Baby feeding schedule book
Baby Feeding Chart - Etsy.de
Etsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Find something memorable, join a community doing good.
( 225 relevant results, with Ads Sellers looking to grow their business and reach more interested buyers can use Etsy’s advertising platform to promote their items. You’ll see ad results based on factors like relevancy, and the amount sellers pay per click. Learn more. )
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
-
More like this
How Often Should I Feed My Baby? Tips for Infant Feeding Schedules
Written by Barbara Brody
In this Article
- What Is a Baby Feeding Schedule?
- How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
- How Much Should I Feed My Baby?
- When to Start Solids
- When to Wean
What Is a Baby Feeding Schedule?
It’s simple: You should nurse or offer a bottle whenever your little one is hungry in the first few months as a newborn. And your baby is going to let you know, loud and clear! But crying isn’t the only clue.
Following your child's lead, instead of trying to stick to a strict time-based schedule, is often called “demand feeding” or “feeding on-demand.” Since your infant can't actually say "I'm hungry,” you’ll want to learn to look for cues that it's time to eat. These may include:
- Leaning toward your breast or a bottle
- Sucking on their hands or fingers
- Opening their mouth, sticking out their tongue, or puckering their lips
- Fussiness
Crying is also a sign of hunger. But if you wait until your baby is very upset to feed them, it can be hard to calm them down.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Every child is different. It also depends on whether your baby is drinking breast milk or formula, since they digest breast milk more quickly.
If you're breastfeeding, your newborn will probably want to nurse every 1.5 to 3 hours. As they get older, they’ll slowly start to nurse less often and fall into a more predictable pattern.
Newborns should nurse eight to 12 times a day for the first month; when your child gets to be 4 to 8 weeks old, they’ll probably start nursing seven to nine times a day.
If they’re drinking formula, your baby will probably want a bottle every 2 to 3 hours at first. As your child grows, they should be able to go 3 to 4 hours without eating.
Newborn growth spurts and hunger
You may notice that your baby sometimes wants to eat more often or a larger amount than normal. This usually happens when a child is growing rapidly. Your child may go through growth spurts around these ages:
- 7-14 days
- 3-6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
How Much Should I Feed My Baby?
There are general guidelines, but no hard and fast rules, for how much your baby should have at each feeding. It depends on their own habits and rate of growth, plus a few other things, such as their age and how often they feed.
Babies usually drink more each time (and feed less often) as they grow and their stomachs can hold more. If you breastfeed, your baby may drink a little less each time but feed more often than babies who get formula.
If you breastfeed, your baby may drink a little less each time but feed more often than babies who get formula.
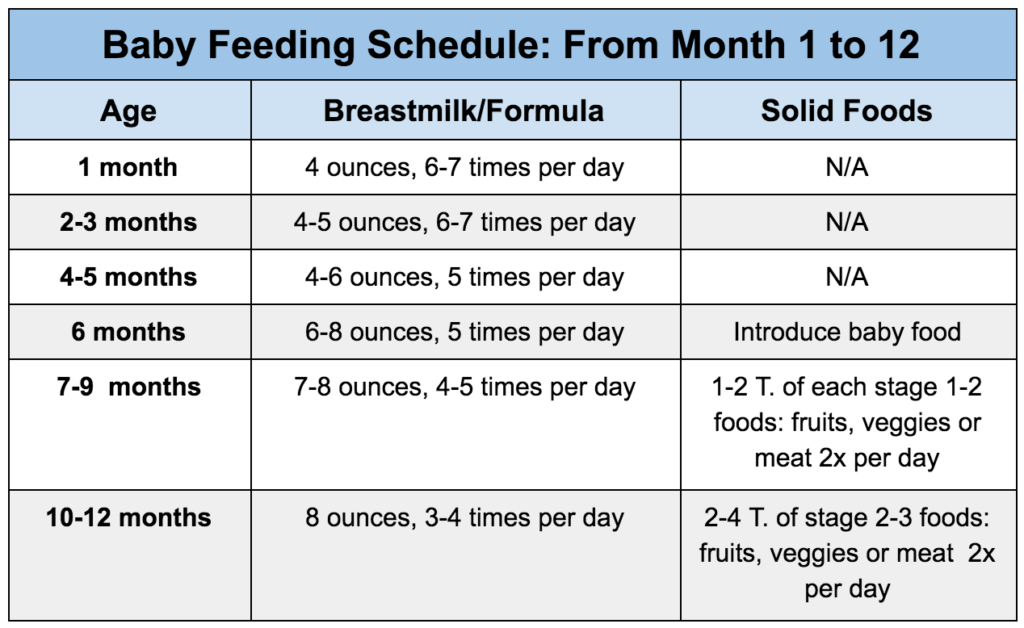
Most babies add about 1 ounce to what they drink per feeding with each month of age. This levels off when they’re about 6 months old, when they usually drink 7 to 8 ounces per feeding. Here’s about much your baby should drink at each feeding when they are:
- Newborn to 2 months.In the first days after your baby is born, they may want only a half ounce of milk or formula at each feeding. This will quickly increase to 1 or 2 ounces. By the time they’re 2 weeks old, they should drink about 2 or 3 ounces per feeding.
- 2-4 months.At this age, your baby should drink about 4 to 5 ounces per feeding.
- 4-6 months. At 4 months, your baby should drink about 4 to 6 ounces per feeding. By the time your baby is 6 months old, they’ll probably drink up to 8 ounces each time you feed them.
Not sure if your baby is getting enough to eat? You can probably relax. If your child has four to six wet diapers a day, has regular bowel movements, and is gaining weight, chances are that they’re doing just fine. If you have any concerns, give your pediatrician a call.
If your child has four to six wet diapers a day, has regular bowel movements, and is gaining weight, chances are that they’re doing just fine. If you have any concerns, give your pediatrician a call.
When to Start Solids
Your baby needs to reach certain stages of development before you add solid food to their diet. If you breastfeed, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) suggests that you feed your baby breast milk alone until they’re about 6 months old. Many babies are ready for solids when they’re about this age.
Here’s how to tell if your baby may be ready for solid food:
- They can hold up their head and keep it steady while seated in a high chair or other infant seat.
- They open their mouth for food or reach out for it.
- They put their hands or toys in their mouth.
- They can take food from a spoon and swallow it instead of dribbling it all out.
- They have doubled their birth weight and weigh at least 13 pounds.
When to Wean
Most babies are ready to be weaned from the bottle by 12 to 18 months, but exactly when it happens is up to you and to your baby. Your baby may be ready to start to wean when they:
Your baby may be ready to start to wean when they:
- Enjoy solid food more
- Eat on a regular schedule
The process takes time, and you can help your baby make the change by giving them a cup to try when they’re around 6 months old. Generally, you should stop bottle use by the time your baby is 2 years old.
If you breastfeed, the AAP suggests that you continue to feed your baby breast milk along with solid food until they’re at least 1 year old. Your child may give you clues that they’re ready to wean. They may:
- Show more interest in solid food or drinking from a cup
- Not want to sit still while you breastfeed
You may want to wean your baby for your own reasons. The process works best when it’s gradual. The AAP notes that if it’s what you and your child want, you can continue to breastfeed after your baby reaches their first birthday.
Read the book “Child mode 0-12 months. Adjust and sleep ”online completely📖 — Ekaterina Nikolaevna Rukhlenko — MyBook.
Does a child need a regimen
As a child sleep consultant, I am often asked for my opinion on the question of whether a regimen is needed or not.
The child definitely needs a routine. I always tell parents whom I consult on children's sleep problems that many sleep problems cannot be solved without a regimen.
If you have some consistency, you will avoid many of the problems of children's sleep.
You will have time for yourself, and you will always be able to plan it with a sufficient degree of predictability.
Your child will sleep well. His body will receive all the health benefits of quality and long sleep.
It will be much easier for you to attract other people to help: grandmothers, nannies during your absence.
Mode is not life with a stopwatch in hand, when all actions are performed strictly by the clock at the same time. But just a predictable, regular alternation of activities and rest during the day, where a certain flexibility is allowed.
If you want your child to sleep well throughout childhood, having a consistent routine is essential.
When the day is built predictably enough, the regulation of sleep and wakefulness occurs without any problems, as the body has established a clear internal rhythm.
In the absence of regularity, it is difficult for our body to figure out when to sleep and when to stay awake, because on different days it receives completely different signals.
Many problems of children's sleep are associated with the inadequacy of the regimen. The most amazing thing is that we as parents create these problems ourselves, without even realizing the problem.
Starting to build a routine: when and how
Depending on the age of your baby, the following situations are possible.
Premature baby
If your baby was born much premature, he will sleep all the time at first. Until he reaches term age, your job is to ensure a calm environment and sleep most of the time. You should follow the doctors' recommendations for feeding, caring for your baby and getting enough sleep. Of course, there can be no talk of any regime during this period.
You should follow the doctors' recommendations for feeding, caring for your baby and getting enough sleep. Of course, there can be no talk of any regime during this period.
Setting up a routine for the first time before six months of age
In the first months of life, your task is to follow the needs of your baby, but at the same time gently help him "tune in" to the current day and night and lengthen the night's sleep. Read more about this in the chapter "Mode from 0 to 3 months".
Chosen type of feeding: breastfeeding or artificial (or feeding with expressed milk) will inevitably influence the number and duration of feedings, lengthening of uninterrupted sleep periods.
By about three months of age (and often a little earlier) you will see certain trends repeating day after day. Write down a typical day for your baby and analyze it. If everything suits you, then great.
If you're complaining about anything, check out the recommendations for the 4 to 6 month regimen in this book. Begin to gently switch to the mode you need.
Begin to gently switch to the mode you need.
Mode change in 6-12 months
You will find it helpful to study the relevant chapters in this booklet and try to understand what exactly you are not comfortable with right now. If there is no mode at all, then use the diagrams in this book as a hint: what to strive for.
How to shift the mode
If the current mode is too late and you want to shift it to an earlier one, always start the shift from the morning rise. For example, the baby sleeps from 22 to 9 in the morning, and you want to transfer to 20-7 in the morning. In this case, laying down at 20 o'clock abruptly and in one day may not bear fruit. It is optimal to start the adjustment from the rise: we start waking up earlier and shift accordingly all day. Depending on the situation, this can be done abruptly on one day or in small intervals every day.
If the baby gets up early
Have you checked your total night's sleep and see that your child is not getting enough sleep? For example, with a norm of night sleep at 11 o’clock, he sleeps only 9. At the same time, he fits in at 22, and gets up at 7? In this case, you can immediately try to start putting the baby to bed earlier at the time you need: if the baby goes to bed much later than the ideal time, he is ready to sleep much earlier. And, most likely, he will fall asleep easily at an earlier time. If this approach does not work, try to smoothly shift the time of laying each day in intervals of 15-30 minutes.
At the same time, he fits in at 22, and gets up at 7? In this case, you can immediately try to start putting the baby to bed earlier at the time you need: if the baby goes to bed much later than the ideal time, he is ready to sleep much earlier. And, most likely, he will fall asleep easily at an earlier time. If this approach does not work, try to smoothly shift the time of laying each day in intervals of 15-30 minutes.
If the child does not sleep well
Many factors affect a child's sleep: problems can be caused by a combination of different causes.
Mode is just one potential factor.
In terms of routine, your child's sleep problems may be due to some of the reasons listed below.
Lack of regularity: when sleeping and feeding occur at completely different times each day.
Chronic sleep deprivation: when the baby sleeps much less time during the day than he needs.
Waking too long during the day between naps, inappropriate for age.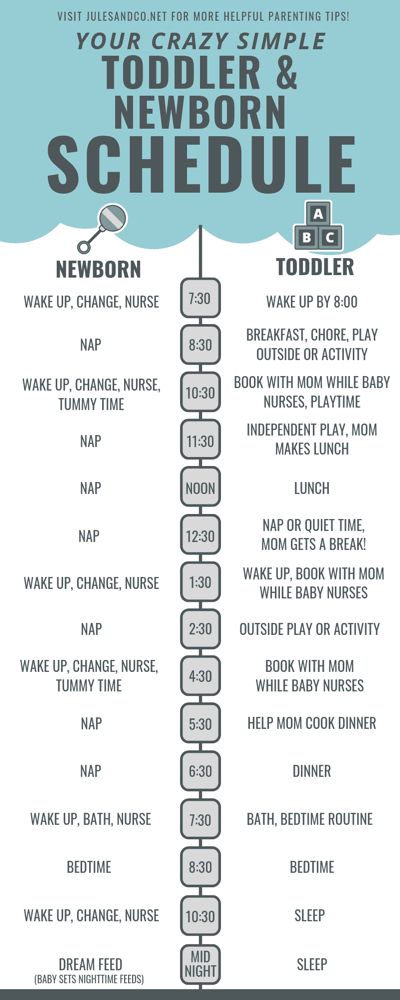 This includes spacing between naps and skipping the right amount of naps too early.
This includes spacing between naps and skipping the right amount of naps too early.
Too late start of the night. If the actual mode is in conflict with the biological norm, certain difficulties arise in sleep.
Feeding and sleep go hand in hand throughout the first year of life. Age-appropriate nutrition in terms of frequency and sufficiency is the basis of any regimen. Night feedings are necessary for your baby until a certain age. It is impossible to build a routine without taking into account the real expectations of a particular age.
Things that happen during the day also affect your child's rhythm. Activity, feedings, exposure to sunlight, walking are all important factors in establishing a defined routine.
So if you want to address your child's specific sleep problems, remember that routine is only part of the equation. Analyze your current situation using the relevant chapter in this book.
Sleep and wake times
These recommendations are guidelines.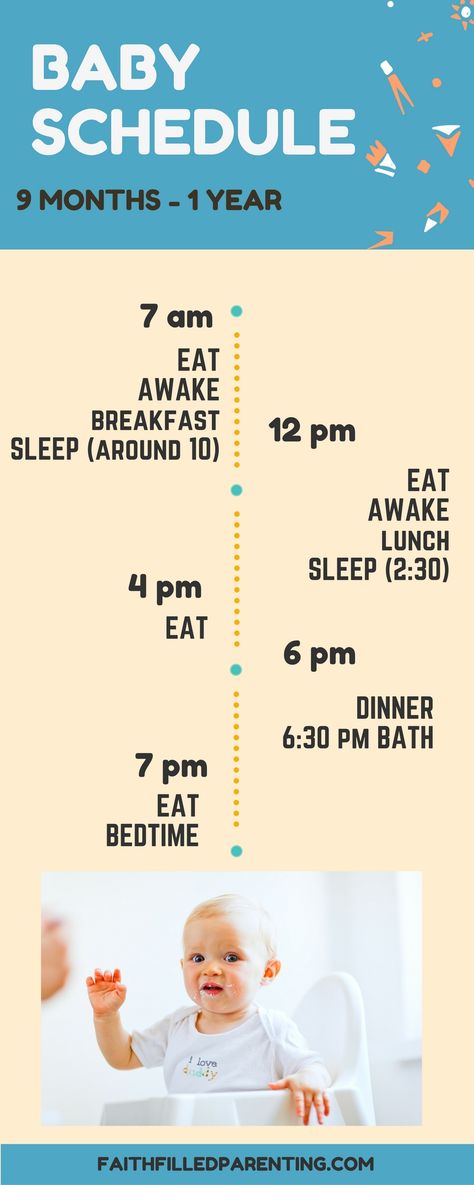 Your child may need a little less or a little more sleep. The need for sleep is influenced by many factors: the stage of the physical and mental development of the baby, age, season, level of sensory stimulation, activity during the day, illness, weather conditions, and others. Always look at your baby, not just the clock.
Your child may need a little less or a little more sleep. The need for sleep is influenced by many factors: the stage of the physical and mental development of the baby, age, season, level of sensory stimulation, activity during the day, illness, weather conditions, and others. Always look at your baby, not just the clock.
Age
Night sleep, hours
Day sleep, hours
A total per day, hours
The maximum wakefulness
Night
Newborn sleep14-16
60 minutes
20-23
9-12 weeks
10-11
5 hours (3 sleep)
14-16
1 hour 20 minutes
20-22
4 -5 -5 months
10-12
4-5 hours (3 sleeps)
2-16
1 hour 45 minutes - 2 hours
19-19.30.
6-8 months
10-12
3.5 hours (2-3 sleeps)
14-15
2-2.5 hours
7-19.30.
8-10 months
11-12
2-3 hours (2 sleep)
12-15
3 hours
19. 00
00
10-15 months
11-12
-14
3-4 hours
19.00
Average wakefulness is the interval from the end of the previous sleep to the start of the next one. If the child does not sleep much longer, overwork accumulates. If the child did not sleep well during the day (less than 50 minutes), then most likely he will endure a shorter interval of wakefulness.
Children are usually able to tolerate a longer interval of wakefulness in the afternoon (between the last daytime and nighttime sleep) and a much shorter interval in the morning (between getting up from a night's sleep and the first sleep). Therefore, the first morning sleep is usually required by the child earlier than through the average wakefulness benchmark.
Signs of fatigue
Overwork increases cortisol (stress hormone), which in turn affects sleep. Depending on the degree of overwork, the child may resist sleep, not sleep at all, wake up frequently, sleep in short naps.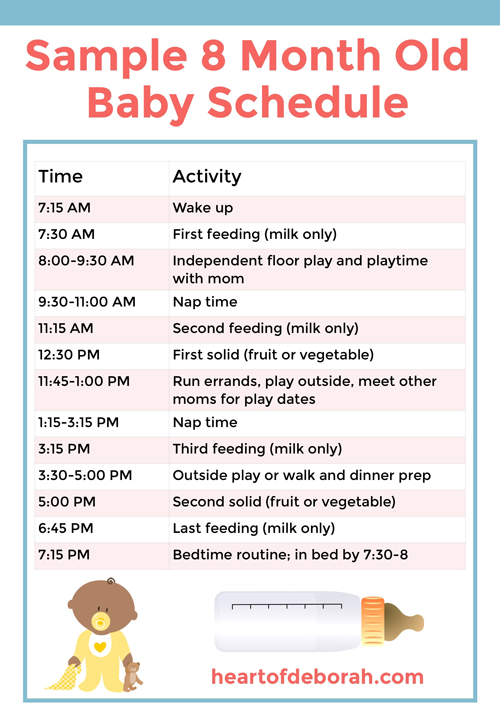 Signs of fatigue vary from child to child and from age to age. You can start by trying to see the typical behavior of tired children.
Signs of fatigue vary from child to child and from age to age. You can start by trying to see the typical behavior of tired children.
There is a concept of the so-called "window" - a period of time when the baby is tired enough to fall asleep, but not too tired yet. If we miss a window, we enter a zone of overwork. Young children can stay awake for very short periods of time and it is very easy to miss a window.
Average wakefulness by age
Newborn - 20-45 minutes
5-8 weeks - 60 minutes
9-12 weeks - 1 hour 20 minutes
4-5 months - 1 hour 20 minutes 9 hours0005
6-8 months - 2-2.5 hours
8-9 months - 3 hours
10-15 months - 3-4 hours
Signs of fatigue in the first months of life
makes strange screeching sounds
Change of mood: whims, crying
Searches and requires breasts
Twas itself by the ears
Cloths fists
Eyes
Fingers
Sumps
0005
Porcery the view of
Signs of fatigue in children from four months to 1 year
It becomes awkward, falls out of the blue, cannot coordinate the
movements for any reason
,requires constant attention
Crying 9000,000,0002 clings for mother, hides face in chest, shoulder
Refuses to eat
Rubs eyes
Yawns
Loses interest in toys
So as soon as you know your child is tired, reduce your activity and sensory stimulation and begin your bedtime ritual.
There are children whose fatigue is extremely difficult to recognize. If your child is just like that, then be guided by the norms of wakefulness by age and start preparing the baby for sleep 20-30 minutes before the expiration of this interval.
Don't expect the child to "fall asleep on its own if it wants to." Often this does not happen. Help your baby get ready for sleep and fall asleep at the right time.
Mode from 0 to 3 months
In the first months, hard mode by the clock is simply not possible. Firstly, the circadian rhythm of the crumbs is still being tuned to the outside world. Secondly, the baby should eat very often. Thirdly, you may face the problem of colic or prolonged crying, which will not allow you to build any kind of routine.
Basic advice under three months of age: look at the baby and arrange feedings and sleep for signs of hunger and fatigue.
Sleep in the first months of life differs significantly from that of older children.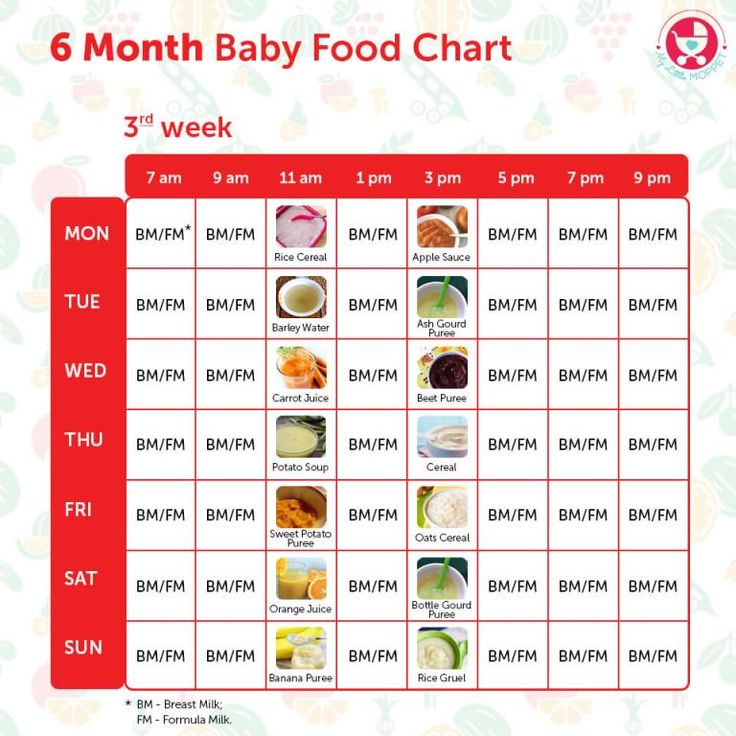
sleep, feeding and development of the baby
04/11/2019
116
By 4 months, the biological rhythms of the child are finally formed, and the structure of his sleep becomes the same as in adults. Therefore, the old ways of laying often stop working, the baby may fall asleep longer, wake up more often at night and constantly breastfeed, and the existing daily routine may no longer work. What to do in this case?
Use our tips to improve your child's routine!
4 months
At this age, children still cannot live according to a clear daily schedule, as they still sleep short dreams during the day and are not able to stay awake for a long time. Therefore, the daily routine of four months. is built based on the time of wakefulness, which is no more than 1.5-2 hours between sleeps. At the same time, an infant needs 9-10 hours of sleep per night with awakenings for feeding and 3-4 daytime sleeps with a total duration of about 4-5 hours. That is, the baby will sleep with this schedule 3-4 times a day. The time of evening bedtime will vary and depend on the end of the last day's sleep. To get your baby to bed on time, be alert for signs of fatigue and stay awake for more than 2 hours. So you will prevent overworking the baby, which will improve the quality of his nightly sleep and reduce the number of night awakenings. Morning should start no later than 07:00-07:30 to form the physiological regime of the day.
That is, the baby will sleep with this schedule 3-4 times a day. The time of evening bedtime will vary and depend on the end of the last day's sleep. To get your baby to bed on time, be alert for signs of fatigue and stay awake for more than 2 hours. So you will prevent overworking the baby, which will improve the quality of his nightly sleep and reduce the number of night awakenings. Morning should start no later than 07:00-07:30 to form the physiological regime of the day.
What to do if a 4-month-old baby slept well but now has trouble getting to bed:
-
Enter your bedtime ritual if you haven't already. In the evening, this can be bathing, light massage, putting on a diaper and clothes for sleep, lullaby and feeding. During the day, the ritual can be left the same, only without hygiene procedures. The ritual should be repeated daily and consist of the same actions. It is carried out by one person - either mom or dad.
-
Check that the room has suitable sleeping conditions for an infant: the temperature is no more than 21-23 degrees in winter and no more than 25 degrees in summer, and the air humidity is approximately 40-60%.
 It is also important to darken the room for all dreams, including daytime, and use white noise.
It is also important to darken the room for all dreams, including daytime, and use white noise. -
Organize the rest of the baby in the crib. The last daytime nap can be done outside in a stroller.
-
Extend the child's sleep by any means, if the morning and afternoon sleep lasts no more than 30-40 minutes.
-
If nothing helps and the baby still constantly wakes up at night, neither motion sickness, nor the chest, nor the nipple work to prolong sleep, then it is worth teaching the child to fall asleep on his own.
-
Make sure your baby gets enough sleep. Otherwise, overwork will accumulate, which will manifest itself in frequent nocturnal awakenings. This is where following a routine can help.
Check our chart to see if your baby is getting enough sleep
How many feeds does a baby need at night?
At four months old, breast milk or formula is still the main food in his diet.
The diet of the breastfed baby this month will consist of feedings every 3-4 hours. The volume of breast milk drunk at a time will be about 118-210 ml. The duration of feeding may vary.
When formula-fed, the volume of the mixture should be calculated from the recommendations of the pediatrician. This is usually 1/6 of the child's actual body weight. At four months, the baby will eat 800-1000 ml. mixture per day every 3-4 hours during the day.
The baby is becoming more and more interested in the world around him and during feeding he can start to be distracted, not eat up and make up for hunger at night. Therefore, it is better to feed the baby in a calm environment.
2-3 feedings are enough at night for a four-month-old baby.
Does the baby wake up at night shortly after feeding and start crying? Instead of refeeding him, try other ways to calm him down, such as petting his tummy and peeing. So the child will not form the habit of falling asleep only with the help of feeding.
So the child will not form the habit of falling asleep only with the help of feeding.
Should we start complementary foods at 4 months? WHO (World Health Organization) recommends introducing complementary foods from 6 months. Therefore, before introducing adult food, it is worth consulting with a pediatrician.
Physical development of a 4-month-old baby
The fourth month is the age when a child already knows a lot and masters new skills.
He is already confidently using both hands at the same time and grasping toys, colorful and shiny objects near him. Soft books, teething rings are a good choice for this age.
For reading, choose large books with different textures inside to develop tactile sensations. Read and sing to your baby every day for a few minutes. This develops the attention and speech of the child. Take a closer look at children's bathing books - their puffy pages are easy to flip through. In addition, they still often squeak, and the pictures in them are bright.⠀
In addition, they still often squeak, and the pictures in them are bright.⠀
The baby already holds his head and chest well, being on his stomach and pushing off the surface with his hands. Also, the child can already begin to roll over from his stomach to his back and push with his legs.
The baby sees better, begins to distinguish colors and notice objects in the distance, although he still prefers to look at faces and things near him. During walks in the fresh air, tell the baby about the surrounding objects, point to them and describe them.
From the age of 4 months, the first teeth erupt. If the baby's salivation increased, redness appeared around the mouth, he began to bite, refuse to eat, became moody, his night's sleep worsened, then most likely the child has a new tooth. In the acute period, teething rings, anesthetic gel recommended by the pediatrician, more attention and warmth from the mother's side will help.