Why does my baby take so long to bottle feed
How Long Should Bottle-Feeding Take? – Baby Care Advice
How fast your baby feeds can affect how much milk he drinks, how much air he swallows, and his enjoyment of feeding. Feeding too quickly or slowly can cause problems. Discover how you can influence how long it takes for your baby to feed.
Ideal feeding times for babiesThe faster your baby feeds the more he's likely to drink. If your baby drinks his formula too quickly, there's a risk he may overfeed (i.e. drink more than he actually needs) and/or swallow large amounts of air. Both of which may result in tummy discomfort or spitting up soon after feeding. If your baby completes his feeds too quickly, this could be because the nipple* is too fast.
If he feeds too slowly, this can occur because the nipple ring is screwed on too tight (see notes on common bottle feeding problems) or because the nipple* is too slow. Both problems can make feeding become very tiring for a young baby and he may fail to finish his feed or fall asleep before the feed is completed - resulting in the need for more frequent feeds.
As a guide, the following times are recommended to bottle feed your baby.
- 20 - 40 minutes for newborn to 3 months.
- 15 - 30 minutes for babies 3 months to 6 months.
- 10 - 20 minutes for babies over 6 months.
* Nipple manufacturers provide a guide on nipple speeds suitable for different age groups. Although a nipple may be recommended for your baby's age, this does not guarantee the speed is suitable for your individual baby. Some babies will have a stronger or weaker suck compared to others.
By Rowena Bennett, RN, RM, CHN, MHN, IBCLC
Copyright www.babycareadvice.com 2020. All rights reserved. Permission from author must be obtained to reproduce all or any part of this article.
How we can help- Your Baby's Bottle-feeding Aversion book
- Baby Care Advice consultation
- Rowena Bennett's Online Bottle-Feeding Aversion Program
In my book, ‘Your baby’s Bottle-feeding Aversion’, I have described physical and behavioral reasons for babies to develop an aversion to bottle-feeding. How to identify the cause and the solutions to match. Included are step-by-step instructions on how to regain your baby’s trust and resolve a feeding aversion caused or reinforced by repeated pressure to feed.
How to identify the cause and the solutions to match. Included are step-by-step instructions on how to regain your baby’s trust and resolve a feeding aversion caused or reinforced by repeated pressure to feed.
While the book was written for bottle-fed babies, many nursing mothers have found that applying the same strategies has also helped them to successfully resolve a breastfeeding aversion.
You might find that reading this book is all you need to do to understand the steps you need to take to resolve your baby’s feeding aversion and get him back to the point of enjoying eating until satisfied.
Baby Care Advice ConsultationsIf you would like an individualized assessment of all reasons for infant feeding problems, not just feeding aversion, we also provide a consultation service. Baby Care Advice consultants have extensive experience in pinpointing the cause of feeding aversion and other behavioral feeding problems such as those related to equipment and the parent’s feeding practices. (For more on what’s included in a consultation).
(For more on what’s included in a consultation).
Six time-saving modules to help your family enjoy feeding again with Rowena's step-by-step plan. Enjoy additional tools to manage anxiety, troubleshoot any issues, introduce new carers, how to manage illness/teething and much more.
- Module 1: Understanding feeding aversions
- Module 2: Identify the cause
- Module 3: Prepare for success
- Module 4: How to resolve your baby's bottle-feeding aversion
- Module 5: What to expect
- Module 6: Troubleshooting
- BONUS: Guided meditations
Consultations
BOOK NOW
Bottle-feeding Consultation
From $500. 00
00
5.0 / 5.0
62 reviews
Breastfeeding Consultation
From $500.00
5.0 / 5.0
16 reviews
Solids Feeding Consultation
From $500.00
5.0 / 5.0
2 reviews
Sleep Consultation
From $500.00
5.0 / 5.0
1 review
Bottle-feeding problems and solutions | From Tiny Tot to Toddler
Babies can sometimes have trouble feeding. Usually, the problem is temporary. The first thing to do is observe your baby. Try to get a feel for her temperament as well as her feeding and sleeping routine.
Your baby sleeps a lot
If your baby sleeps a lot, you probably wonder whether you should wake her to feed. Knowing what’s best isn’t always easy. You can follow her routine and let her sleep if she
Knowing what’s best isn’t always easy. You can follow her routine and let her sleep if she
- Wakes up on her own to feed
- Is an active and effective feeder
- Pees at least 6 times and passes at least 3 stools a day
- Is calm and seems satisfied after feeding
- Has regained her birth weight and continues to put on weight
In this case, there is nothing to worry about. Babies each have their own routine that develops over time.
You may need to wake your baby up to feed her if she sleeps a lot.
Photo: Marie-Ève Bolduc
Some babies sleep so much they may skip some feedings, especially during the first 2 to 3 weeks. This means they will have a hard time getting all the milk they need. If your baby sleeps a lot and doesn’t show the signs described above, you need to stimulate her to drink more.
What to do?
- Keep an eye out for signs that she’s sleeping lightly (she’s moving, making sucking motions, or moving her eyes beneath her eyelids) when it will be easier to wake her up.

- Stimulate her: talk to her, massage her back, legs, arms, etc.
- Leave her in an undershirt or diaper: babies drink less when they are warm.
- See a professional if you’re worried or see no improvement after a few days.
Your baby drinks very slowly
Babies can’t always suck effectively at the start. This is more common among babies who were born a few weeks prematurely (between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy). Even full-term babies may need a few days or weeks to get the hang of things. This situation usually improves with time. Be patient: your baby is learning. Some babies, however, will continue to drink slowly even as they get older.
What to do?
- Change to a faster nipple.
- Stimulate your baby as she feeds by rubbing her feet and tickling her back and sides.
- Run your finger under her chin and across her cheeks to stimulate her.
- Change her diaper or change her position for a few minutes.
Your baby often chokes while drinking
If the nipple you are using flows too quickly and your baby has too much milk in her mouth, she may choke (i. e., she swallows noisily, coughs and spits up a little milk).
e., she swallows noisily, coughs and spits up a little milk).
What to do?
- Change to a slower nipple.
- Take short feeding breaks.
- Avoid laying your baby on her back during feeding since milk will flow into her mouth even when she’s not sucking. Try to feed her in a near-sitting position so that the bottle is tilted only slightly downward (just enough for the nipple to fill with milk and not air). Your baby will then be able to drink at her own pace.
Your baby regurgitates a lot
As long as your baby is happy and putting on weight, regurgitation (“spitting up”) is generally nothing to worry about (see Regurgitation).
Some babies drink very fast, and their stomachs expand too quickly. This makes it easier for them to regurgitate, especially if they are very active and start moving around right after feeding.
If milk is coming out of the bottle too quickly, your baby will drink too much just to satisfy her need to suck. If she regurgitates a lot, the nipple on the bottle may be too fast.
If she regurgitates a lot, the nipple on the bottle may be too fast.
What to do?
If your baby is in good spirits and gaining weight, there’s nothing to worry about. You don’t need to do anything.
If regurgitation seems to be bothering her, watch her drink. If necessary, try these strategies:
- Change to a slower nipple.
- Take short feeding breaks.
- Try to burp her more.
- Avoid laying your baby on her back during feeding. Try to feed her in a near–sitting position so that milk will flow into her mouth more slowly.
- Try to keep activity to a minimum right after feeding.
It’s best to see a doctor if your baby
- Seems to be in pain
- Projectile vomits several times a day
- Wets fewer diapers
- Isn’t putting on enough weight
Your baby refuses the bottle
Your baby normally breastfeeds, and you want to bottle‑feed her? If she has trouble bottle-feeding or refuses to altogether, see the tips on Combining breast and bottle.
Baby won't take a bottle | Philips Avent
search support iconSearch Keywords
Home ›› What to do when your baby refuses a bottle
↑ top
any problems. If your breastfed baby refuses a bottle, don't worry. This is a common occurrence in many babies who are used to breastfeeding. Obviously, this can create certain difficulties for moms, especially if you need to return to work in the near future. nine0003
3 Philips Avent products to help you bottle feed:
So why is your baby refusing to bottle and crying? There are many ways to quickly and easily teach a breastfed baby to a bottle. Here are important tips on what to do when your baby refuses a bottle.
Is the baby refusing the bottle? Take a step back
If your baby cries while bottle feeding, the first thing to do is to start over and rethink your feeding approach and technique. Try the following steps when bottle feeding your baby: [1]
Try the following steps when bottle feeding your baby: [1]
- Lift and tilt your baby's head forward. Before inserting the pacifier into the baby's mouth, make sure that the baby's head is raised and tilted over his body to avoid choking: so that the baby does not choke and have the opportunity to burp during bottle feeding.
- Insert the pacifier. Bring the pacifier to the baby's lips and gently guide it into the baby's mouth. In no case do not try to press the nipple on the baby's lips and try to push it into his mouth. After touching the pacifier to the baby's lips, wait for the baby to open his mouth and take the pacifier. nine0036
- Hold the bottle at an angle. Tilt the bottle at an angle so that the nipple is only half full. So the child can eat at his own pace.
- Let the baby burp during and after feeding. It can be useful for a child to burp not only after feeding, but also approximately in the middle of the process. This will help reduce gas or tummy discomfort that your baby may experience from swallowing too much air.

- Stop in time, do not overfeed the baby. If the baby begins to turn his head away from the bottle or closes his mouth, then he is full and you need to stop feeding.
- Perhaps the flow of milk from the nipple to the baby is weak or, on the contrary, too fast, so he is naughty and refuses the bottle. Try changing the nipple to a nipple with a different flow.
Other tips if your baby refuses the bottle
If you've followed the steps above and your baby still refuses the bottle, don't worry. There are other ways to help bottle feed your baby. Here are some simple tricks you can add to your bottle feeding process. nine0029 [2]
1. Remind your child about mom.
Sometimes a child can be fed by someone other than his mother - dad, grandmother or, for example, a nanny. If your baby fusses while bottle feeding, try wrapping the bottle in something that smells like mommy, like a piece of clothing or some fabric. This will make it easier to feed the baby when the mother is not around.
This will make it easier to feed the baby when the mother is not around.
2. Try to maintain skin contact while bottle feeding. nine0006
Some babies need contact with their mother, so try bottle feeding while leaning against you. However, some babies are better at bottle feeding when they are in the exact opposite position than when they are breastfed. For example, there is a position with bent legs. Lay the child on your bent knees, facing you, pointing the child's legs towards your stomach. During feeding, the baby will be able to look at you and contact you in this way. If your baby refuses a bottle, experiment to see which works best. nine0003
3. Move while feeding.
Sometimes all it takes to get your baby to take the bottle is a little wiggle or walk. The next time your baby starts crying while bottle feeding, try moving around a little rhythmically to calm him down.
4. Try changing the milk temperature.
Try changing the milk temperature.
If the baby still does not want to take the bottle, check if the milk in the bottle is too hot or too cold. Before feeding, put some warm breast milk on the inside of your wrist to check the temperature. Milk should be warm, but if it seemed hot to you, just place the bottle for a short while under a stream of cold water. nine0003
Choosing the right bottle for your baby If you plan to combine bottle feeding with breastfeeding, it is advisable to choose bottles with a nipple that will have a wide base as the bottle will grip closer to the breast. Also pay attention to the fact that the nipple is firm and flexible, the child must make an effort to drink from the bottle, as well as from the breast. Give preference to nipples with an anti-colic valve that vents air out of the bottle. nine0003
Natural bottle allows you to combine breast and bottle feeding. 83.3% of babies switch from a Natural bottle to breastfeeding and back. *
*
If you choose a bottle for artificial feeding, traditional bottles are fine, but it is desirable that the nipple is made of a hypoallergenic material, such as silicone, has an anti-colic valve and did not stick together when bottle fed. In case your baby spit up often, then use special bottles with anti-colic and anti-reflux valve, which reduces the risk of spitting up and colic.
Bottle with unique AirFree valve reduces the risk of colic, gas and spitting up. With this bottle, you can feed your baby in an upright or semi-upright position to reduce spitting up. Due to the fact that the nipple is filled with milk and not air during feeding, the baby does not swallow air, which means that feeding will be more comfortable.
Both bottles are indispensable if you want to breastfeed, bottle feed or just bottle feed your baby. nine0003
“My baby refuses to breastfeed but bottle feeds – help!”
Sometimes a baby gets used to bottle feeding and refuses to breastfeed. Therefore, it is important to use bottles that are suitable for combining breastfeeding with bottle feeding. If, nevertheless, you are faced with the fact that the child refuses to take the breast, try using silicone nipple covers to make the transition from the bottle to the breast and back more imperceptible. nine0013
Therefore, it is important to use bottles that are suitable for combining breastfeeding with bottle feeding. If, nevertheless, you are faced with the fact that the child refuses to take the breast, try using silicone nipple covers to make the transition from the bottle to the breast and back more imperceptible. nine0013
Remember that if you want to combine breastfeeding and bottle feeding, it is worth waiting at least a month before offering a bottle, so that you are lactating and have time to get used to each other and develop a breastfeeding regimen.
Breastfeed and bottle feed your baby with pleasure
Remember that it takes a while for your baby to get used to bottle feeding. This is completely normal. If you have to go to work, be sure to set aside enough time to bottle train your baby beforehand. nine0013
Remember that every child is different, so what works for one may not work for another. With a little time and patience, you will find out what works best for your baby when he refuses a bottle.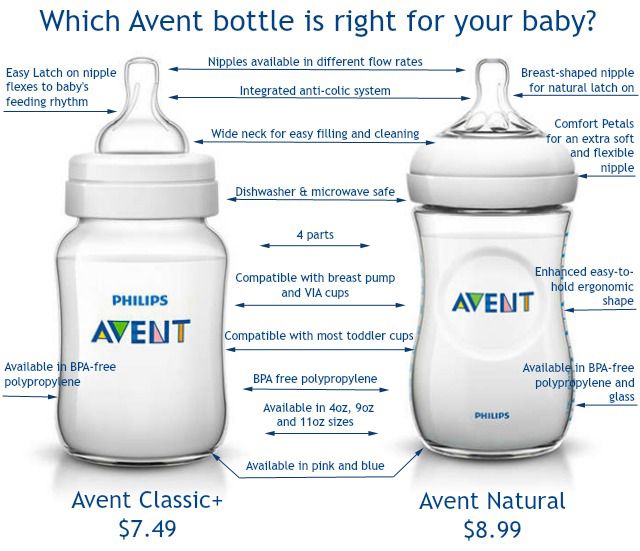
You will identify your child's unique needs. However, if your baby still refuses the bottle after all the steps above, check with your pediatrician.
Articles and tips from Philips Avent
References:
*O.L. Lukoyanova, T.E. Borovik, I.A. Belyaeva, G.V. Yatsyk; NTsZD RAMS; 1st Moscow State Medical University THEM. Sechenova, "The use of modern technological methods to maintain successful breastfeeding", RF, 10/02/2012 3 llli.org - The Baby Who Doesn't Nurse
llli.org - Introducing a Bottle to a Breastfed Baby
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers and save those special moments forever.
Download app:
You are leaving the Philips Healthcare (“Philips”) official website. Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you. Philips makes no warranties regarding any third party websites or the information they contain. nine0003
nine0003
I understand
You are about to visit a Philips global content page
Continue
You are about to visit the Philips USA website.
I understand
Why does the baby always hang on the chest? ❤️ KIDY.eu
- Not enough milk?
- Temporary crises
- What to do in temporary crises?
“My baby just hung on my chest. I know what to feed demand, but he demands endlessly. What to do?!" - is the most common question to lactation consultants. It turns out that the phrase "the baby is hanging on the chest" means different things for everyone. nine0003
It happens that mothers expect that the baby will ask for a breast every 3-4 hours, eat 15 minutes, and sleep the rest of the time. And the requirement of the breast once every 1. 5-2 hours, as most newborns do, is alarming. So: if a baby of the first months of life asks for a breast every hour or two and, having received it, eats up to half an hour, then this is not “hanging”, but the normal behavior of the baby. Over time, the baby will begin to ask for breasts less often, but for now you need to wait. For the mother's body, frequent feedings are also useful: they help a good contraction of the uterus, prevent the development of postpartum complications and regulate the total amount of lactation so that the mother does not experience milk stagnation. It happens differently: the baby asks for breasts in 2-3 hours, but, having received it, eats for an hour or even longer. This may be a variant of the norm, but the situation can be improved. Also, carefully look at the general state of affairs with feeding, if the child lives in the rhythm of “an hour I eat - an hour I rest” or spends more time on the chest during the day than without it. nine0003
5-2 hours, as most newborns do, is alarming. So: if a baby of the first months of life asks for a breast every hour or two and, having received it, eats up to half an hour, then this is not “hanging”, but the normal behavior of the baby. Over time, the baby will begin to ask for breasts less often, but for now you need to wait. For the mother's body, frequent feedings are also useful: they help a good contraction of the uterus, prevent the development of postpartum complications and regulate the total amount of lactation so that the mother does not experience milk stagnation. It happens differently: the baby asks for breasts in 2-3 hours, but, having received it, eats for an hour or even longer. This may be a variant of the norm, but the situation can be improved. Also, carefully look at the general state of affairs with feeding, if the child lives in the rhythm of “an hour I eat - an hour I rest” or spends more time on the chest during the day than without it. nine0003
Not enough milk?
Usually the first thing a mother thinks about is that if a newborn is constantly hanging on her chest, then she does not have enough milk. Absolutely not necessary! But you need to check this version. And only weight gain can reliably show this.
Absolutely not necessary! But you need to check this version. And only weight gain can reliably show this.
Do not rush to get upset, this can be fixed!
- Have a lactation consultant look at your feeding. He will suggest ways to improve, assess whether supplementary feeding is needed and whether lactation should be stimulated. nine0036
- If a consultant is not available, look for improved attachment to the breast. Often this is enough for the breast to begin to be better stimulated to produce milk, and the child to suck out this milk better.
- If the baby has gained a kilogram or more in a month, then we are not talking about a lack of milk. Most likely, you can think about a temporary crisis ...
ATTENTION - this is a very important point!
Often mothers are asked to express milk, evaluate breast size, etc. for testing. But these are all very unreliable signs that are different for all women and they don’t talk about the amount of milk. In mothers, the breast reacts differently to pumping, the amount of glandular tissue is different for everyone (in a small breast it can be much more than in a large one, where adipose tissue predominates). The only thing you can really trust is how your baby grows and gains weight. nine0013 For the first 3 months of life, an increase that indicates a sufficient amount of milk - from 500 grams per month or more.
In mothers, the breast reacts differently to pumping, the amount of glandular tissue is different for everyone (in a small breast it can be much more than in a large one, where adipose tissue predominates). The only thing you can really trust is how your baby grows and gains weight. nine0013 For the first 3 months of life, an increase that indicates a sufficient amount of milk - from 500 grams per month or more.
If a child gained 500-700 grams in a month, but he had to hang on his chest for hours, the mother needs to work on organizing breastfeeding, otherwise the situation usually worsens later. If your baby added less than 500 grams, then, alas, he really does not have enough milk.
Temporary crises
These are situations of a sharp increase in the attachment of babies to the breast or a sharp increase in the duration of feedings. Every nursing mother faces this, it’s just that someone understands what is happening, someone gets scared, and someone simply, out of ignorance, takes steps to stop breastfeeding.
Crises are caused by various reasons:
- Crisis of adaptation when new circumstances appear in the baby's life . Usually adaptation crises: the second week of life, moving or going to work, travel. The baby is trying to calm down and regain confidence in her mother's support through more frequent attachments. The crisis can also be provoked by internal factors: for example, a child is preparing to fall ill, and through an increase in attachment, his body fights the disease with the healing elements of breast milk. Babies also tend to hang on their chests before any kind of developmental leap (usually new skills, such as crawling or walking). Mom's milk and attention give the baby the strength to conquer new heights. nine0036
- Growth spurt crisis . These growth spurts are tied to certain periods of a baby's life: about three weeks, a month and a half, three months, six and nine. During such periods, many children actively grow.
 For such rapid growth, babies need more nutrition than usual, so they quickly empty their breasts, which gives mothers the impression of “missing milk”. There is actually milk in the chest, just on crisis days the child eats it much more energetically and is ready to constantly ask for breasts, to eat more and more. nine0036
For such rapid growth, babies need more nutrition than usual, so they quickly empty their breasts, which gives mothers the impression of “missing milk”. There is actually milk in the chest, just on crisis days the child eats it much more energetically and is ready to constantly ask for breasts, to eat more and more. nine0036
- The most seemingly obvious option to supplement with formula often becomes a “red flag” for the mother’s body: you don’t need so much milk, the child manages anyway. As a result, milk production really begins to decline rapidly.
- In a crisis situation, it is important not to panic, but for a couple of days literally lie down with the baby in bed and patiently feed, shifting from one breast to another as it is empty. You can drink hot tea, use lactogons, but this is not enough without frequent feedings. And most importantly, crises are a very short-term phenomenon, they rarely last longer than 2-4 days! nine0036
What to change?
Let's go back to the most common situation with "chest hanging": the baby gains weight only slightly above the lower limit (500-700 g in the first three months of life or 400-500 g in the next three months). When, with such increases, the child is applied to the breast every 2-3 hours for about half an hour, this is expected. But if the feedings are more frequent and longer, then sucking is ineffective: the baby sucks out a portion of milk for a very long time, enough to eat.
When, with such increases, the child is applied to the breast every 2-3 hours for about half an hour, this is expected. But if the feedings are more frequent and longer, then sucking is ineffective: the baby sucks out a portion of milk for a very long time, enough to eat.
What to do?
- Adjust breastfeeding to the so-called “asymmetric” . When feeding, the breast should be captured deeper from below than from above: the main working parts of the baby's mouth (lower jaw and tongue) are located below, and stimulation from this side should be maximum. This method of application allows the baby to receive milk most efficiently and stimulate the breast to produce new milk.
Bring the baby to the breast at such a height that the nipple is at the level of the spout. On the chest, form a crease with the nipple in the middle so that the thumb is on top of the crease and opposite the baby's nose, and the index and other fingers are below, parallel to the baby's lower lip. When a child feels a breast nearby, he reflexively opens his mouth and throws his head back; then the nipple, which was at the level of the nose, will be directly opposite the mouth. And at this moment, the fold from the chest must be directed into the child's mouth, trying to make the nipple point upwards into the sky. If everything is done correctly, then the baby’s head will be slightly tilted up when sucking, the chin will be tightly pressed to the chest, and the nose is either completely free or touches the chest only with the tip. If the chin does not touch the breast, but the nose is pressed into it, then this is just inefficient sucking, in which the baby has to suck for a very long time to eat, and even the nipples can be injured. nine0036
When a child feels a breast nearby, he reflexively opens his mouth and throws his head back; then the nipple, which was at the level of the nose, will be directly opposite the mouth. And at this moment, the fold from the chest must be directed into the child's mouth, trying to make the nipple point upwards into the sky. If everything is done correctly, then the baby’s head will be slightly tilted up when sucking, the chin will be tightly pressed to the chest, and the nose is either completely free or touches the chest only with the tip. If the chin does not touch the breast, but the nose is pressed into it, then this is just inefficient sucking, in which the baby has to suck for a very long time to eat, and even the nipples can be injured. nine0036 - To increase the amount of milk received per feeding session and reduce the application time, make sure that the feeding is effective . It is a mistake to continue to keep the baby on the chest after he has already emptied it.
 If the baby has eaten the bulk of the milk from the breast and continues to suck, receiving drop by drop, a teaspoon in five minutes, then it is not surprising that he will not be particularly full after an hour. At the same time, if the mother simply transfers the child to another breast, in the same time the baby will receive a full, good portion of milk and eat much better! nine0013 “But I heard that the breast should not be changed often, otherwise the baby will not receive hindmilk,” mothers object. Alas, this recommendation has created a lot of problems where they could have been avoided: it only applies to situations of excess milk production. If lactation is so abundant that the baby has to swallow the lighter foremilk for a long time and actively before he gets to the fatter hindmilk, this makes sense. But if there is not much milk, then the child eats both the anterior portion and the fatter posterior portion, and after that continues to squeeze the last drops out of the breast for another half an hour, instead of receiving the second same portion from the other breast.
If the baby has eaten the bulk of the milk from the breast and continues to suck, receiving drop by drop, a teaspoon in five minutes, then it is not surprising that he will not be particularly full after an hour. At the same time, if the mother simply transfers the child to another breast, in the same time the baby will receive a full, good portion of milk and eat much better! nine0013 “But I heard that the breast should not be changed often, otherwise the baby will not receive hindmilk,” mothers object. Alas, this recommendation has created a lot of problems where they could have been avoided: it only applies to situations of excess milk production. If lactation is so abundant that the baby has to swallow the lighter foremilk for a long time and actively before he gets to the fatter hindmilk, this makes sense. But if there is not much milk, then the child eats both the anterior portion and the fatter posterior portion, and after that continues to squeeze the last drops out of the breast for another half an hour, instead of receiving the second same portion from the other breast. ..
..
Pay attention to the baby's sucking rhythm to help you navigate the timing of the breast change. Forward, more liquid milk flows freely, the baby swallows it quickly and actively. Then the rhythm of the sips slows down, for several sucking movements there is only one swallowing. When the baby has to make 3-4 sucks before swallowing, it means that he has reached fatter and thicker milk.
A little more - and the rhythm is already five or six sucks per sip, the chest is almost empty. At this point, squeeze the breast at the base with one hand, which will squeeze the rest of the fatty hindmilk into the ducts. After the baby swallows a little more actively, but when his throat slows down again, it's time to change the chest. nine0036
Sometimes during times of crisis, it is necessary to transfer the baby from one breast to another several times during one feeding. But this is more effective and will give the child more benefit than keeping him all this time on one breast.