Baby crying when bottle feeding
Bottle Feeding Problems - Why Your Baby Squirms, Appears Uncomfortable – Baby Care Advice
When your baby squirms, appears uncomfortable during a feed, fusses, cries or refuses a bottle, seemingly fights the bottle despite being hungry, it can be challenge to figure out the cause. The timing and type of behavior she exhibits provides vital clues. This article discusses potential reasons for troubled feeding behavior.
Signs of bottle-feeding problemsDoes your baby display troubled behavior in relation to bottle-feeding, such as….
- Refuses a bottle
- Turning away from the bottle.
- Refusing to close her mouth around the nipple.
- Holding nipple in the mouth but not sucking.
- Taking only a small amount and then refusing more.
- Screaming when placed into a feeding position or at the sight of the bottle.
- Milk pouring out of baby's mouth.
- Feeding too quickly.
- Feeding too slowly.
- Falling asleep before the feed is completed.
- Coughing and spluttering when feeding.
- Not consuming as much milk as expected.
- Wanting more milk than expected.
- Throwing up large amounts of milk.
Then there may be steps you can take to remedy the situation and get your baby to calmly and happily take a bottle.
Behavioral reasons‘Behavioral’ means baby’s behavior is in response to the circumstances rather than a physical cause. Behavioral reasons are the most common of all reasons for infant feeding problems. There are numerous behavioral reasons for a baby to experience feeding problems and/or display problematic feeding behavior. Common reasons include:
1. Misinterpreting baby's cues as signs of hunger Does baby at times refuse feeds?Does she take only a little and not want more?
Babies are in an oral stage of develop. Sucking is the primary way babies soothe. They also learn by sucking and mouthing objects. Many babies have a strong desire to suck for reasons that extend beyond hunger, such as tiredness, boredom, discomfort and soothing. There may be times when you mistake your baby’s desire to suck for these reasons as hunger.
Sucking is the primary way babies soothe. They also learn by sucking and mouthing objects. Many babies have a strong desire to suck for reasons that extend beyond hunger, such as tiredness, boredom, discomfort and soothing. There may be times when you mistake your baby’s desire to suck for these reasons as hunger.
Newborn babies have an active sucking reflex. This means a newborn baby may accept a feed even when she’s not hungry, and she might guzzle down the bottle because she cannot choose to not suck when her sucking reflex is triggered. Once her sucking reflex has disappeared (usually by 3 months of age) she will willingly take only the amount she wants to take.
If you have mistakenly interpret her fussing or desire to such as hunger and offer her a feed, she might take a little and refuse the rest, or she refuse from the start. If you try to make her drink more than she wants, she will understandably get upset and fuss, cry and pull back from the bottle.
WHAT TO DO- See Hungry baby for more reasons why babies often appear
- See Infant reflexes
 Unrealistic expectationsIs baby not drinking as much as you expect?Is she fussing if you try to get her to finish a bottle?
Unrealistic expectationsIs baby not drinking as much as you expect?Is she fussing if you try to get her to finish a bottle?In around one third of consultations I have had with parents regarding an infant feeding problem, I found that parents were trying to make their baby drink more than he or she needed. In some cases, this was because of errors made their health professionals. They either failed to adjust calculations as baby matured or failed to consider baby as an individual. As a result, overestimated baby’s milk requirements.
If you think your baby is not drinking enough milk (breast milk or infant formula) you’re naturally going to feel concerned. If your concern translates into trying to pressure her to drink more than she wants or needs (gently or otherwise), you’re going to upset her. So it is very important for your peace of mind and your baby’s enjoyment at feeding times that you have realistic expectations about how much she needs.
- See How much milk does baby need for standard estimations for age and weight, and reason why a baby might take more or less than recommended.
- Follow your baby's feeding cues. Don't try to make her take more when she indicates she has had enough.
Sleeping and feeding are closely related when it comes to the needs of babies. Both are equally important to a baby's health, growth and development and feelings of wellbeing. You are no doubt aware that if your baby does not feed well she might not sleep well. But are you aware that the opposite is equally true. If she’s not getting enough sleep this has the potential to negatively impact on her feeding.
Physical fatigue can cause baby to fuss during feeds or falling asleep before the feed is completed. If you have a hungry/tired baby on your hands, tiredness will usually win out.
If you have a hungry/tired baby on your hands, tiredness will usually win out.
- Ensure baby gets enough sleep.
- Feed her before she becomes too tired.
- Aim to establish a flexible feeding and sleep routine to minimize the risk of feeding and sleep times clashing.
If your baby is often irritable and not sleeping enough, (see Overtired baby for signs and symptoms) you might find that resolving any underlying sleeping problem will cause feeding difficulties to spontaneously resolve once she receives adequate sleep.
- See our sleep section.
- Download or order a paperback copy of my infant sleep book Your Sleepless Baby: The Rescue Guide. There you will find comprehensive information on the reasons and solutions to various infant sleeping problems.
Babies over the age of 4 months can easily become distracted while feeding.![]() They are often much more interested in the activities going on around them than they are in feeding.
They are often much more interested in the activities going on around them than they are in feeding.
Feed your baby in a quiet environment away from noise and distractions of other children.
5. Feeding managementSome feeding problems can be related to what may appear like insignificant details but which can make feeding difficult or uncomfortable for a baby. For example, how you hold your baby will affect her ability to feed from a bottle. If her head is too far forward or too far back or her neck is twisted this can make it difficult for her to suck or swallow.
WHAT TO DOSee How to bottle-fed a baby
6. Feeding aversionDoes your baby refuse to feed even when hungry?Does she scream at the sight of a bottle or when placed into a feeding position?Have you resorted to trying to feed her while asleep?A baby can develop an aversion to feeding when past feeding experiences have taught her that feeding is unpleasant, stressful or painful.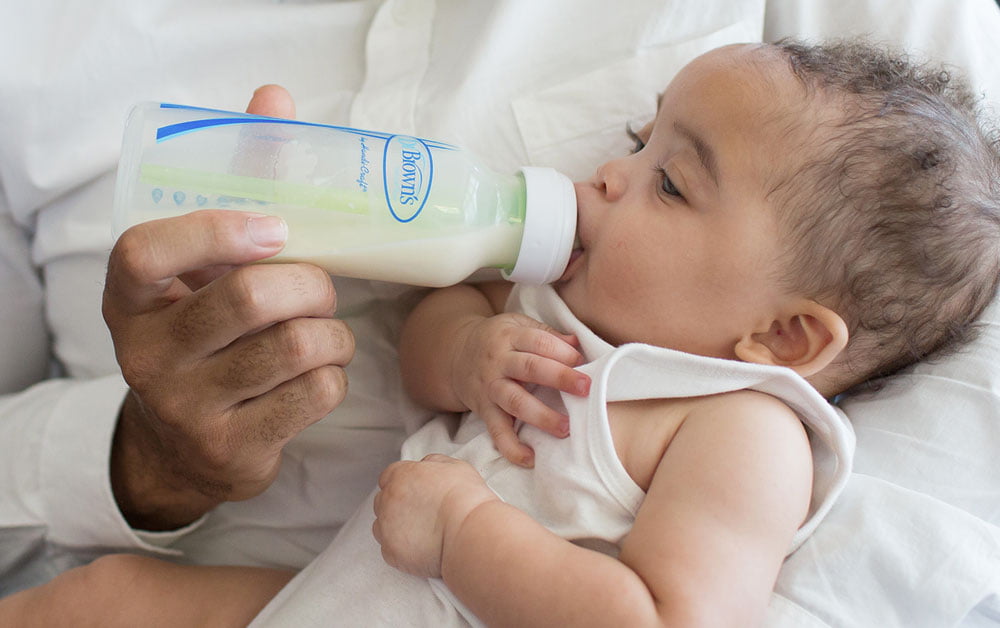 Typically, baby is diagnosed with reflux and/or milk protein allergy or intolerance to explain her aversive feeding behavior. However, a behavioral feeding aversion (related to feeding management rather than a physical cause) is a far more common cause of infant feeding aversion.
Typically, baby is diagnosed with reflux and/or milk protein allergy or intolerance to explain her aversive feeding behavior. However, a behavioral feeding aversion (related to feeding management rather than a physical cause) is a far more common cause of infant feeding aversion.
A feeding aversion is the most complex of all infant feeding problems. An effective solution relies heavily on accurate identification of the cause.
WHAT TO DOSee Feeding aversion for more information. Or purchase or download a copy of 'Your Baby's Bottle-Feeding Aversion: Reasons and Solutions'.
7. Feeding equipmentDoes your baby gag, cough or splutter during feed?Does baby make clicking sounds while feeding?It could be the nipple is too long, too short, too fast or too slow.
The most important piece of feeding equipment is the nipple. The nipple needs to be the right size and speed for your baby's size, age and sucking ability.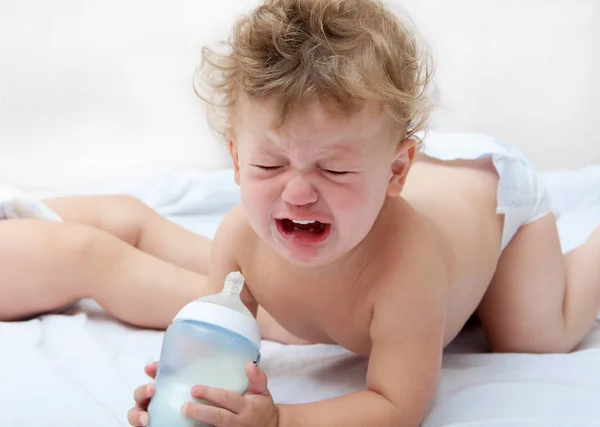 If the nipple is too long, too short, too fast or too slow for your baby, she may experience feeding difficulties and express her frustration by fuss or crying.
If the nipple is too long, too short, too fast or too slow for your baby, she may experience feeding difficulties and express her frustration by fuss or crying.
- See Feeding equipment for more information on choosing a feeding nipple.
- Experiment with nipples of different lengths, shapes and speed.
It's possible her feeding difficulties could be due to the nipple ring being screwed on too tight.
In order to maintain a neutral balance in air pressure within the bottle air needs to be able to enter the bottle to replace the void left by the milk the baby is removing. If the bottle is vented, this is achieved via the venting system. However, in the case of a non-vented bottle, the only ways air can enter the bottle are between the nipple ring and the rim of the bottle and through the holes at the end of the nipple. While sucking, a baby will maintain a seal over the holes at the end of the nipple with her tongue and prevent air entry in this way. If the nipple ring is screwed down tightly this also prevents air entry.
While sucking, a baby will maintain a seal over the holes at the end of the nipple with her tongue and prevent air entry in this way. If the nipple ring is screwed down tightly this also prevents air entry.
If air is prevented from entering the bottle, this causes a negative pressure to build in the bottle. As the pressure builds, baby need to work harder and harder to extract further milk, until such time and the air pressure is returned to normal. The effort required to suck against the negative pressure can cause a newborn baby to tire and fall asleep before completing the feed. An older baby may simply give up or express her frustration.
WHAT TO DOThe nipple collapsing (not all will) or stopping to burp baby allows air to enter through the holes and neutralize the pressure. But you don’t want to wait for this to resolve the problem. By then baby is already tiring or getting frustrated. See ‘Collapsing nipple’ for ways to manage this problem.
9. Feeding patternsIs your baby often take only small amounts, refuse more, but then wants to feed again an hour or two later?
Feeding patternsIs your baby often take only small amounts, refuse more, but then wants to feed again an hour or two later?Some babies develop a grazing or snacking feeding pattern where they will only drink small amounts of formula at a time and then want to be feed frequently, possibly every hour or two. Although this will not cause any problems for a baby, provided she drinks enough formula in total over a 24 hour period, it can become very tiring for parents to keep up with her constant demands for feeding.
WHAT TO DO- Try to encourage your baby to take as much milk as possible within 45 minutes. But don't try to make her feed if she doesn't want to. Stop sooner if she does not want to continue.
- Ensure baby gets plenty of sleep.
- Avoid allowing baby to fall asleep while feeding.
- Support your baby to extend the time between feeds, by offering a little water, a pacifier, a nap, playing with her, or taking her for a walk.
 Aim to encourage her to wait at least 3 hours from time you started her previous feed, but only if it's reasonable to do so without distressing her. If necessary extend the time between feeds gradually. As your baby gets used to going longer periods between feeds she will gradually take larger amounts at each feed.
Aim to encourage her to wait at least 3 hours from time you started her previous feed, but only if it's reasonable to do so without distressing her. If necessary extend the time between feeds gradually. As your baby gets used to going longer periods between feeds she will gradually take larger amounts at each feed.
Unless your baby was born prematurely or is very small for her age, developmentally she no longer requires feeding during the night beyond the age 6 months. If nighttime feeding continues past this age its not going to harm her but it could have a negative effect on her appetite and feeding patterns during the day.
Your baby only needs a certain number of calories in her day (24 hours) to provide for her growth and energy needs. If after the age of 6 months she continues to receive calories from nighttime feeds this will dampen her appetite during the day and she will not need to drink as much formula during daytime feeds. You might find she is content to go for long periods of time between feeds (which is usually what would happen at night). She might fuss or refuse some of her daytime bottles when they are offered simply because she's not hungry at the time. Or she might graze during the day.
You might find she is content to go for long periods of time between feeds (which is usually what would happen at night). She might fuss or refuse some of her daytime bottles when they are offered simply because she's not hungry at the time. Or she might graze during the day.
Nighttime feeding will cause your baby no harm, so if you're happy to continue feeding her during the night there's no reason to change a thing. However, it is important that you don't expect her to consume as much milk during the day as she may have otherwise taken if she did not feed at night.
Many babies will give up night time feedings on their own accord, but others will continue to wake and demand feeds overnight for months and possibly years while parents continue to provide feeds at night. Usually the reason babies continues to demand night feeds beyond the age of 6 months is because they have learned to rely on feeding as a way to fall asleep, or because their internal body clock gets turned around - where the baby has decreased appetite during the day because of the continued night feeds and as a consequence of small feeds during the day the baby wakes hungry during the night. Body clock problems can easily become a cyclical pattern that will continue over the long term unless parents take steps to change the situation. Healthy, thriving babies who continue to demand feedings at night beyond the age of 6 months often require guidance and support from parents to cease feeding at night and turn their body clock around to a normal day-night feeding pattern.
Body clock problems can easily become a cyclical pattern that will continue over the long term unless parents take steps to change the situation. Healthy, thriving babies who continue to demand feedings at night beyond the age of 6 months often require guidance and support from parents to cease feeding at night and turn their body clock around to a normal day-night feeding pattern.
Aim to cease overnight feeds after 6 months of age. However, before attempting to do this it's important to address any feeding to sleep issues your baby might have. She would need to learn to fall asleep in a different way before you will be able to successfully encourage her to cease night feeds.
11. Starting solids earlyHave you started giving your baby solids before the age of 4 months?Have you been advised to start solids early?6 months is the recommended age for starting solid foods. Although a small number of babies may benefit from solids prior to this age, it's generally not recommended to start a baby on solid foods before the age of 4 months. An early start on solids has the potential to cause bottle feeding problems because solid foods may decrease the baby's appetite for milk (breast milk or formula).
Although a small number of babies may benefit from solids prior to this age, it's generally not recommended to start a baby on solid foods before the age of 4 months. An early start on solids has the potential to cause bottle feeding problems because solid foods may decrease the baby's appetite for milk (breast milk or formula).
- If your baby is less than 6 months old, either cease or reduce the amount of solids you offer to see if this helps to improve the situation.
- See our article on starting solids.
If solids are offered prior to bottle feeds, either directly before or mid way between feeds, when it's time for your baby's bottle feed she might be feeling full from the solids, in which case she's probably not going to take much milk from her bottle.
WHAT TO DO- For babies 4 - 9 months (when milk is still the most important food) offer solids 15 - 20 minutes after bottle feeds.

- For babies 9 - 12 months (when solids are becoming increasingly more important to a baby's diet) offer solids shortly before or shortly after her bottle, whichever you find works best. Babies at this age are often down to 3 bottles per day plus 3 main meals and 1 or 2 snacks.
In these early stages of learning to eat solids (4 - 7 months) solids are not needed to add value to a baby's nutritional intake, rather they are offered primarily to provide learning experiences. The baby is exposed to new food proteins that help prime her immune system. She gets to discover new tastes and textures and become accustomed to eating from a spoon. It is at this age that babies are most willing to accept new tastes. So variety rather than quantity is what solids are about.
Many babies, particularly very young babies, experience difficulty self-regulating their dietary intake. Some babies will continue to eat solid foods for as long their parents keep offering. Some babies will prefer eating solids compared to drinking formula. However, too much solids and not enough milk is not a balance diet for a baby. It may be necessary for parents to limit the amount of solids they offer in order to encourage their baby to have a greater appetite for milk feeds.
Some babies will continue to eat solid foods for as long their parents keep offering. Some babies will prefer eating solids compared to drinking formula. However, too much solids and not enough milk is not a balance diet for a baby. It may be necessary for parents to limit the amount of solids they offer in order to encourage their baby to have a greater appetite for milk feeds.
See our article on estimating how much milk your baby needs to make sure she's getting enough.
14. Weaning difficultiesDoes your breastfed baby refuse bottle-feeds?Does your baby have a breast preference?While some breastfed babies willing accept milk from a bottle many will not, at least not straight away.
Difficulty weaning from breast to bottle is rarely resolved by finding the 'right' feeding nipple. (All feeding nipples will feel equally foreign to a breastfed baby. ) Nor does a solution lie in finding a formula with the 'right' taste. All formula will taste strange to a breastfed baby). The difficulty associated with weaning to a bottle most often lies in the fact that bottle-feeding requires a very different sucking action to breastfeeding. While breastfeeding the movement of your baby's tongue milks the breast, where as bottle-feeding requires a sucking action. A baby who has been exclusively breastfed beyond the age of 3 months will often refuse milk from a bottle because it "doesn't feel right" and she doesn't know how to suck from a bottle.
) Nor does a solution lie in finding a formula with the 'right' taste. All formula will taste strange to a breastfed baby). The difficulty associated with weaning to a bottle most often lies in the fact that bottle-feeding requires a very different sucking action to breastfeeding. While breastfeeding the movement of your baby's tongue milks the breast, where as bottle-feeding requires a sucking action. A baby who has been exclusively breastfed beyond the age of 3 months will often refuse milk from a bottle because it "doesn't feel right" and she doesn't know how to suck from a bottle.
It takes time and practice before a breastfed baby learns how to suck on a bottle.
WHAT TO DO- Try offering expressed breast milk in a bottle initially. (Don't be too optimistic and put too much in to start with. It would be a shame to waste it).
- A soft flexible nipple often works better.
NOTE: Many breast fed babies will refuse to accept a bottle while they are still being breastfed at times. They will simply wait until a breastfeed is offered. For these babies it will be the case of breastfeeding or bottle-feeding, but not both.
They will simply wait until a breastfeed is offered. For these babies it will be the case of breastfeeding or bottle-feeding, but not both.
- Your Baby's Bottle-feeding Aversion book
- Baby Care Advice consultation
- Rowena Bennett's Online Bottle-Feeding Aversion Program
In my book, ‘Your baby’s Bottle-feeding Aversion’, I have described physical and behavioral reasons for babies to develop an aversion to bottle-feeding. How to identify the cause and the solutions to match. Included are step-by-step instructions on how to regain your baby’s trust and resolve a feeding aversion caused or reinforced by repeated pressure to feed.
While the book was written for bottle-fed babies, many nursing mothers have found that applying the same strategies has also helped them to successfully resolve a breastfeeding aversion.
You might find that reading this book is all you need to do to understand the steps you need to take to resolve your baby’s feeding aversion and get him back to the point of enjoying eating until satisfied.
Baby Care Advice ConsultationsIf you would like an individualized assessment of all reasons for infant feeding problems, not just feeding aversion, we also provide a consultation service. Baby Care Advice consultants have extensive experience in pinpointing the cause of feeding aversion and other behavioral feeding problems such as those related to equipment and the parent’s feeding practices. (For more on what’s included in a consultation).
By Rowena Bennett, RN, RM, CHN, MHN, IBCLC.
Copyright www.babycareadvice.com 2021. All rights reserved. Permission from the author must be obtained to reproduce all or any part of this article.
Rowena's Online Bottle-Feeding Aversion ProgramSix time-saving modules to help your family enjoy feeding again with Rowena's step-by-step plan. Enjoy additional tools to manage anxiety, troubleshoot any issues, introduce new carers, how to manage illness/teething and much more.
Enjoy additional tools to manage anxiety, troubleshoot any issues, introduce new carers, how to manage illness/teething and much more.
- Module 1: Understanding feeding aversions
- Module 2: Identify the cause
- Module 3: Prepare for success
- Module 4: How to resolve your baby's bottle-feeding aversion
- Module 5: What to expect
- Module 6: Troubleshooting
- BONUS: Guided meditations
Reflux And Bottle Feeding | Feeding Your Baby
There may be times when feeding your baby is challenging. Never ignore any issues you may have – talk to your health visitor, midwife or GP if you have any concerns about bottle feeding. Here are some common feeding issues, and tips on what to do.
- Colic and bottle feeding
- Constipation and bottle feeding
- COVID-19 and bottle feeding
- Reflux and bottle feeding
- Tongue-tie and bottle feeding
Reflux and bottle feeding
When your baby brings up milk, or is sick during or after feeding, this is known as reflux. Reflux, also referred to as posseting or spitting up, is quite common and babies usually grow out of it by the age of 1.
Reflux, also referred to as posseting or spitting up, is quite common and babies usually grow out of it by the age of 1.
What is baby reflux?
The muscle at the bottom of the food pipe (oesophagus) acts as a kind of door into the stomach – so when food or milk travels down, the muscle opens allowing the food into the stomach.
However, while this muscle is still developing in the first year, it can open when it should not (usually when your baby's tummy is full) allowing some food and stomach acid to travel back up again. Acid in the stomach is a normal part of the digestion process – it helps break down food.
In most babies, reflux is nothing to worry about, as long as they are healthy and gaining weight as expected.
What are baby reflux symptoms?
- constant or sudden crying when feeding
- bringing up milk during or after feeds (regularly)
- frequent ear infections
- lots of hiccups or coughing
- refusing, gagging, or choking during feeds
- poor weight gain
- waking at night a lot
GORD
When reflux becomes painful and happens frequently, this is known as ”gastro-oesophageal reflux disease” (GORD). GORD is more serious than mild, everyday reflux. The strong stomach acid can irritate and make the food pipe sore and inflamed, which is painful for your baby and may result in them needing medication.
GORD is more serious than mild, everyday reflux. The strong stomach acid can irritate and make the food pipe sore and inflamed, which is painful for your baby and may result in them needing medication.
The main signs and symptoms of GORD in your baby are:
- spitting up frequently
- tummy (abdominal) pain
- feeding difficulties
- seeming unsettled and grizzly after a feed
These symptoms can lead to your baby not gaining weight, or even losing weight.
Silent reflux
Silent reflux can be confusing as there are no obvious signs or clues (such as spitting up). It's when the food travels back up the food pipe – but it's swallowed rather than spat out so is harder to identify. But your baby may display similar symptoms to those of regular reflux.
Bottle feeding tips for babies with reflux
You can help your baby's reflux by:
- feeding little and often, smaller feeds stop their tummy getting too full
- burping your baby frequently during feeds – have a look at our Guide to burping your baby for techniques
- try to keep your baby upright, for at least an hour, after feeding - this should help keep the milk down
If you are using formula, your GP or health visitor may advise you to use a thicker formula (that's less likely to be brought up), or one that does not contain cows' milk if your baby is allergic to it. If the thickening powder does not help, your GP may recommend medicines that stop your baby's tummy producing as much acid.
If the thickening powder does not help, your GP may recommend medicines that stop your baby's tummy producing as much acid.
If you are mixed feeding (combining breastmilk and formula feeds), have a look at our advice on breastfeeding and reflux.
When to seek medical advice
If your baby has difficulty feeding or refuses to feed, keeps vomiting during or after feeding, talk to your pharmacist, GP, or health visitor. They will be able to give you practical advice on how to ease the symptoms and manage it – they may need to rule out other causes such as an intolerance to cows' milk or allergies.
It might be helpful to keep a record of when your baby feeds, with details of how often and how much your baby brings the food back up, and how often your baby cries or seems distressed. This will help your health visitor or GP decide if your baby needs treatment.
why the baby cries while feeding
While the baby is quite a baby, crying is the only way of his communication with his mother and the outside world. If the baby is restless during feeding, he will let you know that he is uncomfortable. We will analyze what can cause baby crying in such a situation.
If the baby is restless during feeding, he will let you know that he is uncomfortable. We will analyze what can cause baby crying in such a situation.
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
As a rule, the causes of a baby’s tears at the breast or bottle with a mixture are physiological, and there may be several of them.
Abdominal pain
Most likely, the child is worried about colic (they can start from 2-4 weeks of age and usually end by 3 months). Unpleasant sensations are associated with the fact that the infant has an insufficiently developed intestinal microflora and it is difficult for the digestive system to cope with the task assigned to it. Children's crying during colic is accompanied by arching the back and pulling the legs to the stomach - the pain from the formation of gases in the intestines is always acute.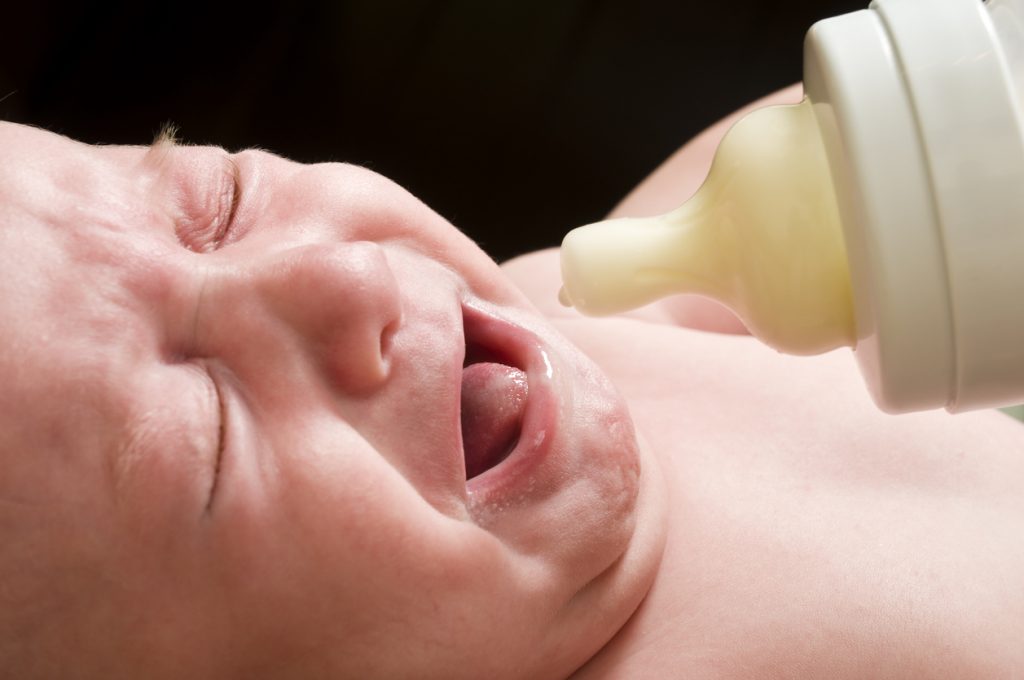 To alleviate the condition of the crumbs, it is useful for a nursing mother to drink teas with fennel, cumin or anise. If your baby is formula-fed, choose formula carefully. Valio Baby baby food is as close as possible to the composition of breast milk and contains the GOS prebiotic, which is necessary for the health of the child's digestive system. The cause of colic is also the wrong feeding technique and, as a result, the capture of excess air by the baby.
To alleviate the condition of the crumbs, it is useful for a nursing mother to drink teas with fennel, cumin or anise. If your baby is formula-fed, choose formula carefully. Valio Baby baby food is as close as possible to the composition of breast milk and contains the GOS prebiotic, which is necessary for the health of the child's digestive system. The cause of colic is also the wrong feeding technique and, as a result, the capture of excess air by the baby.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
Earache
Children under one year old often suffer from otitis media, this is due to the anatomical features of the structure of the nasopharynx in babies in the first months of life. A baby may cry during feeding because swallowing causes a sharp pain in his ears. Very carefully touch the tragus of the baby's auricles - if he cries, then you need to see a doctor.
Headache
It is no secret that many neurological disorders are accompanied by headaches. It becomes especially strong when swallowing. If the baby is constantly crying during feeding, be sure to make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist.
It becomes especially strong when swallowing. If the baby is constantly crying during feeding, be sure to make an appointment with a pediatric neurologist.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa
Crying during feeding may signal that the baby is experiencing discomfort in the mouth or throat. Its cause is most often thrush or pharyngitis. These diseases require treatment under the supervision of a pediatrician.
Lack or excess of breast milk
The lactation of a nursing woman is affected by a considerable number of factors - the psychological state, fatigue, stress, malnutrition and its lack, improper organization of breastfeeding. The baby may cry because he does not have enough milk. Whether the food shortage is really critical is easy to check using the wet diaper method. By the way, the crying of a baby may also indicate that there is too much milk - the stream is too strong and the baby simply chokes.
Unusual taste of breast milk
If a mother ate, for example, something spicy on the eve of feeding, this will certainly affect the taste of milk. The baby, of course, will cry. This cause of children's "grief" is the most easily eliminated - be attentive to your menu and do not upset your beloved baby.
The baby, of course, will cry. This cause of children's "grief" is the most easily eliminated - be attentive to your menu and do not upset your beloved baby.
In addition to the reasons described, the reason for children's tears during feeding can be erupting teeth and inflammation of the gums, as well as nasal congestion with allergies and SARS. Be attentive to your baby. If all is well, the baby should not cry while feeding.
3.4 35
Power supplyShare:
Oksana Ivargizova
Medical Institute. Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk.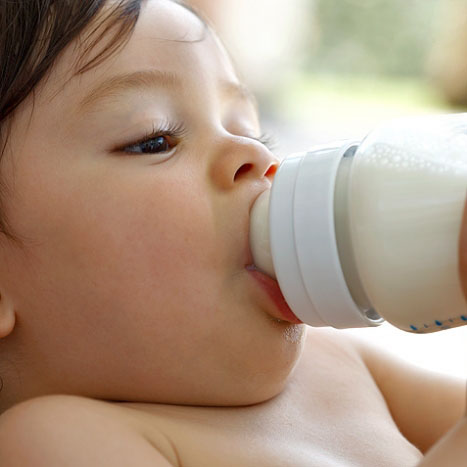 However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
Baby won't take bottle | Philips Avent
search support iconSearch Keywords
Home ›› What to do when your baby refuses a bottle
any problems. If your breastfed baby refuses a bottle, don't worry. This is a common occurrence in many babies who are used to breastfeeding. Obviously, this can create certain difficulties for moms, especially if you need to return to work in the near future.
3 Philips Avent products to help you bottle feed:
So why is your baby refusing the bottle and crying? There are many ways to quickly and easily teach a breastfed baby to a bottle. Here are important tips on what to do when your baby refuses a bottle.
Is the baby refusing the bottle? Take a step back
If your baby cries while bottle feeding, the first thing to do is to start over and rethink your feeding approach and technique. Try the following steps when bottle feeding your baby: [1]
- Lift and tilt your baby's head forward. Before inserting the pacifier into the baby's mouth, make sure that the baby's head is raised and tilted over his body to avoid choking: so that the baby does not choke and have the opportunity to burp during bottle feeding.
- Insert the pacifier. Bring the pacifier to the baby's lips and gently guide it into the baby's mouth. In no case do not try to press the nipple on the baby's lips and try to push it into his mouth.
 After touching the pacifier to the baby's lips, wait for the baby to open his mouth and take the pacifier.
After touching the pacifier to the baby's lips, wait for the baby to open his mouth and take the pacifier. - Hold the bottle at an angle. Tilt the bottle at an angle so that the nipple is only half full. So the child can eat at his own pace.
- Let the baby burp during and after feeding. It can be useful for a child to burp not only after feeding, but also approximately in the middle of the process. This will help reduce gas or tummy discomfort that your baby may experience from swallowing too much air.
- Stop in time, do not overfeed the baby. If the baby begins to turn his head away from the bottle or closes his mouth, then he is full and you need to stop feeding.
- Perhaps the flow of milk from the nipple to the baby is weak or, on the contrary, too fast, so he is naughty and refuses the bottle. Try changing the nipple to a nipple with a different flow.
Other tips if your baby refuses a bottle
If you've followed the steps above and your baby still refuses a bottle, don't worry. There are other ways to help bottle feed your baby. Here are some simple tricks you can add to your bottle feeding process. [2]
There are other ways to help bottle feed your baby. Here are some simple tricks you can add to your bottle feeding process. [2]
1. Remind your child about mom.
Sometimes a child can be fed by someone other than his mother - dad, grandmother or, for example, a nanny. If your baby fusses while bottle feeding, try wrapping the bottle in something that smells like mommy, like a piece of clothing or some fabric. This will make it easier to feed the baby when the mother is not around.
2. Try to maintain body contact while bottle feeding.
Some babies need contact with their mother, so try bottle feeding while leaning against you. However, some babies are better at bottle feeding when they are in the exact opposite position than when they are breastfed. For example, there is a position with bent legs. Lay the child on your bent knees, facing you, pointing the child's legs towards your stomach. During feeding, the baby will be able to look at you and contact you in this way. If your baby refuses a bottle, experiment to see which works best.
During feeding, the baby will be able to look at you and contact you in this way. If your baby refuses a bottle, experiment to see which works best.
3. Move while feeding.
Sometimes all it takes is a little wiggle or a walk to get your baby to take the bottle. The next time your baby starts crying while bottle feeding, try moving around a little rhythmically to calm him down.
4. Try changing the milk temperature.
If the baby still does not want to take the bottle, check if the milk in the bottle is too hot or too cold. Before feeding, put some warm breast milk on the inside of your wrist to check the temperature. Milk should be warm, but if it seemed hot to you, just place the bottle for a short while under a stream of cold water.
Choosing the right bottle for your baby If you plan to combine bottle feeding with breastfeeding, it is advisable to choose bottles with a nipple that will have a wide base as the bottle will grip closer to the breast.
 Also pay attention to the fact that the nipple is firm and flexible, the child must make an effort to drink from the bottle, as well as from the breast. Give preference to nipples with an anti-colic valve that vents air out of the bottle.
Also pay attention to the fact that the nipple is firm and flexible, the child must make an effort to drink from the bottle, as well as from the breast. Give preference to nipples with an anti-colic valve that vents air out of the bottle. Natural bottle allows you to combine breast and bottle feeding. 83.3% of babies switch from a Natural bottle to breastfeeding and back.*
If you choose a bottle for artificial feeding, traditional bottles are fine for you, but it is desirable that the nipple is made of a hypoallergenic material, such as silicone, has an anti-colic valve and did not stick together when bottle fed. In case your baby spit up often, then use special bottles with anti-colic and anti-reflux valve, which reduces the risk of spitting up and colic.
Bottle with unique AirFree valve reduces the risk of colic, gas and spitting up. With this bottle, you can feed your baby in an upright or semi-upright position to reduce spitting up. Due to the fact that the nipple is filled with milk and not air during feeding, the baby does not swallow air, which means that feeding will be more comfortable.
Both bottles are indispensable if you want to breastfeed, bottle feed or just bottle feed your baby.
“My baby refuses to breastfeed but bottle feeds – help!”
Sometimes a baby gets used to bottle feeding and refuses to breastfeed. Therefore, it is important to use bottles that are suitable for combining breastfeeding with bottle feeding. If, nevertheless, you are faced with the fact that the child refuses to take the breast, try using silicone nipple covers to make the transition from the bottle to the breast and back more imperceptible.
Remember that if you want to combine breastfeeding and bottle feeding, it is worth waiting at least a month before offering a bottle, so that you are lactating and have time to get used to each other and develop a breastfeeding regimen.
Breastfeed and bottle feed your baby with pleasure
Remember that it takes a while for your baby to get used to bottle feeding. This is completely normal. If you have to go to work, be sure to set aside enough time to bottle train your baby beforehand.
This is completely normal. If you have to go to work, be sure to set aside enough time to bottle train your baby beforehand.
Remember that every child is different, so what works for one may not work for another. With a little time and patience, you will find out what works best for your baby when he refuses a bottle.
You will identify your child's unique needs. However, if your baby still refuses the bottle after all the steps above, check with your pediatrician.
Articles and tips from Philips Avent
References:
*O.L. Lukoyanova, T.E. Borovik, I.A. Belyaeva, G.V. Yatsyk; NTsZD RAMS; 1st Moscow State Medical University THEM. Sechenova, "The use of modern technological methods to maintain successful breastfeeding", RF, 02.10.2012 3 llli.org - The Baby Who Doesn't Nurse
llli.org - Introducing a Bottle to a Breastfed Baby
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers and save those special moments forever.











