Baby not interested in solid food
What to Do When Baby Won't Eat Solids: 7 Simple Steps
When your baby won’t eat solids, it can be stressful. Learn why your baby is refusing food and how to get them to eat solid foods with 7 simple steps!
The spoon hits the floor.
Your baby makes a nasty face.
They might even shudder or gag.
All from a bite, or an attempt to feed your baby solid foods. It’s totally unexpected when babies respond with such disdain for baby food or table food. As parents, we’re often excited about this new milestone and it’s shocking when your baby won’t eat solids.
In real life though, it’s quite common for babies to gag on solids, seem uninterested, and outright refuse food.
While knowing it’s “normal” for babies to not seem interested in solid foods, even though everyone else’s baby seems to be gulping it down by the jar full, it still leaves the question, “How do you get a baby to eat solids?”
Well, I happen to know a thing or two about that. First, because I’ve personally helped a lot of families get their babies eating solids as a pediatric occupational therapist with over a decade of experience, but also because I’ve been there with my own son…
Going through it as a mom was a whole different ball game.
Of course, I knew that it was normal for babies to refuse baby food when it was first introduced, and I also knew that some babies didn’t much prefer baby food, but my Momma heart was worried. The worrying got worse when I watched my son act like he could’ve cared less about the delicious homemade sweet potatoes that I whipped up, as he turned his face away and threw the spoon across the room.
Meal after meal.
Day after day.
And, week after week.
With each passing day that he refused to eat solids, I got more worried, and more frustrated as I’d watch the food I’d prepared literally go down the drain. There came a point when I knew I needed to do more, to put some of my OT skills to use in my home, and that’s what I’m going to share with you here, because I know how stressful it is when your sweet adorable little baby won’t eat solids.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know :
-
- Why your baby is refusing solids
- Why they used to eat solids, but don’t anymore
- How to get them to eat solids and table foods
- Ways to get them more help (if you need it)
*Keep a look out for the free printable at the end too, if your baby is struggling with table foods!
Affiliate links used below. See our full disclosure.
Why Your Baby Won’t Eat Solids
There are a lot of factors that can actually play a role in any baby’s refusal to eat solid food. We’re going to walk through each of them below, but know that the reason your baby isn’t eating solids could be any one or combination of them. With a little detective work, you’ll figure it out!
Also, age has a little do with it, and will help you hone in on what’s going on.
6 or 7 Month Olds That Refuse Solids:
-
- Baby isn’t ready yet – 6 months of age is the perfect time to introduce baby to solid foods, but sometimes the baby isn’t ready.
 Actually, this is really common when the baby is closer to 4 and 5 months old if you’re starting a little earlier, but is still totally normal at 6 months of age.
Actually, this is really common when the baby is closer to 4 and 5 months old if you’re starting a little earlier, but is still totally normal at 6 months of age.
- Baby isn’t ready yet – 6 months of age is the perfect time to introduce baby to solid foods, but sometimes the baby isn’t ready.
Babies are still learning how to move their tongue and bring toys to their mouth, which helps them get used to having foreign objects in there. Each baby is unique and yours may just need some practice if they are in this age range.
They also may still be developing good trunk and head control, without it, eating is difficult!
Check out the American Academy of Pediatrics recommendations for introducing food and make sure your baby is ready for solids. You can also find my guide to Introducing Solids with more details on milestones to look for when 6 months old.
-
- A strong tongue thrust reflex – Most babies usually lose this reflex that helps them not choke if something accidentally gets into their mouth around 4-6 months, but it may linger for some.
If you notice that your baby still thrusts their tongue out every time you touch the spoon to their lips, they may need a little more time. It’s really hard for them to eat when they keep shoving their tongue out of their mouth!
It’s really hard for them to eat when they keep shoving their tongue out of their mouth!
-
- Doesn’t like the way food feels – Solid food is something so new and unfamiliar to babies, it can take a while for them to get used to the new texture in their mouth. Many babies do in fact get used to the feeling of solids, but some don’t.
Read more about that below under sensory.
8, 9, or 10 Month Olds That Refuse Solids:
-
- Sensory – By 8 months of age, most babies are ready from a developmental standpoint, and at this age, it’s definitely time to get the ball rolling, but some babies (like my son) still refuse. One of the most common reasons why older babies still won’t eat solids is because they don’t like the texture.
This boils down to the way their brains are thinking about (or processing) the sensory input they feel (aka the food in their mouth).
This isn’t a bad thing and doesn’t necessarily mean they have any kind of diagnosis, but it does mean we need to take some extra steps to help them tolerate the texture of food better. You can head to sensory issues with food to learn more.
You can head to sensory issues with food to learn more.
Babies that are sensitive to different textures usually gag immediately at the sight, touch, or taste of food.
-
- Coordination – Eating actually requires a lot of muscle coordination from opening the mouth, pulling food off of a spoon, closing the mouth, and effectively swallowing.
We take this for granted and don’t even think about it, but for some babies, it just isn’t coming natural.
Babies that are having difficulty with coordination, or oral motor skills (find exercises with that link,) usually gag when trying to swallow or after getting the food into their mouth.
Or, the food may fall out frequently, and babies won’t eat solids because they just don’t know how. When they don’t know how to eat, it isn’t that fun, and there isn’t a lot of interest.
If gagging is something you’re concerned about or is happening often, read more in guide on baby gagging.
-
- Food allergies – Believe it or not, sometimes babies will avoid certain types of foods because they’ve associated an upset tummy with the yogurt or cheese for example. It doesn’t happen all the time, but it’s something to consider, especially when it’s very specific allergenic food.
The most common types of food allergens are dairy, egg, soy, wheat, tree nut, peanut, fish, and shellfish. Severe eczema is another indicator that food allergies might be present.
Sometimes, signs become more obvious when cow’s milk is introduced.
-
- Not into baby food – While this is probably the least likely reason your baby is refusing solids, it is possible.
If you’ve consistently offered baby food or infant cereal with no interest from your baby and you don’t see any of the sensory or coordination signs we talked about above, then you might just might want to move on to table and finger foods.
One way to do that is using a Baby Led Weaning approach, before you do that though read my BLW pros and cons.
*Get a seat in my free workshop and learn 5 big feeding mistakes that might be stopping your child from learning to eat. We’ll send you a free workbook too!
Why Baby Won’t Eat Solids Anymore (They Used to?)
-
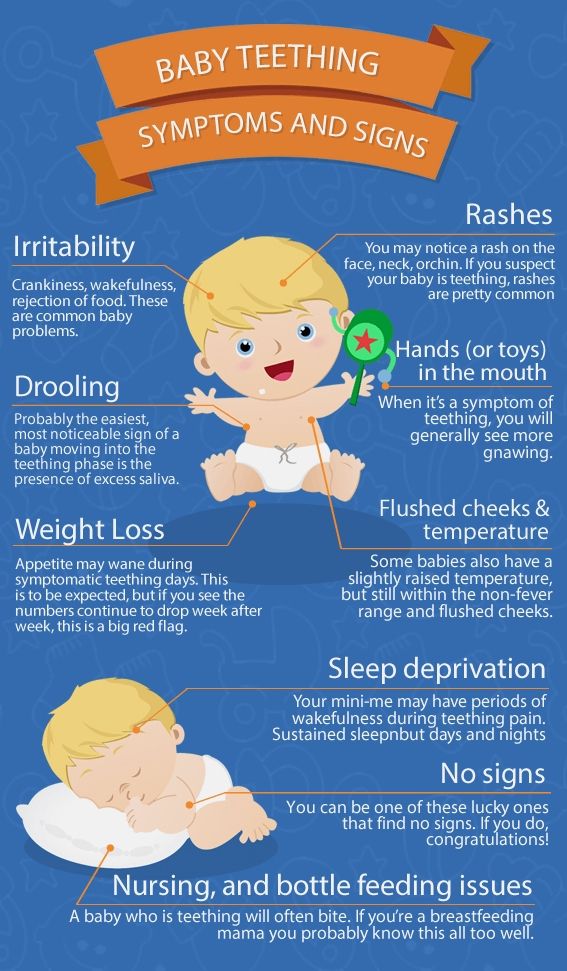
- Some teething babies won’t eat – While it’s not as common, some babies start off eating baby food and then suddenly stop. A frequent cause of this is teething, and some babies teethe for a very. long. time. If your baby’s teeth are swollen, red, and seem to hurt, then this is likely the cause.
Try putting some teething gel on their gums 15-20 minutes before a meal. If you see an improvement, this is likely the culprit. Here’s a natural teething gel I like, but check with your doctor first.
-
- Going through a phase – Babies may get a little bug or slight cold that we aren’t even aware of or have some negative experience with food that seemed too minor to us as the parent, but makes them leery of eating.

- Going through a phase – Babies may get a little bug or slight cold that we aren’t even aware of or have some negative experience with food that seemed too minor to us as the parent, but makes them leery of eating.
If it’s the latter, some sensory sensitivities can develop if a baby goes for a while without eating any food. If this is the case for your baby, you’ll want to follow the steps below and focus on not pressuring your baby to eat. It’s really important that mealtimes are a positive experience.
-
- They’ve outgrown baby food – If your baby is later in their 7th month or older, they may just be sick of solid baby food and ready for the real deal table and finger foods. That may mean it’s time to change up baby’s diet!
I know that seems scary and makes some parents nervous. Don’t worry though, if you think this is why your baby suddenly won’t eat solids anymore, then head to how to transition to table foods.
How to Get Your Baby to Eat Solids
1. The absolute first thing I do with a baby not eating solids is to put a scoop of baby food or some other pureed food like yogurt onto the tray of their high chair.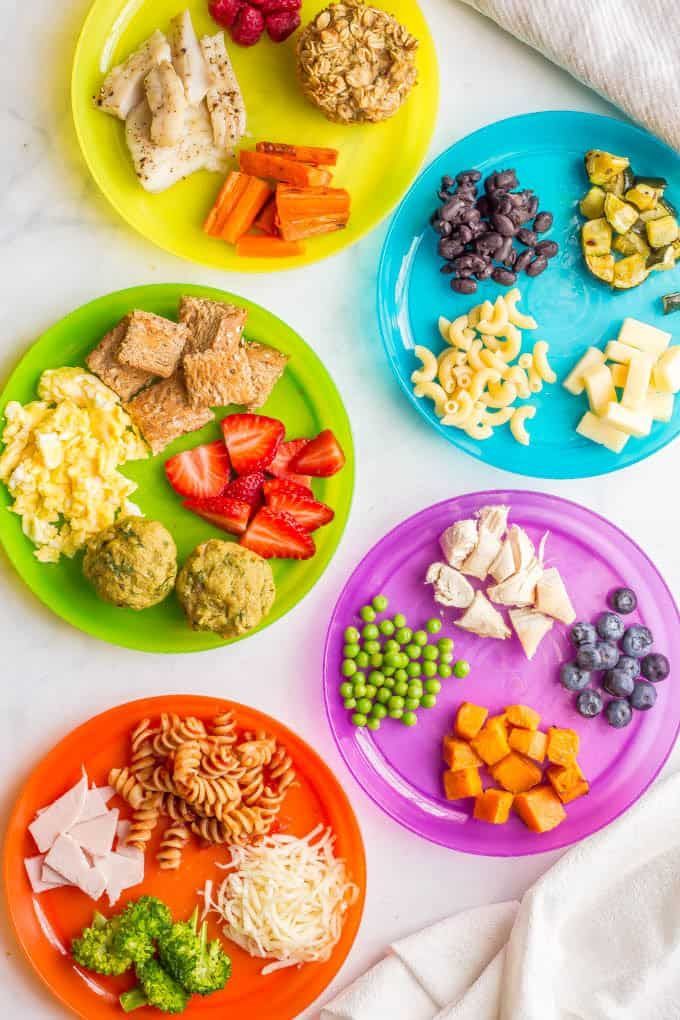
I know, the mess. It’s soooo important for babies to get messy though! If you’re skeptical, you’ve got to read: Why Babies Should Get Messy Eating. It will totally change your perspective and give you the inspiration to embrace the mess.
2. Encourage your baby to touch the food, but don’t force. Be silly and keep it light. Demonstrate.
If they refuse, try and try again. In fact, at every single meal, put a dollop of that food on their tray or even in a bowl that they can play with and touch. If they won’t touch after a few attempts, offer a spoon for them to stick into the food too.
This is one of my favorite beginner spoons that makes it really easy for baby to get some food onto it.
3. Once your child touches the solid food, you’re on your way! Allow them to touch, spread, and put it all over the tray and themselves. This is wonderful for their sensory processing and will make a huge difference in helping them get used to the texture of solids.
If they get upset once they’ve touched the food, or that they are now all messy, be very calm and reassuring.
Have a wet washcloth ready and quickly wipe them down. And, if this is how they respond, it’s a sign that you need to practice playing with these foods a lot! The more they touch and interact with the food, the closer they’ll be to eating it.
4. When baby has the food on their hand and they’re at least tolerating it, show them how to take their hand to their mouth, so they can taste it. You may need to demonstrate if baby won’t let you guide their hand.
Repeat this several times. After they eat from their hands several times, offer them some solid foods from a spoon.
5. You can also give them a large whole raw carrot or celery stalk at meals. I mean the whole darn thing. The point isn’t for them eat it (and if they can get pieces of it off, take it away), but for them to put it into their mouth.
When they do this, it helps desensitize their gag reflex and they get to practice biting, chewing, and moving their tongue around. It’s amazingly powerful and can make a big impact in a baby accepting solid foods. Make sure you demonstrate and keep offering at every meal.
It’s amazingly powerful and can make a big impact in a baby accepting solid foods. Make sure you demonstrate and keep offering at every meal.
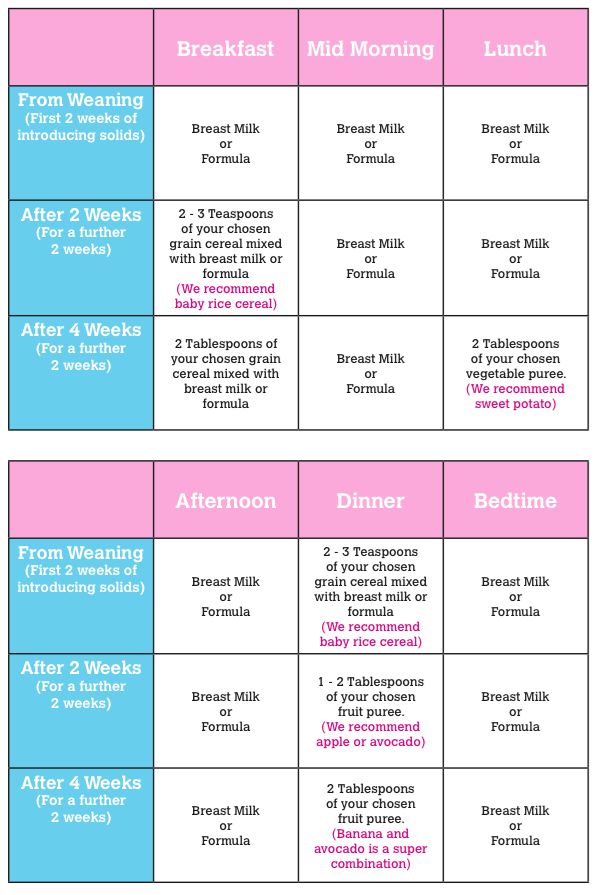
6. Be consistent and patient. I can’t stress this enough, even though it’s often easier said than done! Have regular meals and follow the above steps 1-3 times a day for every meal. You can find sample schedules for babies ages 6 – 7 months, 8 – 10 months, and 11 -14 months if you’d like a guideline to follow.
7. Focus on meals being positive experiences for the baby, even if they aren’t eating anything. As parents, we can bring a lot of stress with us to meals, which can be hard to hide. But, this is definitely a “fake it til you make it” kind of situation.
Take a deep breath, put on a happy face, and work on the above steps. Going into the meal with no expectations of them eating anything will also help keep your frustration level down.
To learn MORE, grab a seat in my free online workshop.
In it, you’ll learn 5 big feeding mistakes that are stopping your baby or toddler from learning to eat table foods! It’s an eye opener and will help you take steps to give them the best start with eating table foods well (even if it already isn’t going well):
Strategies to Use Outside of Meals for Baby’s Refusing Solids
There are a few really powerful strategies you can use away from the highchair that will directly impact your baby eating solids during meals.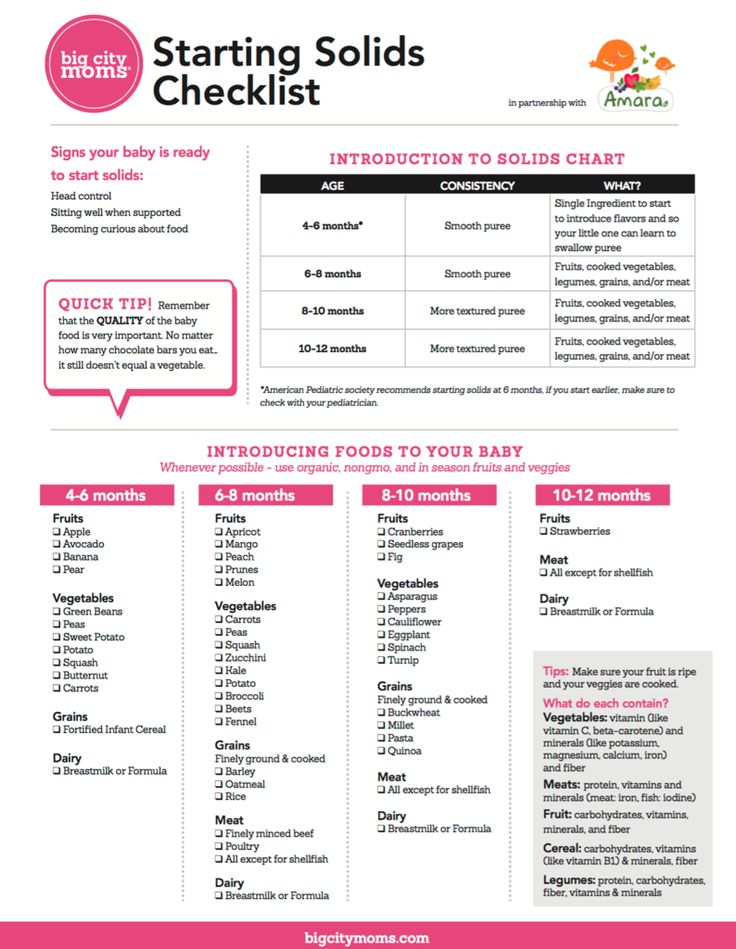 Might seem strange, but if you suspect your baby is refusing because of sensory or coordination difficulties, doing these activities can be total game changers:
Might seem strange, but if you suspect your baby is refusing because of sensory or coordination difficulties, doing these activities can be total game changers:
-
- Brush their teeth – If you haven’t started yet, brush their teeth, and when you do, make sure you’re getting all over their gums and the sides, as well as the top of their tongue.
It only takes a few seconds, but it helps to both desensitize their mouth and improve coordination because the tongue gets practice moving in different directions. If your baby doesn’t like it, take it slow, and try often.
The more often you brush, the bigger the effect. Try for one to three times a day, and consider a vibrating toothbrush (yes, even for babies) for more powerful input in their mouth.
-
- Play in sensory bins – That may be a new term to you or you might be wondering what the heck that has to do with eating, but playing in different textures is super powerful and helps the sensory system understand different textures better.

- Play in sensory bins – That may be a new term to you or you might be wondering what the heck that has to do with eating, but playing in different textures is super powerful and helps the sensory system understand different textures better.
This correlates directly to eating. I can’t tell you how many times I’ve seen a kiddo that plays in sensory bins frequently, suddenly start eating more foods (my son included). Head to Sensory Bin Ideas to learn how to set one up.
-
- Chew on toys – So many babies that won’t eat solids never put toys or teethers in their mouth, which is really easy to overlook. If this is your baby, pull out a bunch of different teethers and have them around the house.
Demonstrate. Dip them in food or juice. Play with them in the bath. The more often they get teethers and toys into their mouths, the more it will help improve the coordination their mouth muscles need to eat and desensitize their gag reflex and sensory system.
I really love this teether because it gets in the back of the mouth and this one vibrates (all my friends get it from me at their baby shower).
Help for the Baby Not Eating Food
I’m not just talking about solid baby food or purees. You may have a baby that won’t eat any type of food, like puffs, cut up fruit, or toast. They’re getting older and older. You’re getting worried.
You may have a baby that won’t eat any type of food, like puffs, cut up fruit, or toast. They’re getting older and older. You’re getting worried.
Following the above steps will be incredibly important for your babies too, especially the strategies for outside of a meal. But, you’ll also want to use the steps I outline in getting your baby to eat table foods.
That’s a whole different animal all within itself, and there are some targeting tips that can make all the difference in your baby eating food.
You’ll want to focus on small pieces, and by 9 months of life be attempting table or finger foods.
While I don’t want you to worry, I know it’s tempting to keep waiting it out, and unfortunately, some doctors advise this quite often. This often does not help your baby to learn to eat wide variety of foods.
Babies instinctively learn to chew between roughly 8 and 11 months of age, when they move past that, it can be much harder for them to accept foods. It’s not impossible, and the same steps apply for older children, but it’s much better to be proactive then taking a “wait and see” approach.
It’s not impossible, and the same steps apply for older children, but it’s much better to be proactive then taking a “wait and see” approach.
Puffs, lil cheese curls, and baby mum mum’s are all great for baby’s first foods.
When to Get More Help for a Baby Not Eating Solids
If your baby doesn’t like solid baby food and won’t accept any table foods of finger foods by 9 months old, it’s a good idea to get an evaluation either from the free early intervention program in your state or from a feeding therapist.
You can also read more about typical feeding milestones for babies just to have a reference point. As I said earlier, all babies develop at a different pace and needing a little more help is very common.
Get My Free Printable: Learn to Eat Table Foods Cheat Sheet
There seem to be more questions than answers when you’re under the daily stress of your baby or toddler not eating table foods. Not to mention all of the well-intentioned bad advice that’s often given. Let’s clear that up.
Let’s clear that up.
I’ve created a free 5 page guide that clearly lists the steps to teach your baby or toddler to eat table or finger foods, plus a FAQ guide for parents to ease their worries when their babies won’t eat!
Get your free Learn to Eat Table Food Cheat Sheet printable here!
More on My Baby Won’t Eat Solids
How to Teach Your Baby to Self-Feed
Mega List of Table Food Ideas
How to Teach Your Baby to Drink from a Straw
The Best Mealtime Utensils and Tools for Babies
Click here to Pin This! (You’ll have as a quick reference)
Alisha Grogan is a licensed occupational therapist and founder of Your Kid’s Table. She has over 17 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
8 Secret Strategies for Sensory Food Aversions in Kids
Why do children have sensory food aversions? And, how can you help them overcome sensory issues with food? Get the answers and 8 simple strategies…
From the very beginning of Your Kid’s Table, I have always wanted to help parents better understand sensory processing and anything related to kids and eating. Over the last few years, I have answered many comments about how the two things are related, and often result in a sensory food aversion.
Over the last few years, I have answered many comments about how the two things are related, and often result in a sensory food aversion.
I wanted to dedicate a post completely to sensory issues with food, to help you understand if sensory processing is playing a role in your child’s picky eating and, perhaps more importantly, what you can do help!
I first noticed my son’s sensory issues with food when I introduced food to him, I knew the red flags (you’ll read about those later), and if I hadn’t introduced specific sensory strategies to help him learn to eat foods, we’d likely still be struggling, years later, because a sensory food aversion is on a whole different level than just your average “picky eating”.
Why Do Kids Have Sensory Issues with Food?
To understand food related sensory issues, we’ve first got to talk about sensory processing, which is our ability to interpret smells, tastes, sounds, touches, sights, and movement from our environment. Although most of us process this information in similar ways, it is completely unique to every individual, to every child. We are bombarded all day long with various sensory input, and eating, which many of us do 5 or 6 times a day, is a huge sensory experience that most of us take for granted.
We are bombarded all day long with various sensory input, and eating, which many of us do 5 or 6 times a day, is a huge sensory experience that most of us take for granted.
As adults, we have been quite desensitized to the textures, flavors, and smells of food, but many of our kids have not. In the first few years of life, mealtimes are all about processing the sensory input they are receiving from various foods. Often, when kids display picky eating, especially those with food aversions/extreme picky eating, the touch, taste, or smell of a food is being processed in their brain as dis-pleasurable in some way. And, by dis-pleasurable, I mean down-right uncomfortable. Think of something that makes you shudder… nails on chalkboard or touching a slug? That feeling that you have may be just as extreme for your child when they touch an orange.
How your child responds to foods, may at least in part, be simply neurological. I hope that this information helps you as the parent depersonalize the refused dinners, at least at little, anyways!
Here’s the good news, children’s brains are extremely plastic. Meaning they are able to easily learn new things. When a child learns something new or experiences something differently, a new connection is made in their brain. The more they have that same experience, the stronger that connection gets, and then they are able to react differently then they had previously because their brain is using a new connection to process the information.
Meaning they are able to easily learn new things. When a child learns something new or experiences something differently, a new connection is made in their brain. The more they have that same experience, the stronger that connection gets, and then they are able to react differently then they had previously because their brain is using a new connection to process the information.
Are you following me here? Let me say it another way by telling you about my son who has a long history of sensory food aversions. Isaac gags and shudders every time he touches chicken, but one day he helps me make chicken in a different way. We cut it into small pieces and serve it with a fun dip in a cool little ramekin. I pretend the chicken is little baby dinosaurs jumping into a pond of ketchup. Then, Isaac is really motivated and relaxed (because he isn’t being pressured), so he picks up his “little baby dinosaurs” and sends them soaring into his dip without a hint of a shudder or gag.
Guess what, his brain just made a new connection, and then I had a starting point to build from!
While I’ve mostly been providing examples of a child who is sensitive to textures because the brain is over processing the input, it is also entirely possible that your child may be undersensitive to sensory input. Think of sensory processing as a spectrum with being sensitive or defensive to input (texture, smell, etc.) at one end and seeking input at the other end with a whole lot of variability in the middle.
Not processing input well can also cause picky eating because children may not feel certain soft textures in their mouth well (as if the sensation is dulled), and thus avoid them. These kids, in particular, will often prefer crunchy foods, seemingly spit out soft foods, or over-stuff their mouths to try and “feel” the food.
*Note that sensory processing isn’t just related to food, head over sensory sensitivities in kids to learn more.
Does My Child Have a Sensory Food Aversion or Disorder?
While there is no specific diagnosis for a “sensory eating disorder” or a sensory food aversion, these terms might be used when your child eats a very limited amount of foods because they have difficulty with how foods smell, taste, feel, or even how they look. Remember this is because of the way their brain is interpreting the sensations they get from food, which leads to the question.
Remember this is because of the way their brain is interpreting the sensations they get from food, which leads to the question.
To help narrow down if your child’s picky eating is related to sensory, it’s first helpful to think about certain groups of kids that sensory processing difficulties affect more than other’s. I’m going to list them here because if your child has one of these diagnoses and has eating difficulties, it is very likely that sensory processing is at least part of the picture. But, having sensory processing difficulties in general DOES NOT mean that your child has one of these diagnoses. Got it? Good!
Kids that fall into one of these groups and are picky eaters, often have sensory based food aversions:
-
- Sensory Processing Disorder (Note that many health care providers acknowledge this diagnosis, but it is not in the current version of the DSM, which means some insurances providers will not accept this as a reason to justify therapy).

- ADD/ADHD
- Children Born Prematurely (The sensory system is one of the last to develop in utero, which is why sensory processing difficulties are common. However, this is not a rule. Many preemies display no difficulties in this area.)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Down Syndrome
- Children Adopted from Orphanages in Eastern European Countries or Russia
- Sensory Processing Disorder (Note that many health care providers acknowledge this diagnosis, but it is not in the current version of the DSM, which means some insurances providers will not accept this as a reason to justify therapy).
So, how do those sensory “difficulties” actually show up in our kids when they are related to food, here are some specific red flags to look for…
Red Flags for Sensory Issues with Food
If you child has most or all of the behaviors here, it is possible that sensory issues with food may be part of the underlying reason your child is selective about what they eat. You will notice some opposite extremes in the list below, which are indicating different ends of the sensory processing spectrum as I discussed earlier. As you’re reading, make a mental checklist of any that you see your child doing regularly:
-
- Gags at the sight, smell, touch, or taste of foods.
 Gagging while trying to eat is a different cause that has to do with the mechanics of eating. Gagging can also be a learned behavior that may have started from either a sensitivity to sensory input or difficulty chewing or swallowing food at some point. Read more on how to help with Gagging at the Smell of Food.
Gagging while trying to eat is a different cause that has to do with the mechanics of eating. Gagging can also be a learned behavior that may have started from either a sensitivity to sensory input or difficulty chewing or swallowing food at some point. Read more on how to help with Gagging at the Smell of Food.
- Gags at the sight, smell, touch, or taste of foods.
-
- Eats only specific types of textures. Most of the time, the preference is crunchy foods, but sometimes soft foods are the preferred. This preference can even be carried over to highly specific requests of certain brands, colors, and flavors of food, feeding therapists call this a food jag.
-
- Avoids or dislikes their hands getting messy, and I’m not just talking about at meals. You will often see your child get uncomfortable with crafts or digging in dirt/sand, etc. (This is an important point, learn more about it in Everything You Need To Know About the Tactile Sense)
-
- Over stuffs or pockets food excessively and/or frequently.
 Pocketing food can also be the cause of poor coordination and/or difficulty chewing.
Pocketing food can also be the cause of poor coordination and/or difficulty chewing.
- Over stuffs or pockets food excessively and/or frequently.
-
- Never went through an oral stage as a baby/toddler where they mouthed and chewed on toys and other objects.
-
- Excessively mouths and chews on various toys past the age of 18 months.
Find more sensory red flags that cover all the senses, not just related to eating. And, if you’d like to dive into understanding sensory as it relates to picky eating, head over to oral sensory processing, you’ll find more tips and activities there!
Are My Child’s Eating Difficulties all Related to Sensory?
I realize I just wrote over 800 words describing how sensory processing may be the cause of your child’s picky eating, but it is rarely the sole cause (have you notice I’ve been hinting about that). Picky eating is a complicated animal that often has many layers to it. Even if sensory processing is the major player, learned behavior and power struggles are most likely at play, too.
It is really important to make sure that you have a good routine and structure in place so that you are able to see the most improvement possible. See my Basic Strategies to Improve Eating and the plan I used to help my son for more strategies to help establish a consistent routine.
How to Get Help for Picky Eaters With Sensory Food Aversions
I want to provide you with some solid strategies to begin to improve your child’s processing of sensory information (and I will in the next section). However, there are more specialized techniques that may be appropriate under the guidance of a therapist. If your child is under 3 and you live in the US, you may qualify for free in home services. Another option is, a private evaluation from an occupational therapist that specializes in feeding and sensory processing may be appropriate. Read all about the ins and outs of feeding therapy.
Learn more about the basics of addressing picky eating. This is really important guys, don’t take this lightly! You will see so much more success with your sensory efforts if you put my 3 Keys to Turning Around Picky Eating in place. Discover what they are and how to use them simply in your home in my FREE workshop. Click here to save your seat!
Discover what they are and how to use them simply in your home in my FREE workshop. Click here to save your seat!
Affiliate links used below. See our full disclosure.
Strategies for a Sensory Food Aversion
With that said, these few tools can be very powerful when used consistently over a period of at least 4-6 weeks because they help to desensitize the sensory system. Come back to these strategies as needed.
-
- Play in a variety of sensory bins at least 5-6 times per week.
-
- Use a vibrating toothbrush two times a day. My kids use these one’s all the time, but for smaller toddler mouths or those that are really sensitive, this brush is a great option.
-
-
- When brushing teeth, encourage your child to allow you to help, and brush the sides of the tongue top of the tongue and inside the cheeks as well.
-
-
- Build off of textures that your child is preferring.
 Think about making small changes to the foods they already like by changing up the brand, flavor, etc. This will help build a bridge to new foods in a way that is comfortable.
Think about making small changes to the foods they already like by changing up the brand, flavor, etc. This will help build a bridge to new foods in a way that is comfortable.
- Build off of textures that your child is preferring.
-
- Encourage them to interact with the food in some way. Take baby steps. They may need to spend some time just touching the food to get used to the texture, for example.
-
- Cook together. This is a no-pressure time that allows kids to explore new foods. They will often feel brave enough to try something new in the fun and relaxed nature of the moment. Again, the key here is breaking down some of that sensitivity through the exploration of food.
-
- If your child falls into the over-stuffing/seeking texture category, you will want to alternate crunchy bites of food with soft food. You can also give the cheeks a firm, but gentle squeeze if the stuffing or spitting out starts, or briskly stroke from the ears to the mouth a few times.
 This is not meant as a punishment, but to give input to help them process the sensation of the food better.
This is not meant as a punishment, but to give input to help them process the sensation of the food better.
- If your child falls into the over-stuffing/seeking texture category, you will want to alternate crunchy bites of food with soft food. You can also give the cheeks a firm, but gentle squeeze if the stuffing or spitting out starts, or briskly stroke from the ears to the mouth a few times.
-
- Use these picky eater friendly foods for inspiration and motivation!
By implementing these strategies in combination with a solid routine, you will likely see some significant changes in your child’s eating. If you’d like a little help getting your routine rock solid so you can build on these other sensory specific tips, then grab this FREE 9 Tips to Improve Your Child’s Eating Printable.
More for Kids with a Sensory Food Aversion
The Best Picky Eating Strategy
What is a Sensory Diet?
Children’s Books to Help with Picky Eating
When Has Picky Eating Gone Too Far… Is it Something More?
Did you pin this?
Just hover over or tap any pic to get the pin it button to appear!
Alisha Grogan is a licensed occupational therapist and founder of Your Kid’s Table. She has over 14 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
She has over 14 years experience with expertise in sensory processing and feeding development in babies, toddlers, and children. Alisha also has 3 boys of her own at home. Learn more about her here.
Food Interest Violation: How to recover?
Category: Articles, Articles of GV consultants.
Some parents of children in the second half of life are faced with the fact that their child eats very little or is not interested in "adult food" at all. This also happens with older children. It happens that a child is fed daily under cartoons or under a theatrical performance with the participation of the whole family. At the same time, the child sucks the breast or drinks an artificial mixture, is quite healthy and develops normally. This daily struggle for every spoonful of food is definitely exhausting for parents. It is not easy in this situation for children, who, as a result of such a meal, may form a negative attitude towards food.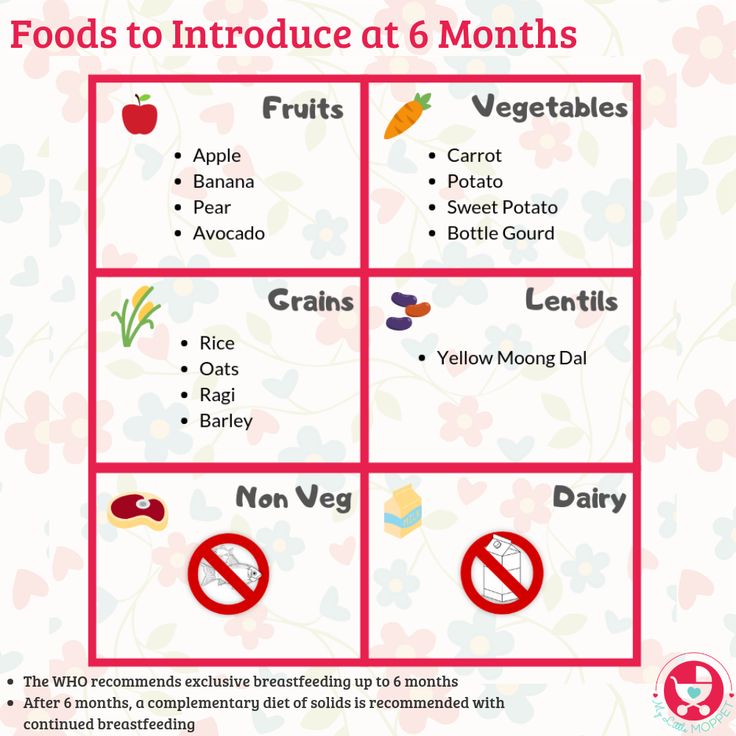 Let's talk today about how to turn feeding from torture into pleasure.
Let's talk today about how to turn feeding from torture into pleasure.
In one of the previous publications, we have already figured out why poor appetite is not treated by weaning a child. Now I want to share information on how you can change this situation and help the child and his parents enjoy eating together. First, consider the possible causes of poor appetite. There can be several reasons for a child not wanting to eat complementary foods. This may be a food interest disorder caused by incorrect, too early or too fast introduction of complementary foods. Or a baby's illness - from a slight malaise with a cold or teething, to anemia and other, more severe conditions.
In case of a mild health disorder, the child's appetite will return as soon as he or she feels better. If a child is seriously ill, the child must first be cured. When a child systematically refuses solid food, does not gain or even lose weight, becomes lethargic and looks sick, you need to see a doctor and get an examination. In the event of a violation of the food interest in a healthy child, parents themselves can help the child form a positive attitude towards food by correcting the mistakes made earlier. In this blog, we will take a closer look at the latter situation.
In the event of a violation of the food interest in a healthy child, parents themselves can help the child form a positive attitude towards food by correcting the mistakes made earlier. In this blog, we will take a closer look at the latter situation.
To begin with, I will describe how it is possible to develop a child's interest in food without much effort. Before introducing complementary foods, it can be useful to warm up the child's interest in "adult" food. To do this, children 4-5 months old and even younger are taken to the table so that the kids can watch how and what the whole family eats. At the same time, it is preferable for parents to hold the child in their arms, and not in a separate deck chair or high chair. Then children can be given spoons, cups, plates, so that they study these objects and try to use them as adults do. When playing with dishes and cutlery no longer satisfies the baby's curiosity, the child begins to persistently reach for food in adult plates.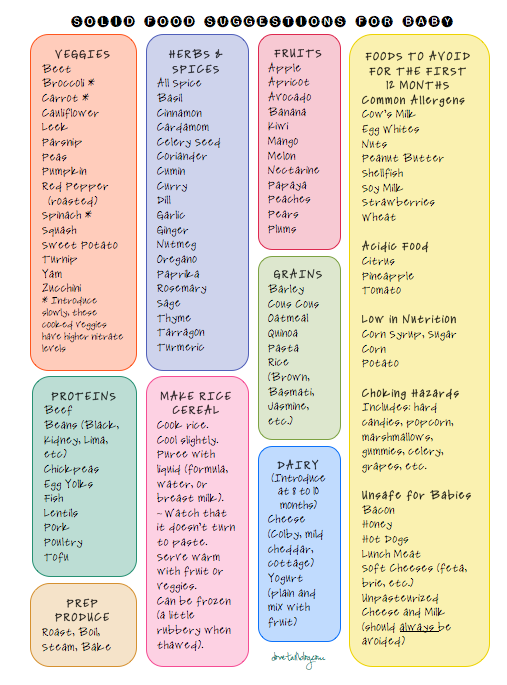 This is the same food interest - one of the signs of readiness for complementary foods.
This is the same food interest - one of the signs of readiness for complementary foods.
Problems with feeding babies with solid food often occur if the child is fed separately from all other family members, at other times, they do not allow him to use a spoon and a cup, so as not to get dirty, not to spill. A child learns a lot through imitation of adults and in such a situation simply does not have a role model, does not imagine what all this is for. As a means to satisfy hunger, children may not consider food until 1.5-2 years old. Before this age, some children eat solid foods out of curiosity and imitate adults. Therefore, cutting back on breastfeeding or formula feeding to make the baby hungry so often does not work.
If the food interest is disturbed, it helps to go through the whole chain again. The older the child, the less time it will take. First of all, all extraneous actions that previously accompanied the meal are removed. They take the child with them to the table, in some cases it is useful to put the child on the lap of an adult, and not in a high chair. The child is given a spoon, a cup, a plate. Food is only offered, but not persuaded or forced to “eat a little more” if the child shows that he has finished eating. When the child feels that they are not being pressured, they are not trying to force feed, he himself will begin to show more interest in food. As long as the child is given a reasonable amount of a variety of foods suitable for age and consistency, and the opportunity to choose how much and how to eat, the child will not suffer from malnutrition.
The child is given a spoon, a cup, a plate. Food is only offered, but not persuaded or forced to “eat a little more” if the child shows that he has finished eating. When the child feels that they are not being pressured, they are not trying to force feed, he himself will begin to show more interest in food. As long as the child is given a reasonable amount of a variety of foods suitable for age and consistency, and the opportunity to choose how much and how to eat, the child will not suffer from malnutrition.
Bon appetit to you and your children!
First published at http://pandaland.kz/blogs/nashi-deti-4/pitanie-26/1-3-goda-43/narushenie-pishhevogo-interesa-kak-vosstanovit
Maria Ivanova
lactation consultant, member of AKEV.
Share
Comments
Complementary foods - what is it and how is it eaten?
home
Articles
Nutrition
Loginevskaya Yana Vladimirovna Pediatrician
24. 04.2019
04.2019
What is weaning and when should we start it? These and many other issues related to child nutrition torment young parents. In the era of the Internet and easy access to information, this information can sometimes become too much.
Let's find out what complementary foods are
Lure - this is the introduction into the diet of a healthy child at a certain age of any food products, homemade or industrially prepared, which supplement breast milk or food imitating it, and contribute to the gradual transfer of the child to the general table. As a rule, complementary foods are thicker in consistency than the child's previous food. If the child has any health problems, the introduction of complementary foods may have its own characteristics.
Complementary purpose in the first year of life to introduce the child to foods other than breast milk / or formula. Timely teach to swallow and chew solid food. And also to avoid deficiency of energy and micronutrients, and vitamins.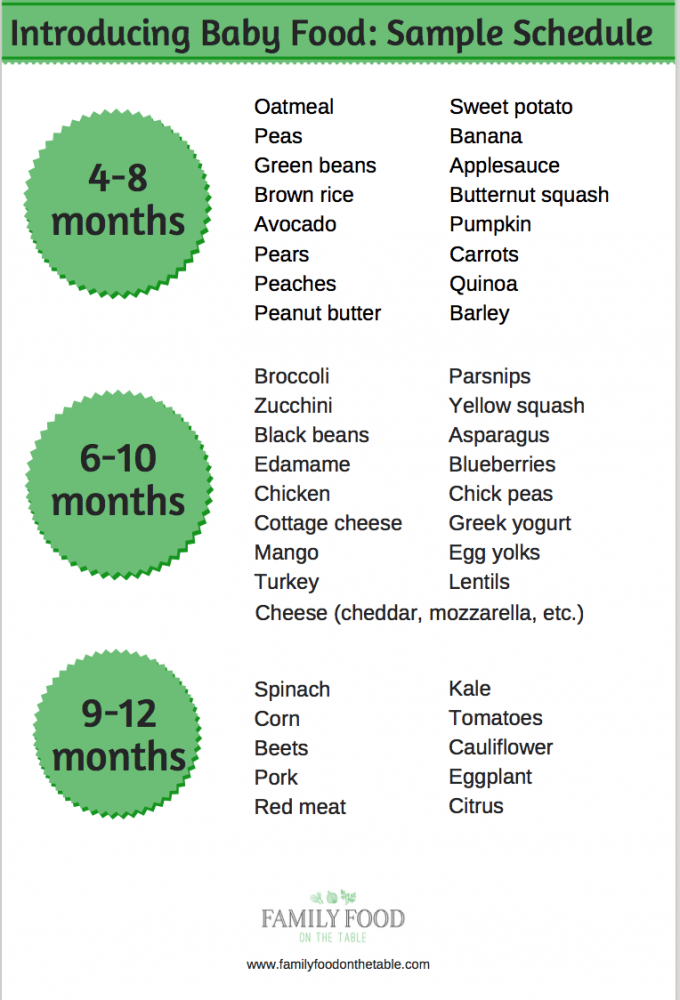
In the literature and other sources, you can find such names as "pediatric" and "pedagogical" complementary foods?
Pediatric Complementary Food , as its name implies, is a classic complementary feeding regimen recommended by the pediatrician at the appointment. Schemes in which there is a gradual replacement of breast milk / formula feeding with cereals, fruit / vegetable purees and other types of products.
Pedagogical complementary food - "Pedagogical" means that first of all the child is taught - they are taught to eat, the correct behavior at the table, they teach that food is joy and pleasure, they show new tastes. The essence of pedagogical complementary foods is that the child’s nutrition begins with “microdoses” (grains of food) that the child receives from his mother’s plate, nothing is puréed or blended, or even warmed up. Nutrition of the child - together with the family, how much he will eat, he will eat so much. Nothing is specially prepared, the family is invited to switch to a healthy diet. The disadvantage of this type of complementary foods is that the child, starting with “micro doses”, does not adequately increase the volume of complementary foods, which can lead to malnutrition of the child at an older age.
The disadvantage of this type of complementary foods is that the child, starting with “micro doses”, does not adequately increase the volume of complementary foods, which can lead to malnutrition of the child at an older age.
In my article, I will rely on modern research and recommendations primarily from the WHO (World Health Organization) and the National Program for Optimizing Feeding in Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation.
What requirements must be met in relation to complementary foods:
- Complementary foods must be timely, introduced at the moment when the child's energy and nutrient requirements exceed what can be provided through breastfeeding (or formula).
- Complementary foods should be adequate, that is, with enough energy, protein and micronutrients to meet the nutritional needs of a growing child.
- Safe - Store or prepare hygienically and feed with clean hands using clean utensils - spoons, plates, not bottles or teats.

- Properly Administered - The child is fed appropriately for hunger cues, and feeding frequency and feeding methods should be appropriate for the child's age.
When do we introduce complementary foods
The optimal age for the introduction of complementary foods is 6 months.
If the child is premature, then the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is delayed by as much as this child was born earlier (that is, if the child was born not at 40 weeks, but, for example, at 36, we have the right to postpone the introduction of complementary foods for 4 weeks, but if we see that at 6 months the child is already quite ready for the introduction of complementary foods, then you can start as early as 6 months). It is advisable to postpone the introduction of complementary foods for no more than 2 months. Try to start the introduction of complementary foods no later than 8 months of the child.
Up to 6 months, breastfeeding fully covers the energy needs of the child. Around 6 months of age, a baby's energy requirements increase dramatically, so it is necessary to add something to his diet in addition to liquid food. Breast milk in terms of its energy value contains 67-68 kcal / 100g, the mixture has approximately the same numbers. Breast milk remains a valuable energy product for children not only in the first year of life, but also after a year. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the volume of the child's stomach by 6 months is about 200 ml, so the food introduced to the child must be thicker than formula or breast milk, otherwise we will still not be able to meet the energy needs of the body. The optimal calorie content of complementary foods should be at least 100 kcal / 100 g.
Around 6 months of age, a baby's energy requirements increase dramatically, so it is necessary to add something to his diet in addition to liquid food. Breast milk in terms of its energy value contains 67-68 kcal / 100g, the mixture has approximately the same numbers. Breast milk remains a valuable energy product for children not only in the first year of life, but also after a year. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the volume of the child's stomach by 6 months is about 200 ml, so the food introduced to the child must be thicker than formula or breast milk, otherwise we will still not be able to meet the energy needs of the body. The optimal calorie content of complementary foods should be at least 100 kcal / 100 g.
Liquid food and liquid quickly fill the stomach. To fill the energy deficit, it is necessary to introduce foods with a higher energy value than breast milk or formula.
WHO ways to increase calories:
-
cook with less liquid
-
Replace part of the water for cooking with breast milk or a mixture (it must be borne in mind that breast milk contains enzymes (lipase) - which begin the digestion and breakdown of food even before it enters the child's body, so instant cereals, when breast milk is added, immediately become liquid, but their energy value is not lost.
What do we focus on when introducing complementary foods:
The main criterion is the readiness of the child to introduce complementary foods - the child shows interest in food, the so-called food interest - he is interested in what his mother eats, actively reaches for food from his parents' plate, wants to taste it.
Indirect criteria
- Child's age about 6 months
- Decreased solid food ejection reflex (active interest in food is never shown until the ejection reflex fades)
- Doubling birth weight (optional item, some babies double their weight before 6 months of age)
- Child can sit with support
- The first teeth appear in a child (again, not always)
Principles of maintaining interest in food
- Parents should remember that in order to form the main criterion for readiness for complementary foods, the child must see how his family eats. The formation of eating habits comes from the family and the immediate environment of the child.
 If, before 6 months, the child has never seen how mom or dad eats, how they eat at the table and what they eat, he may not have a food interest by 6 months. Food interest begins to gradually form as a skill of tracking the actions of an adult from 3 months of age. That is, somewhere from the age of 3 months the child, if you take him with you to the kitchen (dining room), the child begins to observe the process of eating, and gradually this interest - from the interest of "observation" goes to the "desire" to try just like mom or dad.
If, before 6 months, the child has never seen how mom or dad eats, how they eat at the table and what they eat, he may not have a food interest by 6 months. Food interest begins to gradually form as a skill of tracking the actions of an adult from 3 months of age. That is, somewhere from the age of 3 months the child, if you take him with you to the kitchen (dining room), the child begins to observe the process of eating, and gradually this interest - from the interest of "observation" goes to the "desire" to try just like mom or dad. - It is advisable not to feed the baby separately and try to eat with the baby what the baby eats. If you are feeding your child with industrial food (ready-made mashed potatoes in a jar), then try this food with your child. Try to bring the canned food as close as possible to the general view on the table - transfer the puree from the can to a plate, give a spoon. At the age of 8-10 months, the child learns to eat with his hands, so at this age it is advisable that the child has small pieces of food on the plate that he already eats - these can be pieces of boiled potatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, pieces of apple, banana.
 The pieces should be small, 1 x 1 cm, so that the child can grab them with his fingers. In parallel, the mother can supplement the child from the plate with the main food. The child learns to cope with more solid food, learns to chew, swallow. The sooner the skill of swallowing more solid food is worked out, the easier it is for parents in the future. At the age of 10-12 months, the child's fine motor skills are already improving, he is learning to eat with a spoon (be patient, different children do it in different ways and at different speeds)
The pieces should be small, 1 x 1 cm, so that the child can grab them with his fingers. In parallel, the mother can supplement the child from the plate with the main food. The child learns to cope with more solid food, learns to chew, swallow. The sooner the skill of swallowing more solid food is worked out, the easier it is for parents in the future. At the age of 10-12 months, the child's fine motor skills are already improving, he is learning to eat with a spoon (be patient, different children do it in different ways and at different speeds) - Be mindful of the child's physical condition - do not introduce new foods when the child is unwell or tired or teething or has undergone some medical procedure such as a vaccination
- Offer small portions. Some children undereat food because they are initially intimidated by the portion size. Do not insist that the child finishes the portion. Let it be better after some time to ask for another
- Try to keep the area around the child clean! This initially teaches the child to cleanliness at the table and to a neat diet.
 Some children are very sensitive to external stimuli - dirty hands, face, clothes can cause them severe discomfort
Some children are very sensitive to external stimuli - dirty hands, face, clothes can cause them severe discomfort - Help the child if you see that the child is "interested" in food, but tired of fighting with it.
- No games, entertainment or persuasion while eating - in this way you replace food interest with interest in the game. The child will not be able to learn to adequately assess their desires in food. Don't turn food into a show.
Complementary feeding rules:
-
any new product is introduced only to a healthy child. A breastfed baby is given complementary foods up to the breast.
-
the introduction of new foods should not coincide with vaccinations, teething, vacations, or other stress for the child (when stressed, the child may refuse the proposed new product).
-
any new product is introduced in the morning (so parents have time to observe the child, look at his reaction, notice allergic manifestations) If the child has a reaction to a new product, then it is better to write it down, and try to introduce the product again after 5- 10 days.
 Because this reaction may not be related to the product, but caused by other factors. If the negative reaction is repeated, then the introduction of this product is postponed for 3 months.
Because this reaction may not be related to the product, but caused by other factors. If the negative reaction is repeated, then the introduction of this product is postponed for 3 months. -
it is advisable to introduce no more than one new product per day.
-
to get acquainted with the product, the child sometimes needs 10-15 sentences in order for him to start eating it. The reaction of the child in the form of wrinkling, pushing food, curvature of the face does not indicate that the child did not like the food, but only that the new taste is very bright for him and causes a large number of emotions. For children, even neutral tastes can seem very rich, due to the higher sensitivity of the receptors. Therefore, when introductory feeding, it is not recommended to use spices and salt in the preparation of food for the child.
Basic complementary foods
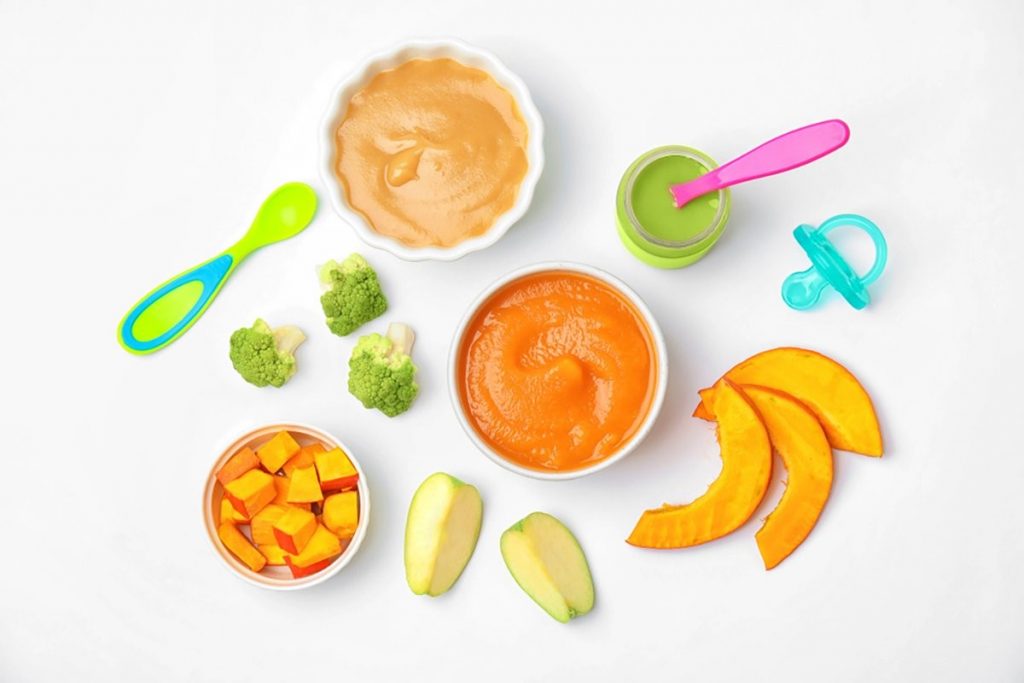
For the first feeding, there are three main types of products: cereals, vegetables and meat.
-
Cereals - Dairy-free cereals are used to start complementary foods. Rice, corn, buckwheat are the first to be introduced - these can be special “instant” baby cereals (we carefully study the composition, make sure that there are no additives, sweeteners, flavor enhancers, vitamins), instant cereals are well suited to start complementary foods, at 6-7 months, in the future you can switch to ordinary "adult" cereals, you can grind ready-made buckwheat or rice with a blender or fork; instant porridges in the form of flakes are also good. Then the rest of the cereals (oatmeal, rye, millet) are introduced. With an allergic burden in the family, the introduction of milk porridges earlier than 12 months is not recommended.
-
Vegetables – first add green/white vegetables (zucchini, cucumber, broccoli, kohlrabi, cabbage and cauliflower), then legumes, colored vegetables (carrots, pumpkin, beets, tomato)
-
Meat - the beginning of complementary foods with the most easily digestible and hypoallergenic meats - rabbit, turkey, then veal, beef, pork, lamb.
 Children with an allergy to cow's milk protein start complementary foods first with pork, then they introduce beef. Children with allergies are also trying to limit the introduction of chicken into the diet, as it is a highly allergenic product. Lamb is introduced to children no earlier than 10 months. Poultry meat - duck, goose - contains refractory fats and is not recommended for introduction into the diet of babies under 3 years of age.
Children with an allergy to cow's milk protein start complementary foods first with pork, then they introduce beef. Children with allergies are also trying to limit the introduction of chicken into the diet, as it is a highly allergenic product. Lamb is introduced to children no earlier than 10 months. Poultry meat - duck, goose - contains refractory fats and is not recommended for introduction into the diet of babies under 3 years of age. -
Fruit and dairy products are not considered essential complementary foods. Can be given for table variety. If the mother wants to give fruits, berries and juices to the child, it is better to use them as a flavoring additive to the main complementary foods or even postpone the introduction to an older age. In children with an allergic tendency, it is recommended not to introduce dairy products up to a year. You have to be careful with berries and fruits. It is best to start complementary foods with seasonal fruits and berries; the least and least likely to cause allergies are currants, blueberries, apples, pears, plums.
 Allergic reactions often occur on strawberries, bananas, citrus fruits.
Allergic reactions often occur on strawberries, bananas, citrus fruits. -
Fish and seafood. Not a main complementary food. But fish, like meat, is a source of protein, rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, as well as minerals and vitamins. It is recommended to introduce fish no earlier than 9-10 months. Again, if the child is allergic, it is advisable to refrain from introducing fish products up to 1 year. We begin to introduce complementary foods with low-fat white varieties of fish in the form of mashed potatoes - ice fish, hake, cod, haddock, pollock, navaga, pike perch, sea bass, dorado.
-
Egg . A product that is rich in many different micro and macro elements, vitamins. However, the egg has a very high allergenicity (included in the very big eight allergens). Considering that a quarter (5-6 g) or half (10-12 g) of the yolk, which are recommended to be administered, contains very few nutrients and energy, it is easier not to give this product than to risk allergic reactions in a child.

-
Whole nuts, peanuts should not be present in a child's diet until at least three years of age. In a number of countries, communities, families, where, for example, peanuts are common as a staple food, they can be used as an additive to complementary foods in a pureed state. Nuts are included in the big eight allergens and are not recommended for introduction into complementary foods for children with allergies up to three years of age.
-
Water . After the introduction of complementary foods, children can begin to offer water as a drink. First as an introduction, later as an additional source of fluid, while reducing the volume of breast milk (mixture). It should be pure water without any additives. It is important to remember that breastfed babies may go without water for quite a long time, due to the fact that they receive enough liquid from breast milk.
-
Tea . The World Health Organization does not recommend including tea in the diet of children under 2 years of age.
 Why? First of all, because of the tannins that are present in tea and can help reduce the absorption of trace elements, including iron and cause anemia. Tea also contains caffeine (it is found in a state associated with tannins and is more often called theine), which can cause excessive stimulating effect on the fragile nervous system of the child., It can also lead to increased heart rate, increased peristalsis of the stomach, increased body temperature - all this can adversely affect the general condition of the child.
Why? First of all, because of the tannins that are present in tea and can help reduce the absorption of trace elements, including iron and cause anemia. Tea also contains caffeine (it is found in a state associated with tannins and is more often called theine), which can cause excessive stimulating effect on the fragile nervous system of the child., It can also lead to increased heart rate, increased peristalsis of the stomach, increased body temperature - all this can adversely affect the general condition of the child. - Salt, sugar are not recommended for introduction into complementary foods under 1 year of age. Spices are introduced into the diet of a child after 2 years of age. These recommendations are based on the high sensitivity of the receptors in young children and the taste of tasteless dishes for children, even for us, is much brighter and richer.
WHAT to feed - the choice of parents. But it must be remembered that no single product (except for breast milk for children in the first months of life) can provide the body with all the nutrients, therefore, when compiling complementary foods, a variety of products should be combined.