When do babies start cluster feeding
Cluster Feeding: Ages, Signs and Tips
By the time baby arrives, you’ve probably mentally prepared for the frequent wakeups you’re about to endure. Sleep deprivation as a new parent is par for the course, after all. What may come as a surprise, however, is the pure exhaustion that accompanies newborn cluster feeding. It’s one of those new parenting things you won’t truly understand until you actually experience it; but it’s totally normal and, thankfully, doesn’t last forever (though it won’t feel like much of a consolation when you’re in the thick of it). Still, it’s helpful to know what to expect so you can mindfully manage the situation rather than panic when the feeding frenzy begins. Ready to get the lowdown on all things newborn cluster feeding? We’re sharing what it is, why it happens, when it starts and how long it’ll last—plus, some tips for how to cluster feed and prepare yourself for the nonstop breast or bottle buffet ahead.
In this article:
What is cluster feeding?
Why do babies cluster feed?
When does cluster feeding start?
How long does cluster feeding last?
Signs of cluster feeding
Tips for how to cluster feed
How to stop cluster feeding
What Is Cluster Feeding?
You may have heard the term thrown around by other parents, or perhaps a lactation consultant said it during a blurry bedside visit at the hospital. So what is cluster feeding, exactly? Baby cluster feeding is pretty much what it sounds like: when your little one wants to be fed in “clusters” throughout the day. Cathleen Hemphill, RN, a nurse and lactation consultant in Raleigh, North Carolina, explains that in their first few days of life, babies typically need to be fed a minimum of eight times in a 24-hour span. But before you set your clock and your expectations, know that newborns typically don’t follow a predictable feeding schedule. “Most infants will want to feed more often than this and will cluster or group several feedings in a shorter amount of time,” Hemphill says.
In general, a typical feeding for a newborn will last between 15 and 20 minutes, leaving baby nourished and satisfied for about three to four hours, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). In contrast, when they’re cluster feeding, “a baby has several feedings within a short amount of time followed by a longer stretch of sleep,” says Amy Peterson, IBCLC, a lactation consultant in Jerome, Idaho. You’ll know that baby is cluster feeding—and that it’s not just their preferred eating schedule—when their routine suddenly changes for two or three days and then just as swiftly returns to a more regular feeding pace.
You’ll know that baby is cluster feeding—and that it’s not just their preferred eating schedule—when their routine suddenly changes for two or three days and then just as swiftly returns to a more regular feeding pace.
Cluster feeding is completely normal, and while not every baby cluster feeds, it can happen with any newborn, regardless of whether they’re breastfed or formula-fed. That said, it’s often harder if you’re a nursing mom, as your milk is likely still coming in, and you may be struggling with breastfeeding—physically or mentally. If you’re exclusively pumping, it may feel like you can’t keep up with baby’s demands—especially if you don’t have a reserve of milk ready to go yet. That said, if you formula feed, you’ll still notice baby’s increased appetite but will have the convenience of being able to supply more milk on demand, which the AAP says is a safe and appropriate way to manage cluster feeding.
Why Do Babies Cluster Feed?
No one knows exactly why babies cluster feed, says Dyan Hes, MD, a pediatrician in New York City, but there are several strong theories.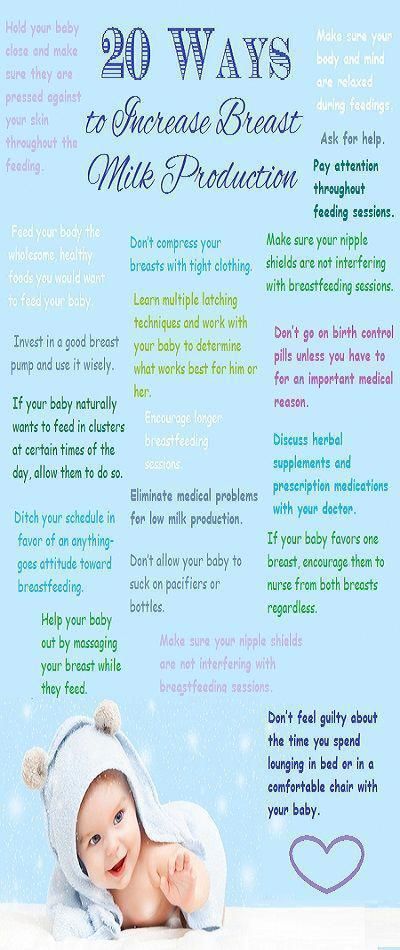 A common belief among experts is that it happens when a newborn is going through a physical or developmental growth spurt. Newborn cluster feeding could also correlate with baby’s routine in utero. “Most pregnant mothers know from fetal movements that as soon as they go to bed, their baby starts moving, and then about four hours later, they have to get up to the bathroom. This is a biological rhythm of activity that continues for the first weeks of life. We see infants feed well around a mother’s previous bedtime, then four hours later they will perhaps start to cluster feed,” explains Hemphill.
A common belief among experts is that it happens when a newborn is going through a physical or developmental growth spurt. Newborn cluster feeding could also correlate with baby’s routine in utero. “Most pregnant mothers know from fetal movements that as soon as they go to bed, their baby starts moving, and then about four hours later, they have to get up to the bathroom. This is a biological rhythm of activity that continues for the first weeks of life. We see infants feed well around a mother’s previous bedtime, then four hours later they will perhaps start to cluster feed,” explains Hemphill.
If you’re breastfeeding, newborn cluster feeding may cause you to worry or wonder if baby’s increased appetite is indicative of low milk supply or if you’re just not feeding them enough. It’s understandable why your mind would jump to that conclusion, but in reality, the opposite is happening. “In the first few days, a baby’s cluster feeding helps to increase and establish mom’s milk supply,” explains Jerrianne Webb, RN, a nurse and lactation consultant in Raleigh, North Carolina.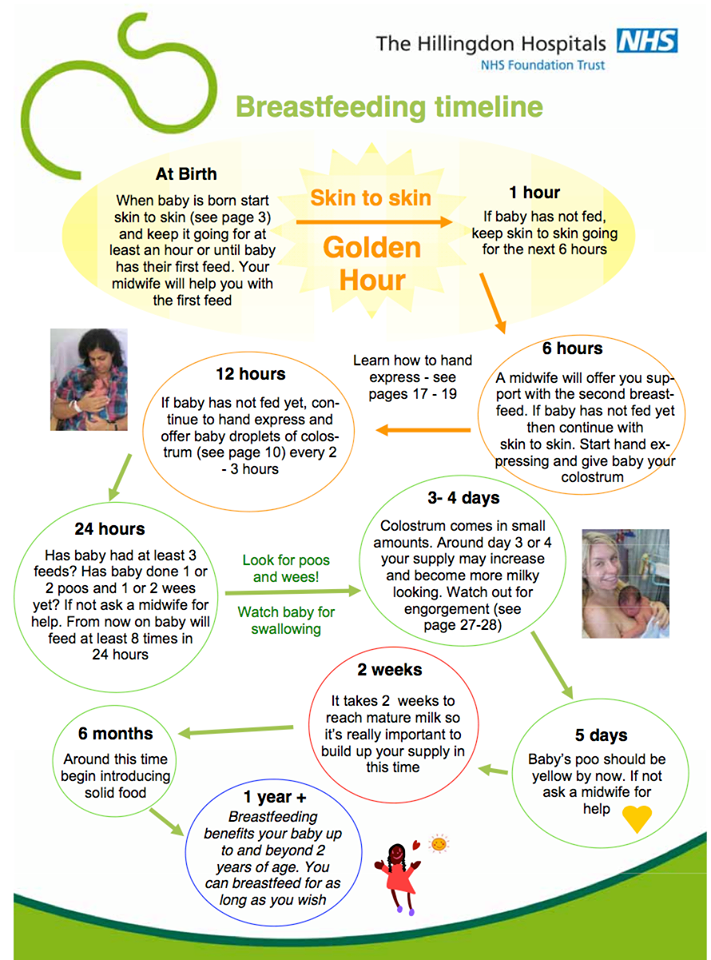 “The baby’s frequent nursing assists in the hormonal process of transitioning mom’s first milk, colostrum, into the abundant mature milk, a transition that usually occurs between postpartum days three and seven.”
“The baby’s frequent nursing assists in the hormonal process of transitioning mom’s first milk, colostrum, into the abundant mature milk, a transition that usually occurs between postpartum days three and seven.”
Oftentimes, babies cluster feed in the early evening, according to Hes, which also happens to coincide with the infamous “witching hour” for babies. Since the only way cluster-feeding babies know how to express their need to eat is through crying, it can be difficult to discern whether they’re being fussy because they’re hungry or because it’s just that time of day. If baby is inconsolable in the early evening but doesn’t seem to want to eat, it could be the result of overstimulation or possibly colic.
When Does Cluster Feeding Start?
Now that you understand what it is and why it happens, you may be wondering: When does cluster feeding start? Sorry to say, you may not get much of a breather after the exhausting work of labor and delivery. According to Hemphill, newborn cluster feeding can start as early as baby’s second day of life. While this may be the last thing you want to deal with while recovering and trying to get the hang of this whole breastfeeding thing, it can actually be very helpful. “[Cluster feeding] is the principle of supply and demand in breastfeeding,” explains Webb. “Baby’s demand [for milk] increases, which, in turn, increases Mom’s supply.” In those first few days after baby is born, the body is working hard to produce milk and increase supply as needed, and since this is triggered by baby feeding from the breast, the more often they feed, the more milk the body will ultimately produce.
While this may be the last thing you want to deal with while recovering and trying to get the hang of this whole breastfeeding thing, it can actually be very helpful. “[Cluster feeding] is the principle of supply and demand in breastfeeding,” explains Webb. “Baby’s demand [for milk] increases, which, in turn, increases Mom’s supply.” In those first few days after baby is born, the body is working hard to produce milk and increase supply as needed, and since this is triggered by baby feeding from the breast, the more often they feed, the more milk the body will ultimately produce.
How Long Does Cluster Feeding Last?
You’re sleep-deprived and desperate for relief—so you want to know: Exactly how long does cluster feeding last? Baby cluster feeding happens in bursts; each usually lasts a few days at a time, says Webb. However, during the first few weeks of life, as your supply continues to build, you can expect baby to want to cluster feed more often than not. After this initial stage, though, you’ll be more equipped to determine if and when baby will go through another cluster feeding phase based on typical development charts. “After the first few weeks, breastfed babies become more predictable,” she says. Cluster feeding ages typically align with growth spurts and occur at three weeks, six weeks, three months and six months. That said, the first three weeks of newborn cluster feeding is often the longest consistent stretch and the most intense for parents.
“After the first few weeks, breastfed babies become more predictable,” she says. Cluster feeding ages typically align with growth spurts and occur at three weeks, six weeks, three months and six months. That said, the first three weeks of newborn cluster feeding is often the longest consistent stretch and the most intense for parents.
Signs of Cluster Feeding
As babies grow, they slowly start needing more and more milk in one feeding to satisfy their appetite. So how do you know if their increased need for milk is, in fact, cluster feeding or just part of their normal growth and development? Here are some common signs of cluster feeding to look for:
- Having a normal, full feeding, and then wanting to be fed again 30 to 60 minutes later—often eating just as much as they would in a regular feeding
- Sleeping deeply for long stretches of time after two or three close feedings
- Acting frustrated during feedings, searching for the nipple when it’s right in front of them or latching on and off
- Acting fussy or irritable when they’re awake but not on the breast
- Eating in frequent, short spurts close together
- Perpetual feedings often occur in the early evening and nighttime hours
Tips for How to Cluster Feed
For a breastfeeding parent, cluster feeding is exhausting in every sense of the word, especially if you’re still trying to get the hang of nursing. Here are some things you can do to make it a little more manageable:
Here are some things you can do to make it a little more manageable:
- Keep track of how many feedings the baby has had. Peterson says, “Cluster feeders still have the expected number of feeds, just not spaced evenly throughout the day/night.”
- Have your partner or a support person help by doing as much as possible between feedings so you can rest
- Avoid trying to force or delay feedings in an effort to get baby back on a schedule, as this will just make them fussier
- Monitor their weight gain if you need peace of mind that they’re getting enough milk, suggests Peterson. “Expect babies to gain about an ounce a day (or more) once mom’s milk shifts from colostrum to milk,” she says
- Stay hydrated and nourished to keep yourself healthy and your supply ample throughout this phase
How to Stop Cluster Feeding
You may be eager to get a little break, but if you’re wondering how to stop cluster feeding, the truth is: it just has to run its course. The best thing you can do is surrender and let baby take the lead. Hemphill stresses the importance of not forcing or delaying feedings in an effort to make cluster feeding end: “The American Academy of Pediatrics, WHO, and UNICEF recommend that infants feed on demand and as often as they want, day or night.”
The best thing you can do is surrender and let baby take the lead. Hemphill stresses the importance of not forcing or delaying feedings in an effort to make cluster feeding end: “The American Academy of Pediatrics, WHO, and UNICEF recommend that infants feed on demand and as often as they want, day or night.”
Newborn cluster feeding is hard on parents, but you can take comfort knowing that it won’t last forever. Until it passes, lean on your support system and rest as often as possible. You’ve got this.
About the experts:
Cathleen Hemphill, RN, BSN, IBCLC, is a nurse and lactation consultant at the University of North Carolina’s Rex Hospital in Raleigh, North Carolina.
Dyan Hes, MD, is a pediatrician and the medical director of Gramercy Pediatrics in New York City. She earned her medical degree from the Sackler School of Medicine at Tel-Aviv University in 1997.
Amy Peterson, IBCLC, is a lactation consultant for Evenflo Feeding and co-author of Balancing Breast and Bottle: Feeding Your Baby.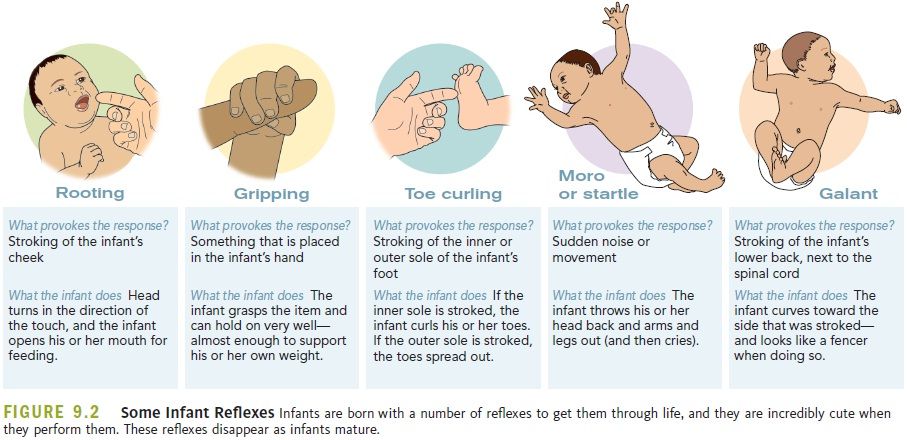 She holds a Bachelor’s degree in early childhood education and works out of Jerome, Idaho.
She holds a Bachelor’s degree in early childhood education and works out of Jerome, Idaho.
Jerrianne Webb, RN, IBCLC, is a lactation consultant for the University of North Carolina. She earned her nursing degree from Presbyterian Hospital School of Nursing in Charlotte, North Carolina.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
How Much Should a Newborn Eat?
Are There Foods to Avoid While Breastfeeding?
Top 12 Benefits of Breastfeeding
Cluster Feeding: Ages, Signs and Tips
By the time baby arrives, you’ve probably mentally prepared for the frequent wakeups you’re about to endure. Sleep deprivation as a new parent is par for the course, after all. What may come as a surprise, however, is the pure exhaustion that accompanies newborn cluster feeding. It’s one of those new parenting things you won’t truly understand until you actually experience it; but it’s totally normal and, thankfully, doesn’t last forever (though it won’t feel like much of a consolation when you’re in the thick of it). Still, it’s helpful to know what to expect so you can mindfully manage the situation rather than panic when the feeding frenzy begins. Ready to get the lowdown on all things newborn cluster feeding? We’re sharing what it is, why it happens, when it starts and how long it’ll last—plus, some tips for how to cluster feed and prepare yourself for the nonstop breast or bottle buffet ahead.
What may come as a surprise, however, is the pure exhaustion that accompanies newborn cluster feeding. It’s one of those new parenting things you won’t truly understand until you actually experience it; but it’s totally normal and, thankfully, doesn’t last forever (though it won’t feel like much of a consolation when you’re in the thick of it). Still, it’s helpful to know what to expect so you can mindfully manage the situation rather than panic when the feeding frenzy begins. Ready to get the lowdown on all things newborn cluster feeding? We’re sharing what it is, why it happens, when it starts and how long it’ll last—plus, some tips for how to cluster feed and prepare yourself for the nonstop breast or bottle buffet ahead.
In this article:
What is cluster feeding?
Why do babies cluster feed?
When does cluster feeding start?
How long does cluster feeding last?
Signs of cluster feeding
Tips for how to cluster feed
How to stop cluster feeding
What Is Cluster Feeding?
You may have heard the term thrown around by other parents, or perhaps a lactation consultant said it during a blurry bedside visit at the hospital. So what is cluster feeding, exactly? Baby cluster feeding is pretty much what it sounds like: when your little one wants to be fed in “clusters” throughout the day. Cathleen Hemphill, RN, a nurse and lactation consultant in Raleigh, North Carolina, explains that in their first few days of life, babies typically need to be fed a minimum of eight times in a 24-hour span. But before you set your clock and your expectations, know that newborns typically don’t follow a predictable feeding schedule. “Most infants will want to feed more often than this and will cluster or group several feedings in a shorter amount of time,” Hemphill says.
So what is cluster feeding, exactly? Baby cluster feeding is pretty much what it sounds like: when your little one wants to be fed in “clusters” throughout the day. Cathleen Hemphill, RN, a nurse and lactation consultant in Raleigh, North Carolina, explains that in their first few days of life, babies typically need to be fed a minimum of eight times in a 24-hour span. But before you set your clock and your expectations, know that newborns typically don’t follow a predictable feeding schedule. “Most infants will want to feed more often than this and will cluster or group several feedings in a shorter amount of time,” Hemphill says.
In general, a typical feeding for a newborn will last between 15 and 20 minutes, leaving baby nourished and satisfied for about three to four hours, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). In contrast, when they’re cluster feeding, “a baby has several feedings within a short amount of time followed by a longer stretch of sleep,” says Amy Peterson, IBCLC, a lactation consultant in Jerome, Idaho. You’ll know that baby is cluster feeding—and that it’s not just their preferred eating schedule—when their routine suddenly changes for two or three days and then just as swiftly returns to a more regular feeding pace.
You’ll know that baby is cluster feeding—and that it’s not just their preferred eating schedule—when their routine suddenly changes for two or three days and then just as swiftly returns to a more regular feeding pace.
Cluster feeding is completely normal, and while not every baby cluster feeds, it can happen with any newborn, regardless of whether they’re breastfed or formula-fed. That said, it’s often harder if you’re a nursing mom, as your milk is likely still coming in, and you may be struggling with breastfeeding—physically or mentally. If you’re exclusively pumping, it may feel like you can’t keep up with baby’s demands—especially if you don’t have a reserve of milk ready to go yet. That said, if you formula feed, you’ll still notice baby’s increased appetite but will have the convenience of being able to supply more milk on demand, which the AAP says is a safe and appropriate way to manage cluster feeding.
Why Do Babies Cluster Feed?
No one knows exactly why babies cluster feed, says Dyan Hes, MD, a pediatrician in New York City, but there are several strong theories. A common belief among experts is that it happens when a newborn is going through a physical or developmental growth spurt. Newborn cluster feeding could also correlate with baby’s routine in utero. “Most pregnant mothers know from fetal movements that as soon as they go to bed, their baby starts moving, and then about four hours later, they have to get up to the bathroom. This is a biological rhythm of activity that continues for the first weeks of life. We see infants feed well around a mother’s previous bedtime, then four hours later they will perhaps start to cluster feed,” explains Hemphill.
A common belief among experts is that it happens when a newborn is going through a physical or developmental growth spurt. Newborn cluster feeding could also correlate with baby’s routine in utero. “Most pregnant mothers know from fetal movements that as soon as they go to bed, their baby starts moving, and then about four hours later, they have to get up to the bathroom. This is a biological rhythm of activity that continues for the first weeks of life. We see infants feed well around a mother’s previous bedtime, then four hours later they will perhaps start to cluster feed,” explains Hemphill.
If you’re breastfeeding, newborn cluster feeding may cause you to worry or wonder if baby’s increased appetite is indicative of low milk supply or if you’re just not feeding them enough. It’s understandable why your mind would jump to that conclusion, but in reality, the opposite is happening. “In the first few days, a baby’s cluster feeding helps to increase and establish mom’s milk supply,” explains Jerrianne Webb, RN, a nurse and lactation consultant in Raleigh, North Carolina. “The baby’s frequent nursing assists in the hormonal process of transitioning mom’s first milk, colostrum, into the abundant mature milk, a transition that usually occurs between postpartum days three and seven.”
“The baby’s frequent nursing assists in the hormonal process of transitioning mom’s first milk, colostrum, into the abundant mature milk, a transition that usually occurs between postpartum days three and seven.”
Oftentimes, babies cluster feed in the early evening, according to Hes, which also happens to coincide with the infamous “witching hour” for babies. Since the only way cluster-feeding babies know how to express their need to eat is through crying, it can be difficult to discern whether they’re being fussy because they’re hungry or because it’s just that time of day. If baby is inconsolable in the early evening but doesn’t seem to want to eat, it could be the result of overstimulation or possibly colic.
When Does Cluster Feeding Start?
Now that you understand what it is and why it happens, you may be wondering: When does cluster feeding start? Sorry to say, you may not get much of a breather after the exhausting work of labor and delivery. According to Hemphill, newborn cluster feeding can start as early as baby’s second day of life. While this may be the last thing you want to deal with while recovering and trying to get the hang of this whole breastfeeding thing, it can actually be very helpful. “[Cluster feeding] is the principle of supply and demand in breastfeeding,” explains Webb. “Baby’s demand [for milk] increases, which, in turn, increases Mom’s supply.” In those first few days after baby is born, the body is working hard to produce milk and increase supply as needed, and since this is triggered by baby feeding from the breast, the more often they feed, the more milk the body will ultimately produce.
While this may be the last thing you want to deal with while recovering and trying to get the hang of this whole breastfeeding thing, it can actually be very helpful. “[Cluster feeding] is the principle of supply and demand in breastfeeding,” explains Webb. “Baby’s demand [for milk] increases, which, in turn, increases Mom’s supply.” In those first few days after baby is born, the body is working hard to produce milk and increase supply as needed, and since this is triggered by baby feeding from the breast, the more often they feed, the more milk the body will ultimately produce.
How Long Does Cluster Feeding Last?
You’re sleep-deprived and desperate for relief—so you want to know: Exactly how long does cluster feeding last? Baby cluster feeding happens in bursts; each usually lasts a few days at a time, says Webb. However, during the first few weeks of life, as your supply continues to build, you can expect baby to want to cluster feed more often than not. After this initial stage, though, you’ll be more equipped to determine if and when baby will go through another cluster feeding phase based on typical development charts. “After the first few weeks, breastfed babies become more predictable,” she says. Cluster feeding ages typically align with growth spurts and occur at three weeks, six weeks, three months and six months. That said, the first three weeks of newborn cluster feeding is often the longest consistent stretch and the most intense for parents.
“After the first few weeks, breastfed babies become more predictable,” she says. Cluster feeding ages typically align with growth spurts and occur at three weeks, six weeks, three months and six months. That said, the first three weeks of newborn cluster feeding is often the longest consistent stretch and the most intense for parents.
Signs of Cluster Feeding
As babies grow, they slowly start needing more and more milk in one feeding to satisfy their appetite. So how do you know if their increased need for milk is, in fact, cluster feeding or just part of their normal growth and development? Here are some common signs of cluster feeding to look for:
- Having a normal, full feeding, and then wanting to be fed again 30 to 60 minutes later—often eating just as much as they would in a regular feeding
- Sleeping deeply for long stretches of time after two or three close feedings
- Acting frustrated during feedings, searching for the nipple when it’s right in front of them or latching on and off
- Acting fussy or irritable when they’re awake but not on the breast
- Eating in frequent, short spurts close together
- Perpetual feedings often occur in the early evening and nighttime hours
Tips for How to Cluster Feed
For a breastfeeding parent, cluster feeding is exhausting in every sense of the word, especially if you’re still trying to get the hang of nursing. Here are some things you can do to make it a little more manageable:
Here are some things you can do to make it a little more manageable:
- Keep track of how many feedings the baby has had. Peterson says, “Cluster feeders still have the expected number of feeds, just not spaced evenly throughout the day/night.”
- Have your partner or a support person help by doing as much as possible between feedings so you can rest
- Avoid trying to force or delay feedings in an effort to get baby back on a schedule, as this will just make them fussier
- Monitor their weight gain if you need peace of mind that they’re getting enough milk, suggests Peterson. “Expect babies to gain about an ounce a day (or more) once mom’s milk shifts from colostrum to milk,” she says
- Stay hydrated and nourished to keep yourself healthy and your supply ample throughout this phase
How to Stop Cluster Feeding
You may be eager to get a little break, but if you’re wondering how to stop cluster feeding, the truth is: it just has to run its course. The best thing you can do is surrender and let baby take the lead. Hemphill stresses the importance of not forcing or delaying feedings in an effort to make cluster feeding end: “The American Academy of Pediatrics, WHO, and UNICEF recommend that infants feed on demand and as often as they want, day or night.”
The best thing you can do is surrender and let baby take the lead. Hemphill stresses the importance of not forcing or delaying feedings in an effort to make cluster feeding end: “The American Academy of Pediatrics, WHO, and UNICEF recommend that infants feed on demand and as often as they want, day or night.”
Newborn cluster feeding is hard on parents, but you can take comfort knowing that it won’t last forever. Until it passes, lean on your support system and rest as often as possible. You’ve got this.
About the experts:
Cathleen Hemphill, RN, BSN, IBCLC, is a nurse and lactation consultant at the University of North Carolina’s Rex Hospital in Raleigh, North Carolina.
Dyan Hes, MD, is a pediatrician and the medical director of Gramercy Pediatrics in New York City. She earned her medical degree from the Sackler School of Medicine at Tel-Aviv University in 1997.
Amy Peterson, IBCLC, is a lactation consultant for Evenflo Feeding and co-author of Balancing Breast and Bottle: Feeding Your Baby. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in early childhood education and works out of Jerome, Idaho.
She holds a Bachelor’s degree in early childhood education and works out of Jerome, Idaho.
Jerrianne Webb, RN, IBCLC, is a lactation consultant for the University of North Carolina. She earned her nursing degree from Presbyterian Hospital School of Nursing in Charlotte, North Carolina.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
Plus, more from The Bump:
How Much Should a Newborn Eat?
Are There Foods to Avoid While Breastfeeding?
Top 12 Benefits of Breastfeeding
The child began to breastfeed more often. This is fine?
This is the period in a baby's life when he begins to breastfeed more often. For example, if yesterday your child ate an average of once every two hours, and today he requires a breast every half an hour or an hour, we are talking about cluster or group feeding.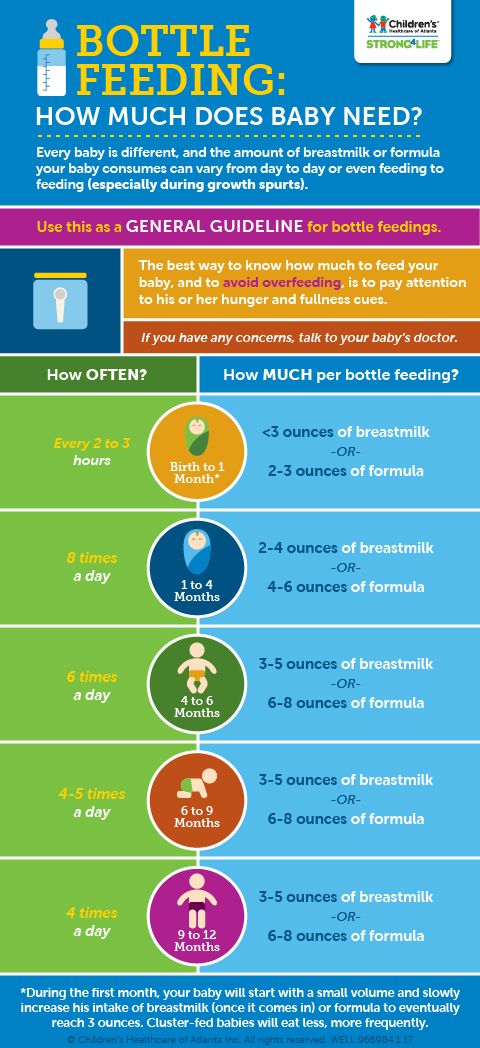 This is a temporary change in the feeding regime, however, parents are unlikely to be happy with such changes and may think that they are doing something wrong. We hasten to reassure you: cluster feeding is normal. nine0003
This is a temporary change in the feeding regime, however, parents are unlikely to be happy with such changes and may think that they are doing something wrong. We hasten to reassure you: cluster feeding is normal. nine0003
This usually happens within the first 28 days of a child's life. As David Hill, Fellow of the American Academy of Pediatrics, says, the first "attack" of cluster feeding usually occurs on the 10-12th day of life, and then repeats in the region of three months. But in general, cluster feedings are typical for the entire first half of a baby's life.
Most often, cluster feedings occur in the late afternoon, when the baby is tired of external stimuli and wants to calm down and fall asleep. Cluster feedings often accompany growth and developmental spurts. Sometimes they can last all day. nine0003
The first weeks and months of a baby's life are a difficult time for him, because he is constantly growing and developing, accepting new conditions of life outside the womb, adapting to the outside world. To do this, he needs not only to get food regularly, but also to calm down, because this big world is such a complicated thing.
To do this, he needs not only to get food regularly, but also to calm down, because this big world is such a complicated thing.
Sucking and being at the mother's breast is a natural need for the baby, so he uses cluster feedings not only to eat, but also to get close contact with the mother. So don't get mad at him, he really needs it. And do not listen to those who say that "that way he will make a dummy out of you." Won't. Listen to yourself and the child, you are doing everything right. nine0003
The good news is that there is evidence that this behavior in a child precedes longer sleep (we're talking about four to five hours). Why, it's a whole chasm of uninterrupted sleep when you have a newborn!
Yes, indeed, cluster feedings can exhaust a mother. But, as the same Hill says, they are important for her, especially if they occur at the initial stage of motherhood. The fact is that by frequent application, the baby stimulates the production of milk, thus helping the mother to quickly establish full lactation. nine0003
nine0003
Of course, the baby needs maternal care and warmth, skin-to-skin contact, but you should not forget about yourself during this exhausting period of group feeding! More precisely, it is strictly forbidden, otherwise you risk bringing yourself to emotional exhaustion. Here's what can be done.
Don't blame yourself or your child. He is all right, all babies have such days, and you are doing everything right - offering him what he needs most now.
Do not forget to drink and eat , because your body is now intensively establishing lactation, which means it consumes a large amount of energy. Eat well and don't limit yourself to kuro-buckwheat.
Sleep between feeds . Facebook and Instagram can wait. Especially if cluster feedings caught you at night, and the baby wakes up every hour. Yes, it will seem to you that it is easier not to sleep at all than to spend time on short sleep sessions, but this is not so.
Connect partner . Yes, you may think that this is rather pointless, because he does not have breasts with milk. But he can carry the baby in his arms while you drink tea or spend time in the shower - during this period it is important to give yourself a little respite.
Don't listen to the "experts" . You will definitely be advised to put the child down and "let him scream" or do something else so that "God forbid, spoil him." But you shouldn't do that. We now know more about children and their needs than ever before. So: cluster feedings will not spoil your baby. He really needs them. In any case, more than senseless motion sickness, attempts to distract and hiss are more necessary. nine0003
It is believed that one episode of grouped feedings should not exceed two days, and the application itself should not exceed an hour. If the baby “hangs” on the chest for an hour and this has been happening for two days, you need to contact a lactation consultant or a pediatrician you trust.
We asked Daria Utkina, a doula and mother-and-child care consultant, to talk about cluster feeding.
Not all babies go through this period, but most do. It seems to me that knowing in itself that this is a physiological norm, and not an epic fail in becoming a milk fairy, already gives a lot of peace of mind. Often women worry that the reason for cluster feedings is the notorious “not enough milk”, although the child has just enough of everything. nine0003
Speaking of support, it's very cool when there are people nearby who also know that cluster feeding is a variant of the norm and you don't have to fight with it. Because even a confident and informed mother will be disturbed by the constant background anxiety of relatives. And if this is the first baby and everything is still completely new, then any comments on the topic “something is not working out for you”, “something is wrong with the child” will fall into the most vulnerable point.
Evening time can also be planned in advance, taking into account the baby hanging on the chest. Arrange with a partner to come to the beginning of vigils, call a postpartum doula or a friend / mother / anyone to be around. nine0003
On the contrary, it helps some women to break the stereotype about crazy evenings at home, pack the baby in a sling where he can feed non-stop, and go out into the world.
Well, adjust expectations all the time. Cluster feedings become a problem when the idea sits in your head that a baby usually eats at least once an hour, or even every three hours. And when everything happens differently, it makes you reconsider your ideas not only about babies, but also about your life with them.
Many of my clients find it helpful to remind themselves of "one thing a day." Especially for those who are accustomed to work tirelessly and assumed that while the baby was sleeping and eating, it would be possible to continue almost in the same rhythm.
Plus, sometimes it happens that cluster feedings are just situations where a child for some reason (inefficient attachment, a short bridle, for example) has to be on the breast all the time to get the right amount of milk. In this case, it would be good to call a consultant on breastfeeding and find out what is the reason. nine0003
During cluster feedings, the mother has a huge responsibility and may feel overwhelmed, exhausted and frustrated. Obviously, dads can't offer to help feed their baby, but there are some important ways they can help moms.
Get up with your mother. This is really important, she will not feel so lonely if the partner tries to cheer her up during feeding (and at the same time not fall asleep next to her).
Bathe, walk, entertain the child (and also his brothers and sisters). Cluster feeding will be much easier for mom if she can focus only on this.
Take on household chores. Clutter in the house is unlikely to help you stay calm. Conversely, if household chores are in order, mom will be less anxious on busy cluster feeding days.
No. What mother eats does not affect the amount of milk. There are no official lists of prohibited or permitted foods during feeding. If the mother or child does not have allergic reactions, then you can eat whatever you want, and even drink two small cups of coffee a day. We hope it's not cold! nine0003
🎖▷ Why you don't have to worry about weight gain with Lamictal
psychology
6,803 2 min read
If you're worried that taking Lamictal (lamotrigine) might cause weight gain, there's good news. It probably won't affect your weight much. If anything, you're more likely to lose weight due to Lamictal than gain weight, but either way, the changes are likely to be pretty small.
The effect of Lamictal on weight has been little studied, and various clinical trials have found minimal effect. In fact, some researchers even considered the drug as a possible remedy for obesity and as a remedy for overeating. This information should be reassuring for people with bipolar disorder, as many of the medications used to treat this condition can cause weight gain. nine0003
In fact, some researchers even considered the drug as a possible remedy for obesity and as a remedy for overeating. This information should be reassuring for people with bipolar disorder, as many of the medications used to treat this condition can cause weight gain. nine0003
Lamictal findings and weight gain or loss
Lamictal is an anticonvulsant that can be used to treat seizures such as epilepsy. It is also used as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder.
In the first clinical trials with the drug, 5 percent of adults with epilepsy lost weight while taking Lamictal, while 1 to 5 percent of patients with bipolar I disorder gained weight while taking the drug. The researchers do not disclose how much weight patients have gained or lost. nine0075 Meanwhile, a 2006 study comparing the effects on weight of Lamictal, lithium, and placebo found that some Lamictal-treated patients gained weight, some lost weight, and most remained about the same weight. Weight changes are usually not many pounds anyway.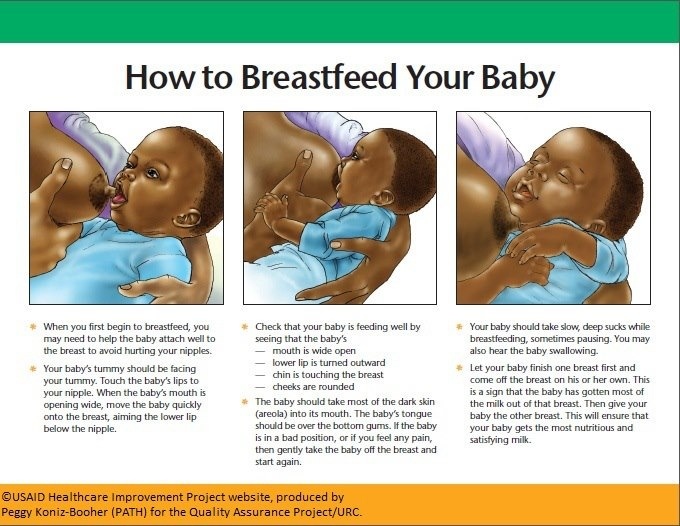 Obese patients taking Lamictal lost an average of four pounds, while the weight of non-obese patients remained virtually unchanged.
Obese patients taking Lamictal lost an average of four pounds, while the weight of non-obese patients remained virtually unchanged.
Relationship between weight gain and other bipolar drugs
Weight gain from medications used to treat bipolar disorder is unfortunately quite common. Some mood stabilizers commonly used for bipolar disorder, especially lithium and Depakote (valproate), carry a high risk of weight gain.
In addition, the atypical antipsychotics Clozaril (clozapine) and Zyprexa (olanzapine) tend to cause significant weight gain in people who take them. Finally, some antidepressants, notably Paxil (paroxetine) and Remeron (mirtazapine), have been associated with weight gain. nine0075 Therefore, if you are already overweight, you and your psychiatrist may want to consider additional weight gain when determining your bipolar medication regimen. Based on this, Lamictal may be a good choice.
Lamictal as a possible treatment for obesity
Lamictal has also been studied as a possible treatment for obesity in people without epilepsy or bipolar disorder.
In a small 40-person clinical trial conducted in 2006, researchers randomly assigned participants to receive either lamictal or placebo for up to 26 weeks. Each participant in the study had a body mass index (BMI) between 30 and 40, placing them in the obese group to the level of severe obesity. Those who took Lamictal lost an average of just over 10 pounds. Those who took the placebo lost about 7 pounds in the meantime, so while those who took Lamictal lost more weight, they didn't lose all that much more. nine0075 Another study in 2009 looked at Lamictal as a remedy for overeating. This study involved 51 people with the condition that 26 of them received Lamictal, and 25 - placebo.
Those who took Lamictal lost more weight than those who took placebo (about 2.5 pounds vs. about one third of a pound) and did have significant improvements in blood sugar and cholesterol lab test results. However, Lamictal did not appear to affect other aspects of the eating disorder when compared to placebo.