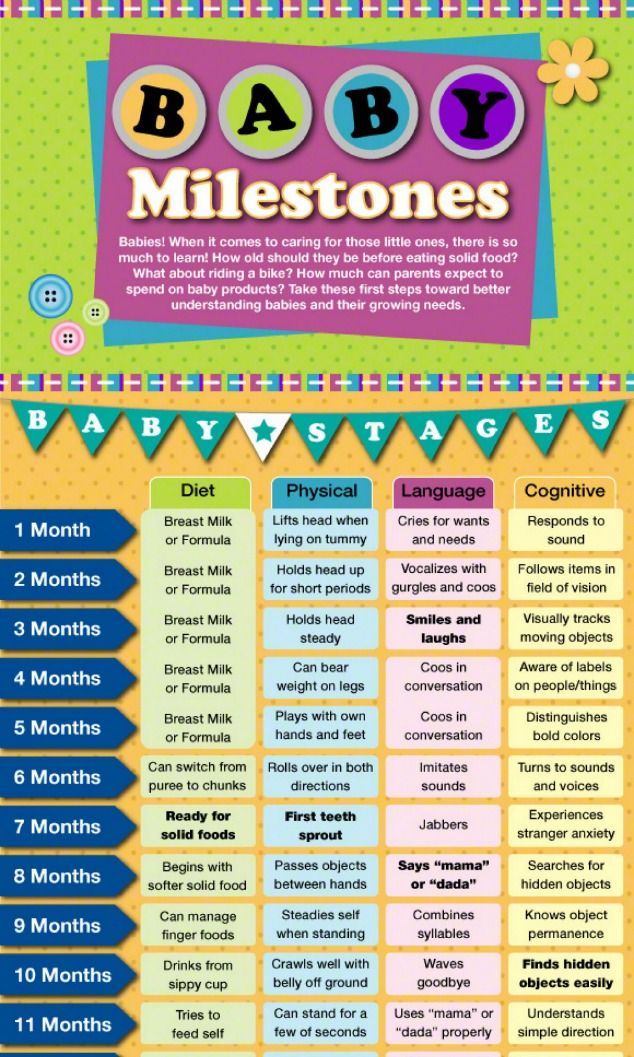
Baby milestones food
Solids, Finger Foods, and More
Written by Gina Shaw
In this Article
- Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
- Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
- Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
- Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
- Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
- Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
- Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
- Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
There are many milestones that need to be achieved when a baby is ready to start to eat solid foods. Here are some of the big ones.
Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
Most pediatricians, and the American Academy of Pediatrics, recommend introducing solid foods to babies when they are between ages 4 and 6 months. That’s when they start to lose the “tongue-thrust reflex” or extrusion reflex, which is important for sucking the breast or bottle when they are younger, but interferes with feeding. Babies at this point can also lift their heads up independently and hold their necks high.
If your baby is around this age, can sit up well with support, and shows interest in the foods they see you eating, it’s probably a good time to venture into feeding your baby solid food. If your baby is exclusively breastfed, it is recommended that you wait until they are 6 months to start solids.
Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
“Chunking up” babies’ food is a process -- obviously, they shouldn’t go straight from rice cereal to raisin bran. But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
Introduce new textures slowly. Good starters are mashed bananas or mashed avocados. You can also use the “staged” store-bought baby foods -- going from the smooth puree of stage 1 to the slightly thicker stage 2 and then the chunkier stage 3 by around 9 months of age. (Babies don’t necessarily have to have a lot of teeth to handle more texture in their foods -- they can often gum soft foods very well!)
(Babies don’t necessarily have to have a lot of teeth to handle more texture in their foods -- they can often gum soft foods very well!)
Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
When babies are ready to eat solid foods, they can sit upright with support and hold up their head and neck. They're capable of sitting in a high chair! That's a serious milestone, but you'll need to follow these safety rules: Always buckle a baby into their chair for safety, even if they are unable to get out with the tray in place. As they get older and become more active, they may be able to squirm out. It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
Babies between ages 7 and 11 months usually tell you they’re ready to eat more grown-up foods by trying to grab them from you. Almost any food that is healthy and nutritious and has a soft texture makes a good finger food, if it’s cut small enough: diced pasta; small pieces of well-cooked vegetables such as carrots, peas, or zucchini; and pea-sized bites of chicken or soft meat. Small, unsweetened round cereals and cereal puffs are also a good choice. Avoid feeding your baby grapes, hot dogs (even cut up), nuts, and hard candy, as they are choking hazards.
Almost any food that is healthy and nutritious and has a soft texture makes a good finger food, if it’s cut small enough: diced pasta; small pieces of well-cooked vegetables such as carrots, peas, or zucchini; and pea-sized bites of chicken or soft meat. Small, unsweetened round cereals and cereal puffs are also a good choice. Avoid feeding your baby grapes, hot dogs (even cut up), nuts, and hard candy, as they are choking hazards.
At first babies “rake” food into their hand, but soon they develop the “pincer grasp” that allows them to pick up small objects between thumb and forefinger. At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
Almost as soon as babies adjust to being fed with a spoon, they'll want to hold and grab the spoon themselves and put it in their mouths. That doesn't mean they're graceful, of course.
Most babies don’t learn to use a spoon effectively until after their first birthday, but let a younger baby who’s interested give it a whirl for practice. Try giving them a soft-tipped spoon to hold while you feed them with another. They can get used to holding the spoon themselves and will also be distracted from grabbing yours.
Try giving them a soft-tipped spoon to hold while you feed them with another. They can get used to holding the spoon themselves and will also be distracted from grabbing yours.
When you think they are ready to actually navigate the spoon into their mouth, try thicker, stickier foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or cottage cheese. Another tip: Put some cream cheese on the spoon and then a few pieces of O-shaped cereal on top. The cream cheese won’t fly everywhere, and the baby can get the experience of actually getting the cereal into their mouth.
Expect a mess! Use a plastic or other waterproof bib, and put a mat under the high chair to make cleanup easier.
Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
Some pediatricians still recommend waiting until children are at least age 1 before offering them certain foods that are considered highly allergenic, like eggs or fish. But current research doesn’t demonstrate any benefit to waiting past a certain age to introduce these foods, unless you have a significant family history of food allergies or other reasons to believe your baby may be predisposed to them.
There is no evidence that introducing highly allergenic foods to children under age 1 makes them any more likely to be allergic to them, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now says it’s fine to give these foods before the baby's first birthday. Many pediatricians are still very cautious about shellfish and peanuts, however, because allergic reactions to these foods can be particularly dangerous.
Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
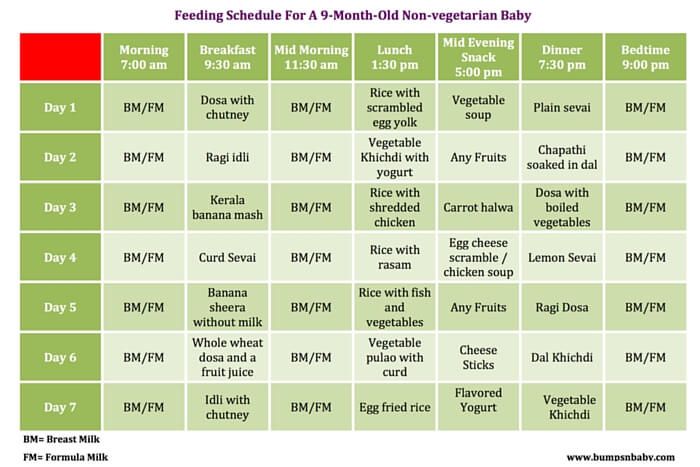
Babies don't need water during their first 6 months of life. They get all the water they need from breast milk or baby formula. Babies under age 6 months should not be given any water at all, because it’s easy to fill up their tiny stomachs -- and they should be filling up on the nutrients they receive from the milk to grow. Once they start eating mostly solid foods, around age 9 months, they can start water with meals using a sippy cup.
If your older baby shows an interest in water that you’re drinking, there’s no harm in letting them have a few sips.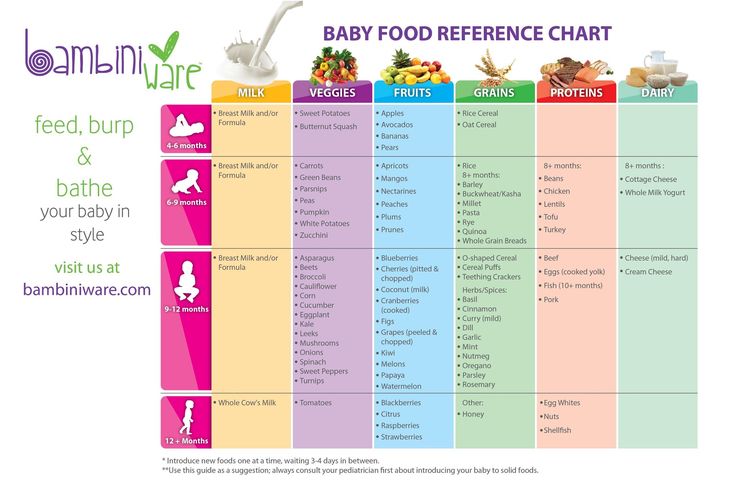 Just don’t let it replace the nutritious breast milk or formula they should be getting.
Just don’t let it replace the nutritious breast milk or formula they should be getting.
Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
Mastering eating with utensils is a long process. Most babies do not become really skilled at it until they are well past their first birthday. Encourage your child to practice safely, and again, be prepared for a little mess. (How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
Solids, Finger Foods, and More
Written by Gina Shaw
In this Article
- Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
- Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
- Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
- Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
- Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
- Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
- Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
- Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
There are many milestones that need to be achieved when a baby is ready to start to eat solid foods.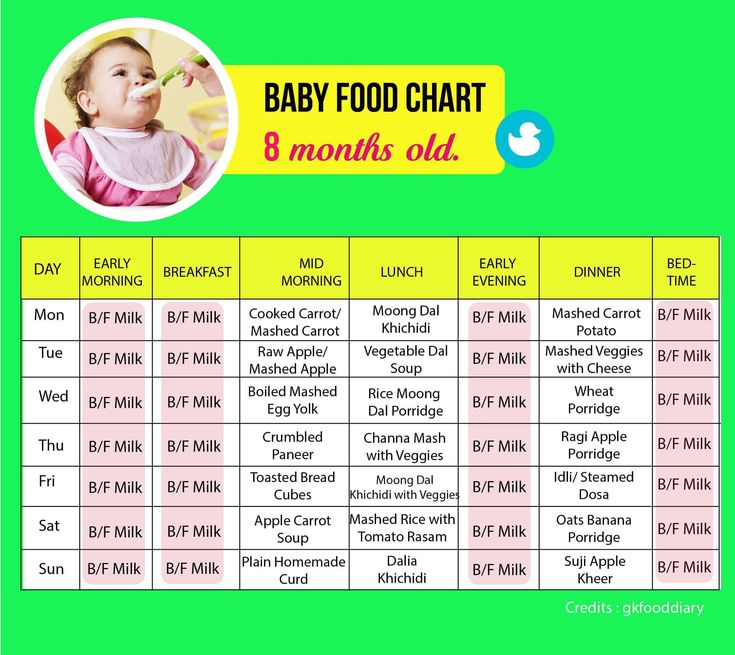 Here are some of the big ones.
Here are some of the big ones.
Baby Milestone 1: When They Can Start Solids
Most pediatricians, and the American Academy of Pediatrics, recommend introducing solid foods to babies when they are between ages 4 and 6 months. That’s when they start to lose the “tongue-thrust reflex” or extrusion reflex, which is important for sucking the breast or bottle when they are younger, but interferes with feeding. Babies at this point can also lift their heads up independently and hold their necks high.
If your baby is around this age, can sit up well with support, and shows interest in the foods they see you eating, it’s probably a good time to venture into feeding your baby solid food. If your baby is exclusively breastfed, it is recommended that you wait until they are 6 months to start solids.
Baby Milestone 2: When They’re Ready to Move From Puree to Chunks
“Chunking up” babies’ food is a process -- obviously, they shouldn’t go straight from rice cereal to raisin bran.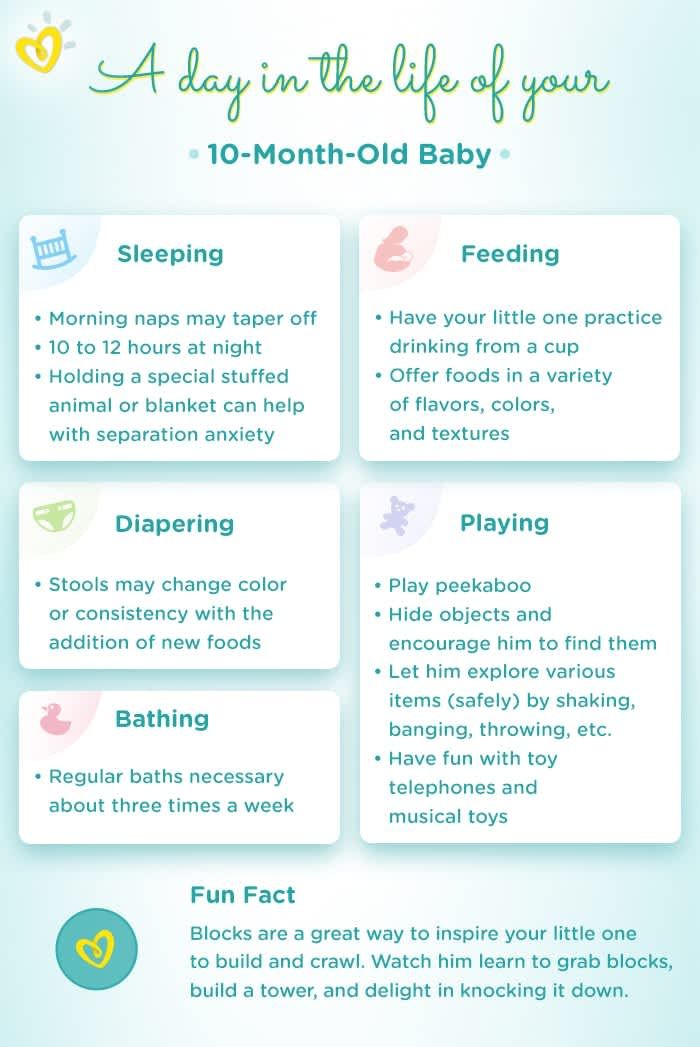 But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
But after the first few weeks of adjusting to eating rather than just drinking their food, your baby should be ready to handle a little more texture in solid foods.
Introduce new textures slowly. Good starters are mashed bananas or mashed avocados. You can also use the “staged” store-bought baby foods -- going from the smooth puree of stage 1 to the slightly thicker stage 2 and then the chunkier stage 3 by around 9 months of age. (Babies don’t necessarily have to have a lot of teeth to handle more texture in their foods -- they can often gum soft foods very well!)
Baby Milestone 3: When They Can Sit in a High Chair
When babies are ready to eat solid foods, they can sit upright with support and hold up their head and neck. They're capable of sitting in a high chair! That's a serious milestone, but you'll need to follow these safety rules: Always buckle a baby into their chair for safety, even if they are unable to get out with the tray in place. As they get older and become more active, they may be able to squirm out.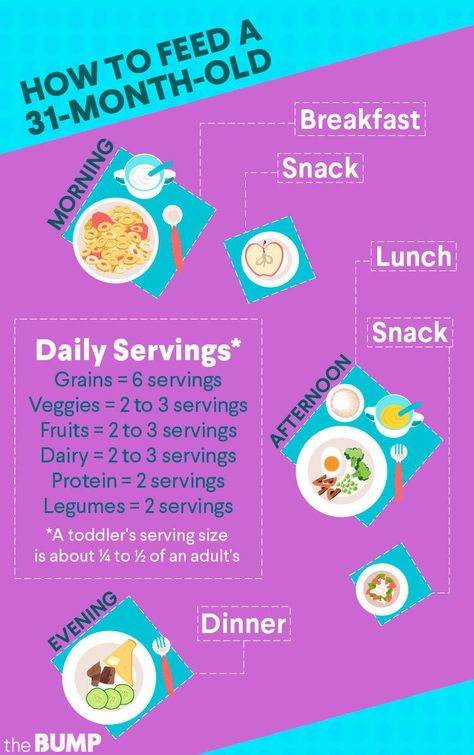 It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
It is a good habit to buckle a child as soon as you place them in their chair -- even if you think there's no chance they could fall out or climb out. You may get distracted for a moment, which happens really easily when we are trying to do a million things at once!
Baby Milestone 4: When They Can Manage Finger Foods
Babies between ages 7 and 11 months usually tell you they’re ready to eat more grown-up foods by trying to grab them from you. Almost any food that is healthy and nutritious and has a soft texture makes a good finger food, if it’s cut small enough: diced pasta; small pieces of well-cooked vegetables such as carrots, peas, or zucchini; and pea-sized bites of chicken or soft meat. Small, unsweetened round cereals and cereal puffs are also a good choice. Avoid feeding your baby grapes, hot dogs (even cut up), nuts, and hard candy, as they are choking hazards.
At first babies “rake” food into their hand, but soon they develop the “pincer grasp” that allows them to pick up small objects between thumb and forefinger. At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
At that point, your baby can become a pro at self-feeding, so encourage finger foods and let your baby explore!
Baby Milestone 5: When They Start Using Spoons
Almost as soon as babies adjust to being fed with a spoon, they'll want to hold and grab the spoon themselves and put it in their mouths. That doesn't mean they're graceful, of course.
Most babies don’t learn to use a spoon effectively until after their first birthday, but let a younger baby who’s interested give it a whirl for practice. Try giving them a soft-tipped spoon to hold while you feed them with another. They can get used to holding the spoon themselves and will also be distracted from grabbing yours.
When you think they are ready to actually navigate the spoon into their mouth, try thicker, stickier foods like yogurt, mashed potatoes, or cottage cheese. Another tip: Put some cream cheese on the spoon and then a few pieces of O-shaped cereal on top. The cream cheese won’t fly everywhere, and the baby can get the experience of actually getting the cereal into their mouth.
Expect a mess! Use a plastic or other waterproof bib, and put a mat under the high chair to make cleanup easier.
Baby Milestone 6: When They Can Try Highly Allergenic Foods
Some pediatricians still recommend waiting until children are at least age 1 before offering them certain foods that are considered highly allergenic, like eggs or fish. But current research doesn’t demonstrate any benefit to waiting past a certain age to introduce these foods, unless you have a significant family history of food allergies or other reasons to believe your baby may be predisposed to them.
There is no evidence that introducing highly allergenic foods to children under age 1 makes them any more likely to be allergic to them, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) now says it’s fine to give these foods before the baby's first birthday. Many pediatricians are still very cautious about shellfish and peanuts, however, because allergic reactions to these foods can be particularly dangerous.
Baby Milestone 7: When They Can Drink Water
Babies don't need water during their first 6 months of life. They get all the water they need from breast milk or baby formula. Babies under age 6 months should not be given any water at all, because it’s easy to fill up their tiny stomachs -- and they should be filling up on the nutrients they receive from the milk to grow. Once they start eating mostly solid foods, around age 9 months, they can start water with meals using a sippy cup.
If your older baby shows an interest in water that you’re drinking, there’s no harm in letting them have a few sips. Just don’t let it replace the nutritious breast milk or formula they should be getting.
Baby Milestone 8: When They Can Completely Feed Themselves
Mastering eating with utensils is a long process. Most babies do not become really skilled at it until they are well past their first birthday. Encourage your child to practice safely, and again, be prepared for a little mess. (How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
(How else will you get the “oatmeal in the hair” pictures that will embarrass them years later?)
Union of Pediatricians of Russia
Nutrition for children from 1 to 3 years of age
The period from 1 to 3 years of life is a crucial stage in the transition to an adult type of nutrition, which has certain features. In order to ensure that all the necessary nutrients enter the child's body and at the same time prevent an excess of individual nutrients, nutrition should be balanced and varied. nine0003
The daily amount of food for children aged 1 to 1.5 years should be 1000-1200 g, from 1.5 to 3 years - 1200-1500 g, the amount of food in one feeding should not exceed 300-350 ml. The diet consists of three main meals per day and two snacks. It is considered optimal when breakfast is 25% of the total energy density of the diet, lunch is 30–35%, dinner is 20%, and additional meals are about 10%. In general, the child can eat the same food as the rest of the family. nine0003
nine0003
In the diet of a child of 1–3 years of age , must be present daily: meat of animals or poultry, dairy and sour-milk products, vegetables, fruits, bread, cereals, vegetable and butter; fish and eggs are included in the diet 2-3 times a week.
Cereal products: bread - 2-3 servings per day, cereals and side dishes - 1 time per day
Fruit and/or vegetables: at least 5 times a day
Dairy products: at least 3 servings per day (including those used to make cereals, yoghurts, fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese, infant formula or breast milk). nine0003
Domestic pediatricians recommend, when compiling a diet for children aged 1–3 years, preference should be given to specialized children's dairy products of industrial production that meet high quality requirements and safety indicators for this age. Most children's dairy products are additionally enriched with vitamins and/or minerals and other biologically active components, taking into account the physiological needs of children of this age.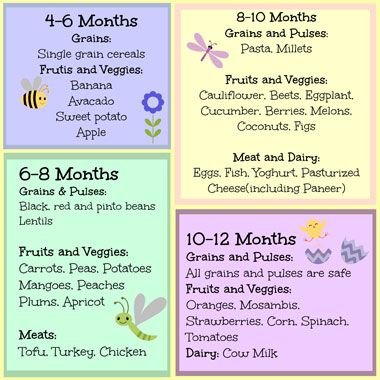 At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the brain and nervous system of the child. nine0003
At the same time, in foreign recommendations, children over 1 year old are offered the gradual introduction of whole cow's milk, which is rich in fats necessary for proper growth and development, the absorption of vitamins A and D, the development of the brain and nervous system of the child. nine0003
Meat dishes: 2-3 times a day
Fish dishes: 2-3 servings per week
Eggs: 2-3 per week
Dietary fats: 3-4 teaspoons of butter and/or vegetable oils per day
When cooking, use the minimum amount of salt and sugar, and do not add them to industrial products.
Offer your child a variety of foods and let them choose for themselves. Children love to eat on their own, so if possible, offer food that the child can eat with their hands. nine0003
It is important to remember that a baby can choke on pieces of food, so whatever you give your baby should be crushed or cut into small pieces that can be easily chewed.
Do not give to a small child: nuts, whole grapes, cherry tomatoes (unless quartered), whole carrots, seeds (such as pumpkin or sunflower seeds), round candies, legumes, raisins, because a child can eat them choke.
Also in the diet of children of the first 3 years of life should not be present:
Mushrooms; canned snacks, pickled vegetables and fruits
Home canned food
Dry concentrates for side dishes
Hot sauces, mustard, horseradish, pepper, vinegar, mayonnaise
Natural coffee
Juices and drinks in the form of dry concentrates; sweet carbonated drinks
Products containing food additives (flavorings, dyes of artificial origin, including chewing gum), popcorn
Combined fats; cakes and pastries
It is important to remember that children of this age should not be given too spicy and spicy foods.
Proper nutrition of a child is a guarantee of health - Children's City Polyclinic No. 1
Every parent wants his child to grow up healthy, smart, happy.
From childhood, we must teach our children to choose from the variety of foods that are really good for health. The nutrition of children is somewhat different from the nutrition of adults. If the child's nutrition system is built correctly, then the child develops normally, both physically and mentally. nine0003
If the child's nutrition system is built correctly, then the child develops normally, both physically and mentally. nine0003
Make your family's way of life by introducing your child to proper nutrition every day. There is no need to arrange constant lectures from this on the topic of what is useful and what is harmful. By actively communicating with your child, setting an example, you instill good eating habits.
Only good things should be spoken at the table. The situation should help the child to relax, then the appetite will be good and the mood will be friendly. Children can help you with serving and decorating dishes. When serving vegetables and fruits, ask the children what vitamins and minerals they contain and why they are so useful. nine0059 In order to organize the proper nutrition of the child, you need to follow several important rules:
Rule 1
Food should be varied.
This is an important condition for the child's body to receive all the substances necessary for growth and development. Every day, the child's menu should include: fruits and vegetables; meat and fish; milk and dairy products; grain products (bread, cereals, cereals). Insufficiency or excess of food consumed by a child can adversely affect the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, contribute to metabolic disorders, increase overweight (even to various degrees of obesity) or lead to malnutrition. nine0003
Every day, the child's menu should include: fruits and vegetables; meat and fish; milk and dairy products; grain products (bread, cereals, cereals). Insufficiency or excess of food consumed by a child can adversely affect the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, contribute to metabolic disorders, increase overweight (even to various degrees of obesity) or lead to malnutrition. nine0003
If the child refuses to eat a healthy dish, invite him to experiment and make the dish unusual.
So, with the help of dried fruits and nuts, you can put a funny face on porridge, use ketchup and greens to draw a pattern on scrambled eggs, put mashed potatoes on a plate in the form of a snowman figure, etc.
What should not be used in children's nutrition:
- Offal other than liver, tongue, heart; blood, liver, raw smoked sausages. nine0101
- Deep-fried food and culinary products, chips.
- Curds, condensed milk with vegetable fats.
- Kumis and fermented milk products containing ethanol (more than 0.5%).
- Cream confectionery containing vegetable protein.
- First and second courses based on fast food concentrates.
- Vinegar, mustard, horseradish, hot peppers and other hot spices and food products containing them, including hot sauces, ketchups, mayonnaises and mayonnaise sauces. nine0101
- Pickled vegetables and fruits.
- Natural coffee and carbonated drinks, apricot kernels, peanuts.
- Products, including confectionery, containing alcohol.
- Food products containing a large amount of food additives in their composition (information is indicated by the manufacturer on consumer packaging).
- Dry concentrates for cooking first and second courses (soups, Dosherak vermicelli, cereals).
Rule 2
Your child should eat regularly.
Compliance with the diet of children is of great importance for the absorption of nutrients by the body. Preschool children are recommended to eat 4-5 times a day, every 3 hours, at the same time, distributing the diet as follows: breakfast - 25%, lunch - 35%, afternoon snack - 15%, dinner - 25% . At school age, it is advisable to have four meals a day, every 4 hours with an even distribution of the daily ration: breakfast - 25%, second breakfast - 20%, lunch - 35%, dinner - 20%. nine0003
Preschool children are recommended to eat 4-5 times a day, every 3 hours, at the same time, distributing the diet as follows: breakfast - 25%, lunch - 35%, afternoon snack - 15%, dinner - 25% . At school age, it is advisable to have four meals a day, every 4 hours with an even distribution of the daily ration: breakfast - 25%, second breakfast - 20%, lunch - 35%, dinner - 20%. nine0003
Try to stop snacking and teach your child to eat only at the table. If this still doesn't work, offer fruit, biscuits, juice for a snack - food that will help drown out hunger, but will not ruin your appetite.
Proper organization of meals at school in the form of hot school breakfasts and lunches
is an important health-improving measure for children-students in extended day groups, whose diet should be 50-70% of the daily norm, which, unfortunately, parents do not have enough are paying attention. Eating sandwiches, pizza, chips, chocolate bars is harmful because - this food is inferior in composition and also irritates the stomach, contributing to the development of gastritis.