What age to feed baby table food
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
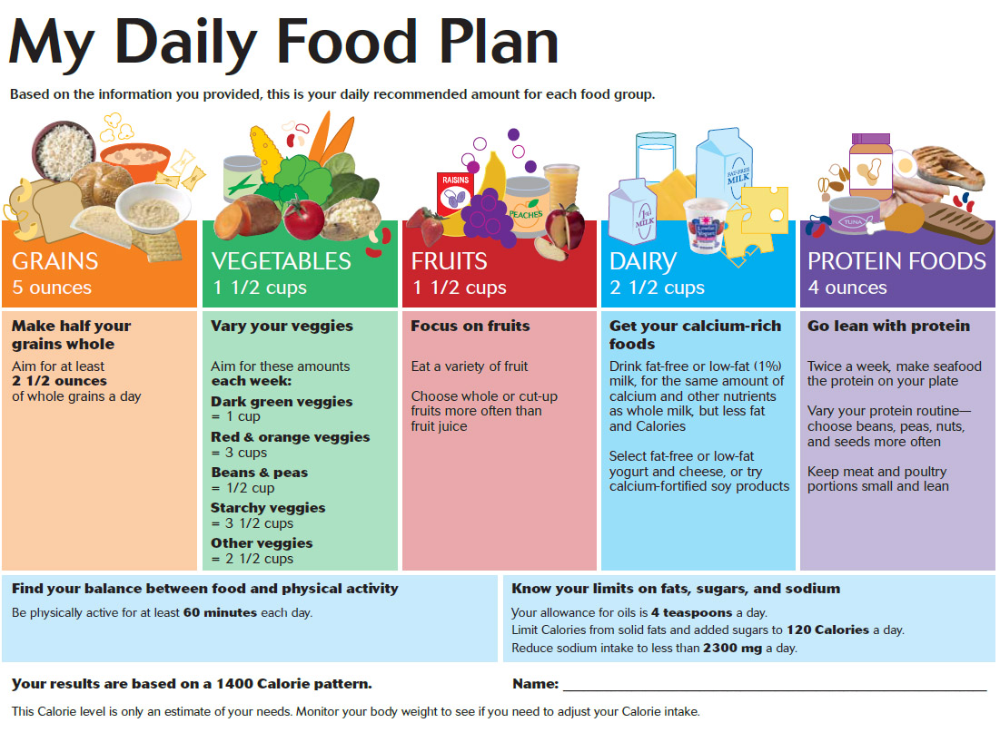
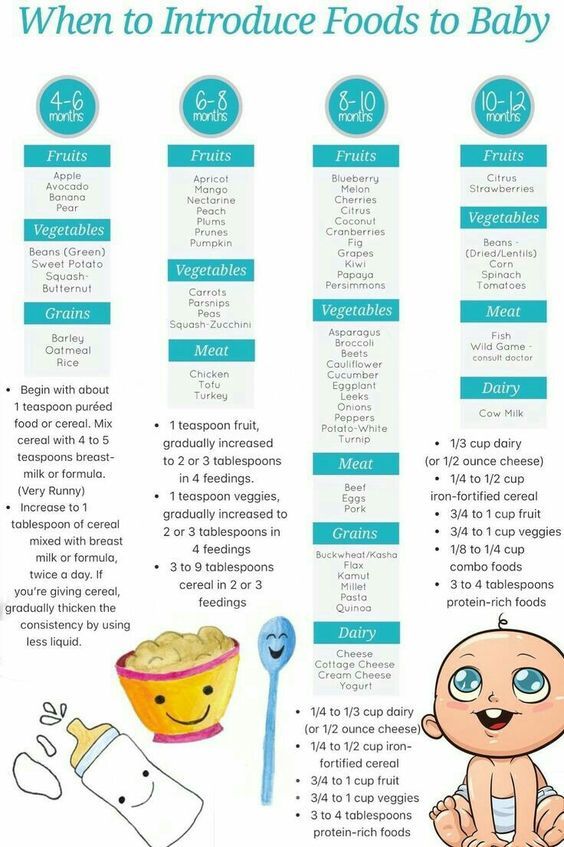
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.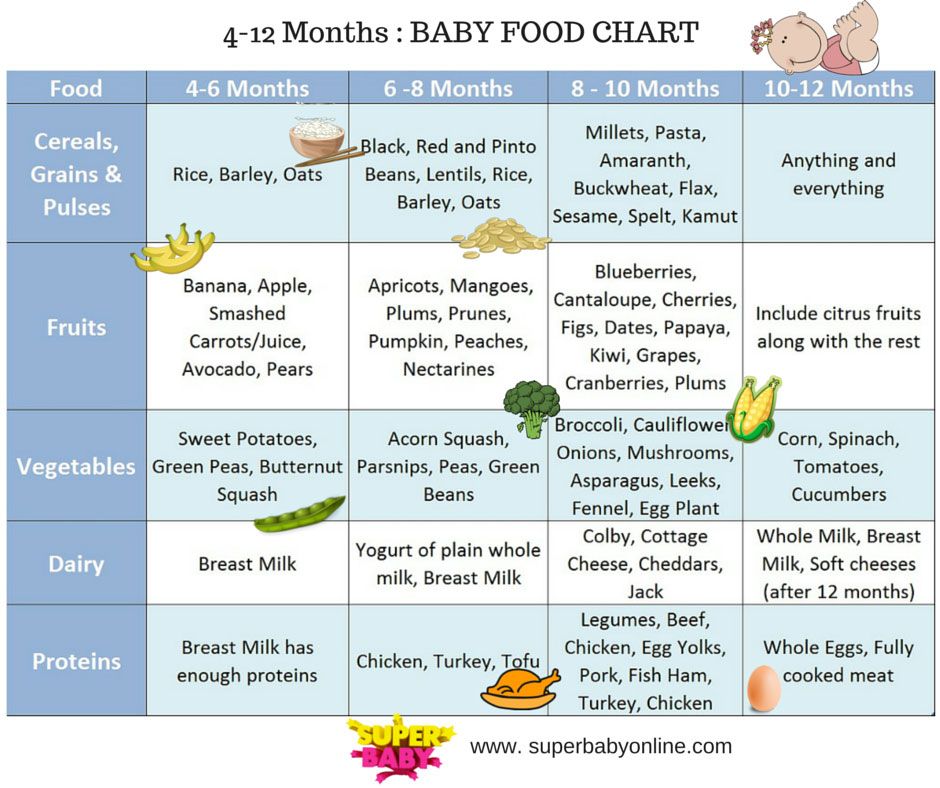
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.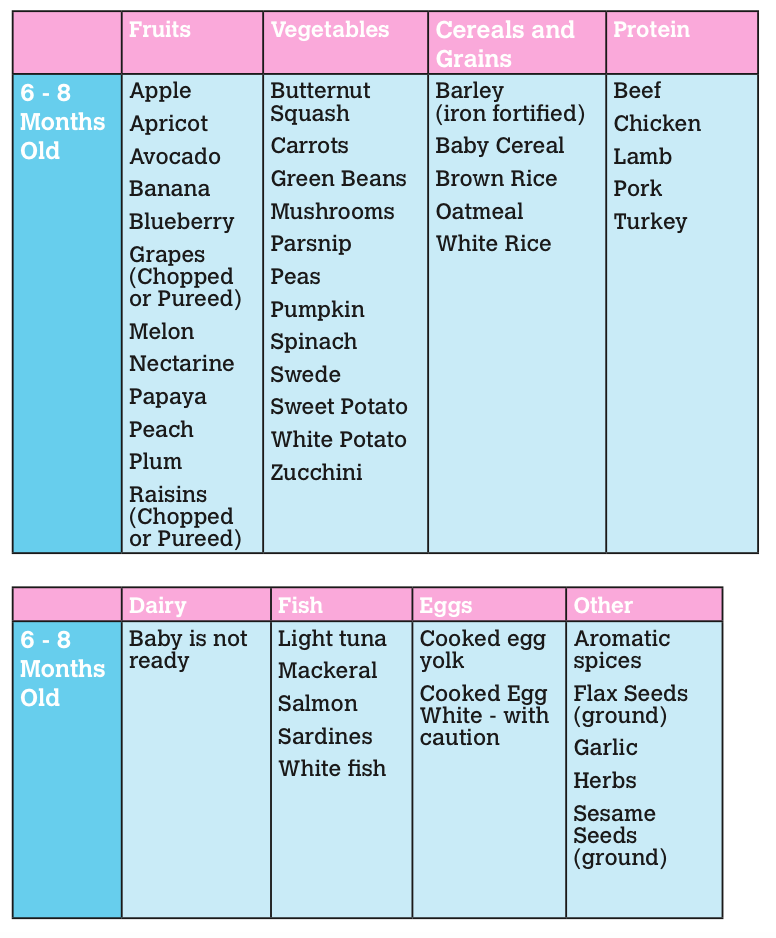
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
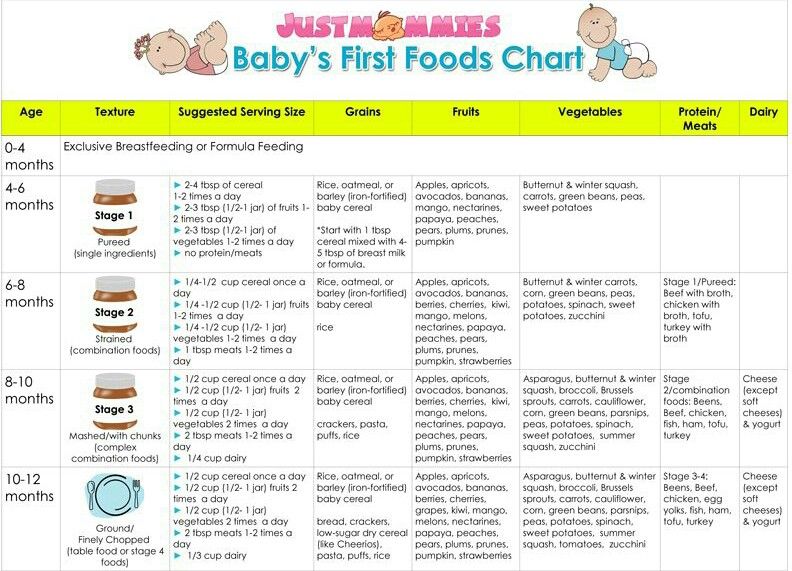
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Feeding Your 8- to 12-Month-Old (for Parents)
By 8 months old, most babies are pros at handling the iron-fortified infant cereals and the puréed foods that are part of their diet, along with breast milk or formula.
Over the next few months, they will start to explore table foods.
Changing Eating Habits
Offer your baby a variety of tastes and textures from all food groups. Start any new food with a trial run (a few days to a week) to look for any allergic reactions. Babies younger than 12 months old should not have:
- honey until after a baby's first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy drinks before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw vegetables, grapes, hard cheese, popcorn, and nuts
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
Babies this age are likely showing more interest in table foods. You can fork-mash, cut up, blend, or grind whatever foods the rest of the family eats. To prevent choking, cook table foods a little longer, until very soft, and cut or shred them into small pieces that your baby can handle safely.
To prevent choking, cook table foods a little longer, until very soft, and cut or shred them into small pieces that your baby can handle safely.
Around 9 months old, infant usually can pick food up between their finger and thumb so they can try feeding themselves.
If you haven't already, have your baby join the rest of the family at meals. They enjoy being at the table.
After the first birthday, babies are ready to switch to cow's milk. If you're breastfeeding, you can continue beyond 1 year, if desired. If you decide to stop breastfeeding before your baby's first birthday, give iron-fortified formula. If your baby is over 12 months, give whole milk.
Let your baby keep working on drinking from a cup, but do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months. After 12 months, you can serve whole milk in a cup, which will help with the move from the bottle.
Feeding Safety
Always supervise when your child is eating. Make sure your child sits up in a high chair or other safe place. Don't serve foods that your baby could choke on.
Don't serve foods that your baby could choke on.
If you're unsure about whether a finger food is safe, ask yourself:
- Does it melt in the mouth? Some dry cereals will melt in the mouth, and so will light and flaky crackers.
- Is it cooked enough so that it mashes easily? Well-cooked vegetables and fruits will mash easily. So will canned fruits and vegetables. (Choose canned foods that don't have added sugar or salt.)
- Is it naturally soft? Cottage cheese, shredded cheese, and small pieces of tofu are soft.
- Can it be gummed? Pieces of ripe banana and well-cooked pasta can be gummed.
Making Meals Work
Keep your baby's personality in mind when feeding your baby. A child who likes a lot of stimulation may enjoy it when you "play airplane" with the spoon to get the food into their mouth. But a more sensitive tot might need the focus kept on eating with few distractions.
If your baby rejects new tastes and textures, serve new foods in small portions and don’t give up. It can take 8-10 tries before a baby accepts a new food.
It can take 8-10 tries before a baby accepts a new food.
How Much Should My Baby Eat?
Infant formula and breast milk continue to provide important nutrients for growing infants. But babies will start to drink less as they learn to eat variety of solid foods.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
Let your baby finger feed or hold a spoon while you do the actual feeding. This is good preparation for the toddler years, when kids take charge of feeding themselves. And if you haven't already, set regular meal and snack times.
who is entitled to and how to apply under the law
Free meals for schoolchildren are one of the measures of social support and stimulation of society - in particular, the younger generation. We talk about who can count on free meals at school in 2022
We talk about who can count on free meals at school in 2022
Alena Gerashchenko
Journalist
Artem Tabunin CEO of the Aksioma processing center,
Service for accounting for preferential and paid meals in schools
Anna Ryzhkova
Editorial Director of the group
Action Education
Candidate of Legal Sciences
Federal Law No. 273 -FZ "On Education in the Russian Federation" regulates the issues of education and support for schoolchildren and students. On March 1, 2020, it was amended to provide primary school students with free meals. The changes came into force on September 1, 2020 and affected the way food is provided, as well as the quality and safety requirements for food used to prepare breakfasts and lunches in schools.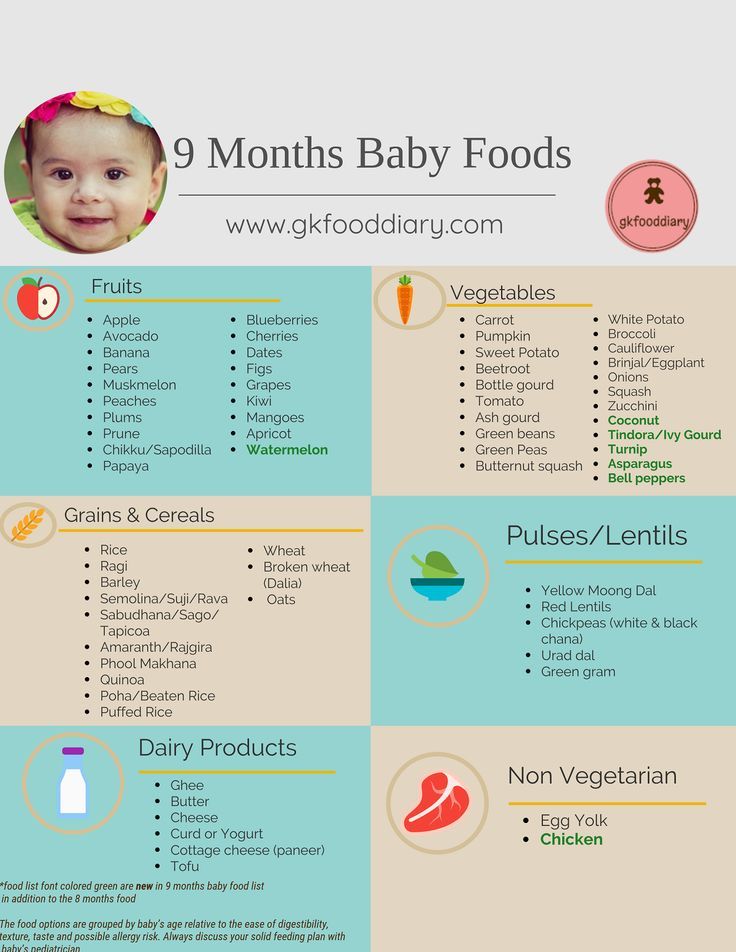 Previously, school cafeterias were also subject to federal safety regulations, but the provision of food was left to educational organizations. Meals were mostly paid: teachers collected money for lunches and took organized groups of children to buffets. Now everything has changed. By September 1, 2023, schools must fully provide each student in grades 1-4 with at least one hot meal per day (not including a hot drink). Money for food comes from the state budget of different levels. nine0003
Previously, school cafeterias were also subject to federal safety regulations, but the provision of food was left to educational organizations. Meals were mostly paid: teachers collected money for lunches and took organized groups of children to buffets. Now everything has changed. By September 1, 2023, schools must fully provide each student in grades 1-4 with at least one hot meal per day (not including a hot drink). Money for food comes from the state budget of different levels. nine0003
Who is eligible for free school meals
Free hot meals are provided to all students in grades 1 to 4 without exception. But only once during the school day. Moreover, it can be either lunch with soup or breakfast with hot porridge. What and when schoolchildren will eat, each school decides for itself, based on the recommendations of doctors.
There are still two free meals a day for students with disabilities. At the same time, disabled children studying at home receive dry rations. nine0004
At the same time, disabled children studying at home receive dry rations. nine0004
Children from low-income families can also count on two free meals a day. This measure of support for low-income families is called state social assistance.
Read also
How to adapt to school
household and social skills, as well as personal things that will help the child feel more confident in the new environment
| more |
How meals at school
As follows from the regulatory documents and as noted by Dmitry Karpukhin, Ph.D. in Law, Associate Professor of the Department of International and Public Law of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, parents are not required to submit any special application for the provision of free meals to their children studying in primary school. This right is unconditional.
But in order for the food in the school cafeteria to be of high quality and safe, parents need to inform the school about the health status of their children, their diagnoses, whether there is an allergy to any food and how it manifests itself. Although this is advisory in nature: parents themselves decide what information about the child's health to provide and whether it should be done. nine0004
Although this is advisory in nature: parents themselves decide what information about the child's health to provide and whether it should be done. nine0004
Your child's health information can be submitted in any format, paper or electronic. These can be certificates from doctors, from clinics, test results showing, for example, that a child has clearly expressed allergens in the blood. Any information about the health of the student will be useful to the school and will allow it to adjust the menu to suit individual needs.
Important to know
How to choose a school backpack that won't hurt your child's posture
Posture must be protected from a young age. However, textbooks weigh a lot - and the health of the student's spine largely depends on the choice of the right school backpack. KP compiled a list of the best models of school backpacks
| More details |
Documents to collect
However, if we are talking about free two meals a day for students with disabilities or children from low-income families, then a package of documents will be needed. nine0003
nine0003
1) Prepare the child's birth certificate and its SNILS, if available.
2) Fill out an application for the provision of food at the expense of the city budget, submit it on the mos.ru website (Moscow) or send it to the social protection authorities (for other cities).
3) Certificates confirming that the child has a disability and (or) documents on the parents' income confirming the family's status as low-income can be attached to the application. In Moscow, the term for consideration of documents is 8 days. But in general, it should not exceed 30 days. nine0004
4) Take the received certificate of preferential meals to the class teacher along with all documents on the child's health, which will allow you to create a menu for him.
Read more0071
Popular Questions and Answers
What law regulates the right to food in school?
Anna Ryzhkova, editorial director of the Action Education group :
- The right to food at school is enshrined in Federal Law No. 273-FZ "On Education in the Russian Federation". Also, food intake by schoolchildren is regulated by Federal Law No. 29-FZ “On the Quality and Safety of Food Products”. Another act regulating school nutrition is Federal Law No. 47-FZ of March 1, 2020 “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On the Quality and Safety of Food Products” and Article 37 of the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation”. nine0003
273-FZ "On Education in the Russian Federation". Also, food intake by schoolchildren is regulated by Federal Law No. 29-FZ “On the Quality and Safety of Food Products”. Another act regulating school nutrition is Federal Law No. 47-FZ of March 1, 2020 “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On the Quality and Safety of Food Products” and Article 37 of the Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation”. nine0003
Why is food provided only in elementary schools?
Artem Tabunin, General Director of the processing center "Axioma", a service for accounting for preferential and paid meals in schools :
- It is unequivocally difficult to answer why hot meals will be provided only to elementary school students. Perhaps the reason is that feeding all the elementary school students is a big burden on the budget. In 2021, 46 billion was spent on innovation. Nutrition for all schoolchildren would require twice as much, and the financial block of the Government of the Russian Federation simply would not miss such a legislative initiative. nine0003
nine0003
Anna Ryzhkova :
- Healthy hot meals at primary school age are very important for the formation of healthy eating habits. The older the children, the more difficult it is to change their eating habits. So we started with younger students.
Where can I download a sample application for free school meals?
Dmitry Karpukhin, Ph.D. In this regard, a unified sample application for free school meals has not been developed. But if the school offers to fill it out, then you can find such an application on the official website of the educational institution. nine0003
Can I refuse free meals?
Artyom Tabunin :
- We keep records of expenses in schools and see that food coverage in the lower grades has grown to 99%. You can opt out of free meals. But it is surprising that there are parents who write statements containing such refusals. There is no unified application form. Therefore, parents, if they believe that the child should eat exclusively homemade food, can make it up themselves. nine0004
But it is surprising that there are parents who write statements containing such refusals. There is no unified application form. Therefore, parents, if they believe that the child should eat exclusively homemade food, can make it up themselves. nine0004
Anna Ryzhkova :
- If a parent does not wish to receive a benefit, schools must take a waiver. It will serve as evidence for the verifiers that the food was offered to the child.
Read also
Adaptation of children after summer holidays
As soon as school classes began, problems began to fall on children and their fathers and mothers. What to do and how to help children cope with adaptation after the summer holidays?
| More details |
Cover photo: Alexey Bulatov
Does your child get free school meals? Did you encounter any problems while applying for it? Share in the comments:
Comments for the site Cackl e
Optimal nutrition for children aged 7 to 9 months
Submitted by useradmin on Thu, 08/12/2021 - 21:24
Number of meals and amount of food
At this age, breast milk is still the most important food for a baby and provides half of his energy needs. Continue to breastfeed your baby on demand day and night. Solid foods cannot replace breast milk in the first year of life. There is no need for additional feeding of the child with breast milk substitutes, subsequent infant formulas (adapted milk formulas for children older than 6 months), because, being breastfed and receiving varied and timely complementary foods, the baby will be provided with all the necessary nutrients. nine0242
Continue to breastfeed your baby on demand day and night. Solid foods cannot replace breast milk in the first year of life. There is no need for additional feeding of the child with breast milk substitutes, subsequent infant formulas (adapted milk formulas for children older than 6 months), because, being breastfed and receiving varied and timely complementary foods, the baby will be provided with all the necessary nutrients. nine0242
Breastfeed after each feeding.
Basic recommendations for complementary feeding of the child:
- The optimal period for introducing complementary foods is the period from the 20th to the 26th week of life.
- Volume: The introduction of complementary foods into the baby's diet should be gradual. Start with 2-3 tablespoons, gradually increasing to 120 ml with each feeding. nine0254 Frequency: Give complementary foods 3 times a day.
- Consistency: the child should be offered family-friendly products from the common table, mashed to a puree-like consistency. From about 8 months, you can start offering your baby food in pieces.
- Variety: try to give a variety of food at each meal. For example: animal products (meat, eggs and dairy products), cereals (grains), root vegetables (and tubers), legumes, fruits, vegetables rich in vitamin A (carrots, pumpkin, spinach), and others (zucchini, cabbage). nine0273
- Animal products must be included in your child's diet. They should be administered as early as possible, given daily. It is necessary to grind them after sufficient heat treatment. Hard-boiled and finely chopped eggs, meat (lean beef and lamb), chicken, turkey and rabbit meat, and fish can be eaten by children even if they have no teeth.
- Foods can be mixed: purees and cereals should include a mixture of cereals, vegetables, beans, eggs, fruits, root vegetables and, if possible, rabbit meat, beef, fish, poultry.
 Milk can be added to cereals. Dense foods are richer in calories and vitamins - their nutritional value for a child is higher than, for example, soups. Children have a high need for energy and nutrients, as well as a small stomach, so the diet should include such dishes that, with a small volume, have a high nutritional value for the child. nine0257
Milk can be added to cereals. Dense foods are richer in calories and vitamins - their nutritional value for a child is higher than, for example, soups. Children have a high need for energy and nutrients, as well as a small stomach, so the diet should include such dishes that, with a small volume, have a high nutritional value for the child. nine0257 - Offer snacks (between meals) such as fruit once or twice a day.
- If your baby was exclusively breastfed, water should be started with the introduction of complementary foods. The need for water depends on the age of the child, the number of meals, the amount and type of food. Offer your child water more often, especially after meals! Let's drink it from a cup. In the first year, boiled and chilled water is recommended.
- When preparing baby food with oil or butter, use no more than half a teaspoon per day. nine0257
- Add one new meal to your child's diet every week.
- Focus on the child: be patient and actively encourage him.
 Don't force your baby to eat. Use a separate plate so that you can see if he ate everything that was offered.
Don't force your baby to eat. Use a separate plate so that you can see if he ate everything that was offered. - Observe your child and respond to his signals. Feed slowly and patiently, at his pace. Try different combinations of foods, flavors and textures to stimulate your child's appetite. Wait until he chews and swallows before offering another portion. nine0257
- Stop feeding when the baby makes it clear that he has eaten.
- As the child grows older, he gradually develops the skills necessary for independent eating (taking pieces of food and putting them in his mouth, choosing products, using cutlery).
- Establish a routine for your main meals and snacks. Limit feeding time to 15-20 minutes. During meals, the child should be exclusively in the high chair at the table.
nine0254 Hygiene: Hygiene (cleanliness) is essential to prevent diarrhea and other illnesses in the child. Use clean utensils and utensils when preparing food and feeding.

 Store food in a safe and clean place in accordance with the terms and rules indicated on them. Remember to follow the basic rules of personal hygiene - wash your hands with soap and water before preparing food and feeding the child, after using the toilet, after performing hygiene procedures and washing the child. Wash your child's hands before eating. nine0257
Store food in a safe and clean place in accordance with the terms and rules indicated on them. Remember to follow the basic rules of personal hygiene - wash your hands with soap and water before preparing food and feeding the child, after using the toilet, after performing hygiene procedures and washing the child. Wash your child's hands before eating. nine0257 Products not recommended during the first year of life:
- Med.
- Cow's (and also goat's) milk. It is not recommended to give it to children in the first year of life, since its composition does not meet the needs of infants and it can contribute to the development of anemia and allergies. To prepare cereals, you can use a small amount (diluted 1: 1 with boiled water) of cow's milk.
- Citrus fruits (lemon, orange, mandarin). nine0257
- Tropical fruits and vegetables.
- Sweets and pastries.
- Fried snacks (chips, croutons, snacks), fast food (fast food).
- Tea, drinks carbonated and/or with a high content of sugar, dyes.
- Industrially processed meat products (sausages, sausages).
- Do not add salt, spices or food additives to baby food. If you use salt when preparing food for your child, add iodized salt. nine0257
Always think about safety: do not give your child peanuts, popcorn, small fruits or whole grapes, pieces of solid food that can choke on.
How to feed your baby
It is important that your baby eat a variety of foods. You can start complementary foods with thick porridge, gradually introducing any one vegetable (pumpkin, carrot, cauliflower or white cabbage) or fruit (apple, pear, plum, banana) puree into it. After that, you can move on to mashed meats (from lean beef, lamb, horse meat, pork, turkey, chicken or rabbit meat) or legumes with vegetables. The child may develop preferences for certain foods. Try to encourage your child to try different things.