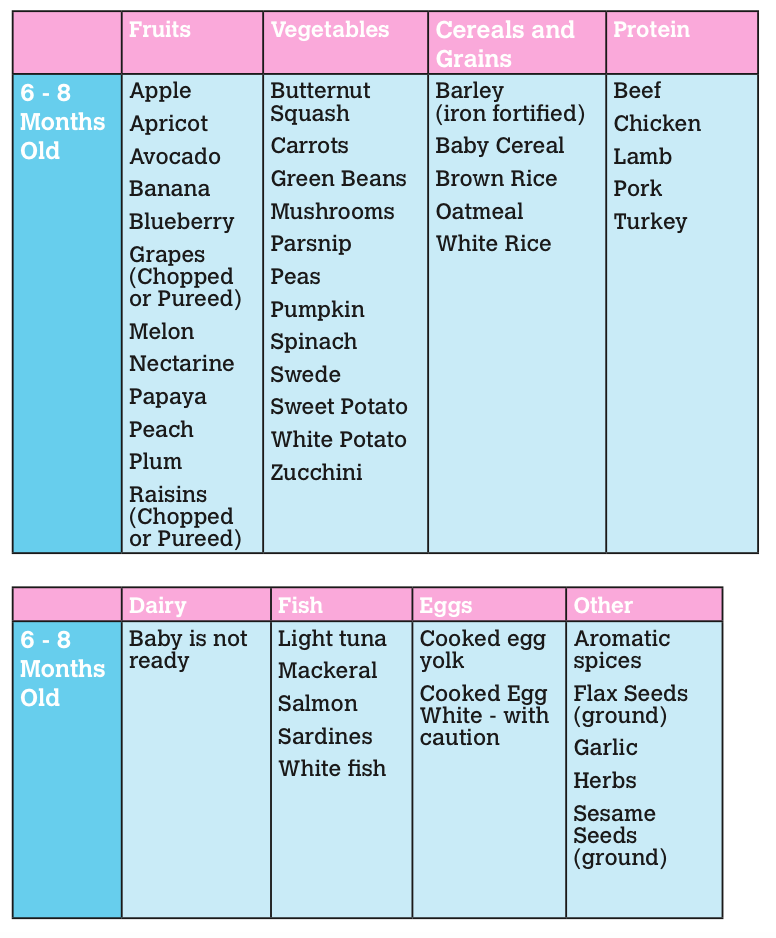
Baby supplemental feeding system
Nursing Supplementers - La Leche League GB
If your baby needs a supplement of expressed breastmilk or formula, a nursing supplementer can help you enjoy the closeness of breastfeeding while your milk production increases.
You can use a supplementer to:
- Stimulate breastmilk production while feeding infant formula or expressed mil, without using bottles.
- Breastfeed an adopted baby.
- Breastfeed as a non-birth parent.
- Maintain breastfeeding if your milk production isn’t able to meet your baby’s needs eg insufficient glandular tissue.
- Maintain breastfeeing if your milk production is compromised eg breast surgery or reduction.
- Encourage a baby who is reluctant to breastfeed.
- Breastfeed a baby who is unable to feed effectively because of sucking or health problems. However this will only work if you baby can feed well enough to obtain milk.
How it works
How to use
Available products
Different supplements
How to use a nursing supplementer
Cleaning
Eliminating supplements
Seek Support
How it works
A nursing supplementer lets a baby get any supplement he needs at the breast without using bottles. The supplementer container holds the milk, which travels through a tube into your baby’s mouth while he breastfeeds. As he swallows, he continues sucking, stimulating your milk production.
If you are breastfeeding expressing your milk, and giving top-ups to your baby, you may find it simpler to use a supplementer, which allows all the feeding to happen at the breast.
A good latch-on
It’s especially important that your baby latches on deeply at the breast when you are using a supplementer. Get help with positioning and attachment so your baby can get milk from the breast as well as from the supplementer.
Different supplements
Expressed breastmilk Your expressed breastmilk is the first choice for a supplement. If your baby has feeding difficulties, expressing will help you maintain and increase your milk production. To find our more about increasing your supply, see our article How to Increase Your Milk Supply. And for more information on Expressing Your Milk our article can help.
Donor milk Human milk banks provide pasteurized, screened donor milk.
Infant formula Concentrated and ready-to-feed forms of infant formula are less likely to clog nursing supplementer tubing than powdered forms. Although expensive, ready-to-feed formula may also be more convenient when you are out and about or at home without help. Powdered infant formula is not sterile, so always follow the NHS guidelines for preparing it.
Available products
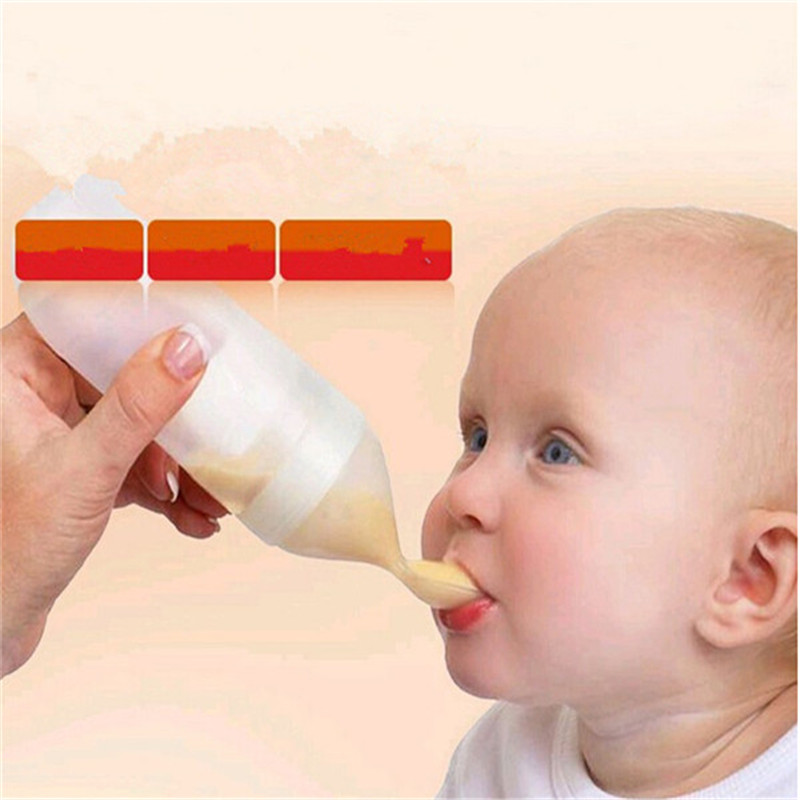
Disposable bag system This uses disposable sterile plastic bags with a top opening and a single tube. Milk only flows when a baby sucks and it is discreet to use as the bags are not bulky or noisy. You can also feed lying down without fear of leaks. When your baby sucks, the flow increases as the flow of milk from your breast decreases. This reinforces proper suckling, making the most of your milk production. (As in photograph above.)
Bottle system This system uses a bottle with a tube for each breast, making switching sides easy or for twins. Each tube can be clamped. Three tube widths are available. Sets can be cleaned and reused. (As seen in the photograph below.)
Each tube can be clamped. Three tube widths are available. Sets can be cleaned and reused. (As seen in the photograph below.)
Homemade system You can make your own supplementer using an ordinary baby bottle, bottle teat and an infant nasogastric feeding tube (size #5 french, 52-75 length). Tubing can be obtained from online suppliers. (As seen in the first and last photos in this article.)
Cut a small hole in the bottle teat so the tube fits tightly. Thread the tube through the teat from the inside and attach the teat normally so the end of the tube sits in the supplement. The tube end is rounded and won’t hurt your baby’s mouth. Pierce a second hole in the teat, or use a teat with a vent to allow air in so your baby won’t need to suck harder as the bottle empties. The bottle needs to stay upright. You may find tucking it into your bra keeps it in place.
Photo courtesy of Michelle Green
How to use a nursing supplementer
Introduce the tube into your baby’s mouth along with the breast at the very beginning of a breastfeed by placing it between your baby’s upper lip and cupped tongue.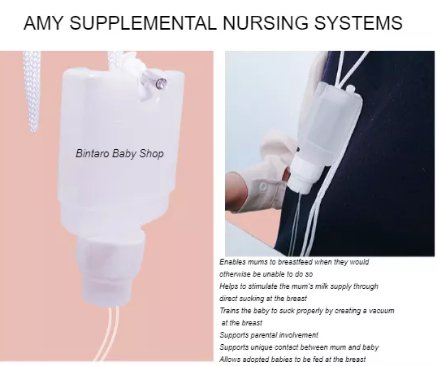 If your baby doesn’t like the feel of the tube on the roof of his mouth try placing it so it lies along his tongue. Or, slip the tube into the corner of your baby’s mouth once he is well-attached at the breast.
If your baby doesn’t like the feel of the tube on the roof of his mouth try placing it so it lies along his tongue. Or, slip the tube into the corner of your baby’s mouth once he is well-attached at the breast.
You may need to extend the tube past the end of your nipple – experiment to see what works for your baby. The tube can be secured to your breast with medical tape. Taping along the tube is generally more secure than taping across it.
To hold the tube in position some mothers use fabric sticking plasters cut from a long strip. They thread the tube under the non-sticky sections.
The tube can be easily removed while the plasters stay in place, reducing skin irritation from tape removal and providing a guide for positioning each time.
Milk flow – too fast or too slow?
Constant milk flow can cause ineffective feeding as your baby will not need to actively suck to get milk. When using a supplementer you will see the milk travel along the tube to your baby’s mouth.![]() Adjust the tube position and container height so your baby gets milk quickly when he starts sucking. Check he isn’t overwhelmed with milk, especially if he has heart or breathing difficulties or is premature.
Adjust the tube position and container height so your baby gets milk quickly when he starts sucking. Check he isn’t overwhelmed with milk, especially if he has heart or breathing difficulties or is premature.
Slow down the flow of milk by lowering the milk container, raising the tubing or using thinner tubing. Or pinch the tube to slow or stop milk flow. If using the bottle system, stop milk flowing by clamping the tube in the slots in the bottle likd. To speed up milk flow, raise the bottle, use wider tubing or use two tubes at the same breast. You may need to adjust the tube in your baby’s mouth to create more suction.
Cleaning
To avoid having to throw away tubing when milk had dried inside, force cold water through the tube at least three times straight after use, using the bottle of a 5-10ml syringe. Using warm water may cause fat to cling to the sides of the tube.
For commercial supplementers follow the manufacturers’ cleaning instructions. For homemade systems, follow the NHS guidance when cleaning the bottles and teats. Wash the tubing with hot soapy water, rinse with clean water and force air through the tube (or spin the tube fast) to dry. Take extra care if using infant formula. Store the clean supplementer parts in a sealed container in the fridge.
Wash the tubing with hot soapy water, rinse with clean water and force air through the tube (or spin the tube fast) to dry. Take extra care if using infant formula. Store the clean supplementer parts in a sealed container in the fridge.
Nasogastic tubes should not be boiled, steamed or chemically sterilised as they are not designed for multiple uses. If your baby is at a higher risk of infection, a commercial system may be a safer option than a homemade system. Replace the nasogastric tube when it starts to stiffen, after about a week.
Eliminating supplements
The use of infant formula is sometimes essential to meet a baby’s nutritional needs. You may need to use formula as a stopgap measure, while you work to increase your milk production. Supplementing with formula without protecting your milk supply may reduce the duration of your breastfeeding experience.
Over time, you may be able to reduce the amount of supplement your baby needs as your milk production increases.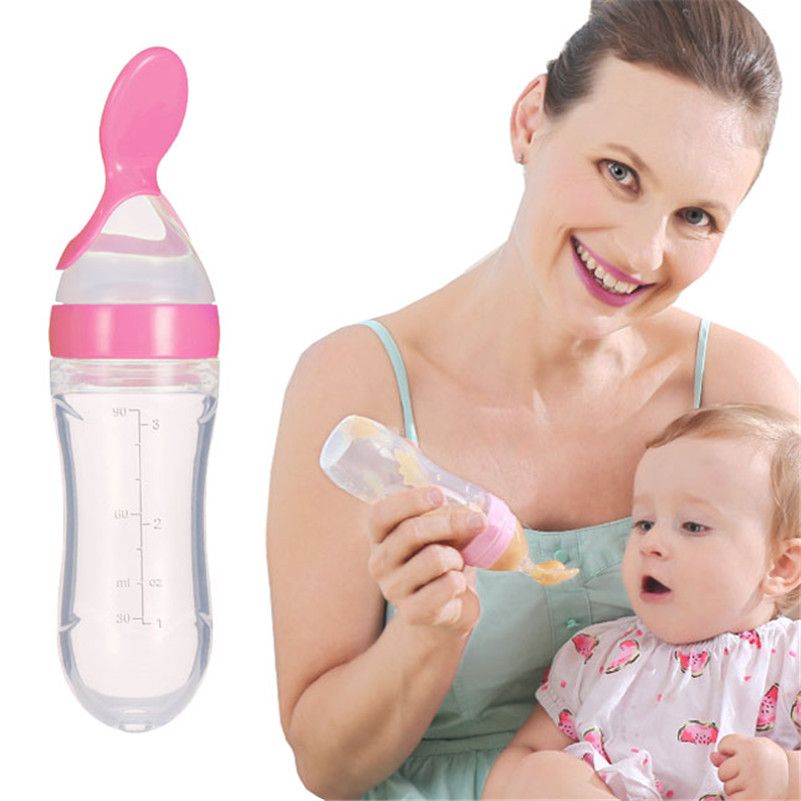 Expressing in between feeds will signal to your breasts to make more milk and give you some milk for the next feed. For more on Increasing Your Milk Supply, see our article.
Expressing in between feeds will signal to your breasts to make more milk and give you some milk for the next feed. For more on Increasing Your Milk Supply, see our article.
Begin the feed with your baby taking milk just from the breast. When he is no longer swallowing regularly start the supplementer. If your baby is reluctant to nurse at all, start the milk flowing at the beginning of a feed to get him started. As your breasts start to make more milk you will notice your baby takes less supplement, especially at certain times of day.
For more information on managing and reducing supplements see My Baby Needs More Milk and Relactation and Induced Lactation.
Seek support
Whether using a supplementer as a temporary or a long-term solution, support from your local LLL Leader and group can be a great help. For individual face-to-face help or a home visit, you could also consult a board certified lactation consultant (IBCLC) or specialist breastfeeding clinic.
Written by Karen Butler, Sue Upstone & mothers of LLLGB. Photos courtesy of Lynn Adams, Rae Vacher Lowe and Alison Widdup.
Photos courtesy of Lynn Adams, Rae Vacher Lowe and Alison Widdup.
Further reading
Comfortable Breastfeeding
My Baby Needs More Milk
My Baby Won’t Breastfeed
Expressing Your Milk
Hand Expressing Your Breastmilk
How to Increase Your Milk Supply
Using donor milk and formula to support breastfeeding
Nipple Confusion
Relactation and Induced Lactation
Mothers’ stories
In praise of at breast supplementers
Breastfeeding with a nursing supplementer
LLLI articles
At breast supplementer nursing
Books
The Womanly Art of Breastfeeding. LLLI. London: Pinter & Martin, 2010.
Exclusively Pumping Breastmilk. Casemore, S. Gray Lion Publishing, 2014
Making More Milk Second Edition. Marasco, L and West, D., NY: McGraw-Hill, 2019.
Other websites
Homemade Supplemental Nursing System
NHS leaflet: Guide to bottle feeding
Increasing milk production
Nursing Supplementers
Please note: LLLGB does not endorse any particular breastfeeding product, aid or device or brand. La Leche League GB supports the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes and subsequent relevant World Health Assembly Resolutions (referred to together as “the Code”). For more information about LLLGB’s support of the Code, see here.
La Leche League GB supports the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes and subsequent relevant World Health Assembly Resolutions (referred to together as “the Code”). For more information about LLLGB’s support of the Code, see here.
Nursing Trainer System: www.lact-aid.com
Supplemental Nursing System: www.medela.co.uk
This information is available in printed form from the LLLGB shop.
Copyright LLLGB 2022.
Everything you need to know about a supplemental nursing system (SNS)
When breastfeeding isn’t going as planned, you may need to try a breastfeeding with a tube.
Photo: iStockphoto
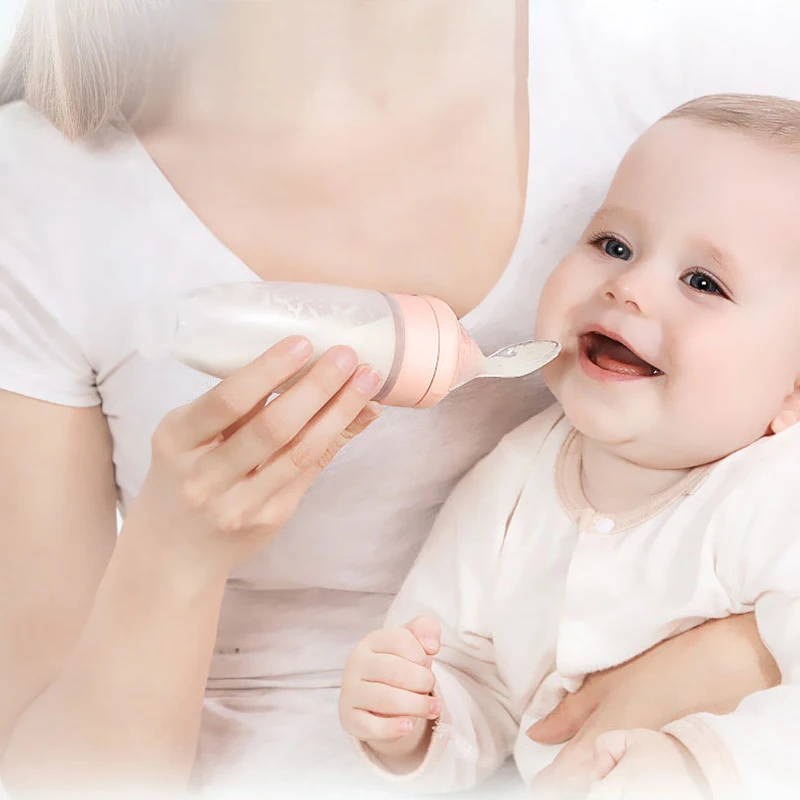
If breastfeeding isn’t going as well as you hoped it would, you may be told to consider using a feeding tube while you breastfeed your baby. This is often known as using a supplemental nursing system (SNS). Read on to learn the ins and outs of breastfeeding with a feeding tube.
What is a supplemental nursing system?A supplemental nursing system allows you to supplement your baby at the breast with breast milk or formula. “Essentially, the baby is breastfeeding at the same time as they are receiving the supplement,” explains international board certified lactation consultant (IBCLC) Taya Griffin.
“Essentially, the baby is breastfeeding at the same time as they are receiving the supplement,” explains international board certified lactation consultant (IBCLC) Taya Griffin.
One end of a very thin, flexible tube is placed in a container, such as a bottle, that contains the milk. The other end is either inserted into the baby’s mouth after she has latched on to mom’s breast, or is attached to the breast with medical tape ahead of time so it’s ready to go. The result is that the baby may get some breastmilk from the breast as well as the supplemental food.
What supplies will I need for SNS?You’ll need a No. 5 French feeding tube, which usually costs around $2, and is available at most medical supply stores (lactation consultants almost always have them on hand), as well as a container like a bottle, plus medical tape. Or, you can purchase a supplemental nursing system kit for around $50. This system comes with a syringe or a small bottle connected to silicone tubing, which hangs around the neck like a necklace.
Which one you go with depends on how long, or often, you plan to supplement with a tube, Griffin explains. Because they’re not made of silicone, the No. 5 French feeding tubes shouldn’t be reused, so they’re best for moms who will be tube feeding only occasionally. She recommends an SNS kit for longer-term users because its tubes can be sterilized.
When to use SNSUsing a tube to supplement can help whenever there is low milk supply, says Griffin. Sometimes parents may need to do so for the short-term to feed their baby while simultaneously bringing their own supply up to meet her demand (a suckling babe stimulates a breast to make more milk). Other parents may have to supplement with a tube for the long-term, because in their situation, a full supply isn’t possible at the breast alone; this may be the case with some people who’ve had a breast reduction or chest contouring surgery, or those with hormonal or other issues that may affect supply.
Adoptive parents, or those who’ve used a surrogate, can also breastfeed with a tube system, as can a non-lactating partner who wants to connect with her baby by breastfeeding, even if she isn’t trying to stimulate a supply.
Tube feeding can also help get a baby back to the breast since it may help her learn that she can, in fact, be satisfied by nursing. “I’ve introduced the tube in situations where baby has started refusing the breast because of slow flow, and we actually get them to start latching on and trusting the breast because we give them the tube right away,” explains Griffin.
You may have also heard of parents placing the tube alongside a finger that is inserted into the baby’s mouth. This type of feeding is usually meant to give baby just a bit of milk so they aren’t so ravenous that they can’t latch on; it can also be used for what’s known as suck training. Griffin cautions that a finger feed should not replace a full feed.
What are the advantages of tube feeding?A tube system can help to boost mom’s milk supply, and may get some breastmilk in your baby at the same time as you supplement. But there is another huge benefit, says Griffin. “The connection between the two of you, the increased use of skin-to-skin contact, all of those kinds of things are increased using the tube,” she explains. “This can be really, really helpful, not just for milk supply, but also for the breastfeeding relationship.” Tube feeding can also cut down on the number of times you need to pump to stimulate supply, since your baby is a natural pump, she notes.
Are there disadvantages to SNS?While Griffin says most young babies take to tube feeding fairly easily, it can be a tougher sell once they hit three or four months of age, since they’re more aware of how the tube feels in their mouth. But even with an older baby, she says it’s worth trying if your supply is low and they won’t accept anything but the breast. “If you can get one feed into them before they clue in to the fact that there’s a tube there, it can still be a win,” she explains.
But even with an older baby, she says it’s worth trying if your supply is low and they won’t accept anything but the breast. “If you can get one feed into them before they clue in to the fact that there’s a tube there, it can still be a win,” she explains.
There’s no doubt that some parents find tube feeding a bit challenging. “It takes practice, and some people find that it starts to get frustrating,” says Griffin, who recommends getting an IBCLC to guide you in the nuances of tube feeding. “It can get a bit demoralizing if it doesn’t work right away, so getting someone to help you use it and assure you that your baby is latching well, and that tube feeding is going well, can be quite a powerful thing,” she says.
If you’ve been advised you need to supplement, and tube feeding is not for you, then Griffin says the alternatives are cup feeding or a slow form of bottle feeding. A lactation consultant can help you sort out which of these options would be best for your baby.
How long do you usually need to supplement for?That depends, says Griffin. If you know you’re never going to have a full supply, then you may need to use an at-the-breast supplementation system for the length of the nursing relationship. Or, it could take only a matter of days to get your baby to trust the breast, or to increase your supply.
If you know you’re never going to have a full supply, then you may need to use an at-the-breast supplementation system for the length of the nursing relationship. Or, it could take only a matter of days to get your baby to trust the breast, or to increase your supply.
Read more:
How to use a breast pump
Quitting breastfeeding won’t make your kid less smart
The best preparation for breastfeeding is accepting it might not happen
Stay in touch
Subscribe to Today's Parent's daily newsletter for our best parenting news, tips, essays and recipes.- Email*
- CAPTCHA
- Consent*
Yes, I would like to receive Today's Parent's newsletter.
 I understand I can unsubscribe at any time.**
I understand I can unsubscribe at any time.**
FILED UNDER: Bottle-feeding Breast milk Formula
Questions and Answers - NCCH
The most important thing about breastfeeding
1. Why is it important to breastfeed a child?
Breast milk is a unique and irreproducible food product, which contains important components that reduce the risk of developing an infectious pathology, allergies, overweight, cardiovascular pathology, and diabetes mellitus in a child. Only with breast milk can a child receive a unique complex of immunoglobulins, enzymes, growth factors, prebiotic fibers, which has not only an immediate, but also a long-term beneficial effect on the subsequent development of the child. During breastfeeding, a close psycho-emotional bond is formed between mother and child, laying the foundation for mental health for the rest of her life. nine0005
2. How do I prepare my breasts for breastfeeding? How to take care of the breasts?
How do I prepare my breasts for breastfeeding? How to take care of the breasts?
Preparation of the breast for feeding includes the usual hygiene procedures (hygienic shower 2 times a day, washing hands with soap) and does not require any special treatment of the mammary glands. Underwear should not be too tight or, on the contrary, very loose.
3. What is the correct way to attach the baby to the breast?
To prevent painful sucking and nipple cracks, it is important that when sucking, the child must grasp not only the nipple, but also partially the areola, while the child's lower lip must be turned outward. nine0005
4. Is there a strict feeding schedule for an infant?
In the first 1-2 months. lactation - a period of adaptation - it is important to feed the child at his request, without missing night feedings. In the future, gradually the intervals between feeding will increase and a regimen that is convenient for mother and child will be formed.
5. Why might a baby be anxious while feeding?
The baby may be anxious during feeding for various reasons. It can be colic, abdominal pain, nasal congestion, as well as insufficient milk supply due to improper nipple grip or the presence of a lactation crisis. nine0005
6. What is a lactation crisis?
Lactation crisis - a temporary decrease in milk production, which is of a functional nature, lasts no longer than 3-4 days, disappears on its own with frequent attachment of the child to the breast. During this period, supplementary feeding of the child with milk mixtures is not required.
7. How can a nursing mother eat so that her baby does not have allergies/colic?
If the child has allergies, the mother should analyze her diet and possible connection with the appearance of allergic reactions (skin or gastrointestinal), exclude foods with a high allergenic potential from the diet: whole cow or goat milk, seafood, honey, nuts, eggs , chocolate, peanuts, citrus fruits, mushrooms. nine0005
nine0005
If the child has colic, whole cow's or goat's milk, fresh vegetables and fruits (which, however, can be taken in baked or boiled form), yeast-containing foods, spices, spicy and fried foods should be excluded.
8. Products that are recommended to be limited to a nursing mother.
The diet of a nursing mother should be varied, complete and balanced. You should not adhere to restrictive diets if the baby is well tolerated with breast milk. Only in the presence of manifestations of food allergies, with colic, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods with a high allergenic and gas-forming potential (beans, peas, white cabbage, fresh yeast pastries, carbonated drinks). nine0005
A breastfeeding mother should not eat fresh onions, garlic, other strong-smelling herbs and spices, pickled foods.
9. How much fluid should you drink per day?
It is advisable for a nursing mother to drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day.![]()
10. Should I express my milk?
It is not necessary to express milk after each feeding. However, pumping may be necessary if you need to stock your own milk (individual bank). In this case, you can express after each feeding of the baby and whenever you feel a “rush” of milk. nine0005
11. What should I do if I have cracked nipples?
The resulting cracks must be treated with special healing creams that do not require rinsing before feeding the baby. In your underwear, you should put special absorbent pads to keep the nipple dry or special nipple shields that do not allow the nipple to come into contact with the linen. With deep cracks or severe soreness of the nipples, it is necessary to start feeding the baby through special silicone pads on the nipples. If sucking through the pads is impossible, then it is worth temporarily stopping feeding the child from the diseased breast until the cracks are completely healed. nine0005
12. If I have mastitis, can I continue breastfeeding? Is it dangerous for the baby?
If I have mastitis, can I continue breastfeeding? Is it dangerous for the baby?
In case of lactational mastitis, in case of taking antibiotics that are compatible with breastfeeding and the absence of pus with milk, you can continue feeding from the breast, including from the patient. This does not pose a danger to the baby, since breast milk contains a large number of antibacterial factors.
13. What should I do if I am unable to establish lactation? nine0004
The vast majority of women can successfully breastfeed. Only in 2-3% of cases (primary hypogalactia) lactation is insufficient, in connection with which the child can be supplemented with milk mixtures with the continuation of measures to stimulate lactation.
14. Until what age should I breastfeed? How can I make it easier for both me and the baby to endure weaning?
It is considered permissible to breastfeed up to 2 years of age or more if the woman wishes. nine0005
nine0005
However, after one year, the frequency of breastfeeding should be reduced to 1-2 times a day, and after 2 years, the advisability of breastfeeding is most likely questionable.
During the weaning period, a close friend or relative can help the mother. During this period, it is important to exclude the joint sleep of the mother with the child while providing him with increased attention during the daytime in the form of organizing joint games and developing activities.
15. Until what age should you feed at night? How to wean from night feedings? nine0004
Night feedings, if desired, mothers can keep up to 2 years of age, but not more than 1 time per night. The absence of night feedings contributes to a deeper sleep of the child, the proper functioning of his digestive organs and, as a result, the formation of a good appetite in the morning and afternoon.
Weaning from night feeds is best done with the help of a person close to the baby who is assigned night care for a few days.
16. Is it possible to partially replace breast milk with cow/goat milk? Which one is closer to my mother's? nine0004
If it is necessary to supplement with a lack of mother's milk, it is important to use only adapted infant formulas, which, unlike whole cow's or goat's milk, correspond to the physiological needs of the child.
17. How can you tell if your baby is getting enough milk?
Often a lack of milk is suspected in case of restless behavior of the child during or after feeding, or judged by the amount of milk eaten per feeding or per day. However, both approaches cannot give a clear idea of sufficient lactation. A clearer indicator is the increase in the body weight of the child per day, which should be at least 20 g for a full-term child in the first months of life. In addition, it is important to assess the general condition of the child, tissue turgor, urination frequency, and the nature of the stool. nine0005
18. When should I supplement my baby with formula?
When should I supplement my baby with formula?
Supplementation with formula should only be carried out after consultation with a pediatrician, after a thorough assessment of the child's nutrition, general condition and physical development.
19. How can I tell if formula is right for my baby?
If the mixture is well tolerated, the child does not experience discomfort while eating, does not vomit, has regular mushy stools without pathological impurities, clear skin, physiological weight gain. nine0005
20. How do I switch to another formula?
The transition to another mixture should be gradual - no faster than 3-5 days. On the first day of administration, the amount of the "new" mixture should be no more than 10-30 ml, which can be added to one bottle to the "old" mixture.
In the future, the amount of the "new" mixture is increased daily by 30 ml. at every feeding.
21. Do I need to supplement my baby with water?
Breastfed babies do not need to drink water, except in special cases (high room temperature, dehydration of the baby in case of vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature). nine0005
nine0005
A formula-fed baby may require additional water intake in the amount of one feeding - 150-200 ml / day. if desired by the child.
22. How do I hold my baby and bottle properly if I am formula feeding him?
It is important when bottle feeding your baby to hold him in your arms so that he lies as in a cradle. When holding the bottle, you must be careful to ensure that the mixture or milk completely fills the nipple. It is necessary to tilt the bottle so that the air bubble is above the level of the nipple and the baby cannot swallow air. nine0005
Formula milk
23. What is formula and formula feeding?
Mixed feeding is the feeding of a child of the first year of life with breast milk in an amount of at least 1/5 of the daily amount of food (150-200 ml) in combination with infant milk formulas.
Formula feeding is the feeding of infant formula alone or in combination with breast milk, which is less than 1/5 of the daily intake. nine0005
nine0005
24. Why shouldn't a baby be allowed to fall asleep with a bottle?
Sucking a bottle in bed while lying on your back can cause some milk to enter the Eustachian tube, which connects part of the larynx to the middle ear, which can cause inflammation of the middle ear. Also, when a child falls asleep, part of the milk mixture may remain in the oral cavity and promote the growth of bacteria that destroy tooth enamel. In addition, a child can get used to falling asleep only with a bottle and keep this habit for a long time. nine0005
25. If we travel far from home, is it better to take ready-made formula with us or dilute it on the road?
It is recommended to consume formula immediately after preparation. Therefore, it is better to take formula powder with you, a thermos with warm water to dilute it, and prepare the mixture just before feeding the baby.
The main thing about baby food
26. Why is nutrition so important in the first 2 years of life? nine0004
Why is nutrition so important in the first 2 years of life? nine0004
A child's nutrition in the first two years of his life has the greatest impact on the further development of the child's body. It is during this period that the foundations of proper metabolism are laid. A rationally organized diet at this time can reduce the risk of further development of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
27. Why is it said that "immunity is in the gut"?
The human gastrointestinal tract performs not only digestive, but also a pronounced immune function. Up to 80% of all immunocompetent cells of the human body are located in the intestinal mucosa, thanks to which protection against potentially dangerous microorganisms is carried out throughout a person's life. nine0005
28. Does the baby need additional vitamins in winter and spring?
If the child receives foodstuffs that are not fortified with vitamins, then additional intake of vitamins in preventive doses should be carried out throughout the year, given the low level of vitamins in natural products.![]()
29. How to choose food if you have been diagnosed with celiac disease?
With celiac disease, all products from wheat, rye, barley and oats are excluded from the child's diet: bread, pasta, confectionery, sausages, etc., including the flour of these cereals. nine0211 For celiac disease, products from rice, corn, buckwheat, millet (millet), sago are used.
30. Can adults eat mashed potatoes from a jar?
Baby food, including cans, is a product of high quality and guaranteed safety, therefore, if necessary, it can be used in the human diet at any age.
31. Will the child be able to get enough, will he have enough nutrients if I feed him only industrial food? nine0004
A diet made up of only commercial baby foods can fully satisfy a child's basic nutritional and energy needs. However, for the formation of proper eating behavior and chewing skills from 8-10 months. it is desirable to gradually expand the child's diet by introducing some home-made products (meat soufflé, steam cutlets, finely chopped boiled vegetables, pasta), as well as bread and biscuits.
From 4 to 6 months - First food
The timing of the introduction of complementary foods is individual for each child and lies in the range of 4-6 months. The baby is ready to take the first solid food if he drinks well from a spoon and does not push it out with his tongue, if he remains unsatisfied after feeding with breast milk or formula, and if he actively shows interest in the parents' food and tries it. nine0005
33. Where to start: with cereals, vegetables or fruits?
Complementary foods should be started either with vegetable puree or porridge. For children with reduced body weight and frequent loose stools, it is advisable to start with porridge, for children with overweight or with a tendency to constipation - with vegetable puree. After that, you can enter the fruit.
34. When, how and what to inject? (Complementary food table.) General recommendations.
| Name of products and dishes (g, ml) | Age (months) | |||
| 4 to 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 to 12 | |
| Vegetable puree | 10-150 | 170 | 180 | 200 |
| Milk porridge | 10-150 | 150 | 180 | 200 |
| Fruit puree | 5-60 | 70 | 80 | 90-100 |
| Fruit juice | 5-60 | 70 | 80 | 90-100 |
| Curd* | 10-40 | 40 | 40 | 50 |
| Yolk, pcs. | - | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Meat puree* | 5-30 | 30 | 50 | 60-70 |
| Fish puree | - | - | 5-30 | 30-60 |
| Kefir and other fermented milk drinks | - | - | 200 | 200 |
| Rusks, biscuits | - | 3-5 | 5 | 10-15 |
| Wheat bread | - | - | 5 | 6 |
| Vegetable oil | nine0262 1-35 | 5 | 6 | |
| Butter | 1-4 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
* — not earlier than 6 months.
The sequence of introducing certain products and complementary foods depends on the nutritional status of the child and the functional state of his digestive system. So, for children with reduced body weight, frequent stools, it is advisable to prescribe cereals as the first complementary foods, with excess nutrition, constipation - vegetable puree. nine0005
New product to be given before breastfeeding/formula, starting at 1 tsp. with a gradual increase in volume to the age norm.
35. Why start with a one-component diet?
In order to identify a possible intolerance reaction to a particular food, it is important to start complementary foods with monocomponent meals.
36. Is it true that fruits contain acid that is harmful to teeth?
Fruits are rich in various organic acids that have a positive effect on digestion. However, excessive consumption of juices can adversely affect tooth enamel. Therefore, do not exceed the recommended age limits for fruit juices and purees. nine0005
nine0005
37. Is it true that for a baby with a risk of developing allergies, it is better to start complementary foods as late as possible?
Numerous studies have shown that later (after 6 months) introduction of complementary foods to children at risk of developing allergies does not reduce the likelihood of developing it, and in some cases even increases it.
38. What measures to take to prevent allergies?
In order to prevent allergies, it is important to continue breastfeeding and start introducing complementary foods with single-ingredient foods no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6 months. In this case, the first complementary foods should be dairy-free gluten-free cereals or vegetable purees from green-white vegetables. nine0005
39. How can a food allergy manifest itself?
Food allergies can manifest themselves in different ways. Skin manifestations of allergies can be in the form of dryness and redness of the skin, the appearance of single or multiple rashes on various parts of the body, itching. An allergic lesion of the gastrointestinal tract can be manifested by the presence of regurgitation, vomiting, refusal of the child to eat, abdominal pain, loose stools or constipation, mucus or blood in the stool. Less commonly, swelling of the eyes, nasal mucosa, and respiratory tract can develop. nine0005
An allergic lesion of the gastrointestinal tract can be manifested by the presence of regurgitation, vomiting, refusal of the child to eat, abdominal pain, loose stools or constipation, mucus or blood in the stool. Less commonly, swelling of the eyes, nasal mucosa, and respiratory tract can develop. nine0005
40. What should I do if I notice redness and rashes on my baby's skin after introducing a new product? When can I give the product that caused the allergy again? Or is this allergy for life?
If after the introduction of a new product, dry skin or rashes appear, then for some time the product should be excluded from the child's diet. This reaction to the product may be temporary, so its administration can be repeated after 1 month. after the complete disappearance of the pathological process on the skin. Most often, allergic reactions to food in early childhood do not persist for life. nine0005
41. What vegetables and fruits do not cause allergies?
Any product can cause an allergic reaction. However, it is possible to single out low-allergenic products to which allergic reactions develop the least. Among the vegetables are cauliflower, broccoli, zucchini, white cabbage, green beans, green peas, squash, potatoes. Among the fruits are green apples, pears, yellow plums.
However, it is possible to single out low-allergenic products to which allergic reactions develop the least. Among the vegetables are cauliflower, broccoli, zucchini, white cabbage, green beans, green peas, squash, potatoes. Among the fruits are green apples, pears, yellow plums.
From 6 to 9 months - diet expansion
42. What kinds of fish are recommended for a first acquaintance?
Fish is introduced into the diet of children from 8-9 months. age. It is better to start with low-fat or “lean” varieties of fish, which include: hake, haddock, pollock, pike perch, navaga.
43. When can I switch to multi-ingredient dishes?
Multi-ingredient meals are usually introduced to the child from 8 months. age.
44. What should be done to diversify the baby's diet? nine0004
Increasing the variety of the diet increases its nutritional value and "accustoms" the child to new tastes.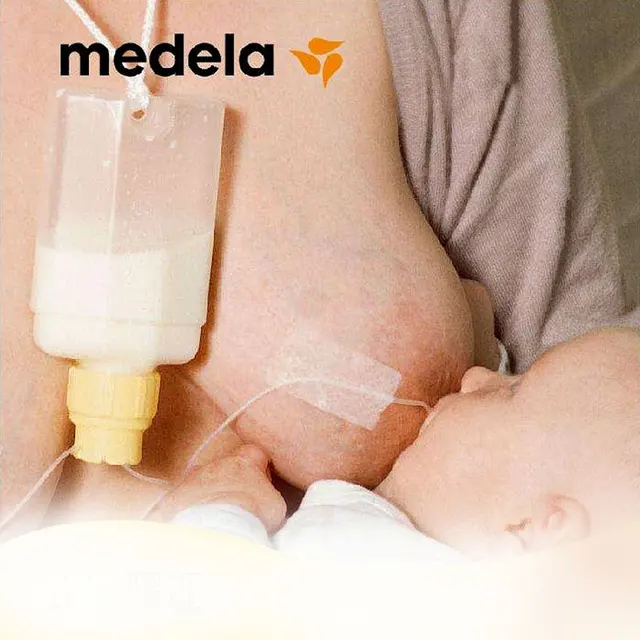 In order to expand his child's diet, it is necessary to offer him not only new products, but also their various combinations, which is easiest to do with the help of industrial food products, a rich assortment of which at any time of the year will help form a varied and balanced diet for your baby.
In order to expand his child's diet, it is necessary to offer him not only new products, but also their various combinations, which is easiest to do with the help of industrial food products, a rich assortment of which at any time of the year will help form a varied and balanced diet for your baby.
45. Should vegetable oil be added to vegetable puree? nine0004
Despite the fact that some vegetable purees of industrial production already contain vegetable oil, it is recommended to add it to vegetable puree or porridge, given the pronounced nutritional and energy value of this product.
46. Is it true that it is better to combine meat or fish with vegetables? What is a meat and vegetable and fish and vegetable dish?
The combination of meat or fish with vegetables promotes better absorption of animal proteins, iron, so this combination is considered optimal. nine0005
Meat-and-vegetable or fish-and-vegetable dishes are ready-to-cook complementary foods, the content of meat or fish in them is 16-20%.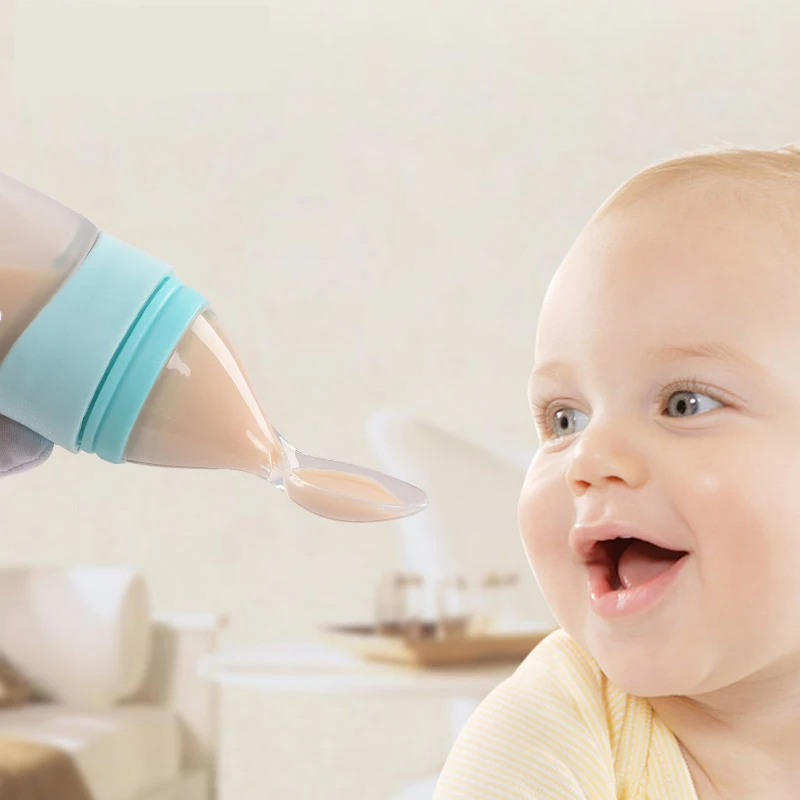
47. Why can't children under one year old drink cow's milk, but can you cook porridge based on it?
Whole cow's milk is not an adapted food product for a child of the first year of life, and therefore it is not recommended to use it as an independent food, but it can be used for cooking porridge in order to increase the nutritional value of the finished dish. nine0005
From 9 to 12 months - adaptation to the adult table
After 1.5-2 years, the child's diet can be gradually expanded by introducing dishes from the "general" table, but on condition that a specialized product for children aged 1 to 3 years is preserved in 1 feeding (milk formulas, the so-called 3 or 4 formulas) and the presence of proper culinary processing of products. Boiling, baking, stewing, steaming is recommended. nine0005
49. How many fish per day can a child under one year old eat?
From 8 months age child 1-2 times a week instead of a meat dish, you can offer fish puree, in an amount of not more than 70 g per day.
50. What kind of food will help the baby to train chewing skills?
To develop the skills of chewing and swallowing hard food after 8 months. instead of pureed or mashed boiled vegetables, you can gradually begin to introduce finely chopped vegetables containing individual small pieces into the child’s diet; mashed and mashed boiled meat should be replaced with finely chopped meat, as well as meatballs, soufflé, steam cutlets. Cookies, bread, dryers, soft pieces of fruit, muesli also help to train the skills of chewing solid food. nine0005
51. How much salt can a baby eat? What are the consequences of excess salt?
It is not recommended to add salt to a child's food until the age of one, taking into account the amount of natural mineral salts in food products sufficient for this age. After a year, home-cooked food can begin to add a little salt. Additional salting of industrial products is prohibited. The rate of consumption of table salt is 3 g per day.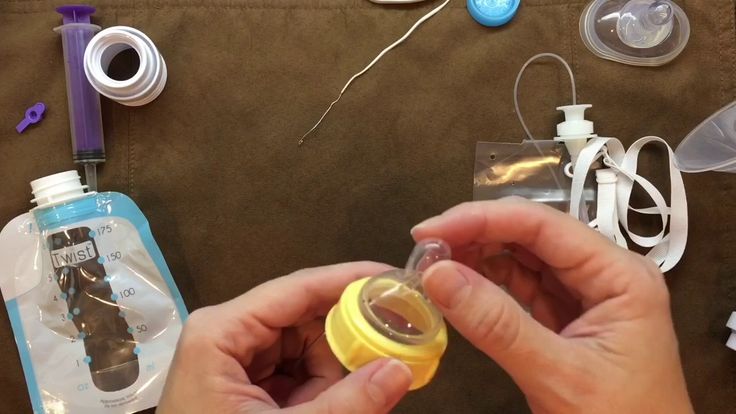 (1/2 tsp). An excess of salt in a child's diet can lead to metabolic disorders and, as a result, to overweight, an increase in the load on the kidneys and heart, which can subsequently cause hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease. nine0005
(1/2 tsp). An excess of salt in a child's diet can lead to metabolic disorders and, as a result, to overweight, an increase in the load on the kidneys and heart, which can subsequently cause hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease. nine0005
52. Why is starch added to puree?
The addition of starch to some vegetable or fruit purees binds the excess water that is released during the puréeing of fruits and vegetables, resulting in a "stable" consistency of the finished product, which makes feeding the baby more convenient.
53. Why is vitamin C added to fruit purees?
During the preparation of fruit purees, the natural content of vitamin C in fruits decreases due to their heat treatment. To compensate for this loss, an additional amount of vitamin C is introduced into the puree, which is also a good natural preservative. nine0005
54. What does “no added (added) sugar” mean?
This means that no additional sugar (sucrose) has been added to this product, and the natural taste of the product, including its sweet taste, is due only to natural sugars that are part of the original fruits or vegetables.![]()
55. Can grains cause allergies?
Cereals, like any food, can cause food allergies, regardless of the type of cereal. nine0005
Myths about baby food
is an approved component and is included in most infant formulas and food products for both healthy and sick children.
57. Myth: Is gluten a bad ingredient in baby food? nine0004
Gluten is a complex cereal protein with high biological and nutritional value and is beneficial for any child. The exception is children suffering from a rare congenital disease associated with gluten intolerance - celiac disease.
58. Myth: “Milk fat in baby food can harm a child’s health…”
Milk fat is a valuable source of nutrients and energy and therefore is included in most dairy products for baby food: cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt , some types of milk porridges, baby milk formulas. Milk fat is a source of cholesterol, phospholipids, gangliosides, which play an important role in the formation of metabolism and the development of the child's brain. nine0005
nine0005
Breastfeeding revisited
A mother's right to early breastfeeding is stated in the Joint Declaration WHO and UNICEF 1989 "Protection, promotion and support of breastfeeding: a special role for maternity services" 9004. This document outlines 10 principles for successful breastfeeding, including:
- health professionals should help mothers initiate breastfeeding within the first half hour after birth
- should show mothers how to breastfeed and how to maintain lactation, even if they are temporarily separated from their children
- supplementation of newborns with food or drink other than breast milk is excluded, except in cases due to medical indications,
- it is necessary to practice 24/7 stay of mother and newborn together in one room
- Breastfeeding should be encouraged on demand rather than on schedule:
- should not be given to newborns who are breastfed, no sedatives and devices that mimic the mother's breast (nipples, bottles, etc.
 ).
).
Preparing to breastfeed
The most important preparation is your conscious desire to breastfeed, and that there are solutions to virtually most breastfeeding difficulties.
If you have never breastfed before, you may wonder if your nipples are good enough to breastfeed, especially if they are small or flat. Since the baby does not actually suckle, but actually "milks" the breast, as it were, like a small efficient milk machine, the shape of the nipples practically does not play a role. In rare cases, there are so-called inverted nipples that retract when you try to bring them into the correct position. But this does not have to be an obstacle to feeding. In this case, during pregnancy, you can cut small holes in the bra so that the tips of the breasts protrude from them. When the baby is brought to the breast later, you can start feeding by gently pulling on the nipple with your hand or with a breast pump so that it is easier for the baby to latch onto the breast. nine0211 Some women, during pregnancy, find stretch marks on the chest, the same as on the abdomen and thighs, appearing when the skin is stretched. We don't have scientific proof of how much the formation of such stretch marks can be eliminated with a light rubbing, for example, olive oil or moisturizer, but this folk remedy, in any case, is not at all dangerous.
nine0211 Some women, during pregnancy, find stretch marks on the chest, the same as on the abdomen and thighs, appearing when the skin is stretched. We don't have scientific proof of how much the formation of such stretch marks can be eliminated with a light rubbing, for example, olive oil or moisturizer, but this folk remedy, in any case, is not at all dangerous.
Baby to the breast, not breast to the baby
Almost all maternity wards now practice feeding according to the baby's needs, the so-called "self-regulation", i.e. you feed your baby when he starts to show that he is hungry. Take your time, let the baby calm down, let him feel the warmth emanating from your chest, the smell of milk, so that he awakens his appetite and wants to eat. It can be difficult to feed both a sleepy baby who wants to lie still, and one who is hungry, agitated and angry. nine0211 To avoid sore nipples and to ensure that your baby gets enough of your milk, there are some important points to pay attention to:
- A newborn baby should not twist or stretch their neck to reach the breast.
 Take care that it lies well, keep it in a comfortable position next to you, belly to belly and facing towards the chest so that the tip of the nose is at the same height as the nipple.
Take care that it lies well, keep it in a comfortable position next to you, belly to belly and facing towards the chest so that the tip of the nose is at the same height as the nipple. - When a rather hungry baby only slightly feels the touch of the nipple on the lips, he begins to search, opening his mouth. Only when you see that the mouth is well open and the tongue is in the lower part of it, do you pull the child towards you so that he can grasp a sufficient part of the breast. Remember that the baby is not actually suckling, but is squeezing out the surging milk from the breast into the mouth with a wave of the tongue. nine0627
- With a correct grip on the nipple and areola, the baby will feel the nipple against the palate. The child should not hang on the chest. Sore nipples, as a rule, are explained by the fact that the baby had to stick to the breast in order to keep the nipple in the mouth. Despite the fact that children are small, their mouth muscles have significant sucking power.
 Sucking creates pressure that can lead to internal hemorrhage and injure the nipple. To avoid this, you need to keep the baby so close to you that his chin is in contact with the chest. When a baby lies flat with no need to turn his head, and has enough of his chest in his mouth, his nose will usually be free and the baby can breathe without difficulty. The noses of newborns are specially adapted for this purpose, their upturned shape has a useful function. nine0627
Sucking creates pressure that can lead to internal hemorrhage and injure the nipple. To avoid this, you need to keep the baby so close to you that his chin is in contact with the chest. When a baby lies flat with no need to turn his head, and has enough of his chest in his mouth, his nose will usually be free and the baby can breathe without difficulty. The noses of newborns are specially adapted for this purpose, their upturned shape has a useful function. nine0627
How long to keep the baby at the breast
After saturation, the baby will "fall off" from the breast and by the expression of his contented face you will understand that he got everything he wanted. In the second half of the year, a satiated child, without releasing the mother's nipple, will bite him, smile, flirting with his mother. It is not necessary to track the duration of stay at the breast by hours, and by weights - the amount of milk eaten. This only leads to anxiety and fear in the mother.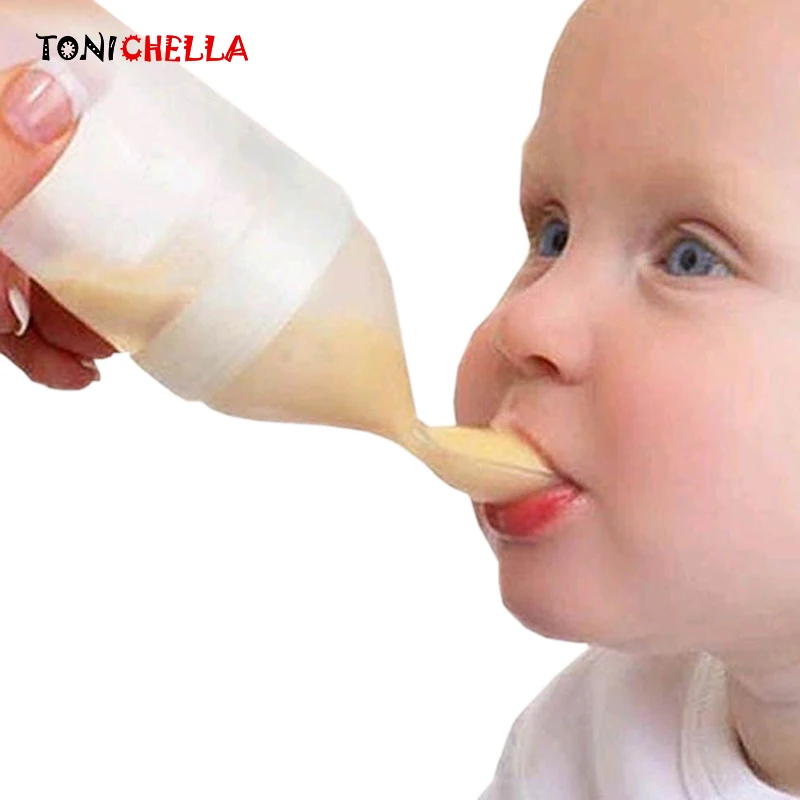 nine0211 Everyone has their own way of sucking, and it can change over time. Some children suck eagerly and are quickly sated, others arrange moments of rest for themselves.
nine0211 Everyone has their own way of sucking, and it can change over time. Some children suck eagerly and are quickly sated, others arrange moments of rest for themselves.
Let the baby empty one breast properly before giving the other if necessary. Since the most fat-rich milk comes at the end, it is important that the baby can get it.
After each feeding, the infant should be held in an upright position, for example, in the arms facing you. Rock your baby, stroking and patting on the back and buttocks. Wait for the moment when he makes a dull sound - this means that the air that came with the milk has come out. If you don't do this, the air will make your baby uneasy. nine0005
Difficulty sucking
If the baby is having difficulty latching on properly, the tongue may be obstructing. In order to function properly when suckling, the tongue must be under the bottom of the nipple. In case of difficulties in connection with this, it is good to consult a doctor or those who help you.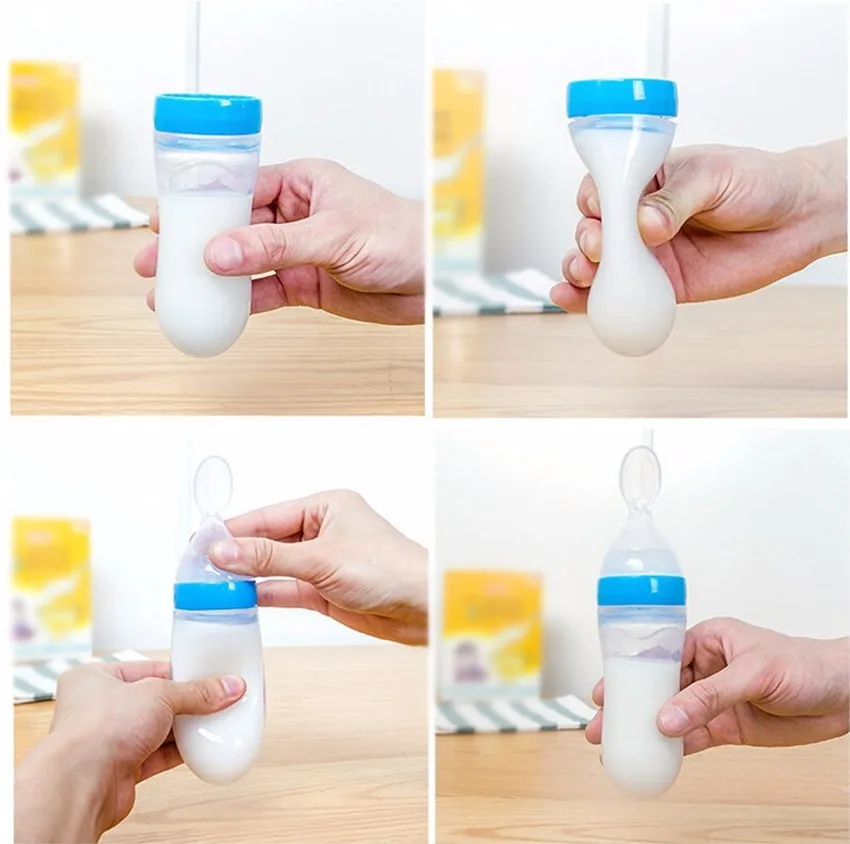
If the breast is full of milk and very firm, it may be difficult for the baby to grasp enough of it to suck properly. Expressing a small amount of milk by hand or with a handy pump can help in this case. The same applies to inverted nipples. When you pull out the nipple with your hand or using a breast pump before feeding, you help your baby latch on properly. nine0211 Some children are distracted at first, sometimes it takes them a while to figure out what's what. Remember that the child does not yet have a sufficient skill of eating through the mouth. If he is crying, try to calm him down before you offer him the breast. You may need all your maternal patience, but don't be afraid to ask for help if you don't feel like feeding is going well.
You will get milk sooner if you feed your baby as often as he wants, this is also the best remedy for painful breast fullness at first. If you still have trouble with this, you can resort to expressing with your hand or a breast pump - this relieves the pressure. nine0211 The milk ejection reflex is important for the baby to get milk. You may sometimes feel it as a tingling or pinching sensation in your chest. Women who have repeatedly gone through childbirth often feel again the same hormones that activate this reflex. The milk ejection reflex is stimulated by touch on the nipples (in some mothers, milk begins to drip during the shower) and acts simultaneously in both breasts. You can also activate it yourself, for example, twist the nipple with your fingers, which is sometimes also useful if the child sucks weakly or if the nipples are injured: this will save them from the first intensive sucking of the child. nine0005
nine0211 The milk ejection reflex is important for the baby to get milk. You may sometimes feel it as a tingling or pinching sensation in your chest. Women who have repeatedly gone through childbirth often feel again the same hormones that activate this reflex. The milk ejection reflex is stimulated by touch on the nipples (in some mothers, milk begins to drip during the shower) and acts simultaneously in both breasts. You can also activate it yourself, for example, twist the nipple with your fingers, which is sometimes also useful if the child sucks weakly or if the nipples are injured: this will save them from the first intensive sucking of the child. nine0005
What to do if there is not enough milk
Probably every nursing mother has moments when she thinks that her baby does not have enough breast milk. Often such fears are unfounded.
But there are also times when milk production can actually decrease or not meet the increased needs of the child. Lactation is cyclical with crises recurring every 1.5-2 months. The first crisis is the hardest to overcome. We must remember that this phenomenon is temporary. The main thing is not to panic and grab the box of artificial nutrition. It is better to think about how you can help the cause, and this is possible. nine0211 First check that you are following all the conditions for successful breastfeeding.
Lactation is cyclical with crises recurring every 1.5-2 months. The first crisis is the hardest to overcome. We must remember that this phenomenon is temporary. The main thing is not to panic and grab the box of artificial nutrition. It is better to think about how you can help the cause, and this is possible. nine0211 First check that you are following all the conditions for successful breastfeeding.
Secondly , if there is a lack of milk, give the child both breasts, increase the number of feedings, give the child both breasts at each feeding: first one, which he will empty completely, if necessary, it can be expressed, and then for a short time the other, it is not have to express. It is important that both breasts receive a signal to release milk.
Third, , milk production is facilitated by taking a glass of liquid 15 minutes before feeding. It can be tea with milk, milk diluted in half with boiled water, kefir, compote, rosehip broth, juice or water. nine0211 Fourth , you can prepare special lactogenic drinks from nettle, mint, anise, lettuce seeds, dill (fennel) seeds, oregano and apply them if necessary for 2-3 weeks. The herb is brewed at the rate of one tablespoon per glass of boiling water, allowed to infuse for 2-3 hours, filtered and taken orally in small sips of half a glass twice a day. Lemon, honey, syrup are added to taste.
nine0211 Fourth , you can prepare special lactogenic drinks from nettle, mint, anise, lettuce seeds, dill (fennel) seeds, oregano and apply them if necessary for 2-3 weeks. The herb is brewed at the rate of one tablespoon per glass of boiling water, allowed to infuse for 2-3 hours, filtered and taken orally in small sips of half a glass twice a day. Lemon, honey, syrup are added to taste.
In summer you can make juice from dandelion leaves. Fresh young dandelion leaves are well washed, passed through a meat grinder, squeezed out the juice, salt to taste and let it brew for 30-40 minutes. It is taken in the same way as an infusion of herbs. nine0211 The use of 2-3 walnuts has a stimulating effect (in the absence of an allergic reaction).
Milk-producing carrots (also in the absence of allergies). Carrot juice is prepared just before the reception and drunk half a cup twice a day. You can cook 3-4 tablespoons of grated carrots and pour it with 1 cup of milk or cream.
An effective way to stimulate lactation is acupressure (see fig.).
|
|
| Referring to the diagram, find three points above the breasts, two below them and four on each arm. They can be identified by a painful sensation when pressed. Each of these points should be massaged with the index or middle finger clockwise for 30-60 seconds 2 times a day between feedings, in the sequence corresponding to the numbers in the figure. |
A relaxing neck and back massage, a relaxing warm shower or bath promotes lactation. It can be useful for a woman to increase the flow of milk by spending a couple of days in bed, giving herself complete rest. Promotes increased lactation and marital affection. nine0211 There are other means of increasing milk production, but they are prescribed by a doctor after he has investigated the reasons for the decrease in lactation.
Why is early attachment necessary? Early application (in the first half hour after birth) also helps to increase the amount of milk and the duration of the lactation period. In infants, early attached to the breast, there is a lower (3.3 times) incidence, better dynamics of weight compared with children attached to the breast one day after birth. Early application also reduces the chance of bilirubin toxicity causing jaundice in newborns. Until what age does a child need According to WHO/UNICEF recommendations, breast milk fully satisfies a child's nutritional needs for at least the first six months. How to keep your breasts in shape while breastfeeding To keep your breasts in shape, follow these tips.  It is very important that the baby be placed on the mother's stomach immediately after birth. Skin-to-skin contact allows the baby to feel the mother's warmth. After all, after nine months spent in a “comfortable home”, he enters a new, alien, cold world. Let the child not suck, but even if he licks the nipple, then at least a few drops of colostrum will fall into his mouth. Professor I.A. Arshavsky calls early application "passive immunization" of the child, that is, a kind of vaccination against many diseases. nine0005
It is very important that the baby be placed on the mother's stomach immediately after birth. Skin-to-skin contact allows the baby to feel the mother's warmth. After all, after nine months spent in a “comfortable home”, he enters a new, alien, cold world. Let the child not suck, but even if he licks the nipple, then at least a few drops of colostrum will fall into his mouth. Professor I.A. Arshavsky calls early application "passive immunization" of the child, that is, a kind of vaccination against many diseases. nine0005
Early attachment promotes the formation of a healthy microflora in the child. In a newborn, the intestines, skin and mucous membranes are sterile. During the first contacts with the outside world, they are colonized by microorganisms. It has been proven that microorganisms from the mother's skin take root better than others on the child, and even opportunistic microbes from the mother's skin less often lead to the development of diseases than the same microbes, but brought from other sources. In 1/3 of children attached to the breast not earlier than a day later, there is a violation of the formation of the intestinal flora. These children are more likely to suffer from intestinal disorders. Laying out on the stomach is the logical conclusion of childbirth. It signals to the mother and child that the stressful situation ended successfully, that both of them did not work in vain and emerged victorious. The harmony that existed between them before has been restored. Now you can relax and enjoy each other. From childbirth that ended with early attachment, the child brings out the knowledge that a way out of difficult circumstances can and must be found. Separated from his mother, he gets a rather negative experience. nine0211 The first eye contact is of great importance for establishing a deep emotional connection between parents and a child.
It has been proven that microorganisms from the mother's skin take root better than others on the child, and even opportunistic microbes from the mother's skin less often lead to the development of diseases than the same microbes, but brought from other sources. In 1/3 of children attached to the breast not earlier than a day later, there is a violation of the formation of the intestinal flora. These children are more likely to suffer from intestinal disorders. Laying out on the stomach is the logical conclusion of childbirth. It signals to the mother and child that the stressful situation ended successfully, that both of them did not work in vain and emerged victorious. The harmony that existed between them before has been restored. Now you can relax and enjoy each other. From childbirth that ended with early attachment, the child brings out the knowledge that a way out of difficult circumstances can and must be found. Separated from his mother, he gets a rather negative experience. nine0211 The first eye contact is of great importance for establishing a deep emotional connection between parents and a child. It is important that the first face that the child sees is the face of mom or dad. Skin-to-skin contact is necessary because the tactile analyzer is the leading one in newborns and is most developed in the womb of the mother. This is evidenced by observations of nature itself. It is known that mammals not only and not so much wash their young when they are licked, but, first of all, they create a powerful stream of impulses that enter the brain and make all body systems work. Without this licking, animal babies simply die. A woman, clutching a born child to her breast in agony, forgets about her suffering, her face brightens, and at this moment mutual understanding is established between her and the child, allowing you to feel each other without words. nine0005
It is important that the first face that the child sees is the face of mom or dad. Skin-to-skin contact is necessary because the tactile analyzer is the leading one in newborns and is most developed in the womb of the mother. This is evidenced by observations of nature itself. It is known that mammals not only and not so much wash their young when they are licked, but, first of all, they create a powerful stream of impulses that enter the brain and make all body systems work. Without this licking, animal babies simply die. A woman, clutching a born child to her breast in agony, forgets about her suffering, her face brightens, and at this moment mutual understanding is established between her and the child, allowing you to feel each other without words. nine0005
mother's milk  Milk also satisfies the need to drink, so the baby does not need additional liquid until some new food is introduced into his diet.
Milk also satisfies the need to drink, so the baby does not need additional liquid until some new food is introduced into his diet.
In the UN international document "Plan of Action for the Implementation of the Declaration on the Survival, Protection and Development of Children in 90 years”, signed by the representative of our country, the goal is “to ensure that all women breastfeed their children only during the first 4-6 months of life and continue breastfeeding, using additional food, in the second year of life.”
Digestive system of an infant in the first four months (and in some up to a year) is not adapted for the processing of any food other than breast milk.Therefore, the introduction of complementary foods at this age causes rejection by the body, which is expressed in an allergic reaction.Do not introduce any complementary foods into the diet in the first 4-6 months! In the second half of the year, be guided by the state of health of the child and your own. If possible and mutual desire of mother and baby, breastfeeding, in combination with additional nutrition, can last up to 1. 5-2 years. The child himself refuses to breastfeed for the third year of life, when his "I" actively asserts itself.Further breastfeeding would interfere with the normal development of the child's personality ka. nine0005
5-2 years. The child himself refuses to breastfeed for the third year of life, when his "I" actively asserts itself.Further breastfeeding would interfere with the normal development of the child's personality ka. nine0005
Wear a tight-fitting bra at all times. In order for the chest to breathe, the bra must be made of natural fabric. It must be worn day and night from the moment of pregnancy, as the breasts begin to increase in size until the end of the lactation period. For lactating women, special bras with fasteners are produced that allow one breast to be released during feeding. Some women use a bra with a cut-out nipple area (you can make it yourself), although not everyone will like it, because you really want to press the baby to your body. nine0211 Do chest exercises regularly. Gymnastics helps to increase lactation and maintain the shape of the breast. It must be performed during pregnancy, the entire lactation period and some time after its completion. If you do the exercises correctly, you will feel tension in the muscles going from the chest to the armpits. The exercise plan is shown below. They can be performed sitting or standing. Each exercise is performed 8 to 25 times.
It must be performed during pregnancy, the entire lactation period and some time after its completion. If you do the exercises correctly, you will feel tension in the muscles going from the chest to the armpits. The exercise plan is shown below. They can be performed sitting or standing. Each exercise is performed 8 to 25 times.
Description of exercises A Arms bent at the elbows joined in front of the chest, palms up. At the expense of 1-2, press the palms into each other, at the expense of 3-4, relax the palms without changing the position of the hands. B "Scissors". Hands are spread apart. On account 1, cross your arms in front of your chest, on account 2 - spread apart. With each crossing, the arms rise higher and higher. On the count of 10, they cross over their heads. Then, with each crossing, the arms gradually lower to the starting position. 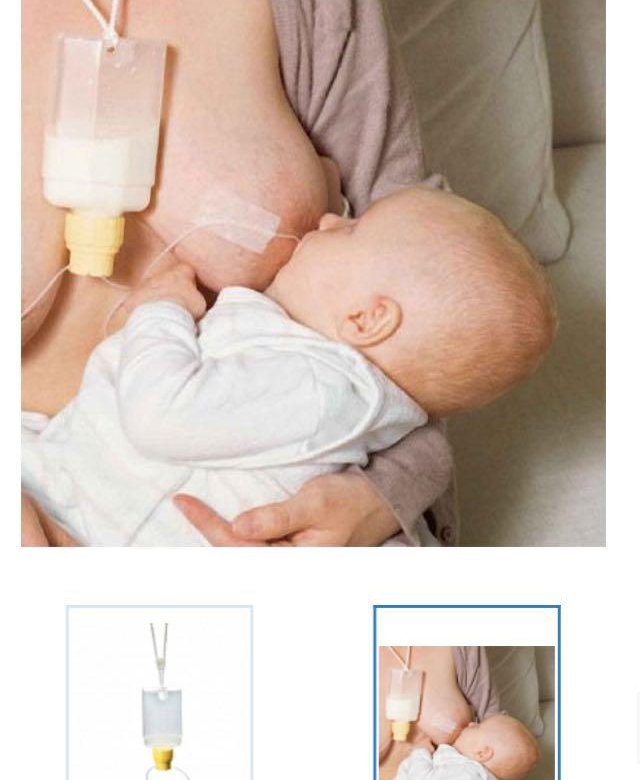
.