2 day old baby not feeding
Breastfeeding sleepy and reluctant babies
Go backThere are lots of reasons why your baby may be reluctant to feed. It doesn’t mean you aren’t doing a good job as a mum. Don’t put too much pressure on yourself to know all the answers straight away and speak to your midwife or health visitor if you have any questions or concerns, or are looking for ways to make feeding more comfortable.
How often should my baby feed?
All babies are different, but it's very common for babies not to feed all that much in the first 24-48 hours, and some don't attach at all. However, from day 2-3 days babies should become much more awake and feed in more frequent (but probably irregular) bursts at least 6 times in 24 hours.
How do I know if my baby's getting enough milk?
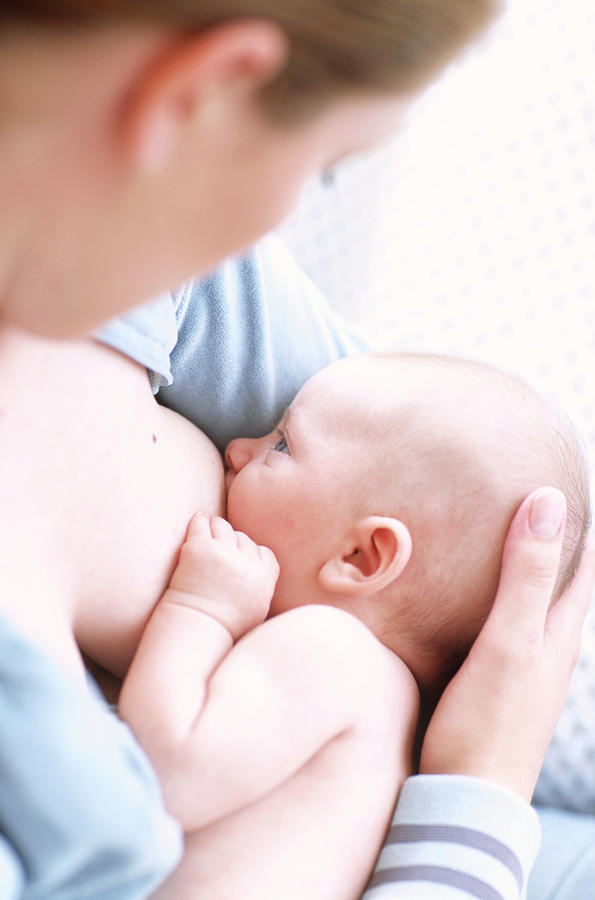
Photo of a baby breastfeeding
Breastfeeding at first can be really hard to get used to and you might find yourself wondering if your baby has had enough milk - it can be very hard to judge how much breastmilk your baby has had, but they are clever wee things and you have to have some faith that your baby knows whether it needs more milk. There are signs to look out for if you think your baby isn't getting enough milk.
Why are some babies reluctant to feed?
This happens most often when babies don't get skin-to-skin contact with mum soon enough or for long enough after the birth. Ideally, you want skin-to-skin contact with your baby straight away and for as long as it takes for your baby to want to feed. If you don’t have any complications, your midwife will help you get skin-to-skin with your baby quickly after they are born. Some reluctant babies are just too tired, sore, or sedated to feed after birth, and others can't because they are premature, ill or jaundiced.
What if I miss my baby's signs that they're hungry?
New mums sometimes miss or don't understand their baby's feeding signs – our page about learning your baby's cues explains what you should be looking for. Don’t worry if it takes a while to get used to when your baby wants a feed – it's something you are both learning together and it's baby steps for both of you. It's completely understandable to be worried about how much milk your baby is getting if they're not feeding in the early hours and days. It might help to know that babies are born with several days' supply of fluid and stored fat to get them by until they're ready to feed.
It's completely understandable to be worried about how much milk your baby is getting if they're not feeding in the early hours and days. It might help to know that babies are born with several days' supply of fluid and stored fat to get them by until they're ready to feed.
What's the solution?
Your midwife will check in on you to make sure your baby is well and to help you spot the signs that they're ready to feed – remember you can ask your midwife (in the hospital or at home) to help show you how to get in a comfortable position to help get your baby feeding. This video shows just this – very often all it takes is some help with positioning, skin-to-skin contact and a little patience!
Top tips to encourage a reluctant or sleepy baby to breastfeed
Tip #1: Hand expressing to keep your milk supply up
Start hand-expressing your colostrum – this is the first milk you make, and helps protect your baby from illness and infection. You can give this to your baby by syringe, spoon, dropper or cup. Expressing helps to build a good milk supply for when your baby is ready to feed. If this is your first time breastfeeding, it will take some time to get used to expressing your milk. You can find out more about expressing here.
You can give this to your baby by syringe, spoon, dropper or cup. Expressing helps to build a good milk supply for when your baby is ready to feed. If this is your first time breastfeeding, it will take some time to get used to expressing your milk. You can find out more about expressing here.
In the first couple of days you only make small amounts of colostrum so don’t become disheartened if it is difficult or takes time. It will get easier as each day and week goes by.
Tip #2: Try lots of skin-to-skin contact
Aim for lots of skin contact and being close to soothe your baby and give them the opportunity to feed.
Tip #3: Try to find a comfortable feeding position
Biological 'laid back' breastfeeding positions can help encourage babies to feed. Your midwife will be able to show you comfortable ways to feed. You can find out more about feeding positions here.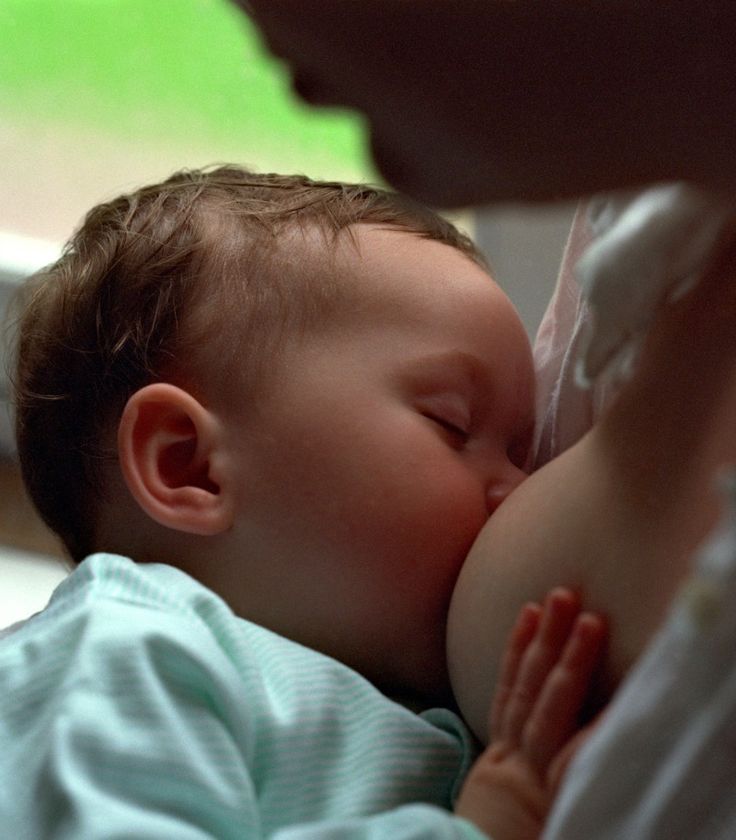
Tip #4: Get your baby ready for a feed
Massaging your baby's skin, changing their nappy and expressing a little milk for them to taste can help get your baby interested in feeding.
Tip #5: Don’t force your baby to feed
Don’t push your baby by the head or try to force them to feed as this could put them off completely.
Getting to know your baby
Learning your baby's cues
Signs your baby isn't getting enough milk
Refusing the breast
Looking after yourself with a newborn
The Scotland wide donor milk bank
This article was created as part of
Explore this article's topics:
Feeding Breastfeeding Common breastfeeding challenges Expectant Parents Baby (0-1 years)
Last updated: 31 May, 2022
Feeding Your Newborn (for Parents)
How you feed your newborn is the first nutrition decision you make for your child.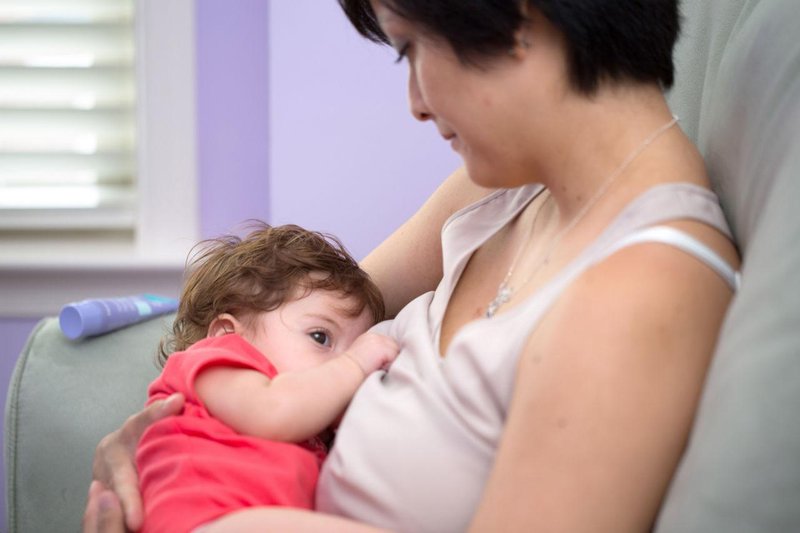 These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
These guidelines on breastfeeding and bottle feeding can help you know what's right for you and your baby.
Breast or Bottle?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that babies be breastfed exclusively for about the first 6 months. After they start on solid foods, babies should breastfeed through the first year of life and even beyond, if desired.
But breastfeeding isn't possible or preferable for all new moms. Deciding to breastfeed or bottle feed a baby is usually based on the mother's comfort level with breastfeeding and her lifestyle. In some cases, breastfeeding may not be recommended for a mom and her baby. If you have any questions about whether to breastfeed or formula feed, talk to your pediatrician.
Remember, your baby's nutritional and emotional needs will be met whether you choose to breastfeed or formula feed.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding your newborn has many benefits. Perhaps most important, breast milk is the perfect food for a baby's digestive system.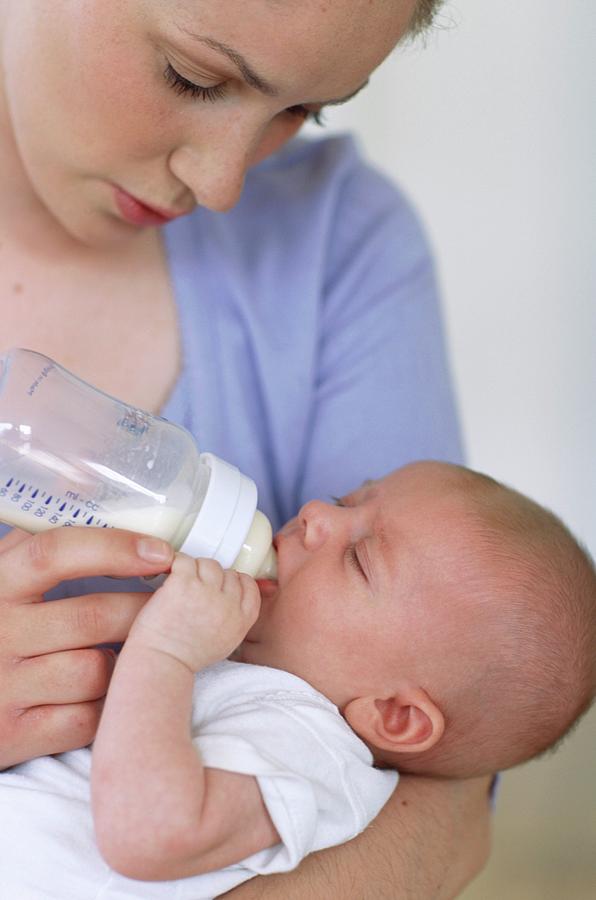 It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
It has the nutrients that a newborn needs, and it’s easily digested. Commercial formulas try to imitate breast milk, and come close, but can't match it exactly.
Breast milk has
antibodiesthat help protect babies from many infections, including diarrhea and ear and lung infections. Breastfed babies are less likely to develop medical problems such as diabetes, high cholesterol, asthma, and allergies. Breastfeeding also might make a child less likely to become overweight.
Breastfeeding is great for moms too. It burns calories, so can help nursing moms lose the weight gained during pregnancy. Breastfeeding also may offer protection from breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Some moms find breastfeeding easier and quicker than formula feeding — it needs no preparation, and you don't run out of breast milk in the middle of the night. Also, breastfeeding costs little. Nursing mothers do need to eat more and may want to buy nursing bras and pads, a breast pump, or other equipment. But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
But these expenses are generally less than the cost of formula.
Breastfeeding meets a variety of emotional needs for both moms and babies. The skin-to-skin contact can enhance the emotional connection, and providing complete nourishment can help new moms feel confident in their ability to care for their newborn.
Limitations of Breastfeeding
With all the good things known about breastfeeding, why doesn't every mother choose to breastfeed?
Breastfeeding requires a big commitment from a mother. Some new moms feel tied down by the demands of a nursing newborn. Because breast milk is easily digested, breastfed babies tend to eat more often than babies who are fed formula. This means moms can be in demand as often as every 2 or 3 hours in the first few weeks. This can be tiring, but it's not long before babies feed less often and sleep longer at night.
Some new mothers need to get back to work outside the home or separate from their babies from time to time for other reasons.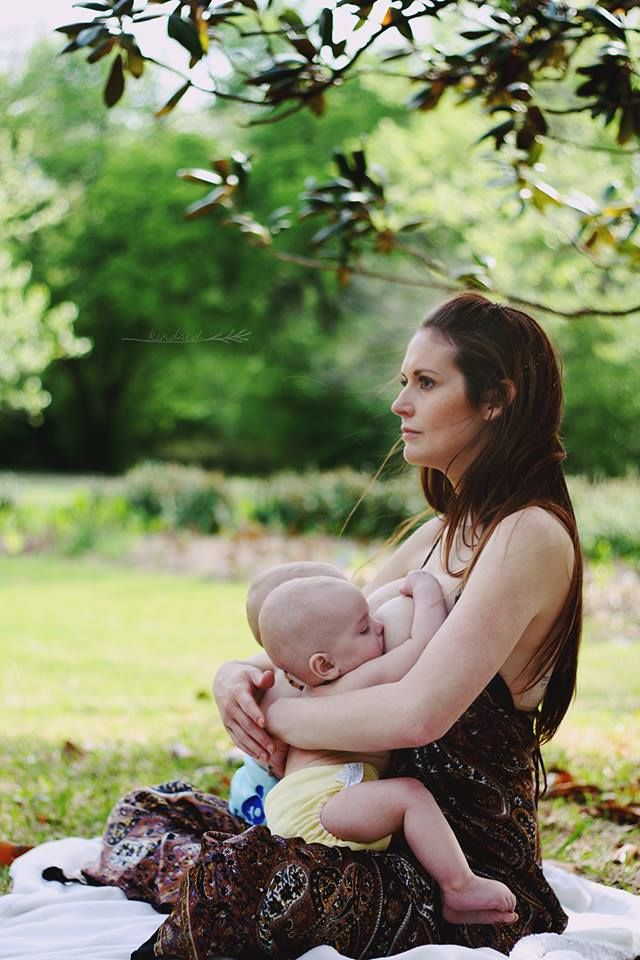 Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Some opt for formula feeding so other caregivers can give the baby a bottle. Mothers who want to continue breastfeeding can use a breast pump to collect breast milk to be given in a bottle, so their babies still get its benefits even when mom isn't there to breastfeed.
Fathers and other family members may want to share in feeding the baby. When mom is breastfeeding, dad or siblings may want to stay close by. Helping mom get comfortable, or providing a burp cloth when needed, will let them be part of the experience.
When breastfeeding is going well, other family members can help by giving the baby pumped breast milk in a bottle when mom needs a break.
Some moms may feel embarrassed or worried about breastfeeding. These feelings usually end after a successful breastfeeding process is set. It can help to get advice from those who've gone through the experience. Most hospitals and birthing centers offer in-depth instruction on breastfeeding to new moms. Your pediatrician, nurse practitioner, or nurse can answer questions or put you in touch with a lactation consultant or a breastfeeding support group.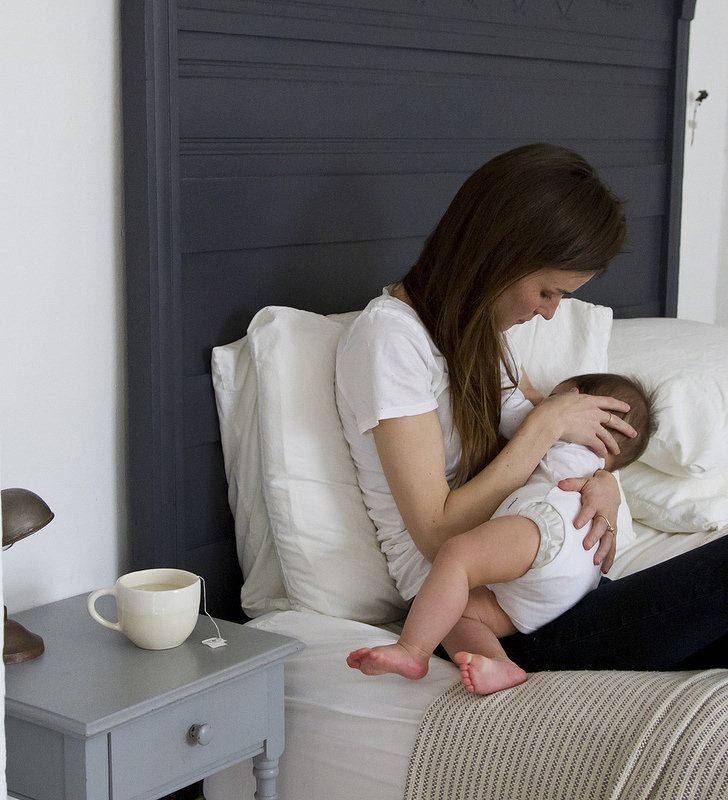
In some cases, a mother's health may affect her ability to breastfeed. Moms getting chemotherapy for cancer and those who have HIV should not breastfeed, for example.
If you have a medical condition or take any medicines regularly, talk with your doctor about whether it's OK to breastfeed. If you have to stop nursing temporarily, continue to pump breast milk to maintain milk production. If you or your baby are sick, continue to breastfeed if you can. Talk to the doctor if you have any concerns.
In some situations, it may not possible to breastfeed, such as when a baby is very sick or born early. Mothers should talk with their baby's doctor about expressing and storing milk. Often, a baby who can't breastfeed can get breast milk through a feeding tube or bottle.
Some moms who have inverted nipples may have trouble breastfeeding, but a lactation consultant usually can help them overcome this. Likewise, women who have had plastic surgery on their breasts should be able to successfully breastfeed.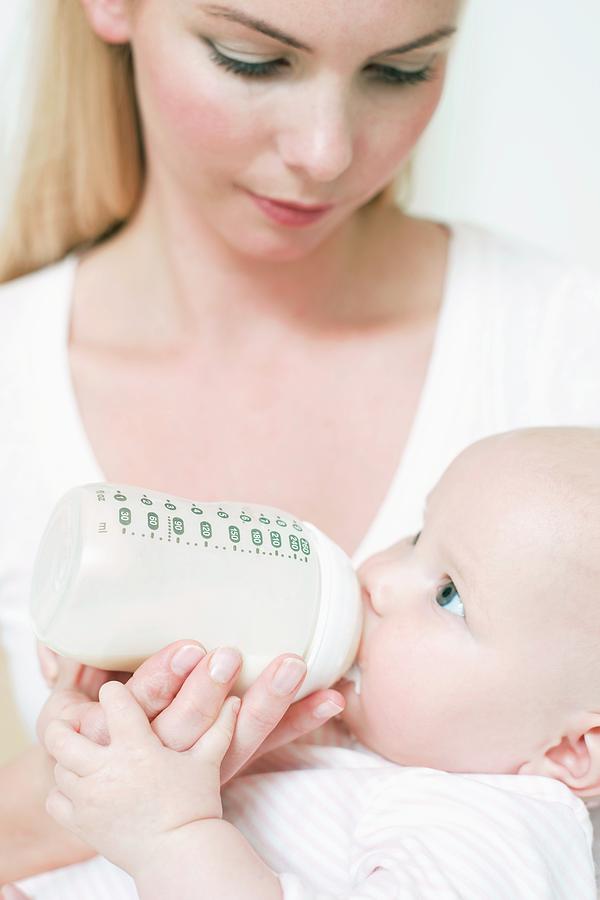 Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Talk with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Hold off on pacifiers or bottles until your baby has gotten used to and is good at breastfeeding. Lactation professionals recommend waiting until a baby is about 3–4 weeks old before offering artificial nipples of any kind (including pacifiers).
Benefits of Formula Feeding
Commercially prepared infant formula is a nutritious alternative to breast milk. Bottle feeding can offer more freedom and flexibility for moms, and make it easier to know how much the baby is getting.
Because babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, a baby who is getting formula may need fewer feedings than one who breastfeeds. Formula feeding also can make it easier to feed the baby in public, and lets the father and other family members help feed the baby, which can enhance bonding.
Limitations of Formula Feeding
Just as breastfeeding has its unique demands, so does bottle feeding. Bottle feeding takes organization and preparation, especially if you want to take your baby out. Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
Store-bought formula can be pretty expensive, but do not try to make your own formula at home.
It's important to make sure that you have enough formula on hand, and bottles that are clean and ready to be used.
Here are a few guidelines for formula feeding:
- Carefully follow directions on the label when preparing formula. Do not add more water than directed.
- Bottles left out of the refrigerator longer than 1 hour and any formula left in the bottle that a baby doesn't finish should be discarded.
- Prepared bottles of formula can be stored in the refrigerator up to 24 hours and carefully warmed just before feeding. You don't have to warm formula, but most babies prefer it.
- A bottle of formula can be warmed by holding it in running warm water or setting it in a pan of warm water. A bottle of formula (or breast milk) should never be warmed in a microwave. The bottle can heat unevenly and leave "hot spots" that can burn a baby's mouth.

How Often Do Newborns Eat?
Your newborn will nurse about 8 to 12 times per day during the first weeks of life. In the beginning, mothers may want to try nursing 10–15 minutes on each breast, then adjust the time as needed.
Breastfeeding should be on demand (when your baby is hungry), which is generally every 1–3 hours. As newborns get older, they'll nurse less often and have longer stretches between feedings. Newborn babies who are getting formula will likely take about 2–3 ounces every 2–4 hours. Newborns should not go more than about 4–5 hours without feeding.
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling against their mothers' breasts
- crying
A feeding schedule is not necessary — you and your baby will get into a routine.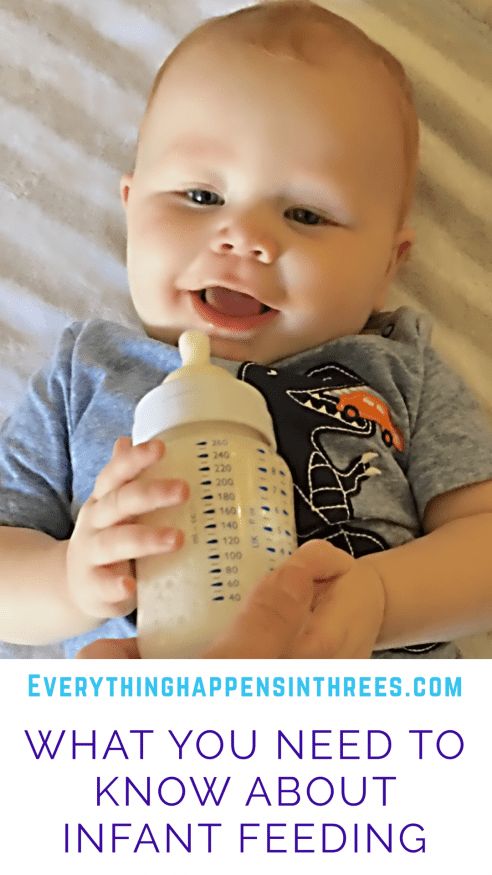 Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
Babies know (and will let their parents know) when they're hungry and when they've had enough. Watch for signs that your baby is full (slowing down, spitting out the bottle or unlatching from breast, closing the mouth, turning away from the breast or bottle) and stop the feeding when these signs appear.
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. There may be other times when your infant seems hungrier than usual. Continue to nurse or feed on demand. Nursing mothers need not worry — breastfeeding stimulates milk production, and your supply of breast milk will adjust to your baby's demand for it.
Is My Newborn Getting Enough to Eat?
New parents often worry about whether their babies are getting enough to eat.
Babies are getting enough to eat if they:
- seem satisfied
- have about 6–8 wet diapers a day
- have regular bowel movements (poops)
- sleep well
- are alert when awake
- are gaining weight
A baby who is fussing, crying, seems hungry, does not appear satisfied after feeding, and has fewer wet diapers may not be getting enough to eat. If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
If you're concerned that your baby isn't getting enough to eat, call your doctor.
Most infants "spit up" a small amount after eating or during burping, but a baby should not vomit after feeding. Vomiting after every feeding might be a sign of an allergy, digestive problem, or other problem that needs medical care. If you have concerns that your baby is spitting up too much, call your doctor.
Should Newborns Get Nutritional Supplements?
Breast milk has the right combination of vitamins and easily absorbed iron for newborns. A healthy infant being nursed by a healthy mother doesn't need extra vitamins or nutritional supplements, with the exception of vitamin D. Breastfed babies should begin vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life, continuing until they get enough vitamin D-fortified formula or milk (after 1 year of age).
Breastfeeding mothers who follow vegetarian diets that do not include animal products need vitamin B12 supplements.
Iron-fortified formula has the right blend of vitamins and minerals for a baby, so supplements usually aren't needed. Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Infants drinking less than 1 liter, or about a quart, of formula a day may need a vitamin D supplement.
Water, juice, and other foods usually aren't necessary during a baby's first 6 months. Breast milk and formula provide everything babies need nutritionally until they start eating solid foods. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about feeding your newborn.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
What is constipation in a newborn
The contents of a baby diaper is one of the key topics that young mothers discuss. They pay attention to the frequency of the stool, its consistency, color and smell. One of the most common problems they complain about to doctors or to each other is constipation in babies. We figure out what the baby’s chair depends on and how many days he may not go to the toilet for the most part.
Normal neonatal stool
During fetal development, nutrients are supplied to the baby through the umbilical cord. Through it, the metabolic products of the fetus are also excreted. The digestive system of a newborn begins to work only after childbirth, so it is logical that the baby does not poop in utero. But this does not mean that nothing gets into it.
Through it, the metabolic products of the fetus are also excreted. The digestive system of a newborn begins to work only after childbirth, so it is logical that the baby does not poop in utero. But this does not mean that nothing gets into it.
During this period, the child actively swallows amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid). Its excretion from the body begins after the birth of the child and the start of breastfeeding. For the first time, a newborn goes to the toilet on the second day after birth. This stool is not like a baby's usual feces. Over time, he will return to normal.
How does the baby's stool change in the first months of life?
| Age | Child's chair |
| 1–3 days after birth | The chair is dense, pasty. Usually dark, sometimes greenish in color. The passage of meconium can cause discomfort to the baby. |
| 3–5 days after birth | The chair gradually brightens, becomes mushy. Usually does not cause any inconvenience to the child. But some problems may arise due to the fact that the digestive tract of the baby "learns" to work and is colonized by bacteria. |
| 2 weeks after birth | The work of the gastrointestinal tract is normalized. If the mother feeds the baby with breast milk, the stool is creamy, yellow. On artificial feeding it can be thicker. Not always homogeneous, there may be inclusions. Due to the immaturity of the enzymatic system, it is greenish in color. |
| 1 month after birth | A month old baby can poop from one to several times a day. The chair is normalized and is both pasty and quite hard. Some children may also have stool retention. But if the separation of feces does not cause discomfort and anxiety in the baby, they should not bother the mother either. |
| 2 months after birth | The work of the intestine continues to improve. Two-month-old baby no longer goes to the toilet after every feed. The number of bowel movements is reduced to 1-2 per day. The stool is still not hard, more like slurry. It can be homogeneous and interspersed. |
Constipation is not considered that the baby cannot go to the toilet for a certain time. The main criteria at this age are not stool retention, but unpleasant sensations during defecation (the child cries before pooping), a large amount of stool and its hard consistency.
Because of what the child does not walk on large
Constipation is a reduction in the number of bowel movements relative to their normal number for this age. In addition, such a disorder of the stool is accompanied by the discharge of a large amount of dense stool. Thus, constipation is not just a decrease in the number of bowel movements, but also a change in the stool itself.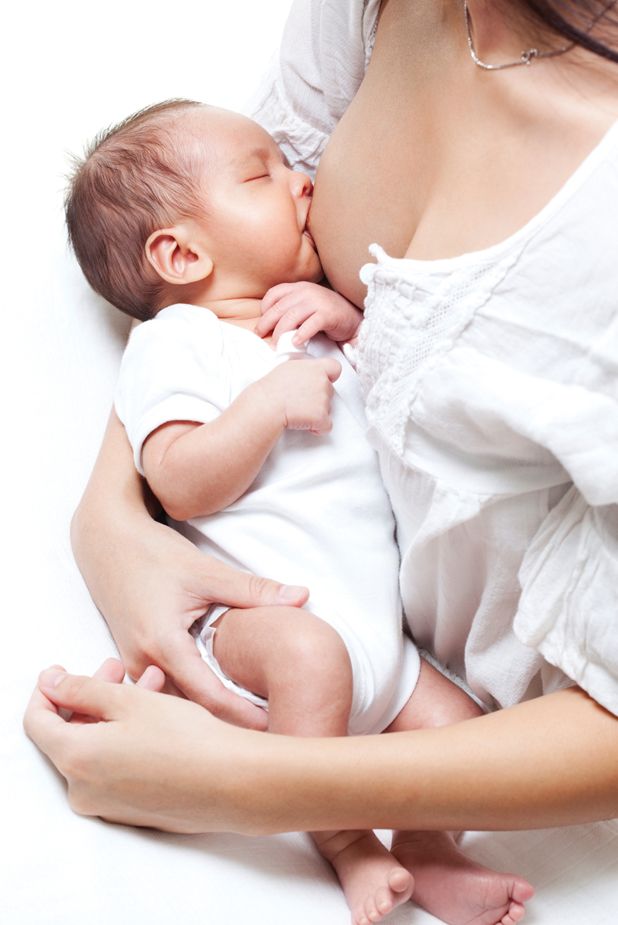
Other signs of constipation in a baby include the following:
- change in stool odor;
- a large amount of gases;
- anxiety of the baby during washing;
- restless sleep in a baby with frequent awakenings;
- intense crying that cannot be stopped.
Even if the baby goes to the toilet every day, but at the same time his feces become plentiful and dry, this indicates constipation in the child. At the same time, the absence of a bowel movement for several days, which does not cause any inconvenience to the baby, and normal mushy stools, even after a break, are not considered grounds for making such a diagnosis.
Causes of impaired defecation can be both normal and pathological. The most common causes of constipation in babies are:
- congenital malformations of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruption of the digestive glands;
- violation of the normal colonization of the gastrointestinal tract by flora;
- the predominance of the mixture over breast milk;
- insufficient fluid intake;
- unsuitable mixture for the baby;
- allergic reactions;
- Iron-deficiency anemia.

Most often, the problem lies in improperly selected nutrition or dysbacteriosis in babies. The fact is that the child's intestines are sterile, and until the flora returns to normal, constipation can develop even in a one-month-old baby. Usually this condition does not require medical intervention, but the baby needs some help anyway.
Constipation is not just a delay in stool, but also a change in its consistency. It can be difficult for a young mother to understand when the lack of bowel movements is normal, and when the child needs help. Our doctors at a remote consultation will help you understand when a child needs help, advise on how to organize a baby’s diet and choose the right formula for him.
When constipation of the baby requires medical attention
Most often, problems with defecation in infants occur due to improper feeding or due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract. However, in some cases, the absence of a chair requires medical intervention. It is especially dangerous if the newborn cannot go to the toilet and his meconium has not passed 2 days after birth.
However, in some cases, the absence of a chair requires medical intervention. It is especially dangerous if the newborn cannot go to the toilet and his meconium has not passed 2 days after birth.
This may indicate congenital problems with the gastrointestinal tract, which require additional diagnosis and examination by a neonatologist. In addition, other symptoms may indicate them. The main ones are:
- blood streaks or black blotches appear in the feces;
- close relatives have diagnosed diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- the child burps frequently and profusely;
- he has vomiting with bile impurities;
- the child gains little or no weight;
- his stomach is very distended;
- the child's stool is like a ribbon;
- he refuses breast or bottle;
- the child cries a lot, and the parents cannot calm him down;
- his temperature rises;
- there are traces of calomania on the diaper, but the feces themselves do not go away.
If such symptoms are observed in the maternity hospital, it is necessary to report them to the neonatologist on duty. If they are found after discharge from the hospital, you need to call a pediatrician or report these symptoms during a patronage bypass. In cases where the child begins to vomit profusely and the temperature rises sharply, you need to call an ambulance.
Important! The minimum weight gain for children in the first three months of life is 150 grams per week or 600 grams per month. In the first month, the increase is calculated from the minimum weight, and not from birth weight.
How to treat stool problems in an infant
To help the baby cope with constipation, you need to understand what caused its development. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a survey of the mother and a physical examination - the doctor palpates the abdomen, examines the anus and performs a rectal examination. To determine the cause, an examination is also carried out - general tests of urine, blood and feces, ultrasound and others if necessary.
If pathologies are detected, a small patient is sent for treatment to a gastroenterologist, who will prescribe the appropriate treatment for the child. In other cases, it is recommended to change the lifestyle of both the nursing mother and the baby:
- A nursing mother is recommended a light diet without fried and fatty foods, with plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits. It is also worth reducing the amount of sugar in the diet, as it can cause fermentation in the digestive tract.
- Try to keep breastfeeding or mixed feeding as long as possible. Breast milk helps the digestive tract to ripen and form the correct flora.
- When transferring to artificial feeding, make sure that the mixture does not contain palm oil. It impairs the digestive processes and can cause constipation.
- If these measures do not help, the child may be prescribed pro- and prebiotics, which help to normalize the intestinal flora, after which the digestive processes also normalize.

- As prescribed by the doctor, the baby may be prescribed laxatives, glycerin suppositories, microenemas and gas tubes. However, you should not get carried away with these drugs, since their constant use can lead to hypotension.
Massage of the abdomen can also help the newborn - stroke the baby's tummy in a circular motion in a clockwise direction and gently press the legs to the stomach. This will improve peristalsis and help the stool pass. A warm bath can also help the baby - it will relax the muscles and make it easier to pass the stool.
If we are not talking about pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, normalizing the nutrition of mother and child helps to fight constipation. Our doctors will help you choose the best diet, tell you when your child needs supplementary feeding, and determine when he needs medication.
FAQ
How do you know if a baby is constipated?
+
Normally, a child’s stool may be absent for several days, if the baby himself is calm at the same time, and the feces after that are soft and pass without problems.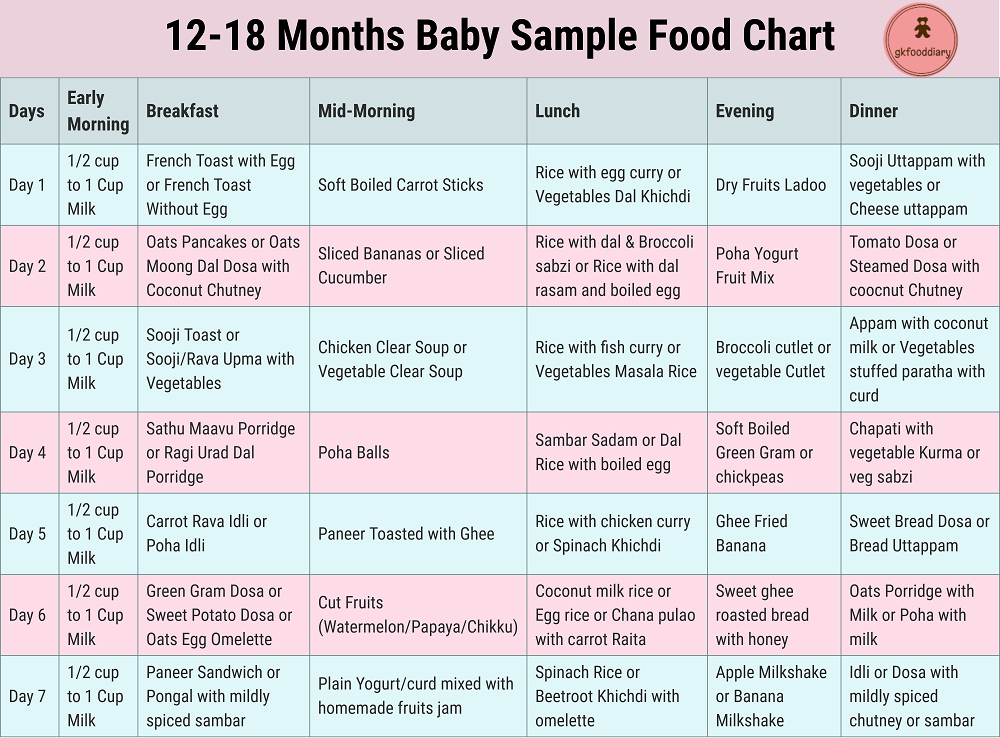 A sign of constipation is the presence of a hard plentiful stool and difficulty with the bowel movement itself.
A sign of constipation is the presence of a hard plentiful stool and difficulty with the bowel movement itself.
Why is there a delay in stool in infants?
+
Stool retention can develop due to the immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract of the child, pathologies in the development of the intestines or digestive glands, dysbacteriosis, dehydration, an improperly selected mixture, or flaws in the diet of a nursing mother.
Can a newborn baby be given a laxative for constipation?
+
Do not give a newborn baby any medication without first consulting a doctor. Your doctor will assess the severity of your constipation and suggest ways to treat it with or without a laxative.
What to do if the baby has constipation? Should I force my baby to poop?
+
If the child is not bothered by anything, and the feces after the pass pass without problems, then there is no need to interfere in these processes.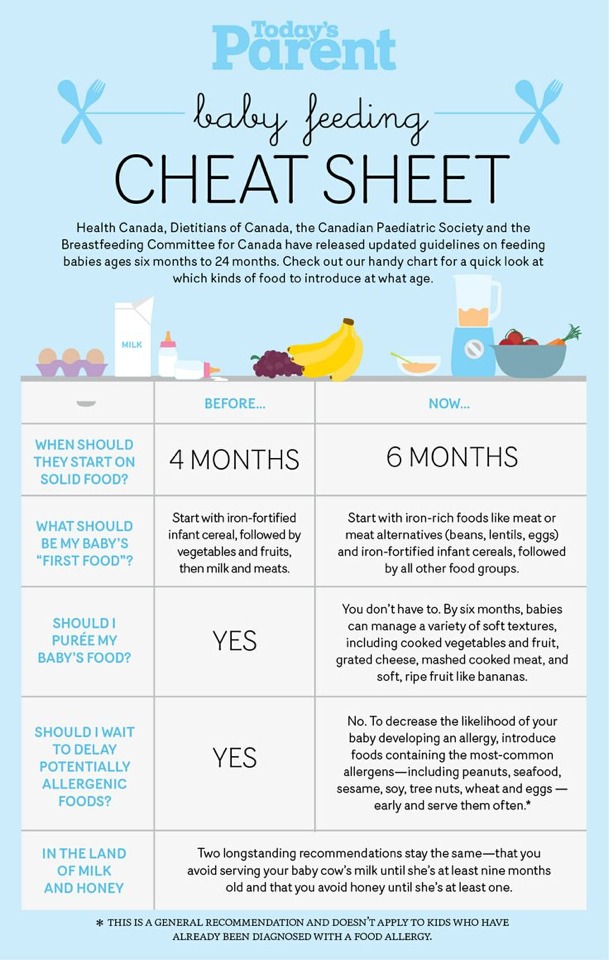 If the baby is clearly having difficulty with bowel movements, consult a doctor to find methods that facilitate this process.
If the baby is clearly having difficulty with bowel movements, consult a doctor to find methods that facilitate this process.
Can planting help with constipation?
+
Theoretically, an upright posture can help a child cope with constipation. However, these methods are rather auxiliary and will not lead to a stable result. It is more effective to adjust the diet and make sure that the child does not have dehydration.
Expert opinion
The absence of a chair in a child does not always mean that the baby has developed constipation. It is indicated by hard plentiful stools, restlessness and a swollen belly of the baby. The cause of a violation of the stool can be both pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, and flaws in the diet of the mother or baby. To determine when constipation requires treatment, the doctors of our service will help. They are available at any time of the day without queues and long waiting times.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Pruzhinin Mark Yulievich pediatrician
Experience 30 years
Consultations 1572
Articles 104
An experienced pediatrician with extensive experience and clinical experience in various medical organizations, resuscitation and intensive care and neuroinfection. Works with leading experts, attends international and Russian conferences.
Works with leading experts, attends international and Russian conferences.
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding essential for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it on the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother.
Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
This whole process is justified from a biological point of view. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with the breast in his mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
The daytime naps of a one-month-old baby feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2.5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for suckling. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person who deliberately harms an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.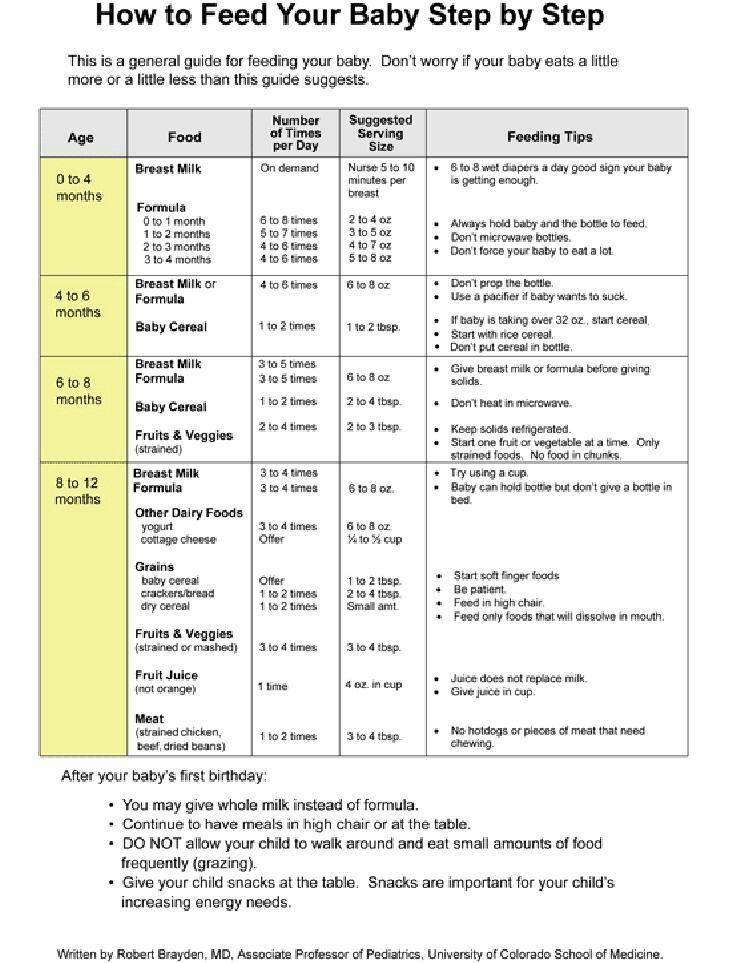
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed much less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen.
 And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months. - At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.
- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications. At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk.
 But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.
But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness. - At seven months, the frequency of applications is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times. The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
- In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding on waking from daytime naps recall this habit again.
 The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ... - Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons. The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him.
 At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours. - At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast. The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
- At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes be breastfed every time he comes to his mother, i.e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child.
 There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down. - At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking. The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1. 5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Mothers who do not think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when feeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is not true. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when counseling mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists.