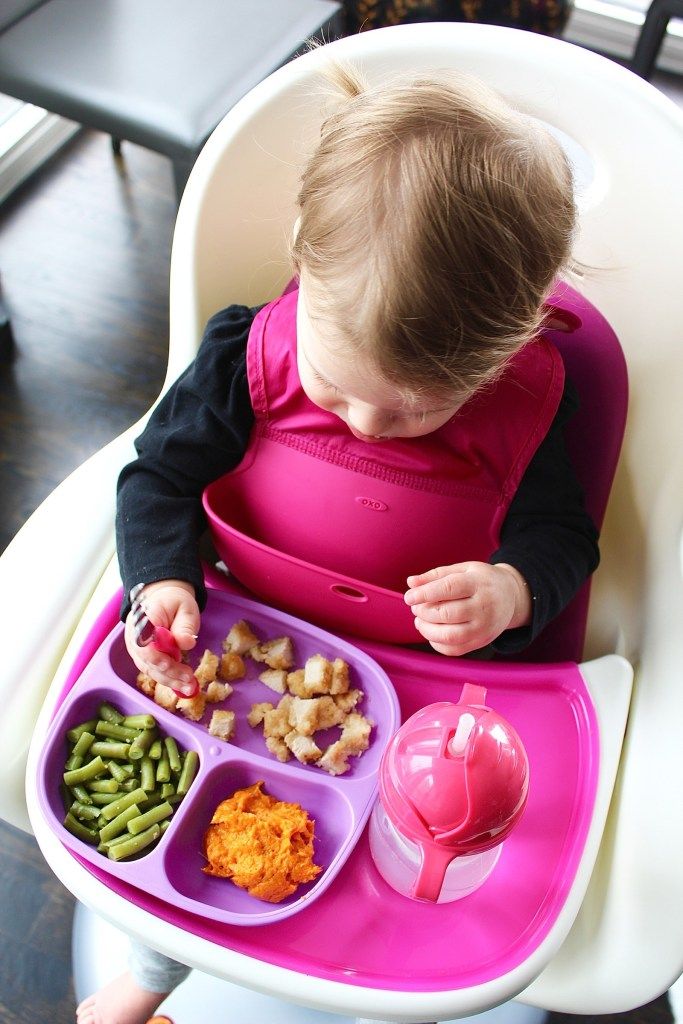
Baby making noise when feeding
The Sounds of Breastfeeding | La Leche League Canada
First time parents are often surprised by the feeding noises that come with breastfeeding a baby. Breastfeeding and parenting books don’t usually mention these sounds. Photos are silent and many expectant parents have never spent time with a breastfeed baby. So, what are the sounds of breastfeeding and what do they tell us?
In the first three to five days your milk volume is small to match your baby’s small tummy size. Your baby may suck several times before you hear a swallowing sound. As the milk volume increases your baby will suck rapidly at the beginning of each feeding to trigger the letdown of your milk (milk ejection reflex). Once your milk starts flowing, your baby will usually suck once or twice for each swallow. A baby who is getting a good mouthful of milk with each suck makes a small gulping noise with each swallow. This is sometimes too quiet to hear. After swallowing, your baby will breathe out with a puff of air that sounds like a “k-ah” sound. After breathing out (exhaling) your baby will breathe in and swallow again, repeating the cycle. When your milk is letting down strongly, your baby will suck, swallow, breath, suck, swallow, breathe in a rhythmic gulp/”k-ah” pattern.
Sometimes you may hear a “clicking” sound. Your baby may or may not also have noticeable dimples in the cheeks with each suck. And you may have sore nipples. These signs, together or individually, may suggest that your baby has not achieved a deep latch. A “click” indicates that your baby is breaking the seal on the breast. This causes your nipple to slip in your baby’s mouth and often creates a sore nipple. If you are hearing clicking, try improving the latch by bringing your baby’s chin deeply onto your breast. Your baby’s nose should tilt away from the breast as your baby’s head tips back. The nose often touches the breast but it shouldn’t be poking into it. You shouldn’t feel like you have to hold your breast back so your baby can breathe. Chin in, nose tilting away, head back is the same position you take when you drink something.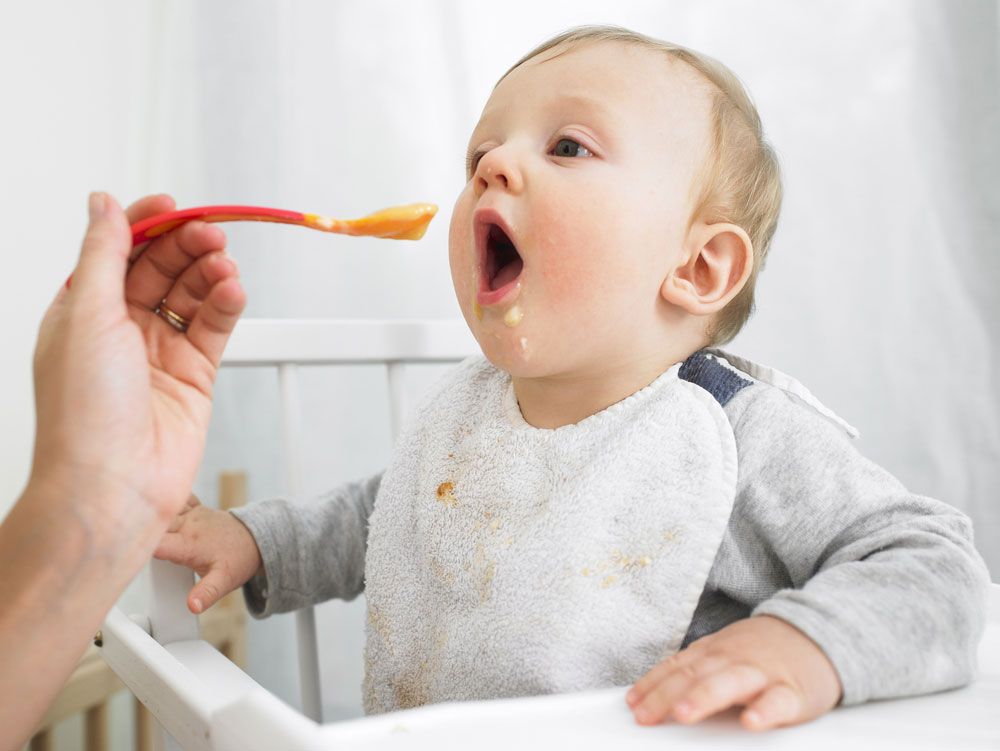 (Try it now, pretend to take a drink of water. See how your chin goes forward and your head tips back?)
(Try it now, pretend to take a drink of water. See how your chin goes forward and your head tips back?)
When you feel that your baby is not latched well, it is important to deal with it right away. If it feels painful you may have to unlatch your baby from the breast by slipping a finger in the corner of her mouth to break the suction. Then you can try latching again. However, usually the latch can be adjusted while your baby is still latched. If your baby’s chin is tucked into her chest, she will not be able to hold onto the breast with her mouth. She will have difficulty swallowing. (Try it now. Tuck your chin into your chest and swallow. It is very hard.) You can try adjusting your baby so that her chin presses into your breast and her head tips back. In this position your baby can drink comfortably, just like you do.
If the clicking, dimpling or sore nipples persist, contact a La Leche League Leader or an International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC) to review your latch. In most cases, an adjustment to the positioning fit between you and your baby quickly resolves the problem. Persistent soreness or poor latch may need further investigation to ensure that your baby does not have a tongue or lip tie or some other issue.
In most cases, an adjustment to the positioning fit between you and your baby quickly resolves the problem. Persistent soreness or poor latch may need further investigation to ensure that your baby does not have a tongue or lip tie or some other issue.
You may hear something that sounds like your milk is hitting the back of your baby’s throat, or like your baby is drowning when your milk lets down. Some mothers have a strong milk ejection reflex. This means that your baby can get a lot of milk with each suck. Your newborn may find this amount of milk hard to handle. This may make your baby pull away from the breast when the flow is strongest. Adjusting your position so you are laying back with your baby on top of your breast can help manage the milk flow. This is another situation in which a La Leche League Leader can help you work out the best positioning for you and your baby.
Sometimes babies make grunting noises or have raspy or squeaky breathing. These sounds may be fine but you should discuss with your healthcare provider or International Board Certified Lactation Consultant (IBCLC).
The most important thing to remember is that breastfeeding should not be painful. If you are experiencing nipple pain something is not right, no matter how good the latch looks from the outside. The next thing to consider is whether or not your baby is producing adequate wet and poopy diapers for his age and is gaining weight appropriately. See How to Know Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk for more information.
If you are pain free and your baby is growing well then the noises of breastfeeding are just funny noises and you will probably learn to love them.
Please consider supporting LLLC.
Updated 2022
When Should a Parent Be Concerned With a Baby’s Noisy Breathing?
| Wendy Healy
Newborn, Pediatrics.
Parents like watching their babies sleep. They find joy in seeing their adorable little ones rest so peacefully. But sometimes babies breathe noisily, making sounds that can cause parents to wonder if something is wrong.
One of the main causes of noisy breathing, or stridor, is called laryngomalacia—a long name for a condition that usually is harmless and resolves on its own. Laryngomalacia is caused by floppy tissue falling over the larynx (voice box) and partially blocking the airway when a child breathes in.
The sound from laryngomalacia is often a high-pitched squeak that often worsens when the baby is agitated, feeding, crying, or sleeping on his or her back. Symptoms usually start within a few weeks or months of birth.
While laryngomalacia is the most common cause of noisy breathing in babies and toddlers, it requires intervention in only a small number of children, according to Jocelyn Kohn, MD, an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist with Stanford Medicine Children’s Health Specialty Services in Walnut Creek. Dr. Kohn also sees patients in the East Bay as part of our partnership with John Muir Health.
“This condition is referred to by some as a birth defect, but I prefer to think of it as an immaturity of the voice box that 90% of children grow out of,” said Dr. Kohn.
Kohn.
In most cases, children will outgrow laryngomalacia by the time they’re 2 and the larynx develops, she added. “As children get bigger and stronger, their larynx gets stronger too,” she said. But a small number of cases will require surgery, which is safe and effective.
Parents may notice these symptoms in their child:
- Noisy breathing (stridor)
- Difficulty feeding
- Not gaining weight
- Gastro reflux (spitting, vomiting, and regurgitation)
- Choking while feeding
- Apnea (stopping breathing during sleep)
- An indentation in the neck and chest with each breath
Severity can vary. “Some babies I see have mild cases, just making a squeaking noise, while others can be more severe. Pediatricians always advise parents to ask their doctor about anything that concerns them,” she said. “This is good advice. But in the case of laryngomalacia, it’s usually nothing that requires treatment.”
In the worst cases, when babies are not sleeping restfully, have difficulty eating, and aren’t gaining weight, it’s best to talk with the doctor. “These may be signs that an intervention by an otolaryngologist is needed,” Dr. Kohn said.
“These may be signs that an intervention by an otolaryngologist is needed,” Dr. Kohn said.
When children with laryngomalacia fail to gain weight, it’s usually because they’re using so much energy just to breathe that they’re exhausted, she said. Breathing difficulties are often seen as an indentation in a child’s chest and neck, indicating that he or she is having trouble getting enough air.
In these cases, specialists take a closer look by inserting a camera down the throat to see what’s happening in the larynx. “Seeing something ourselves can help reassure parents or guide further treatment,” said Dr. Kohn.
If laryngomalacia is worsened by reflux, Dr. Kohn will treat it with medications. Babies can also be positioned to lessen the breathing problem. Most noisy breathing happens when babies are lying flat on their back, which is the correct position for sleeping. Babies who are awake and being watched can be placed on their stomach to help alleviate the problem.
“We tell parents to put gravity on their side. Keeping a baby upright when feeding, frequent tummy time, and positioning them on their stomach while awake all help,” advised Dr. Kohn.
Keeping a baby upright when feeding, frequent tummy time, and positioning them on their stomach while awake all help,” advised Dr. Kohn.
Very severe cases, and those that last past two years, may require surgery, which is effective in most children, according to Dr. Kohn. She performs a supraglottoplasty, which adjusts the supraglottis, the tissue above the vocal cords. Although the surgery requires general anesthesia, it’s minimally invasive, using endoscopes and microscopes inserted down the throat. Excess tissue is removed, and tight areas are released.
“Babies usually spend one night in the hospital and recover well, with most experiencing mild discomfort that resolves quickly. Most babies can start feeding again right after surgery,” Dr. Kohn said.
There are many reasons for noisy breathing, including cysts, hemangiomas, and inhaled objects, in addition to laryngomalacia. In case of anything with a sudden onset, or if a child put something in his or her mouth and can’t breathe, seek emergency care immediately.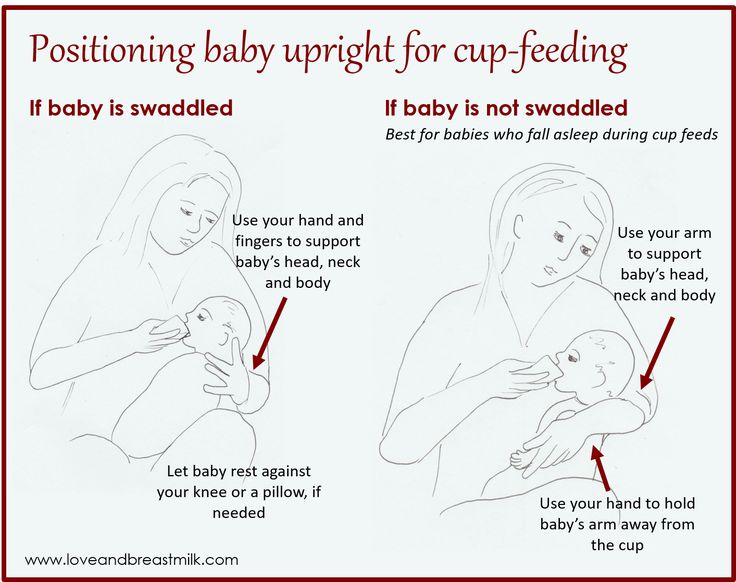
Learn more about laryngomalacia in a HealthTalks podcast from Stanford Medicine Children’s Health.
Authors
Tags: newborn, otolaryngology, pediatrics
Breastfeeding in the first month: what to expect
Not sure how to establish lactation and increase milk production? If you need help, support, or just want to know what to expect, read our first month breastfeeding advice
Share this information
The first weeks of breastfeeding are a very stressful period. If at times you feel like you can't handle it, know that you are not alone. Feeding your baby all day long is completely natural and helps produce breast milk, but can be quite tiring at times. Be patient, think about yourself and remember: after the first month, when milk production stabilizes, it will become easier.
How often should a baby be breastfed?
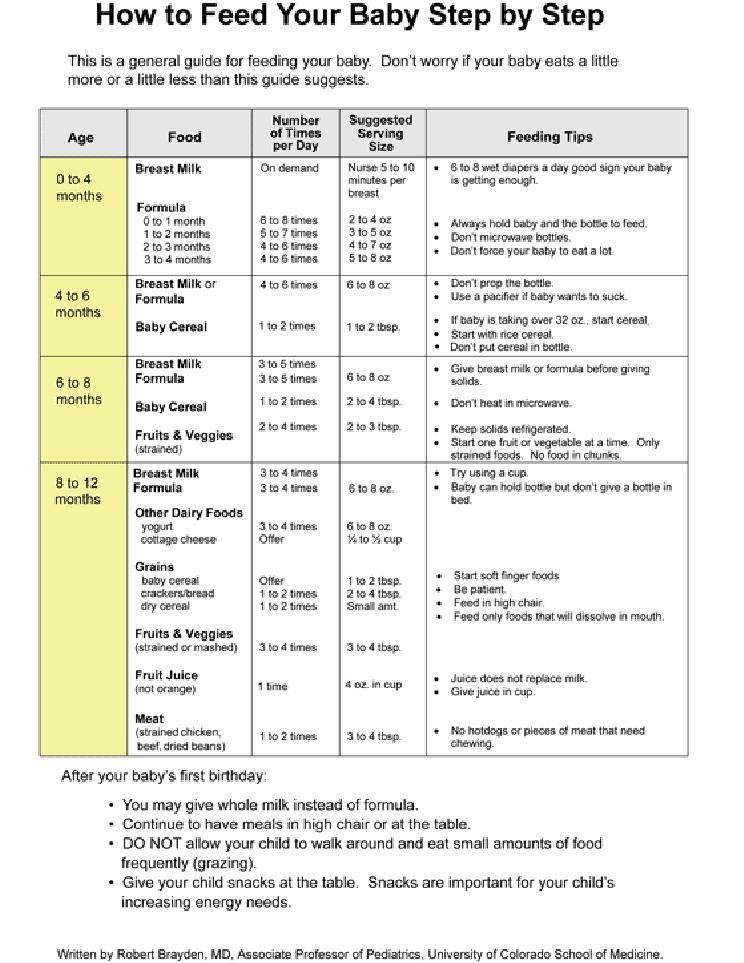
Babies are born with a small stomach that grows rapidly with increasing milk production: in the first week it is no larger than an apricot, and after two weeks it is already the size of a large chicken egg.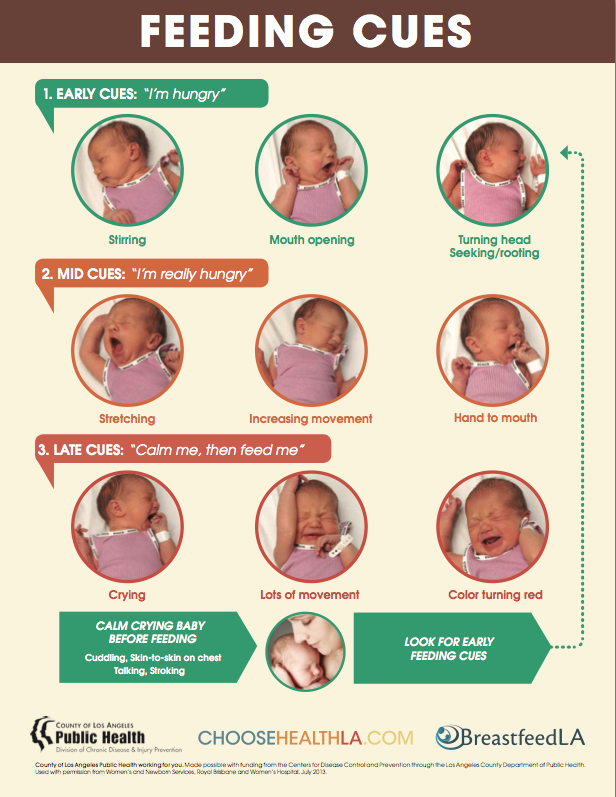 1.2 Let the child eat as much as he wants and when he wants. This will help him quickly regain the weight lost after birth and grow and develop further.
1.2 Let the child eat as much as he wants and when he wants. This will help him quickly regain the weight lost after birth and grow and develop further.
“Be prepared to feed every two to three hours throughout the day. At night, the intervals between feedings can be longer: three to four or even five hours, says Cathy Garbin, a recognized international expert on breastfeeding. Some eat quickly and are satiated in 15 minutes, while others take an entire hour to feed. Do not compare your breastfeeding regimen with that of other mothers - it is very likely that there will be nothing in common between them.
At each feed, give your baby a full meal from one breast and then offer a second one, but don't worry if the baby doesn't take it. When the baby is full, he lets go of his chest and at the same time looks relaxed and satisfied - so much so that he can immediately fall asleep. The next time you feed, start on the other breast. You can monitor the order of the mammary glands during feeding using a special application.
Why does the child always ask for a breast?
The first month is usually the hardest time to breastfeed. But do not think that because the baby is constantly hungry and asks for a breast almost every 45 minutes, then you do not have enough milk.
In the first month, the baby needs to eat frequently to start and stimulate the mother's milk production. It lays the foundation for a stable milk supply in the future. 3
In addition, we must not forget that the child needs almost constant contact with the mother. The bright light and noise of the surrounding world at first frighten the baby, and only by clinging to his mother, he can calm down.
Sarah, mother of three from the UK, confirms: “Crying is not always a sign of hunger. Sometimes my kids just wanted me to be around and begged for breasts to calm them down. Use a sling. Place the cradle next to the bed. Don't look at the clock. Take advantage of every opportunity to relax. Forget about cleaning. Let those around you take care of you. And not three days, but six weeks at least! Hug your baby, enjoy the comfort - and trust your body."
Let those around you take care of you. And not three days, but six weeks at least! Hug your baby, enjoy the comfort - and trust your body."
Do I need to feed my baby on a schedule?
Your baby is still too young for a strict daily routine, so
forget about breastfeeding schedules and focus on his needs.
“Volumes have been written about how to feed a baby on a schedule, but babies don't read or understand books,” Cathy says. - All children are different. Some people can eat on a schedule, but most can't. Most often, over time, the child develops his own schedule.
Some mothers report that their babies are fine with scheduled feedings, but they are most likely just the few babies who would eat every four hours anyway. Adults rarely eat and drink the same foods at the same time of day - so why do we expect this from toddlers?
Offer your baby the breast at the first sign of hunger. Crying is already the last stage, so be attentive to early signs: the baby licks his lips, opens his mouth, sucks his fist, turns his head with his mouth open - looking for the breast. 4
4
What is a "milk flush"?
At the beginning of each feed, a hungry baby actively sucks on the nipple,
thereby stimulating the milk flow reflex - the movement of milk through the milk ducts. 5
“Nipple stimulation triggers the release of the hormone oxytocin,” explains Cathy. “Oxytocin is distributed throughout the body and causes the muscles around the milk-producing glands to contract and the milk ducts to dilate. This stimulates the flow of milk.
If the flushing reflex fails, milk will not come out. This is a hormonal response, and under stress it may not work at all or work poorly. Therefore, it is so important that you feel comfortable and calm when feeding.
“Studies show that each mother has a different rhythm of hot flashes during one feed,” Kathy continues, “Oxytocin is a short-acting hormone, it breaks down in just 30-40 seconds after formation. Milk begins to flow, the baby eats, the effect of oxytocin ends, but then a new rush of milk occurs, the baby continues to suckle the breast, and this process is repeated cyclically.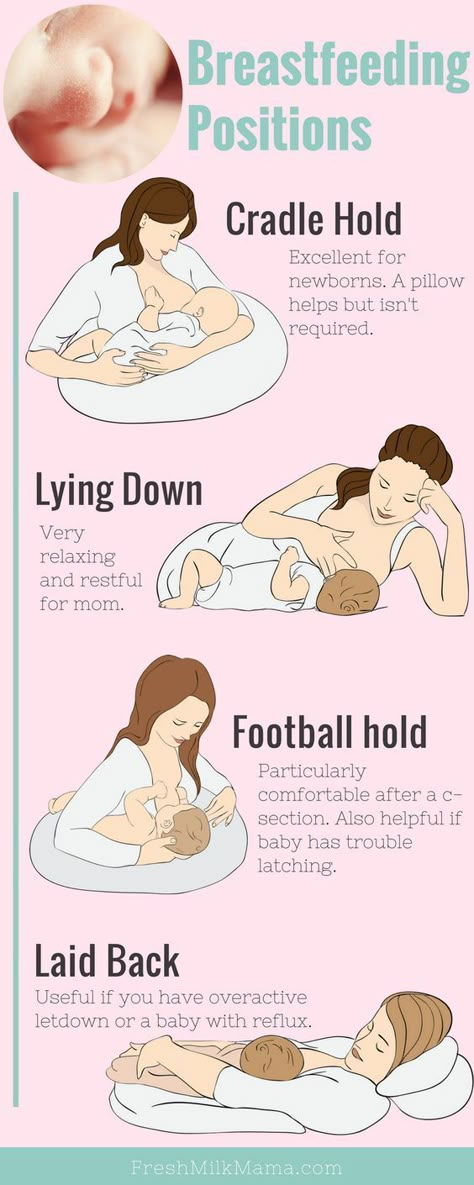 That is why, during feeding, the child periodically stops and rests - this is how nature intended.
That is why, during feeding, the child periodically stops and rests - this is how nature intended.
The flow of milk may be accompanied by a strong sensation of movement or tingling in the chest, although 21% of mothers, according to surveys, do not feel anything at all. 5 Cathy explains: “Many women only feel the first rush of milk. If you do not feel hot flashes, do not worry: since the child eats normally, most likely, you simply do not understand that they are.
How do you know if a baby is getting enough milk?
Since it is impossible to track how much milk a baby eats while breastfeeding, mothers sometimes worry that the baby is malnourished. Trust your child and your body.
After a rush of milk, the baby usually begins to suckle more slowly. Some mothers clearly hear how the baby swallows, others do not notice it. But one way or another, the child himself will show when he is full - just watch carefully. Many babies make two or three approaches to the breast at one feeding. 6
6
“When a child has had enough, it is noticeable almost immediately: a kind of “milk intoxication” sets in. The baby is relaxed and makes it clear with his whole body that he is completely full, says Katie, “Diapers are another great way to assess whether the baby is getting enough milk. During this period, a breastfed baby should have at least five wet diapers a day and at least two portions of soft yellow stool, and often more.”
From one month until weaning at six months of age, a baby's stool (if exclusively breastfed) should look the same every day: yellow, grainy, loose, and watery.
When is the child's birth weight restored?
Most newborns lose weight in the first few days of life. This is normal and should not be cause for concern. As a rule, weight is reduced by 5-7%, although some may lose up to 10%. One way or another, by 10–14 days, almost all newborns regain their birth weight. In the first three to four months, the minimum expected weight gain is an average of 150 grams per week. But one week the child may gain weight faster, and the next slower, so it is necessary that the attending physician monitor the health and growth of the baby constantly. 7.8
But one week the child may gain weight faster, and the next slower, so it is necessary that the attending physician monitor the health and growth of the baby constantly. 7.8
At the slightest doubt or signs of dehydration, such as
dark urine, no stool for more than 24 hours, retraction of the fontanel (soft spot on the head), yellowing of the skin, drowsiness, lethargy, lack of appetite (ability to four to six hours without feeding), you should immediately consult a doctor. 7
What is "cluster feeding"?
When a baby asks to breastfeed very often for several hours, this is called cluster feeding. 6 The peak often occurs in the evening between 18:00 and 22:00, just when many babies are especially restless and need close contact with their mother. Most often, mothers complain about this in the period from two to nine weeks after childbirth. This is perfectly normal and common behavior as long as the baby is otherwise healthy, eating well, gaining weight normally, and appears content throughout the day. 9
9
Cluster feeding can be caused by a sharp jump in the development of the body - during this period the baby especially needs love, comfort and a sense of security. The growing brain of a child is so excited that it can be difficult for him to turn off, or it just scares the baby. 9 If a child is overworked, it is often difficult for him or her to calm down on his own, and adult help is needed. And breastfeeding is the best way to calm the baby, because breast milk is not only food, but also pain reliever and a source of happiness hormones. 10
“Nobody told me about cluster feeding, so for the first 10 days I just went crazy with worry - I was sure that my milk was not enough for the baby,” recalls Camille, a mother from Australia, “It was a very difficult period . I was advised to pump and supplement until I finally contacted the Australian Breastfeeding Association. There they explained to me what was happening: it turned out that it was not about milk at all.
Remember, this is temporary. Try to prepare dinner for yourself in the afternoon, when the baby is fast asleep, so that in the evening, when he begins to often breastfeed, you have the opportunity to quickly warm up the food and have a snack. If you are not alone, arrange to carry and rock the baby in turns so that you have the opportunity to rest. If you have no one to turn to for help and you feel that your strength is leaving you, put the baby in the crib and rest for a few minutes, and then pick it up again.
Ask your partner, family and friends to help you with household chores, cooking and caring for older children if you have any. If possible, hire an au pair. Get as much rest as possible, eat well and drink plenty of water.
“My daughter slept a lot during the day, but from 23:00 to 5:00 the cluster feeding period began, which was very tiring,” recalls Jenal, a mother from the USA, “My husband tried his best to make life easier for me - washed, cleaned, cooked, changed diapers, let me sleep at every opportunity and never tired of assuring me that we were doing well.
If you are concerned about the frequency of breastfeeding, it is worth contacting a specialist. “Check with a lactation consultant or doctor to see if this is indicative of any problems,” recommends Cathy. “Resist the temptation to supplement your baby with formula (unless recommended by your doctor) until you find the cause. It may not be a matter of limited milk production at all - it may be that the child is inefficiently sucking it.
When will breastfeeding become easier?
This early stage is very special and does not last long. Although sometimes it seems that there will be no end to it, rest assured: it will get easier soon! By the end of the first month, breast milk production will stabilize, and the baby will become stronger and learn to suckle better. 2.3 Any problems with latch on by this time will most likely be resolved and the body will be able to produce milk more efficiently so inflammation and leakage of milk will begin to subside.
“The first four to six weeks are the hardest, but then things start to get better,” Cathy assures. It just needs to be experienced!”
The longer breastfeeding continues, the more benefits it brings, from saving on formula and improving sleep quality 11–13 to boosting your baby's immune system 14 and reducing your risk of certain cancers. 15
“When you feel like you're pushing yourself, try to go from feed to feed and day to day,” says Hannah, a UK mom. “I was sure I wouldn’t make it to eight weeks. And now I have been breastfeeding for almost 17 weeks, and I dare say it is very easy.”
Read the resource Breastfeeding Beyond the First Month: What to Expect
Literature
1 Naveed M et al. An autopsy study of relationship between perinatal stomach capacity and birth weight. Indian J Gastroenterol .1992;11(4):156-158. - Navid M. et al. , Association between prenatal gastric volume and birth weight. Autopsy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11(4):156-158.
, Association between prenatal gastric volume and birth weight. Autopsy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1992;11(4):156-158.
2 Neville MC et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volumes in lactating women during the onset of lactation and full lactation .Am J Clinl Nutr . 1988;48(6):1375-1386. at the beginning and at the peak of lactation." Am F Clean Nutr. 1988;48(6):1375-1386.
3 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
4 Australian Breastfeeding Feeding cues ; 2017 Sep [ cited 2018 Feb ]. - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
- Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Feed Ready Signals; September 2017 [cited February 2018]
5 Kent JC et al. Response of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric breast pump. J Human Lact . 2003;19(2):179-186. - Kent J.S. et al., Breast Response to Different Types of Electric Breast Pump Stimulation. J Human Lact (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 2003;19(2):179-186.
6) Kent JC et al . Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395. - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
7 Lawrence RA, Lawrence RM. Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
Breastfeeding: A guide for the medical profession. 7th ed. Maryland Heights MO, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. 1128 p . - Lawrence R.A., Lawrence R.M., "Breastfeeding: A guide for healthcare professionals." Seventh edition. Publisher Maryland Heights , Missouri, USA: Elsevier Mosby; 2010. P. 1128.
8 World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child growth standards; 2018 [cited 2018 Feb] - World Health Organization. [Internet]. Child Growth Standards 2018 [cited February 2018].
9 Australian Breastfeeding Association . [ Internet ]. Cluster feeding and fussing babies ; Dec 2017 [ cited 2018 Feb ] - Australian Breastfeeding Association [Internet], Cluster Feeding and Screaming Babies; December 2017 [cited February 2018].
10 Moberg KU, Prime DK. Oxytocin effects in mothers and infants during breastfeeding. Infant . 2013;9(6):201-206.- Moberg K, Prime DK, "Oxytocin effects on mother and child during breastfeeding". Infant. 2013;9(6):201-206.
11 U.S. Department of Health & Human Services [Internet]. Surgeon General Breastfeeding factsheet; 2011 Jan 20 [cited 2017 Feb] - Department of Health and Human Services [Internet], "Breastfeeding Facts from the Chief Medical Officer", Jan 20, 2011 [cited Feb 2017]
12 Kendall-Tackett K et al. The effect of feeding method on sleep duration, maternal well-being, and postpartum depression. clinical lactation. 2011;1;2(2):22-26. - Kendall-Tuckett, K. et al., "Influence of feeding pattern on sleep duration, maternal well-being and the development of postpartum depression." Clinical Lactation. 2011;2(2):22-26.
13 Brown A, Harries V.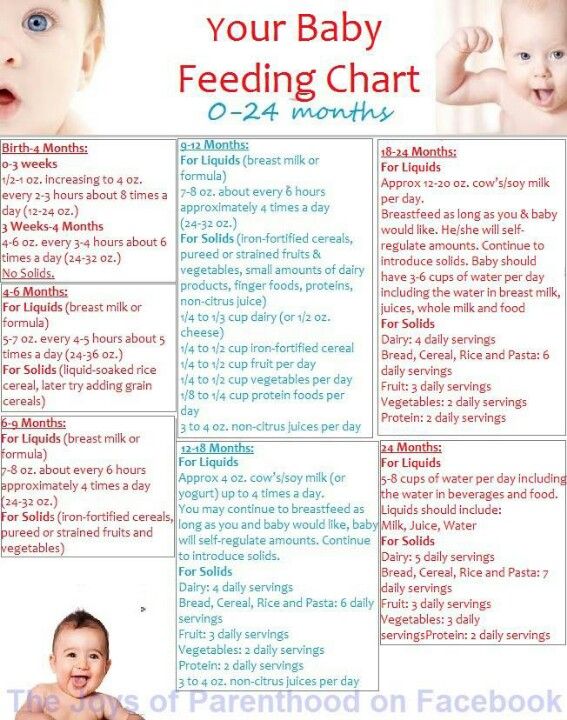 Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
Infant sleep and night feeding patterns during later infancy: Association with breastfeeding frequency, daytime complementary food intake, and infant weight. Breast Med . 2015;10(5):246-252. - Brown A., Harris W., "Night feedings and infant sleep in the first year of life and their association with feeding frequency, daytime supplementation, and infant weight." Brest Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2015;10(5):246-252.
14 Hassiotou F et al. Maternal and infant infections stimulate a rapid leukocyte response in breastmilk. Clin Transl immunology. 2013;2(4). - Hassiot F. et al., "Infectious diseases of the mother and child stimulate a rapid leukocyte reaction in breast milk." Clean Transl Immunology. 2013;2(4):e3.
15 Li DP et al. Breastfeeding and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev .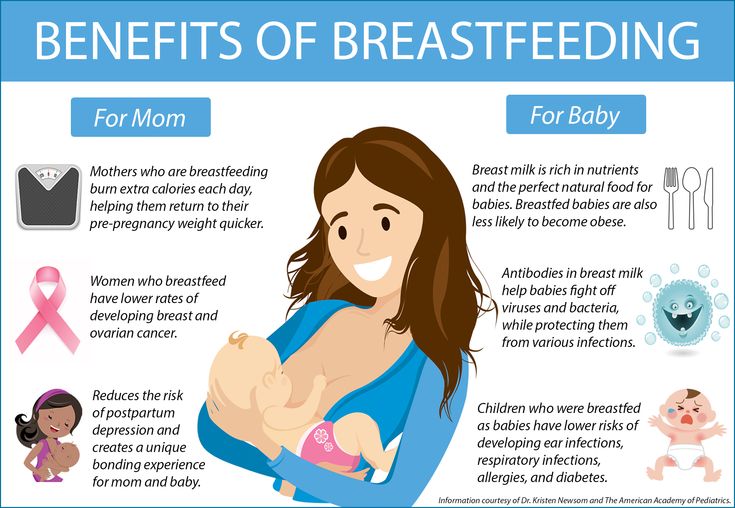 2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
2014;15(12):4829-4837. - Lee D.P. et al., "Breastfeeding and the risk of ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 epidemiological studies." Asia Pas J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4829-4837.
Lactose insufficiency - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
The main food of babies is milk (breast or formula). It contains many different nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates), which, with the help of special digestive enzymes, are broken down into simple components and digested. But in young children, the gastrointestinal tract is still immature, there are few enzymes in it, others are not at all or they are not yet working at full capacity. When the baby grows up, there will be more enzymes, the digestive system will mature, but for now there may be various problems with it.
All milk (women's, cow's, goat's, artificial mixtures) and dairy products contain the carbohydrate lactose, also called "milk sugar". In order for lactose to be absorbed, the lactase enzyme must break it down, but if the child has little or no lactase enzyme, then lactose is not broken down and remains in the intestine. As a result, there is always a large amount of milk sugar in the intestines, which begins to ferment, and where there is fermentation, conditionally pathogenic flora actively reproduces. What we feel during fermentation: intestinal motility increases (it rumbles), plus gas formation increases (the stomach swells). But in an adult, this is usually a one-time situation due to some inaccuracies in nutrition, and it quickly passes. But in babies, everything is different, especially since they lack the enzyme not once, but constantly. What it looks like: The milk sugar lactose retains water, hence loose stools. In the child’s stomach, “rumbles and boils”, colic begins, the stool becomes frothy, greens, mucus and even blood may appear in it. If at first the stool was liquid, then constipation appears, and all this changes in a circle: yesterday there was diarrhea, today and tomorrow there is no stool at all, the day after tomorrow it is liquid again.
In order for lactose to be absorbed, the lactase enzyme must break it down, but if the child has little or no lactase enzyme, then lactose is not broken down and remains in the intestine. As a result, there is always a large amount of milk sugar in the intestines, which begins to ferment, and where there is fermentation, conditionally pathogenic flora actively reproduces. What we feel during fermentation: intestinal motility increases (it rumbles), plus gas formation increases (the stomach swells). But in an adult, this is usually a one-time situation due to some inaccuracies in nutrition, and it quickly passes. But in babies, everything is different, especially since they lack the enzyme not once, but constantly. What it looks like: The milk sugar lactose retains water, hence loose stools. In the child’s stomach, “rumbles and boils”, colic begins, the stool becomes frothy, greens, mucus and even blood may appear in it. If at first the stool was liquid, then constipation appears, and all this changes in a circle: yesterday there was diarrhea, today and tomorrow there is no stool at all, the day after tomorrow it is liquid again. And the most unpleasant thing is endless colic and endless crying, there is no rest for both the parents themselves and the baby. Mom at some point notices that the baby is crying just after feeding, and then a variety of advice falls upon her. “Your milk is bad, better give the mixture,” says the beloved mother-in-law. “Only breasts and nothing else!” - advise breastfeeding gurus. As a result, the mother tries one thing or the other, but neither breast milk nor artificial mixture gives relief to the child. Colic, crying and problems with the stomach and stool continue. The parents are in a panic because they don't understand what is going on. In fact, this is a typical picture of bright lactase deficiency (LN), or insufficient production of the lactase enzyme.
And the most unpleasant thing is endless colic and endless crying, there is no rest for both the parents themselves and the baby. Mom at some point notices that the baby is crying just after feeding, and then a variety of advice falls upon her. “Your milk is bad, better give the mixture,” says the beloved mother-in-law. “Only breasts and nothing else!” - advise breastfeeding gurus. As a result, the mother tries one thing or the other, but neither breast milk nor artificial mixture gives relief to the child. Colic, crying and problems with the stomach and stool continue. The parents are in a panic because they don't understand what is going on. In fact, this is a typical picture of bright lactase deficiency (LN), or insufficient production of the lactase enzyme.
various reasons
There are several types of lactase deficiency, and it is with them that confusion arises.
Congenital lactase deficiency is a genetic and very rare disease (one case in several thousand newborns), it is difficult to confuse it with something, since it is very difficult. The diagnosis is made in the maternity hospital or in the first days after birth, the child does not have lactase at all, he quickly loses weight, he is immediately started to be fed intravenously or through a tube. Some experts (but not doctors) on breastfeeding read once that congenital lactase deficiency is an extremely rare disease, and that’s all - they further began to assure young mothers: “In fact, LN is extremely rare, you don’t have it, you don’t need to listen to doctors ", etc. Yes, congenital LN is a rare disease, but the key word here is "congenital", and there are other types of lactase deficiency.
The diagnosis is made in the maternity hospital or in the first days after birth, the child does not have lactase at all, he quickly loses weight, he is immediately started to be fed intravenously or through a tube. Some experts (but not doctors) on breastfeeding read once that congenital lactase deficiency is an extremely rare disease, and that’s all - they further began to assure young mothers: “In fact, LN is extremely rare, you don’t have it, you don’t need to listen to doctors ", etc. Yes, congenital LN is a rare disease, but the key word here is "congenital", and there are other types of lactase deficiency.
Transient lactase deficiency in infants . And this is exactly the condition that occurs very often. The baby was born, and so far he still has little lactase enzyme, plus little normal intestinal microflora. Hence the colic, and loose stools, and mucus, and greenery, and crying, and the nerves of the parents. After a while, the child's digestive system will fully mature, all enzymes will begin to work actively, the intestines will be populated with what is needed, and "lactase deficiency" will disappear. Therefore, such a LN is called "transient", that is, temporary, or passing. It passes for someone a month after birth, for someone longer - after six to seven months, and there are children in whom lactase deficiency completely disappears only by the year.
Therefore, such a LN is called "transient", that is, temporary, or passing. It passes for someone a month after birth, for someone longer - after six to seven months, and there are children in whom lactase deficiency completely disappears only by the year.
Secondary lactase deficiency. This condition appears if a person has had some kind of intestinal infection, and it does not matter if it is an adult or a baby. For some time after the illness, the child does not tolerate milk (any), and then with proper nutrition and sometimes even without treatment, everything quickly passes.
Lactase deficiency in adults. There are people in whom the lactase enzyme begins to be lacking only in adulthood, this happens for various reasons: for some, lactase ceases to be produced in the right amount after some kind of illness, for other people, the activity of this enzyme simply fades over time by itself. yourself. As a result, at some age, a person begins to tolerate milk and dairy products poorly, although before that everything was fine. The symptoms are the same as in babies: he drank milk and after that the stomach rumbles, boils, and the stool is liquid. Sooner or later, a person realizes that milk is not his product, and simply stops drinking it in its pure form.
The symptoms are the same as in babies: he drank milk and after that the stomach rumbles, boils, and the stool is liquid. Sooner or later, a person realizes that milk is not his product, and simply stops drinking it in its pure form.
what to do
If there is transient lactase deficiency, then what to do with it? First you need to understand if it exists at all. Why does the child have problems with the stomach, stool, why does he cry all the time? Is it neurology, common colic, errors in the mother's diet, an inappropriate mixture (if the baby is bottle-fed), improper breastfeeding technique, lactase deficiency, or a reaction to the weather? It can be difficult to figure it out right away, but if the tests show that there is lactase deficiency, then it is most likely in it. Now what to do next - treat it, wait for the enzymes to mature, or something else? Firstly, everything here will depend on how much the enzyme is lacking and, therefore, on how much LN worries the child and parents. Some children lack the enzyme quite a bit, so their colic is mild and children cry quite normally. Plus, the violation of the stool is also not very bright: there are a couple of times a slightly liquefied stool, but that's all. In other children, the lack of lactase is more pronounced, the child does not cry, but simply yells after each feeding, if at first he gained weight well, then after two months the increase is minimal, problems with stools begin in parallel (day - constipation, day - diarrhea), stool sometimes green, sometimes with mucus. Atopic dermatitis appears on the skin (the skin is the first to react to problems with the gastrointestinal tract). Parents have no rest day or night: the baby cries - he is fed - he cries again, they try to calm him down in other ways. But nothing helps. Mom and dad are in a panic, and no one has the strength anymore.
Some children lack the enzyme quite a bit, so their colic is mild and children cry quite normally. Plus, the violation of the stool is also not very bright: there are a couple of times a slightly liquefied stool, but that's all. In other children, the lack of lactase is more pronounced, the child does not cry, but simply yells after each feeding, if at first he gained weight well, then after two months the increase is minimal, problems with stools begin in parallel (day - constipation, day - diarrhea), stool sometimes green, sometimes with mucus. Atopic dermatitis appears on the skin (the skin is the first to react to problems with the gastrointestinal tract). Parents have no rest day or night: the baby cries - he is fed - he cries again, they try to calm him down in other ways. But nothing helps. Mom and dad are in a panic, and no one has the strength anymore.
If parents see that the child may have signs of lactase deficiency, that he needs help, first of all, you need to look for a good doctor.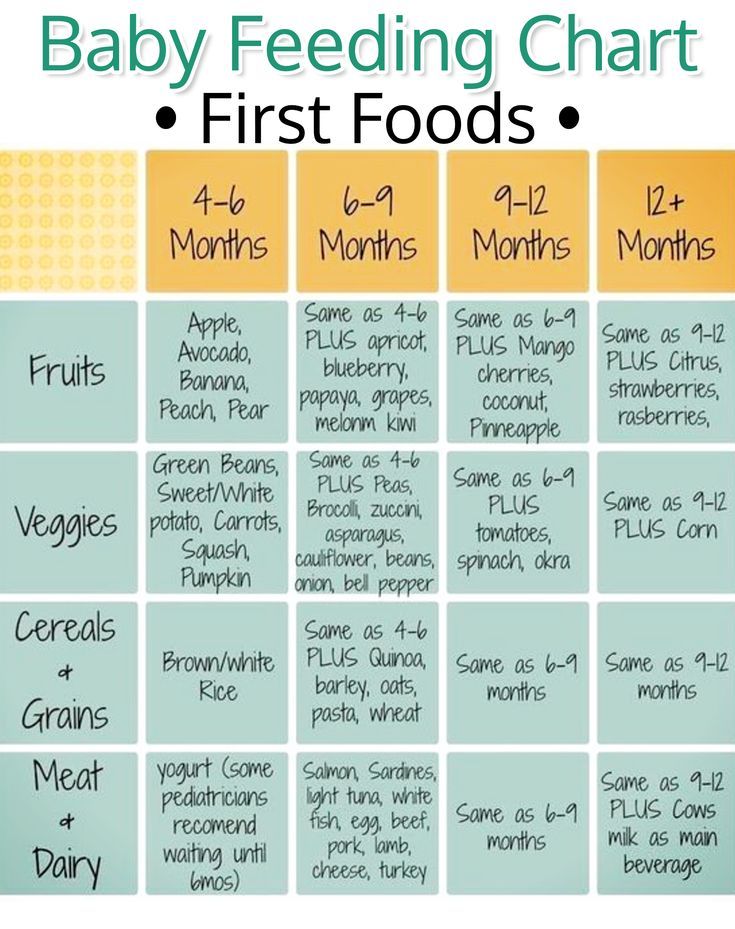 Only an experienced pediatrician will be able to figure out why the baby has colic or green stools, what the numbers in the tests say, and what is the norm for one baby and the pathology for another. And of course, it is not necessary to cancel breastfeeding and immediately prescribe lactose-free or low-lactose artificial mixtures (even as a supplement). By itself, milk sugar lactose is very necessary for a child, when lactose is broken down, its components (glucose and galactose) go to the development of the brain, retina, for the life of normal intestinal microflora. So do not completely eliminate this sugar, you need to help it break down. With a strongly pronounced LN, the missing enzyme is given before each feeding (it has long been learned to produce and it is sold in pharmacies), with a dim clinic, its dose can be reduced. And it is also possible that there is lactase deficiency (even according to tests), but it does not need to be treated, there are almost no symptoms.
Only an experienced pediatrician will be able to figure out why the baby has colic or green stools, what the numbers in the tests say, and what is the norm for one baby and the pathology for another. And of course, it is not necessary to cancel breastfeeding and immediately prescribe lactose-free or low-lactose artificial mixtures (even as a supplement). By itself, milk sugar lactose is very necessary for a child, when lactose is broken down, its components (glucose and galactose) go to the development of the brain, retina, for the life of normal intestinal microflora. So do not completely eliminate this sugar, you need to help it break down. With a strongly pronounced LN, the missing enzyme is given before each feeding (it has long been learned to produce and it is sold in pharmacies), with a dim clinic, its dose can be reduced. And it is also possible that there is lactase deficiency (even according to tests), but it does not need to be treated, there are almost no symptoms.
But what cannot be done is to listen to non-specialists who deny either lactase deficiency itself or its treatment. They see the cause of all problems with the child's stomach and stool either in the wrong technique of breastfeeding, or partially admit that there is immaturity of the enzyme, but this is natural and will pass by itself. Yes, for some, LN is expressed easily and will pass quickly, but what about those parents whose child yells day and night, covered with a crust from atopic dermatitis and stopped gaining weight? Wait for the time to come and the enzymes to mature? Alas, with pronounced lactase deficiency (even if transient), enterocytes (intestinal cells) often suffer, so it is simply necessary to help such a child.
They see the cause of all problems with the child's stomach and stool either in the wrong technique of breastfeeding, or partially admit that there is immaturity of the enzyme, but this is natural and will pass by itself. Yes, for some, LN is expressed easily and will pass quickly, but what about those parents whose child yells day and night, covered with a crust from atopic dermatitis and stopped gaining weight? Wait for the time to come and the enzymes to mature? Alas, with pronounced lactase deficiency (even if transient), enterocytes (intestinal cells) often suffer, so it is simply necessary to help such a child.
If you see your baby showing signs of lactase deficiency, look for a doctor who is committed to breastfeeding and has extensive experience. He will definitely help to find out why the baby is crying, why he has a stomach ache or has problems with stool. And then the life of the parents and the child will return to normal.
"Transient" (temporary) lactase deficiency in someone passes a month after birth, in someone longer - after six to seven months, and there are children in whom lactase deficiency completely disappears only by the age of one
If the tests show that there is a lactase deficiency, then the matter is most likely in it.