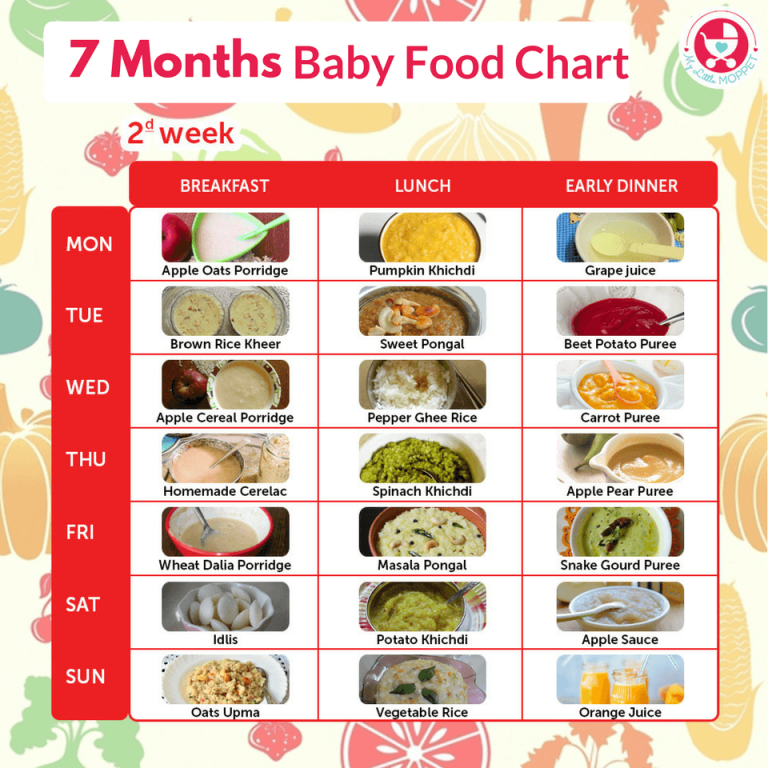
Baby foods after 6 months
Baby's first foods: The 10 best foods for babies
These 10 first foods are ideal for your baby because they're full of essential nutrients, reasonably priced, easy to prepare, and delicious. Avocados contain healthy fats, while bananas are loaded with potassium. Blueberries are bursting with antioxidants, whereas broccoli offers fiber and folate. Both lentils and meat are packed with protein. Prunes can help with constipation, and yogurt helps form healthy bones and teeth. Sweet potatoes and winter squash are great sources of beta-carotene and vitamin C.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, it's important to offer your baby a variety of healthy foods. There are lots of healthy, baby-friendly foods out there, but these 10 recommended by doctors and dietitians alike stand out from the pack. From vitamin-rich fruits and veggies to meats and beans loaded with protein, these superfoods are full of essential nutrients, reasonably priced, easy to prepare, and delicious.
Many are also favorite first foods. Before introducing solids, talk to the doctor about your baby's readiness for solids, and which foods to introduce and when. Then introduce foods one at a time, waiting at least three days after each new food to watch for any allergic reaction.
Avocados
BabyCenter parents are all about avocado as a first food. This buttery fruit-vegetable is rich in healthy unsaturated fats that help boost brain development. In fact, the fat composition of avocados is somewhat similar to that of breast milk.
Serving ideas: Mash avocado with a fork, or make baby guacamole.
Bananas
Known as a good source of potassium, this grab-and-go fruit also contains vitamins B6 and C, fiber, and magnesium.
Serving ideas: Make banana and mango puree. Or, for your little one's first smoothie, puree banana and peach chunks with whole-milk yogurt.
Blueberries
Blueberries are bursting with antioxidants. The deep, brilliant blue of these berries comes from flavonoids that benefit your baby's eyes, brain, and even urinary tract.
Serving ideas: Blend or mash blueberries well and swirl a spoonful of the juicy purple puree into yogurt, or top silky coconut milk rice pudding with blueberry compote.
Broccoli
This cruciferous vegetable is a rich source of essential nutrients, including fiber, folate, and calcium. Introduce your baby to broccoli's bold flavor early, and you'll be expanding their tastes and encouraging a lifelong love of green vegetables.
Advertisement | page continues below
Serving idea: Steam until soft, cut into pieces small enough for your child to eat safely, and then chill. Steaming takes the bite out of broccoli, and some babies prefer the texture and taste when it's cold.
Lentils
Beans and other legumes pack lots of lean protein and fiber. But unlike larger beans, little lentils simmer into a pleasing mush just right for baby bites. They're also one of the cheapest healthy foods you can buy.
Serving ideas: Cook finely diced carrots along with the lentils. As your baby gets older, double up on nutrient-rich foods by making lentil and spinach stew.
As your baby gets older, double up on nutrient-rich foods by making lentil and spinach stew.
Meat
Lack of iron can cause anemia. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends meat as a first food because it's such a great source of protein, zinc, and iron, especially red meat and dark poultry meat. Plus, babies absorb iron more easily from meat than from iron-fortified cereals, another common first food.
Serving ideas: If your baby is new to solids, try our easy turkey or chicken puree recipe. As they get older, introduce new flavors with chicken curry with green beans and zucchini or shepherd's pie.
Prunes
Whether you call them "prunes" or "dried plums," these humble fruits don't sound glamorous – but they're soft, sweet, and full of fiber. Your baby may suffer from constipation when switching to solids, as it's a big change for their system. Add pureed prunes to your baby's diet to aid digestion and keep things moving.
Serving ideas: Serve pureed prunes alone or mixed with other foods, such as oatmeal, cereal, or applesauce, for a naturally sweet treat.
Sweet potatoes
Sweet potatoes are one of the more popular first foods for babies, who tend to like both their sweetness and texture. These colorful root vegetables are packed with beta-carotene, vitamin C, and minerals, including iron and copper.
Serving ideas: Serve sweet potato puree alone or swirled into pureed chicken or turkey.
Winter squash
Orange- or yellow-fleshed hard winter squashes such as butternut, acorn, and pumpkin boast many benefits, one of which is they're exceptionally rich in beta-carotene, recognized for being great for eyes. Squash is also an excellent source of vitamin C. Natural sweetness and a creamy texture add to the appeal of winter varieties.
Serving ideas: Roast a winter squash like butternut, scoop out the flesh, and puree it for an easy first food. As your baby gets older, introduce new flavors and textures with dishes like smashed chickpea and butternut chili.
Yogurt
Creamy yogurt is rich in calcium and vitamin D, necessary for healthy bones and teeth. Your baby can have it at 4 to 6 months, long before they'll be ready for cow's milk.
Your baby can have it at 4 to 6 months, long before they'll be ready for cow's milk.
Opt for plain yogurt with no added sugar. Also look for a brand with the most live cultures, which help regulate the good bacteria in your baby's digestive tract. Make sure you pick up whole-milk yogurt – babies need the calories from fat.
Serving ideas: Yogurt is fine on its own, or swirl in pureed berries or other fresh fruit, applesauce, or mashed avocado.
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Foods to avoid feeding your baby
Foods to avoid giving your baby include honey, cow's milk, soy milk, fruit juice, sugar-sweetened beverages, unpasteurized foods, and foods with added sugars or too much sodium. Choking hazards are a serious concern, so don't offer large chunks, raw vegetables, nuts and seeds, hard or crunchy foods, sticky foods, or dollops of nut butters. If allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema, check with the doctor about introducing allergenic foods such as egfgs, peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, and shellfish.
As your baby grows, they'll be eager to sample food from your plate – and you'll be eager to introduce some variety. But not all foods are safe for your child.
Foods to avoid: Birth to 6 months
All food and beverages except breast milk or formula: The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends feeding your baby only breast milk or formula for about the first 6 months.
Foods to avoid: 6 to 12 months
Honey: Honey can harbor spores of Clostridium botulinum, which causes botulism. An adult's intestinal tract can prevent the growth of these spores, but in a baby the spores can grow and produce life-threatening toxins.
Cow's milk and soy milk: Stick with breast milk or formula until your child's first birthday. Why? Your baby can't digest the proteins in cow's milk and soy milk during the first year, and these beverages contain minerals in amounts that can damage your baby's kidneys.
Fruit juice and sugar-sweetened beverages: Juice (even 100 percent fruit juice) and sugar-sweetened beverages such as soda and sports drinks aren't recommended for children under 12 months. When babies fill up on these drinks, they miss out on getting the nutrients they need. And though fruit juice seems healthy, it has far more calories and sugar than fresh fruit and can contribute to weight gain and tooth decay. The AAP recommends no fruit juice for babies, and just 4 ounces per day maximum for toddlers ages 1 to 3.
Unpasteurized foods: Don't give babies and children unpasteurized juice or cider or unpasteurized (raw) dairy products. These may contain harmful bacteria and parasites that can lead to serious illness or death.
Added sugars: Avoid added sugar in the diets of children under age 2, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services advise. These are sugars and syrups that are added to foods or beverages when they are processed or prepared. This doesn't include sugars found in milk and fruits. Too much added sugar in children's diets has been linked to obesity and increased risk for future health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and avoid those that list 1 g or more of "Added Sugars."
This doesn't include sugars found in milk and fruits. Too much added sugar in children's diets has been linked to obesity and increased risk for future health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. Check the Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods, and avoid those that list 1 g or more of "Added Sugars."
Too much sodium: Sodium is an essential nutrient primarily consumed as salt. However, too much can be harmful. Children this age don't need more than 1,200 mg of sodium per day, according to the USDA and DHHS. Check the Nutrition Facts label when buying canned, frozen, and packaged foods.
Large chunks: A chunk of food can get stuck in your baby's throat. The AAP recommends that you cut food into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch. For example, cut up fruits such as grapes, cherry tomatoes, and strawberries, and shred or finely chop meats, vegetables, and cheeses.
Advertisement | page continues below
Raw vegetables: Soft-cook vegetables such as carrots, celery, and broccoli, and dice, shred, or cut them into pieces no larger than 1/2 inch before serving.
Nuts and seeds: Remove seeds and pits from fresh fruit such as watermelon, peaches, plums, and cherries before serving. And don't feed your baby nuts or seeds, such as sunflower or pumpkin seeds. Seeds may be too small to choke on but can get stuck in a child's airway and cause an infection.
Hard or crunchy foods: Nuts, popcorn, and pretzels are all choking hazards, as are all hard candies and cough drops.
Sticky foods: Chewing gum and sticky foods – such as jelly or gummy candies, dried fruit, and marshmallows – can get lodged in your baby's throat. Stringy, melted cheese can also be a choking hazard.
Nut butter: The sticky consistency of peanut butter and other nut butters can make it hard for your baby to swallow it. Spread nut butter thinly on bread or crackers. Or thin it with water or applesauce.
Learn more about preventing choking in young children.
Find out about choosing safe finger foods and which foods can be unsafe for toddlers and children up to age 5.
The latest on children and food allergies
Doctors used to recommend waiting until age 1 or even later to introduce solid foods that are common allergens, especially with children at risk for allergies. But the AAP has changed its tune, because studies show that these delays don't help prevent allergies and may even increase the risk of them.
You may be told to introduce foods one at a time, waiting three to five days after each new food to watch for any allergic reaction. Or your doctor may say it's fine to start multiple new foods at once. If you believe your baby is likely to have food allergies – for example, if allergies run in your family or your baby has eczema – check with their doctor to determine the best strategy for introducing allergenic foods, which include eggs, milk, peanuts, wheat, soy, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
Read more about food allergies in children.
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
diet for a 6-month-old baby with breast and artificial feeding, an approximate menu for a week in the table, a diet for a day
Published: 02/10/2021
Reading time: 4 min.
Number of reads: 228416
Author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna
Pediatrician, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Allergist-Immunologist
Changes in a child in the first year of life are very rapid, and each month is not like another. The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different.
Content: Hide
- The first feeding of 6 months
- The start of complementary foods in 4-5 months
- The second half of life
- for a week for a child at 6 months
The first lure of 6 months
If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods.
However, the rate of expansion of the child's diet in this situation will be accelerated. Before the 8th month of life, it is necessary to introduce all basic food groups into the baby’s menu, since in the second half of the year the need for additional intake of nutrients and micronutrients is very high. Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced.
Complementary feeding starts at 4-5 months
In today's life, the nutrition of a nursing mother, unfortunately, is not always complete. Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions.
Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions.
If a child is bottle-fed, then by the 4th month of life, the baby will not have enough adapted formula alone, and in this group of children, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods usually shifts a month earlier than in breast-fed babies. Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture.
Fruit puree and juice can be another possible complementary food for children under 6 months of age without allergy symptoms. In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month.
Second six months of life
Children over 6 months of age can supplement their diet with cereals containing gluten.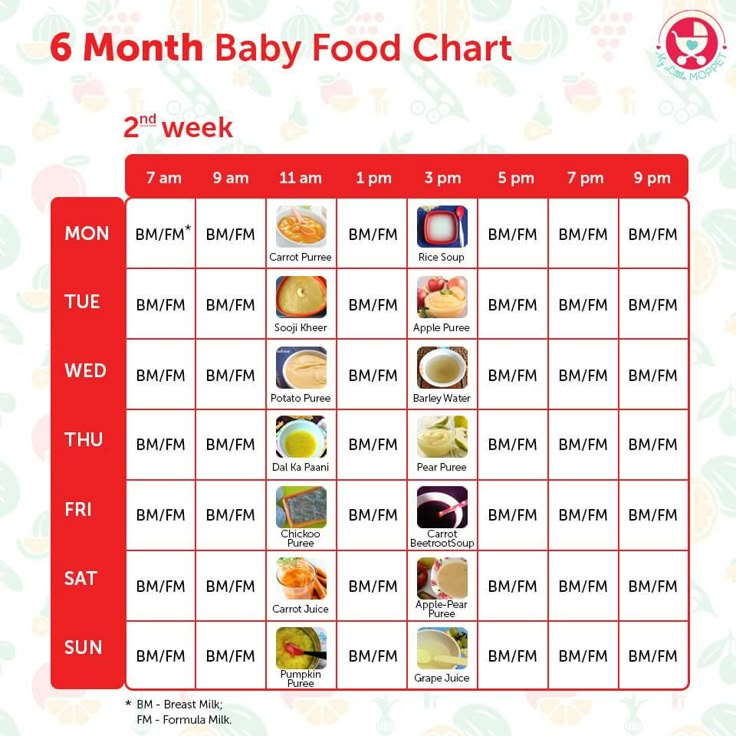 First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life.
From the age of 6 months, the baby's diet is expanded with such important products as meat and cottage cheese. These products are a source of high-quality protein, fats, and are also rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and phosphorus. Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals).
To enrich the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids in the second half of the year, the menu includes vegetable oil in the amount of 3–5 grams per day, which can be added to the complementary food dish. The volume of each feeding is approximately 150-170 ml, and the child can already stand up to 3.5 hours between meals.
The volume of each feeding is approximately 150-170 ml, and the child can already stand up to 3.5 hours between meals.
In the table below, we offer a menu of 6 months for a week for a child who started receiving complementary foods at the age of 4-5 months, and by the time the second half of life begins, dairy-free gluten-free cereals, vegetable and fruit purees have already been introduced into his diet.
1st day
| Meeting | menu | ml/g |
| Breast milk/mixture | 150 | 50 |
| Lunch (12.30) | Vegetable soup with beef, olive oil | 100/30/3 | 9 9006 900 66 9 |
| Afternoon snack (16.00) | Plum puree with cottage cheese | 60/40 |
| Breast milk/formula | 60 066 | |
Lunch (12. 30) 30) | soup puree made of cauliflower and broccoli, olive oil | 80/3 |
| souffle from meat of rabbits | ||
| Afternoon snack (16.00) | Milk porridge "Delicious afternoon snack with Bebi Premium cookies and pears" | 100 | 9007 1
| food intake | menu | ml/g |
| Early morning | breast milk/mixture | 150 | COMLACE (09) cherry Bebi Premium» | 100 |
| 0065 Breast milk/mixture | 150 | |
| children's soluble cookies "BEBIKI" Classic | ||
| Bebi Premium Kids Instant Herbal Tea | 50 | |
| Bedtime 065 Breast milk/formula | 150 | |
Rate the article
(Number of votes: 23, average 4. 8)
8)
Share with friends:
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he smiles happily at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding or have had to switch to formula or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods.
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc.). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them.
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can we wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age.
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well.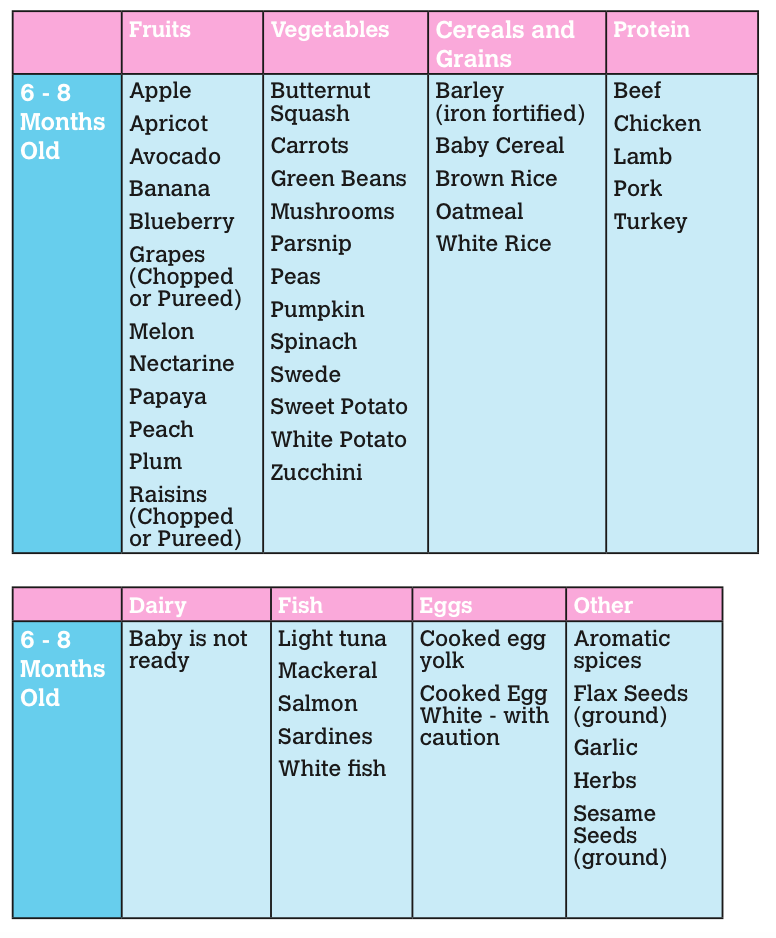
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa.
If the first complementary foods are introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them.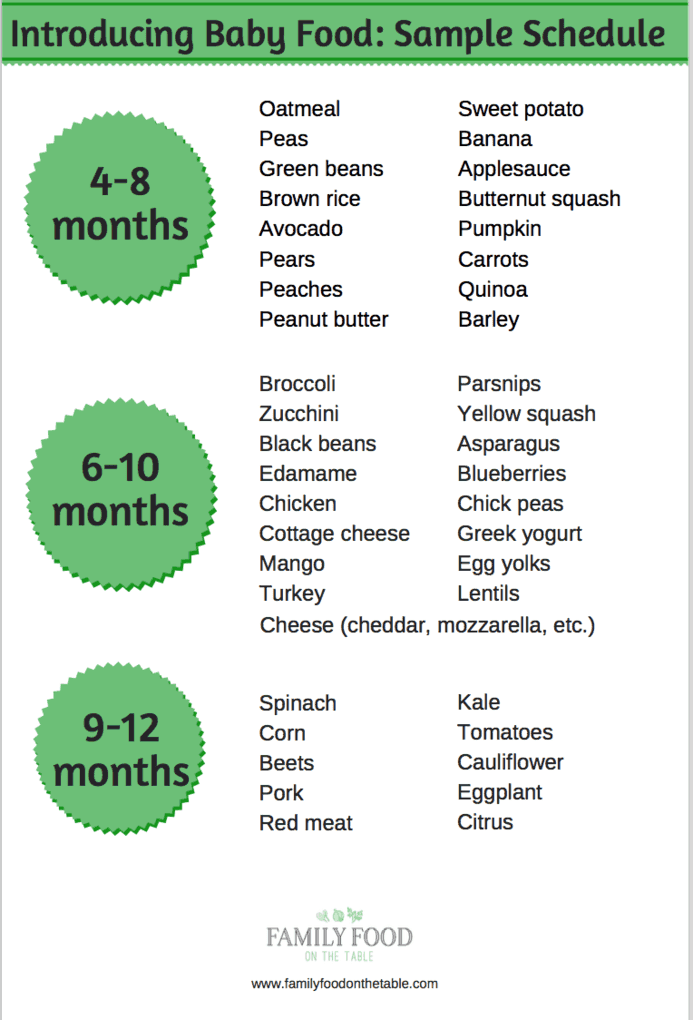 It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity.
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- new products are not introduced in the event of acute illnesses, and before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually "dilute" this product with a new one. For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster.
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby.
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives.
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens.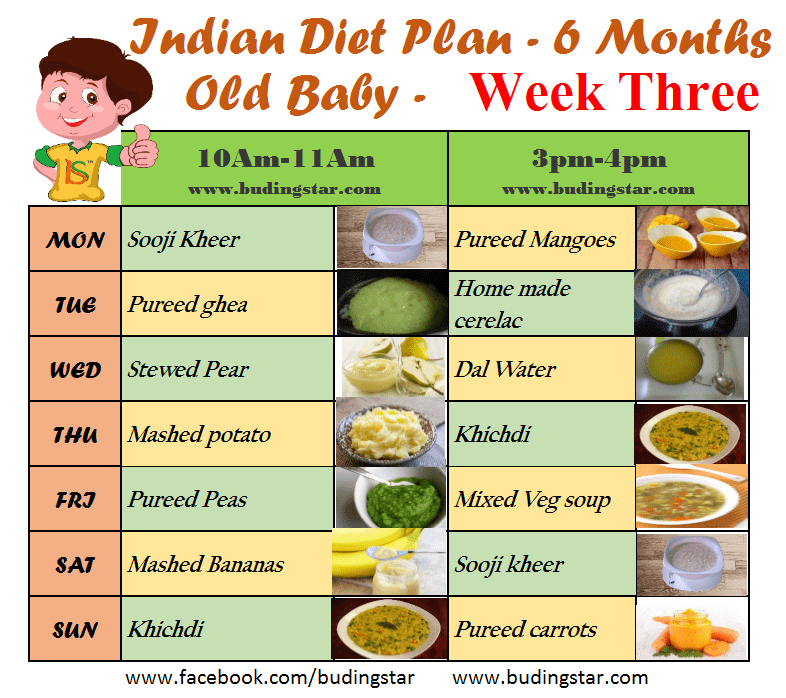 From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml | |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI 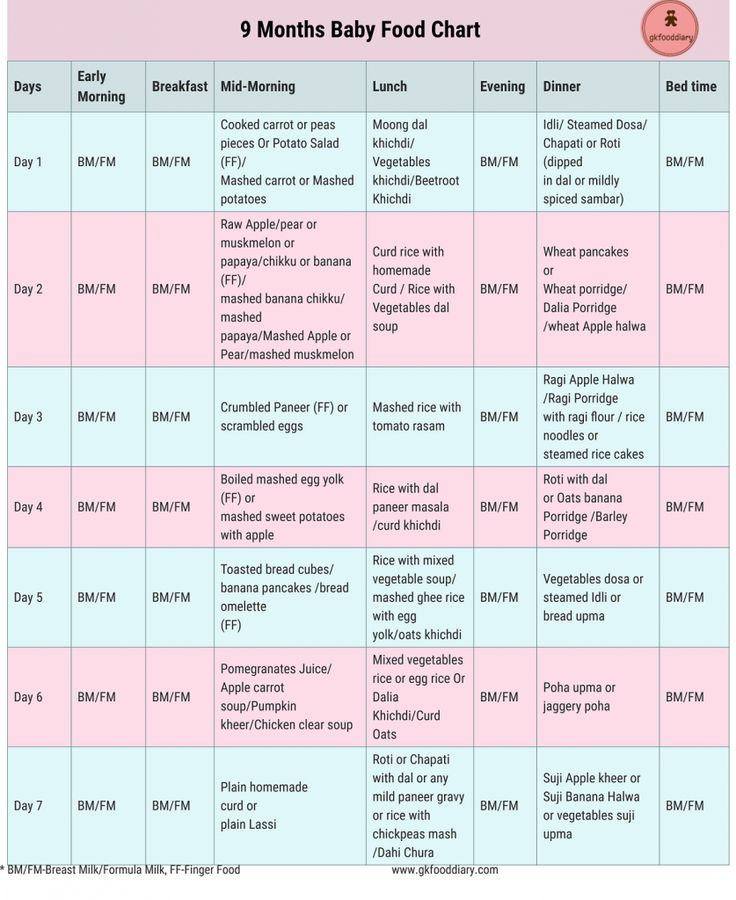
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding
22 hours Breast milk