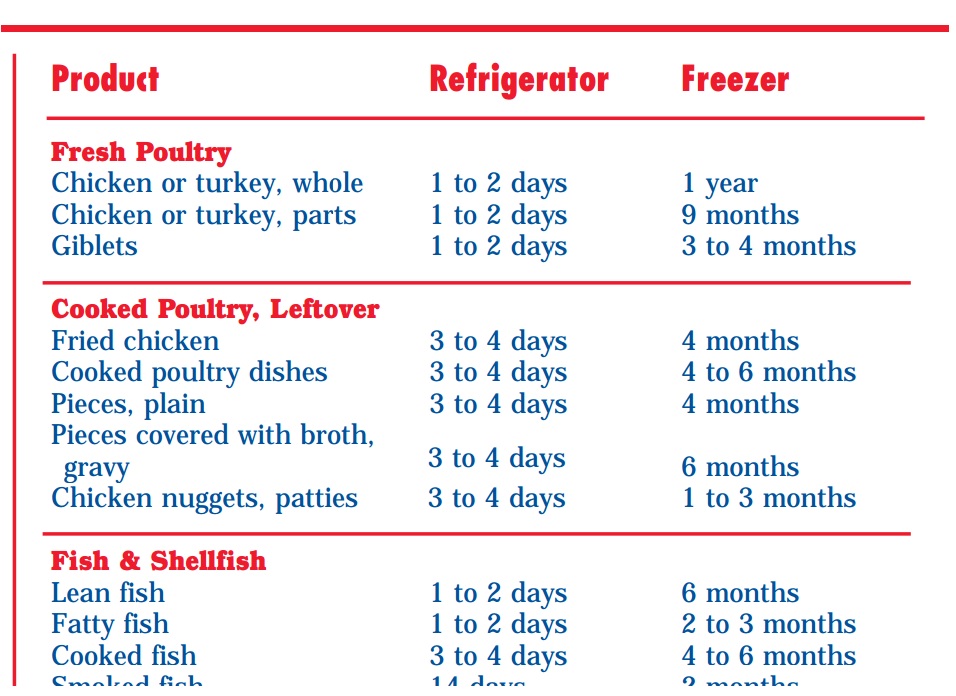
Baby feeding after birth
Baby's first 24 hours | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Baby's first 24 hours | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
The first day of your new baby’s life is thrilling and exhausting for both of you. This page explains what your newborn baby can sense, and how the umbilical cord and placenta can be managed. It has general information for you if you have had a healthy, full-term pregnancy – 37 to 42 weeks’ gestation.
What will my newborn baby look like?
When your baby is born, their skin might be blue and mottled. They are likely to be covered in amniotic fluid, blood and vernix, which is a cheesy white substance. This is normal.
Their skin will start to become pink as they start to breathe — which is about a minute after birth. Your baby’s hands and feet may still appear blueish for several hours.
The amniotic fluid and the vernix are there because they were there in the womb. They are important for your baby to be able to smell and taste after birth. These familiar things help your baby to feel secure outside the womb.
Birth of the placenta and cutting the umbilical cord
After you have given birth to your baby, you will have more contractions that will help you deliver the placenta. Once this happens, the umbilical cord, which is connected to the placenta, will be clamped in two places and cut. Your support person might be invited to cut the cord.
Skin-to-skin contact
After a normal vaginal birth, your newborn baby will be put on your chest for skin-to-skin contact. Your baby needs sleep and food, and they need to feel secure and warm, so they need to feel your skin.
Doing this simple thing:
- reduces newborn crying
- helps start and sustain breastfeeding
- helps maintain your baby’s body temperature
After this first contact, they will be weighed, measured and observed to make sure they are healthy.
If you have a caesarean section, ask your midwife to make sure your baby has skin-to-skin contact with you as early as possible. It may be possible for you or your partner to hold your baby-skin-to skin in theatre and in recovery.
Feeding
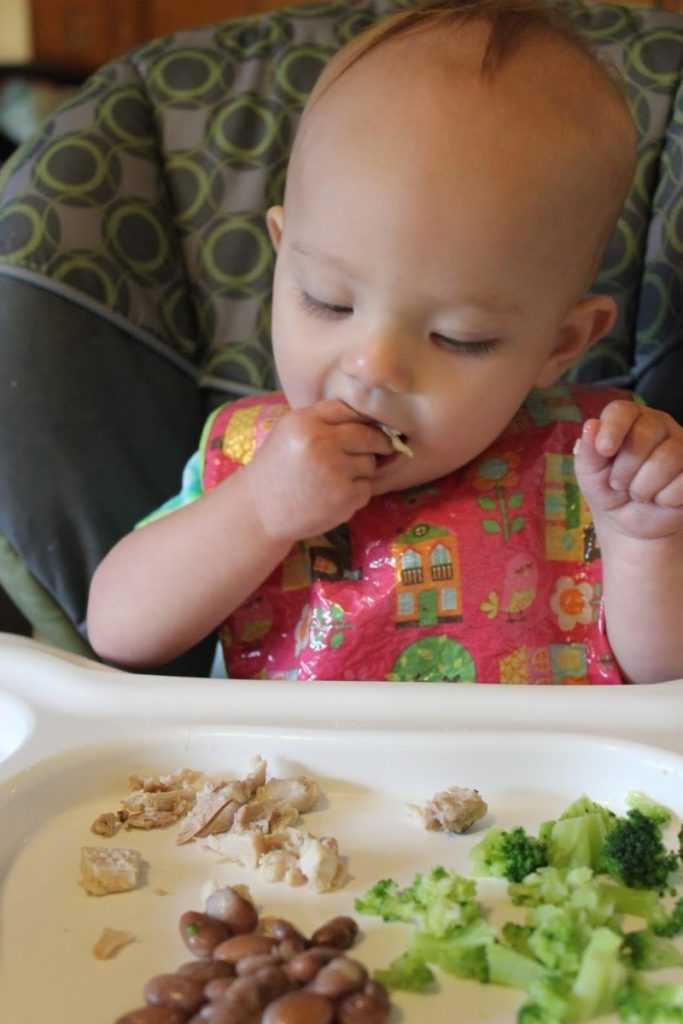
Babies start to show signs of wanting to feed soon after birth and usually attach and suck at the breast about 50 minutes after birth. They may then breastfeed for an hour or more. Put your baby against your chest, and they will probably find your breast and start feeding. If that doesn’t happen, you can ask your midwife or a lactation consultant for help.
The first milk you make is called 'colostrum'. It’s thick and often yellowish, rather than pure white. It’s the ideal milk for your baby. Normally a small amount is produced — your baby’s tummy is just the size of a marble.
If they haven’t fed an hour or so after birth, try again a couple of hours later. You can also express some colostrum to feed to your baby on a spoon.
Weighing and measuring
After skin-to-skin contact and the first breastfeed, your midwife might offer to weigh your baby, and measure your baby’s length and head circumference. Your baby doesn’t need to be washed for at least 24 hours.
Vitamin K
At the time of weighing, your midwife will also offer to give your baby a vitamin K injection to prevent bleeding from vitamin K deficiency.
Cord blood collection if you are Rh negative
If your blood group is Rh negative, some blood will be taken from the umbilical cord to determine whether your baby’s blood group is compatible.
Sleeping
Your baby will stay with you so you can bond and respond easily to their needs. They’ll probably sleep soon after their first feed, and that might last 6 hours or so. They will probably sleep for more than half of their first day in the world.
Apgar scores
One of the main observations made after birth is called an Apgar score. It assesses your baby’s adjustment to life outside the womb.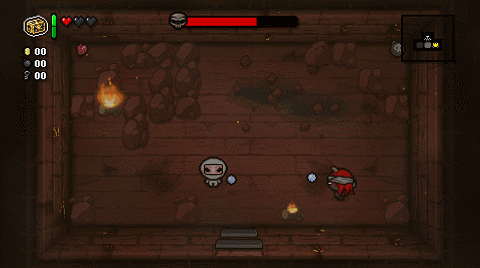 The Apgar score is measured at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth while the baby is on your chest. Sometimes it is measured again at 10 minutes after birth.
The Apgar score is measured at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth while the baby is on your chest. Sometimes it is measured again at 10 minutes after birth.
It records your baby’s heart rate, breathing, colour, muscle tone and reflexes. The maximum score is 10. A score of 7 or above usually means your baby is doing well. It is not an ability or intelligence test, and it doesn’t predict your baby’s health later in life.
What will my newborn baby see, hear, smell, taste and feel?
Your baby has been listening to your voice for the last half of your pregnancy and will recognise it when you speak to them after birth. Your partner or support person’s voice may also be familiar if they have also been talking near your baby. Your baby will feel secure when they hear your voices and may respond by turning their head towards you. Your baby will also be able to hear your heart beating as they did in the womb.
Your baby’s vision is blurred at birth but they will be able to focus on your face from about 30 centimetres away. This is called the ‘cuddle distance’. It is roughly the distance from your breast to your face. Your baby will make the connection between what they hear and what they see.
This is called the ‘cuddle distance’. It is roughly the distance from your breast to your face. Your baby will make the connection between what they hear and what they see.
Your baby will smell and taste the amniotic fluid and your colostrum, which has a similar flavour.
Urine and meconium
Within the first 24 hours your baby will probably pass urine and meconium (newborn faeces) at least once. Meconium is black and sticky. Your baby’s poo will change colour and consistency over the next few days.
More information
You can call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby, 7 days a week on 1800 882 436 to speak with a maternal child health nurse to find out more.
Sources:
Cochrane (Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants), National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) (NICE Guideline CG37: Postnatal care up to 8 weeks after birth), World Health Organization (WHO) (Recommendations on newborn health), Raising Children Network (After baby is born: what to expect in the first few hours), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Breastfeeding timeline)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.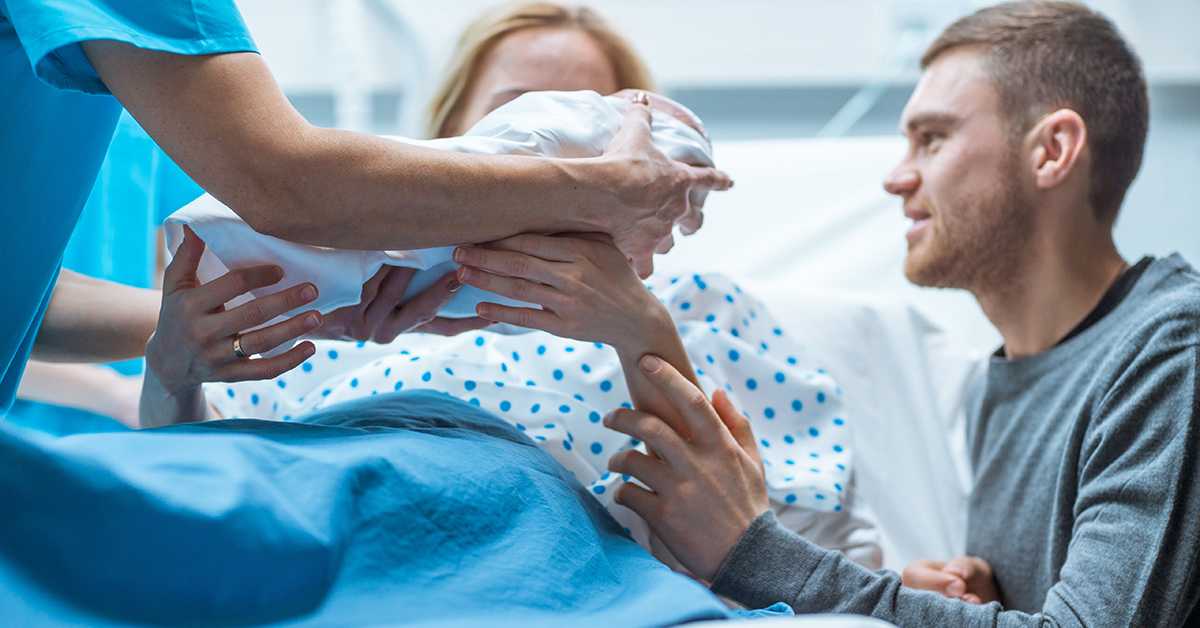
Last reviewed: September 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Mum's first few days after giving birth
- Mum's first 24 hours after birth
- Your baby in the first few days
- Birth injury (to the baby)
- What is kangaroo care?
Need more information?
Newborn clothes & dressing a newborn | Raising Children Network
How many clothes does a newborn need? And what newborn clothes are best? Get answers to these questions and more in our guide to dressing a newborn.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborns behaviour | Raising Children Network
Newborn behaviour baffling you? Here's all you need on newborns behaviour with articles, videos and resources on crying, colic and more.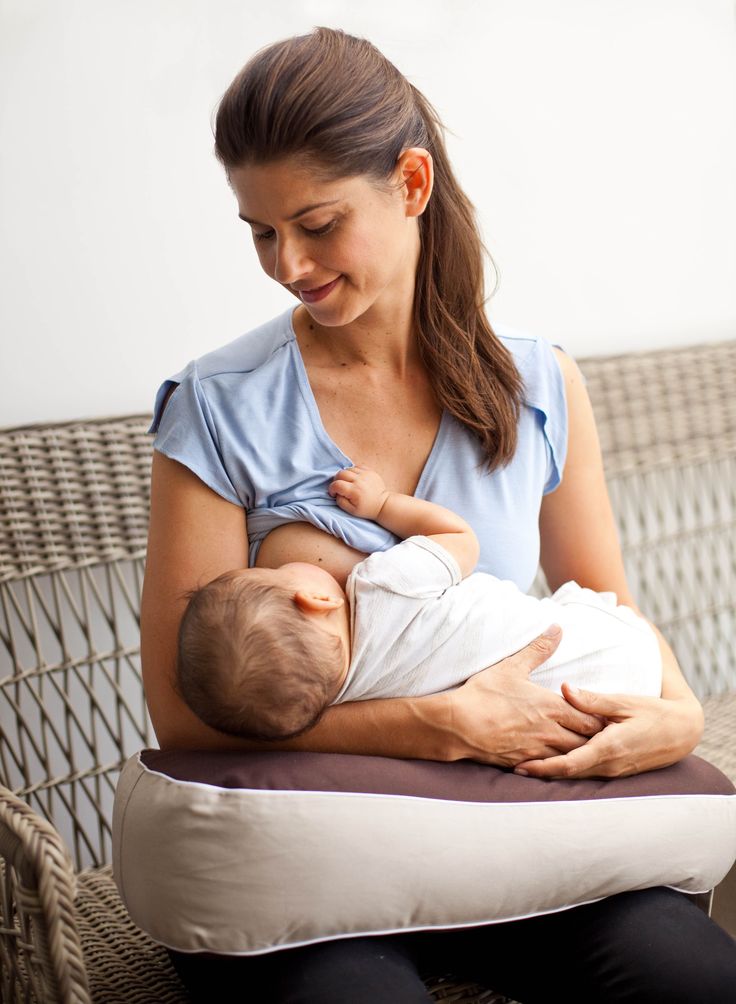
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborn bloodspot screening - MyDr.com.au
Newborn screening tests can detect rare but serious genetic or metabolic disorders in newborn babies.
Read more on myDr website
Dressing a newborn
When dressing your newborn, here are a few things to consider, like which clothes to use, how to dress them and making sure the change table is safe.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Newborn essentials
Here is a newborn's essentials checklist including vaccinations and immunisations, health checks, nappy changing and breastfeeding and bottle feeding.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Wind, burping & newborn babies in pictures | Raising Children Network
Newborns might have wind from swallowing air when crying or feeding. Burping can help newborns get rid of wind. See how to burp your newborn – in pictures
Burping can help newborns get rid of wind. See how to burp your newborn – in pictures
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborns development | Raising Children Network
Want to track newborns development? Here's all you need on newborn development with articles, videos and resources on growth, relationships and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Is my newborn safe? - MyDr.com.au
Dr Norman Swan explains the risks of COVID-19 to your newborn.
Read more on myDr website
Newborns sleep | Raising Children Network
Need help understanding newborn sleep? Here’s all you need on newborn sleep with articles, videos and resources on safe sleep, sleep habits, tiredness and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborns safety | Raising Children Network
Newborn safety stressing you? Here’s all you need on newborns safety with articles, videos and resources on first aid, CPR, equipment, car seats and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.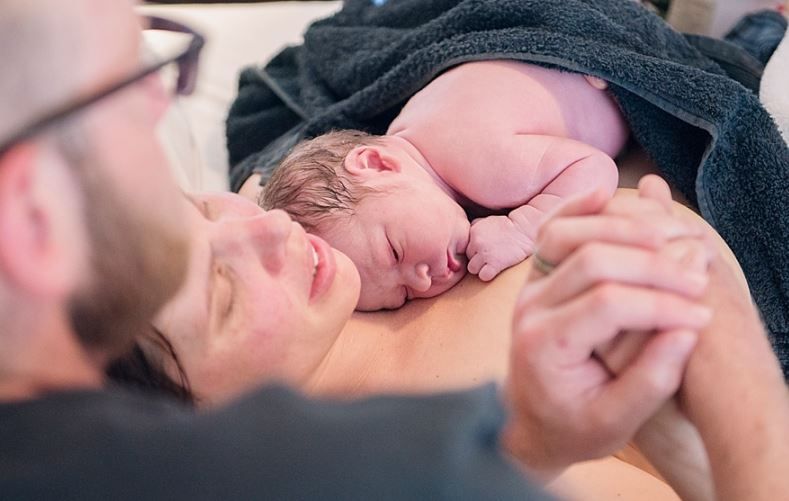
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Breastfeeding: the first few days
In the first few days, you and your baby will be getting to know each other. It may take time for both of you to get the hang of breastfeeding.
This happens faster for some women than others. But nearly all women produce enough milk for their baby.
Preparing to breastfeed before the birth
It's good to find out as much as you can about breastfeeding before you have your baby. It may help you feel more confident when you start breastfeeding your baby.
It may help you feel more confident when you start breastfeeding your baby.
Antenatal classes usually cover the most important aspects of breastfeeding, such as positioning and attachment, expressing, and how to tackle common breastfeeding problems.
Find antenatal classes near you.
You can find out about breastfeeding from your midwife, family and friends, and useful helplines and websites.
There are lots of groups and drop-ins, some specially designed for pregnant women who want to know more about breastfeeding. You can find out more by asking your midwife, health visitor, local peer supporter or GP. Or visit your local Children's Centre.
Skin-to-skin contact
Having skin-to-skin contact with your baby straight after giving birth will help to keep them warm and calm and steady their breathing.
Skin-to-skin means holding your baby naked or dressed only in a nappy against your skin, usually under your top or under a blanket.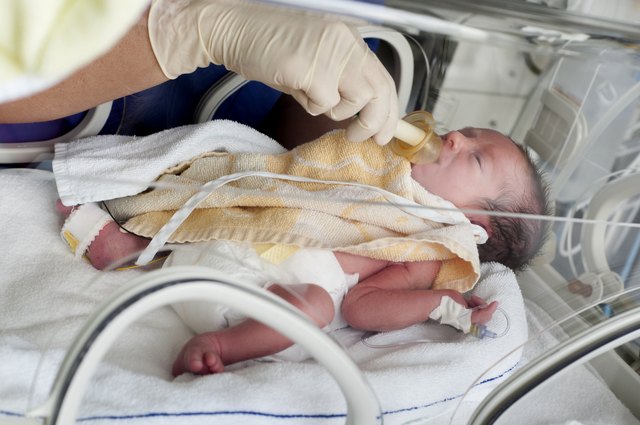
Skin-to-skin time can be a bonding experience for you and your baby. It's also a great time to have your first breastfeed. If you need any help, your midwife will support you with positioning and attachment.
Skin-to-skin contact is good at any time. It will help to comfort you and your baby over the first few days and weeks as you get to know each other. It also helps your baby attach to your breast using their natural crawling and latching-on reflexes.
You'll still be able to bond with and breastfeed your baby if skin-to-skin contact is delayed for some reason, for example if your baby needs to spend some time in special care.
If necessary, your midwife will show you how to express your breast milk until your baby is ready to breastfeed. They can also help you have skin-to-skin contact with your baby as soon as it's possible.
Skin-to-skin after a caesarean
If your baby is delivered by caesarean, you should still be able to have skin-to-skin contact with your baby straight after delivery.
Colostrum: your first milk
The fluid your breasts produce in the first few days after birth is called colostrum. It's thick and usually a golden yellow colour. It's a very concentrated food, so your baby will only need a small amount, about a teaspoonful, at each feed.
Your baby may want to feed quite often, perhaps every hour to begin with. They'll begin to have fewer, but longer feeds once your breasts start to produce more "mature" milk after a few days.
The more you breastfeed, the more your baby's sucking will stimulate your supply and the more milk you'll make.
Your let-down reflex
Your baby's sucking causes muscles in your breasts to squeeze milk towards your nipples. This is called the let-down reflex.
Some women get a tingling feeling, which can be quite strong. Others feel nothing at all.
You'll see your baby respond when your milk lets down. Their quick sucks will change to deep rhythmic swallows as the milk begins to flow. Babies often pause after the initial quick sucks while they wait for more milk to be delivered.
Babies often pause after the initial quick sucks while they wait for more milk to be delivered.
Occasionally this let-down reflex can be so strong that your baby coughs and splutters. Your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter can help with this, or see some tips for when you have too much breast milk.
If your baby seems to be falling asleep before the deep swallowing stage of feeds, they may not be properly attached to the breast. Ask your midwife, health visitor or breastfeeding supporter to check your baby's positioning and attachment.
Sometimes you'll notice your milk letting down in response to your baby crying or when you have a warm bath or shower. This is normal.
How often should I feed my baby?
In the first week, your baby may want to feed very often. It could be every hour in the first few days.
Feed your baby as often as they want and for as long as they want. They'll begin to have fewer, but longer feeds after a few days.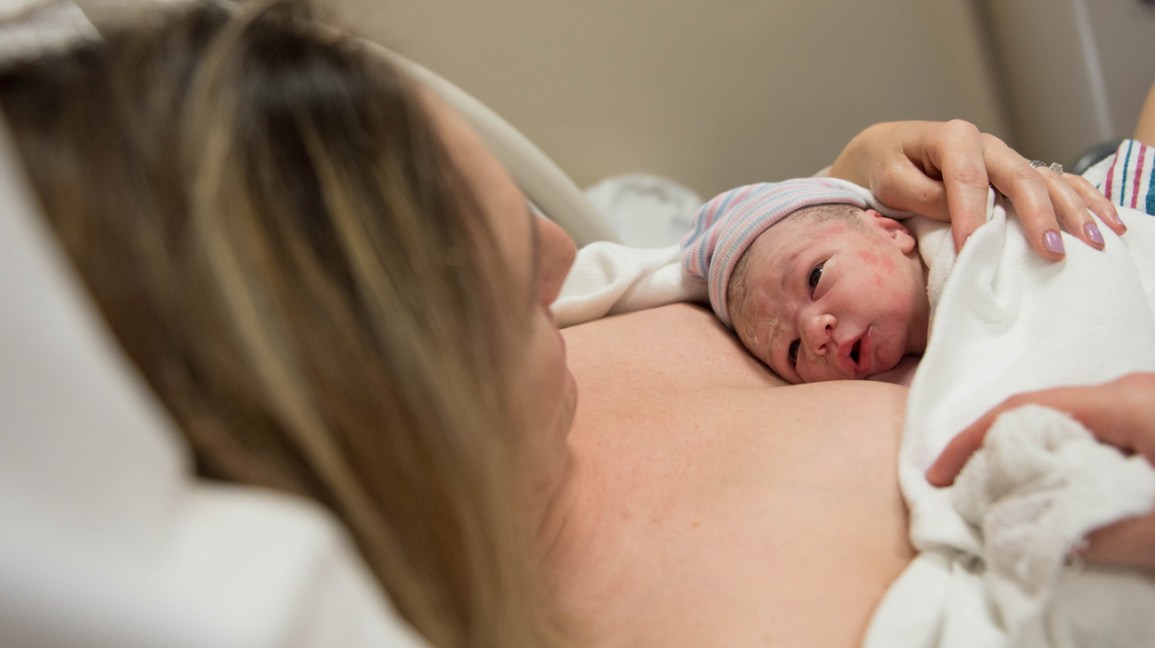
As a very rough guide, your baby should feed at least 8 to 12 times, or more, every 24 hours during the first few weeks.
It's fine to feed your baby whenever they are hungry, when your breasts feel full or if you just want to have a cuddle.
It's not possible to overfeed a breastfed baby.
When your baby is hungry they may:
- get restless
- suck their fist or fingers
- make murmuring sounds
- turn their head and open their mouth (rooting)
It's best to try and feed your baby during these early feeding cues as a crying baby is difficult to feed.
Building up your milk supply
Around 2 to 4 days after birth you may notice that your breasts become fuller. This is often referred to as your milk "coming in".
Your milk will vary according to your baby's needs. Each time your baby feeds, your body knows to make more milk for the next feed. The amount of milk you make will increase or decrease depending on how often your baby feeds.
Feed your baby as often as they want and for as long as they want. This is called responsive feeding. In other words, responding to your baby's needs. It's also known as on-demand or baby-led feeding.
In the beginning, it can feel like you're doing nothing but feeding. But gradually you and your baby will get into a pattern and the amount of milk you produce will settle down.
It's important to breastfeed at night because this is when you produce more hormones (prolactin) to build up your milk supply.
In the early weeks, before you and your baby have become comfortable with breastfeeding, "topping up" with formula milk or giving your baby a dummy can lower your milk supply.
Speak to a midwife or health visitor if you are worried about breastfeeding or you think your baby is not getting enough milk.
They might suggest giving your baby some expressed breast milk along with breastfeeding.
Find out more about how to tell if your baby is getting enough milk and tips for building up your milk supply.
Dealing with leaking breasts
Sometimes, breast milk may leak unexpectedly from your nipples.
Wearing breast pads will stop your clothes becoming wet with breast milk. Remember to change them frequently to prevent an infection.
Expressing some milk may also help. Only express enough to feel comfortable as you do not want to overstimulate your supply.
If your baby has not fed recently, you could offer them a feed as breastfeeding is also about you being comfortable.
Help and support for breastfeeding
- Find out more about positioning and attachment, including how to get comfortable and make sure your baby is properly attached.
- If you are having difficulties with breastfeeding, take a look at breastfeeding problems.
- Ask a midwife or health visitor for help. They can also tell you about other breastfeeding support available near you.
- Search online for breastfeeding support in your area.

- Call the National Breastfeeding Helpline on 0300 100 0212 (9.30am to 9.30pm daily).
Got a breastfeeding question?
Use the Start4Life Breastfeeding Friend chatbot for fast, friendly, trusted NHS advice anytime, day or night.
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
Sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
Community content from HealthUnlockedBreastfeeding a newborn | What to Expect in the First Week
The first week of a baby's life is a wonderful but hectic time, especially if you haven't breastfed before. Our breastfeeding tips will help you settle in as quickly as possible
Share this information
The first time after childbirth, mothers are often confused. The body is still recovering, and you are already starting to get to know your newborn baby. The emotional state during this period can be unstable, especially between the second and fifth day, when many women have milk 1 and at the same time postpartum depression begins 2 . In addition, people around often expect (and demand) that a woman come to her senses as soon as possible and become a “super mom”. But the best thing to do this first week is just to be with your baby and get breastfeeding going.
The emotional state during this period can be unstable, especially between the second and fifth day, when many women have milk 1 and at the same time postpartum depression begins 2 . In addition, people around often expect (and demand) that a woman come to her senses as soon as possible and become a “super mom”. But the best thing to do this first week is just to be with your baby and get breastfeeding going.
When should I start breastfeeding my newborn?
Try to breastfeed your baby within the first hour after birth. When the baby latch onto the breast and begins sucking rhythmically, it stimulates the mammary gland cells and starts milk production. 1 It is not for nothing that this time is called the “magic hour”!
“Ideally, the baby should be placed on the mother's stomach immediately after birth so that it can immediately attach to the breast. He won't necessarily eat, but he should be able to,” explains Cathy Garbin, an internationally recognized expert on breastfeeding.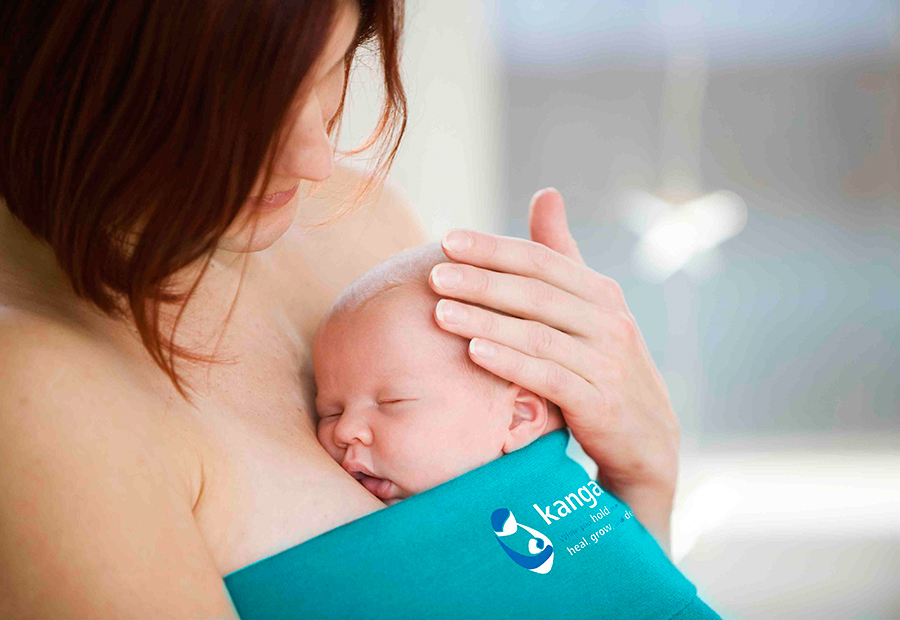
“Hold your baby and let him find the breast on his own and put the nipple in his mouth. This is called the breast-seeking reflex. On the Internet you can watch videos that show what this process looks like. If the baby does not latch onto the nipple on its own, the midwife will help to properly attach it to the breast. But for starters, it’s good to give the baby the opportunity to do it on their own. In this case, the optimal position for the mother is reclining. ”
Don't spend that special first hour of your baby's life weighing and swaddling—or at least wait until he's suckling for the first time. Enjoy hugs and close skin-to-skin contact. This promotes the production of oxytocin, the hormone of love, in you and your baby, and oxytocin plays a key role in the supply of the first breast milk - colostrum. 3
“As soon as the obstetricians were convinced that our son was healthy, the three of us — me, my husband and our baby — were left to give us the opportunity to get to know each other.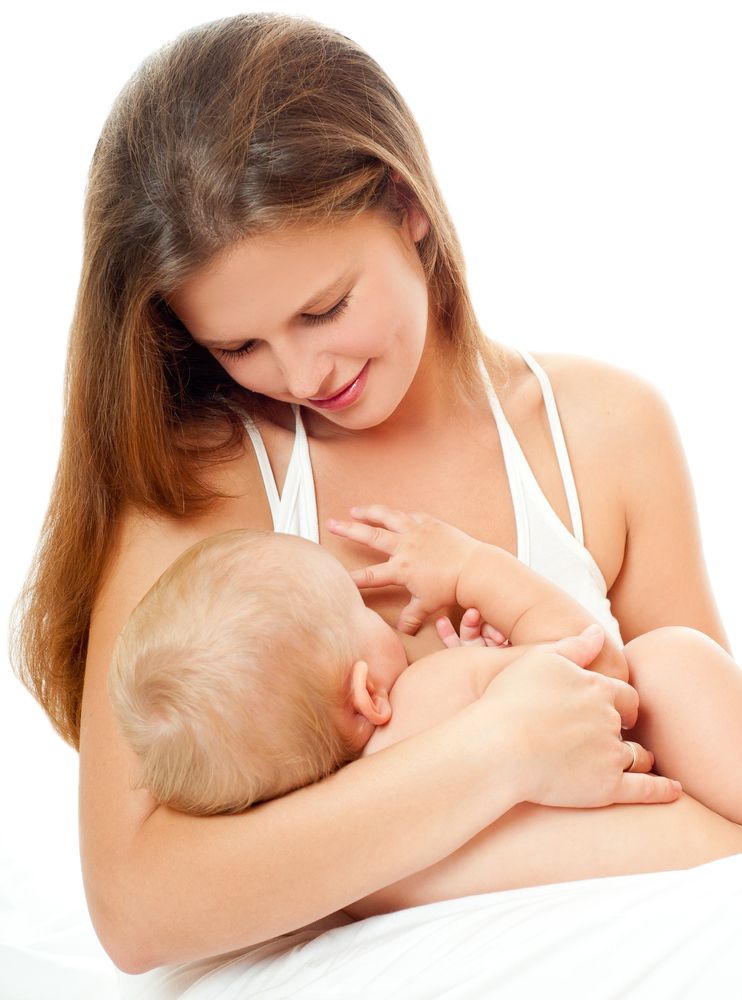 It was a very special hour - an hour of awkwardness, turbulent emotions and bliss. During this time, I breastfed my son twice, ”recalls Ellie, a mother of two from the UK.
It was a very special hour - an hour of awkwardness, turbulent emotions and bliss. During this time, I breastfed my son twice, ”recalls Ellie, a mother of two from the UK.
Did you know that breastfeeding helps to recover after childbirth? This is because oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions. In the first hours after childbirth, this contributes to the natural release of the placenta and reduces blood loss. 4
What if the birth did not go according to plan?
If you had a cesarean section or other complications during childbirth,
You can still make skin-to-skin contact with your baby and breastfeed him in the first hours after birth.
“If you can't hold your baby, have your partner do it for you and make skin-to-skin contact with the baby. This will give the baby a sense of security, care and warmth so that he can hold on until you recover, ”Katie advises.
If the baby is unable to breastfeed, it is advisable to start expressing milk as early as possible and do so as often as possible until the baby is able to feed on its own. “While breastfeeding in the first hours after birth lays an excellent foundation for the future, it is not so important,” Cathy reassures. “It is much more important to start lactation so that in the future, if necessary, you can start breastfeeding.”
“While breastfeeding in the first hours after birth lays an excellent foundation for the future, it is not so important,” Cathy reassures. “It is much more important to start lactation so that in the future, if necessary, you can start breastfeeding.”
To start milk production, you can express milk manually or use a breast pump that can be given to you at the hospital. 5 And with expressed precious colostrum, it will be possible to feed the child. This is especially important if the baby was born premature or weak, since breast milk is extremely healthy.
If a baby was born prematurely or has a medical condition and cannot be breastfed immediately, this is no reason not to continue breastfeeding. “I have worked with many new mothers who were unable to breastfeed their baby for the first six weeks due to preterm labor or other reasons. Nevertheless, all of them later successfully switched to breastfeeding,” says Kathy.
Does the baby latch on correctly?
Correct breastfeeding is essential for successful breastfeeding 6 , as it determines how effectively the baby will suckle milk and hence grow and develop.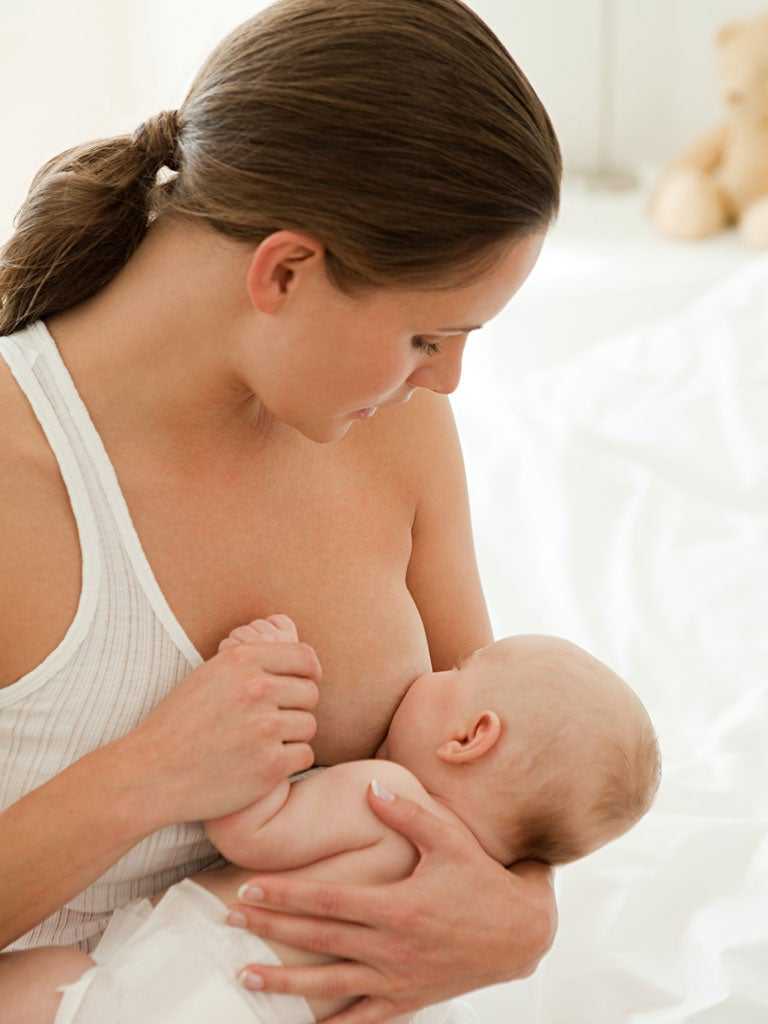 Latching on the breast incorrectly can cause sore or damaged nipples, so don't hesitate to ask your doctor to check that your baby is properly attached to the breast, even if you are told that everything is fine and you do not see obvious problems - especially while you are in the hospital.
Latching on the breast incorrectly can cause sore or damaged nipples, so don't hesitate to ask your doctor to check that your baby is properly attached to the breast, even if you are told that everything is fine and you do not see obvious problems - especially while you are in the hospital.
“While I was in the hospital, I called the doctor at every feed and asked me to check if I was breastfeeding correctly,” says Emma, mother of two from Australia. - There were several cases when it seemed to me that everything seemed to be right, but it was painful to feed, and the doctor helped me take the baby off the breast and attach it correctly. By the time I was discharged, I had already learned to do it confidently.”
When applying to the breast, point the nipple towards the palate. This will allow the baby to take the nipple and part of the areola under it into their mouth. It will be easier for him to suck if he has both the nipple and part of the areola around in his mouth. 6
6
“When a baby latch on properly, it doesn't cause discomfort and it causes a pulling sensation, not pain,” Cathy explains. - The baby's mouth is wide open, the lower lip may be slightly turned outward, and the upper one lies comfortably on the chest. The body language of the child indicates that he is comfortable. There isn't much milk at this early stage, so you probably won't notice your baby swallowing, but he will suckle a lot and nurse frequently."
How often should a newborn be fed?
The frequency and duration of breastfeeding in the first week can vary greatly. “The first 24 hours of life are completely different for different children. Someone sleeps a lot (after all, childbirth is tiring!), And someone often eats, says Katie. - Such a variety greatly confuses young mothers. Everyone gives different advice, so it's important to remember that every mother and child is different."
“Colostrum is thicker than mature breast milk and is produced in smaller amounts, but has many benefits. When the baby eats colostrum, he learns to suck, swallow and breathe until milk begins to flow in more volume, ”explains Cathy.
When the baby eats colostrum, he learns to suck, swallow and breathe until milk begins to flow in more volume, ”explains Cathy.
Milk usually arrives on the second or fourth day after birth. Until this time, the baby is applied to the breast 8-12 times a day (and sometimes more often!), including at night. 7 Feeding may last 10-15 minutes at this stage, or 45 minutes or even an hour, as the baby is just beginning to develop the muscles and coordination needed to suckle effectively.
“At first, the intensity of feeding is very high, often higher than many people realize, and this is shocking to most new mothers,” says Cathy. - Sometimes mom has no time to go to the toilet, take a shower and have a snack. It usually comes as a surprise."
Camille, a mother from Australia, experienced this. “The first week, Frankie ate every two hours, day and night, and each time it took half an hour to an hour to feed,” she recalls. “My husband and I were completely exhausted!”
Do I need to feed my newborn on a schedule?
The good news is that frequent feeding promotes lactation and stimulates milk production. 7 The more your baby eats, the more milk you will have. Therefore, forget about feeding your newborn on a schedule - this way he will have less chance of feeding. Try to feed your baby when he signals that he is hungry 8 :
7 The more your baby eats, the more milk you will have. Therefore, forget about feeding your newborn on a schedule - this way he will have less chance of feeding. Try to feed your baby when he signals that he is hungry 8 :
- tossing and turning in her sleep;
- opens eyes;
- turns his head if he feels a touch on his cheek;
- sticks out tongue;
- groans;
- licks lips;
- sucks fingers;
- is naughty;
- whimpers;
- is crying.
Crying is the last sign of hunger, so when in doubt, just offer your baby the breast. If he bursts into tears, it will be more difficult to feed him, especially at first, when both of you are just learning how to do it. As your baby grows, he will likely eat less frequently and take less time to feed, so breastfeeding will seem more predictable.
Does breastfeeding hurt?
You may have heard that breastfeeding is not painful at all, but in fact, in the first days, many new mothers experience discomfort. And this is not at all surprising, given that the nipples are not used to such frequent and strong sucking.
And this is not at all surprising, given that the nipples are not used to such frequent and strong sucking.
“Breastfeeding can be uncomfortable for the first couple of days – your body and your baby are just getting used to it. If a baby eats for too long and does not latch well, the sensations are almost the same as from unworn new shoes, Cathy compares. Just as tight shoes can rub your feet, improper suckling can damage your nipples. Prevention is always better than cure, so if the pain persists after a few days of feeding, contact a lactation consultant or healthcare professional.”
Maria, a mother from Canada, agrees: “Although my son seemed to latch onto the breast well, he damaged his nipples while feeding, and I was in pain. As it turned out, the reason was a shortened frenulum of the tongue. The breastfeeding specialists at our city clinic have been of great help in diagnosis and treatment.”
In addition, you may experience period cramps during the first few days after breastfeeding, especially if this is not your first baby. This is the so-called postpartum pain. The fact is that oxytocin, which is released during breastfeeding, contributes to further contraction of the uterus to restore its normal size. 4
This is the so-called postpartum pain. The fact is that oxytocin, which is released during breastfeeding, contributes to further contraction of the uterus to restore its normal size. 4
When milk arrives, the breasts usually become fuller, firmer and larger than before delivery. In some women, the breasts swell, harden and become very sensitive - swelling of the mammary glands occurs. 10 Frequent breastfeeding relieves these symptoms. For more breast care tips, read our article What is Breast Swelling?
How often does the newborn urinate and defecate?
What goes into the body must go back out. Colostrum
has a laxative effect, helping to eliminate meconium - the original feces. It looks a little scary - black and sticky, like tar. 11 But don't worry, it won't always be like this. Breastfed babies usually have a slightly sweet smell of stool.
How many times a day you will need to change diapers and how the contents should look like, see below.
Day one
- Frequency: once or more.
- Colour: greenish black.
- Texture: sticky like tar.
Day two
- Frequency: twice or more.
- Colour: dark greenish brown.
- Texture: less sticky.
Day three
- Frequency: twice or more.
- Colour: greenish brown to brownish yellow.
- Texture: non-sticky.
Fourth day and then the entire first month
- Frequency: twice or more.
- Color: yellow (feces should turn yellow no later than by the end of the fourth day).
- Texture: grainy (like mustard with grains interspersed). Leaky and watery.
The baby's urine should be light yellow. On average, babies urinate once a day for the first two days. Starting around the third day, the number of wet diapers increases to three, and from the fifth day onwards, diapers have to be changed five times a day or more often. In addition, during the first few days, the weight of wet diapers increases. 11
In addition, during the first few days, the weight of wet diapers increases. 11
Is the baby getting enough breast milk?
Since very little milk is produced at first,
You may feel that this is not enough for your baby. But if you feed your baby on demand, you will produce exactly as much milk as he needs. If you want to keep the process under control, be guided by the frequency of diaper changes above. If your baby soils less diapers, check with your doctor.
“For the first three or four weeks, most babies just eat and sleep. If the child is worried and constantly asks for a breast, you should consult with your doctor, ”Katie recommends.
Sometimes the baby may vomit after feeding. If the vomit is the color of milk, this is not a cause for concern. But if there are orange, red, green, brown or black blotches in it, or the child vomits with a "fountain", consult a doctor. You should also consult a doctor if the baby has a high temperature, the fontanel (soft spot on the head) has sunk, blood is found in the stool, and also if the weight recorded at birth has not recovered within two weeks. 11
11
But if there are no frightening symptoms and the baby is growing at a normal pace, it means that he has enough milk. Soon you will both get used to breastfeeding and establish a more stable routine.
For the next step in breastfeeding, see Breastfeeding in the First Month: What to Expect.
Literature
1 Pang WW, Hartmann PE. Initiation of human lactation: secretory differentiation and secretory activation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2007;12(4):211-221. - Pang, W.W., Hartmann, P.I., "Lactation initiation in the lactating mother: secretory differentiation and secretory activation." G Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12(4):211-221.
2 Shashi R et al. Postpartum psychiatric disorders: Early diagnosis and management. Indian J Psychiatry . 2015; 57( Suppl 2): S 216– S 221. - Shashi R. et al., Postnatal mental disorders: early diagnosis and treatment. Indian J Saikiatri. 2015; 57(App 2):S216-S221.
2015; 57( Suppl 2): S 216– S 221. - Shashi R. et al., Postnatal mental disorders: early diagnosis and treatment. Indian J Saikiatri. 2015; 57(App 2):S216-S221.
3 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206. - Moberg K, Prime DK, "The effects of oxytocin on mother and child during breastfeeding." Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
4 Sobhy SI, Mohame NA. The effect of early initiation of breast feeding on the amount of vaginal blood loss during the fourth stage of labor. J Egypt Public Health Assoc . 2004;79(1-2):1-12. - Sobhi SI, Moham NA, "Early initiation of breastfeeding and its effect on vaginal bleeding in the fourth stage of labor." G Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2004;79(1-2):1-2.
2004;79(1-2):1-2.
5 Meier PP et al. Which breast pump for which mother: an evidence-based approach to individualizing breast pump technology. J Perinatol . 2016;36(7):493. - Meyer P.P. et al., Breastpump Selection: A Scientific Approach to Customizing Pumping Technology. J Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology). 2016;36(7):493-499.
6 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women ’ s 2007;52(6):638-642. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." W Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
7 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al.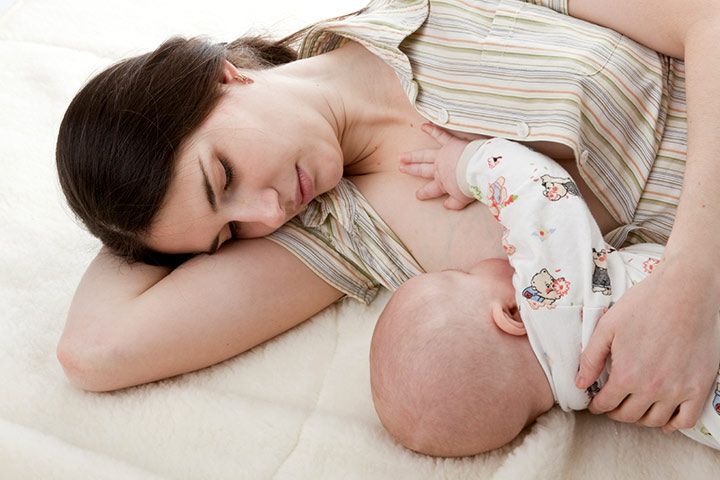 , "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
, "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
8 Australian Breastfeeding Association [ Internet ]. Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
9 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd . 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Guidelines S -3 for the management of inflammatory breast disease during breastfeeding." Geburtskhilfe und Frauenheilkünde. 2013;73(12):1202-1208.
10 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
Breastfeeding on demand
You can often hear from a nursing mother: "I feed on demand, my baby requires a breast every 3.5 hours." Or: “I have always fed on demand. In a year, we already had 1 feeding in the evening, and my child calmly refused to breastfeed. Before talking about the demand of the child, it is necessary to find out what modern women mean when they say - "I breastfeed."
Modern mothers consider breastfeeding essential for feeding their baby. Just for feeding. Breast milk is food, the mother supplies the baby with the nutrients necessary for growth and development. When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
When a baby suckles at the breast, he eats. Breastfeeding makes sense only as a process of supplying proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
During suckling, the baby receives the nutrients it needs with mother's milk. This is the absolute truth. There is another unconditional truth, which is not given any importance in modern society, it is not taken into account and is not considered. Breastfeeding for a child is communication with the mother. We need to figure out how the child understands feeding on demand? Can he understand anything at all? Is there any difference for him how he is fed, for 15-20 minutes after 3.5 hours or in some other way?
What is on-demand feeding
On-demand feeding of a newborn baby means putting it to the breast for every squeak or search. Squeak and search movements in newborns, even as early as the second or third day of life, begin to appear much more often than after 3.5 or 2.5 hours. The need for attachments increases rapidly, and by the 10-12th day of life, the need to attach to a child may occur 15-16 or more times a day.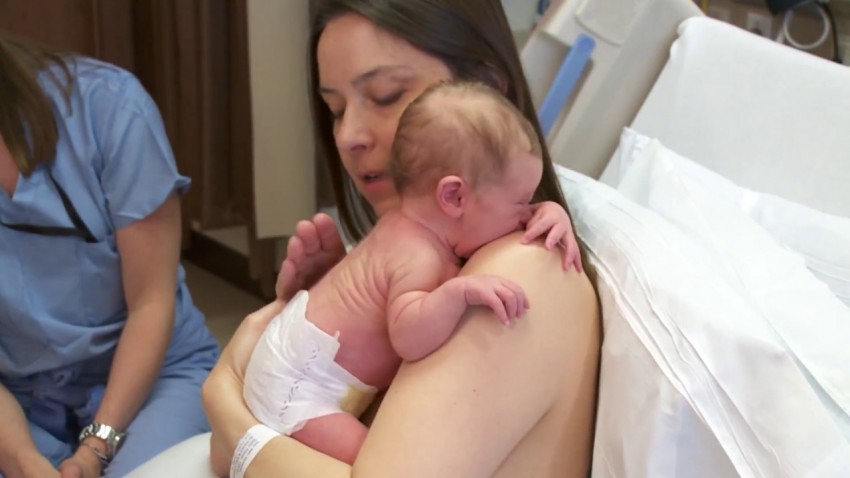 Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
Applications vary in duration. The baby can fall asleep and sleep while sucking for, for example, 1.5-2 hours. Can release the breast after 1-2 minutes. And then ask her again. Why does a child need such frequent contact with his mother's breast?
That's why. Being in the mother's belly, in a calm, familiar environment, listening to the noises of the mother's body, being in a warm, cramped, confined space, the baby sucked his fist, fingers, loops of the umbilical cord, swallowed amniotic fluid. Learned to suck and swallow. After birth, experiencing discomfort for any, the most insignificant reason, the baby tries to get rid of it. You can get rid of discomfort by getting into the usual conditions of a comfortable stay. The only place where the baby after birth can feel the sensations familiar to him is in the arms of the mother. The only familiar action is sucking. The only familiar taste and smell is the taste and smell of milk and lube in the areola. Milk and lubricant have an odor and taste similar to the taste and smell of amniotic fluid. Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
Therefore, experiencing discomfort, the baby squeaks, or begins to look for an object to suck with his mouth. Ideally, it is immediately applied to the chest. The baby becomes warm, cramped, he hears the beating of his mother's heart, breathing, grumbling in the intestines, he sucks and feels the familiar taste and smell. If such an action happens constantly, the baby gains confidence, no matter what happens, he will solve all his problems with his mother. The place of comfort is now under the breast, and you can suck on the breast.
This whole process is justified from a biological point of view. A newborn child does not feel the feeling of hunger, this feeling is not formed in him. It will begin to form at about two months of age. How to feed a creature that does not experience hunger ?! How to encourage him to take some action to get food? This can be done only at the expense of some other incentives. This stimulus for the newborn is constant bodily discomfort, thanks to which he wants to suckle all the time! The most intense, frequent and prolonged sucking in infants is observed in the first two or three months of life. It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
It is in these first months that the main weight gain of the baby occurs.
Feeding in the first month
Baby falls asleep with the breast in his mouth, sleeps sucking for a while. Falling asleep deeply, lets go of the chest. After sleeping for a while, he wakes up, and is applied on waking. After sleep, he can stay awake for some time, for example, an hour and a half. During wakefulness, he may feel discomfort 2-3 times, for example, from a completely natural desire to pee, and having called his mother for help, having kissed for a couple of minutes, he will do his deeds. Then he will want to sleep, feel discomfort and, kissing his chest, will again fall asleep sucking. After some time, he will wake up and attach again. Then again a little "walk". And after some time, he will fall asleep at the chest again.
The daytime naps of a one-month-old baby feeding on demand vary in duration and number. There can be 4-6 dreams during the day, and they can last from 5-15 minutes to 2-2. 5 sometimes 3 hours. "Around" each dream, the baby is applied to the chest, and applied between dreams several times. At night, the child falls asleep at the breast. Usually in the early morning hours, he begins to fuss and apply. In the morning, he almost never fully wakes up. The baby sleeps, from time to time, sucking on his mother's breast. Waking up in the morning, the baby is again applied to the chest. If you count all the attachments that have happened in a baby of one month of age, then approximately 16-20 attachments are obtained. This is how a newborn human cub behaves if it is given the opportunity to behave in accordance with physiological and psychological needs, which, by the way, are genetically determined. The child of the first months of life does not separate his personality from the personality of the mother and from her breast. Mom and her breasts, and everything connected with them, are the universe of the baby and himself.
In most cases, a modern woman, being afraid to “accustom a child to hands”, strives to limit his requests for sucking. A pacifier and a bottle of tea or water come to her aid in this matter. They, too, can be sucked ... The need for sucking seems to be satisfied. But only the need for communication with the mother during suckling is not satisfied, the peculiar chain of mutual assistance and cooperation between mother and baby is destroyed, the formation of maternal affection and concentration is disrupted. Is the difference in the two actions noticeable to the reader: the baby cried, the mother took him, put him to her chest and started rocking him, or gave him a pacifier and started rocking the stroller, even with the words “Why are you crying, my sun?”
The modern woman who gives a pacifier and pumps a stroller is not a bad person who deliberately harms an infant. She is simply in captivity of prejudices regarding the relationship between mother and baby. She does not know how to behave correctly, does not know what to do in accordance with the natural needs of the child. If you tell her what the child really needs, she will exclaim in horror: “What is it, don’t let him get away with?!” Indeed, the child of the first months of life must not be let off the hook. For a woman who does not know how to comfortably carry a baby, and who does not know how to feed him in various positions (sitting, lying, standing and even moving), this can be very difficult. Especially if she is not sure of the correctness of her actions.
An action that should become automatic for the mother of a newborn: when the baby cries or shows other signs of anxiety, put the baby to the breast.
And then?
The baby is growing. A fairly stable rhythm of daytime sleep begins to form in him, and a 3-4-month-old baby behaves quite differently from a newborn. Feeding on demand at this age looks something like this...
- At three months, the baby has 10-12 feeds during the day and 2-4 at night. There are frequent applications for a short time, but their number is reduced. There may be a long night break in feedings, about 5 hours, but this is very rare. Much more often the night break is 2.5-3.5 hours. By this age, the baby's body is noticeably rounded.
- At four months, the baby begins to breastfeed much less frequently. The main feedings are associated with sleep: the baby suckles before bedtime, during awakening and during sleep, both daytime and nighttime. In this regard, he has a fairly accurate feeding regimen. And many babies stop breastfeeding when they wake up after daytime sleep, sometimes as early as 2.5-3 months.
- At five months, the baby has 8-10 daytime feedings and 2-3 nighttime, attachments as well as in the fourth month of life, they are organized around dreams - the baby eats when going to bed and some babies suck during awakening.
- Feeding regimen changes at six months. The most active sucking shifts to the last 2-3 hours before waking up from a night's sleep. The period of daytime wakefulness can be divided into two periods: in the morning, when the baby sucked during the night is rarely applied to the breast, and in the evening, when attachments become very frequent. In total, there can be 7-10 day applications and 3-4 night applications.
At this age, the baby begins a period of acquaintance with new food - pedagogical complementary foods. Sometimes there are attachments associated with the introduction of complementary foods, the baby “washes down” samples of new food with mother's milk. But many children do not want to drink complementary foods. When complementary foods are introduced to an on-demand baby, it is never meant to replace feedings with complementary foods. This is practically impossible, because the main feedings of the baby are associated with sleep, and mother's breakfasts, lunches and dinners, during which the baby gets acquainted with new food, are located between the baby's dreams, during his wakefulness.
- At seven months, the frequency of applications is about the same.
- At eight months, the feeding regimen changes. Since the baby shows high motor activity and is very busy exploring the surrounding space, in the daytime he forgets to breastfeed. In this regard, the number of daily feedings can be reduced to 6-8 times.
The baby compensates for the reduction in daytime feedings by increasing the frequency and duration of nighttime feedings up to 6 times.
- In the second half of the year, babies who stopped breastfeeding on waking from daytime naps recall this habit again. The baby’s daytime sleep in the second half of life, as well as in the region of a year and older, looks something like this: the baby falls asleep sucking, sleeps quietly for a while, for example 1-1.5 hours, then starts tossing and turning, fiddling, worrying, at this moment the mother lies down next to , gives him a breast and the baby can fill up 10-15-30 minutes sucking. Mom may well use this time for her own rest - lie down, read, while the baby sleeps while sucking. I know my mother, a lover of embroidery, who used this time specifically for embroidery ...
- Breastfeeding becomes more frequent at nine to ten months. In the daytime, this is 4-6 full feedings and about the same number of attachments for various reasons.
The baby has new reasons for attachment. If, during active actions to master the world, the baby fills a bump or gets scared, he calms down with his mother's breast. There may be situations when you can comfort the baby by sitting next to him and hugging him. At night, 4-6 feedings remain, the baby begins to suckle more actively in the morning between 3 and 8 hours.
- At eleven months, a baby can already have 2-3 complete complementary foods. Initiation to adult food in the mind of a child is not associated with breastfeeding: attachment to the mother's breast is something other than the desire to get enough of the product they like. As a rule, after the baby has eaten, he feels the need to attach himself to the breast. The number of daily feedings remains the same in the child, but the number of short-term attachments increases. There are active mid-morning feedings between 4 and 8 o'clock in the morning.
- At ten or twelve months, the baby, if he is already walking, can sometimes breastfeed every time he comes to his mother, i.
e. about every 15-30 minutes. Attachments around dreams and night sucking persist. Therefore, if a mother says that a child suckles once or twice a day, this means that there is no feeding at the request of the child. There are restrictions imposed by the mother, with which the baby has come to terms. He treats breast sucking like food, sucks on a pacifier or a finger to fall asleep or soothe, or falls asleep just like that, without calming down.
- At twelve months, the baby is applied in about the same way.
- At the age of one and a half years, there may already be one daytime nap, so there are fewer attachments associated with sleep. Preserved for morning sucking. The baby is very free with his mother's breasts. Sometimes it happens that he comes up to suck just for pleasure. For example, like this: he comes up, climbs on his knees, looks into his mother’s face, smiles, starts to swarm in his shirt, gets breasts, smiles at his breasts, sucks for 30 seconds and leaves.
As for the number of feedings per day when feeding a child on demand, their number is almost never less than 12. A newborn has 12 or more attachments, mostly they are all associated with dreams. And a child, say 1.5-2 years old, can also have about 12 attachments, only 3-4 are associated with sleep, and the rest are short-term attachments for various reasons. I suggest to all mothers reading this text - do not count the application, do not notice their duration. Breastfeed your baby as often as he asks, when you feel the need to.
Mothers who do not think about breastfeeding without looking at the clock may get the impression that when feeding on demand, the mother can do nothing but feed the baby. This is not true. After the birth of a baby, a mother begins another life, she is called life with a baby. That's all. The child is with the mother, not the mother with the child! Feel the difference! You need to be able to organize your life in a different way, in the first months, of course, the help of loved ones is very necessary. In the tradition of many peoples, it was customary for the first 40 days after childbirth to remove a woman from any housework and household chores, she was engaged only in a child. In some nations, objects that the mother of a newborn touched were considered “unclean”, therefore, they preferred to protect the mother from the rest of the household, allocating her a separate “corner” of the house, where no one bothered her and she did not interfere with anyone. Among the Slavs, such a restrictive custom was called a six-week. By 1.5-2 months, the rhythm of daytime dreams begins to form, and the baby has a kind of “regime”, the mother becomes more free.
For a mother who can't imagine breastfeeding without looking at the clock, and who is sure that the “right” baby is the baby lying quietly in her crib all the time, feeding on demand will be a complete hassle. It will be much easier for such a mother if she stops looking at the clock and ties the baby to herself with a large scarf or uses a patchwork holder (sling). It will become easier for her if she stops running between the nursery and the kitchen, but takes the baby with her to the kitchen and carries him around the house with her, doing housework, in a box, a cradle, a special chair, if she tries not to put him off often, and pick up as soon as possible, postponing the baby only in case of emergency and not for long.
Breastfeeding is not the same as house arrest. In the conditions of modern society, it is possible to organize the exit of a nursing mother to work from about 6 months of age of the baby. If necessary, you can start working from the age of 4 months, but, of course, it is better not every day of the week and not full time. It is the responsibility of a breastfeeding consultant to help a mother organize her return to work.
Sometimes, when counseling mothers on breastfeeding, I suggest that they forget for a second that they are already living in the 21st century. I propose to return, for example, to the cave and ask what they will do if the child woke up at night, how to calm him down? If you are walking through the forest and trying not to attract the attention of predators, how to make the baby silent? If the child is thirsty, what will you give him? What is the baby used to, for thousands of years of its existence? To the fact that he sleeps on his mother while she wanders through the forest with a digging stick in search of roots, and wakes up when mother stops. Since mom stopped, then there is time to wake up and suck. Therefore, even now the child sleeps well, tied to the mother with a patchwork holder, wakes up when the mother, having done a few household chores, sits in a chair to take care of the baby.
Some mother, reading about the cave, will be offended, saying that she is a civilized creature. But please think. Man, mother's breast and mother's milk have been created by evolution over millions of years. They are made for each other. Baby food has created progress and more recently. The skills of motherhood and breastfeeding have also been lost by our society quite recently. A person is not physiologically adapted to artificial feeding and a pacifier. The mother's breast will not produce enough milk at 6-7 feedings per day. Nature did not know, when creating man as a mammal, that the time would come when the need for breastfeeding would be satisfied by some kind of pacifiers and nipples.
Changes that occur during the formation of the personality of a child who did not have full contact with the mother during prolonged breastfeeding are noted by modern research by psychologists and sociologists.