Babies gulping when feeding
How to Have a Calm-Gulp Free Feeding
Free Shipping on Orders $60+ (US Only)
Learn More
Start typing and hit Enter
Shopping Cart
Register
Back to login
How to Have a Calm-Gulp Free Feeding
By :Amy Peterson 13 May 2019
Babies feed many times each day. As moms, we want this to be a happy experience for our babies. Helping your baby have a gulp-free feeding is one way to make the feeding calm. Sometimes a mom may hear her baby gulp during a feeding, but sometimes gulping can be more subtle and quiet.
If your baby is struggling with gulping during bottle-feeding, you will be able to see it in your baby’s feeding behaviors even if you can’t hear it. A baby’s face will look worried with a furrowed brow when she feels overwhelmed. You might even notice your baby’s arms move up to block the bottle, or hos hands shift from a closed position to fingers that are spread apart. These are signs that the feeding doesn’t feel right for your baby. If your baby is struggling with some gulping during a feeding, here are some tips that may help.
LOOK AT YOUR BABY’S LIPS
Your baby’s lips need to form a complete seal on the nipple. If there are gaps between your baby’s lips and the nipple, chances are your baby is swallowing extra air which can sound like gulping. Using a nipple that gradually widens at the base and has a place for your baby’s lips to rest is helpful for many babies. You may need to try more than one nipple to see which works best for your baby.
CHECK THE BOTTLE FLOW
Most babies start with a slow flow nipple. Keep in mind that brands flow differently from one another, so a slow nipple from one brand might flow faster than a slow nipple from a different brand. Use a nipple, such as the Evenflo Feeding Balance + Nipple, that allows your baby to swallow after every one or two sucks without gulping.
FEED IN A SEMI-UPRIGHT POSITION
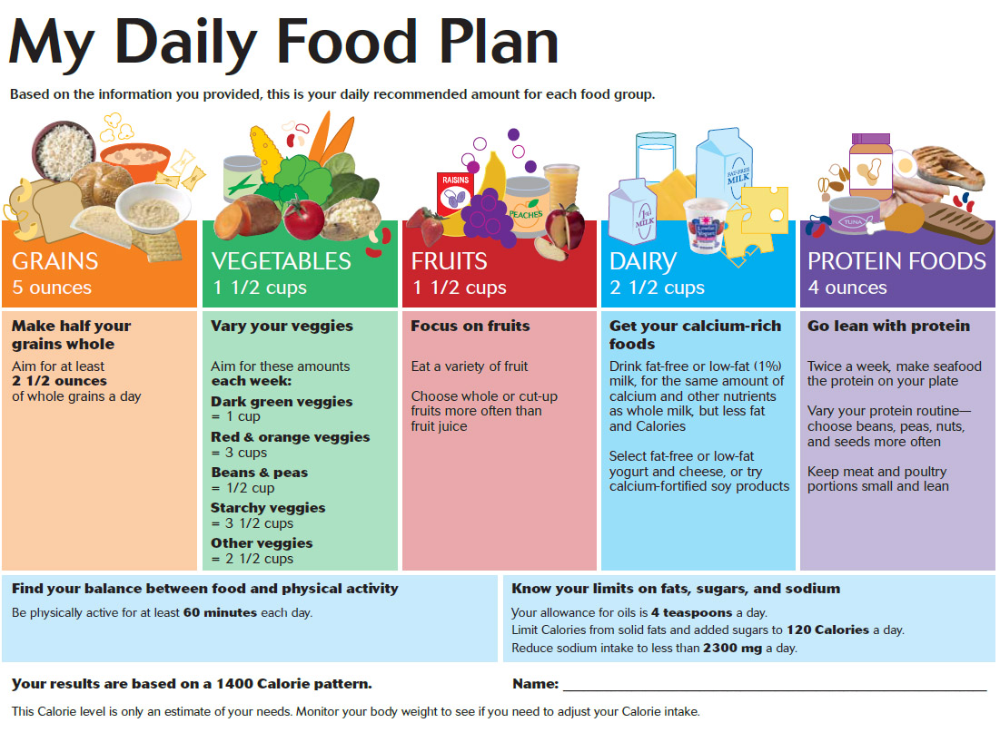
Bottle-feeding your baby a slightly upright position allows the milk to collect in the mouth, rather than the at the throat, so your baby can have a controlled swallow. For example, think of drinking from a cup while sitting up versus lying down. When lying down, gravity causes the milk to rush to the back of the throat which can result in gulping. A more upright position can prevent the need to gulp.
For example, think of drinking from a cup while sitting up versus lying down. When lying down, gravity causes the milk to rush to the back of the throat which can result in gulping. A more upright position can prevent the need to gulp.
ALLOW YOUR BABY TO REST BRIEFLY DURING A FEEDING
When a baby breastfeeds, milk stops flowing periodically between letdowns. This is nature’s way of allowing the baby a brief rest to catch his/her breath. Many babies will stop sucking and rest during bottle-feeding on their own. But if your baby tends to continuously swallow which can lead to gulping, help you baby rest by leaving the nipple in the mouth and tipping it down slightly so the milk doesn’t reach the nipple tip. When your baby starts sucking again, let the milk flow again.
Previous Post
Next Post
Choking, Gulping, Gagging - Symptoms
by Jan Gambino Patient Expert
Does your baby experience choking, gulping, gagging and coughing during a feeding? How about arching and fussiness? Sound like your baby? Then read on. These worrisome noises from the tiny digestive system of your baby may signal a swallowing problem, GERD or both.
Recently, I attended the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) meeting to learn more about pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). I met a team of doctors and speech language pathologists who wanted to find out how common dysphagia (a medical term for a swallowing disorder) was in a group of babies diagnosed with GERD. The study was presented at the meeting and the results were surprising.
GERD and dysphagia have overlapping symptoms including: arching, gagging, coughing and feeding refusal.
The researchers identified a group of babies who had been diagnosed with GERD.
Out of the large group, the researchers studied a smaller group with symptoms of both GERD and dysphagia.
The symptoms of dysphagia include:
Irritable after feedings/colic symptoms
Milk dribbling from the mouth
Coughing with feeds
Gagging
Air intake/Gas
Big gulps when swallowing
Slow feeding
Congestion
Poor color with feeds (medical term: cyanosis)
Arching
Refusing to eat
Respiratory issues
Poor tongue control
A feeding evaluation was completed for all babies with symptoms suggestive of GERD and dysphagia. The researchers found that many babies were diagnosed with dysphagia upon testing. However, they were surprised to find that many of the babies evaluated had severe dysphagia. Risk factors for GERD and dysphagia include developmental delay and poor weight gain. Reflux medications were not found to prevent dysphagia and the vast majority of the infants were on a prescription medication at the time of the study.
Dysphagia may be under-diagnosed in infants since there are many similarities in symptoms. Certainly Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) are more common so doctors will be more inclined to treat reflux first. However, if a baby does not respond to medical treatment, it may be necessary to investigate other causes of the symptoms. A speech language pathologist with training and expertise in infant swallowing and feeding problems is skilled at identifying and treating feeding problems. Unfortunately, a feeding specialist may not be available in every community. It might be necessary to get a referral to a larger regional hospital, children's hospital or feeding clinic. Once the problem is identified, parents and caregivers can be trained to use special feeding techniques at home to help a baby eat and grow.
Meet Our Writer
Jan Gambino
Jan wrote for HealthCentral as a patient expert for Acid Reflux.
Top-3 breastfeeding questions
Rinat Akhmetov's Humanitarian Center's hotline continues to receive requests from breastfeeding mothers from Donbass. Ksenia Solovei, Head of the National Movement in Support of Breastfeeding “Milk Rivers of Ukraine”, UNICEF Partner in the Breastfeeding Support Program in Crisis Situations, spoke about the three most common experiences of young mothers.
LOW MILK IN THE BREAST
Many mothers worry that the newborn is not full because there is not enough milk in the breast. You can actually understand whether this is true or not by how the child gains weight and how many times a day he urinates. nine0003
Nursing mothers should be guided by the recommendations of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine (Order No. 149 of 03.20.08), which states that a child should gain 500 g and more every month. Please note: control weighing (weighing the baby before and after breastfeeding) does not provide reliable information about whether the mother’s body produces enough breast milk, and is an ineffective indicator.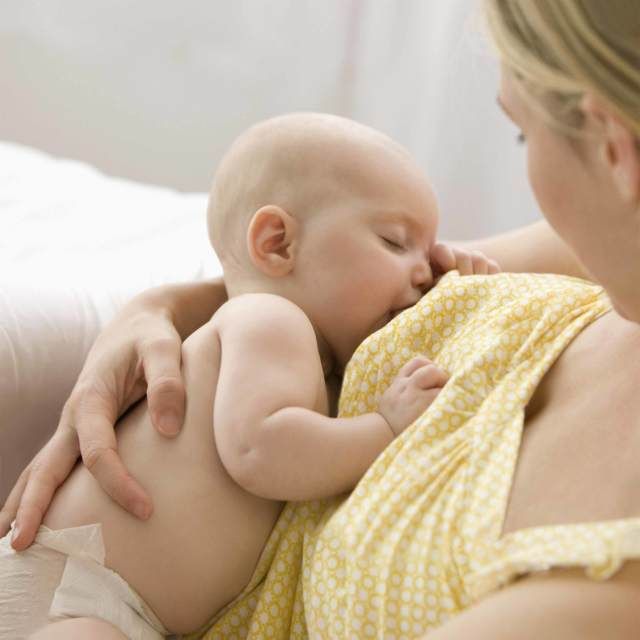 Since the baby is fed on demand, he eats a different amount of breast milk each time, and it is impossible to say whether it is little or not. In addition, the child gains weight chaotically - on one day he gains a lot, on another he may not gain weight or even lose a little, and then add a lot again. Therefore, you need to weigh the child no more than 1 time per week. Weekly weight must be at least 125 g.
Since the baby is fed on demand, he eats a different amount of breast milk each time, and it is impossible to say whether it is little or not. In addition, the child gains weight chaotically - on one day he gains a lot, on another he may not gain weight or even lose a little, and then add a lot again. Therefore, you need to weigh the child no more than 1 time per week. Weekly weight must be at least 125 g.
In addition, a child (aged 12 days to 6 months), who is gaining weight well, urinates 10-12 times a day (that's 6 full diapers), urine should be clear and odorless.
If the baby is not gaining enough, this may indeed indicate that the baby is not getting enough breast milk. In this case, it is important to check whether breastfeeding is organized correctly. Answer the questions for yourself:
- Am I breastfeeding correctly? nine0006 This means that you do not have cracked nipples, you do not have pain to feed, you do not use nipples, pacifiers or nipple shields. It can be seen how the baby swallows milk during feeding, while feeding the baby’s mouth is open as wide as possible, he captured the nipple and a lot of areola from below, the chin rests on the chest, the lower lip is turned out, the nose remains free.
It can be seen how the baby swallows milk during feeding, while feeding the baby’s mouth is open as wide as possible, he captured the nipple and a lot of areola from below, the chin rests on the chest, the lower lip is turned out, the nose remains free.
- How often do I breastfeed during the day? The baby feeds on demand and you can put him to the breast even 20 minutes after he has let go of the breast if he asks again. You do not have breaks in feeding more than 2 hours. nine0003
- Is my baby feeding enough at night? On average, your baby wakes up about 2-3 times (or more) during the night to suckle.
If one or more of these questions does not correspond to the described option, your body is "working" at half strength and it is very important that you change the situation. These are the basic principles by which the female body works in order to produce the right amount of milk. By following these simple rules, after 3-7 days your body will be able to start producing more milk. nine0003
nine0003
If you are doing all of these, but your baby is underweight, contact a lactation consultant to help you decide on a breastfeeding strategy together.
BABY IS LONG AT THE BREAST
In the first month, breastfeeding can last from 10-15 minutes and more than 30-60 minutes - this is a common occurrence if the baby is gaining weight well. Attachment to the breast for a child is a very important process, not only in terms of saturation. He helps him in a variety of situations - for example, when the child is agitated, burst into tears - the best calmer for the baby is breast sucking. In stressful situations, infants prefer to “survive” unpleasant moments by sucking on their breasts; it is known that breast milk contains sedative and analgesic factors. Many mothers talk about the fact that in the evening, children like to spend a lot of time under their breasts. This is not associated with a decrease in lactation. This is explained by the fact that having survived the whole day, the baby is tired, the nervous system is already overloaded and the child needs help to cope with this, and prolonged breast sucking is the best antidepressant and sedative for him. nine0003
nine0003
However, there are situations when, with frequent feedings, the baby suckles for a long time and gains weight poorly, then it is worth checking the correct attachment to the breast and the organization of feedings in general (see above).
TOO MUCH MILK IN THE BREAST
There are situations when milk flows like a river from the breast and the baby chokes and chokes while sucking. What to do in this case? This happens to many mothers, especially at the very beginning of breastfeeding. This is due to the fact that at the beginning of each feeding, the hormone oxytocin begins to eject milk from the breast. And if the baby is still small, then he may not be able to cope with a strong flow of breast milk, he may begin to choke, cough. nine0003
A mother can learn to recognize when such situations arise by listening to her baby suckle. Usually, when milk is ejected, the child begins to actively swallow milk and quite loudly. At such moments, the mother can take the breast from the baby (insert a finger between the baby's gums and release the nipple) and wait a minute when this flow of milk subsides. And then put it on your chest again. Another option is to change your feeding position. Lie down and place your baby on top of your chest. In this case, the pressure of milk will be less and the baby will be more comfortable sucking. nine0003
And then put it on your chest again. Another option is to change your feeding position. Lie down and place your baby on top of your chest. In this case, the pressure of milk will be less and the baby will be more comfortable sucking. nine0003
As part of the Let's Help the Children program, the Rinat Akhmetov Humanitarian Center, in cooperation with UNICEF, provides information support to mothers affected by the conflict in Donbas. You can ask an online question to a lactation consultant here.
Share news:
To parents about the prevention of dental diseases in young children
Dental caries is the most common human disease. Caries occurs in people of all ages, but most actively occurs in children. The condition of our child's teeth largely depends on us. It is necessary to think about the prevention of caries in a child from the beginning of pregnancy, because. laying of the rudiments of milk teeth occurs at 6-10 weeks of pregnancy. The expectant mother must strictly follow the recommendations of the gynecologist on the regime of work and rest, the woman must consume daily vegetables and fruits, milk, eggs, fish, meat. A woman should carefully look after her teeth, because. in soft plaque on the teeth there is a huge amount of microbes and their decay products, when swallowed, prerequisites are created for the emergence and development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs. The expectant mother should have all her teeth cured, because. a sick tooth can become a source of chroniosepsis for the mother, while the unborn child suffers at the same time. nine0003
laying of the rudiments of milk teeth occurs at 6-10 weeks of pregnancy. The expectant mother must strictly follow the recommendations of the gynecologist on the regime of work and rest, the woman must consume daily vegetables and fruits, milk, eggs, fish, meat. A woman should carefully look after her teeth, because. in soft plaque on the teeth there is a huge amount of microbes and their decay products, when swallowed, prerequisites are created for the emergence and development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs. The expectant mother should have all her teeth cured, because. a sick tooth can become a source of chroniosepsis for the mother, while the unborn child suffers at the same time. nine0003
The child is born. Prevention of dental diseases should begin from the first days of his life. In order for a child to form a healthy dentoalveolar system, it is necessary to pay serious attention to the development of healthy functions of breathing, sucking, then chewing, swallowing, and subsequently posture. If a child has a bad habit of breathing through the mouth and a pediatric ENT doctor has established that there are no anatomical obstacles to nasal breathing, it is necessary to ensure that the child sleeps with his mouth closed. To do this, conditions are created for the correct position (pose) of the child during sleep: the baby's head should not be thrown back or too raised. An indicator of the correct position of the head is a calm closing of the lips. If during sleep the child still opens his mouth, by touching the child's chin with a finger, raise his lower jaw until it touches the upper. If this measure is not enough, the child should be shown to a pediatric orthodontist. nine0003
If a child has a bad habit of breathing through the mouth and a pediatric ENT doctor has established that there are no anatomical obstacles to nasal breathing, it is necessary to ensure that the child sleeps with his mouth closed. To do this, conditions are created for the correct position (pose) of the child during sleep: the baby's head should not be thrown back or too raised. An indicator of the correct position of the head is a calm closing of the lips. If during sleep the child still opens his mouth, by touching the child's chin with a finger, raise his lower jaw until it touches the upper. If this measure is not enough, the child should be shown to a pediatric orthodontist. nine0003
A child is born with such a position of the jaws that for their physiologically correct ratio in the future, a certain load on them is required in the form of an active sufficient duration of sucking and then chewing. If a child is fed with mother's milk, he works to "get" it. If the baby is artificially fed, it is necessary to create conditions under which he would have to expend effort to suck milk out of the bottle through the nipple.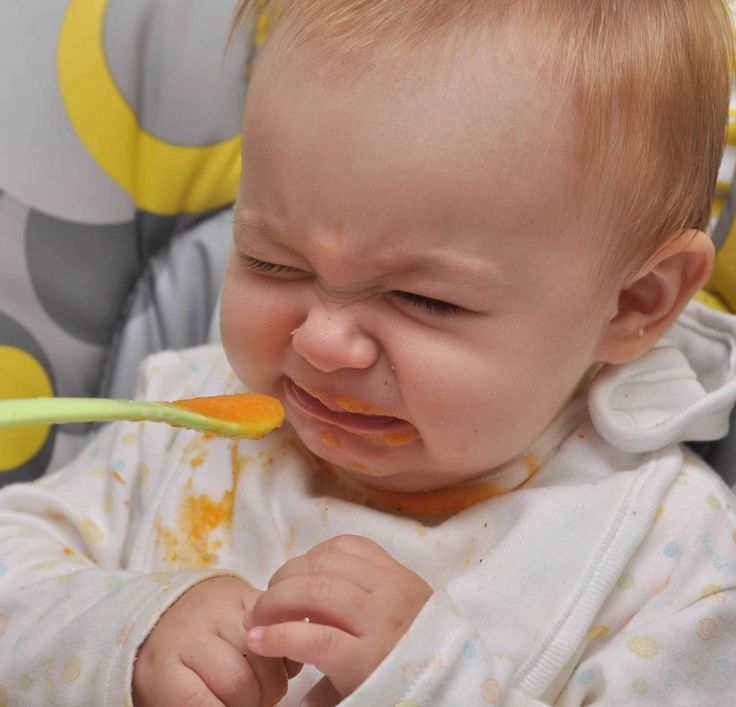 The nipple should be short and firm. There should be three holes, but small ones, otherwise the baby will choke, not have time to swallow food. After tipping over the bottle, the food should not flow out of the hole, but drip down. With active sucking, the child's tongue, lips, and lower jaw are involved in movement. Without such gymnastics, the movement of the lower jaw of the child forward may be delayed and it will remain underdeveloped. nine0003
The nipple should be short and firm. There should be three holes, but small ones, otherwise the baby will choke, not have time to swallow food. After tipping over the bottle, the food should not flow out of the hole, but drip down. With active sucking, the child's tongue, lips, and lower jaw are involved in movement. Without such gymnastics, the movement of the lower jaw of the child forward may be delayed and it will remain underdeveloped. nine0003
The child is full, but there is no complete satisfaction in sucking, he is worried, sucks his tongue or lip, does not fall asleep. In such cases, he can be given a pacifier for a short time - before the onset of deep sleep, after which the pacifier must be removed from his mouth.
Bad habits of sucking the tongue, fist, finger are formed from early childhood - in the first 3 months of a child's life. To prevent them, it is recommended to put on a baby's undershirt with protective sleeves, specially sewn mittens or fix a light splint on the child's elbow joint during wakefulness, making it impossible to reach the mouth with a pen. nine0071 During teething, due to irritation of nerve receptors, itching appears in the places of teething. Babies become irritable, restless, sleep poorly, eat poorly. It is necessary to give the child a “nibble” on a plastic or rubber ring, and give a pacifier while falling asleep. It is unacceptable to use a dummy after the age of one year, as well as to use it during the waking period. This bad habit leads to deformation of the dentition.
nine0071 During teething, due to irritation of nerve receptors, itching appears in the places of teething. Babies become irritable, restless, sleep poorly, eat poorly. It is necessary to give the child a “nibble” on a plastic or rubber ring, and give a pacifier while falling asleep. It is unacceptable to use a dummy after the age of one year, as well as to use it during the waking period. This bad habit leads to deformation of the dentition.
For the correct development of teeth and jaws, a timely transition to eating from a spoon and a cup, a transition to taking more dense, and then solid food, requiring biting and chewing, is necessary. Starting from 4-5 months, before giving yogurt or other bottled food to the baby through the nipple, 1/3 portion of this food should be given from a spoon. While the baby is hungry, he will push his lower jaw towards the spoon and try to remove food with his lips. Tasty food (juices, fruit and vegetable purees, kissels) should also be given from a spoon. When spoon-feeding, it should be brought to the lips, and not put into the mouth. The kid should reach for it, this tension is a kind of training of the jaws and muscles. A spoon for a child at the end of the first year of life should become the main cutlery. But for the last evening feeding, an exception can be made. The baby is tired by this time, feed him from a bottle through a nipple. He eats his portion, and sucking movements calm him down, deep sleep comes faster. nine0071 Food is the main source of building materials for developing teeth and should contain the optimal amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, microelements. But an excess of refined carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, honey, etc.) creates conditions for the occurrence of caries - first of all, the immature insular apparatus is overloaded, which leads to a violation of carbohydrate metabolism in the body, a decrease in caries resistance of tooth tissues, and after teething sugar-rich food is fermented in the mouth to lactic acid, which acts directly on the immature tissues of the tooth, because the erupting teeth are poorly mineralized, dental caries quickly develops and progresses, leading to tooth decay already at the age of 2-3 years.
When spoon-feeding, it should be brought to the lips, and not put into the mouth. The kid should reach for it, this tension is a kind of training of the jaws and muscles. A spoon for a child at the end of the first year of life should become the main cutlery. But for the last evening feeding, an exception can be made. The baby is tired by this time, feed him from a bottle through a nipple. He eats his portion, and sucking movements calm him down, deep sleep comes faster. nine0071 Food is the main source of building materials for developing teeth and should contain the optimal amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, microelements. But an excess of refined carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, honey, etc.) creates conditions for the occurrence of caries - first of all, the immature insular apparatus is overloaded, which leads to a violation of carbohydrate metabolism in the body, a decrease in caries resistance of tooth tissues, and after teething sugar-rich food is fermented in the mouth to lactic acid, which acts directly on the immature tissues of the tooth, because the erupting teeth are poorly mineralized, dental caries quickly develops and progresses, leading to tooth decay already at the age of 2-3 years. nine0003
nine0003
Not only the composition, but also the form of culinary processing of food affects the dentoalveolar system. The majority of the population, and especially children, consume mostly soft, crushed food (cereals, soft bread, mashed vegetables, chopped meat, etc.), which does not contribute to the natural cleaning of teeth from soft plaque during the act of chewing. With poor self-cleaning of the oral cavity, a lot of sticky food residues accumulate, which contribute to the reproduction of microorganisms. Under the influence of bacteria, food remnants stuck in the interdental spaces undergo decay, fermentation and decay, which leads to the formation of soft plaque, halitosis. When all the teeth have erupted in a child, he needs food that requires vigorous chewing: meat, preferably a boiled piece, and not cranked. Let the children gnaw carrots, turnips, apples, bagels, crackers. With vigorous chewing, the jaws will develop correctly and a normal swallowing function will be formed.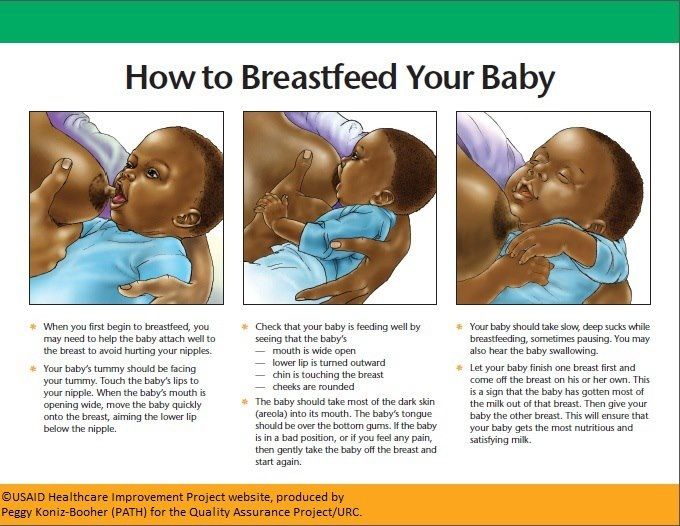 Pay attention to the child's face when swallowing. Swallowing normally should not cause grimaces on the face, and no tension. nine0003
Pay attention to the child's face when swallowing. Swallowing normally should not cause grimaces on the face, and no tension. nine0003
Teeth should be brushed from the moment they enter the mouth. In the beginning, to clean the first milk teeth, soft wipes or terry cloth flaps soaked in warm boiled water are used. From the age of one and a half, teach your child to rinse his mouth after eating. Immediately, children swallow everything that falls into their mouths, so they should be taught to rinse their mouths in the following sequence: first ask them to immediately spit out water from their mouths when they take it into their mouths, then teach them to hold it in their mouths, then, passing water between their teeth, rinse and spit it out water. One of the available and reliable methods of preventing dental caries is oral hygiene, the observance of which contributes to the prevention of diseases of the teeth and surrounding tissues. Practice shows that preschool children pay extremely insufficient attention to oral care. Proper oral care, started at an early age, reduces the cleanliness of dental diseases. Do not forget that a personal example is better than any words and arguments. Where parents brush their teeth in the family, this hygienic rule enters into the life of the whole family. Give your child a toothbrush by age 2. Of course, it should be a small brush, the length of the working part (bristles) should not exceed the sum of the diameters of the three adjacent teeth of a child with soft bristles. First, let the child brush his teeth with a moistened brush, without paste, let alone powder, which he can inhale. When he learns to brush his teeth without paste and spit out water when rinsing, move on to brushing with toothpastes: “Mint”, “Family”, “Berry”, “Children's”, “Orange”, “Just you wait”, “Artek”, “ Moidodyr. In case of diseases of the teeth and surrounding tissues, it is necessary to use therapeutic and prophylactic pastes containing biologically active components. They have a beneficial effect on the teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Proper oral care, started at an early age, reduces the cleanliness of dental diseases. Do not forget that a personal example is better than any words and arguments. Where parents brush their teeth in the family, this hygienic rule enters into the life of the whole family. Give your child a toothbrush by age 2. Of course, it should be a small brush, the length of the working part (bristles) should not exceed the sum of the diameters of the three adjacent teeth of a child with soft bristles. First, let the child brush his teeth with a moistened brush, without paste, let alone powder, which he can inhale. When he learns to brush his teeth without paste and spit out water when rinsing, move on to brushing with toothpastes: “Mint”, “Family”, “Berry”, “Children's”, “Orange”, “Just you wait”, “Artek”, “ Moidodyr. In case of diseases of the teeth and surrounding tissues, it is necessary to use therapeutic and prophylactic pastes containing biologically active components. They have a beneficial effect on the teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity. So, with bleeding gums, it is better to use toothpastes "Forest", "Chrolophilic", "New", "Chamomile", "Balm". If the child has a lot of carious teeth, we recommend toothpastes: Cheburashka, Belorozovaya, Zhemchuk, Fluorodent. Teach your child how to brush their teeth. To clean the teeth, sweeping, circular, reciprocating movements with a brush are used. Sweeping movements are necessary to clean the buccal, palatine, lingual, labial surfaces of the teeth, reciprocating - mainly to clean the chewing surfaces. Circular movements are carried out when cleaning the lingual, palatine and labial surfaces of the teeth, but after sweeping. nine0003
So, with bleeding gums, it is better to use toothpastes "Forest", "Chrolophilic", "New", "Chamomile", "Balm". If the child has a lot of carious teeth, we recommend toothpastes: Cheburashka, Belorozovaya, Zhemchuk, Fluorodent. Teach your child how to brush their teeth. To clean the teeth, sweeping, circular, reciprocating movements with a brush are used. Sweeping movements are necessary to clean the buccal, palatine, lingual, labial surfaces of the teeth, reciprocating - mainly to clean the chewing surfaces. Circular movements are carried out when cleaning the lingual, palatine and labial surfaces of the teeth, but after sweeping. nine0003
Gradually increase the duration of brushing your teeth to 3-3.5 minutes. Teeth cleaning should be supervised and assisted by adult family members.
It is very important to take your child to a pediatric dentist once a year, even if you think the child's teeth are healthy. Firstly, the initial forms of caries are asymptomatic, and carious cavities are localized in places that are inaccessible to viewing with just an eye without a dental mirror and probe. And teeth can be destroyed very early, even at the age of 2 years, and at 2 years old, 18-25% of children already have carious cavities. It is very important to be cured in time, and that means to keep milk teeth. nine0003
And teeth can be destroyed very early, even at the age of 2 years, and at 2 years old, 18-25% of children already have carious cavities. It is very important to be cured in time, and that means to keep milk teeth. nine0003
The child needs to be prepared for dental visits; refrain from talking in his presence about the fear you feel when you visit the dentist. A child who has never had a toothache sits quietly in a chair and allows himself to have his tooth fixed.
Untimely treatment of milk teeth entails diseases of the rudiments of permanent ones, which are located under the roots of milk teeth.
In children aged one to three years, a herpes infection occurs in the form of acute herpetic stomatitis. The first signs of the disease are a sudden increase in body temperature, salivation, redness of the oral mucosa. Report the child’s illness to the preschool institution and, after the diagnosis is made by a pediatric dentist, isolate the child from other children in the family, provide him with separate dishes, a bed, a towel, ventilate the room, create conditions for the penetration of sunlight into the room, strictly follow the instructions of the pediatric dentist, otherwise the disease can go into a chronic relapsing form, which is unfavorable for the health of the child himself and he becomes dangerous for the surrounding children, especially during the period of relapses.