Can a four month old have baby food
Feeding Your 4- to 7-Month-Old (for Parents)
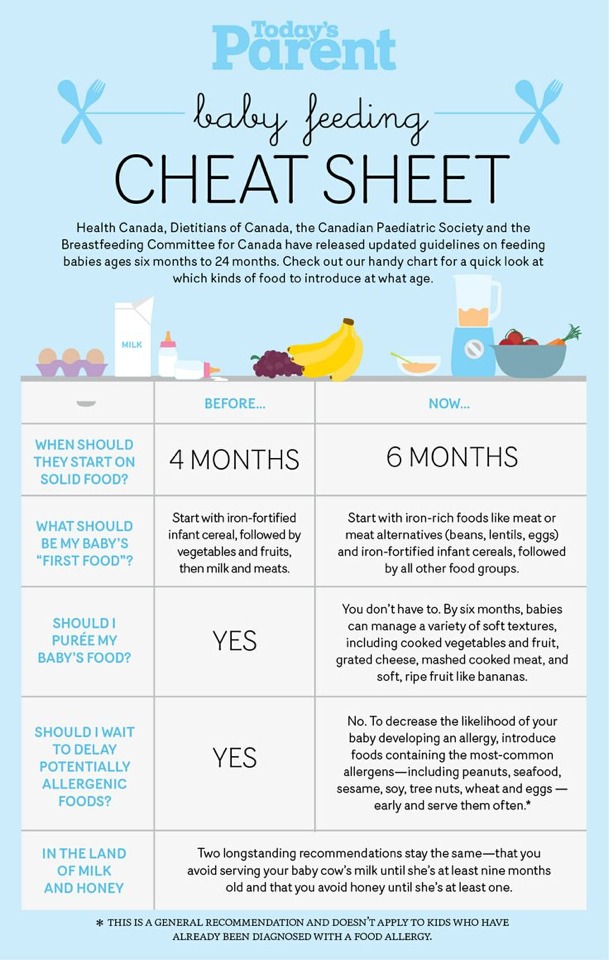
Most babies this age are ready to try solid foods. Experts recommend starting solid foods when a baby is about 6 months old, depending on the baby's readiness and nutritional needs.
Be sure to check with your doctor before giving any solid foods.
Is My Baby Ready to Eat Solid Foods?
How can you tell if your baby is ready for solids? Here are a few hints:
- Does your baby swallow food or push it out of their mouth? Babies have a natural tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food back out. Wait until this reflex disappears (typically when babies are 4–6 months old).
- Can your baby support their own head? To eat solid food, an infant needs good head and neck control and should be able to sit up.
- Is your baby interested in food? Babies who stare, reach and grab, and open their mouths for food are ready to try solid foods.
If your doctor gives the go-ahead but your baby seems frustrated or uninterested in solid foods, try waiting a few days before trying again. Breast milk and formula will still meet nutritional needs as your baby learns to eat solid foods. But after 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — like iron and zinc — that solid foods provide.
Do not add cereal or other food to your baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain.
Watch for signs that your child is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your child stop when full. A child who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the breast or the bottle. With solid foods, they may turn away, refuse to open their mouth, or spit the food out.
How Should I Start Feeding My Baby Solid Foods?
When your baby is ready and the doctor says it’s OK to try solid foods, pick a time of day when your baby is not tired or cranky. You want your baby to be a little hungry, but not so hungry that they’re upset. So you might want to give your baby a little breast milk or formula first.
Have your baby sit supported in your lap or in a high chair with a safety strap.
Most babies' first food is iron-fortified infant single-grain cereal mixed with breast milk or formula. Place the spoon near your baby's lips, and let the baby smell and taste it. Don't be surprised if this first spoonful is rejected. Wait a minute and try again. Most food offered to your baby at this age will end up on the baby's chin, bib, or high-chair tray. Again, this is just an introduction.
When your little one gets the hang of eating cereal off a spoon, it may be time to try single-ingredient puréed meat, vegetables, or fruit. The order in which you give them doesn't matter, but go slow. Offer foods that are high in iron and zinc — such as meat, poultry, eggs, and beans — especially if your baby is breastfeeding. Try one food at a time and wait several days before trying something else new. This will let you identify any foods that your baby may be allergic to.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
Possible signs of food allergy or allergic reactions include:
- rash
- bloating or an increase in gassiness
- diarrhea
- vomiting
Get medical care right away if your baby has a more severe allergic reaction, like hives, drooling, wheezing, or trouble breathing.
If your child has any type of reaction to a food, don't offer that food again until you talk with your doctor.
Babies shouldn't have:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday.
 It can cause botulism in babies.
It can cause botulism in babies. - unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy beverages before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.
- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Tips for Feeding Your Baby Solid Foods
With the hectic pace of family life, most parents try commercially prepared baby foods at first. They come in small, convenient containers, and manufacturers must meet strict safety and nutrition guidelines.
If you prepare your own baby foods at home, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Follow the rules for food safety, including washing your hands well and often.
- To preserve the nutrients in your baby's food, cook it in ways that keep the most vitamins and minerals. Try steaming or baking fruits and vegetables instead of boiling, which washes away the nutrients.
- Freeze portions that you aren't going to use right away.

- Whether you buy the baby food or make it yourself, texture and consistency are important. At first, babies should have finely puréed single-ingredient foods. (Just applesauce, for example, not apples and pears mixed together.)
- After your baby is eating individual foods, it's OK to offer a puréed mix of two foods. As babies get older, they will learn to eat a greater variety of tastes and textures.
- If you use prepared baby food in jars, spoon some of the food into a bowl to feed your baby. Do not feed your baby right from the jar — bacteria from the baby's mouth can contaminate the remaining food. If you refrigerate opened jars of baby food, it's best to throw away anything not eaten within a day or two.
- Around 6 months of age is a good time for your baby to try a cup. You might need to try a few cups to find one that works for your child. Use water at first to avoid messy clean-ups. Do not give juice to infants younger than 12 months.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
When Can My Baby Start Eating Solid Foods? (for Parents)
A friend just started giving her 3-month-old applesauce and rice cereal. My son is just 2 weeks younger than hers, and I am wondering if I should be introducing solids soon too. When should I start?
– Taylor
Doctors recommend waiting until a baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Starting before 4 months is not recommended.
At about 6 months, babies need the added nutrition — such as iron and zinc — that solid foods provide. It’s also the right time to introduce your infant to new tastes and textures.
Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but don't start until your baby is at least 4 months old.
How do you know it’s the right time to start solid foods? Here are some signs that babies are ready:
- They have good head and neck control and sit up in a high chair.

- They're interested in foods. For example, they may watch others eat, reach for food, and open their mouths when food approaches.
- They don’t push food out of their mouths, which is a natural tongue reflex that disappears when they’re between 4–6 months old.
- They weigh twice their birth weight, or close to it.
Talk to your doctor about the right time to start solid foods.
How Should I Start Solids?
When the time is right, you can start with a single-grain, iron-fortified baby cereal. Start with 1 or 2 tablespoons of cereal mixed with breast milk, formula, or water. Feed your baby with a small baby spoon. Don’t add cereal or other food to a baby's bottle because it can lead to too much weight gain. Let your baby practice eating from a spoon and learn to stop when full.
When your baby gets the hang of eating the first food, introduce others, such as puréed meat, fruits, vegetables, beans, lentils, or yogurt. Try one food at a time and wait a few days before trying something else new to make sure your baby doesn't have an allergic reaction.
Foods that are more likely to cause allergies can be among the foods you introduce to your baby. These include peanuts, eggs, cow’s milk, seafood, nuts, wheat, and soy. Waiting to start these foods does not prevent food allergies. Talk to your doctor if you are concerned about food allergies, especially if any close family members have allergies, food allergies, or allergy-related conditions, like eczema or asthma.
Infants with severe eczema or egg allergies are more likely to have allergies to peanuts. Talk to your doctor about how and when to introduce these foods to your child.
When starting your baby on solids, avoid:
- foods with added sugars and no-calorie sweeteners
- high-sodium foods
- honey, until after the first birthday. It can cause botulism in babies.
- unpasteurized juice, milk, yogurt, or cheese
- regular cow's milk or soy drinks before 12 months instead of breast milk or formula. It’s OK to offer pasteurized yogurt and cheese.

- foods that may cause choking, such as hot dogs, raw carrots, grapes, popcorn, and nuts
Also, do not give fruit juices to infants younger than 12 months old.
Over the next few months, introduce a variety of foods from all the food groups. If your baby doesn't seem to like something, don’t give up. It can take 8 to 10 tries or more before babies learn to like new foods.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: February 2021
Complementary foods at 4 months | Useful tips from the Tyoma brand
It is well known that the ideal time to introduce complementary foods is between 4 and 6 months of age. The presence of a child's teeth or the ability to sit are not signs of a child's readiness for complementary foods. It is important that the baby does not have a reflex of pushing the spoon with his tongue, and he can swallow food thicker than breast milk or formula well.
The pediatrician will help determine the exact start date for complementary foods, and in most cases this is the golden mean of 5-5. 5 months. But there are situations when complementary foods need to be started from 4 months, including even a child who is exclusively breastfed.
5 months. But there are situations when complementary foods need to be started from 4 months, including even a child who is exclusively breastfed.
In what cases are complementary foods introduced from 4 months?
- The child is not gaining weight well or is lagging behind in physical development.
- The child has functional digestive disorders (regurgitation, constipation).
- The mother has little breast milk or it is poorly absorbed.
- The child has a reduced appetite or is not digesting formula well.
- The child has signs of iron deficiency (anemia).
- The child has a pronounced food interest: he watches with interest the food of adults, reaches for food.
- The child stopped eating formula and began to demand food more often.
How to start complementary foods at 4 months?
The first product of complementary foods, regardless of the age and type of feeding of the baby (breast or artificial), should be energy-intensive foods: either porridge or vegetable puree. Porridge can be chosen first if the child has loose or unstable stools, and also if the child is underweight. After 4-5 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g)
Porridge can be chosen first if the child has loose or unstable stools, and also if the child is underweight. After 4-5 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge, butter can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of porridge in 150 g)
Mashed vegetables can be the first meal of the day if a child is prone to constipation, when it is better to choose zucchini, which can have a mild laxative effect on the child's stool. Starting from the 4-5th day of the introduction of vegetable puree, vegetable oil can be gradually added to it (up to 5 g per serving of vegetables in 150 g).
What foods can be introduced into the diet of a child at 4 months?
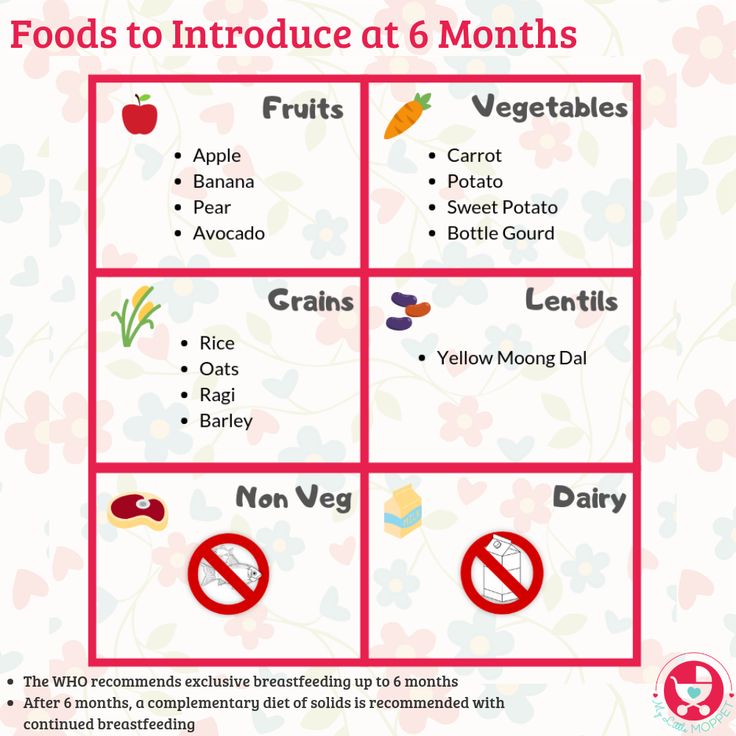
Kashi
Of the first cereals, it is better to give preference to buckwheat or rice. They must be dairy-free and can be diluted with water or breast milk, or the mixture that the baby eats. Later, you can introduce corn and oatmeal.
Vegetables
The first vegetable puree can be zucchini, broccoli, or cauliflower.
Fruit
The third type of complementary food can be fruit puree from apples or pears. Later, you can introduce mashed banana or apricot. At first, fruit puree can not be given to the child separately, but it is better to mix it with cereal or vegetables so that the child does not begin to prefer the sweet taste of fruits. When the amount of fruit puree reaches 50 g or more, it can also be given separately, for example, after the child has eaten porridge or for an afternoon snack.
Juices
Juices should not be the first feeding, in addition, they can not be introduced into the baby's first year of life at all, given their sweet taste and low nutritional value.
Can you make your own first meal?
You can prepare the first complementary foods yourself, but it is safer to use hypoallergenic monocomponent cereals or commercially produced purees prepared to high quality standards for baby food. In addition, it is important to consider that industrially produced baby cereals are often fortified with vitamins and minerals, which makes them especially useful for the first feeding.
How to start the introduction of a new product?
Complementary foods are introduced before breastfeeding or formula. The introduction of a new product should be gradual. But how is it?
- On day 1, give your baby 1 tsp. complementary foods before breastfeeding or formula
- On day 2 - 3 tsp. (15 g)
- On day 3 - 6 tsp. (30 g)
- Day 4 - 50 g
- Day 5 - 70 g
- Day 7 - 100 g
- For 8-10 days - bring to 150 g.
Please note that if complementary foods are introduced from 4 months, then the introduction of 1 new product may take longer than the introduction of complementary foods from 5 or 6 months, namely up to 10 days or more, depending on the reaction of the baby.
Important!
If on the 8-10th day of the introduction of a new product, the baby still cannot eat 100-150 ml of porridge or puree at once, then this amount can be divided into 2 or even 3 doses, for example, give 50 ml of porridge in the morning, 50 ml in the afternoon and 50 ml in the evening. Why do this? So that the child gradually gets used not only to the new product, but also to its quantity. In the future, you need to try to gradually increase the one-time amount of the product to the age volume.
Why do this? So that the child gradually gets used not only to the new product, but also to its quantity. In the future, you need to try to gradually increase the one-time amount of the product to the age volume.
Questions and answers
Will the amount of breast milk decrease if we start introducing complementary foods from 4 months?
Of course, with the introduction of complementary foods, breast milk will be produced less, but only by the amount of complementary foods introduced. As long as you breastfeed your baby on demand and attach him to the breast every time after giving complementary foods, as well as maintaining nightly breastfeeds, you will maintain long-term successful breastfeeding.
Dear parents, remember that the introduction of complementary foods is a creative process that requires an individual approach and attention to the needs of the child. The proposed complementary feeding schemes in terms of time and quantity of introduced products are advisory in nature and do not imply their forced introduction.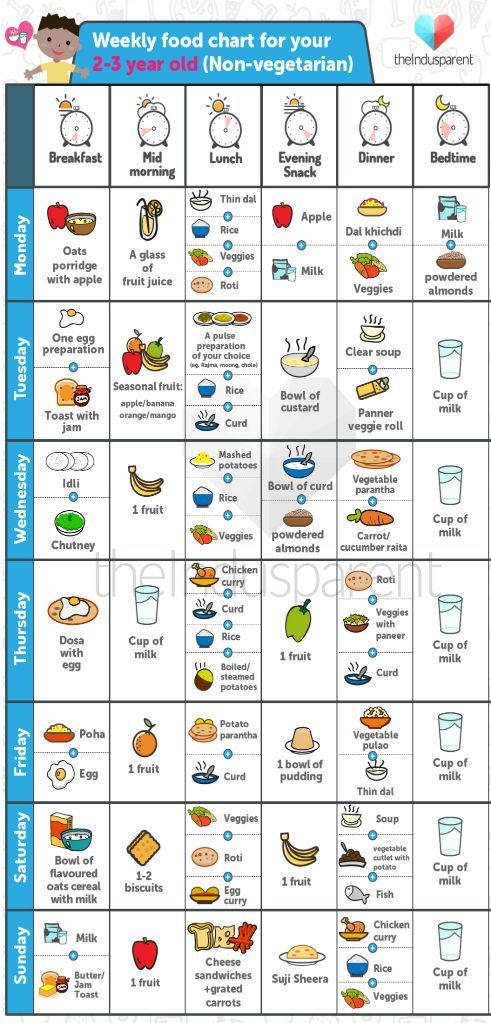
4 to 6 months
Breast milk is the best food for your baby.
It is very important that the baby consumes breast milk for as long as possible.
The right age to start complementary foods
It is recommended to start introducing complementary foods into the baby's diet no earlier than 4 months, but no later than 6 months*. At this age, the baby is in the active phase of development and reacts with curiosity to everything new! Some babies at 4 to 5 months of age can no longer satisfy their appetite with breast milk alone and need complementary foods for healthy growth. Other children have enough breast milk, and they are ready for the introduction of complementary foods only after 6 months. The decision to start complementary foods should always be made according to your baby's development. Do you feel like your baby is not getting enough breast milk? Does your baby hold his head on his own, show interest in new foods or a spoon? Then it's time to start feeding.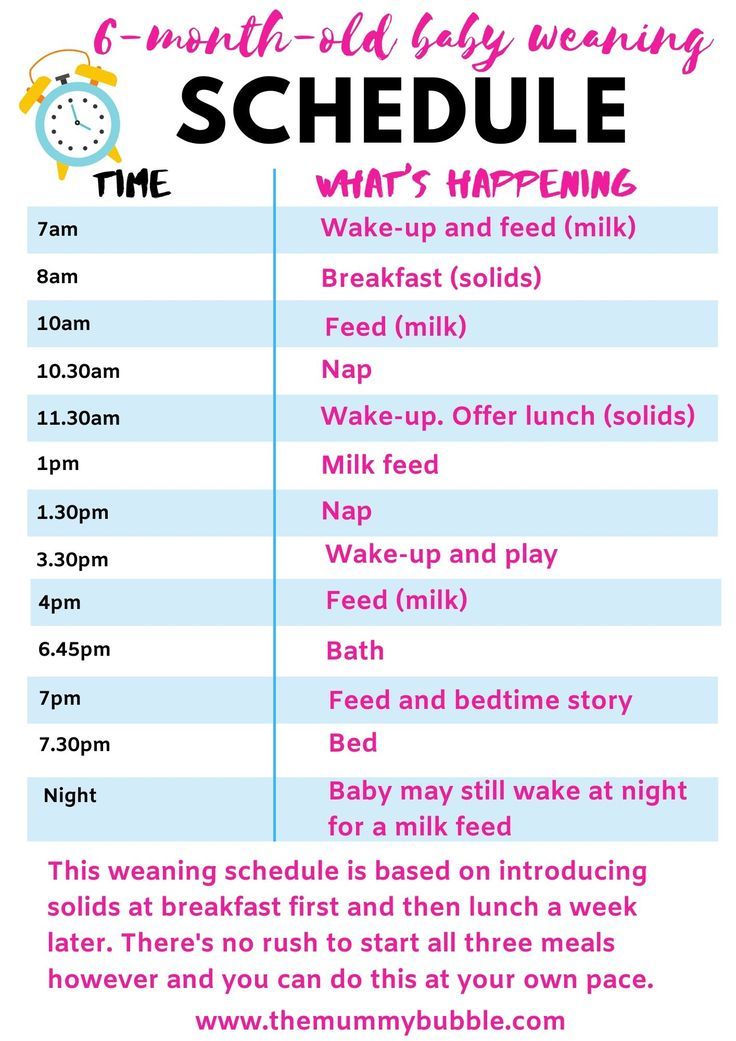 If in doubt, consult your pediatrician.
If in doubt, consult your pediatrician.
If your baby spits out the first spoonfuls of puree, be patient. After all, he must first learn to swallow it. Start with a few scoops and give your child time to get used to the new form of feeding.
*Recommendation of the Nutrition Committee of the European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN)
Why is complementary food so important for the baby?
After 4-6 months of life, only mother's milk or milk formulas are not enough to supply the child's body with all the nutrients and necessary energy. In addition, the transition to solid food trains the muscles of the mouth. And finally, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child will get acquainted with the variety of taste directions, which is also important for his development.
When to start complementary foods?
Gradually replace one breastfeed with complementary foods. First for lunch, then for dinner and finally for lunch. The mouse eats breakfast with the usual dairy food.
The mouse eats breakfast with the usual dairy food.
Starting complementary foods with HiPP products is easy. The first spoonfuls will be vegetable or fruit purees HiPP:
First step: lunch
We recommend that you start complementary foods at lunchtime with HiPP vegetable puree (for example, "Zucchini. My first puree", "Cauliflower. My first puree" or "Broccoli .My first puree"). Then, for satiety, feed your baby as always: breast or bottle. The amount of vegetable puree can be increased daily by 1 spoon. Be patient if your baby does not immediately love vegetables. Try repeating the vegetable puree in the following days. Next week, you can expand your diet with other varieties of HiPP vegetables (for example, "Carrots. My first puree" or "Potatoes. My first puree").
If your baby tolerates vegetables well, in the third week you can introduce grain porridge into the diet, and as a dessert, offer a few spoons of fruit puree enriched with vitamin C. Vitamin C helps to better absorb iron in the body.