Feeding baby solids with no teeth
Can Babies Eat Solids Before Teeth?
Many new moms have this question in mind, “Is my baby ready to make the transition to table food?.” Somewhere even when they know that their baby is ready, they don’t really know how to make the change.
You must be thinking it’s high time to transit your baby from puree food to table food, but you are not sure how to manage it. Try to relax your mind a bit about it. Transiting to table food is not that difficult and your baby can manage eating solid food before their teeth come out.
Did you know, many babies are not given pureed food at all, that they are fed solid food from the beginning? This mainly happens where the parents have an approach to introduce solid foods.
What is considered table food anyway?
There is no historic mystery about the table food; still, many parents are not sure about how to introduce table food to their child. Here is the answer to your question. Table food for baby is any food that your baby is already having but it is not in pureed form. Table food is any food that is age appropriate, you can feed your baby the food that the whole family eats. The only thing you need to keep in mind is the food should not be pureed.
What age can my baby switch from pureed food to table food?
There is no specific age for starting solid foods, but according to studies, it’s mainly after six months that baby can start eating solid foods. You should observe your child while he/she is eating solid food, check their ability to mash and gum foods.
One important part of moving to solid food is your baby’s ability to pick the food themselves or self-feed. A good pincher grasp is required and along with it, your baby also needs to be able to gum and mash the food.
Here are a few signs that your baby can eat table food without teeth:
- Your baby doesn’t need spoon feeding
- Doesn’t enjoy eating pureed food at mealtimes
- Grabs spoon or try to feed himself
- Chews easily without teeth and mashes food
- Baby can grasp properly and can move food towards his/her mouth easily
How can my baby eat solid food if he does not have teeth?
Babies don’t need teeth to eat solids; instead, they mash the food with their gums.
Molars are basically the teeth we use for chewing food. Most babies don’t get their molars until 10-16 months or older. The last pair of molars comes when the child is around two years old. The ability to eat solid foods depends on a child’s ability and not whether they have teeth or not. The 20 baby teeth all come by the age of two and a half year. The permanent teeth continue to develop under the jaw.
So, stop stressing!
More than likely your little one is ready for the big change. They will seem a bit confused at first, but they will LOVE diving into their food on their own terms. Not only do table foods taste better than purees, but it helps them with their independence and helps improve their hand-eye coordination.
125 first foods for babies with no teeth
by Jo
Can you imagine eating food without any teeth? Just with your gums alone? I surely find it hard to picture, but we were once like our little ones. Toothless, like a 100 year old grandma. Luckily, there are first foods for babies with no teeth. And I found 125 of them for you to read about.
Toothless, like a 100 year old grandma. Luckily, there are first foods for babies with no teeth. And I found 125 of them for you to read about.
PIN IT FOR LATER
The original article was written back in 2018. This is a 2021 updated version.
Since then, I have re-written and updated this post to reflect the changes I have gone through when it came to my own beliefs/thoughts and how I word things when talking about feeding kids. As such, the remains of the original article can be seen in the comments section. Word of caution, it’s not something that makes too much sense anymore and some parts I am not very proud of. I even considered deleting the comments altogether, but that doesn’t seem just right either. Either way, I hope this article helps you, even a bit.
Yes, the Pinterest pins show blueberries and they are a choking hazard, but do read the entire post. I have tried to give suggestions for each type of food so as to make them safe even for little ones.
If I missed anything, give me a shout.
But how can babies even chew without teeth?
Well, the truth is, they don’t need teeth to chew.
Chewing involves movements of the jaw, tongue and cheek. Teeth are used later on to break up more complex fibres.
This is technically done with the teeth that are more at the back of the mouth, called molars. The first molars show up somewhere between 13 and 19 months old, as you can see from the graph below.
So if we were to wait that long before we gave our little ones any food that can be easily munched on with the gums, then we would seriously endanger his or her capabilities of dealing with food (not to mention the fact that after around 8 months, the gag reflex moves further down the tongue and babies might experience a higher risk of choking if they are not accustomed to table foods yet).
Furthermore, babies are already experienced in munching away, because they would have spent a lot of time already with their fingers in their mouth, biting toys and other objects.
So encourage them to explore these with their lips, tongue and jaw, at the same time being careful of any pieces that might come off and increase the risk of choking.
So, assuming little one doesn’t have any teeth yet, what can I give him?
See the list below.
But before anything else, make sure baby meets the three signs he or she is ready to begin in the first place. I cannot stress this enough, guys, and it will save you lots of trouble down the road.
There was a time when the recommendations said to start solids at 4 months+ and I’m not sure that all the baby food manufacturers have come up-to-date with the current official advice regarding infant feeding. Always watch the signs in your baby and judge whether he or she is ready. This usually happens at around 6 months, give or take.
Here you go, some ideas of first foods for babies with no teeth. I also added some notes and suggestions of serving for some of them. This is regardless of the method you use, baby led weaning or traditional. At some point, you’ll have to start giving them table foods.
This is regardless of the method you use, baby led weaning or traditional. At some point, you’ll have to start giving them table foods.
And because I’m a fan of food groups, I have split them accordingly, for easier reference.
Note: please be aware of choking hazards. I find this article sums up pretty well what are the foods you need to pay extra attention to. As your little one develops his ability to chew, you need to be careful, teeth or no teeth.
Fruits and veggies
As a general rule, go for the ripest you can get, in the beginning, as these are usually softer for babies just starting out.
- Avocado. Serve as is, sliced into wedges, or served on toast, mashed, with an egg on top. You can also try a guacamole recipe, which is basically adding some tomato, red onion, a bit of pepper and some lemon juice to a mashed avocado. For an easier grip, you can toss it through some breadcrumbs or ground nuts.
- Banana.
 Serve as is, sliced or mashed. Here is a tip on how to offer it if baby is at the beginning, doing baby led weaning and has tiny hands. Also, here’s my recipe of baby’s chocolate you can make with banana and avocado.
Serve as is, sliced or mashed. Here is a tip on how to offer it if baby is at the beginning, doing baby led weaning and has tiny hands. Also, here’s my recipe of baby’s chocolate you can make with banana and avocado. - Apricot. Pick a softer variety, the riper, the better. Cut into wedges or mash.
- Tomato. Try serving them as such or on top of a pizza toast (just a slice of toast, with some mozzarella and tomatoes and baked for 10 minutes in the oven). My youngest sometimes enjoys it cut wedge-style.
- Peach. Extra ripe are usually softer.
- Mango. Go for the ripe ones.
- Strawberry. Remove the hull (the leafy and usually white part on top) before giving it to baby. Halved would be best. The bigger ones even cut into 4 pieces.
- Watermelon. Melts in the mouth. Remove the seeds and only give the red parts to baby.
- Pear. Peel it and if it’s too hard, you can bake it in the oven for a while, with cinnamon on top.
- Apple. Peel and cook it in the oven, like the pear, or shred it on a grater (I used to do this in the beginning when Emma was small; the finer side of the grater also turns the apple into applesauce).

- Muskmelon.
- Honeydew melon.
- Carrot. Steam, boil or bake in the oven to make it soft. Don’t offer raw to babies just starting out.
- Cauliflower. Steam, boil or bake in the oven with some seasoning on top.
- Broccoli. Here are 10 basic techniques for cooking broccoli from scratch, explained in-depth. Plus, you’re getting a free cheatsheet with the 3 ingredients that make broccoli taste good.
- Potato. Boil, bake or even steam until very soft.
- Sweet potato. Cook in the same way as a normal potato.
- Pumpkin. Bake in the oven until soft.
- Zucchini. Baked or boiled until it’s soft. Also grated works really well, incorporated in baked batters.
- Beetroot. Steam or boil. Be careful, though, as it contains a high amount of nitrates and it is not ok for baby to have in big quantities or too often. If you offer a varied menu, it shouldn’t be a problem.
- Grape. Cut them in quarters lengthways. Use this if you’re short on time.

- Satsumas or easy peelers. Cut in half for safety.
- Clementines.
- Raisins. If you leave them to hydrate in water for 1 hour or so they should give up their sweetness. They are a choking hazard as per the link I shared above, so pay extra attention. Better incorporate them in baked foods.
- Blueberry. Smash/squish them for safety or cut them in half.
- Blackberry. I would halve these in the beginning, as there are some quite big.
- Cucumber. I would only offer the middle part in the beginning, as it’s softer and easier to manage for babies just starting out.
- Peas. Great for improving that pincer grasp.
- Sweetcorn.
- Baked beans. Great source of iron.
- Plum.
- Kiwi.
- Dried apricots. Great source of iron, like any dried fruit, really. A bit on the sweet side, so be mindful of that.
- Cherries. Cut in half or quarters.
- Sour cherries. Serve the same as cherries.
- Pineapple.
- Orange.
 Cut the pieces in half or more.
Cut the pieces in half or more. - Raspberries.
- Olives. Beware of how salty they are. If left in water, they will lose their saltiness.
- Papaya.
- Dried cranberries. Same as raisins, so better incorporate them in a batter/dough.
- Parsnips. Boil, steam or bake in the oven with some seasoning on top. You can remove the center which is usually harder.
- Butternut squash. Bake or steam.
- Bell pepper. Bake or boil.
- Green beans. Boil or steam.
- Chickpeas. Best boiled or turned into hummus or falafel.
- Onion. Boiled or baked.
- Turnips. Boiled until soft. You can make a veggie broth by boiling most of the hard veggies.
- Cabbage. Boiled or baked.
- Mushrooms. Make a sauce for pasta or bake them in the oven.
- Lentils. Turn them into soup or stews.
- Eggplant. Baked in the oven is your best bet.
- Asparagus. Can be a bit hard, but baby can munch away if properly cooked, like in the oven or steamed.

- Edamame. Never cooked them, but I guess either boiled or steamed.
- Kaki fruit.
- Lychee. Just make sure to peel the outer shell.
- Grapefruit. Cut each slice in three smaller pieces or more, depending on size.
- Pomelo. Cut each slice in multiple pieces.
- Lemon. My youngest loves his lemons cut into wedges and he just sucks at the pulp.
- Figs
- Passion fruit
- Yam. It’s a root vegetable and can be cooked in a similar way to a sweet potato.
- Brussel sprouts. Boiled, steamed or baked with seasoning.
- Nectarine. Go for riper ones and cut into wedges.
- Ugli fruit.
- Plantains. They look like bananas, but you have to cook them. They come from Jamaica, I believe.
Related posts
- 14 smash cake ideas – healthy, no sugar
- Blueberry galette (a recipe great for blw)
- 33 tips to easily end picky eating for good
- 5 alternatives to baby cereal that won’t break the bank + 1 tip
- Why you should not feed your baby smoothies, overnight oats, maple syrup and other foods
- Bread and butter pudding (baby friendly, also great for babies with no teeth)
Meat/poultry/fish
- Salmon.
 I usually bake it in the oven, wrapped loosely in baking paper or foil, for around 20 minutes.
I usually bake it in the oven, wrapped loosely in baking paper or foil, for around 20 minutes. - Cod. Cook the same way as salmon.
- Haddock.
- Mince meat. You can cook some meatballs.
- Steak. Serve in shredded strips, like the chicken.
- Chicken. Serve in shredded strips for babies to suck on and munch away later on.
- Tuna. I am guilty of buying cans of it, but if you can bake it from scratch, that’s even better. Squeeze a bit of lemon to give it some flavour.
- Crab. If your little one is not allergic to seafood, you can give it a go.
- Prawns/shrimp. Great finger food.
- Homemade sausages.
Breads/cereal
- Bread. To prevent it from sticking to the roof of the mouth, toast it. Or make some french toast.
- Rice. Great in rice puddings.
- Porridge
- Porridge fingers
- Millet. Boiled in milk or turned into a pudding (see my recipe here)
- Quinoa.
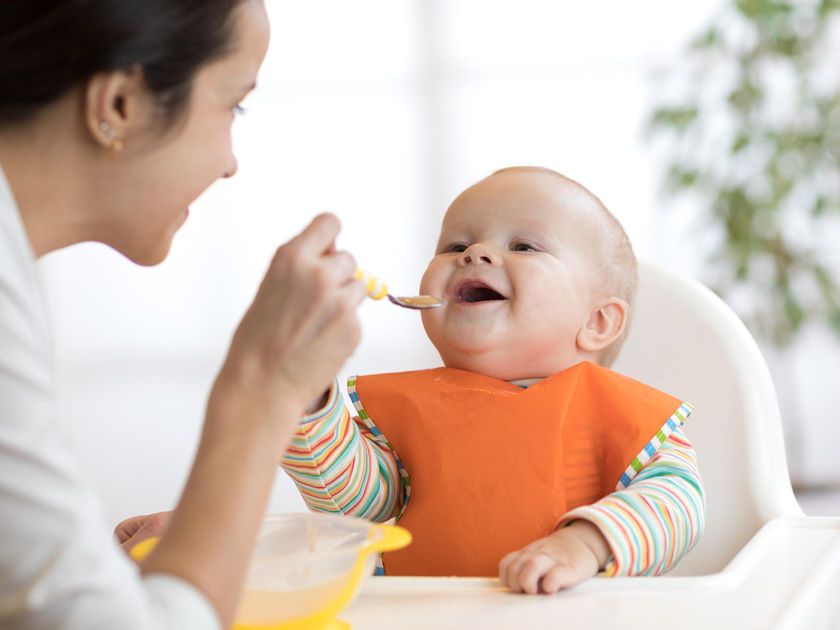 Boiled and eaten as a side or added to porridge, for example.
Boiled and eaten as a side or added to porridge, for example. - Amaranth. Same as quinoa.
- Buckwheat. Same as the above.
- Semolina pudding.
- Spaghetti
- Pasta. Macaroni, penne, fussili or bowtie shapes work well for beginners.
- Noodles
- Homemade pizza
- Polenta
- Cous-cous
- Naan bread
- Pitta bread
- Tortillas
- Rice cakes. Go for the lowest salt option.
- Shreddies. Simple, no flavor, no added salt or sugar, just 100% wholegrain. Serve in milk.
- Focaccia
- Chapatti fingers (an Indian flat bread)
Eggs (in the UK, those that have a lion stamped on the shell are salmonella-free, therefore the yolk can be left runny when cooked – otherwise please cook the yolk completely)
- Boiled eggs
- Poached eggs (only in the UK)
- Fried eggs (just don’t use oil and fry in a non-stick pan)
- Scrambled eggs
- Omlette
- My baked omlette
Dairy
- Yoghurt
- Cheddar cheese.
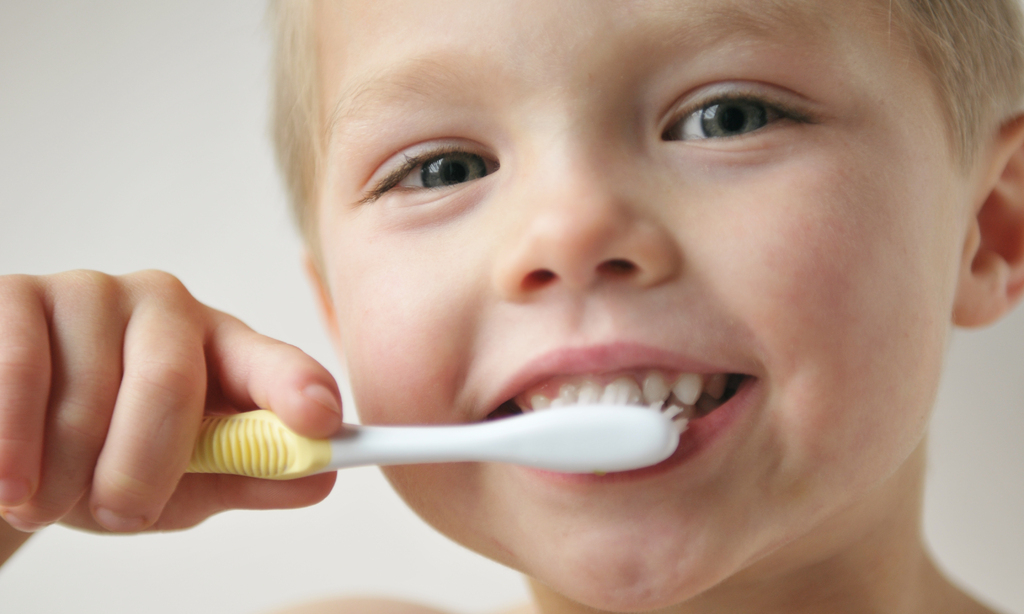 Just watch out for salt and the amount present. Grated is best at the beginning.
Just watch out for salt and the amount present. Grated is best at the beginning. - Mozarella. Choose the lowest salt option.
- Sana. It’s an Eastern European type of dairy, similar to yogurt, but slightly drinkable.
- Kefir. Similar to sana. You can find them in the European section in the supermarket.
- Curd cheese. I have a recipe for it here. It’s a no-salt version of cheese, perfect for babies.
- Cottage cheese. Just make sure the salt levels are okay.
Others
- Tofu. Just watch out for the salt content.
- Homemade muffins (try this carrot muffins recipe)
- Homemade pinwheels
- Homemade banana bread
- Homemade biscuits (easiest recipe: 100 g flour, 100 g butter and 100 g of homemade curd cheese or ricotta cheese; everything mixed and baked in the oven)
- Pancakes
- Waffles. Here’s a basic recipe to follow, which is infinitely customizable. A bit of waffle theory never hurt.

- Fritters. I have a recipe here, very adaptable to what you have in your pantry.
- Homemade nuggets
- Any homemade cake-like consistency, as long as there is no sugar, maple syrup, honey (if baby is under 1 year old), whole nuts, etc.like this baked oatmeal cake.
- Homemade popsicles or anything that’s made out of fruit and yogurt and frozen.
- Peanut butter. It is best to spread it on toast or on slices of banana. Just make sure it’s 100% nuts.
- Almond butter. Same as peanut butter.
- My apple pudding
BONUS:
126. 2 ingredient cookies. The easiest snack ever. Pair it with some dairy and you’re good to go.
127. 3 ingredient pancakes. The fluffiest and easiest pancake recipe out there. Make sure to read my notes on timing and flipping and why those are the key elements for the fluffiness.
128. Spiced biscuits. I think these are great for when little ones are teething.
129. Easy scones. With only 3 ingredients at the base, these are soft and fluffy. Don’t overmix the batter though.
Don’t overmix the batter though.
130. A kid friendly brownie with a secret nutritious ingredient.
You are probably thinking: is there anything she hasn’t mentioned?
In fact, I haven’t mentioned the leafy vegetables, like spinach, lettuce, salad etc because babies might have a hard time tearing them apart so as not to stick to the roof of their mouths.
I also didn’t mention pomegranate, because of its high choking risk.
What comes next?
Knowing what to feed your kids might be a little easier now that you have this list, but actually getting them to eat or at least try any food is another story entirely.
This is why I have put together a 7-part blog series about how to get your little one to eat any food. It is based on more than 3 years of feeding little tummies, observing and taking mental notes about everything I did and everything they did at mealtimes.
I think you’ll find it useful and worth reading. You can save it on Pinterest for later reading or share with someone you know.
You can save it on Pinterest for later reading or share with someone you know.
Thanks!
Ioana x
START READING HERE >>
Categories Baby food, Blog, Featured, The basics Tags baby led weaning, BLW, finger foods, first foods© 2022 WEANINGFUL • Built with GeneratePress
Introducing solid food to a baby: how to teach a baby to chew
It is generally accepted that most babies are ready to be introduced to food in pieces at 6-8 months. In fact, age in the development of chewing skills is not the main thing. The baby should be ready for the introduction of solid foods both physically (to be able to actively work with the tongue and press it correctly against the palate) and psychologically: food interest should “wake up”, the desire to look into the parent’s plate and try what adults eat.
“The appearance of the first chewing movements occurs at 4–5 months, at the same time the gag reflex moves from the middle to the back third of the tongue,” says pediatrician Yulia Rakhimbekova. - And if during this period you do not introduce complementary foods, but continue to stimulate only the sucking reflex, then the chewing reflex that is not supported by practice will begin to fade. A few years ago, the baby, before the appearance of the first milk teeth, received drying, crackers or even a chicken bone from his mother and learned to “chew” with his gums. Today, parents often introduce complementary foods after 6 months and later, when 2-4 front teeth have already appeared in the mouth. But these teeth are used for biting, it is impossible to chew them, and - what is important! - they prevent the baby from chewing with their gums. This is how the moment is lost. Further, normally at the age of 7-12 months, the child continues to strengthen the skills of biting and chewing, developing lateral movements of the tongue and the ability to move food to the teeth with the tongue. He is already able to eat cereals, chopped fruits and vegetables. Of course, everything is individual.
- And if during this period you do not introduce complementary foods, but continue to stimulate only the sucking reflex, then the chewing reflex that is not supported by practice will begin to fade. A few years ago, the baby, before the appearance of the first milk teeth, received drying, crackers or even a chicken bone from his mother and learned to “chew” with his gums. Today, parents often introduce complementary foods after 6 months and later, when 2-4 front teeth have already appeared in the mouth. But these teeth are used for biting, it is impossible to chew them, and - what is important! - they prevent the baby from chewing with their gums. This is how the moment is lost. Further, normally at the age of 7-12 months, the child continues to strengthen the skills of biting and chewing, developing lateral movements of the tongue and the ability to move food to the teeth with the tongue. He is already able to eat cereals, chopped fruits and vegetables. Of course, everything is individual. Full-term or premature, healthy or with health problems, have teeth or have not yet appeared - one way or another, by the year the baby should produce high-quality chewing movements with the jaws. But this will only happen if the parents gradually taught him this. It does not happen that a child is fed only with breast milk, but at the age of one he sat down at the table, took a spoon and began to eat busily from the common table.
Full-term or premature, healthy or with health problems, have teeth or have not yet appeared - one way or another, by the year the baby should produce high-quality chewing movements with the jaws. But this will only happen if the parents gradually taught him this. It does not happen that a child is fed only with breast milk, but at the age of one he sat down at the table, took a spoon and began to eat busily from the common table.
If the baby is over two years old, and he is accustomed to pureed food, chews reluctantly or does not know how to chew at all, please be patient: to catch up you will need time - from a month to six months.
Why you need to learn to chew before the age of
The ability to chew solid food is absolutely necessary for a child:
-
for strong teeth
The inability and unwillingness of the baby to chew solid pieces of food leads to a violation of the formation of bite, and subsequently - the oval of the face. Milk teeth are not sufficiently stressed and may fall out prematurely.
The use of products mainly in a puree-like state negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: it provokes the appearance of allergies, intestinal disorders, bloating, and constipation. Since the food that you just need to swallow does not mix well with saliva, the baby's digestive enzymes are poorly produced. The gastrointestinal tract becomes "lazy", receiving only tender food, which is no longer for the child's age. As a result, problems grow like a snowball: underdevelopment of the enzyme apparatus, excess weight, increased sensitivity of the intestine.
“The inability to chew is not the direct cause of speech delay or lack thereof,” says speech therapist Tamara Novikova. “At the same time, this is an indicator of negative changes in articulatory tone. It is likely that the child will be uncomfortable, uncomfortable pronouncing some sounds, because this also requires efforts.
“Until the age of 1.5, we ate only pureed food, as we choked on pieces. It didn’t bother me at all: 15 seconds in a blender - and you’re done. To be honest, it was even more convenient for me, because it was faster and easier to feed. Only now he refuses to eat meat ”- a similar story can be found on any parent forum. Many mothers feel sorry for their babies (and themselves) by giving them pureed food. But the age of 1–2 years is quite dangerous in terms of manipulating a child with parental opinion. Make every effort to ensure that the little one cannot blackmail you with his unwillingness to chew and swallow hard pieces, because in the future this can turn into much more problems.
Food "pieces" should appear in the children's diet no later than the first tooth erupts. The ability to chew well is the key to healthy teeth and clear articulation. Why does a baby refuse to chew? Why is this happening?
Too early or abrupt change in food consistency
Do not immediately switch from homogeneous puree to food in pieces: at first the baby may simply not understand that it is also edible, and the absence of "normal", from his point of view, food will make him nervous. The logical result of this is streams of tears and a tightly compressed mouth. Do not worry! Each baby has its own pace of development and maturation of body systems. If you have introduced solid foods according to all the rules, and the baby stubbornly refuses “solid” foods, consult a specialist (pediatrician, gastroenterologist, neurologist).
The logical result of this is streams of tears and a tightly compressed mouth. Do not worry! Each baby has its own pace of development and maturation of body systems. If you have introduced solid foods according to all the rules, and the baby stubbornly refuses “solid” foods, consult a specialist (pediatrician, gastroenterologist, neurologist).
Disorders of articulatory tone
“The conditions in which a woman today carries and gives birth to a child are far from ideal,” explains speech therapist Tamara Novikova. - A large percentage of expectant mothers work to the last, exposing themselves to stress and hypoxia, drive a car, do not always give up bad habits - all this indirectly affects the development of dysarthria (impaired tone of the muscles of the speech apparatus) in the child in the future, because a weakened fetus is already forming in utero . What do we get next? A tongue that cannot turn food over in the mouth, poor functioning of the muscles that close, raise and lower the jaw, and an unwillingness to chew. Parents who give up breastfeeding too early also do a disservice to the baby. To get milk from the mother's breast, the baby needs to work hard - work his muscles. With a regular bottle, articulatory tone is much more difficult to develop. Nevertheless, all these difficulties can be overcome.
Parents who give up breastfeeding too early also do a disservice to the baby. To get milk from the mother's breast, the baby needs to work hard - work his muscles. With a regular bottle, articulatory tone is much more difficult to develop. Nevertheless, all these difficulties can be overcome.
Physiological problems
The baby may refuse to chew even if it is difficult for him to swallow. Trying to cope with solid food can cause him to cough and even vomit. Swallowing disorders may be associated with malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract or other diseases: for example, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, stomatitis, inflammation of the oral cavity and larynx. “Possible problems that can interfere with high-quality chewing will definitely show up during the child’s medical examination,” pediatrician Yulia Rakhimbekova reassures. - Do not neglect the dispensary appointments of doctors. Up to a year, a child should visit the dentist twice, 4 times - at the neurologist, 3 times - at the surgeon. If necessary (for example, there is a suspicion of a short frenulum of the tongue), the baby can be referred for a consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
If necessary (for example, there is a suspicion of a short frenulum of the tongue), the baby can be referred for a consultation with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
How to introduce solid food to your baby
There is no special technique for teaching chewing, because everything should go on as usual. However, with the help of our tips, you will help your baby master this skill faster.
- Photo
- Getty Images/Foodcollection
-
Organize a space. Think in advance where the baby will feel most comfortable: in a high chair or on your lap.
-
Pick a moment. It is important that the child is not too hungry - otherwise he will be nervous, and your efforts will go down the drain, but at the same time he wants to eat.
-
Prepare cutlery.
 Use a light plastic spoon with a rounded handle for feeding - then the baby can use it independently.
Use a light plastic spoon with a rounded handle for feeding - then the baby can use it independently. -
Consider your diet. “Usually we advise mothers to offer their babies pieces of an apple or soft biscuits that they will bite into and thus learn to chew. An inquisitive kid will definitely agree to taste a new product, and at the same time understand why he needs his teeth, and practice chewing movements, says Yulia Rakhimbekova. “Any dish that you think is appropriate at the moment will do, considering whether it’s part of dinner, a snack between meals, or a dessert after a hearty meal.” When buying a jar of puree, be guided by the markings on the label: among the jars recommended for the age of 8-10 months, you will definitely find those that say "pieces that teach you to chew."
-
Take your time. Start small meals. If the baby refuses a new complementary food, do not insist. Make the consistency of the offered dishes thicker over time - thanks to this, the need to work with the jaws, lips, and tongue develops.
 If the dish is too thick, add some water or milk.
If the dish is too thick, add some water or milk. -
Use his curiosity. At 4-7 months, your baby will be persistently procrastinating in his mouth and trying to chew whatever you give him. Your job is to make sure it's safe. The main thing is to avoid sudden transitions in the diet: you should not give hard carrots if before that the baby ate only ground cereals and mashed potatoes.
-
Do not distract. Let the baby focus on the process of eating, then the actions of the hands, tongue and lips will be coordinated as much as possible.
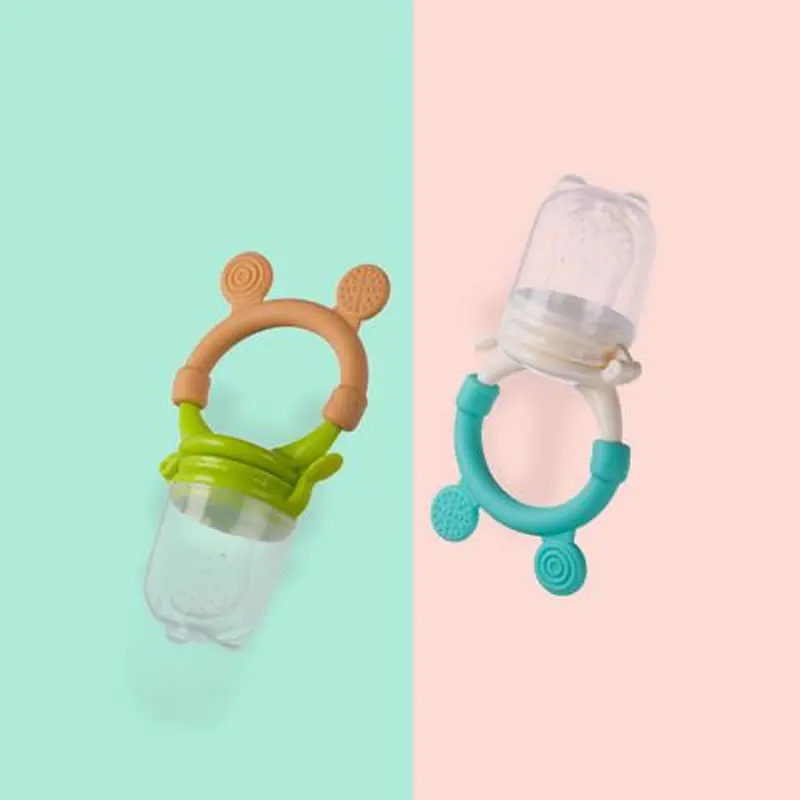
Mom's helper: nibbler
Nibbler is a device reminiscent of the methods of our grandmothers, when some product (an apple or a lump of sugar) was wrapped in gauze and a child without danger to life could procrastinate it in his mouth for a long time. Nibbler promotes the taste of the product, activates salivation and trains chewing movements. The main thing is to monitor the integrity of the mesh and rinse it thoroughly after use.
How to overcome dislike for solid food
- Photo
- Getty Images/Tetra images RF
“If parents delay the transition of the child to solid food, as a rule, problems begin,” says Yulia Rakhimbekova. - Even a two-year-old baby's eating behavior is already formed, it becomes very difficult to teach him to chew and just make him take something unusual in his mouth. The main advice in this case is not to rush, not to pressure and in no case starve (they say, nothing, get hungry - eat). The transition from pureed food to "pieces" should be gradual. Involve the child in cooking, chop the product together, first in a blender, using a meat grinder or grater, a little later with a fork. Remember that children are very fond of imitating, so be sure to practice “joint dining”, where you will chew food together with great pleasure.
What else can help you teach your little one to chew merrily and with appetite:
-
Arrange “rainbows” on a plate, fold “houses”, “draw” animals from slices of boiled carrots, beans, broccoli and cauliflower, fresh cucumbers and tomatoes. If at first the baby does not chew very well, just feed him with the usual pureed food. Try to cut into pieces first of all the foods that he likes the most.
Add small-small pieces of soft fruits (eg pears), boiled vegetables, berries (raspberries) to cereals and purees. Gradually increase the size and number of pieces in the dish.
-
Play. Take, for example, a piece of boiled carrot and depict a bunny: “How does a hare eat a carrot? Like this! Can you do that?"
-
Invite guests and also eat out - practice situations where the ability to grind food simply will not be.
-
Contact a speech therapist: he will show you how to properly conduct speech exercises and speech therapy massage.
 Such a massage (5–7 minutes of exercise per day 3–4 times a week) will correct changes in tone and help in training the muscles of the articulatory apparatus.
Such a massage (5–7 minutes of exercise per day 3–4 times a week) will correct changes in tone and help in training the muscles of the articulatory apparatus.
More useful and interesting materials about child development are in our channel on Yandex.Zen.
Evgenia Karpovskaya
How to switch a child to solid food - what is BLW
The BLW theory was introduced in 2010 in the book Baby-Led Weaning by Jill Rupley and Tracey Marquette. This approach to first foods is popular in the US, while there is not much information about it on the Russian-language Internet. In this article, we will talk about what are the features of BLW, what foods can be given to a child and what should not be, what precautions should be taken into account.
Baby-Led Weaning can be translated as “baby food of choice”. You can apply this method no earlier than six months of age, it is better - from eight months. According to BLW, from this age, the child can be given regular food (which one - we will discuss below), while continuing to breastfeed or feed formula milk.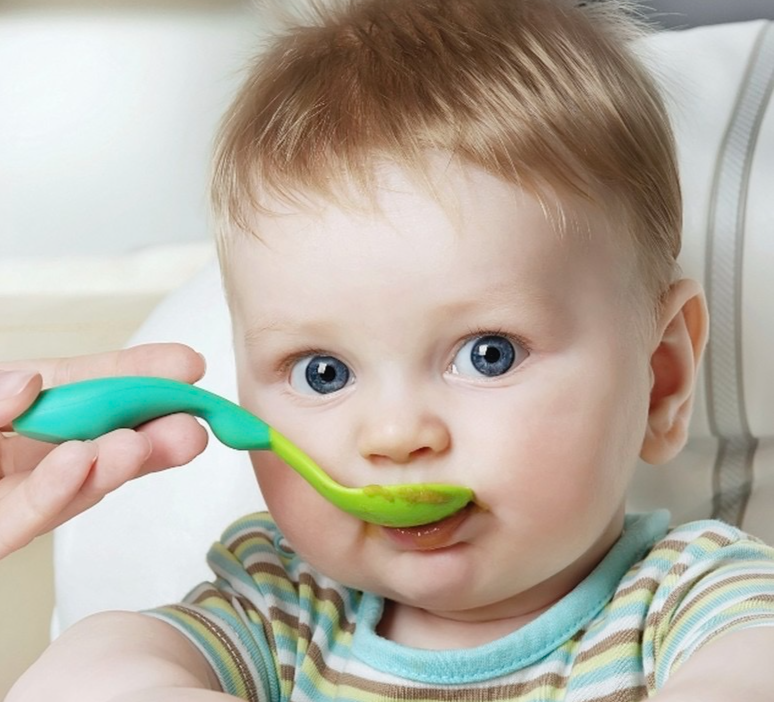
Benefits of BLW
Compared to baby purees, BLW has a number of advantages, in particular:
- You don't have to spend time preparing baby purees.
- The child can be at the family table from the very beginning and eat the same food as the parents.
- This feeding method promotes the development of visual and fine motor skills.
- A child learns to chew, swallow and decides for himself what and how much to eat - this is how the foundations of healthy eating behavior are laid.
Also read: From 1 year and older - what and how to feed a small child
How to understand that a child can be given solid food
- There are several signs - how to understand that a child can already be given regular food:
- The child can sit up alone with little or no support.
- The child wants to chew something, even if he does not yet have teeth.
- He takes food with his thumb and forefinger instead of his palm.
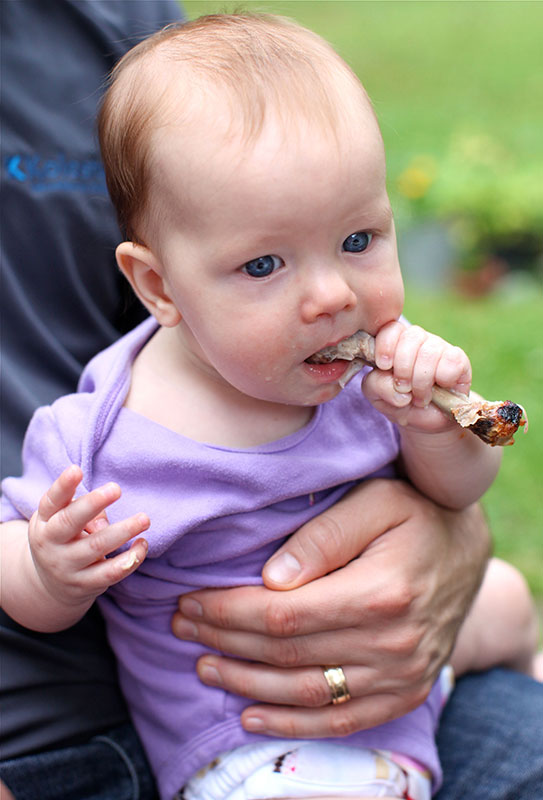

- The child shows interest in food, grabs food from the table.
- It is advisable to consult a pediatrician before giving a normal meal to a child.
What foods can be given as first complementary foods
Of course, not all foods can be given as first complementary foods. Foods that are suitable for first foods according to BLW are:
- Steamed or baked vegetables (broccoli, carrots, pumpkin pulp, zucchini).
- Ripe fruits (apple, banana, avocado, mango, watermelon, peach, pear, plum).
- Protein food (natural cheese, egg yolk, meat, liver).
- Carbohydrates (gluten-free pasta, brown rice, millet, buckwheat, gluten-free bread).
Also read: 6 Months and Older - Which Dairy Products to Give to Young Babies
BLW First Feeding Rules - Do's and Don'ts
- Make sure your child is ready for regular meals.
- Continue breastfeeding or bottle feeding until at least 10–12 months of age.

- Sit the child in a comfortable position - he should sit upright without leaning back.
- Cut food into large pieces so that it is easy for the child to take them.
- Start with soft foods: ripe fruits, steamed vegetables.
- Take your child to the family table.
- Get ready for a mess.
- Take your time and don't rush your baby - eating will take at least 10-15 minutes.
- Pay attention to signals - for example, if a child scatters food, he may have already eaten.
- Do not offer complementary foods if the child is tired or in a bad mood.
- Do not coax your child to eat another bite and do not offer too much food at a time.
- If your child doesn't want to eat regular food and likes baby purees more, don't be upset. Fortunately, there are many foods available for children today that can be spoon-fed, such as baby yogurt, cottage cheese spreads, and others.
See also: Baby food - 7 dairy products for young children
Precautions - things to consider
- Avoid foods that a child can choke on, such as nuts, grapes, cherries, grape tomatoes.
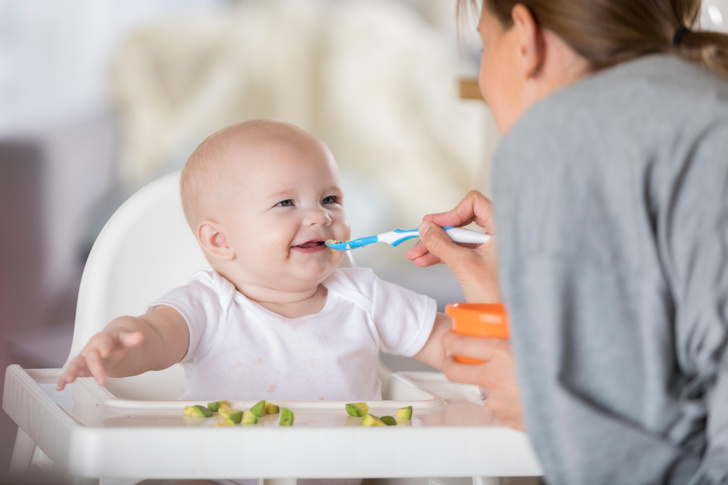

- If you want to give your child foods such as cherries and grapes, cut them in half and remove the pits.
- Hard foods that a child cannot chew should be boiled (eg carrots).
- Find out in advance how to give first aid if a child chokes.
- Be careful with foods that can cause allergies: foods containing gluten, peanuts and other nuts, egg whites, seafood and some types of fish, citrus fruits.
- Do not give your baby unhealthy food and fast food: chips, popcorn, foods containing sugar, sweets.
- Banned honey, sugar and chocolate. Salt - in very small quantities with the permission of a doctor.
- Never leave a child with food unattended.
Based on materials from parents.com, mamanatural.com, malyshi.livejournal.com
The information and recipes contained in this Blog may not meet the user's expectations, are presented for use without regard to the individual characteristics of the user's health and are used by the user at their own discretion and under personal responsibility.