Baby poop while feeding
How often should a newborn poop?
Yes, it's normal if your baby is pooping after every single feeding. You’ll quickly discover that when it comes to newborns, poop frequency comes in a wide range of normal.
Some babies are just more productive poopers than others. It’s perfectly okay to end every feeding with a diaper change, or to not see a single bowel movement for a few days. Your baby pooping a lot probably isn’t an issue, unless you’re changing three or more extra-watery diapers a day. In that case, it could be diarrhea, which is something to let your baby's doctor know about.
How often should a newborn poop?
It varies. Poop habits differ a lot from baby to baby. The average frequency is one or more bowel movements daily. But some newborns produce five or more dirty diapers a day in their first 2 weeks of life, while others go for days without pooping.
It’s not unusual for newborns to poop a lot, since they spend most of their waking hours eating. In general, breastfed babies poop more than formula-fed ones. In fact, your baby may poop while nursing and again once they’re done – which is why you may want to wait a few minutes after you're finished breastfeeding before swooping in with a clean diaper.
Because breastfed poops contain more liquid, they’ll look more watery than the stools of formula-fed babies. (See real photos of the different kinds of baby poop here.)
When a breastfed newborn poops after every feeding during the first few weeks, take it as a good sign – it means they’re getting plenty of milk. Even though formula-fed babies may have less frequent bowel movements than breastfed babies, it's normal for them to poop after every feeding as well.
The frequency of your baby's bowel movements may start to slow down by the time they're around 6 weeks old, but some babies continue their pattern of pooping after every feeding for much longer. (It’s not uncommon for some 1-year-olds to poop five times a day.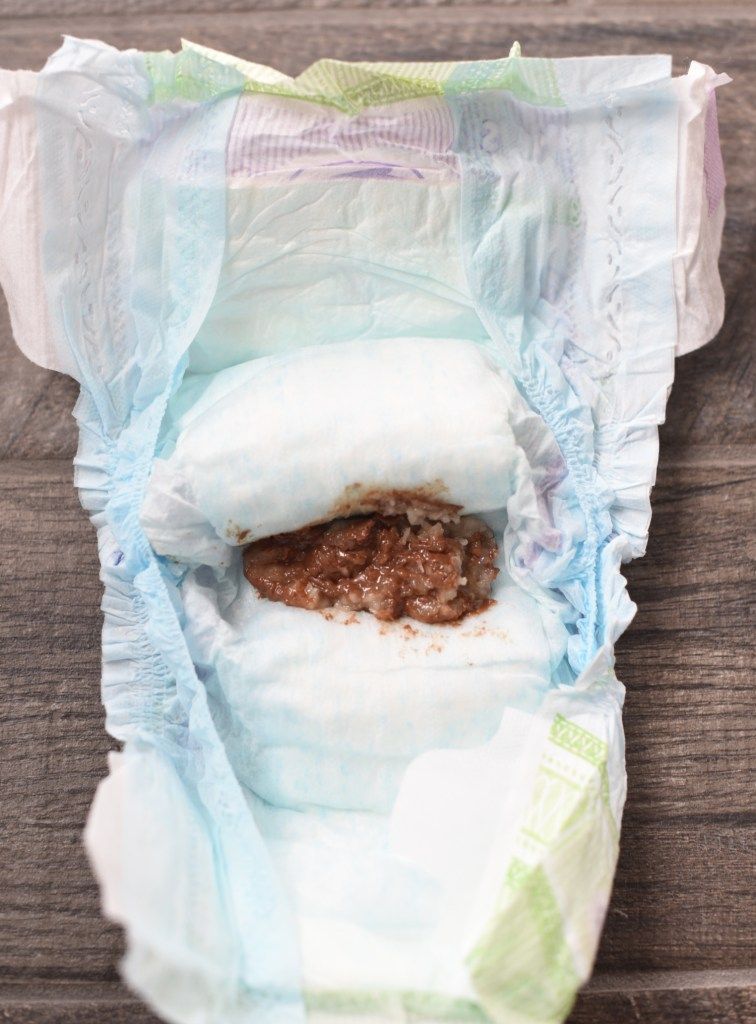 )
)
How long can a baby go without pooping?
If your baby hasn’t had a bowel movement in a few days, there’s no need to immediately fear the big “C” (aka, constipation). Babies can go days, or even a week, without producing a dirty diaper. A breastfed baby can go even longer – as long as two weeks without pooping if they haven’t started on solid foods yet.
Advertisement | page continues below
If the bowel movements your baby does make are soft, constipation probably isn’t an issue. Exclusively breastfed babies rarely get constipated because breastmilk is an economical food. Your baby gets just what they need, with little waste leftover to poop out.
True constipation in babies typically happens from a change in diet, a lack of fluids, or an illness. The telltale sign is hard, dry stools. If your baby is constipated, they may get extra fussy and look like they’re straining uncomfortably when they try to go.
Should I ever be worried about my baby pooping a lot?
Generally, if your baby's bowel movements are fairly consistent and they’re acting like their usual self, frequent poops aren't a cause for concern.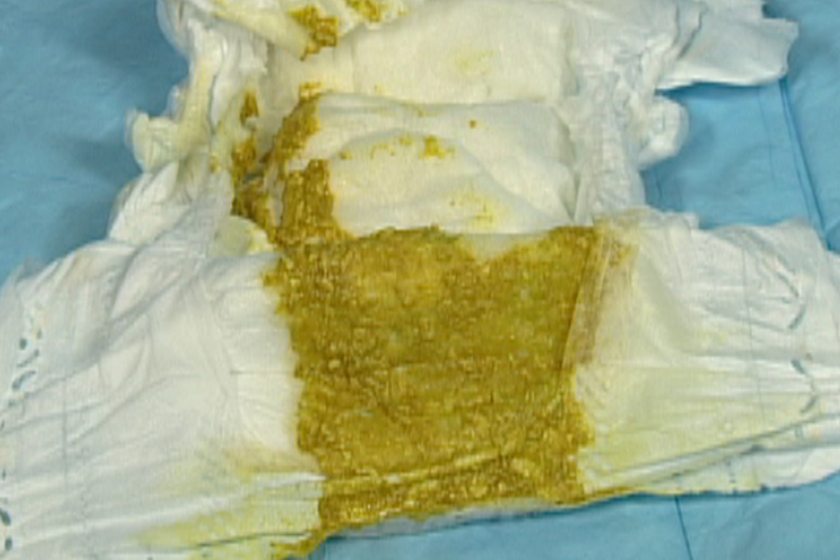 However, if there's a sudden change in your baby's pooping pattern and their stool becomes watery, check with their doctor. Very watery bowel movements could be a sign of an infection.
However, if there's a sudden change in your baby's pooping pattern and their stool becomes watery, check with their doctor. Very watery bowel movements could be a sign of an infection.
Call the doctor if your baby has any of these other poop-related symptoms:
- Pulling their legs up to their stomach (a sign that their tummy hurts)
- Straining to have a bowel movement
- Poop that looks like small, hard pebbles or is extra watery
- Irritability
- A swollen belly
- Blood in their poop
If my baby is pooping a lot, are they more prone to diaper rash?
Babies who have frequent bowel movements can be more susceptible to diaper rash. Constant contact with stool can irritate the sensitive skin on their bottom.
The best way to prevent diaper rash is to keep your baby’s bottom clean and dry. To start, change their diapers more often. Wash their skin clean with warm water during each change.
You may want to coat the area with a diaper rash cream or a product containing zinc oxide or petroleum jelly to create a barrier. And instead of putting on a new diaper right away, let your baby go diaper-less for a little while each day so their bottom can fully air dry. If these tips don’t relieve the diaper rash, give your baby's doctor a call.
And instead of putting on a new diaper right away, let your baby go diaper-less for a little while each day so their bottom can fully air dry. If these tips don’t relieve the diaper rash, give your baby's doctor a call.
Read more:
A new parent's guide to baby poop
Age-by-age guide to feeding your baby
How much formula newborns and babies need
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Baby Poop Guide | Children's Hospital Colorado
No one said it’s pretty or fun, but it’s a fact: As a new parent, you’ll spend a lot of time looking at your baby’s poop. The good news? All those diaper changes can give you insight into your baby’s health.
Our experts have created a baby poop guide to give you the 411 on your baby’s number two, with special information for babies in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) or with ongoing medical needs.
Infant poop frequency
Stool frequency in babies varies, so don’t put too much stock into how many times a day your baby “should” be pooping. Babies can poop as frequently as every feeding or as infrequently as every two to three days. Neither of these situations should cause you alarm. Breastfed infants tend to poop more frequently than formula-fed infants.
Babies can poop as frequently as every feeding or as infrequently as every two to three days. Neither of these situations should cause you alarm. Breastfed infants tend to poop more frequently than formula-fed infants.
When should I call my pediatrician?
While every baby’s poop schedule is unique, if your baby hasn’t pooped in four days, you should call your pediatrician. This could be a sign of constipation.
Infant poop color
For new parents, or even experienced parents, the color of your baby’s poop can surprise you. Babies can create a rainbow of poops, but it typically doesn’t mean there’s a problem.
Almost all infants’ first poops will be thick, black and tarry looking. These stools are called meconium and are completely normal.
When your baby starts breastfeeding or drinking formula, their poop will turn green or yellow and have a more liquid consistency. Breastfed babies’ poop will stay in the green-yellow-brown palette as long as they continue breastfeeding.
Formula-fed babies’ poop will typically be slightly lighter, but similar in color to breastfed babies. Slight changes in color are typically the result of your baby’s intestinal lining or how they digest milk and aren’t concerning.
As your baby begins to eat solid food, it will change the color of their poop. This is natural, but certain colors can tell you something about your baby’s health or signal a warning sign.
Red baby poop
While it may look startling, red poop is almost always caused by red food or medicine. The exception? Bloody stool, which can signal allergies or bleeding in their gastrointestinal tract. Call your doctor if you see blood in your baby’s poop.
Green baby poop
This is completely normal, even when it’s dark green. Dark green poop is usually caused by bile, a fluid made in your baby’s liver that aids digestion. Inspect dark green poop closely (yes, this is your parental duty) to make sure it’s not black, as that could be cause for concern.
Black baby poop
If your baby has black poop after their very first poops, it could be a sign of stomach bleeding. Look at the poop under bright light and if it’s black instead of dark green, call your doctor.
Yellow baby poop
Any poop that is yellow, orange or brown is completely normal.
White or light grey baby poop
This is the one shade that should almost always alert you of a problem. White baby poop could signal that your baby has a liver condition and isn’t digesting food properly.
When should I call my pediatrician?
Most colors are normal but call your doctor if your baby’s poop is white, black or has blood in it.
Infant poop consistency
Baby poop is softer and more liquid than older kids’ stool. The following consistencies are normal for breastfed and formula-fed infants:
- Soft and somewhat runny
- Slightly seedy
- Pasty (more common in formula-fed babies)
If your baby’s poop strays too far from these textures, that’s when you should get concerned.
When should I call my pediatrician?
Two situations should ring minor alarm bells:
- Very loose or watery stool for three or more diapers, which could lead to dehydration
- Hard, pellet-like poop — a sign of constipation
Never give your infant laxatives, enemas, suppositories or other stool stimulators without asking your doctor first.
What to know about poop for babies with complex medical needs
Babies who spend time in the NICU or have complex medical needs often need extra care or follow different developmental timelines than other babies. Parents need to learn new information about their baby’s condition and what to look for.
When it comes to baby poop, parents whose babies have medical conditions should be on the lookout for the same things mentioned above, with a few additions.
Poop for babies with gastrointestinal issues
Babies with gastrointestinal conditions or complications will face the greatest impact to their digestive systems. Their bowel movements and developmental schedule won’t be the same as their peers’. Here are some gastrointestinal issues that affect a baby’s poop:
Their bowel movements and developmental schedule won’t be the same as their peers’. Here are some gastrointestinal issues that affect a baby’s poop:
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC): This is a serious intestinal disease for premature babies that occurs when the small or large intestine becomes inflamed. This can sometimes create a hole in the intestinal wall that allows waste to move into the baby’s bloodstream or abdomen, which can make the baby very sick. Both diarrhea and constipation can be symptoms of NEC. Some babies with NEC need to have some of their bowel removed, which affects their ability to absorb food. This can make them more prone to liquid stool and weight gain issues, even as they grow older. Our neonatal and gastrointestinal experts work together to get the best results for babies with NEC.
- Babies with blockage or narrowing of bowels: These bowel issues often require surgery. Bright green poop or no pooping for the first few days of life are warning signs for blocked or narrow bowels.

Reaction to medication
When babies leave the NICU, they sometimes remain on medication or have different dietary needs. This may change the color or consistency of their poop. These changes shouldn’t alarm you, but you should know what to expect, so you can spot anything that really is a problem.
- Antibiotics: When babies are on antibiotics at home, they often have looser stool and are at higher risk for developing diaper rash. If your baby is on antibiotics, try to change their diaper soon after they poop and apply a barrier cream like Vaseline® or Desitin® as a preventive measure.
- Fortified breastmilk or medication: If your baby needs more calories, they may be given fortified breastmilk for feeding at home. Our doctors might prescribe medication to take at home for several conditions. Both of these could change your baby’s poop, so talk to your doctor to know what to expect.
I want tips and advice about
BehaviorHealthMental HealthParentingSafetyfor
Before Birth (Prenatal)Babies (0-1) Toddlers (2-4)Kids (5-10)Pre-Teens & Teens (11+)
how to recognize, causes, treatment, how to stop diarrhea in a baby?
Every mother knows that babies poop frequently: a breastfed baby may have the same bowel movements as the feeding frequency. And babies often have tummy ache and colic due to the fact that the gastrointestinal tract is completely immature and is just beginning to be populated by beneficial bacteria. Therefore, it is not always clear to a young mother whether everything is fine with her baby. How do you know when something is wrong?
And babies often have tummy ache and colic due to the fact that the gastrointestinal tract is completely immature and is just beginning to be populated by beneficial bacteria. Therefore, it is not always clear to a young mother whether everything is fine with her baby. How do you know when something is wrong?
For a baby under three months old, the normal frequency is three to six times a day if the baby is breastfed, and about two times a day if he is bottle-fed. At the same time, the frequency of the stool can also change normally, due to the fact that the baby was nervous or the mother changed the menu. Therefore, when talking about diarrhea in a baby, they first of all take into account not how often he poops, but the volume and nature of the stool, as well as the behavior of the baby himself.
You can suspect diarrhea in a baby if he poops twice as often as usual, the stool becomes much thinner (in a breastfed baby, it is usually liquid and poorly formed), changes color, pathological impurities appear in it: a lot of mucus, blood, foam, undigested food particles, if complementary foods have already begun. The behavior of the baby also changes: he cries, presses his legs to his chest, or, conversely, stretches out to the line. The tummy may swell and growl.
The behavior of the baby also changes: he cries, presses his legs to his chest, or, conversely, stretches out to the line. The tummy may swell and growl.
If the diarrhea is caused by an infection, the child has a fever and becomes lethargic.
Causes of diarrhea in infants
The most common cause of diarrhea in infants is dysbiosis, that is, a change in the composition of the intestinal microflora. This may be due to a viral or bacterial infection, but is usually due to other causes such as:
- late attachment to the breast;
- artificial feeding;
- products not according to age;
- use of antibiotics;
- food allergy;
- lactose intolerance;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcerative colitis and others).
One way or another, all these conditions disrupt the normal balance between beneficial and harmful microbes in the intestines, and consequently, digestion and intestinal motility: too much fluid remains in the intestinal lumen, which causes diarrhea.
Treatment of diarrhea in children
Seek immediate medical attention if:
- there is blood in the baby's stool;
- diarrhea accompanied by vomiting;
- the child has a fever;
- the baby stops peeing or peeing less than four times a day;
- no tears during crying, skin and mucous membranes become dry;
- fontanel sinks;
- the baby's skin, if folded, does not straighten out immediately.
If your baby is stable, you can try to manage the diarrhea on your own. Change diapers more often: feces irritate baby's delicate skin. If complementary foods are introduced, cancel it, leave only breast milk or formula that the baby eats constantly.
Give the child a drink. Adherents of breastfeeding argue that the baby has enough liquid contained in breast milk. This is true, but only if the child is healthy. During diarrhea, fluid loss increases several times, and it is dehydration that is the most common cause of death from intestinal infections. You can supplement it with plain boiled water, but it is better with a special solution of salts, which are also actively lost during diarrhea (Regidron, Trisol, Ringer's Solution, Humana Electrolyte). If the child is older than nine months, you can give rice water.
You can supplement it with plain boiled water, but it is better with a special solution of salts, which are also actively lost during diarrhea (Regidron, Trisol, Ringer's Solution, Humana Electrolyte). If the child is older than nine months, you can give rice water.
To restore the normal balance of microflora, you can (and should) give probiotics. The best option is a complex of bifido- and lactobacilli. Both are important for normal digestion and microbial balance. You can start taking probiotics before visiting your doctor.
Note
Probiotics are sold in pharmacies in various forms: tablets, capsules, sachets (powder in sachets). However, it should be remembered that for young children, complex microorganisms in the form of drops are most convenient for use.
If diarrhea does not stop within two to three days, be sure to contact your pediatrician.
Statistically, children experience at least one or two episodes of diarrhea every year until they are five years old. Therefore, diarrhea in itself is not yet a reason for panic: usually its cause is the immaturity of the baby's gastrointestinal tract and the disruption of the normal balance of microflora. Most of the time, you can deal with this problem on your own. But, if the child has a fever, blood appears in the feces, there are signs of dehydration: the skin and mucous membranes are dry, there is little urine, there are no tears, the fontanel sinks, consult a doctor immediately!
Therefore, diarrhea in itself is not yet a reason for panic: usually its cause is the immaturity of the baby's gastrointestinal tract and the disruption of the normal balance of microflora. Most of the time, you can deal with this problem on your own. But, if the child has a fever, blood appears in the feces, there are signs of dehydration: the skin and mucous membranes are dry, there is little urine, there are no tears, the fontanel sinks, consult a doctor immediately!
How many times should a newborn poop
Tiunova Elena
Published: 01/15/2023
Reading time: 6 minutes
1865
Even the most squeamish girls with the birth of a baby become tireless researchers of the contents of a dirty diaper.
- Isn't it a lot? But not a little? Isn't it rare? But not often? Is the color normal? Is the consistency good? Is it supposed to smell like this? - young mothers are ready to discuss these subtleties at any time, regardless of the enthusiasm of the interlocutor. They can be understood.
They can be understood.
On the one hand, a newborn does not know how to do much - eat, sleep and, in fact, dirty a diaper. Therefore, there are few topics for discussion at first, but I want to talk. On the other hand, it is indeed possible to draw conclusions about the state of health of the infant from the answers to these specific questions.
Frequency and nature of stool in a breastfed child.
In the first two or three days after birth, the baby passes the original stool - meconium. If a young mother does not know about this, she may be frightened by a sticky dark mass that is difficult to wash off. When a woman has milk, the baby's feces brighten, acquire a mushy texture and a milky, slightly sour smell.
In the first month and a half, the baby may poop after each feeding.
If before 4-6 weeks of life he poops less than once every 24-36 hours, this may indicate a lack of nutrition. Weight gain must be controlled. On average, for the first weeks of life, it should be 125-150 g.
As for consistency and color, the stool should be mushy, from bright yellow to greenish in color.
This is important!
If the baby eats with appetite, gains well, behaves actively, then the shade of the contents of the diaper is not so important. Anxiety should be caused by an admixture of blood in the stool, streaks of mucus, blisters and a sharp putrid smell. This should be reported to the pediatrician immediately.
After one and a half months, the baby may start to poop less often. For many mothers, this is a source of serious concern. If the baby does not poop for a day, two, three, anxiety covers. But this condition for a breastfed baby is most often the norm. If the child behaves as usual, and the stool after the delay is soft and moves away effortlessly, then everything is in order.
Should alert hard shaped stools, crying and strong straining during bowel movements - these are signs of constipation.
Recent studies from the American Academy of Pediatrics suggest that, with normal health and behavior, a baby aged 4-6 weeks and before the introduction of complementary foods may pass stools even once a week or less. But be attentive to the condition of the baby and still consult a doctor before ignoring a ten-day stool retention in crumbs.
But be attentive to the condition of the baby and still consult a doctor before ignoring a ten-day stool retention in crumbs.
With the introduction of complementary foods, the baby's stool will become more formed, but should still retain a soft consistency.
This is important!
When the baby begins to receive complementary foods, he should defecate at least once a day. If the baby has signs of constipation - rare or formed hard ("sheep") stools, difficult bowel movements - you need to consult a doctor to find and eliminate its cause.
Frequency and character of stool in a formula-fed child.
A bottle-fed newborn can poop once a day even in the first weeks.
After one and a half months, formula-fed babies should have a bowel movement daily.
Formula-fed babies will have a firmer stool consistency than breastfed babies, but should still be soft. Hard, shaped stools in infants, regardless of the method of feeding, are a sign of constipation.
Color may vary depending on mix. It is usually yellow or dark yellow. Too bright or very dark shades, a pronounced green color is a deviation from the norm, you need to consult a doctor.
What can affect stool frequency and consistency?
Food. The frequency and nature of the baby's stool is primarily influenced by the type and quality of the food he receives. For babies, it is important that the mother's diet is balanced and varied, so that she does not smoke or drink alcohol. If the child is allergic - so that the mother does not eat foods that cause an allergic reaction. Properly selected milk formula is important for babies on artificial feeding. If these conditions are not met, it will immediately be noticeable in the stool of a newborn.
Functional disorders. In newborns, malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract may occur not due to illness, but due to the immaturity of the body - both the gastrointestinal tract itself and the nervous system. That is, a healthy baby without errors in nutrition can still experience constipation or diarrhea.
That is, a healthy baby without errors in nutrition can still experience constipation or diarrhea.
Infectious diseases. Often, it is by the nature of the stool of a newborn that one can notice that an infection has entered the body. Rapid loose stools, foam, an unpleasant odor will immediately indicate the onset of the disease.
Taking medications. Iron preparations have the most pronounced effect on the color of the stool: it becomes gray-black. If the child does not take iron-containing medicines, then this color of the stool is an alarm. It may indicate intestinal bleeding.
If the child is on IV, Nutrilak Premium COMFORT can help normalize stools. The mixture is specially designed for sensitive tummies.
So, a dirty diaper is not "fuuu", but a source of valuable information about the well-being of the baby. If you have doubts about what you saw, do not hesitate to consult your doctor.
Author of article
Tiunova Elena
Pediatrician of the highest category, nutritionist, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department of faculty pediatrics and propaedeutics of childhood diseases, Ural State Medical University
About the author
Share on Vkontakte Share on Odnoklassniki
Contents of the article
- Frequency and nature of stool in a breastfed child.