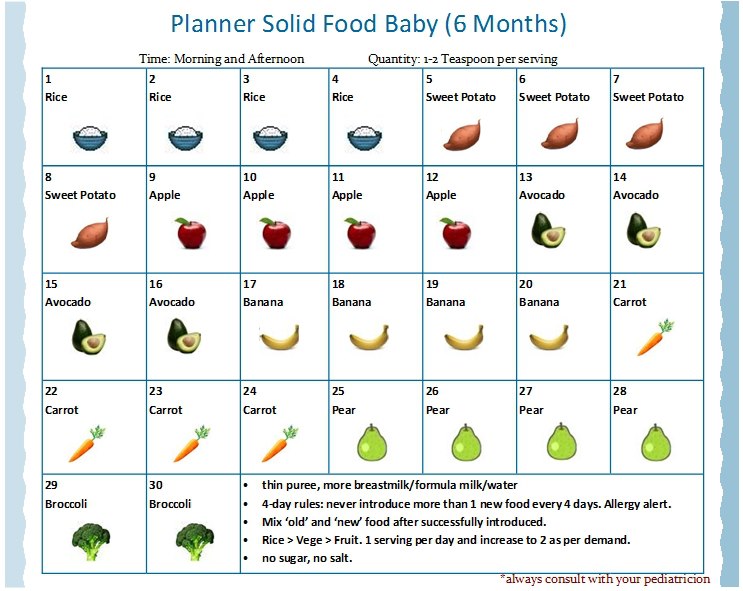
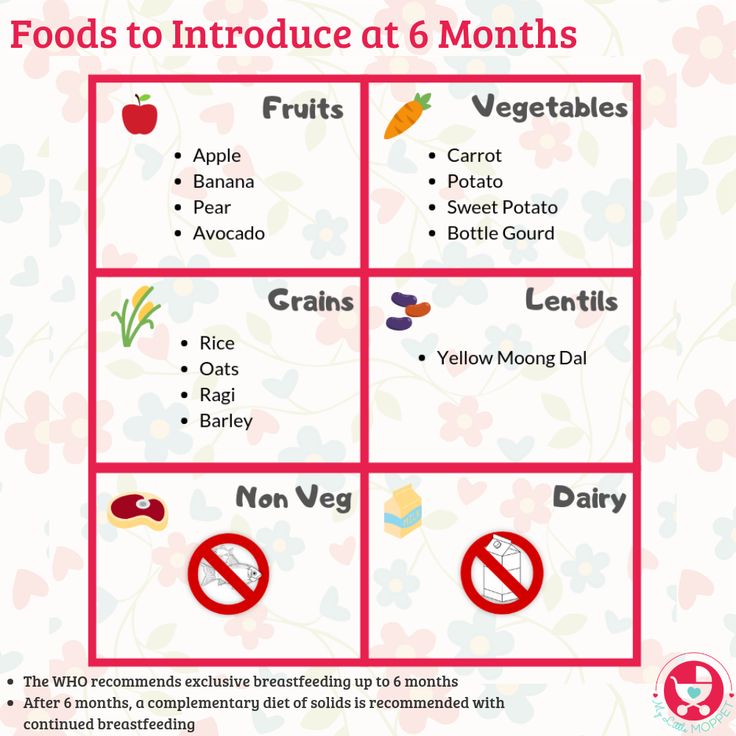
6 month old baby solid food quantity
Feeding your baby: 6–12 months
At 6 months of age, breastmilk continues to be a vital source of nutrition; but it’s not enough by itself. You need to now introduce your baby to solid food, in addition to breastmilk, to keep up with her growing needs.
Be sure you give your baby her first foods after she has breastfed, or between nursing sessions, so that your baby continues to breastfeed as much as possible.
When you start to feed your baby solid food, take extra care that she doesn’t become sick. As she crawls about and explores, germs can spread from her hands to her mouth. Protect your baby from getting sick by washing your and her hands with soap before preparing food and before every feeding.
Your baby's first foods
When your baby is 6 months old, she is just learning to chew. Her first foods need to be soft so they’re very easy to swallow, such as porridge or well mashed fruits and vegetables. Did you know that when porridge is too watery, it doesn't have as many nutrients? To make it more nutritious, cook it until it’s thick enough not to run off the spoon.
Feed your baby when you see her give signs that she's hungry – such as putting her hands to her mouth. After washing hands, start by giving your baby just two to three spoonfuls of soft food, twice a day. At this age, her stomach is small so she can only eat small amounts at each meal.
The taste of a new food may surprise your baby. Give her time to get used to these new foods and flavours. Be patient and don’t force your baby to eat. Watch for signs that she is full and stop feeding her then.
As your baby grows, her stomach also grows and she can eat more food with each meal.
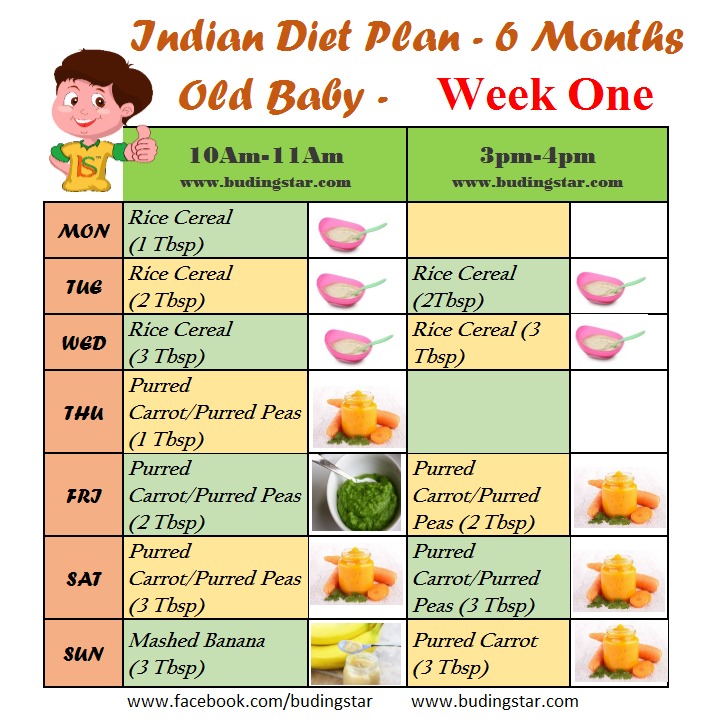
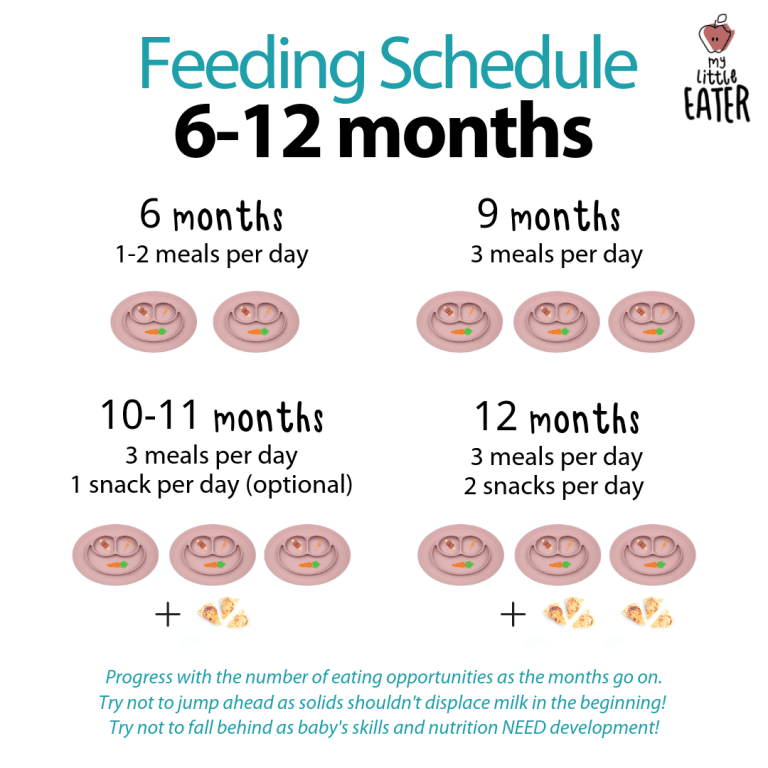
Feeding your baby: 6–8 months old
From 6–8 months old, feed your baby half a cup of soft food two to three times a day. Your baby can eat anything except honey, which she shouldn't eat until she is a year old. You can start to add a healthy snack, like mashed fruit, between meals. As your baby gets increasing amounts of solid foods, she should continue to get the same amount of breastmilk.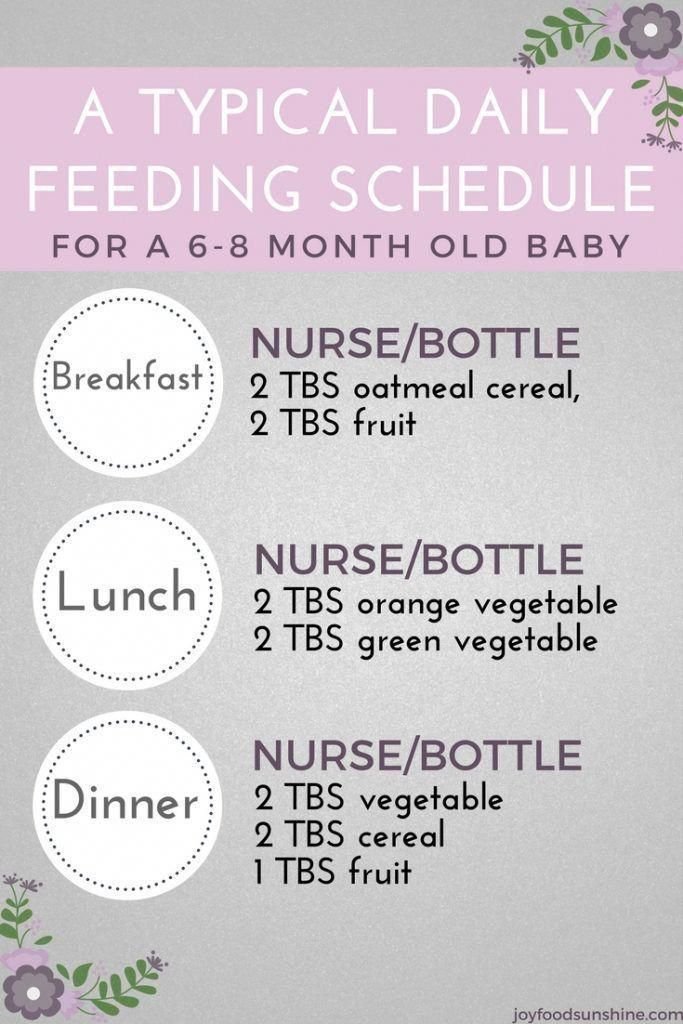
Feeding your baby: 9–11 months old
From 9–11 months old, your baby can take half a cup of food three to four times a day, plus a healthy snack. Now you can start to chop up soft food into small pieces instead of mashing it. Your baby may even start to eat food herself with her fingers. Continue to breastfeed whenever your baby is hungry.
Each meal needs to be both easy for your baby to eat and packed with nutrition. Make every bite count.
Foods need to be rich in energy and nutrients. In addition to grains and potatoes, be sure your baby has vegetables and fruits, legumes and seeds, a little energy-rich oil or fat, and – especially – animal foods (dairy, eggs, meat, fish and poultry) every day. Eating a variety of foods every day gives your baby the best chance of getting all the nutrients he needs.
If your baby refuses a new food or spits it out, don’t force it. Try again a few days later. You can also try mixing it with another food that your baby likes or squeezing a little breastmilk on top.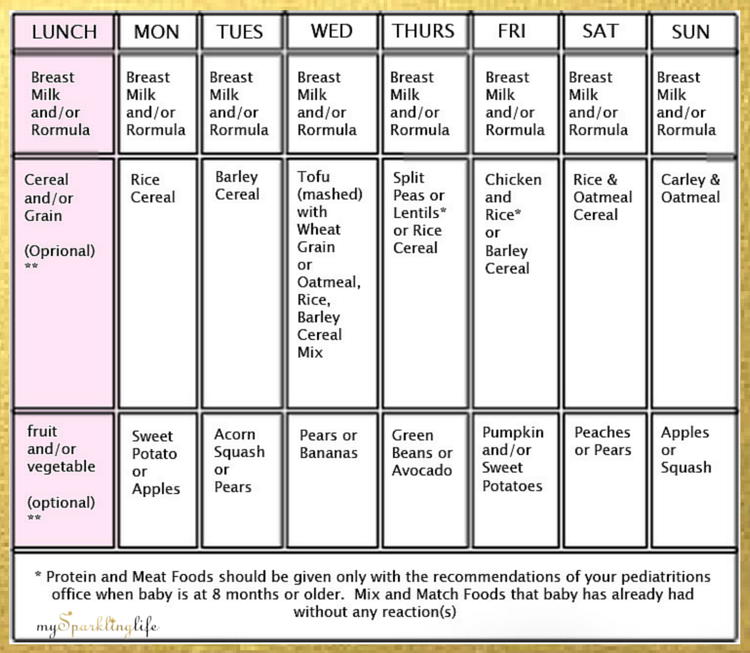
Feeding non-breastfed babies
If you're not breastfeeding your baby, she’ll need to eat more often. She'll also need to rely on other foods, including milk products, to get all the nutrition her body needs.
- Start to give your baby solid foods at 6 months of age, just as a breastfed baby would need. Begin with two to three spoonfuls of soft and mashed food four times a day, which will give her the nutrients she needs without breastmilk.
- From 6–8 months old, she’ll need half a cup of soft food four times a day, plus a healthy snack.
- From 9–11 months old, she’ll need half a cup of food four to five times a day, plus two healthy snacks.
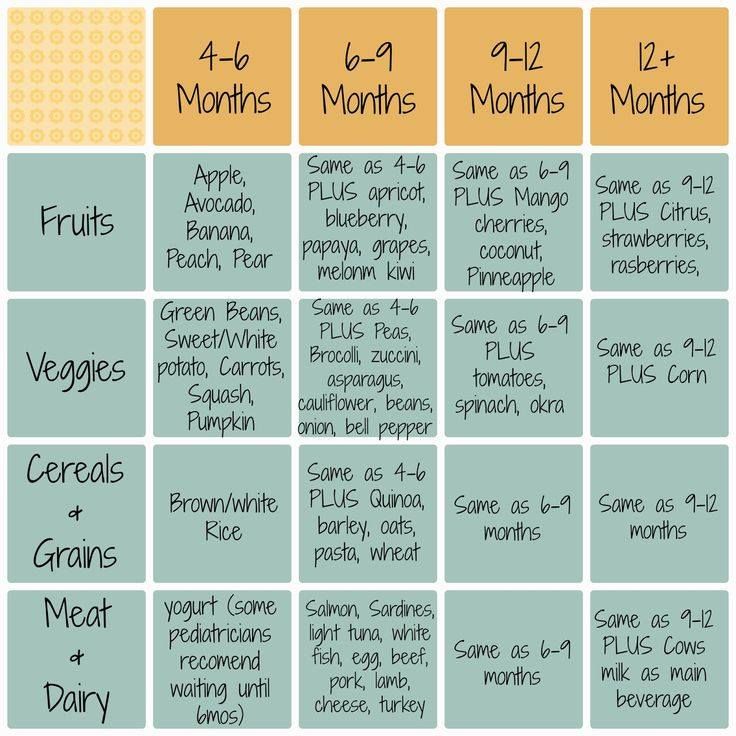
How much should my baby eat? A guide to baby food portions
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
Wondering how much to feed your baby? This can be hard to figure out, especially when you're starting solids and most of your baby's food ends up on your little one or the floor. It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
It's also difficult to determine how much an 8-month-old (or older baby) should eat – babies this age are more interested in solid foods but still get most of their nutrition from breast milk or formula. This visual guide to baby food portions can help you figure out how much your baby should eat at every stage.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby eat?
Do you worry that your baby is eating too little or too much? Your baby will self-regulate her food intake based on what their body needs, so let their appetite be your guide.
It's helpful to have a reference point, however. Here are photos of how much solid food a baby typically eats in a day. You can also ask your baby's doctor for feeding advice.
This visual guide shows:
- Portions for infants who are new to solids (typically 4 to 6 months)
- Two sample meals for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
- Three sample meals and two snacks for an older baby (8 to 12 months) from a menu developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
Your little one may eat less or more than what's shown here. Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Your job is to provide a variety of healthy foods at regular intervals without pressure, and their job is to decide what and how much to eat.
Photo credit: iStock.com / UntitledImages
Watch for signs your baby is full
Lots of factors – including activity level, growth spurts or plateaus, illness, and teething – will affect your baby's appetite, which can vary daily.
End feeding when they signal that they're done. Signs of being full include:
- Turning their head away
- Refusing to open their mouth for another bite after they've swallowed (resist the urge to encourage your baby to have one last spoonful)
- Leaning back in their chair
- Playing with the spoon or food rather than eating
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 4- to 6-month-old should eat
When your baby is developmentally ready for solids, typically around 4 to 6 months, talk to their doctor about introducing solid foods. The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
The first bites are mostly about them getting used to the idea of having something different in their mouth.
- Start with a very small amount, 1 to 2 teaspoons, of a single-ingredient puree.
- Gradually increase to 1 to 2 tablespoons of food once a day.
- Follow your baby's fullness cues.
Popular first foods include pureed mango, banana, chicken, turkey, beef, peas, sweet potatoes, and infant cereal. It's up to you what food to start with, but wait 3 to 5 days between introducing each new food to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction or food intolerance. (And remember, no cow's milk or honey until age 1.)
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much a 6- to 8-month-old should eat
As your little one gets more comfortable with solids, you can increase the frequency of meals and variety of food.
- Transition from one to two meals a day, typically by 8 months.
- Over time, add a second food to each meal.
 The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods.
The photo above is an example of a meal with two foods. - Once you've worked up to two meals with two foods each, aim for a balance of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains in their daily diet.
- Whenever you introduce a new food, start with a very small amount, a teaspoon or two, to allow your baby to get used to its flavor and texture.
- Start with a soupy consistency. Gradually add more texture as their eating skills improve.
Expect their intake of breast milk or formula to go down. They'll start drinking less of it as they eat more solid foods. Provide healthy options at mealtimes, and let them choose how much to eat.
Note: The jars in all photos are standard 4-ounce baby food jars.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
Cereal and fruit make an easy combination for a morning meal.
Grain: Iron-fortified, whole-grain infant cereal is a popular first grain. At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
At 6 months, a typical daily portion of infant cereal mixed with breast milk or formula might be 2 to 3 tablespoons, increasing to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) by 8 months. (It's best to avoid rice cereal, though.)
Fruit: Babies love the natural sweetness of fruits like pears, apples, berries, prunes, and stone fruits. Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of fruit puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) of mashed or minced fruit.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for a younger baby (6 to 8 months)
If you serve a grain and fruit in the morning, consider offering a protein-rich food and vegetable later in the day. Your child may eat more or less than the amounts shown.
Protein: A baby might transition from eating 1 to 2 tablespoons of meat puree at 6 months to 2 to 4 tablespoons at 8 months, for example. Other good protein sources include cheese, unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt, tofu, beans, and lentils.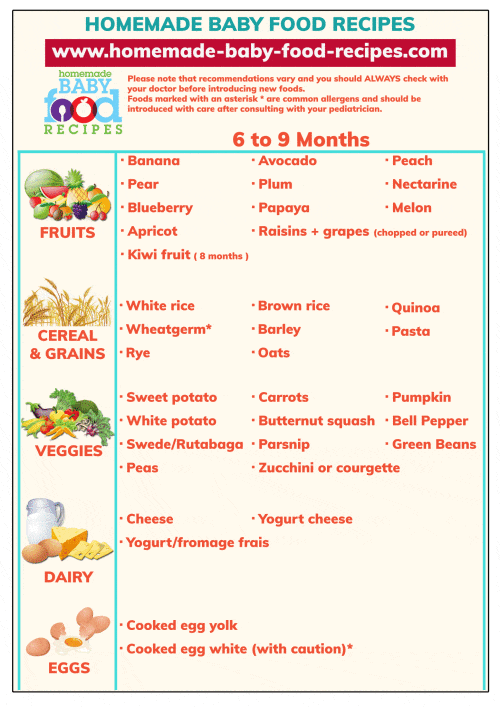
Vegetables: Between 6 and 8 months, a baby will typically transition from about 2 to 3 tablespoons of vegetable puree a day to 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup). Try classic favorites like carrots, spinach, or butternut squash, as well as less traditional first foods such as parsnips, beets, or asparagus.
As your child's eating skills improve, gradually add more texture by dicing or mincing foods.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much an 8- to 12-month-old should eat
By 8 months or so, your baby is likely getting the hang of eating and needs to eat more calories to support their growing body. But since their little belly can't hold a lot of food, they'll need to eat more often. Every baby is different, but this may be a good time to try offering a third solid food meal.
During this period:
- Continue to give your baby breast milk or formula.
- Add morning and afternoon snacks. (Some babies this age are happy with breast milk or formula as their snack, while others gravitate toward solid foods.
 ) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
) Once you've added a third meal and snacks, your baby will be eating or drinking something about every two to three hours.
- Continue to aim for a mix of proteins, vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Introduce coarser and chunkier textures, for example, by dicing or mincing food instead of pureeing it, and graduate to soft finger foods as your baby's eating skills improve.
- Avoid foods with added sugars. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and try to steer clear of foods that list 1 gram or more of "Added Sugars."
- Provide healthy options, and let your baby choose how much to eat.
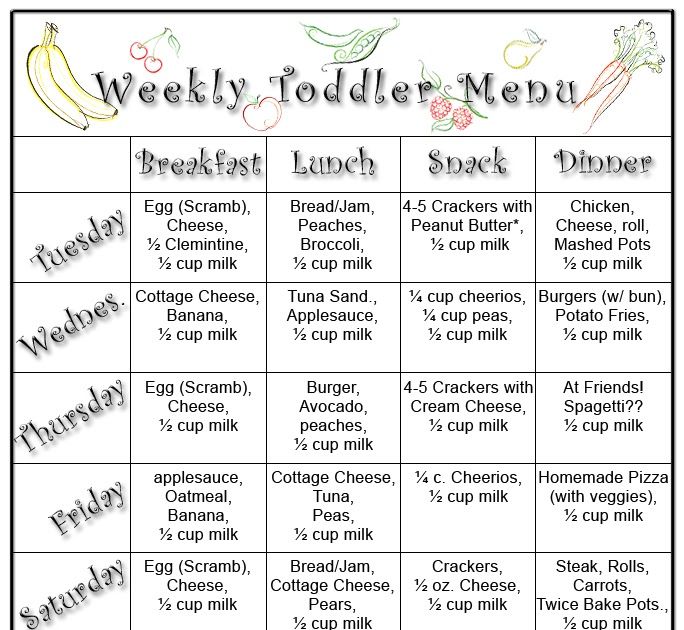
To visualize daily portions for an 8- to 12-month-old, check out the following photos of a typical day's menu for a baby this age, developed by the AAP.
Your child may eat more or less than these amounts. If you're concerned about how much your baby is eating, talk to their doctor for advice.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Breakfast for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a breakfast consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) whole-grain infant cereal mixed with formula or breast milk
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Morning snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a morning snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Note: This is an example of a morning snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Lunch for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a lunch consisting of:
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt or cottage cheese, or minced meat
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2 cup) diced or mashed yellow or orange vegetable
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Afternoon snack for an older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features an afternoon snack consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit or unsweetened plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 whole-grain teething biscuit or cracker
Note: This is an example of an afternoon snack, which babies typically add sometime between 8 and 12 months. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
Dinner for older baby (8 to 12 months)
The AAP sample menu for a baby 8 to 12 months features a dinner consisting of:
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) minced or ground poultry or meat, or diced tofu
- 4 to 8 tablespoons (1/4 to 1/2) cup diced, cooked green vegetable
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) noodles, pasta, rice, or potato
- 4 tablespoons (1/4 cup) diced fruit
Note: This is an example. Your baby may eat different foods and amounts.
Photo credit: Karla Martin for BabyCenter
How much should my baby drink once they start eating solids?
Breast milk or formula will fully meet your child's hydration needs until they're about 6 months old. They may start drinking less as solid foods become a bigger part of their diet. Here are typical daily amounts by age – your baby's intake may be different, however.
6 to 8 months: 24 to 32 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
8 to 12 months: 24 ounces of formula, or continued breastfeeding on demand
Water: You can offer your baby water once they start eating solids, but let them self-regulate how much they drink. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends giving babies who are 6 to 12 months old 4 to 6 ounces of water a day, but what your baby decides to drink may vary. They may drink more on a hot day, for example.
Avoid juice: Juice isn't recommended for babies younger than 12 months.
Photo credit: iStock.com / SDI Productions
Your baby has the final say
Keep in mind that these portions are an estimate. The truth is, every baby is different, and there's no set amount of food that's appropriate for every baby at every stage.
If you're worried about whether your baby is eating enough – or too much – the best advice is to look for and respond to signs that your baby is full.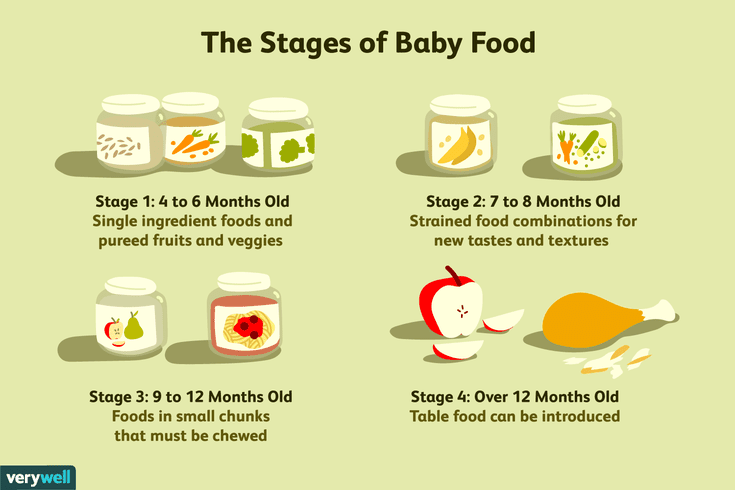
Your baby's doctor will chart their weight gain at regular intervals. If the doctor sees a consistent growth curve and doesn't have other concerns, your baby is most likely eating the right amount of food.
Hungry for more?
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
The 10 best foods for babies
The worst foods for babies
Using spices and seasoning in baby food
Elizabeth Dougherty
Elizabeth Dougherty is a veteran parenting writer and editor who's been contributing to BabyCenter since 2015. She's an intrepid traveler, devoted yogi, and longtime resident of Silicon Valley, where she lives with her husband and son.
Advertisement | page continues below
Complementary foods at 6 months | Useful tips from the Tyoma brand
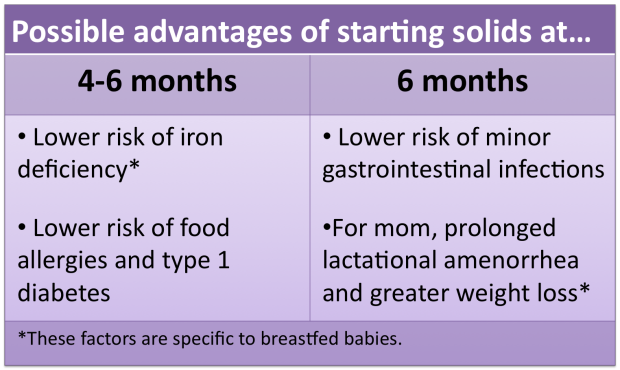
Pediatricians around the world, including experts from the World Health Organization, unanimously believe that the introduction of complementary foods should be carried out in the interval of 4-6 months.
Early introduction of complementary foods (up to 4 months). fraught with the development of allergic reactions and indigestion.
Late introduction of complementary foods, from 7 months, can lead to a deficiency in the child's diet of essential nutrients, an iron deficiency state at the age of 9-10 months, eating disorders, delayed development of chewing skills and swallowing of thick foods.
With the normal development of the child and the absence of signs of iron deficiency anemia, complementary foods can be introduced from 6 months. This applies to both formula-fed and breast-fed babies.
Signs that a baby is ready to breastfeed include
- Absence of the spoon-ejection reflex
- the presence of a bright food interest in the baby to the food of adults
It is important to remember that a child’s lack of teeth and the ability to sit are not signs of a baby’s unpreparedness for eating thick foods.
It is very important to understand the main goals of the introduction of complementary foods:
- Provide the child with the necessary nutrients.
- Develop a child's food interest, introduce him to new tastes.
In no case should the introduction of complementary foods be of a violent nature, since this will not only not contribute to the development of a child’s food interest, but can also lead to a complete refusal of the baby from complementary foods, which will destroy the main goals of complementary foods.
How to start introducing complementary foods at 6 months of age?
The first product of complementary foods, regardless of the start date of the introduction of complementary foods and the type of feeding of the baby (breast or artificial), should be energy-intensive foods: porridge, or vegetable puree.
If the child has a liquefied or unstable stool, and there is also a lack of body weight, then it is better to choose porridge as the first complementary food. After 3-4 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g)
After 3-4 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g)
If the child has a tendency to constipation, then it is better to choose vegetable marrow puree as the first complementary food, which can have a mild laxative effect on the child's stool. Starting from the 3-4th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g)
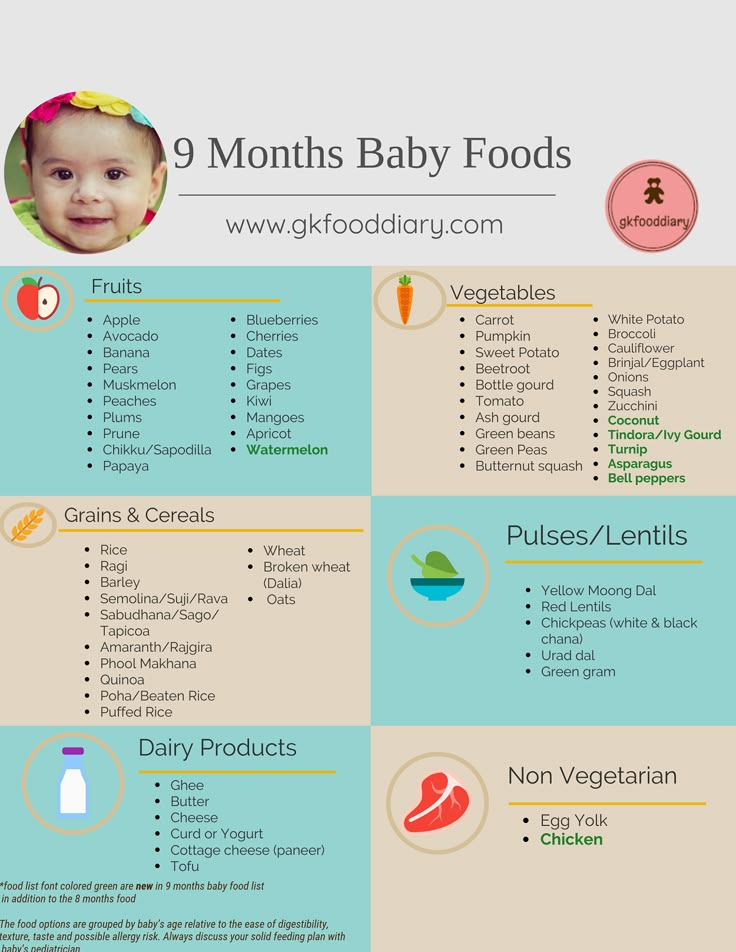
What products are better to give preference to at 6 months?
Kashi
The first cereals can be buckwheat, rice or corn. They must be dairy-free and can be diluted with water or breast milk, or the mixture that the baby eats. Later, you can introduce oatmeal and millet porridge
Vegetables
The first vegetable puree can be zucchini, broccoli, or cauliflower. Later, kohlrabi, potatoes, green beans, white cabbage, green peas, celery can be introduced into the diet.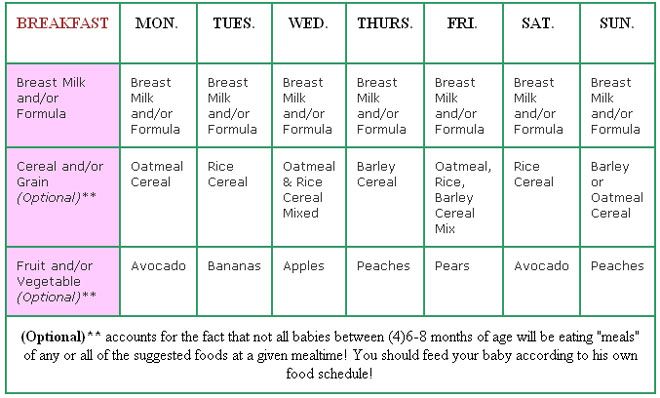
Fruit
The third type of complementary foods can be fruit puree from apples, pears or bananas. Later, you can introduce mashed apricot, peach. For starters, fruit puree may not be given to the child separately, but it is better to mix it with cereal or vegetables so that the child does not begin to prefer the sweet taste of fruits. When the amount of fruit puree reaches 50 g or more, it can also be given separately, for example, after the child has eaten porridge or cottage cheese.
Juices
Juices should not be the first feeding, in addition, they can not be introduced into the baby's first year of life at all, given their sweet taste and low nutritional value.
Basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods from 6 months
- A faster introduction of the main complementary foods into the child's diet compared to their introduction from 4 or 5 months, namely, bringing the amount of one product to the age volume can be carried out in 5-7 days.
- Introduction of complementary foods before breastfeeding or formula.
- Feeding the child is carried out not at the request of the child, but at the request of the mother. What it means: you should try to introduce complementary foods regularly and at the same time, allocating for this conditionally time for the future breakfast, lunch and dinner (afternoon snack).
How to start the introduction of a new product?
The introduction of a new product should be gradual.
- On day 2 - 3 tsp. (15 g)
- On day 3 - 6 tsp. (30 g)
- Day 4 - 50 g
- Day 5 - 100 g
- On the 7th day - 150 g
Important!
If on the 5-7th day of the introduction of a new product, the baby still cannot eat 100-150 ml of porridge or puree at once, then this amount can be divided into 2 doses, for example, give 100 ml of porridge in the morning and 50 ml in the evening.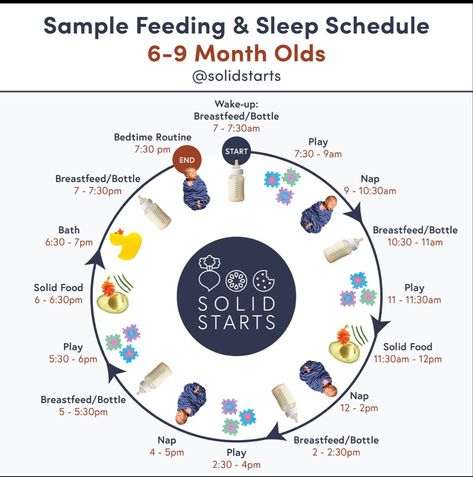
From the second week of the introduction of a new product, one milk feeding can be completely replaced with complementary foods.
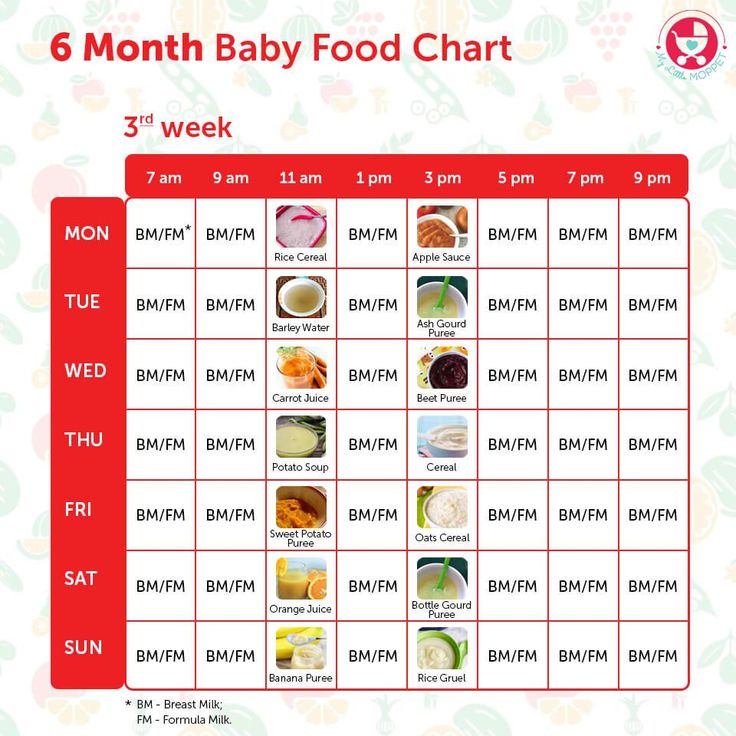
Approximate weekly feeding schedule
If we start complementary foods with vegetable puree, then the schedule might look something like this:
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Lunch (14:00): broccoli 10-150 grams. Supplementing with breast milk or infant formula
- Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
2 weeks
From the second week, you need to start introducing dairy-free porridge.
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): porridge 10-150 g, supplemented with breast milk or infant formula
- Lunch (14:00): Broccoli 150 grams.
 Vegetable oil 5 g Supplementary feeding with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml
Vegetable oil 5 g Supplementary feeding with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml - Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula
3 week
From the third week, you need to start introducing meat puree, which is most convenient to add to vegetable puree
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): porridge 150 g, supplemented with breast milk or infant formula
- Lunch (14:00): Broccoli 150 grams. Vegetable oil 5 g Meat puree 5-20 g Supplementation with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml
- Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula
4 week
From the fourth week, you can introduce fruit puree, which is most convenient to add to porridge
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): porridge 150 g, fruit puree up to 50 g
- Lunch (14:00): Broccoli 150 grams.
 Vegetable oil 5 g Meat puree 20 g Supplementation with breast milk or infant formula
Vegetable oil 5 g Meat puree 20 g Supplementation with breast milk or infant formula - Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula
From the fifth week, you can begin to introduce the second type of porridge, which is most convenient to start adding to the first type, gradually displacing its amount.
From the sixth week, you can enter another type of vegetable puree. And so on.
By 7 months two milk feedings can be completely replaced with complementary foods.
Complementary foods at 6 months | Useful tips from the Tyoma brand
Pediatricians around the world, including experts from the World Health Organization, unanimously believe that the introduction of complementary foods should be carried out in the interval of 4-6 months.
Early introduction of complementary foods (up to 4 months).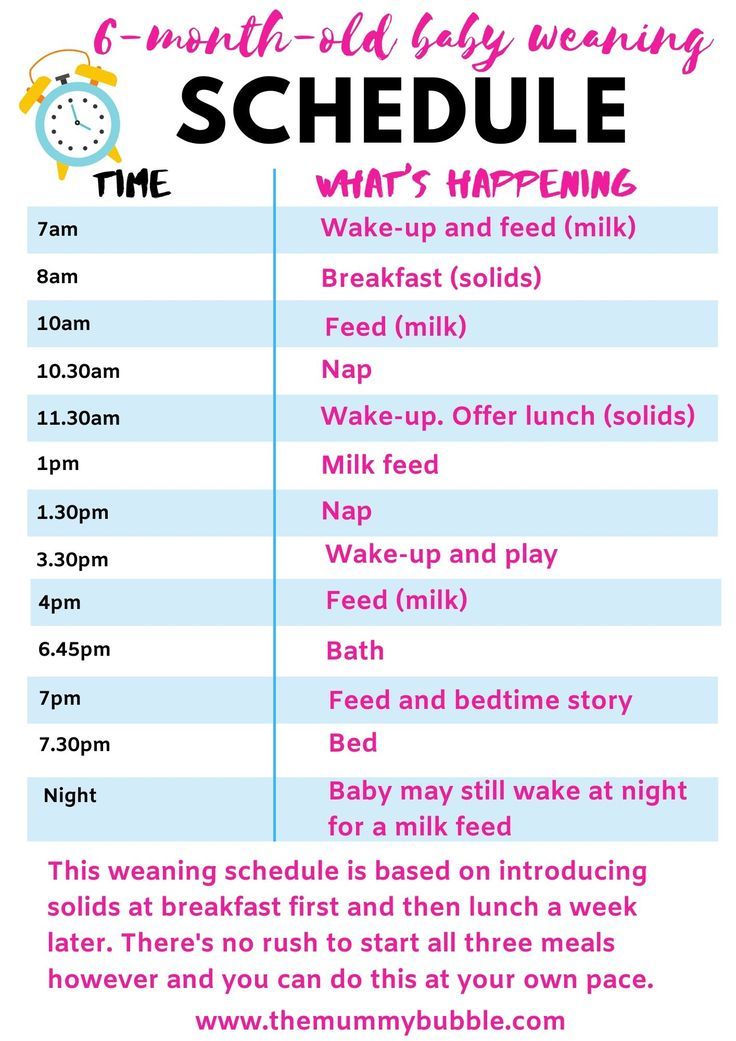 fraught with the development of allergic reactions and indigestion.
fraught with the development of allergic reactions and indigestion.
Late introduction of complementary foods, from 7 months, can lead to a deficiency in the child's diet of essential nutrients, iron deficiency at the age of 9-10 months, eating disorders, delayed development of chewing skills and swallowing of solid food.
With the normal development of the child and the absence of signs of iron deficiency anemia, complementary foods can be introduced from 6 months. This applies to both formula-fed and breast-fed babies.
Signs that a baby is ready to breastfeed include
- Absence of the spoon-ejection reflex
- the presence of a bright food interest in the baby to the food of adults
It is important to remember that a child’s lack of teeth and the ability to sit are not signs of a baby’s unpreparedness for eating thick foods.
It is very important to understand the main goals of the introduction of complementary foods:
- Provide the child with the necessary nutrients.

- Develop a child's food interest, introduce him to new tastes.
In no case should the introduction of complementary foods be of a violent nature, since this will not only not contribute to the development of a child’s food interest, but can also lead to a complete refusal of the baby from complementary foods, which will destroy the main goals of complementary foods.
How to start introducing complementary foods at 6 months of age?
The first product of complementary foods, regardless of the start date of the introduction of complementary foods and the type of feeding of the baby (breast or artificial), should be energy-intensive foods: porridge, or vegetable puree.
If the child has a liquefied or unstable stool, and there is also a lack of body weight, then it is better to choose porridge as the first complementary food. After 3-4 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g)
If the child has a tendency to constipation, then it is better to choose vegetable marrow puree as the first complementary food, which can have a mild laxative effect on the child's stool. Starting from the 3-4th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g)
Starting from the 3-4th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g)
What products are better to give preference to at 6 months?
Kashi
The first cereals can be buckwheat, rice or corn. They must be dairy-free and can be diluted with water or breast milk, or the mixture that the baby eats. Later, you can introduce oatmeal and millet porridge
Vegetables
The first vegetable puree can be zucchini, broccoli, or cauliflower. Later, kohlrabi, potatoes, green beans, white cabbage, green peas, celery can be introduced into the diet.
Fruit
The third type of complementary foods can be fruit puree from apples, pears or bananas. Later, you can introduce mashed apricot, peach. For starters, fruit puree may not be given to the child separately, but it is better to mix it with cereal or vegetables so that the child does not begin to prefer the sweet taste of fruits. When the amount of fruit puree reaches 50 g or more, it can also be given separately, for example, after the child has eaten porridge or cottage cheese.
When the amount of fruit puree reaches 50 g or more, it can also be given separately, for example, after the child has eaten porridge or cottage cheese.
Juices
Juices should not be the first feeding, in addition, they can not be introduced into the baby's first year of life at all, given their sweet taste and low nutritional value.
Basic rules for the introduction of complementary foods from 6 months
- A faster introduction of the main complementary foods into the child's diet compared to their introduction from 4 or 5 months, namely, bringing the amount of one product to the age volume can be carried out in 5-7 days.
- Introduction of complementary foods before breastfeeding or formula.
- Feeding the child is carried out not at the request of the child, but at the request of the mother. What it means: you should try to introduce complementary foods regularly and at the same time, allocating for this conditionally time for the future breakfast, lunch and dinner (afternoon snack).
How to start the introduction of a new product?
The introduction of a new product should be gradual.
- On day 2 - 3 tsp. (15 g)
- On day 3 - 6 tsp. (30 g)
- Day 4 - 50 g
- Day 5 - 100 g
- On the 7th day - 150 g
Important!
If on the 5-7th day of the introduction of a new product, the baby still cannot eat 100-150 ml of porridge or puree at once, then this amount can be divided into 2 doses, for example, give 100 ml of porridge in the morning and 50 ml in the evening.
From the second week of the introduction of a new product, one milk feeding can be completely replaced with complementary foods.
Approximate weekly feeding schedule
If we start complementary foods with vegetable puree, then the schedule might look something like this:
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Lunch (14:00): broccoli 10-150 grams.
 Supplementing with breast milk or infant formula
Supplementing with breast milk or infant formula - Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
2 weeks
From the second week, you need to start introducing dairy-free porridge.
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): porridge 10-150 g, supplemented with breast milk or infant formula
- Lunch (14:00): Broccoli 150 grams. Vegetable oil 5 g Supplementary feeding with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml
- Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula
3 week
From the third week, you need to start introducing meat puree, which is most convenient to add to vegetable puree
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): porridge 150 g, supplemented with breast milk or infant formula
- Lunch (14:00): Broccoli 150 grams.
 Vegetable oil 5 g Meat puree 5-20 g Supplementation with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml
Vegetable oil 5 g Meat puree 5-20 g Supplementation with breast milk or infant formula up to 50 ml - Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula
4 week
From the fourth week, you can introduce fruit puree, which is most convenient to add to porridge
- Morning feeding (6:00 am): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Breakfast (10:00): porridge 150 g, fruit puree up to 50 g
- Lunch (14:00): Broccoli 150 grams. Vegetable oil 5 g Meat puree 20 g Supplementation with breast milk or infant formula
- Afternoon snack (18:00): breast milk or infant formula 180-200 ml
- Night feeding (22:00): breast milk or infant formula
From the fifth week, you can begin to introduce the second type of porridge, which is most convenient to start adding to the first type, gradually displacing its amount.