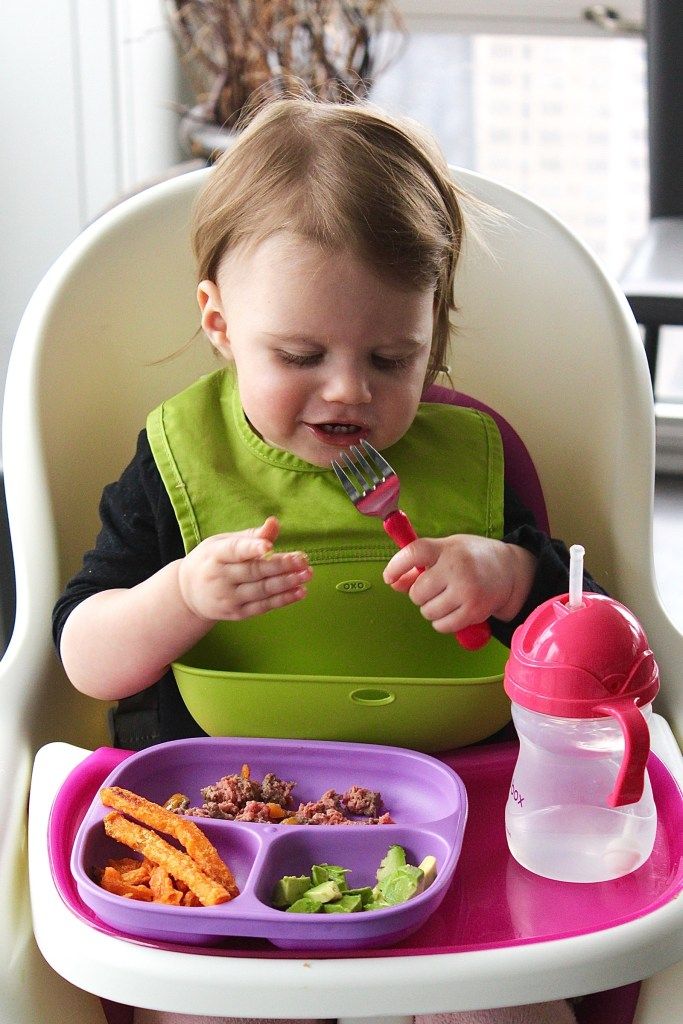
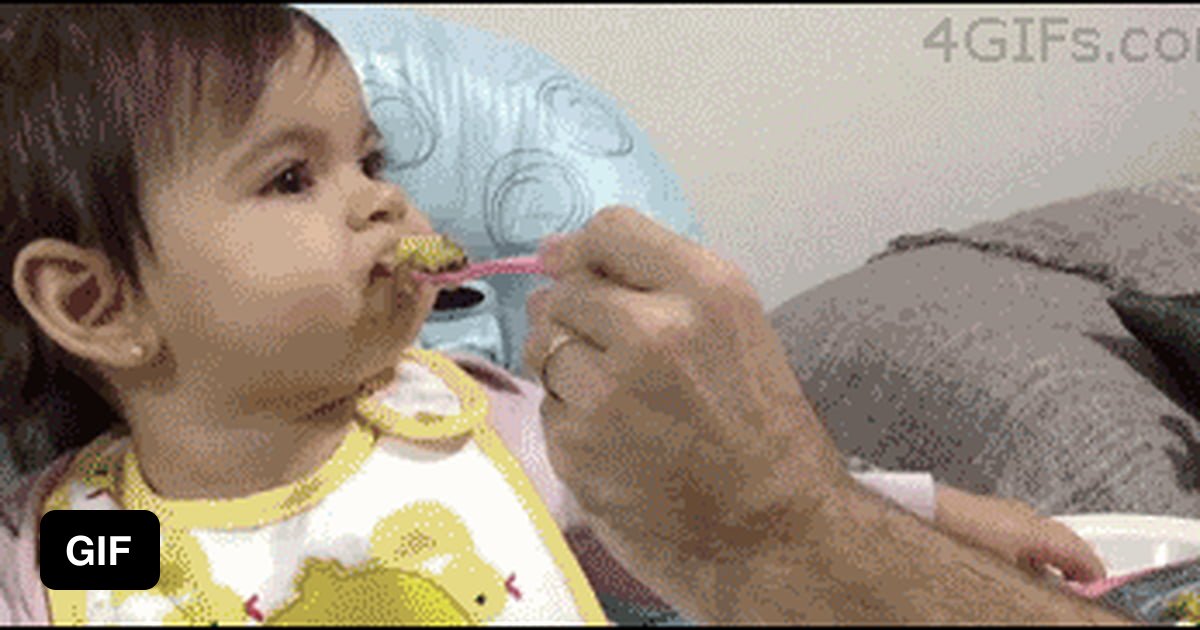
3 week old baby sleeping through feedings
Sleep and Your Newborn (for Parents)
Newborns don't yet have a sense of day and night. They sleep around the clock, and because their tiny stomachs don't hold enough breast milk or formula to keep them satisfied for long, they wake often to eat — no matter what time of day or night it is.
How Long Will My Newborn Sleep?
Newborns should get 14–17 hours of sleep over a 24-hour period, says the National Sleep Foundation. Some newborns may sleep up to 18–19 hours a day.
Newborns wake every couple of hours to eat. Breastfed babies feed often, about every 2–3 hours. Bottle-fed babies tend to feed less often, about every 3–4 hours.
Newborns who sleep for longer stretches should be awakened to feed. Wake your baby every 3–4 hours to eat until he or she shows good weight gain, which usually happens within the first couple of weeks. After that, it's OK to let your baby sleep for longer periods of time at night.
The first months of a baby's life can be the hardest for parents, who might get up many times at night to tend to the baby. Each baby has a different sleep pattern. Some start to sleep "through the night" (for 5–6 hours at a time) by 2–3 months of age, but some don't.
How Should Babies Sleep?
During the first weeks of a baby's life, some parents choose to room-share. Room-sharing is when you place your baby's crib, portable crib, play yard, or bassinet in your own bedroom instead of in a separate nursery. This keeps baby nearby and helps with feeding, comforting, and monitoring at night. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends room-sharing without bed-sharing.
While room-sharing is safe, putting your infant to sleep in bed with you is not. Bed-sharing increases the risk of SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome) and other sleep-related deaths.
Follow these recommendations for a safe sleep environment for your little one:
- Always place your baby on their back to sleep, not on the stomach or side. The rate of SIDS has gone way down since the AAP began recommending this in 1992.

- Use a firm, flat sleep surface. Cover the mattress with a sheet that fits snugly.
- Do not put anything else in the crib or bassinet. Keep plush toys, pillows, blankets, unfitted sheets, quilts, comforters, sheepskins, and bumper pads out of your baby's sleep area.
- To avoid overheating, dress your baby for the room temperature and don't overbundle. Don't cover your baby's head while they're sleeping. Watch for signs of overheating, such as sweating or feeling hot to the touch.
- Keep your baby away from smokers. Secondhand smoke increases the risk of SIDS.
- Offer a pacifier to your baby at sleep time, but don’t force it. If the pacifier falls out during sleep, you don’t have to replace it. If you're breastfeeding, wait until breastfeeding is firmly established.
- Watch out for other hazards, such as items with cords, ties, or ribbons that can wrap around a baby's neck, and objects with any kind of sharp edge or corner. Look around for things that your baby can touch from a seated or standing position in the crib.
 Hanging mobiles, wall hangings, pictures, draperies, and window blind cords could be harmful if they are within a baby's reach.
Hanging mobiles, wall hangings, pictures, draperies, and window blind cords could be harmful if they are within a baby's reach. - Don’t let your baby fall asleep on a product that isn’t specifically designed for sleeping babies, such as a sitting device (like a car seat), a feeding pillow (like the Boppy pillow), or an infant lounger (like the Dock-a-Tot, Podster, and Bummzie).
- Don’t use products or devices that claim to lower the risk of SIDS, such as sleep positioners (like wedges or incliners) or monitors that can detect a baby’s heart rate and breathing pattern. No known products can actually do this.
- Don’t use weighted blankets, sleepers, or swaddles on or around your baby.
- Make sure that all sleep surfaces and products you use to help your baby sleep have been approved by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and meet federal safety standards.
Helping Your Newborn Sleep
Newborns follow their own schedule. Over the next couple of weeks to months, you and your baby will begin to settle into a routine.
Over the next couple of weeks to months, you and your baby will begin to settle into a routine.
It may take a few weeks for your baby's brain to know the difference between night and day. Unfortunately, there are no tricks to speed this up, but it helps to keep things quiet and calm during middle-of-the-night feedings and diaper changes. Try to keep the lights low and resist the urge to play with or talk to your baby. This will send the message that nighttime is for sleeping. If possible, let your baby fall asleep in the crib at night so your little one learns that it's the place for sleep.
Don't try to keep your baby up during the day in the hopes that your little one will sleep better at night. Overly tired infants often have more trouble sleeping at night than those who've had enough sleep during the day.
If your newborn is fussy it's OK to rock, cuddle, and sing as your baby settles down. Swaddling (wrapping the baby in a light blanket) can also help to soothe a crying baby. If you swaddle your baby and they start trying to roll over, that is a sign that you can stop swaddling. For the first months of your baby's life, "spoiling" is definitely not a problem. In fact, newborns who are held or carried during the day tend to have less colic and fussiness.
If you swaddle your baby and they start trying to roll over, that is a sign that you can stop swaddling. For the first months of your baby's life, "spoiling" is definitely not a problem. In fact, newborns who are held or carried during the day tend to have less colic and fussiness.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
While most parents can expect their newborn to sleep or catnap a lot during the day, the range of what is normal is quite wide. If you have questions about your baby's sleep, talk with your doctor.
Bed-Sharing (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
The practice of bed-sharing — parents sharing a bed with their infant — is a hot topic. Supporters of bed-sharing believe that a parent's bed is just where a baby belongs. But others worry that bed-sharing is unsafe.
Co-Sleeping, Room-Sharing, and Bed-Sharing
Many people use the terms "bed-sharing" and "co-sleeping" to describe the same thing, but there are differences:
- Co-sleeping: This is when a parent and child sleep in close social or physical contact of each other, meaning that each can tell that the other is nearby.
Room-sharing and bed-sharing are types of co-sleeping:
- Room-sharing: This is when parents have a crib, bassinet, portable crib, or play yard in the room with them near the bed. Or, they attach a bedside sleeper to the side of their bed.
- Bed-sharing: This is when parents and infants sleep together in a bed, couch, or chair. This has raised concerns because bed-sharing with an infant increases the risk sleep-related deaths, including sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
Why Do Some Parents Bed-Share?
Bed-sharing supporters believe — and some studies support their beliefs — that bed-sharing:
- encourages breastfeeding by making nighttime breastfeeding more convenient
- increases how many months a mother breastfeeds her baby
- helps babies fall asleep more easily
- helps babies and mothers get more nighttime sleep
- gives moms more time to be close to their infants
But the risks of bed-sharing can outweigh the benefits.
Why Is Bed-Sharing Unsafe?
In some cultures, bed-sharing is common and the number of infant deaths related to it is low. Differences in mattresses, bedding, and other cultural practices may account for the lower risk in these countries.
But health experts warn parents not to place their infants to sleep in adult beds due to serious safety risks. Bed-sharing increases the chance of suffocation, strangulation, and SIDS.
An adult bed has many safety risks for a baby, including:
- suffocation from a soft mattress, memory foam, waterbed, or loose or soft bedding such as pillows, blankets, or quilts
- entrapment and suffocation when an infant gets trapped or wedged between a mattress and headboard, wall, or other object
- strangulation in a bed frame that allows part of an infant's body to pass through an area while trapping the baby's head, or from dangling cords
Babies should always be placed to sleep on their backs on a firm mattress or other firm sleep surface (such as in a portable crib) without any pillows, blankets, toys, stuffed animals, or other items.
Because of the risks involved, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) warn against bed-sharing. The AAP does recommend the practice of room-sharing without bed-sharing. Sleeping in the parents' room but on a separate surface lowers a baby's risk of SIDS.
Bed-Sharing & SIDS
Bed-sharing increases a baby's risk of dying from SIDS, especially in preterm infants (preemies), babies who had a low birth weight, and healthy full-term infants younger than 4 months old.
Other things that increase this risk of death while bed-sharing include:
- a baby sleeping on a couch alone or with a parent
- a baby sleeping between two parents
- a mother who smokes
- parents who are very tired
- a parent who has recently used alcohol or drugs
- bed-sharing with pillows or bedcovers
- bed-sharing with other children
How Can We Room-Share Safely?
To keep your little one close, but not in your bed, put a bassinet, play yard, or crib next to your bed. This lets you keep that desired closeness, which can be especially important if you're breastfeeding. Having an infant sleep in a separate space in the same room as the mother reduces the risk of SIDS. You also might consider a bedside sleeper, which attaches to your bed, letting you and your baby be next to each other but on separate surfaces.
This lets you keep that desired closeness, which can be especially important if you're breastfeeding. Having an infant sleep in a separate space in the same room as the mother reduces the risk of SIDS. You also might consider a bedside sleeper, which attaches to your bed, letting you and your baby be next to each other but on separate surfaces.
Make sure that all sleep surfaces and products you use to help your baby sleep have been approved by the CPSC and meet federal safety standards.
Experts recommend that infants sleep in their parents' room without bed-sharing until their first birthday. If parents prefer to move the baby to another bedroom, it's best to wait until the child is at least 6 months old.
How to Bed-Share as Safely as Possible
Some parents decide bed-sharing is best for their family despite the risks. If you choose to have your baby in bed with you, follow these precautions:
- Always place your baby on their back to sleep to reduce the risk of SIDS.

- Dress your baby in minimal clothing to avoid overheating.
- Offer a pacifier to your baby at sleep time, but don’t force it. If the pacifier falls out during sleep, you don’t have to replace it.
- If you swaddle your baby and the baby starts trying to roll over, stop swaddling.
- Don't place your baby to sleep alone in an adult bed.
- Don't place your baby on a soft surface to sleep, such as a soft mattress, sofa, or waterbed. Make sure your bed's mattress is firm.
- Make sure your bed's headboard and footboard don't have openings or cutouts that could trap your baby's head.
- Make sure your mattress fits snugly in the bed frame so that your baby won't become trapped between the frame and the mattress.
- Don't cover your baby's head while they're sleeping.
- Don't have pillows, comforters, quilts, and other soft or plush items on the bed. You can dress your baby in a sleeper instead of using blankets.
- Don't place your bed near draperies or blinds where your child could be get caught in and strangled by cords.

- Don't fall asleep with your baby on your chest.
- Don't sleep on couches, recliners, or rockers with your baby.
- Don’t use weighted blankets, sleepers, or swaddles on or around your baby.
Also:
- Don’t let your baby fall asleep on a product that isn’t specifically designed for sleeping babies, such as a sitting device (like a car seat), a feeding pillow (like the Boppy pillow), or an infant lounger (like the Dock-a-Tot, Podster, and Bummzie).
- Don’t use products or devices that claim to lower the risk of SIDS, such as sleep positioners (like wedges or incliners) or monitors that can detect a baby’s heart rate and breathing pattern. No known products can actually do this.
- Don't smoke, drink alcohol, or use medicines or drugs that can make you less alert or keep you from waking up.
Avoid bed-sharing with infants who are at greatest risk of SIDs. This includes those younger than 4 months, preterm babies, and those who had a low birth weight.
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding necessary for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day. Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother.
Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
This whole process is biologically justified. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with breast in mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
The daytime naps of a one-month-old infant feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2.5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest.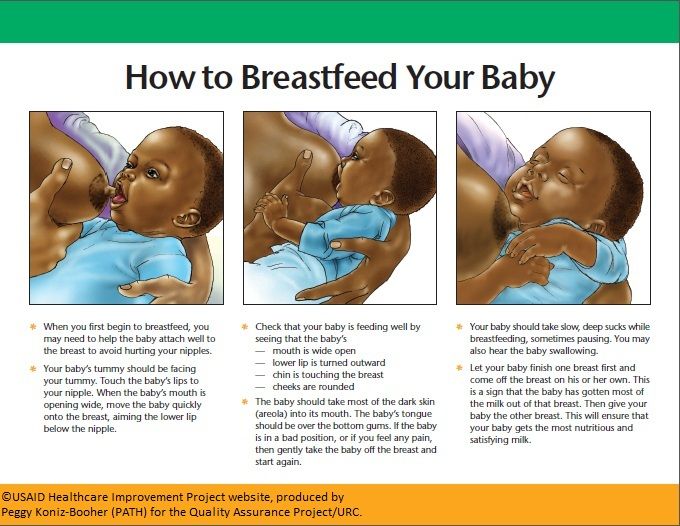 If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for suckling. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person deliberately harming an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
What's next?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed noticeably less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen.
 And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months. - At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.
- At six months, the feeding regimen changes. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications. At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk.
 But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.
But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness. - At seven months, the frequency of application is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times. The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
- In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding when waking up after daytime naps recall this habit again.
 The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ... - Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons. The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him.
 At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours. - At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast. The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
- At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child.
 There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down. - At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking. The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for fun. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1. 5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Moms who don't think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when breastfeeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is wrong. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking back at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when I advise mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists. These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
These are changes with a minus sign. It would be better if they were not, these changes.
Breastfeeding is important not only for the baby, it is also important for the mother. During on-demand feeding, the woman's feelings change, a stronger attachment to the baby is formed, the woman becomes more sensitive to the needs of the baby. Deeper affection and understanding are not only preserved in infancy. They persist for life. For clarity, imagine what happens to a woman’s feelings if she tries to “withstand” a child, endures his crying, anxiety. What happens to a woman if she uses the recommendation from one very popular parenting book: "Go to the child if he cries for more than 15 minutes"? Speaking in abstract terms, humanity is interested in reviving the practice of breastfeeding. The revival of this practice is impossible without mothers realizing the true reasons for the child's need for attachment to the breast.
Lilia Kazakova, pediatrician,
Head of Breastfeeding and Child Care Counselors
How to wake up a baby for feeding and whether to wake up in the afternoon
05/29/2020
95
For any parent, the question of whether to wake up a baby is not easy. On the one hand, there are fears that a child who has been sleeping for a long time will not be able to fall asleep in time later, and on the other hand, how to raise such an angel, who was laid down for so long...
On the one hand, there are fears that a child who has been sleeping for a long time will not be able to fall asleep in time later, and on the other hand, how to raise such an angel, who was laid down for so long...
Let's discuss situations where it is important to wake up a child and how to do this so that his sleep is not affected.
Let's start with the smallest children. You've probably heard the phrase "never wake a sleeping baby." But it is not always fair. Some newborn babies wake up on their own for feedings, while others need to be awakened. Whether or not you need to wake your baby depends on their age, weight, and overall health.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends waking your baby for feedings if he sleeps more than 4 hours in the first two weeks of life. On average, a baby needs feeding every 2-3 hours.
Frequent feeding is very important for several reasons:
- The baby's stomach is very small, the baby quickly digests breast milk.
 Faster than a mix. Therefore, physiologically, the child necessarily needs frequent feedings every 2-3 hours.
Faster than a mix. Therefore, physiologically, the child necessarily needs frequent feedings every 2-3 hours. - Babies can sometimes sleep even when hungry, thus malnourished, which affects their development.
- After birth, the baby loses 5-10% of its body weight. And in the first weeks he needs to gain weight. Lack of milk or formula slows down this process.
- A short interval between feedings helps to maintain lactation. That allows you to avoid problems with a shortage of milk in the future.
Tears already signal strong hunger. Therefore, it is better to breastfeed the baby before the baby starts crying. Learn to recognize the early signs of hunger: the baby puts his hand in his mouth, smacks his lips, tossing and turning when he sleeps.
Do I need to wake my baby up for feeding during the day? In general, if an infant sleeps for more than 3 hours in one dream during daylight hours, he must be awakened. Then the mother can feed the already awakened baby.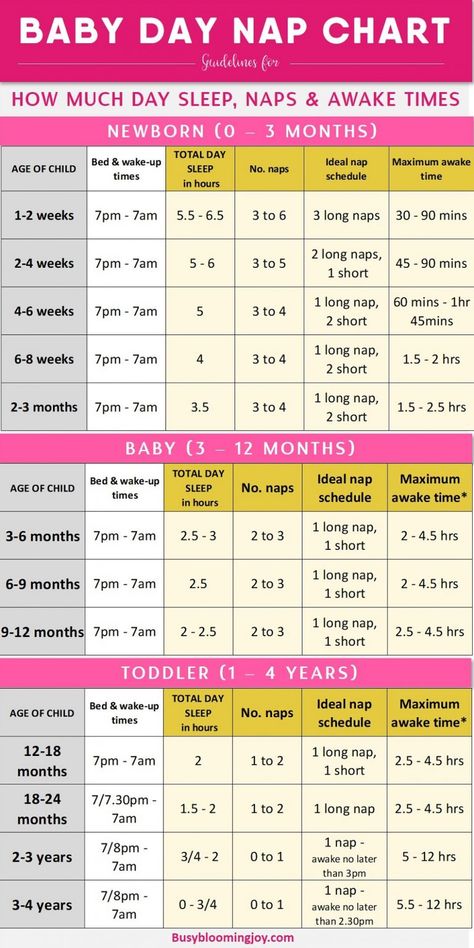 This makes it possible to adjust the work of the biological rhythms of the baby.
This makes it possible to adjust the work of the biological rhythms of the baby.
How to Wake Up
- Help your child gradually fall asleep by stroking their arms, legs or lightly tickling them.
- Change diaper. Often this is enough for the baby to wake up and be ready to eat.
- Undress and place skin to skin on your chest. You can squeeze a few drops of milk onto your baby's mouth. He will smell and taste it and begin to suck on the breast.
- Speak - he will hear your voice and wake up.
- Do not turn on bright lights. A dim light is sufficient. The bright light will blind your eyes.
- If the baby has attached to the breast but has not begun to suckle, stroke his cheek.
How long to feed
As soon as the baby wakes up and starts to feed, make sure that the feed is long enough to empty at least one breast. So we will know that he ate hind milk, which is necessary for the growth of the child's body. Some babies take 45 minutes or more to feed one breast, and some do it in 10 minutes.
Some babies take 45 minutes or more to feed one breast, and some do it in 10 minutes.
The sucking reflex promotes falling asleep. Therefore, make sure that the baby does not fall asleep while feeding. If he falls asleep, change position, lift him up to burp, and then start feeding again.
By 6 months you will have a more or less predictable eating schedule. But each baby will have his own. Some of the children eat every 2 hours, and someone is able to stay without food for 3-4 hours by the second month of life. This is especially true for children who are formula fed.
The time intervals between feedings increase as the child grows older. By the age of six months, many babies can already go without supplements at night or are able to sleep for longer periods.
If a baby wakes up too often after 6 months and asks for food in the dark, perhaps this is no longer hunger, but a way to relax and fall asleep.
Avoid using a pacifier in the first weeks after delivery. The pacifier helps the child to calm down and prolong sleep. So you may not notice that your baby is hungry. Therefore, start using a pacifier no earlier than 4-6 weeks and when you are lactating.
The pacifier helps the child to calm down and prolong sleep. So you may not notice that your baby is hungry. Therefore, start using a pacifier no earlier than 4-6 weeks and when you are lactating.
Should the baby be woken up to feed formula? As with breastfeeding, the newborn needs frequent formula feeding. But the interval will be more than 3-4 hours.
When it is necessary to wake up the child
It is important to wake up the baby in the morning if he fell asleep later than 7.00. This is especially true for children who still sleep 1-2-3 times during the day and have already developed a relatively stable routine. So you create the perfect routine in the morning.
After waking up, children need time to work up their fatigue for the next nap, the ideal window for which is around 9and 13 hours (depending on age).
Therefore, if the baby slept until 8 am, he simply will not be able to fall asleep in his first daytime sleep.
In order for the baby to wake up calmly without tears, you can enter a wake-up ritual. It allows the child to smoothly transition from a sleepy state to wakefulness.
It allows the child to smoothly transition from a sleepy state to wakefulness.
Example of a wake-up ritual:
- Opening curtains/lights on
- Welcome words and a kiss
- Snacks, nursery rhymes after sleep
- Cheerful song
Then you can get up and start breakfast. For older children, such a ritual is also necessary.
The awakening ritual has different tasks:
- Marks the end of sleep,
- Teaches a child that everyday sounds are not a reason to wake up,
- Helps prevent baby from crying when waking up.
It will also be useful to have a light alarm. If the baby wakes up early, he will stay in bed until he sees the light on the clock.
When to wake up a baby after a nap
Many babies from 4 to 8 months sleep three times a day.
In this mode, it is important to wake up the baby after the third nap no later than 17.00. The duration of this segment is about 45 minutes, but not more than an hour. Then you can easily put the baby to bed by 19 o'clock.
Then you can easily put the baby to bed by 19 o'clock.
Transition to one nap
At the age of 15-18 months there is a transition to one nap. It can be long and take place in different ways.
For example:
In the morning, the baby falls asleep easily and sleeps up to 2 hours. But then it is difficult to put it in lunch. And by the evening without rest at lunchtime, he is already overworked and falls asleep with difficulty.
Therefore, if this is your case, you can pick up the child after 60-75 minutes. At the same time, move the start of the second sleep 15 minutes later. But if the baby sleeps for 1 hour in the morning and then it’s already difficult to fall asleep a second time, start putting him down only at lunchtime.
One nap after 2 years
Between 2.5-5 years, daytime sleep may disappear. Here again, the story described above is often repeated. It seems that the child falls asleep perfectly during the day, sleeps for a long time, but in the evening, laying down is delayed until 10-11 pm.