Which enzyme is used in making baby foods
Enzymes Essay; Enzymes used in the Baby Food industry - GCSE Science
- Search
- Join over 1.2 million students every month
- Accelerate your learning by 29%
- Unlimited access from just £6.99 per month
Extracts from this document...
Enzymes used in the 'Baby Food' industry Enzymes allow chemical reactions to be carried out under milder conditions (lower temperature and pressure), thus saving costs. Since most supplements are not substrates for enzymes, the enzymes usually do not interact with them. You should be able to mix most supplements and medicines with enzymes. Enzymes may affect the properties of time-released medications increasing the rate at which they are broken-down, and thus, released. The enzymes which are used in baby food are there because they allow the food to be pre-digested in the baby's stomach. ...read more.
The main two enzymes used in the baby food industry are 'protease' and 'lipases'. A protease enzyme is usually used to break down protein it does this when it breaks peptide bonds by a process called hydrolosis. These bonds are linked together to create an amino acid. The best condition for use of protease is in acidic areas. Finally the proteases occur naturally in all organisms. A lipase is a water-soluble enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester bonds in water-insoluble, lipid substrates. ...read more.
A protease in another industry is not used as it creates a higher mortality rate in the medicine industry for HIV/Aids. This enzyme has therefore been made into an alternate structure but with the same properties but not with the same processes. This in turn creates a social factor to be seen when treating the disease so the scientists have made a new type of ingredient called NNRTI to serve the same purpose as the protease enzyme. ?? ?? ?? ?? ...read more.
The above preview is unformatted text
This student written piece of work is one of many that can be found in our GCSE Humans as Organisms section.
Found what you're looking for?
Here's what a teacher thought of this essay
3 star(s)
***
A few good points but this is otherwise a rather superficial overview of the topic. The author should double check finished work to make sure it reads well and makes sense.
Marked by teacher Adam Roberts 30/07/2013
Not the one? Search for your essay title...
- Join over 1.2 million students every month
- Accelerate your learning by 29%
- Unlimited access from just £6.99 per month
See related essays
-
5 star(s)
protein to boost their immune system * When someone is pregnant they need proteins so that they get passed through to the child. In lactation (breast-feeding) there needs to be extra so that there is enough for the child and you Kwashiorkor Many protein rich foods are expensive.
-
5 star(s)
who fail to develop measles immunity after the first dose. [13] The second dose is given to everyone because it is impossible to distinguish which children have and which have not been immunised by the first vaccination without putting them at risk.
-
4 star(s)
Ventricular pressure continues to rise until eventually the pulmonary and aortic valves are forced open and blood is ejected into the pulmonary artery and aorta'. When the heart rate is increased the amount of time the diastole and systole take place is shortened, so that more blood is pumped out in one minute.
-
3 star(s)
This type of pace maker works on a requirement only bases. These may be used when patients whose sino-arterial node sends out signals too slowly, or the electrical pathway is partly or completely blocked, or the timing of atrial and ventricular contractions is uncoordinated (asynchronous), in this case a double chamber pace maker is used.
-
3 star(s)
doing surgery, that doctor would pass on to the next visited patient a potentially life threatening disease. He insisted that those doctors who worked for him wash their hands in calcium chloride after an operation and before visiting a new patient.

-
Water * Acts a solvent * Absorbs heat (temperature regulation) * Provides a medium for chemical reactions Salt * Maintains the osmotic balance in the body Change in Diet Obesity Kwashiorkor Pregnancy Puberty (Girls) Is excess growth Diet high in fat Leads sudden gain of weight Blockage of blood vessels
-
Respiration may completely stop due to the denaturation of all the enzymes associated with breaking down respiratory substrate. I have used a higher proportion of respiratory substrate in comparison to yeast because in order for the yeast to respire at an optimum rate throughout the experiment there must be excess substrate present.
-
The stronger heart moves more blood with each beat and therefore can do the same amount of work with fewer beats. This means that in my experiment, someone with a higher BMI (of 30, for example) may have a lower resting heart rate than those with a lower BMI.
- Over 160,000 pieces
of student written work - Annotated by
experienced teachers - Ideas and feedback to
improve your own work
Which enzyme is used in making baby foods? | Superminis
Being a parent is a very exciting feeling at first, but it is sometimes hard too. You have to deal with many changes in your everyday routine. Caring can be fun too but it is also a responsible job. Unfortunately for many reasons the mother is not able to breastfeed her child or can’t take care of her child's nutrition. Therefore there is no option other than to formula feed.
You have to deal with many changes in your everyday routine. Caring can be fun too but it is also a responsible job. Unfortunately for many reasons the mother is not able to breastfeed her child or can’t take care of her child's nutrition. Therefore there is no option other than to formula feed.
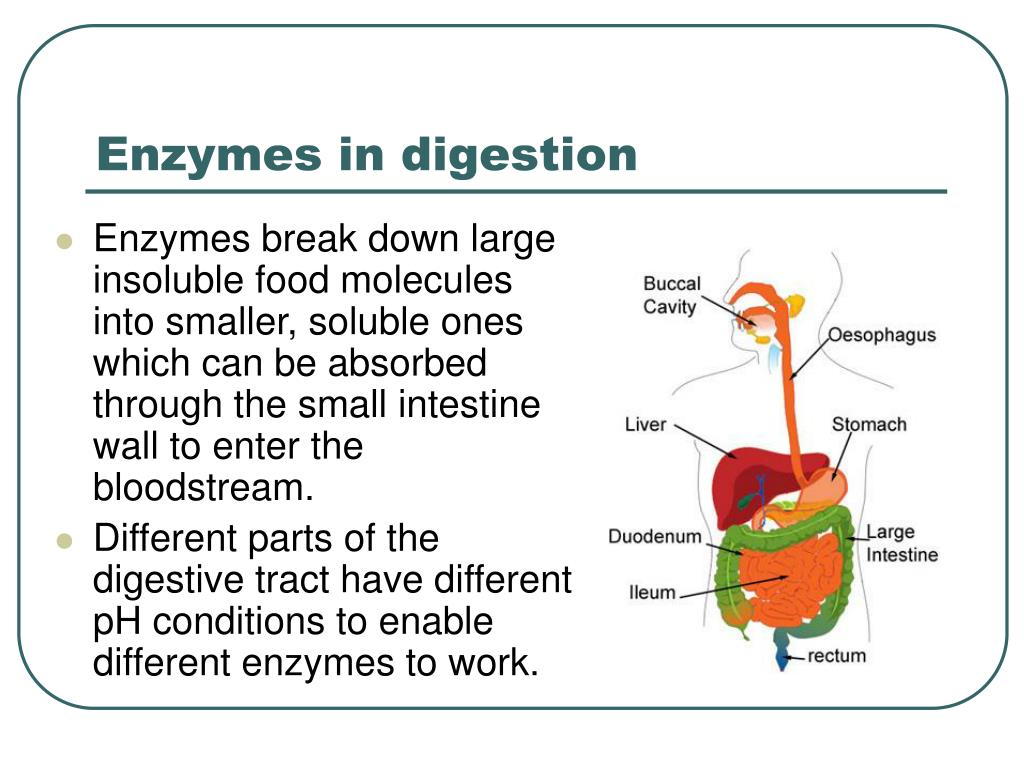
After birth, the baby is so delicate and is in the underdevelopment stage, therefore the baby's body needs nutrients which promote all-over growth. But like many other parts of the baby, the GI tract is also under development. The GI tract in a baby is responsible for the digestion and absorption of nutrients but it needs extra support. So enzymes play an important role in that. In this article, we will talk about which enzymes are used in making baby food. Before moving to it, we have to understand first what enzymes actually are and their role in the body.
Enzymes and Their Role in the Body?An enzyme is a biological catalyst which speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction in a cell. It is almost a protein which is not destroyed during chemical reactions and is used by the body again and again. A cell has thousands of different enzymes in it and everyone is used for a specific reaction. All living things have enzymes in their bodies which are produced naturally, but they can also be manufactured.
It is almost a protein which is not destroyed during chemical reactions and is used by the body again and again. A cell has thousands of different enzymes in it and everyone is used for a specific reaction. All living things have enzymes in their bodies which are produced naturally, but they can also be manufactured.
The enzyme consists of 1000s of amino acids which are linked in a specific way. The unique shapes are formed due to the fold of enzyme chains. These shapes are responsible for providing the enzyme with the characteristic chemical potential.
The metabolic process of the initial stage depends upon the enzymes which react with a molecule called a substrate. Substrates get converted into other molecules due to enzymes, the other distinct molecule is called products.
Enzymes play an important role in maintaining life processes therefore they are a key element in clinical diagnosis. Except in the class of ribozymes (RNA), the macromolecular components of all enzymes are made up of protein.
Enzymes also play an important role in aiding digestion which is the process of turning the food we eat into energy. There are various enzymes present in our Slavia, pancreas, intestine and stomach which break down fats, protein and carbohydrates and use these nutrients for growth and cell repair.
They also help with:
- Breathing.
- Building muscle.
- Nerve function.
- Ridding our bodies of toxins.
Now you know what important role Enzymes play in our body. Therefore, many baby food companies use enzymes to enhance the flavour, solubility, and digestibility of nutrients in baby foods. They are also added to produce some functional ingredients. Some important enzymes used for baby boys are given below-
Lipase-
Lipase is a water-soluble enzyme which is used in baby foods because it helps your baby break down the food. The breakdown food is easy to digest and the body can easily absorb the important nutrients from it. To fortify baby foods, lipases are used to produce pure concentrates of Functional lipids such as omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and DHA has a unique role in infants' brain and eye development. This Lipase enzyme is also naturally produced in the pancreas but it can also be found in the digestive tracts of newborn babies.
To fortify baby foods, lipases are used to produce pure concentrates of Functional lipids such as omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and DHA has a unique role in infants' brain and eye development. This Lipase enzyme is also naturally produced in the pancreas but it can also be found in the digestive tracts of newborn babies.
Protease
Protein plays a crucial role in adults as well as babies. Protein helps in a child’s growth, maintenance and repair of the body, it also helps to maintain proper balance and pH of body fluids. But babies are not able to digest protein when they eat solid foods therefore the food is treated with protease enzyme. This type of food is easier for a baby's digestive system to digest because it predigests some of the protein. Babies easily get the essential amino acids from food because of the protease enzyme.
Lactase
Lactose is a sugar which is present in milk and other dairy products. Lactose is most important for babies' health and development. 40% of babies' energy comes from lactose which helps babies to absorb calcium and iron. But the baby is not able to break the lactose into simple sugar therefore, lactase enzyme plays an important role in that. If there is a lack of lactase enzyme in the baby's body then lactose can’t be broken down and acts as a great food source for gut bacteria. It also leads to problems like lactose intolerance.
40% of babies' energy comes from lactose which helps babies to absorb calcium and iron. But the baby is not able to break the lactose into simple sugar therefore, lactase enzyme plays an important role in that. If there is a lack of lactase enzyme in the baby's body then lactose can’t be broken down and acts as a great food source for gut bacteria. It also leads to problems like lactose intolerance.
Due to an unhealthy lifestyle, an increase in pollution and other environmental factors, caring for a baby is getting tough day by day. Parents are so much worried about their child's growth and whether he\she is getting proper nutrition or not. But don’t worry, we have mentioned above the important Enzyme which should be there in baby foods. So whenever you visit any shop or market to buy baby foods, always check for these enzymes, whether they are present or not. Time flies too fast, so spend your maximum time with your baby.
Back to Blogs
Lactazar for children
How many times a day should Lactazar be given to a child? The instructions do not exactly say the number of times a day.

According to the official recommendations for use, Lactazar is taken in each milk feeding (at the rate of 1 capsule per 100 ml of milk). Therefore, if your child is still receiving only milk food, then Lactazar is given at each feeding. If dairy-free complementary foods are introduced (fruit and vegetable purees, meat, etc.), then the addition of Lactazar to such feeding is not required. nine0005
What is the best way to dilute Lactazar - in milk or in water?
According to the official recommendations for the use of "Lactazar for children", the contents of the capsule must be diluted in milk or milk food before use. Dilution in water is not provided. When using Lactazar for Children, the time and volume of milk / mixture for dilution is determined by the period necessary to obtain a homogeneous suspension.
Formula-fed child, diagnosed with lactase deficiency. What is better - to give the usual mixture with Lactazar or buy a special low-lactose one? nine0003
The selection of the optimal mixture for the baby should be carried out by a specialist, based on his physical condition and assessment of the severity of lactase deficiency. There is an opinion that for feeding a baby with lactase deficiency, it is better to use a regular mixture and additionally take lactase preparations, since the intake of milk sugar is very important for the proper formation of organs and systems in a child, especially the brain. The validity of the use of low-lactose and lactose-free mixtures is determined by the pediatrician observing the child. nine0005
There is an opinion that for feeding a baby with lactase deficiency, it is better to use a regular mixture and additionally take lactase preparations, since the intake of milk sugar is very important for the proper formation of organs and systems in a child, especially the brain. The validity of the use of low-lactose and lactose-free mixtures is determined by the pediatrician observing the child. nine0005
Is it possible not to dilute Lactazar, but simply pour the capsule directly into the child's mouth?
Due to the risk of asphyxia with dry powder, it is strictly forbidden to give the contents of the capsule undiluted in milk to a child.
Is it necessary to use Lactazar during night feeding?
When Lactazar is prescribed, it must be given to the child at every milk feeding (breast milk/formula), i.e. including at night.
Can expressed milk with diluted Lactazar be stored in the refrigerator?
When feeding with expressed milk, Lactazar should be given to the child, diluted in a portion of milk immediately before feeding. According to the officially approved recommendations of the manufacturer, the use of Lactazar for the preparation of milk nutrition for the future, for the purpose of storage and use after a period of time, is not provided. The enzyme included in Lactazar is used without prior exposure (without adding an enzyme preparation to the product, diluting and leaving for fermentation). nine0005
According to the officially approved recommendations of the manufacturer, the use of Lactazar for the preparation of milk nutrition for the future, for the purpose of storage and use after a period of time, is not provided. The enzyme included in Lactazar is used without prior exposure (without adding an enzyme preparation to the product, diluting and leaving for fermentation). nine0005
My baby is 2 weeks old, all symptoms point to lactase deficiency, the doctor prescribed Lactazar. Can lactase deficiency appear so early?
Yes, maybe. Temporary (transient) lactase deficiency, which most often occurs in newborns, usually manifests itself at 2-3 weeks of a child's life.
Is it possible for a breastfeeding mother to use Lactazar so that the enzyme gets to the child directly through breast milk? nine0003
Lactase preparations work only in the intestinal lumen. The only substrate for lactase action is lactose. The enzyme is not absorbed into the blood. The remains of unclaimed enzyme are excreted from the body naturally with feces. The drug cannot enter breast milk. Therefore, in order to make up for the lactase deficiency in a child, Lactazar must be given to him, and not to a nursing mother.
The drug cannot enter breast milk. Therefore, in order to make up for the lactase deficiency in a child, Lactazar must be given to him, and not to a nursing mother.
My baby is currently mixed-fed - I breastfeed first and then supplement with formula. How to take Lactazar in this case - give 1 capsule before the breast and add 1 capsule per 100 g of the mixture to the mixture? nine0003
If you are breastfeeding and additionally giving formula, then this is mixed feeding - you give the baby Lactazar (previously diluted in expressed milk) 1 time before breastfeeding, then bottle-feed the baby with formula. The calculation of Lactazar is carried out from the ratio of 1 capsule per 100 ml of milk (total amount - both breast and in the mixture).
What are the causes of lactase deficiency (complicated pregnancy, malnutrition of a nursing mother, heredity)? nine0003
The most common causes of lactase deficiency are hereditary predisposition, prematurity of the child and the presence of inflammatory bowel disease. In newborns, we are usually talking about the so-called transient lactase deficiency - a condition that occurs in normal full-term children due to the immaturity of the enzyme system of the gastrointestinal tract.
In newborns, we are usually talking about the so-called transient lactase deficiency - a condition that occurs in normal full-term children due to the immaturity of the enzyme system of the gastrointestinal tract.
We are on artificial feeding, now we eat 120 ml of the formula for one feeding, will one Lactazar capsule be enough for this volume? nine0003
The recommended dose of Lactazar is calculated according to the formula: for 100 ml of milk or milk formula - one capsule of lactase enzyme 700 units. If the baby eats more than 100 ml of milk in one feeding, two capsules are supposed to be used. The degree of lactase deficiency in children may be different, i.e. in some, the degree of enzyme deficiency is significant, in others it is minimal. It is advisable to select an effective dosage individually, depending on the clinical picture. If you have any doubts about the application, it is recommended to consult with a supervising pediatrician. nine0005
After what time should the dose of Lactazar be reduced?
As a rule, the symptoms of temporary lactase deficiency (frequent, watery, frothy stools, bloating, colic, regurgitation) disappear by the end of the 4th month of a child's life.
Lactazar is canceled gradually, as the intestinal enzyme system matures, carefully monitoring the baby's condition. It is better to start withdrawal with daytime feedings, and not with evening or nighttime feedings, so that if lactase deficiency symptoms recur, they can be controlled. When canceling the lactase preparation, control by the pediatrician is necessary. nine0005
With congenital lactase deficiency, lactose intolerance (milk sugar) persists throughout life, therefore, when drinking milk or other products containing lactose, an additional intake of a lactase enzyme, such as Lactazar, is necessary.
The doctor prescribed Lactazar and Acipol. Lactazar is used simultaneously with dairy food. Acipol for children from 3 months of age is recommended to be taken with food, dissolving the contents of the capsule in water or milk. Let's say I cooked porridge for a child, is it possible to add both Lactazar and Acipol to it at the same time? nine0003
Interaction studies with the simultaneous use of Lactazar and Acipol have not been conducted. The combined use of lactase enzyme and probiotics is not limited. Based on the recommendations for the use of Lactazar, it is taken in each milk feeding, and Acipol - 2-3 times a day with meals, children from 3 months of age are recommended to dissolve the contents of the capsule in water or milk. Therefore, when preparing porridge with milk, you can add Lactazar to it at the rate of 1 capsule per 100 ml and the contents of the Acipol capsule, provided that the temperature of the dish does not exceed 37 ° C. nine0005
The combined use of lactase enzyme and probiotics is not limited. Based on the recommendations for the use of Lactazar, it is taken in each milk feeding, and Acipol - 2-3 times a day with meals, children from 3 months of age are recommended to dissolve the contents of the capsule in water or milk. Therefore, when preparing porridge with milk, you can add Lactazar to it at the rate of 1 capsule per 100 ml and the contents of the Acipol capsule, provided that the temperature of the dish does not exceed 37 ° C. nine0005
Can Lactazar be added to milk formula based on goat's milk?
Lactazar is recommended as an additional source of the lactase enzyme, which breaks down the milk disaccharide lactose. Therefore, Lactazar is added to any dairy food containing lactose.
Lactazar can be added to milk formula made from both cow's and other types of milk, including goat's.
Food enzymes
Food enzymes nine0004 The dynamic development of biotechnology and scientific discoveries in the field of enzymology have made enzyme preparations an indispensable element of many food technologies. The use of enzymes makes it possible to increase the speed of technological processes, significantly increase the yield of finished products, improve their quality, save valuable raw materials and reduce the amount of waste.
The use of enzymes makes it possible to increase the speed of technological processes, significantly increase the yield of finished products, improve their quality, save valuable raw materials and reduce the amount of waste. Organs and tissues of farm animals, cultivated plants, special strains of microorganisms (mold fungi, bacteria) are used to produce enzyme preparations for food purposes. nine0005
Enzyme preparations of microbial origin are obtained by cultivating specific microorganisms capable of producing certain enzymes. Currently, most of the enzymes in the industry are produced using bacteria and mold fungi in special bioreactors (fermenters) under strictly controlled conditions. There are bacterial enzyme preparations obtained by deep cultivation of bacteria, and fungal preparations obtained by surface cultivation of microscopic fungi. nine0005
Enzyme preparations with amylolytic, proteolytic, lipolytic, pectolytic, oxidase activity are used in food technology. They are used in brewing, winemaking, baking, in the production of alcohol, fruit and vegetable juices, yeast, cheese, cottage cheese, meat and fish products, protein hydrolysates, invert syrup, and in the processing of starch.
They are used in brewing, winemaking, baking, in the production of alcohol, fruit and vegetable juices, yeast, cheese, cottage cheese, meat and fish products, protein hydrolysates, invert syrup, and in the processing of starch.
Modern technologies make it possible to expand the scope of enzyme preparations. Today, there are about 15 food industries where enzymes are successfully used, and in each industry a separate group of enzymes achieves specific goals that either improve the quality of the product, or increase the yield of this product or reduce the cost of the process, and therefore reduce the cost of production. . nine0005
Flour production and bakery
The quality of bread is determined by the characteristics of the chemical composition of flour and the activity of its enzyme complex. It is possible to obtain good quality bread only when the rates of microbiological processes and biochemical transformations are harmoniously combined in the process of dough making. Enzymatic hydrolysis of high-molecular components of raw materials (proteins and carbohydrates) to a certain extent contributes to the intensification of these transformations and, ultimately, has a positive effect on the quality of bread. nine0005
Enzymatic hydrolysis of high-molecular components of raw materials (proteins and carbohydrates) to a certain extent contributes to the intensification of these transformations and, ultimately, has a positive effect on the quality of bread. nine0005
The effectiveness of the use of certain enzyme preparations in bread baking largely depends on the quality of the flour. The baking properties of flour, especially the quality of gluten and the activity of its own enzymes, determine the requirements for enzyme preparations.
Baking enzymes are used as additives to flour and as part of dough leavening agents to compensate for low quality indicators of flour, improve dough structure and quality characteristics of the finished product. In bread baking, mainly five enzyme preparations are used. nine0005
Improvement of the gluten framework: Protease, Xylanase, Glucose oxidase, Lipase.
Increasing the gas-holding capacity of dough and bread volume: Alpha-amylase, Xylanase, Glucose oxidase, Lipase.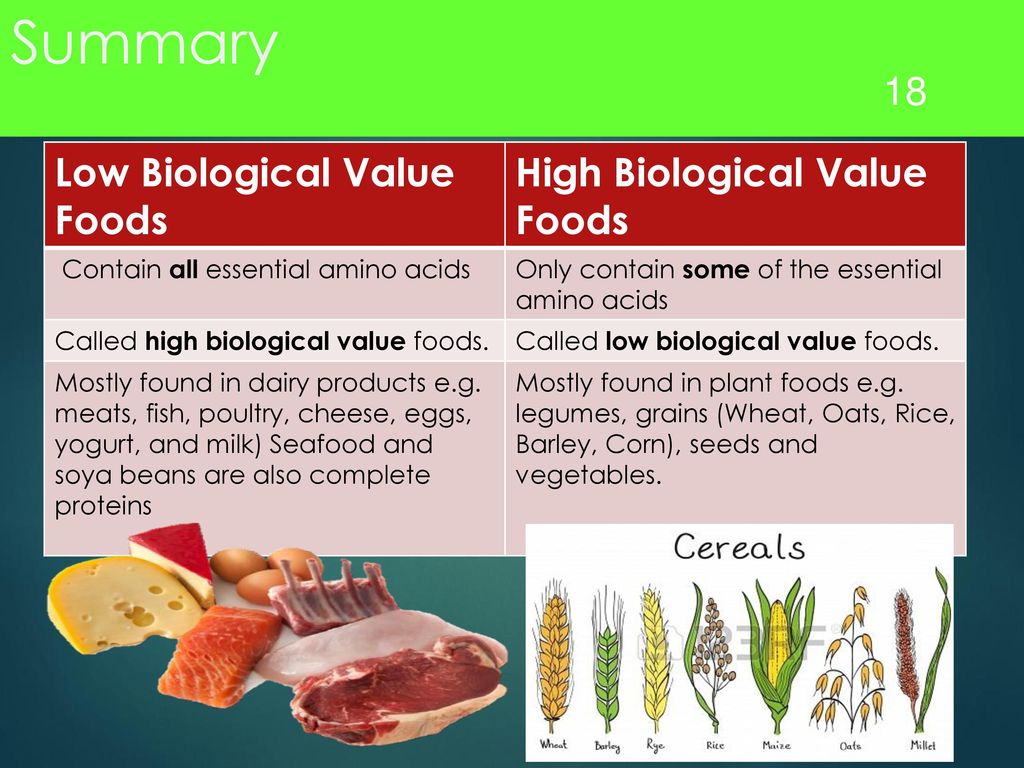
Color, taste and aroma improvement: Alpha-amylase, Lipase.
Crumb structure improvement: Alpha-amylase, Xylanase, Glucose oxidase, Lipase.
Shelf life extension: Alpha-amylase. nine0005
Confectionery production
Depending on the type of raw materials and the type of technological process, confectionery products are divided into two groups: floury and sugary. Flour products include cookies, biscuits, crackers, waffles, gingerbread, muffins, cakes, rolls, cakes, etc. etc..
In the production of flour confectionery products using yeast, such as biscuits, crackers, muffins, it is advisable to use complex preparations with a predominance of proteolytic action, but containing alpha-amylase in their composition. The combined action of these enzymes provides the yeast with fermentable sugars and low molecular weight nitrogenous substances. nine0005
In the production of long biscuits using chemical leavening agents, when a lot of effort is directed to the relaxation of gluten, it is advisable to use proteolytic enzyme preparations along with a mechanical effect on gluten proteins during a long technological process.
For custard and raw gingerbread, proteolysis is of the greatest importance, but along with the need for controlled relaxation of the dough, maintaining the freshness (softness) of the product is also important. In the production of such types of products, it is advisable to use complex enzyme preparations with a predominance of proteolytic activity. nine0005
In the production of semi-finished biscuits, complex enzyme preparations with moderate activity of proteolytic enzymes and low alpha-amylase (dextrinating) ability are required. With this combination, moderate relaxation of gluten is ensured, which contributes to a better rise of the dough during baking and the formation of a finely porous airy structure of finished products. The formation of dextrins, in turn, contributes to the preservation of their freshness.
Complex enzyme preparations containing proteases and alpha-amylase are used to speed up and facilitate the processing of dough in the preparation of a puff semi-finished product in order to improve its elastic properties and prevent shrinkage during baking. The use of such enzyme preparations in the production of wafers makes it possible to optimally reduce the viscosity of the wafer dough, and contributes to the production of thin crispy wafer sheets. nine0005
The use of such enzyme preparations in the production of wafers makes it possible to optimally reduce the viscosity of the wafer dough, and contributes to the production of thin crispy wafer sheets. nine0005
The confectionery industry uses the enzyme Invertase to produce molded fondant candy shells, round fondant shells and liquid fruit fillings such as cherry liqueur. The use of Invertase is due to the need to obtain a semi-soft or liquid consistency at high concentrations of sugar that prevent fermentation. Accelerating or slowing down the action of invertase is achieved by changing the concentration of the applied drug, the amount of water and the temperature regime. nine0005
Processing of fruits, berries, vegetables
Along with modern equipment and new technological processes, in the processing of fruits, berries and vegetables, enzymes make it possible to increase the depth of processing of raw materials and thereby reduce the amount of waste, increase the productivity and profitability of enterprises. At the same time, in some cases it is necessary to have a set of enzyme preparations containing a certain complex of enzymes, in others, preparations of individual enzymes are required. nine0005
At the same time, in some cases it is necessary to have a set of enzyme preparations containing a certain complex of enzymes, in others, preparations of individual enzymes are required. nine0005
In accordance with the specifics of fruit and berry raw materials and the purpose of their use, enzyme preparations can be divided into six groups:
1. Enzymes intended for obtaining unclarified juices, increasing yield and increasing extractivity - Pectinase.
2. Enzymes intended for obtaining clarified juices, increasing yield, increasing extractivity and ensuring complete hydrolysis of pectin and protein substances - Pectinase, Pectin lyase, Acid Protease. nine0005
3. Enzymes that macerate fruit and berry tissue, increase the yield and homogeneity of juices with pulp - Pectin lyase.
4. Enzymes intended for obtaining clarified fruit and berry wine materials, increasing the yield and increasing the extractivity of wine materials - Pectinase, Glucoamylase.
5. Enzymes contributing to the prevention of oxidative processes and the development of aerobic microorganisms in juices, wines, soft drinks - Glucose oxidase.
Enzymes contributing to the prevention of oxidative processes and the development of aerobic microorganisms in juices, wines, soft drinks - Glucose oxidase.
6. Enzymes catalyzing the inversion of sugar syrups in the production of soft drinks and commercial syrups - Invertase. nine0005
Manufacture of alcoholic beverages
Starch, as the main component of the dry matter of grain raw materials, from which alcohol is formed, is not directly fermented by yeast. Therefore, it must be hydrolyzed to fermentable sugars, this requires the use of enzymes that hydrolyze starch to fermentable sugars, are a source of nitrogen nutrition for yeast and, when starchy raw materials are saccharified, partially destroy the cell walls of raw materials. nine0005
Grain malt used for a long time as a source of amylolytic enzymes provides a fairly deep saccharification and fermentation, however, the rate of starch saccharification when using malt remains quite low, which makes it difficult to intensify the fermentation process.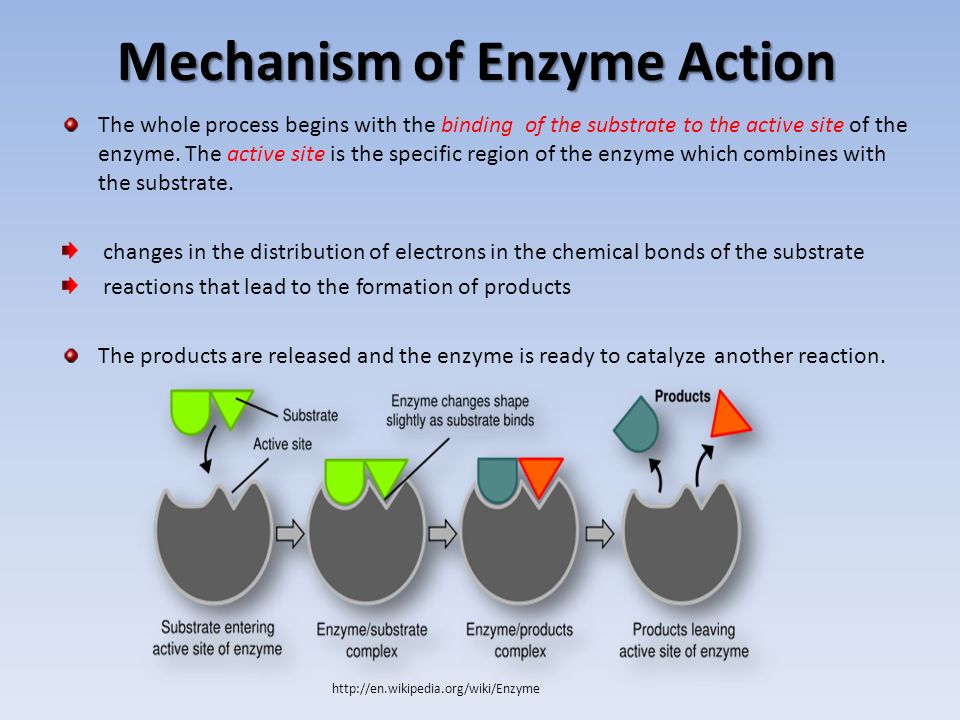 The use of enzyme preparations of microbial origin (Alpha-amylase, Glucoamylase) makes it possible to significantly increase the concentration of the necessary enzymes in the medium and ensure deep hydrolysis of starch in a relatively short period. nine0005
The use of enzyme preparations of microbial origin (Alpha-amylase, Glucoamylase) makes it possible to significantly increase the concentration of the necessary enzymes in the medium and ensure deep hydrolysis of starch in a relatively short period. nine0005
In addition to the saccharification stage, enzyme preparations with a strong thinning activity (Alpha-amylase) are used at the stage of water-heat treatment of raw materials in order to soften the mode of boiling, reduce the viscosity of batches and facilitate their further transportation. When using enzyme preparations at the stage of preparation of wort for yeast generation, it is necessary to ensure intensive protein hydrolysis in order to enrich the yeast wort with valuable nitrogen nutrition.
Thus, for alcohol production processing starch-containing raw materials, it is necessary to use enzyme preparations with amylolytic, proteolytic and cytolytic effects. nine0005
Brewing
During the production of beer according to the usual technological scheme, the necessary enzymes (for the preparation of grain raw materials and the conversion of extractives into a soluble state at the mashing stage) are formed during the malting process.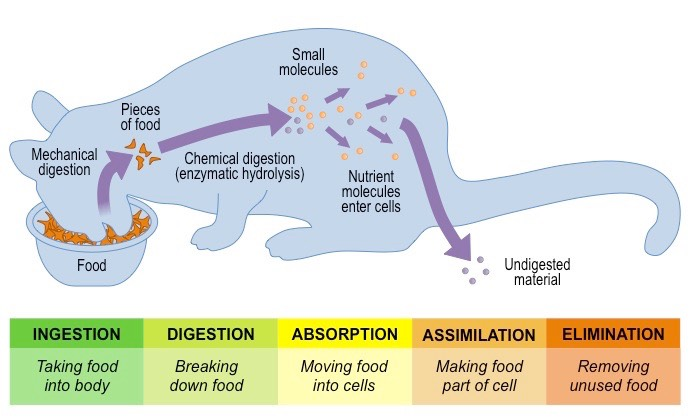
The main enzymes formed during the malting process and of the most significant importance in brewing technology are:
1. Amylolytic enzymes that thin and saccharify starch (Alpha-amylase bacterial, Amylorizin, Glucoamylase). nine0166 2. Proteolytic enzymes that break down barley proteins to peptides of various molecular weights and free amino acids (Protease).
3. Cytolytic enzymes that hydrolyze non-starch polysaccharides that dissolve the cell walls of the grain endosperm, thereby facilitating the access of amylases and proteases to the corresponding substrates (Cellulase).
Each of the above processes must go through with a certain depth in order to ensure the normal flow of mash filtration, wort fermentation, clarification and filtration of beer, as well as the creation of certain physical and chemical properties (pricing, transparency, storage stability) and taste qualities of the finished product. nine0005
The use of enzyme preparations of microbial origin (amilorizin, amylosubtilin, protorizin) to replace malt with unmalted barley allows intensifying the process, avoiding the loss of valuable components of raw materials for respiration and seedling formation, and generally increasing the profitability of brewing.
Meat and fish processing
Recently, enzyme preparations have been increasingly used in meat and fish processing. This is due to their ability to produce specific biologically active components in the tissues of meat and fish: organic acids, bacteriocins, enzymes, vitamins, which improves the sanitary, microbiological, organoleptic indicators of the finished product, and also allows intensifying the production process. nine0005
Enzymatic methods improve the quality of meat, meet the growing demands of consumers and increase the degree of processing of raw materials. There are two main directions for the use of enzymes in the meat industry: tenderization of tough meat and restructuring of fresh low-quality meat raw materials and trimmings (trimming) to obtain a high-quality product.
Meat and culinary industries mainly use protein degrading enzymes (Protease, Collagenase) as well as protein crosslinking enzymes (Transglutaminase) as texture improvers. Recently, new directions for the use of traditional enzymes in molecular cuisine have become popular.