loss
Children
Food
VOICE recommends
The health of a newborn is directly dependent on his nutrition.
⚡️⚡️⚡️ TO STAY CONNECTED NO matter what, LOOK FOR US IN Yandex.Zen, VK, Telegram, Odnoklassniki.
If you can breastfeed, great, it's the best food for your baby. But if for some reason natural feeding is not possible, this is not a reason to panic: there are now many healthy mixtures that can replace mother's milk. Study our rules for artificial feeding, and everything will work out!
When to switch to artificial feeding
- Inability to breastfeed for medical reasons. With some diseases, as well as when taking a number of medications, breastfeeding is prohibited, since milk can be dangerous for the baby due to the content of toxic substances. Sometimes the reason to stop breastfeeding may be the child's disease (for example, cleft lip or severe malformations).
- Cessation of lactation. If there is not enough milk or it has disappeared completely, there is nothing to do, you need to supplement the baby with mixtures.
 As a rule, mixed and artificial feeding solve the problem.
As a rule, mixed and artificial feeding solve the problem. - Impossibility of regular feeding. For example, you can go to work or end up in a hospital, and this is not a reason to starve a child, but a reason to switch to mixed or artificial feeding: the rules for feeding and portion sizes change somewhat.
- Inadequate nutritious milk from the mother. Sometimes the problem is solved by changing your diet, but if the milk remains watery and the baby is screaming with hunger, then it's time to supplement him with mixtures, and later switch to them completely.
- The wish of the child's mother. No matter how pediatricians talk about the benefits of breastfeeding, sometimes women who have every opportunity to breastfeed still prefer to give their baby a bottle. Well, that's your right. Just learn first the rules of artificial feeding of infants!
Rules for artificial feeding of a child
It is best to consult a pediatrician, but in principle, if the baby is not lactose intolerant, any mixture approved by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia will do.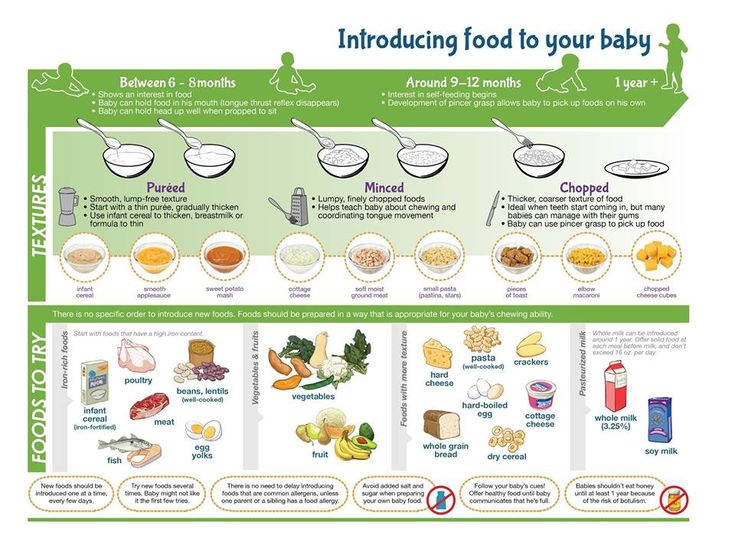 It is great if the mixture contains Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids, they contribute to the harmonious development of the nervous system.
It is great if the mixture contains Omega 3 and Omega 6 fatty acids, they contribute to the harmonious development of the nervous system.
For example, Nutricia's "Malyutka" formula meets all the standards and rules of artificial feeding, is produced according to European technologies with the strictest quality control and is recommended as an alternative to breast milk even for newborns. Nutricia regularly evaluates the quality and demand for its products among consumers and doctors, analyzing the results of independent surveys of pediatricians and mothers with children up to 24 months of age.Iodine, selenium, zinc, iron with enough vitamin C (for better absorption), choline, taurine, L-carnitine are modern ingredients, the amount of which is specially selected in formulas to meet the needs of children.The quality is monitored by the Dutch research center Numico, the milk base for formulas is made in the most environmentally friendly country - Ireland, and production is open in Russia, at a plant in Istra, which received the international ISO 22000 certificate - maximum food safety control who in.
Bibikol New Zealand brand mix is made on the basis of wholesome goat milk. The range of the brand includes mixtures for the smallest and older children, and the quality of the products is confirmed by Russian pediatricians. As a rule, formula feeding does not cause serious side effects even during the adaptation period.
The Dutch brand Kabrita also makes milk formulas based on goat's milk, which is easier to digest than traditional cow's milk. The brand's products contain vitamins, microelements and other functional ingredients necessary for the development of the child.
The mixes of another Dutch brand, Friso, are considered among the best due to their high quality. The brand offers mixtures for both newborns and older children. Subject to the rules for artificial feeding, this is an excellent choice for babies of different ages.
2. How do I know if formula is right for my baby?
If possible, the transition to artificial feeding should be done according to the rules, gradually replacing breast milk with formula. Pediatricians believe that adaptation to a new diet in babies under the age of one year takes from 3 to 7 days. During this period, stool changes, gas formation are possible, and this should not be frightened. As a rule, after a week, the baby stops worrying about the tummy and gets used to the new mixture. If this does not happen, it is worth choosing another food for him. For example, instead of the usual milk mixture, offer a fermented milk analogue. Major brands, like Nutricia's Malyutka, always have both options in their product line.
Pediatricians believe that adaptation to a new diet in babies under the age of one year takes from 3 to 7 days. During this period, stool changes, gas formation are possible, and this should not be frightened. As a rule, after a week, the baby stops worrying about the tummy and gets used to the new mixture. If this does not happen, it is worth choosing another food for him. For example, instead of the usual milk mixture, offer a fermented milk analogue. Major brands, like Nutricia's Malyutka, always have both options in their product line.
Formula milk can be used from birth
To improve digestion, a pediatrician can recommend cultured milk formula for formula feeding
3. How to choose a feeding bottle?
Feeding bottles come in plastic and glass, and each option has its own advantages, there are no strict rules for artificial feeding in this regard. Plastic ones are safer because they don't break. They are lighter, so it is convenient to take them with you for a walk. Glass is good because it can be sterilized many times, while plastic can deteriorate. Which bottle to choose for a newborn depends on the age of the baby. For the smallest, glassware is better, since sterility is in the first place. For older babies outside the home, it is better to use plastic bottles, but for home feeding, still leave glass bottles.
Glass is good because it can be sterilized many times, while plastic can deteriorate. Which bottle to choose for a newborn depends on the age of the baby. For the smallest, glassware is better, since sterility is in the first place. For older babies outside the home, it is better to use plastic bottles, but for home feeding, still leave glass bottles.
4. How to properly store baby food?
Prolonged exposure to non-standard temperatures, both low and high, can change the organoleptic properties of the product, affect its solubility, and cause swelling of the foil bag or the protective membrane of the can. In case of repeated heating and cooling of the mixture, especially in winter, further use of the product may cause a painful reaction in the child. Therefore, it is very important to observe temperature control from 0ºС to +25ºС. Formula feeding regulations do not recommend storing product near heat sources such as stoves, electric kitchen appliances, radiators, or on windowsills.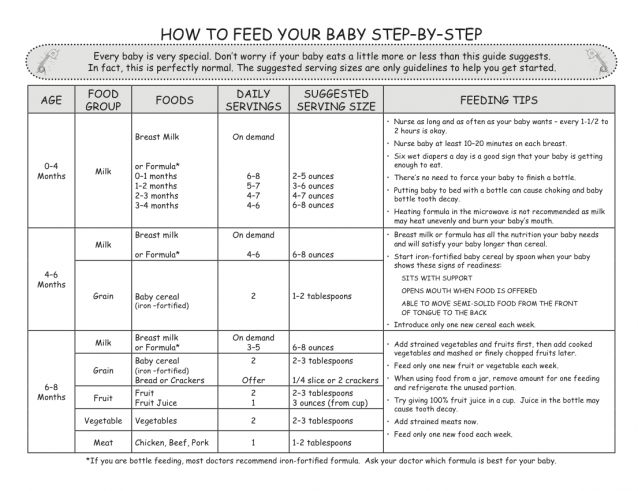
5. How long can I keep formula formula?
Less than an hour. If the baby has not finished eating, and you intend to finish feeding him in 15-20 minutes, you can not prepare a new mixture. But if the baby has eaten enough, and the feeding regimen for artificial feeding provides for the next feeding only after 2.5 - 4 hours, then the leftovers should be poured out, and a new portion should be prepared for the next time.
6. Does my child need probiotic formula?
GOS/FOS prebiotics are natural dietary fibers similar in composition to breast milk prebiotics, they are added as high-quality mixtures to improve digestion. The child quickly and painlessly gets used to such a mixture, absorbs it well and encounters stool disorders less often. Rules for artificial feeding of newborns and older children recommend giving preference to such mixtures, although this is not a strict requirement.
7. How do you know if your baby is eating enough?
You can use the Shkarin formula: The volume of the mixture per day = 800 ml + 50 x (M-2), where M is the number of months of the child's life. But this method is only suitable for babies older than 2 months. For newborns, everything is very individual, since babies are born with different weights and heights, so if you are afraid that the baby is malnourished or overeating, consult a doctor before feeding the baby formula again.
8. Should I change my formula?
If there is no reason to doubt the quality of the mixture and its tolerance by the baby, you should not change your child's usual diet just because the new mixture seems more useful, modern, etc. to you. Replacing the mixture can be a real stress for the child's body. And there is no guarantee that a new diet will not cause any signs of intolerance. Replacing the mixture is justified when passing the next age limit, and even in this case, the rules for artificial feeding recommend remaining faithful to one manufacturer.
9. What is the correct way to mix?
According to the rules of artificial feeding, most mixtures are prepared as follows: cool boiled water to a temperature of 50-60 ° C (a higher temperature cannot be used, live bifidobacteria die and some vitamins are destroyed). Pour it into a bottle, add the exact amount of the dry mixture there. Close the bottle, mix the mixture thoroughly, shaking the contents of the bottle. Look at the light so that there are no lumps, the milk should turn out homogeneous. To check the temperature of the food - put a few drops on your wrist or elbow crease (the most sensitive place). The mixture should be slightly warmer than body temperature—i.e. practically not felt.
10. Technique and rules of artificial feeding
How to formula feed correctly? In order to make it comfortable not only for the baby, who should be in a semi-vertical position, but also for the mother during feeding, you can use additional pillows by placing them under the back. The position of the mother's legs can be different: you can put your foot on the foot, you can put a low bench under your feet, you can feed the baby in the prone position, while gently holding the baby. To reduce air swallowing, tilt the bottle so that the milk fills the nipple and the air rises to the bottom of the bottle. Hold your baby upright for a few minutes after feeding to reduce the chance of spitting up.
The position of the mother's legs can be different: you can put your foot on the foot, you can put a low bench under your feet, you can feed the baby in the prone position, while gently holding the baby. To reduce air swallowing, tilt the bottle so that the milk fills the nipple and the air rises to the bottom of the bottle. Hold your baby upright for a few minutes after feeding to reduce the chance of spitting up.
Mistakes in artificial feeding
- Blame yourself for being an "artificial" baby. Yes, mother's milk is considered the best food for babies, but if for some reason you cannot provide a child with them, this is not a reason to declare yourself a bad mother. Numerous children were bottle fed and did not experience any fatal consequences. Learn the rules of artificial feeding and follow them without blaming yourself needlessly.
- Feed on demand. Artificial feeding rules suggest feeding by the hour, not on demand.
 The mixture is digested longer than mother's milk, so it is important to withstand breaks between feedings.
The mixture is digested longer than mother's milk, so it is important to withstand breaks between feedings. - Ignore the rules for the introduction of complementary foods when artificially fed. Do not introduce complementary foods earlier than at 6 months, and be sure to consult with your pediatrician beforehand.
- Forgetting to drink water. For high-quality assimilation of mixtures, water is necessary! Be sure to let the baby drink.
- Feeding regular milk instead of formula. Neither cow's nor even wholesome goat's milk is suitable for children. Use only special formulas and follow all the rules of artificial feeding that we have talked about.
Artificial feeding - Healthy Russia
In some situations, breastfeeding is not available and the baby has to be switched to formula. How to set it up correctly?
Sometimes there are situations in which the mother cannot breastfeed the child and it has to be transferred to artificial feeding.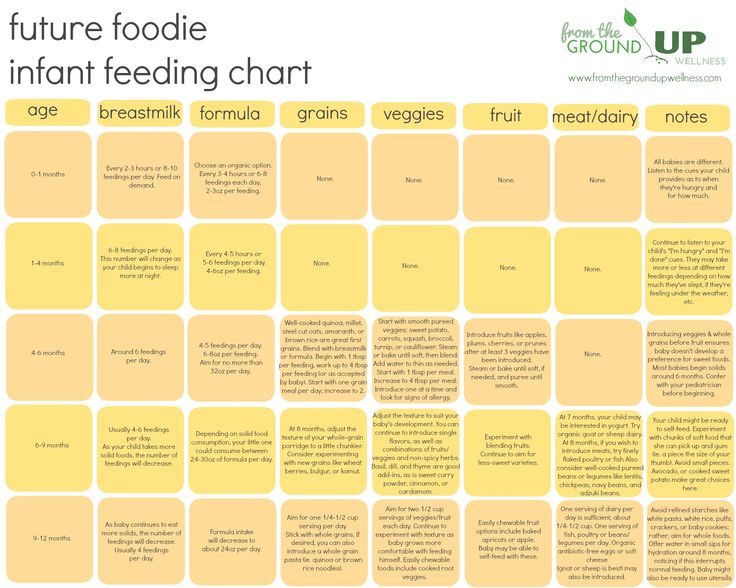 How to properly set up this process?
How to properly set up this process?
When to stop breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is a completely natural process for every woman. It provides not only nutrition for the baby, but also his emotional contact with his mother. If a woman is healthy, breastfeeding is easy. But there are cases in which a mother has to refuse breastfeeding: - when taking certain medications, - with prolonged stay in the hospital and surgical operations, - with infectious diseases, - with diseases of the mammary glands, - due to a long trip, - with prolonged absence of lactation.
What to feed
Human breast milk is ideally formulated for the needs of the baby. Therefore, it cannot be fed with whole cow's or even goat's milk. Their composition is very different from human milk and leads not only to indigestion in a child, but also to growth and development problems. For artificial feeding of a baby, special adapted mixtures are intended, the composition of which manufacturers try to bring as close as possible to a woman's breast milk. They usually include whey proteins, casein, lactose, a composition of vegetable oils, as well as minerals and vitamins that meet the needs of the child at certain periods of his development. The specific mixture is selected only by the pediatrician, depending on the health of the baby. Parents should not independently choose adapted mixtures based on their own preferences or financial capabilities without first consulting a specialist.
They usually include whey proteins, casein, lactose, a composition of vegetable oils, as well as minerals and vitamins that meet the needs of the child at certain periods of his development. The specific mixture is selected only by the pediatrician, depending on the health of the baby. Parents should not independently choose adapted mixtures based on their own preferences or financial capabilities without first consulting a specialist.
What to buy
- Purchase pediatric recommended formula . Buy it at a pharmacy or specialty store. When buying, be sure to check the expiration date. Mixtures packaged in metal cans are stored longer than those packed in plastic or foil bags and boxes. - Buy several bottles of in different sizes and several teats so that you have a supply. Select nipples according to your child's preference. Many babies have a hard time transitioning to bottle feeding, so it's a good idea to get a pacifier that's best suited to simulate breastfeeding at first.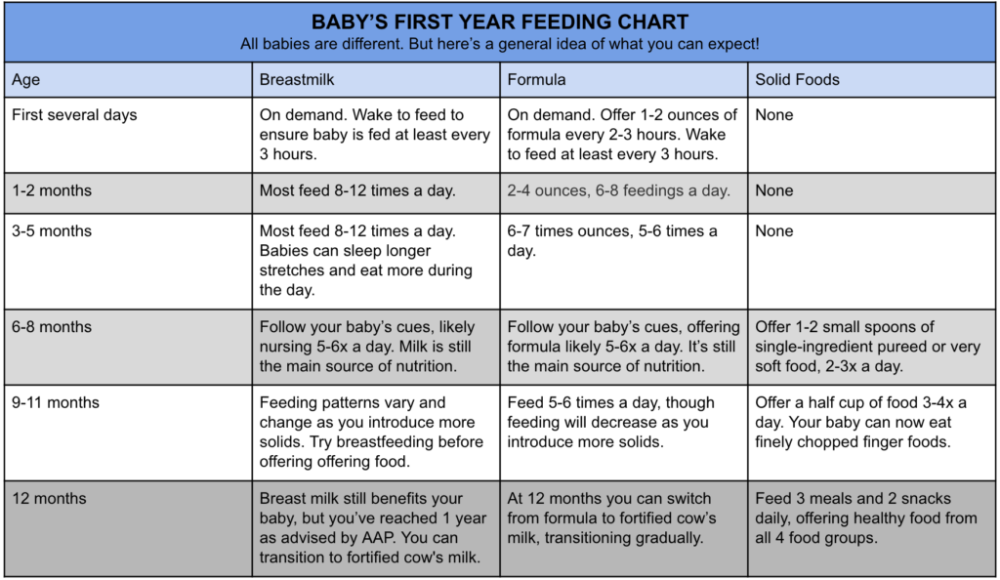 - Stock up necessary accessories for artificial feeding: a bottle brush, a sterilizer, a device for heating and maintaining the temperature of the mixture. Electrical appliances do not have to be taken new, they can be purchased from hand or taken from relatives and friends. After all, they are rarely used for more than a year and, as a rule, remain in excellent condition.
- Stock up necessary accessories for artificial feeding: a bottle brush, a sterilizer, a device for heating and maintaining the temperature of the mixture. Electrical appliances do not have to be taken new, they can be purchased from hand or taken from relatives and friends. After all, they are rarely used for more than a year and, as a rule, remain in excellent condition.
Important!
- Modern adapted mixes are usually sold dry and require dilution with water. Prepare the mixture, strictly following the instructions on the packaging. Lack or excess of dry mix can adversely affect the baby's digestion. - If possible, gradually infuse mixture, starting with 10 ml once a day. - Carefully monitor the reaction of the baby's body to the mixture. If you experience a allergic reaction to your skin, persistent constipation, diarrhea, or increased gas, contact your pediatrician immediately. - Carefully observe hygiene rules when preparing adapted formula, washing bottles and teats.
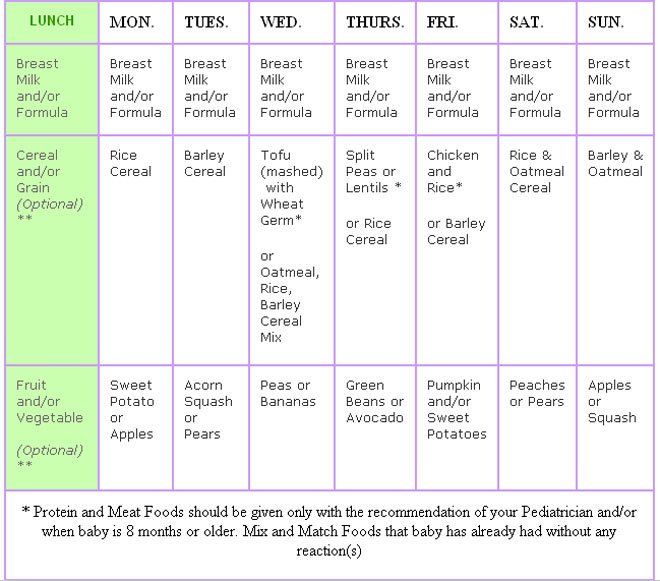
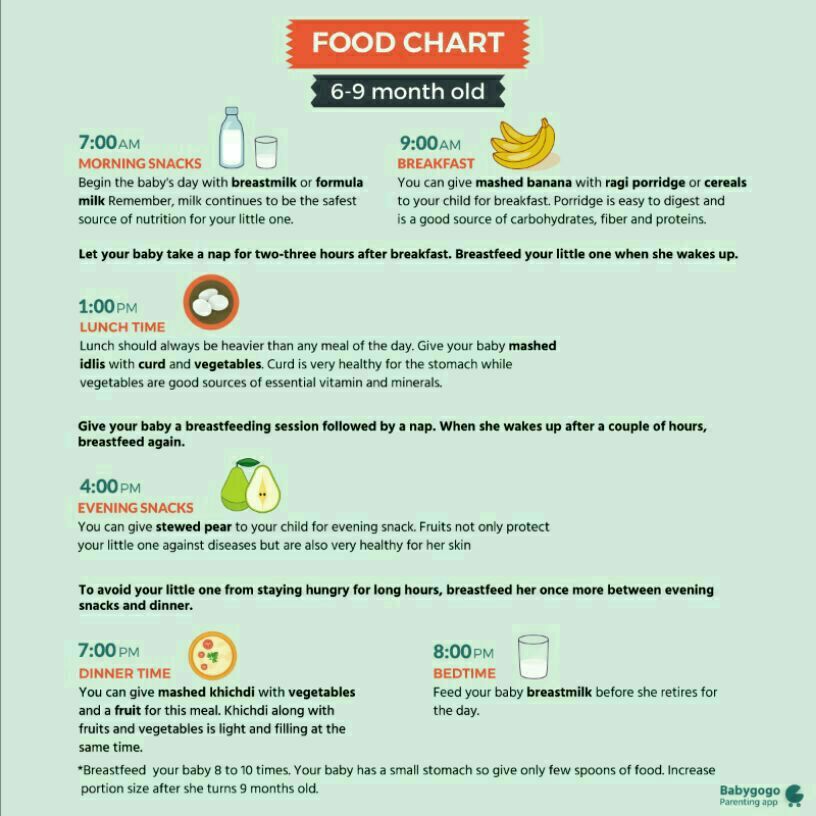
How to feed
The amount of food for formula feeding is usually the same as the amount of breast milk the baby needs. Before starting the introduction of the mixture, consult with the pediatrician so as not to overfeed the baby. Usually, formula feeding is carried out according to a specific regimen : the number of feedings and the volume of the mixture that the child should eat in each feeding are assigned. Since formula usually lingers in the stomach longer than breast milk, formula feeds fewer feeds. Many kids find it difficult to adapt to this regimen. And, after consulting a doctor, parents can switch to the so-called free artificial feeding, in which the child himself determines the frequency of feeding and the amount eaten. This mode is suitable for experienced parents who are well aware of the needs of their child - when he is really hungry, and when he needs affection and communication with adults. It is important not to overfeed the child - he should eat no more than the recommended amount of the mixture per day.