Baby solid food diet
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.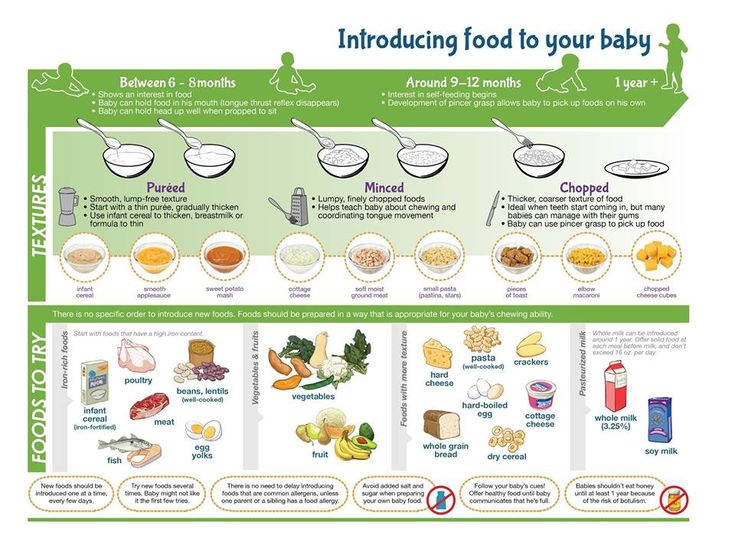
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.

- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.
- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
Listen
Español
Text Size
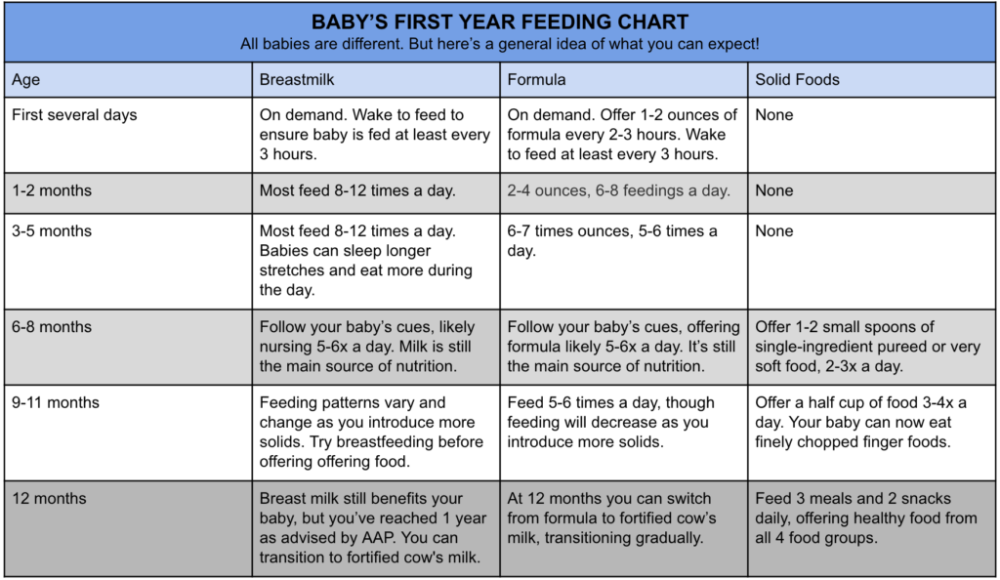
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water. (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Solid food | Tervisliku toitumise informatsioon
From the age of 6 months, in addition to breast milk, the baby needs to be supplemented to provide the necessary amount of energy and nutrients.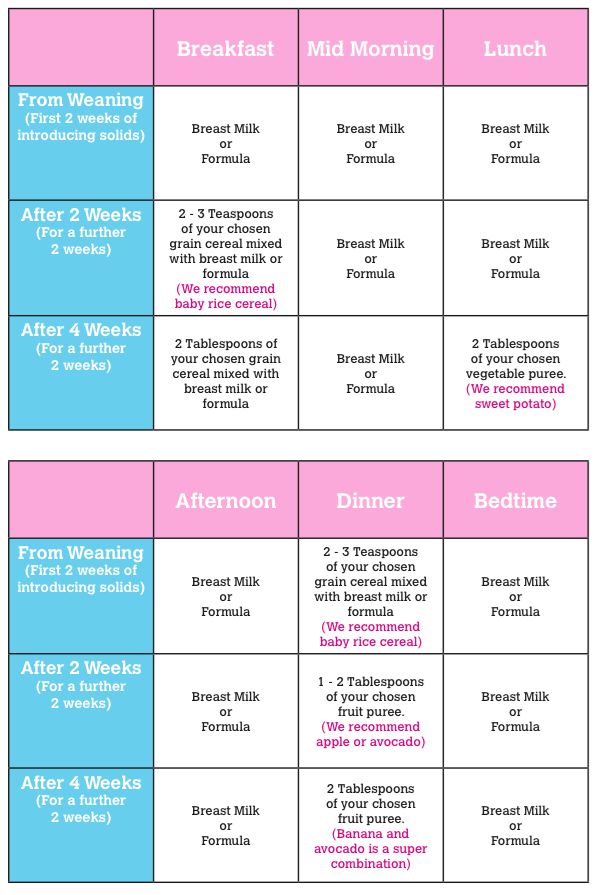 As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, so that the food is varied . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
As you grow older, you can gradually switch to regular food (cooking it without frying, and also without adding salt and sugar). Children over 1 year of age, in addition to regular food and complementary foods, can continue to drink breast milk, but by the age of two, the child should completely switch to a common table. Exposure of a child to grain-containing foods during breastfeeding may protect him from gluten intolerance in the future. When offering a child complementary foods or regular food, care should be taken, so that the food is varied . Both during breastfeeding and during the transition to regular food, the baby may experience gases or allergies .
For children over two years of age, the same nutritional recommendations apply as for adults, but the recommended serving sizes are smaller.
Children under three years old (actually, a person of any age) do not need salty or sweet snacks, sodas, deep fried and/or very sweet and salty foods!
By the sixth month of life, the infant's eating habits and digestive system are mature enough to offer more solid foods in addition to breast milk.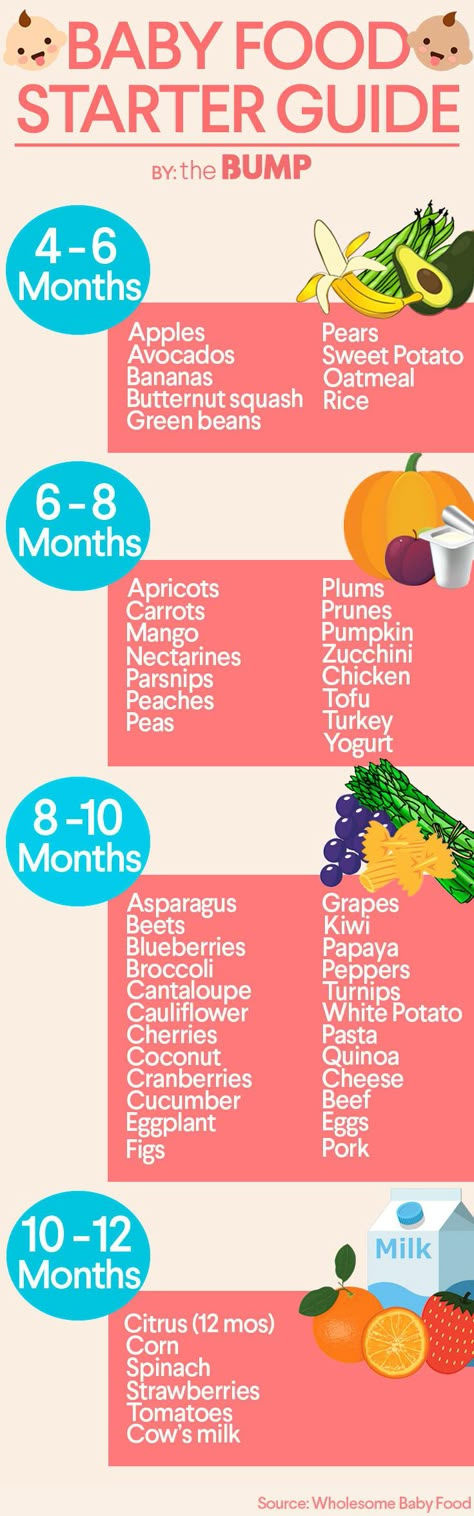 Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i.e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it.
Proteins, carbohydrates and fats contained in regular food are different from the easily digestible sugars, fats and proteins that enter the baby's body with breast milk. Therefore, a so-called certain familiarization period is needed so that the baby's digestive system has time to get used to a new type of food. If the baby is breastfed as often as before, then these feeds cover about 2/3 of the energy needed by an 8-month-old baby. The remaining approximately 200 kilocalories should come from the various macronutrients found in complementary food ingredients, i.e. proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Complementary foods are needed so that the child can slowly move to the common table, as well as to obtain the nutrients necessary for age. Complementary foods for babies are a completely unfamiliar thing. It differs significantly from breast milk and will take time to learn how to eat it.
Proper complementary food is food that is hard enough to eat with a spoon, contains all the important types of food (except sweets), is rich in nutrients and does not contain salt or sugar. Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development.
Complementary foods should always be offered to the child from a spoon and never from a bottle, as in this case the child will never understand what to eat in an upright position using a spoon. In addition, bottle feeding contains too much water, so it may not provide enough energy and nutrients. As the child grows older, you can allow him to put pieces of food in his mouth with his fingers. Simultaneously with the gradual introduction of solid food into the baby's diet, his interest in breast milk gradually begins to fade. This is completely natural and as the first birthday approaches, you can start to slowly reduce the number of breastfeeds. All children are different, so their preferences and needs are also different, but it is important that the child's diet is varied and covers all the nutritional needs of a growing body for life and development.
Complementary foods for infants by month:
0-6 months
6-8 months
9-11 months
substances can be markedly reduced.
World Health Organization recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for children aged 6-23 months.
| Age (in months) | Frequency Frequency | The portion for 1 feeding | food consistency |
| 6 | 9000 1 or 2 times a day | 7
quantity | Finely pounded or mashed |
| 6-8 | 2-3 feedings per day 1 10047 up to 1 DL | Crowned or pureed | |
| 9-11 | 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 snacks per day | 9000 1-1.5 DL 1111111111111111111111 | Crowned or finely busy |
| 12-2-23 | 3-4 feeding per day 1-2 snacks | .5 DL | Small pieces |
The recommendations in the table are general and give an idea of how much a child could eat on average, however the exact amount and frequency of feedings may vary from child to child. The child must learn to understand that when the feeling of satiety has come, eating should be stopped. A child is full when he turns his head away and doesn't want to eat anymore. However, it is important to make sure that the baby still ate at least a little, as many children refuse to eat before they even start eating. We need to find a balance between these two extremes. The child should be introduced as early as possible to the regularity of meals and the fact that constant snacking should be avoided during the day. The baby is fed approximately every three hours: this can be breast milk, the main meal or a snack.
The child must learn to understand that when the feeling of satiety has come, eating should be stopped. A child is full when he turns his head away and doesn't want to eat anymore. However, it is important to make sure that the baby still ate at least a little, as many children refuse to eat before they even start eating. We need to find a balance between these two extremes. The child should be introduced as early as possible to the regularity of meals and the fact that constant snacking should be avoided during the day. The baby is fed approximately every three hours: this can be breast milk, the main meal or a snack.
how and when to introduce a child to solid food
Solid food: how and when to introduce a child to solid food Expecting new skills from the baby, do not rush things. It is necessary to acquaint the child with solid food no earlier than 6-7 months. At this time, the desire to scratch the gums, ready for the appearance of the first teeth, will coincide with the interest in adult food.
Dry initial milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 1 NutriValio for feeding children from birth to 6 months Read more
Follow-up dry milk formula adapted by Valio Baby 2 NutriValio for feeding children from 6 to 12 months More
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months More
Children are born with a vital, unconditioned reflex - sucking. They are ready to suck on their mother's breasts, but all solid objects that have fallen into their mouths are automatically pushed out so as not to choke (a protective reflex is triggered). Therefore, parents are not recommended to accustom the baby to solid foods too early. This will cause not only rejection, but sometimes vomiting. The ideal time is considered to be the start of complementary foods. When the first teeth begin to grow in the child, you can replace the homogenized puree with food with the addition of soft fibers. They will be to the taste of the baby, as they will massage itchy gums. An important clue for parents is also the child's interest in adult food. If the baby looks into your plate, tries not to suck on mashed potatoes in a spoon, but to remove it with his upper lip and chew - it's time to introduce more solid food into the children's menu. First, at the tip of the spoon, offer the baby vegetable and cereal side dishes, closer to 9months you can give pieces of well-boiled meat. The kid does not immediately learn to chew them, and the food will come out with a stool almost in its original form. It's not scary, over time the child will learn everything. It is important not to ignore his desire, you will have to pay for the pedagogical miscalculation and literally teach the child to chew.
The ideal time is considered to be the start of complementary foods. When the first teeth begin to grow in the child, you can replace the homogenized puree with food with the addition of soft fibers. They will be to the taste of the baby, as they will massage itchy gums. An important clue for parents is also the child's interest in adult food. If the baby looks into your plate, tries not to suck on mashed potatoes in a spoon, but to remove it with his upper lip and chew - it's time to introduce more solid food into the children's menu. First, at the tip of the spoon, offer the baby vegetable and cereal side dishes, closer to 9months you can give pieces of well-boiled meat. The kid does not immediately learn to chew them, and the food will come out with a stool almost in its original form. It's not scary, over time the child will learn everything. It is important not to ignore his desire, you will have to pay for the pedagogical miscalculation and literally teach the child to chew.
Of course, not everything can go according to plan. The most common reasons why a child refuses solid food:
The most common reasons why a child refuses solid food:
-
The pieces of food are too big.
-
You are using the wrong feeding technique.
-
The spoon is big for a child.
-
The child has unpleasant associations - perhaps you gave him medicine from this spoon. Do not use everyday baby utensils for unpleasant procedures.
-
The child is in a bad mood or does not feel well.
In no case do not force the baby to eat if he refuses. Gently try again and again. Set an example - eat the first spoon yourself, showing the crumbs how tasty his food is. If the child still cannot cope with solid food, it is worth contacting a pediatric osteopath. The baby may have a non-standard structure of the maxillofacial system, subluxation of the jaw associated with birth trauma, problems with muscle tone. The timely introduction of solid food is very important not only for the full nutrition of the child, it affects his future speech activity. Breastfeeding is a good prevention of speech therapy problems. In order to suck milk from the breast, the child needs to make more efforts than when feeding from a bottle - this is a good (and what is valuable - natural) training of the jaws and muscles of the tongue, and it must be continued by introducing the crumbs to solid food in time. Of course, a baby with a piece of an apple in his hands (and in his mouth) must be looked after so that he does not choke. By the way, for the development of the chewing and speech apparatus, it is useful to grimace with the baby during the game - this strengthens the facial muscles well.
Breastfeeding is a good prevention of speech therapy problems. In order to suck milk from the breast, the child needs to make more efforts than when feeding from a bottle - this is a good (and what is valuable - natural) training of the jaws and muscles of the tongue, and it must be continued by introducing the crumbs to solid food in time. Of course, a baby with a piece of an apple in his hands (and in his mouth) must be looked after so that he does not choke. By the way, for the development of the chewing and speech apparatus, it is useful to grimace with the baby during the game - this strengthens the facial muscles well.
2.71 7
FoodShare:
Ivargizova Oksana
Medical Institute. Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Pavlova, specialization - pediatrics
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Oksana Ivargizova
How to choose a milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
We want to make our site more convenient for you, so we collect analytical data about your visit using cookies. By continuing to use the site, you agree to this. For more information on the collection and processing of data, please see the Personal Data Processing Policy.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to this. For more information on the collection and processing of data, please see the Personal Data Processing Policy.
Password recovery
To recover your password, enter your e-mail, which you specified during registration. We will send you a message with further instructions to this e-mail
Thank you for contacting us!
A letter with information to reset your password
has been sent to your mail
Back to the site
YOUR CITY -
?
Yes Change
We want to make our site more convenient for you, so we collect analytical data about your visit using cookies. By continuing to use the site, you agree to this. For more information on the collection and processing of data, please see the Personal Data Processing Policy.