At what age can i feed my baby yogurt
When can babies eat yogurt, and which baby yogurt is best?
Most babies can start eating yogurt as soon as they start eating solids – around 4 to 6 months. Yogurt is an excellent choice for one of your baby's first foods because it contains calcium, protein, and vitamins. The best option is plain, unsweetened, pasteurized yogurt (regular or Greek) made from whole milk and containing "live cultures."
What kind of yogurt is best for babies?
Nearly all flavored and fruit-on-top yogurts, even products marketed for babies, contain added sugar, which can contribute to tooth decay and obesity. The USDA guidelines recommend that children under 2 years old get no added sugar from their diet. Choosing plain yogurt is the easiest way to avoid added sugar.
To see whether a product has added sugar, check the nutrition label. Look at the line under "Total Sugars" to see how much of the sugar in a product is added sugar. (All yogurt contains some natural sugar in the form of lactose. )
Yogurt made from whole milk is best for babies and toddlers because they need the calories and fat in full-fat dairy products. Don't offer your child reduced-fat or fat-free yogurt before age 2 unless your healthcare provider advises it.
Greek yogurt is strained for a rich, creamy texture, and has twice as much protein as regular yogurt, making it another good choice for babies. Plus, it's often easier to find Greek yogurt in sugar-free varieties.
Is yogurt healthy for babies?
In addition to being a good source of calcium and protein, some types of yogurt contain live cultures, also known as probiotics. These are living microorganisms (bacteria) used to convert milk to yogurt, or added to yogurt afterward. They promote the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut, which researchers believe may help with digestion.
How can you tell whether yogurt has this good bacteria? The product label should state that the yogurt contains live or active cultures, which means the organisms haven't been destroyed by heat during processing. However, a label that says "made with active cultures" does not mean that the yogurt still contains living cultures, only that the yogurt was made with them (as all yogurt is).
However, a label that says "made with active cultures" does not mean that the yogurt still contains living cultures, only that the yogurt was made with them (as all yogurt is).
It can be hard to tell if a yogurt contains a significant amount of beneficial bacteria. One way is to look for the Live & Active Cultures seal by the International Dairy Foods Association. This seal identifies products that contain at least 100 million live and active cultures per gram. But participation in the program is voluntary, so a product without the seal isn't necessarily short on cultures.
You may wonder why it's okay for babies to eat yogurt, when drinking cow's milk isn't recommended until a baby is at least 12 months old.
Advertisement | page continues below
Actually, a little bit of cow's milk, like the amount in the occasional serving of yogurt, won't hurt your baby. It's just not a good replacement for the breast milk or formula that still makes up most of their diet for the first year.
That's because babies can't digest cow's milk as easily or completely as breast milk or formula. And cow's milk doesn't have the ideal proportion of fats and nutrients that your baby gets from breast milk or formula.
For more information, see our article on when and how to introduce cow's milk to your child.
Yogurt allergies in babies
If your baby has been diagnosed with a milk allergy or shows signs of a food allergy (such as eczema), don't give them yogurt until you've checked with your healthcare provider.
Otherwise, as with any new food, wait at least three days after introducing yogurt before giving your baby another new food. That way, if your baby has an allergic reaction, it will be easier to tell what caused it.
Common symptoms of an allergic reaction include itchy red spots or patches, swelling around the lips or eyes, or vomiting within two hours of eating the recently introduced food. If you notice any of these symptoms, don't give your baby any more of the food until you've checked in with your provider.
Lactose intolerance – which is different from a milk allergy – is very rare in babies. Even if your child becomes lactose intolerant, it may be fine for them to eat yogurt. The production process breaks down much of the lactose, making yogurt more easily tolerated than other dairy products.
Yogurt recipes for babies
Your baby may not be a fan of plain yogurt, so try adding flavor (and nutrients) by mixing in fruit or vegetables. For babies who are new to solids, start with pureed fruit and cooked, pureed vegetables. For older babies, you can add soft fruit and cooked vegetables chopped into small pieces. Mashed avocado, applesauce, oatmeal, and wheat germ are also good additions.
Never give honey to a baby younger than 12 months because it may contain bacteria that can cause botulism in children that age.
Try these baby food recipes with yogurt:
- Yogurt and berry swirl
- Baby guacamole
- Tropical fruit salad
When Can Babies Eat Yogurt?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on March 14, 2021
In this Article
- Introducing Your Baby to Yogurt
- Nutritional Benefits of Yogurt for Your Baby
- How to Prepare Yogurt for Your Baby
- Tips for Introducing New Foods to Your Baby
When you begin to offer your baby solid food around six months, you introduce them to a variety of tastes, flavors, and textures. Before you begin, it’s important to know how to safely introduce allergenic foods.
Before you begin, it’s important to know how to safely introduce allergenic foods.
Yogurt is a great food choice once your baby is introduced to solids. Yogurt is safe for babies as long as you pay close attention to nutrition labels and watch for any allergic reactions. Talk to your doctor first if there is a history of dairy allergy or lactose intolerance in your family.
Introducing Your Baby to Yogurt
Be sure to read labels on yogurt and make sure to avoid two specific ingredients:
- Honey. Honey isn't safe before 12 months because your baby may contract a type of food poisoning called botulism.
- Added sugar. Many yogurts have added sugar or sweeteners that have no benefit for your baby. Try sweetening yogurt with fruit instead.
You should only introduce one new food at a time to your baby, and wait at least three days before introducing another. By doing this, you can pinpoint an allergic reaction if they have one. Since dairy allergies are common, this is especially important when offering yogurt to your baby.
Since dairy allergies are common, this is especially important when offering yogurt to your baby.
Watch for these signs of an allergic reaction:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash
- Swelling around the lips or eyes
If your baby has an allergic reaction, stop feeding them yogurt and call your pediatrician. They can provide guidelines of when to try offering yogurt again to see if the allergy goes away with time.
Nutritional Benefits of Yogurt for Your Baby
Yogurt is rich in protein and calcium, as well as phosphorus and B vitamins. While protein aids in muscle development and calcium promotes strong bones and teeth, most of yogurt's health benefits seem to come from its live bacterial content. Yogurt and other fermented foods that contain specific strains of live bacteria are known as “probiotic.” Probiotic foods like yogurt may help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in your baby’s gut. Over time, probiotic foods may even prevent a wide range of health issues including obesity and diabetes.
A serving size for your baby is about half a cup of yogurt. Some yogurt brands are fortified with added protein and vitamins that are fine for your baby, but read labels carefully to look for added sugar and honey as ingredients.
How to Prepare Yogurt for Your Baby
Once you have established that your baby isn't allergic to either yogurt or individual fruits, add chopped or mashed fruits to your baby’s yogurt for added taste and sweetness. Make sure the pieces are small enough that they aren't a choking hazard.
Great chopped or mashed fruits to add to yogurt include:
- Strawberries
- Blueberries
- Peaches
- Banana
You can spoon-feed your baby or let them hold the spoon and try to feed themself. Of course, they might make a mess. This is part of their learning about food as they are introduced to solids.
Tips for Introducing New Foods to Your Baby
Before offering new foods, ask these questions:
- Can my baby hold their head up independently? This is an important developmental milestone for eating solid food.

- Is my baby interested in eating? Your baby may watch you eat with interest, or even try to grab your food and taste it. When you offer your baby a spoon, they should open their mouth to eat.
- Can my baby move food to their throat? If you offer food with a spoon, your baby may push it out with their tongue first. This is called the tongue-thrust reflex. With time they will learn to use their tongue to push the food to the back of their mouth and swallow.
Offer a variety. As your baby starts to eat solid foods, they need variety in their diet. This helps ensure your baby is receiving all of the nutrients they need and also helps expand their palate for new tastes.
Normalize new foods. Once you introduce a new food to your baby and you've confirmed they aren't allergic to it, try to offer it to them again at least twice a week. Not only does this familiarize your baby with new foods, but it can also prevent food allergies. Additionally, when your baby is learning to eat, they watch you. Make sure to offer them the same foods the rest of the family is eating for encouragement.
Additionally, when your baby is learning to eat, they watch you. Make sure to offer them the same foods the rest of the family is eating for encouragement.
Consider Allergens. By the time your baby is 12 months old, they should be introduced to each of the common allergenic foods:
- Cooked egg
- Creamy peanut butter
- Cow’s milk (dairy)
- Tree nuts (such as cashew or almond paste)
- Soy
- Sesame
- Wheat
- Fish and other seafood
By introducing these foods early in life, you can reduce your baby’s chance of developing food allergies.
Is it possible for children to have kefir? - how much and when can you start giving yogurt to your child
05/12/2020 39814
Contents of the article
- Why are fermented milk products (CMP) better than milk? nine0013
- At what age can kefir be given to a child?
- When is yogurt not allowed for a child?
- What kind of kefir to give to children?
- Why is adult kefir not suitable?
Kefir children can and should. It contains components useful for the child *, **, ***:
It contains components useful for the child *, **, ***:
- squirrels,
- milk fat,
- calcium and phosphorus,
- vitamins A, B1, B2, B12,
- probiotics and prebiotics.
Probiotics are beneficial microorganisms that come from food. They help fight harmful microbes and help digest food**.
Prebiotics are substances that stimulate the proper functioning of the intestines and its inhabitants. They are formed when the microbes of the starter are digested in the milk**.
Why are fermented milk products (CMP) better than milk?
They are easier to digest and cause fewer unpleasant reactions*. nine0008
Why?
Microorganisms in the CMP and the fermentation process that they start are useful: they break down milk proteins a little.
Such a fermented protein in the CMP is more easily processed in the intestines of the baby and is more fully absorbed. In addition, milk protein, "cut" into pieces, rarely causes allergies.
In addition, milk protein, "cut" into pieces, rarely causes allergies.
Milk sugar (lactose) is also broken down by live probiotics to lactic acid. Lactic acid inhibits harmful microbes in the gut. A low lactose product suitable for children who cannot digest it *, **. nine0008
At what age can yogurt be given to a child?
Kefir is added to complementary foods when the baby is 8 months old***.
As with other new foods, give your child a small amount first - 1 teaspoon. If allergy does not appear: rash, itching, diarrhea, shortness of breath - by 9 months, increase the amount of kefir to 200 ml per day. Give kefir for an afternoon snack alternately with other KMP * (biolact, or children's yogurt). They replace each other: the main thing here is that the baby is tasty. nine0008
Offer yogurt at night to children who want a snack before bed*.
How much kefir is enough for children up to a year and older - see the tables:
Table 1.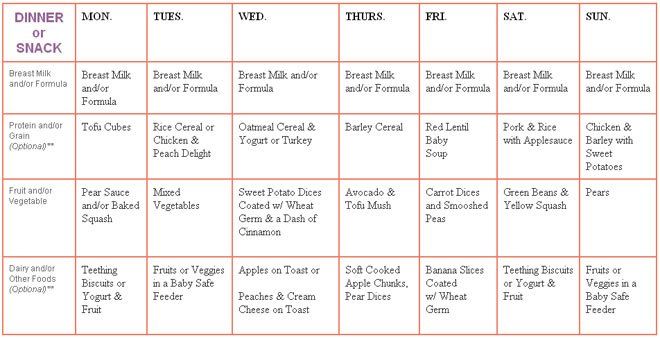 Total amount of fermented milk products per day * in the first year.
Total amount of fermented milk products per day * in the first year.
From the age of 1, the amount of cottage cheese increases in the child’s diet and cheese is added, so the amount of kefir is as follows:
A child prone to constipation may be given up to 200 ml of CMP
per day from 12 months.
When is yogurt not allowed for a child?
When there is a pronounced allergy to cow's milk protein. It is determined by observations and confirmed by analyzes if suspicions arise.
It is likely that your child has a dairy allergy if you notice the following symptoms after drinking kefir ****:
- Regurgitation, vomiting, constipation, colic, blood in the stool or shortness of breath. With shortness of breath, call a doctor immediately.
- A child scratches the skin around his mouth after drinking kefir.
- Dairy products in complementary foods consistently cause diarrhea, weight gain has clearly decreased.

What kind of kefir to give to children?
Kefir for children under 3 years old - only marked "for nutrition of young children", prepared at a dairy plant. Choose a manufacturer that you consider conscientious. nine0008
Industrial production conditions mean that only beneficial microbes will be in kefir. Dangerous bacteria in baby food will cost the plant dearly.
At home, “wild” microbes from the air can get into the product, even if you use a special starter*.
Why is adult kefir not suitable?
Kefir for children is made from the highest quality milk and a starter that is definitely safe for babies. Children's and adult kefir are different products. nine0008
Thus, kefir is one of the best products for young children without allergies to milk protein. Drink kefir with your baby: it is also useful for you, and he will like to be like a mother.
Sources:
* http://pediatr-russia. ru/sites/default/files/nacprog(2019).pdf
ru/sites/default/files/nacprog(2019).pdf
** https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/kislomolochnye–produkty–v–pitanii–detey–rannego–vozrasta/viewer
*** https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/primenenie–kislomolochnyh–produktov–v–pitanii–detey–opyt–i–perspek...
**** Allergy to cow's milk proteins in children. Clinical recommendations of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2018
(1 ratings; article rating 5.0)
When can you give your child yogurt
— Anastasia Ivanovna, please tell us why fermented milk products are introduced into the child's diet?
— Fermented milk products improve digestion, strengthen the immune system. Kefir contains B vitamins, proteins, enzymes and amino acids necessary for healthy development and growth, as well as bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, which have a good effect on the balance of microflora. nine0008
Pediatricians recommend giving yogurt to a baby in the second half of life:
- with artificial feeding - from 7-8 months;
- when breastfeeding - from 8 months.

But some gastroenterologists argue that it is better to delay this moment until 11-12 months due to the immaturity of the enzymatic system.
— What are the consequences for parents who introduce kefir into their child's diet too early?
- Symptoms can be very diverse: from an upset of the baby's gastrointestinal tract (constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, colic) to allergic reactions, when you need to immediately remove a specific fermented milk product from the diet. Sometimes in such cases, an elimination diet lasting 5-6 months is prescribed. Then fermented milk products are given again and look at the reaction of the child's body.
In addition, with early lactic acid feeding, a child may experience kidney failure due to acid and mineral salts, which are part of kefir. nine0008
— What is the difference between special children's kefir and "adult"?
- If we are talking about biokefir, then this product contains a lot of living microorganisms (lacto- and bifidobacteria). It can be given to a child as complementary foods, alternating with regular kefir, if these products are tolerated normally. You can also offer a child sour-milk mixtures, which differ from kefir in low acidity and are additionally enriched with vitamins. These products can also be alternated with kefir. nine0008
It can be given to a child as complementary foods, alternating with regular kefir, if these products are tolerated normally. You can also offer a child sour-milk mixtures, which differ from kefir in low acidity and are additionally enriched with vitamins. These products can also be alternated with kefir. nine0008
— How to introduce kefir into complementary foods for a child: should it be offered gradually and according to what scheme?
- Of course, like any other new product, kefir is introduced gradually, starting with a teaspoon, and preferably at lunchtime, in order to track the possible adverse reaction of the baby.
- Breastfed babies can be offered yogurt no earlier than eight months. At the same time, by the year and up to three years, the volume of kefir in the children's diet can be 200 ml per day. nine0013
- Formula-fed children can be given kefir from seven months. And by the year, its normal volume is also brought up to 200 ml per day.
- Which kefir is better for children under one year old: ready-made from the store or cooked at home? How to make kefir for babies at home?
- It is better to give preference to kefir bought in a store. An industrial product is inspected, tested and processed under certain conditions. Homemade kefir is “kinder”, our grandmothers will say, but everyone has different cooking methods and conditions. With the same mistress, even the percentage of fat content in milk no one will ever be able to track. Therefore, it is better not to start the first feeding with homemade kefir. nine0008
An industrial product is inspected, tested and processed under certain conditions. Homemade kefir is “kinder”, our grandmothers will say, but everyone has different cooking methods and conditions. With the same mistress, even the percentage of fat content in milk no one will ever be able to track. Therefore, it is better not to start the first feeding with homemade kefir. nine0008
— What should parents pay attention to when buying yogurt for a child?
- First of all, the expiration date is important. Kefir retains its beneficial properties for only three days, then nothing but alcohol remains in it. With a specific smell, it is better not to take risks and abandon the dubious product. Before choosing a lactic acid product, it is advisable to read about its composition on the package - the fewer obscure words, that is, additives, the better. The most useful products are not always on the shelves of stores. nine0008
— Diarrhea after yogurt in a child is not uncommon. What should parents do if the baby has an upset gastrointestinal tract on kefir?
What should parents do if the baby has an upset gastrointestinal tract on kefir?
- This product is immediately canceled: for a period of one to three months. If the allergic reaction is severe, the doctor may prescribe an elimination diet and appropriate therapy. After the product is canceled, the child must be shown to the pediatrician, especially if the baby's reaction to the introduction of kefir is accompanied by one or more symptoms: on the part of the skin - bright redness, swelling, itching, peeling, and on the part of the gastrointestinal tract - disorders, constipation or diarrhea and other signs food allergies. nine0008
— Is it possible to replace kefir with other fermented milk products?
— Complementary foods can be started with other fermented milk products. For example, the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences recommends fruit purees with goat curd for complementary foods. Such a product is also available in the MAMAKO ® line. It is suitable for babies who do not want to drink kefir because of its consistency. A child may not like liquid kefir, but he is happy to eat cottage cheese. The goal - getting all the vitamins and minerals from fermented milk products - will be achieved in any case. nine0008
It is suitable for babies who do not want to drink kefir because of its consistency. A child may not like liquid kefir, but he is happy to eat cottage cheese. The goal - getting all the vitamins and minerals from fermented milk products - will be achieved in any case. nine0008
Acquaintance with fermented milk products is better to start with children's adapted ready-made kefir. Purchased baby kefir has low acidity, and it is enriched with vitamins. The product is included in the children's diet gradually, starting with one teaspoon, during the day, since the work of the baby's gastrointestinal tract will change in any case. The main thing is that there are no allergic reactions. The introduction of a new product always involves increased attention from the mother and observation of the reaction of the child. nine0008
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years.











