Baby won t feed during day
Breastfeeding sleepy and reluctant babies
Go backExplore this article's topics:
Feeding Breastfeeding Common breastfeeding challenges
There are lots of reasons why your baby may be reluctant to feed. It doesn’t mean you aren’t doing a good job as a mum. Don’t put too much pressure on yourself to know all the answers straight away and speak to your midwife or health visitor if you have any questions or concerns, or are looking for ways to make feeding more comfortable.
How often should my baby feed?
All babies are different, but it's very common for babies not to feed all that much in the first 24-48 hours, and some don't attach at all. However, from day 2-3 days babies should become much more awake and feed in more frequent (but probably irregular) bursts at least 6 times in 24 hours.
How do I know if my baby's getting enough milk?
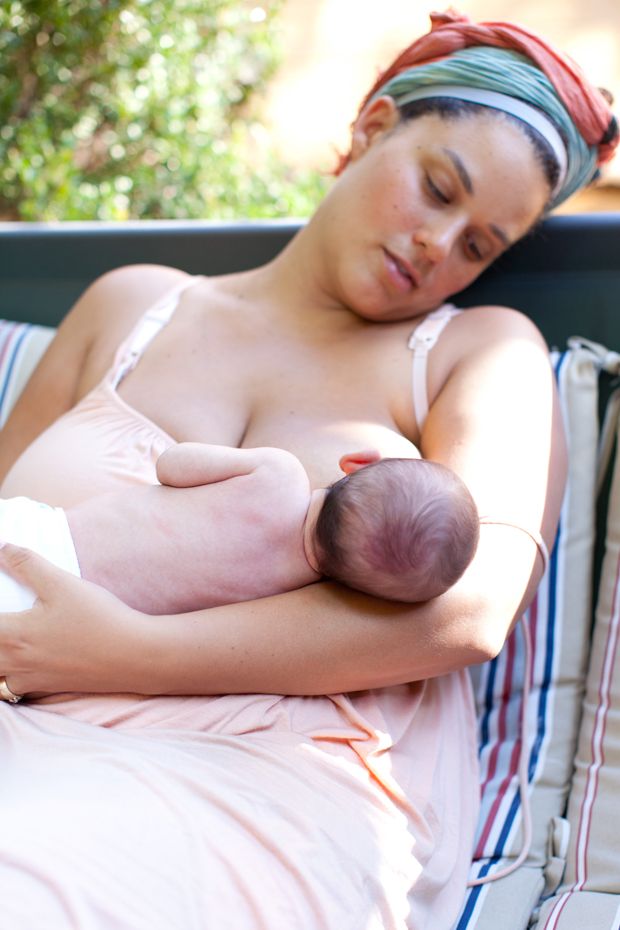
Photo of a baby breastfeeding
Breastfeeding at first can be really hard to get used to and you might find yourself wondering if your baby has had enough milk - it can be very hard to judge how much breastmilk your baby has had, but they are clever wee things and you have to have some faith that your baby knows whether it needs more milk. There are signs to look out for if you think your baby isn't getting enough milk.
Why are some babies reluctant to feed?
This happens most often when babies don't get skin-to-skin contact with mum soon enough or for long enough after the birth. Ideally, you want skin-to-skin contact with your baby straight away and for as long as it takes for your baby to want to feed. If you don’t have any complications, your midwife will help you get skin-to-skin with your baby quickly after they are born. Some reluctant babies are just too tired, sore, or sedated to feed after birth, and others can't because they are premature, ill or jaundiced.
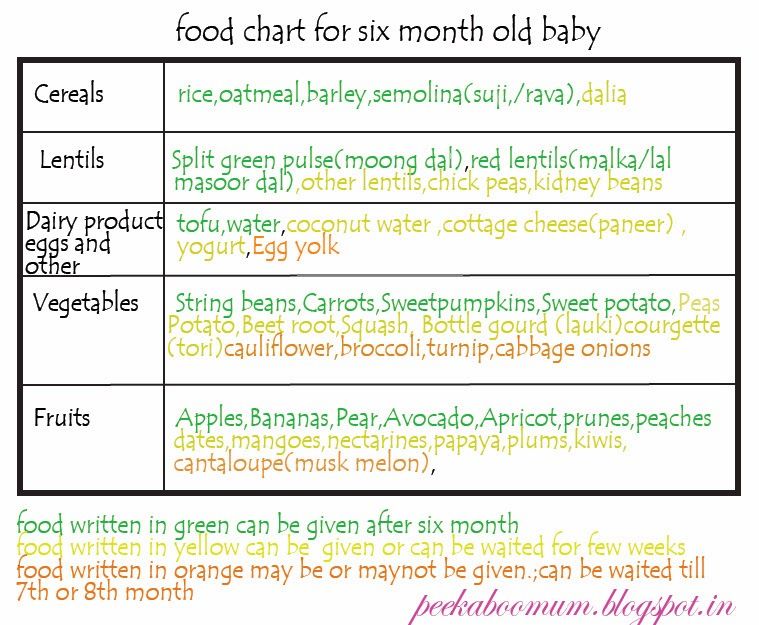
What if I miss my baby's signs that they're hungry?
New mums sometimes miss or don't understand their baby's feeding signs – our page about learning your baby's cues explains what you should be looking for. Don’t worry if it takes a while to get used to when your baby wants a feed – it's something you are both learning together and it's baby steps for both of you. It's completely understandable to be worried about how much milk your baby is getting if they're not feeding in the early hours and days. It might help to know that babies are born with several days' supply of fluid and stored fat to get them by until they're ready to feed.
It's completely understandable to be worried about how much milk your baby is getting if they're not feeding in the early hours and days. It might help to know that babies are born with several days' supply of fluid and stored fat to get them by until they're ready to feed.
What's the solution?
Your midwife will check in on you to make sure your baby is well and to help you spot the signs that they're ready to feed – remember you can ask your midwife (in the hospital or at home) to help show you how to get in a comfortable position to help get your baby feeding. This video shows just this – very often all it takes is some help with positioning, skin-to-skin contact and a little patience!
Top tips to encourage a reluctant or sleepy baby to breastfeed
Tip #1: Hand expressing to keep your milk supply up
Start hand-expressing your colostrum – this is the first milk you make, and helps protect your baby from illness and infection. You can give this to your baby by syringe, spoon, dropper or cup. Expressing helps to build a good milk supply for when your baby is ready to feed. If this is your first time breastfeeding, it will take some time to get used to expressing your milk. You can find out more about expressing here.
You can give this to your baby by syringe, spoon, dropper or cup. Expressing helps to build a good milk supply for when your baby is ready to feed. If this is your first time breastfeeding, it will take some time to get used to expressing your milk. You can find out more about expressing here.
In the first couple of days you only make small amounts of colostrum so don’t become disheartened if it is difficult or takes time. It will get easier as each day and week goes by.
Tip #2: Try lots of skin-to-skin contact
Aim for lots of skin contact and being close to soothe your baby and give them the opportunity to feed.
Tip #3: Try to find a comfortable feeding position
Biological 'laid back' breastfeeding positions can help encourage babies to feed. Your midwife will be able to show you comfortable ways to feed. You can find out more about feeding positions here.
Tip #4: Get your baby ready for a feed
Massaging your baby's skin, changing their nappy and expressing a little milk for them to taste can help get your baby interested in feeding.
Tip #5: Don’t force your baby to feed
Don’t push your baby by the head or try to force them to feed as this could put them off completely.
Getting to know your baby
Learning your baby's cues
Signs your baby isn't getting enough milk
Refusing the breast
Looking after yourself with a newborn
The Scotland wide donor milk bank
This article was created as part of
Last updated: 31 May, 2022
Nursing Strikes - La Leche League International
My Baby Is Suddenly Refusing to Nurse.
 Does That Mean It’s Time to Wean?
Does That Mean It’s Time to Wean? A baby who is truly ready to wean will almost always do so gradually, over a period of weeks or months. If your baby or toddler has been breastfeeding well and suddenly refuses to nurse, it is probably what is called a “nursing strike,” rather than a signal that it’s time to wean. Nursing strikes can be frightening and upsetting to both you and your baby, but they are almost always temporary. Most nursing strikes are over, with the baby back to breastfeeding, within two to four days.
First thing to remember is to feed the baby. The other important thing is to protect your supply.
Nursing strikes happen for many reasons. They are almost always a temporary reaction to an external factor, although sometimes their cause is never determined. Here are some of the most common triggers of nursing strikes:
- You changed your deodorant, soap, perfume, lotion, etc. and you smell “different” to your baby.
- You have been under stress (such as having extra company, returning to work, traveling, moving, dealing with a family crisis).

- Your baby or toddler has an illness or injury that makes nursing uncomfortable (an ear infection, a stuffy nose, thrush, a cut in the mouth).
- Your baby has sore gums from teething.
- You recently changed your nursing patterns (started a new job, left the baby with a sitter more than usual, put off nursing because of being busy, etc.).
- You reacted strongly when your baby bit you, and the baby was frightened.
- You are newly pregnant and your milk supply may be reduced.
- You are ovulating and your milk supply may be temporarily reduced.
- You have been pumping less time or with less frequency when away from baby.
- You have been sick and/or taking a medication (including some methods of birth control), which can have a negative impact on your supply.
One additional consideration is a strong or overactive letdown (OALD), where your milk comes in so fast and sprays hard that baby can’t control it well and closes his mouth, refusing the breast.
Only you know for certain which, if any, of the above factors apply in your current situation. No matter what the cause, a nursing strike is upsetting for everyone. The baby may be difficult to calm and unhappy. You might feel frustrated and upset. Remember your baby isn’t rejecting you. Breastfeeding will almost always get back to normal with a little time.
Getting over the nursing strike and getting your baby back to the breast takes patience and persistence. Get medical attention if an illness or injury seems to have caused the strike. See if you can get some extra help with your household chores and any older children so that you can spent lots of time with the baby.
Try to relax and concentrate on making breastfeeding a pleasant experience. Stop and comfort your baby if he or she gets upset when you try to nurse. Extra cuddling, stroking, and skin-to-skin contact with the baby can help you re-establish closeness.
Additionally, these time-tested suggestions have helped many nursing parents overcome a nursing strike. They are best to try before a baby’s normal feeding times, to assure that baby is not hungry and likely more resistant at the breast.
They are best to try before a baby’s normal feeding times, to assure that baby is not hungry and likely more resistant at the breast.
- Try not to stress about it. (So easy to say, not to do.) The baby will pick up on stress. Play calming music, lower lights in the house, go skin to skin as much as possible.
- Nurse the baby as he is asleep, just awakening, or is very drowsy. As we drift to sleep or awaken, we are in a more primitive state of mind and since breastfeeding is a survival behavior for babies, sometimes they revert to feeding well at this time.
- Vary nursing positions.
- Nurse when in motion. In this case, a sling or cloth carrier can be useful.
- Give the baby extra attention and skin to skin contact.
- Hold the baby in a sling or baby carrier between attempts to nurse to increase bonding.
- Lay in bed to play with baby while you are topless, with no pressure to nurse. Just the open invitation if baby searches for the breast.
- Nurse in a quiet, darkened room free of distractions.
- Stimulate your let-down and get your milk flowing before offering the breast so the baby gets an immediate reward.
- Take a warm bath together with lots of skin to skin snuggling and no pressure to nurse.
- Sleep together, giving baby easy access to the breast while sleeping.
- Spend time around other nursing babies and toddlers. Sometimes peer pressure can be a good thing! A LLL meeting is a natural place to do this. Playgroups or busy store nursing rooms can also be helpful.
While you are trying to persuade your baby back to the breast, you’ll want to make sure baby gets enough milk to sustain him and you keep your milk supply flowing.
You may consider feeding by cup, spoon, eyedropper, or syringe while you work on getting him back to the breast. You might feed baby by bottle, making sure to practice paced bottle feeding. Tilting a bottle or using fast-flow nipples can sometimes confuse baby and bring on a nursing strike. You may find that his need to suck will encourage him to nurse instead of “just eating” by the other methods. Try to keep in mind, this could all be over in a day or two.
You may find that his need to suck will encourage him to nurse instead of “just eating” by the other methods. Try to keep in mind, this could all be over in a day or two.
While baby is refusing breast, you need to extract your milk as often as baby has been nursing. Some moms find hand expression to be effective, while others rely on pumping. Not only does this practice protect your supply, it also saves you from potential clogged ducts or mastitis.
Take one hour at a time. Be gentle with yourself. Your local LLL Leader can offer support and more suggestions if these don’t seem to be working.
Finally, if this strike goes on and days turn into weeks, this may signal the end of your nursing journey. Please recognize what a gift you have given your child! It can be an emotional time, especially when your “plan” was to nurse longer. Not to mention hormonal changes as your milk supply diminishes. Take care of yourself and manage the weaning carefully to avoid clogged ducts or mastitis. We recognize each nursling’s breastfeeding journey is entirely individual and unique. This is yet another step in your motherhood journey. Congratulate yourself on your breastfeeding effort!
We recognize each nursling’s breastfeeding journey is entirely individual and unique. This is yet another step in your motherhood journey. Congratulate yourself on your breastfeeding effort!
If the child does not eat well: what to do and what not to do
What to do if the child does not want to eat.
- Malyusik, well, one more spoon - and that's it! Last! I ate only two, let's have a little more, here's the most delicious piece for you! - says the average mother, offering a spoon with one hand, playing the accordion with the other, showing the trick with the disappearance of the handkerchief with the third, turning the cutlets over with the fourth, while doing somersaults on one leg.
Sound familiar?
Every dad has an instinct to bring home food, and mom has to feed the baby food. And if he refuses to eat, a signal is triggered - "I'm a bad mother" or "the child is sick."
In this case, the most important thing for a parent to understand is whether the child DOES NOT WANT or CANNOT eat?
If the baby is running around, having fun and looking good, without showing any signs of illness, then most likely he does not want to eat. There can be many reasons:
There can be many reasons:
- A breastfeeding child prefers milk and dairy products, intuitively understanding that he needs calcium, and now milk is healthier for him than soup.
- The child wants a cookie, not vegetables.
- He really wasn't hungry. For example, his metabolism is slow, breakfast has not yet been digested, and lunch is already being offered. Or the child was sitting in front of the TV after breakfast and his appetite had not yet had enough time to play out. Compared to the boy next door who was outside all day.
- If a child is not genetically destined to become Uncle Styopa, then he can eat much less than his peer, who has tall parents.
- Psychological problems. If earlier you accidentally gave your child a bitter cucumber, then he may refuse any green food. Or you yell at the child during the meal, and for him the food is perceived as a trauma.
If your child is lively, but at the same time he has a "bad appetite", then this is not his problem, but yours - the psychological problem of an unsatisfied instinct. If a child jumps, jumps, he has healthy nails, hair, etc., think less about what he lacks. Better think about something nice))
If a child jumps, jumps, he has healthy nails, hair, etc., think less about what he lacks. Better think about something nice))
An active child = not a hungry child.
Wait for the natural desire and correctly distribute energy costs - walk more often, send the child to the sports section, or simply say: “If you don’t want to, take a walk, dinner is not earlier than seven and no snacks.” That is, if your child simply does not want to eat, normalize feeding - strictly at a certain time and without snacks. The body will get used to secrete gastric juice strictly according to the schedule.
And one more thing. There are no rules about how much a child should eat. He can eat a kilo (and make you very happy) and 9Send 00 grams to the toilet. Or eat 100 g and learn everything.
But it is much more difficult if the child CANNOT eat.
Causes:
- If you are breastfeeding, you may have “tight breasts”, when it is very difficult for the baby to suck milk.

- The child has a runny nose, and when he eats, he begins to choke.
- Food hot, cold, sour, bitter.
- He has sores in his mouth (for example, from toys), and they hurt when food gets on them.
- Teeth are cut, gums hurt.
- Bowel problems. The stomach starts to hurt while eating.
- The child simply fell ill (cold, SARS, poisoning, influenza, etc.). If the child is sick, and he is not dystrophic, then you should not force him to eat. The body fights infections better when it's hungry. But be sure to drink.
If a child at first shows appetite and interest in food, but refuses to eat through a spoon or two, then, most likely, the process of eating causes him certain difficulties.
If the baby CANNOT eat and you can't identify or eliminate the cause, the best thing to do is contact your pediatrician. The doctor will accurately determine the problem and give the necessary recommendations.
Our clinic has a wonderful pediatrician Yuliya Vladimirovna Sinyagina with 17 years of experience! You can sign up to her))
Bon appetit everyone! As well as strength, patience and satisfied instincts!
Back to article list
Misplaced feeding schedule: why does your baby eat all night and how to change it?
03/12/2017
134892
79
feeding and sleep
3-6 months --9 months-18 months
Natalya Trofimova
Natalya Trofimova
Senior Snipe consultant, pediatrician
2222 Mom of two daughters
Does your baby eat little or rarely during the day, but hangs on her chest for a long time at night or often asks for a bottle? This is called a "shifted feeding schedule". With this organization of nutrition, the child receives the bulk of the calories at night. During the day, feedings are either short or rare, or the baby refuses the breast or bottle altogether. After six months, there may be difficulties with the introduction of complementary foods, especially with unformed nutritional interest.
With this organization of nutrition, the child receives the bulk of the calories at night. During the day, feedings are either short or rare, or the baby refuses the breast or bottle altogether. After six months, there may be difficulties with the introduction of complementary foods, especially with unformed nutritional interest.
Child crisis calendar
Why is this happening?
- During periods of crisis in a child's development (a developmental leap, teething, an acute illness, any strong emotional experiences), a temporary and sharp increase in the number of feedings is normal, it just needs to be waited out.
- Babies in their first months of life can “mix day and night” and, accordingly, stay awake and eat mostly at night.
- Older children become interested in everything and are easily distracted during the daytime feedings, butting for a short time, because they have too many important things to do during the day.
- With the introduction of complementary foods, mothers sometimes begin to replace daytime feedings with breast milk or formula with low-calorie fruit and vegetable purees, and the child has to “get” calories at night.

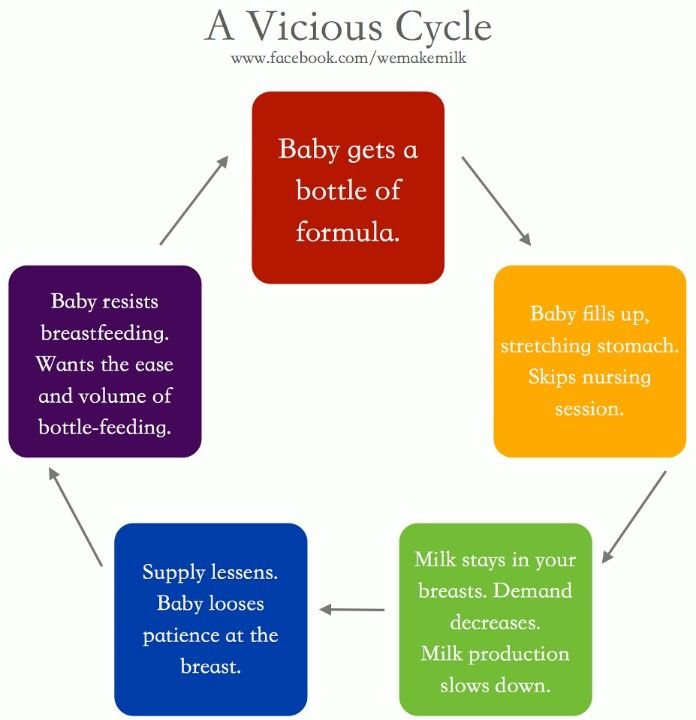
- Mixed-fed, when breast milk and formula are clearly separated by time of day. When breastfeeding only during the day, the baby may refuse the breast if he prefers a bottle that is given only at night. And vice versa, when feeding during the day with a mixture, and at night with a breast, if the baby prefers the breast.
- Breastfeeding mother works outside the home or is separated most of the day from the baby (even with the possibility of pumping). When sleeping together, the baby is often applied, replenishing contact and helping to stimulate lactation. This option is not bad as a solution, provided that co-sleeping is suitable for the family and everyone gets enough sleep.
Answer a few questions to find out if your feeding schedule is shifted:
- How many times does the child eat during the day and how, how many times does he wake up at night?
- Does he eat for a long time every night when he wakes up, are sips audible, or is it mostly short attachments with superficial sucking for a couple of minutes?
- Are the daily feeds long, does the baby let go of the breast when it is full, or is it often torn off and distracted?
- Can a baby fall asleep without breastfeeding or a bottle (both day and night) or is this the only way to fall asleep?
Frequent nightly “snacking” does not always indicate that the feeding schedule has been shifted. If feeding is a way to relax and fall asleep, then when awakened at night between sleep cycles, the breast or bottle will again be required to fall asleep. This is an association with sleep, the way and habit of falling asleep.
If feeding is a way to relax and fall asleep, then when awakened at night between sleep cycles, the breast or bottle will again be required to fall asleep. This is an association with sleep, the way and habit of falling asleep.
What such feedings usually look like:
- The baby wakes up every 1–1.5 hours at night and asks for food, and during the day he usually eats after 3 hours, which means that he is unlikely to experience hunger.
- The child eats very little at night: he kissed his chest for a minute or a bottle, ate 10-20 ml and fell asleep - in this case, he does not have a goal to eat.
- If there is an association for sleep, but the daily appetite does not suffer, mother and baby get enough sleep, there is nothing to worry about. In order for the number of nightly awakenings and feedings to allow sufficient sleep, even if there is an association for sleep, the child must be well suited to sleep and wakefulness.
Is it possible to change the habit of eating at night and when should I wait?
As much as one would like to reduce the number of night feedings, there are situations when they are necessary. For example, a baby in the first months of life does not gain weight well, there are problems with lactation (little milk, false breastfeeding), adaptation to a therapeutic mixture with a specific taste and refusal to wake up, the baby feels unwell (sick, teeth are being cut), a child is experiencing a developmental leap, stress, a long separation from her mother.
For example, a baby in the first months of life does not gain weight well, there are problems with lactation (little milk, false breastfeeding), adaptation to a therapeutic mixture with a specific taste and refusal to wake up, the baby feels unwell (sick, teeth are being cut), a child is experiencing a developmental leap, stress, a long separation from her mother.
The assistance will depend on the age and the reason for the predominance of night eating. In the first months of life, with the "confusion of day and night," it is important to show the baby when it is day and when it is night. For daytime sleep, you do not need to create a strong blackout, and at night you need to ensure maximum darkness in the room. Limit overly long naps. All activities, walks, communication - during the day, no games at night.
If the baby is distracted during feedings and “forgets” to eat, you need to create the most calm atmosphere during feedings: turn off the TV, do not use the phone, retire to a darkened quiet room, turn on white noise. You can put a bright scarf around your neck, slingobuses, any baby rattle on a ribbon. Try a different position with less visibility, such as kneeling facing you or in a sling.
You can put a bright scarf around your neck, slingobuses, any baby rattle on a ribbon. Try a different position with less visibility, such as kneeling facing you or in a sling.
With the introduction of complementary foods, do not rush to replace breastfeeding or mashed formula. The first vegetable or fruit purees are not comparable in calories to breast milk and formula. Occupying volume in the stomach, they reduce milk intake during the day. Complementary foods can fully replace feeding only after 8 months, when it will make up about 20–30% of nutrition and the baby will eat cereals, meat, and vegetables.
On mixed feeding, it is desirable to supplement the baby with the mixture in the required amount after each application to the breast, or feed the mixture by the hour (at regular intervals), and breastfeed on demand.
A working mother who is breastfeeding and co-sleeping has the hardest time reducing nighttime feedings. To do this, you need to feed the baby often enough during the day, a maximum of 3–3.








/imgs/2020/05/29/12/3933015/7cf142452ac7f89551afc432db0e634f8b6b47e5.jpg)