When to stop feeding baby
Breastfeeding - deciding when to stop
Breastfeeding
The World Health Organization recommends that all babies be exclusively breastfed for 6 months, then gradually introduced to appropriate foods after 6 months while continuing to breastfeed for 2 years or beyond.
Stopping breastfeeding is called weaning. It is up to you and your baby to decide when the time is right.
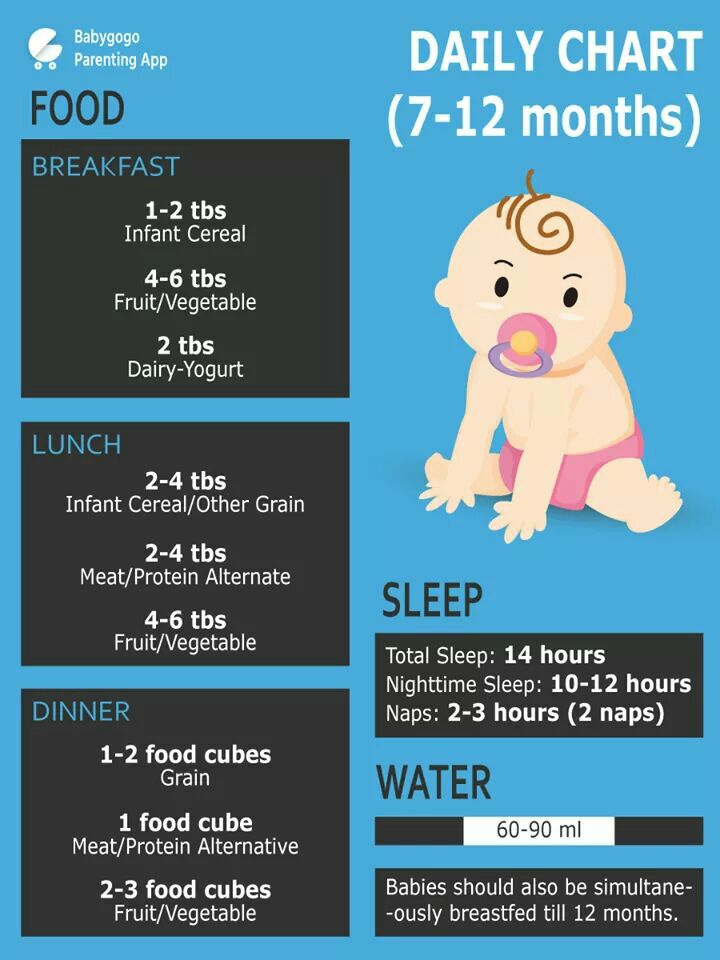
Some babies decrease the number of breastfeeds as they begin to commence solid feeds. The first foods are really educational tastes and not much food is ingested. Once they’re established on solids, and start taking 3 solid feeds a day, they start gaining the nutritional benefits from solids and rely more on them for their growth and development (around 9 months).
Breastmilk in the first year
Breastmilk contains all the nourishment needed to promote normal healthy growth and development in babies in their first 6 months of life and remains the most important food during their first year.
Solids during your baby’s first year complement breastmilk and do not replace breastfeeds. Your baby should still breastfeed on demand, as your breastmilk is their primary source of nutrition until closer to the end of their first year.
Babies weaned from breastmilk prior to their first birthday will need to be given infant formula. Please consult your maternal and child health nurse for further information on this.
Infant formulas are generally not necessary after the first 12 months, as your child should then be consuming a large range of foods including dairy products. If you need to replace a milk feed (breastfeed or formula), full cream cow’s milk can be used.
Breastfeeding benefits
Breastfeeding even for a short time is beneficial.
In the first few days after your baby’s birth, your breasts produce colostrum. This rich substance contains vital ingredients, including immunoglobulins and cells that help your baby’s immune system.
There is ample evidence that babies who are breastfed for the first 6 months of life do not experience as many (or as severe) episodes of common childhood illnesses. These include gastroenteritis, respiratory illnesses and middle ear infections.
These include gastroenteritis, respiratory illnesses and middle ear infections.
Stopping breastfeeding early
Sometimes, weaning needs to happen earlier or more quickly than planned.
It is normal for a parent to feel sad when they wean, especially if it is earlier than expected. A parent may feel they have no choice but to wean. However, most breastfeeding difficulties can be overcome with help. An Australian Breastfeeding Association counsellorExternal Link, lactation consultant or maternal and child health nurse can offer you information and support.
Returning to the paid workforce need not mean having to wean. Many parents combine breastfeeding with part or full-time work, study and other commitments.
Take your time to wean your baby
Depending on your baby’s age and need for sucking, you can wean either to a cup or bottle. If you decide on a bottle, eventually your baby will need to be weaned from that.
Start with whichever breastfeed of the day your baby seems least interested in. If the breasts are uncomfortable when a feed is missed, you may need to express a small amount for comfort, to avoid blocked ducts or discomfort from fullness. Reduce either the time of expressing or volume removed over days for the breasts to adjust. Then cut out another breastfeed every few days or even each week, depending on your breast comfort and your baby’s willingness to cooperate.
If the breasts are uncomfortable when a feed is missed, you may need to express a small amount for comfort, to avoid blocked ducts or discomfort from fullness. Reduce either the time of expressing or volume removed over days for the breasts to adjust. Then cut out another breastfeed every few days or even each week, depending on your breast comfort and your baby’s willingness to cooperate.
The concentration of antibodies to bacterial and viral diseases in breastmilk is increased as weaning progresses and milk supply reduces. This ensures that your baby is protected as they are being introduced to new foods and exploring new surroundings.
Remember to give your baby plenty of cuddles during the weaning process so that you and your baby still have plenty of close time together.
Slowly reducing the number of breastfeeds protects your baby during the weaning period and will also help you avoid problems such as mastitis. If you need to wean your baby quickly, talk to a healthcare professional or a lactation consultant about caring for your breasts.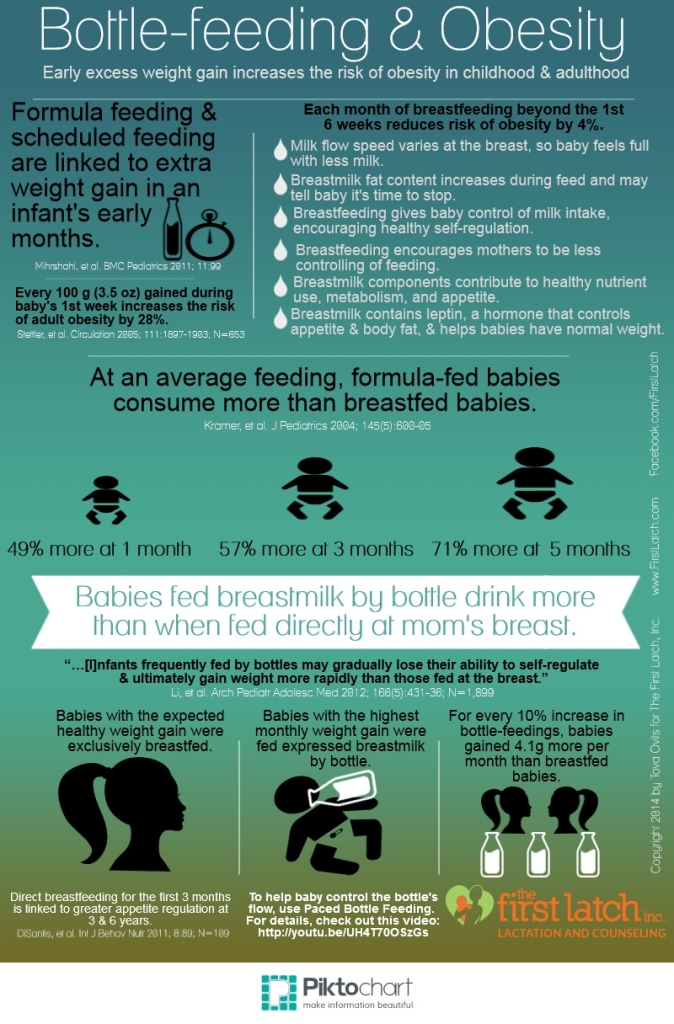
When to introduce solid foods
Breastmilk or infant formula should be your baby’s main source of nutrition for around the first year of life. Health professionals recommend exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months, with a gradual introduction of appropriate foods in the second 6 months and ongoing breastfeeding for 2 years or beyond.
Babies show they are ready to start solids when they:
- start showing interest when others are eating
- start making gestures that seem to say ‘feed me too’
- stop pushing out any food put in their mouth (disappearance of the tongue-thrust reflex)
- start being able to hold their head up and sit without support.
Talk to your maternal and child health nurse about your baby’s readiness to eat.
Iron requirements
A baby born at full term has a store of iron passed on from the mother during pregnancy. You may be concerned about your baby’s store of iron running low at around 6 months of age.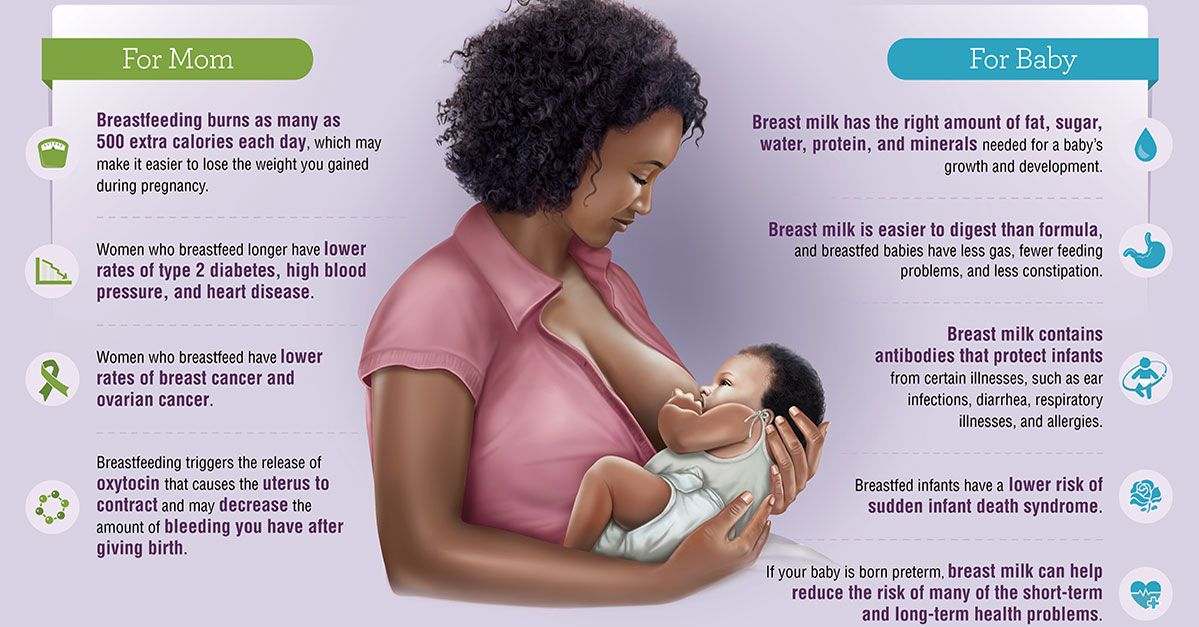 Breastmilk contains small amounts of readily absorbed iron, and recent studies have shown that the risk of iron deficiency is very low in full-term healthy breastfed babies who continue to breastfeed past 6 months as solids are introduced.
Breastmilk contains small amounts of readily absorbed iron, and recent studies have shown that the risk of iron deficiency is very low in full-term healthy breastfed babies who continue to breastfeed past 6 months as solids are introduced.
Breastfeeding while pregnant
If you become pregnant, you may choose to continue to breastfeed or you may like to gradually wean your baby. This is an individual choice. Whether or not you choose to continue breastfeeding, it is important to maintain a healthy diet.
Seek advice from your health professional or the Australian Breastfeeding AssociationExternal Link.
Extended breastfeeding
Some parents and babies enjoy breastfeeding so much they are in no hurry to stop. It is not unusual for children up to 4 years of age to continue to be breastfed.
Family members and friends may feel uncomfortable about extended breastfeeding and it can be helpful to have information to give your family and friends about why you have decided to keep breastfeeding.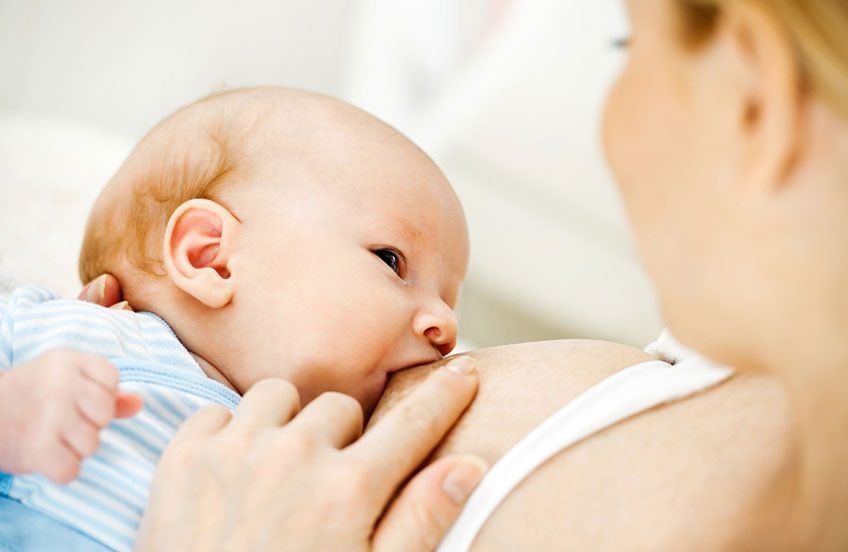 This may include information about the continued health benefits, security and comfort for your child.
This may include information about the continued health benefits, security and comfort for your child.
The child who does not want to be weaned
You may be ready to cease breastfeeding, but your child may resist all your attempts to do so. Your approach will depend on your child’s age. There are many strategies for weaning a baby.
Unfortunately the child would need to be able to take a bottle, sippy cup, or straw cup comfortably before you are able to wean, to ensure they are able to take adequate feed volumes.
If your child can talk and understand well, talk with them about your breastfeeding. Explain that you are going to stop and introduce other ways that you can enjoy being close together. You could seek professional advice about weaning or difficulties associated with weaning.
Where to get help
- Your maternal and child health nurse
- Australian Breastfeeding Association Breastfeeding HelplineExternal Link Tel. 1800 686 268
- A lactation consultant – contact Lactation Consultants of Australia and New Zealand (LCANZ)External Link Tel.
 (02) 9431 8621
(02) 9431 8621 - Maternal Child Health Line Tel. 13 22 29 (24 hours, 7 days)
- Your GP (doctor)
Weaning: When and how to stop breastfeeding
When’s the right time to stop breastfeeding your baby, and what’s the best way to do it? Read on for plenty of practical weaning advice
Share this content
Once you’ve established breastfeeding, how long should you continue? Three months? Six months? A year? Or several years?
The World Health Organization (WHO) and other health bodies recommend that babies are fed entirely on breast milk for their first six months of life and continue having their mother’s milk alongside other foods – known as complementary foods – until at least the age of two.1
This is because breast milk isn’t just food. A natural comforter if your child is worried or tired, it also contains immunity-boosting components that increase dramatically in number whenever she’s ill. 2
2
Anthropologists estimate the natural age for humans to stop breastfeeding is even higher than two. Looking at factors including tooth development, body weight, comparison with other primates and historical evidence, some say it could be two to four years, while others believe our ancestors might have been breastfed until the ages of six or seven.3
Today, more than 60% of mums in developed countries give their baby some formula or complementary food before the age of six months,4 even though WHO guidelines don’t recommend this.
When’s the right time to start weaning my baby?
Weaning is the process of stopping feeding your baby with breast milk. Ideally, the first step towards weaning your baby is introducing complementary foods alongside your breast milk around the age of six months. The weaning process continues until breast milk is completely replaced by other foods and drinks.
“After six months, your baby begins to need higher levels of certain nutrients – such as iron, zinc and vitamins B and D – that she can’t get from your breast milk or her own reserves alone,” explains UK health visitor and nurse Sarah Beeson.
“But solid food will only complement your baby’s milk intake to start with, and replace it gradually. Breast milk will remain her major source of nutrients for many months to come.”
A typical seven-month-old still gets 93% of her calories from milk. Even at 11 to 16 months, milk may still provide around half her daily calorie intake.5
“Mums sometimes think breast milk isn’t important once their baby has started eating solids, but in fact there’s no better milk for her, however old she is,” says Sarah.
Indeed the entire weaning process can take as long as mum and baby want it to: “When to stop breastfeeding is your choice,” says Sarah. “Don’t feel pressured by what friends are doing or what family members – or even strangers – say. All that matters is what feels right for you and your baby.”
How to stop breastfeeding
Whenever you decide to start weaning your child off breast milk, it’s best to do it gradually. Stopping breastfeeding suddenly could put you at risk of engorgement, blocked ducts or mastitis, as well as being an abrupt change for your baby’s digestive and immune systems to cope with. It may also be difficult for you both emotionally.
It may also be difficult for you both emotionally.
Do I need to stop breastfeeding?
Sometimes mums mistakenly think they need to stop breastfeeding when they don’t. If you’re returning to work, breastfeeding can be a great way of maintaining intimacy during a big change in both your lives. You can express milk for your baby at work and keep nursing sessions as a special time together at the beginning and end of the day. Or if you need to travel without your baby, you could express milk to take or send home.
If you get ill, it doesn’t always mean you need to stop breastfeeding either – read our advice on breastfeeding while you’re sick and be sure to consult with your healthcare professional.
Stopping breastfeeding before six months
If you feel unable to continue breastfeeding until the six-month mark and want to try mother-led weaning, start by cutting out one breastfeed a day and replacing it with a bottle of formula.
“Ideally, start with the mid-day feed. Babies are remarkable and can identify the scent of their mother’s milk nearby, so ask your partner or a relative to give your baby the bottle while you are in another room,” says Sarah.
Babies are remarkable and can identify the scent of their mother’s milk nearby, so ask your partner or a relative to give your baby the bottle while you are in another room,” says Sarah.
“Be mindful of good hygiene when preparing feeds. It may be that your baby takes fewer feeds of expressed breast milk than from the breast during a 24-hour period. Don’t force her to take more milk than she wants.”
You’ll probably notice your breasts feel full and tender as your body adjusts to producing less milk. If this becomes uncomfortable, try expressing a little breast milk – just enough to relieve the discomfort without stimulating your body to make more.
Once your body is used to this new volume – usually after a few days – cut out another feed each day. Repeat until you’re no longer breastfeeding and your baby is fully weaned.
“I had complications after my first birth which meant I lost a lot of weight very quickly and I also suffered with mastitis. My supply was low and at three months, I needed to stop,” says Jennifer, mum of two, UK. “I swapped one feed at a time so didn’t struggle too much physically, but I found it hard mentally.”
“I swapped one feed at a time so didn’t struggle too much physically, but I found it hard mentally.”
If you want to maintain the intimacy and health benefits of breastfeeding, but need to cut back, try partial weaning, where only some of the feeds are replaced with formula.
Stopping breastfeeding after six months
As your baby starts to have solid foods at around six months, you will find that her breastfeeds naturally become less frequent over time. Within a year she will probably be down to a couple of feeds a day, complemented by meals and healthy snacks.
However, if you’d like to cut back further, do it gradually, dropping one breastfeed at a time and offering your baby formula milk instead if she is less than 12 months old. Cow’s milk should wait until she is at least a year old.
“My son was down to three breastfeeds a day and having three meals plus snacks when I decided to start weaning him. I gradually replaced each feed with a bottle of formula – leaving the night one until last, at 11 months,” says Ruth, mum of one, UK. “The slow pace meant I had no problems, just a little fullness for a few days.”
“The slow pace meant I had no problems, just a little fullness for a few days.”
There are various ways to distract your child from the change in her feeding patterns. Some mums offer a drink and a snack instead, which you could share to bring a feeling of closeness. You could also alter your daily routine, play a favourite game, or replace a feed with a cuddle from you or your partner. Some children will take longer than others to feel happy with the change, but things will get easier over time. If you’re having any difficulties with weaning, it’s always helpful to seek support from your healthcare professional.
Stopping breastfeeding naturally over time
If you choose to let your toddler decide when to stop breastfeeding (known as baby-led weaning or natural-term breastfeeding), the weaning process is likely to be slow and gradual. Over the months, her feeds will probably become shorter and less frequent, while some mums report their child simply losing interest one day.
“My daughter self-weaned at four,” says Sarah, mum of one, UK. “She gradually slowed down and hardly fed at all from three-and-a-half. Then she seemed to forget when we were on holiday. Six months on, she sometimes wants to latch on, but knows the milk is gone.”
Your body should have plenty of time to adapt, so you’re unlikely to experience any uncomfortable engorgement. You may find it tough emotionally, though, so make time for plenty of cuddles and bonding moments.
“Baby-led weaning was right for me because my son had never had formula or a bottle. I didn’t want to stop suddenly and deny him,” says Kelly, mum of one, UK. “He lost interest at two-and-a-half. It was the best scenario for us, although I was quite emotional.”
What if I need to stop breastfeeding quickly?
Although it’s best not to stop breastfeeding abruptly, sometimes it’s necessary for health reasons, or because you and your baby can’t be together.
If your baby has been breastfed until this point, you’ll almost certainly need to express milk to avoid your breasts becoming uncomfortably engorged. Some women find a breast pump easiest for this, while others prefer to do it by hand. Again, only express enough to ease any discomfort – you don’t want to encourage your body to produce more milk.
Some women find a breast pump easiest for this, while others prefer to do it by hand. Again, only express enough to ease any discomfort – you don’t want to encourage your body to produce more milk.
While your breasts may feel swollen and tender at first, they will adapt. Your breast milk contains something called feedback inhibitor of lactation (FIL). When your baby stops breastfeeding, FIL tells your body to slow production, but it may take a few days or even weeks for your breasts to adjust.
Taking paracetamol or ibuprofen can help to relieve any pain (although ibuprofen has contraindications for those with asthma). Always follow the manufacturer’s and pharmacist’s guidance and consult a healthcare professional about any medications you need to take.
“I had to give up breastfeeding suddenly when my daughter was eight months old because I needed to take strong painkillers,” says Peggy, mum of one, Switzerland. “I found it very hard – she kept looking for my breast and crying. I held her tightly against me for reassurance while giving her a bottle. After a month, she seemed OK with it.”
I held her tightly against me for reassurance while giving her a bottle. After a month, she seemed OK with it.”
Can I continue breastfeeding if I want to get pregnant again?
While breastfeeding is a natural contraceptive, it’s not foolproof. And it’s unlikely to be effective after six months, or if you’re not exclusively breastfeeding. This means you could conceive while still nursing your child.
Pregnant breastfeeding mums sometimes receive conflicting advice about whether to wean. Tandem feeding two children of different ages is certainly possible and when your new baby arrives, your body will produce milk to fit each of their needs.
Some mums find that their older child weans naturally during the pregnancy or drops certain feeds. This may be due to changes in the composition of your milk during pregnancy, which mean that it tastes different and less sweet.6 If your breastfeeding child is under a year old when she starts to wean, keep an eye on whether she continues to gain weight.
You should take advice from your healthcare professional if you want to continue breastfeeding while pregnant if you have previously had a premature birth, a miscarriage or are suffering any bleeding.
If you need medical help to conceive, you may find that doctors will not administer certain fertility drugs or treatments if you’re breastfeeding. Discuss all the options before making a decision on weaning.
The last word on baby weaning
Whenever and however you stop breastfeeding, be gentle with yourself and your baby. It’s a big shift physically, hormonally and emotionally for you both, so do it with thought and care.
“While my body coped with weaning fine, I felt very emotional. It was something we’d shared for so long and it had come to an end,” says Jane, mum of two, USA. “I was working long hours, five days a week, and breastfeeding made me feel very relevant in their lives. But when that stopped, we soon found other ways to bond.”
References
1 World Health Organisation. [Internet] Health Topics: Breastfeeding: 2018 [Accessed: 08.02.2018]. Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/en
[Internet] Health Topics: Breastfeeding: 2018 [Accessed: 08.02.2018]. Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/en
2 Hassiotou et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
3 Dettwyler KA. When to wean: biological versus cultural perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2004; 47(3)712-723.
4 Victora CG et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490.
5 Dewey KG et al. Breast milk volume and composition during late lactation (7-20 months). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984;3(5):713-720.
6 Prosser CG et al. Mammary gland function during gradual weaning and early gestation in women. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1984;62(Pt 2):215-228.
Termination of breastfeeding | Stopping breastfeeding
When is it time to stop breastfeeding and what is the best way to do it? Read our article for useful practical tips on weaning.
Share this information
How long should breastfeeding continue? Three months? Six? Year? Or maybe a few years?
The World Health Organization (WHO) and other authorities recommend that infants be exclusively breastfed for the first six months and then continue to be breastfed along with other foods (complementary foods) for at least two years. 1
The fact is that breast milk is not just food. It is a natural sedative if the child is anxious or tired. In addition, milk contains immune-boosting components, the amount of which increases dramatically when the baby gets sick. 2
According to anthropologists, the natural age of a person to stop breastfeeding is even more than two years. Given factors such as tooth development, body weight, comparison with other primates, and historical evidence, some scientists believe that breastfeeding may last up to two to four years. A number of researchers even believe that our ancestors breastfed children up to six or seven years of age. 3
3
Today, more than 60% of mothers in developed countries start giving their babies formula or complementary foods before six months of age, 4 although WHO does not recommend this.
When is it time to stop breastfeeding?
Weaning means that you gradually stop breastfeeding your baby. Ideally, the first step in this process is the gradual introduction of complementary foods, starting at about six months of age. In this case, breastfeeding continues. The weaning process continues until the mother's milk has been completely replaced by other foods and drinks.
“After six months, the baby needs higher doses of certain nutrients, such as iron, zinc, vitamins B and D, that he cannot get from breast milk or from his own reserves,” says Sarah Beeson, health visitor from Great Britain.
“But solid food should at first only supplement the main diet with breast milk and gradually replace it. Mother's milk remains the main source of nutrition for the baby for many months to come. ”
”
On average, a seven-month-old baby gets 93% of its calories from breast milk. And even between the 11th and 16th months, milk provides him with about half of the daily calorie intake. 5
“Sometimes moms think that breastmilk isn't that important once a baby has started solid foods, but the truth is, no matter how many months old a baby is, there's nothing better than your milk,” continues Sarah.
In fact, the process of finishing breastfeeding can take as long as mother and baby want. “When to stop breastfeeding is up to you,” says Sarah. The only thing that matters is what you think is right for you and your child.”
How to wean
Whenever you decide to start weaning your baby, it's best to do it gradually. An abrupt cessation of breastfeeding can lead to lactostasis, blockage of the milk ducts and mastitis, and in a child such a sudden change can adversely affect the state of the digestive and immune systems. In addition, it will be difficult for both of you psychologically.
When should I stop breastfeeding?
Sometimes mothers mistakenly believe that it is time to stop breastfeeding, when in fact there is no reason to. If you're returning to work, breastfeeding can be a great way to stay close to your baby during this difficult time for both of you. You can express milk at work, and morning and evening feeding sessions will give you the opportunity to spend time alone with your baby. If you need to leave without your baby, you can also express milk and bring or send it home.
If you get sick, this is not always a reason to stop breastfeeding. Read our advice in the article on breastfeeding when sick and consult with your healthcare professional.
Weaning up to six months
If you cannot continue breastfeeding until six months and want to try weaning your baby, start by replacing one feeding a day with a bottle of formula.
“It's best to start with midday feedings. Babies are very alert and able to smell breast milk nearby, so ask your partner or relative to give your baby a bottle when you're in the other room,” Sarah advises.
“Be hygienic when preparing food. Be prepared for the fact that the baby will take fewer servings of expressed milk per day than if he was fed directly from the breast. Don't make him eat more milk than he wants."
You will probably feel that your breasts are fuller and more tender. This is due to the fact that your body is rebuilding to produce less milk. If this creates discomfort, try expressing some milk—just enough to relieve the discomfort without stimulating extra production.
When your body adjusts to the new volume - usually after a few days - replace with formula for one more meal a day. Continue this until you have changed all feedings and your baby is completely weaned.
“I had complications after my first birth, as a result I lost a lot of weight very quickly, and besides, I developed mastitis. Lactation was very weak, and at three months I was forced to stop breastfeeding,” recalls Jennifer, a mother of two from the UK, “I gradually replaced one feeding, so physically it was easy, but mentally it was hard for me. ”
”
If you want to maintain closeness with your baby and all the health benefits of breastfeeding, but still need to cut down on breastfeeding, try partial weaning, replacing only a few feeds a day with formula.
Weaning after six months
Once your baby starts eating solid foods (about six months old), you will notice that breastfeeding naturally occurs less and less. For a year, it can be reduced to just a couple of times a day, and feedings will be replaced by full meals and healthy snacks.
Anyway, if you intend to continue to reduce breastfeeding, do it gradually, replacing one feeding at a time. Use formula milk if your baby is under 12 months old. With cow's milk, you should wait at least up to a year.
“When I decided to wean my son, I breastfed him three times a day and gave him other foods three times plus light snacks. Gradually, I replaced all breastfeedings with formula. By 11 months, we only had one nighttime breastfeed left,” says Ruth, a UK mom.
There are various ways to distract a child from changes in his diet. Some mothers suggest that instead of breastfeeding something to drink and eat together to maintain a sense of closeness. You can also change your daily routine, play your favorite game, or replace feeding with caresses - from you or from your partner. Some children take longer to get used to the new food, but in the end everything falls into place. If you are having difficulty weaning, ask your healthcare provider for advice.
Ending breastfeeding naturally
Ending breastfeeding can be guided by the baby's wishes. This is called baby-initiated weaning, or the natural termination of breastfeeding. Such a process is likely to be long and gradual. Month after month, feeding sessions will become shorter and less frequent, until one day the child completely loses interest in the breast.
“My daughter stopped breastfeeding on her own when she was four years old,” says Sarah, a mother from the UK. And once, when we were on vacation, she seemed to just forget about her breasts. Now, six months later, she sometimes still asks for breasts, but she already knows that there is no milk there.
And once, when we were on vacation, she seemed to just forget about her breasts. Now, six months later, she sometimes still asks for breasts, but she already knows that there is no milk there.
You will have a huge amount of time for the body to adapt, so there should be no discomfort or swelling of the breast. However, you may find it difficult emotionally, so spend more time petting and bonding with your baby.
“Child-initiated termination of breastfeeding was right for me because I never gave my son formula or a bottle. I didn’t want to abruptly stop feeding and refuse him,” recalls Kelly, a mother from the UK, “He himself lost interest in breasts at the age of two and a half years. For us, it was the best scenario, although emotionally it was not very easy for me.”
What if you need to stop breastfeeding quickly?
It is best not to stop breastfeeding abruptly, but sometimes it is necessary for medical reasons or because you cannot be near the baby.
If you have been breastfeeding your baby up to this point, you will most likely have to express your milk to avoid breast swelling. Some mothers prefer to use a breast pump for this, others find it easier to express milk manually. You only need to pump a little, just to eliminate the discomfort, otherwise your body will take it as a signal to produce more milk.
At first, the breasts may swell and become tender, but this will pass. Breast milk contains a so-called feedback lactation inhibitor. When breastfeeding is stopped, this inhibitor tells your body to slow down milk production, but it can take days or even weeks for your breasts to rebuild.
Certain medications can relieve pain and should be discussed with your doctor. Always follow your pharmacist's instructions or directions, and consult your healthcare professional before taking any medication.
“I had to abruptly stop breastfeeding when my daughter was eight months old because she had to take strong painkillers,” says Peggy, a mother from Switzerland. “It was very difficult because the baby was constantly looking for a breast and crying. I held her tightly to me as I gave her a bottle. This calmed her, and after a month everything was all right.
“It was very difficult because the baby was constantly looking for a breast and crying. I held her tightly to me as I gave her a bottle. This calmed her, and after a month everything was all right.
Can I continue breastfeeding if I want to get pregnant again?
Breastfeeding is a natural contraceptive. However, this method is not the most reliable, especially after six months or if you are not exclusively breastfeeding. This means that you can get pregnant even while you are breastfeeding.
Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers sometimes receive conflicting advice about whether to stop breastfeeding. Consistent feeding of two children of different ages is of course possible, and with the advent of the second baby, your body will produce the kind of milk that both of them need.
It is not uncommon for an older child to refuse to breastfeed or skip feedings if the mother is pregnant. This may be due to changes in milk composition that occur during pregnancy. Milk can change the taste and become less sweet. 6 If your baby is under one year of age when he starts to stop breastfeeding, make sure he continues to gain weight.
Milk can change the taste and become less sweet. 6 If your baby is under one year of age when he starts to stop breastfeeding, make sure he continues to gain weight.
Talk to your doctor if you want to continue breastfeeding during pregnancy, but have had a preterm birth or miscarriage, or have any bleeding in the past.
If you need medical help to conceive, certain drugs and procedures may not be suitable while you are breastfeeding. Discuss all possible options before deciding to stop breastfeeding.
And finally...
Whenever you decide to end breastfeeding, and whatever method you choose to do so, be kind to yourself and your baby. This is a huge change for both of you physically, hormonally, and emotionally, so proceed thoughtfully and carefully.
“Although my body responded normally to stopping breastfeeding, it was psychologically difficult for me. The thing that united us for so long is over, - Jane, a mother of two children from the USA, shares her impressions, - I worked long hours, five days a week, and breastfeeding made me feel that I occupy a special place in the lives of children. But when it stopped, we soon found other ways to be together.”
But when it stopped, we soon found other ways to be together.”
Literature
1 World Health Organization. [Internet] Health Topics: Breastfeeding: 2018 [Accessed: 02/08/2018]. Available from : http://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/en - World Health Organization. "Health Issues: Breastfeeding" [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2018 [Visit 02/08/2018]. Article linked: http://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/e
2 Hassiotou et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4): e 3. - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
3 Dettwyler KA. When to wean: biological versus cultural perspectives. Clin Obstet Gynecol . 2004; 47(3)712-723. - Dettwiler KA, "Time to wean: weaning from a biological and cultural point of view". Klin Obstet Ginekol (Clinical obstetrics and gynecology). 2004; 47(3):712-723.
2004; 47(3)712-723. - Dettwiler KA, "Time to wean: weaning from a biological and cultural point of view". Klin Obstet Ginekol (Clinical obstetrics and gynecology). 2004; 47(3):712-723.
4 Victora CG Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475-490. - Victor S.J. et al., "Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms and long-term effects". Lancet 2016;387(10017):475-490.
5 Dewey KG et al. Breast milk volume and composition during late lactation (7-20 months). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr . 1984;3(5):713-720. — Dewey C.G. et al., "Amount and composition of breast milk in late lactation (7-20 months)". F Pediatrician Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984;3(5):713-720.
6 Prosser CG et al. Mammary gland function during gradual weaning and early gestation in women. Aust J Exp Biol Med 9021 9029 Sci. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228. - Prosser S.G. et al., "Breast Function During Gradual Weaning and Early Gestation." Aust J Exp Biol Med Sai. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228.
Aust J Exp Biol Med 9021 9029 Sci. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228. - Prosser S.G. et al., "Breast Function During Gradual Weaning and Early Gestation." Aust J Exp Biol Med Sai. 1984;62( Pt 2):215-228.
Pediatrician "SM-Doctor" about the age until which a child should be breastfed
Some new mothers try to do this as early as possible. Others continue to put the baby to the breast at 4 and 5 years. Play their role and "national" characteristics. For example, in the UK, only a third of babies in their six months still receive mother's milk, while the rest are transferred to formula. And in the UAE, the law prescribes to breastfeed children up to two years, otherwise you can get severe punishment.
In fact, it is on the number “two years” that most doctors around the world agree. It is believed that after this age, mother's milk no longer brings additional health benefits. Is it so? we deal with experts.
It is believed that after this age, mother's milk no longer brings additional health benefits. Is it so? we deal with experts.
Tatyana Kuznetsova
TATYANA KUZNETSOVA
pediatrician, nephrologist, breastfeeding consultant at the SM-Doctor clinic.
On the recommendation of the World Health Organization and the UN Children's Fund, it is desirable to maintain breastfeeding up to 2 years, longer - at the mutual desire of the mother and child. Domestic pediatricians, based on practical experience and scientific research, voice the figure up to 1.5 years.
It is now not uncommon to see mothers who breastfeed their children after two years of age. Such prolonged breastfeeding is commonly referred to as long-term feeding.
In any case, after 2.5 years, the child goes through the process of natural extinction of the sucking reflex, there is a gradual self-weaning and, thus, the smooth completion of breastfeeding.
Regardless of the recommendations, the choice always remains with the mother. And the duration of breastfeeding will depend, first of all, on the readiness of both the mother and the child to stop this process.
And the duration of breastfeeding will depend, first of all, on the readiness of both the mother and the child to stop this process.
What are the health risks of early weaning?
Breast milk substitutes do not contain anti-infectious factors, so an artificially fed baby is more likely to get intestinal infections and respiratory diseases. These include frequent acute respiratory viral infections, otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia, intestinal infections (usually of a viral nature) with prolonged diarrhea, fungal intestinal diseases, as well as a formidable life-threatening condition - necrotizing enterocolitis of newborns.
Quite often in children on mixtures, intolerance to animal milk proteins (bovine, goat) develops with the development of allergic reactions, in particular, food allergies in the form of atopic dermatitis. Unfortunately, in the future such children are at risk for the development of allergic bronchitis, bronchial asthma.
Artificial feeding increases the risk of developing diabetes mellitus, as well as obesity associated with excess formula intake that exceeds the needs of the child. Perhaps the development of seizures due to excess content in mixtures of sodium, calcium, phosphorus.
Infants receiving artificial formula may have reduced intellectual development due to a lack of amino acids, omega fatty acids, which are necessary for the growing brain of a child.
In addition, according to some studies, not breastfeeding increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome.
And what are the disadvantages of late weaning?
Not only abroad, but also in Russia, there are many studies that have proven the benefits of mother's milk at any time of feeding. After a year, breast milk changes its composition, but not for the worse.
The main reason for these changes is that milk is no longer the main food for the baby, and other functions come to the fore.
The older the child becomes, the greater the concentration of immunoglobulins in milk increases, which protect the child from infectious diseases. Breast milk contains leukocytes and a number of anti-infectious factors, as well as antibodies against infectious agents previously transferred by the mother.
How does breastfeeding affect the child's psyche?
Today it is becoming very fashionable to instill early independence in children, and premature weaning is seen by some parents as a means to make the child more independent.
However, psychologists who are closely involved in the study of child development warn that premature weaning can, on the contrary, provoke a delay in emotional development and increase dependence on parents. Imposed independence turns into psychological isolation and abandonment. It is much better to give the child the opportunity to become independent when he is ready for it.
This is well illustrated by the results of foreign studies: for example, one of them showed that the greatest achievements in school were in children who were fed longer. And in the course of another, they found that the longer a child breastfeeds, the better social adaptation goes later, at the age of six to eight. Both mothers and teachers acknowledged that babies who were breastfed for a long time were much less likely to develop problem behaviors.
And in the course of another, they found that the longer a child breastfeeds, the better social adaptation goes later, at the age of six to eight. Both mothers and teachers acknowledged that babies who were breastfed for a long time were much less likely to develop problem behaviors.
Yes, and Russian doctors, who undertook to study the effect of breastfeeding on the neuropsychic development of children, found that babies who ate their mother's milk for a long time show much better results both at two years, in tests of speech development, and at three years , in tests of the correct performance of skills.
Many long-term mothers successfully combine feeding with work, and also take their children to kindergartens. Applications remain only at bedtime and at night. The rest of the time, the baby usually does not need to breastfeed. Ideally, the child should stop asking for breasts during the day, and then at bedtime and at night. As a rule, this happens about 2. 5 - 3 years.
5 - 3 years.
But if the child continues to breastfeed after 3.5 years, this may indicate some psychological problems of the baby or mother, in this case it is advisable to contact a psychologist, but not an ordinary one, but a friendly one for long-term feeding.
What if I can't breastfeed?
Sergey Butriy
SERGEY BUTRIY
Pediatrician, author of books on child health
A well-known doctor spoke about this in a podcast for Cuprum.
- One of the most "explosive" topics in the pediatrician's office after vaccinations is breastfeeding. Now it's fashionable to be for GW. Of course, formula is not quite the same as breast milk. There is only one "but".
Mothers who fail to breastfeed for health reasons experience a tremendous sense of guilt. They are pressed by society, other mothers, breastfeeding consultants. Many become depressed because of this, trying to feed through physical pain.