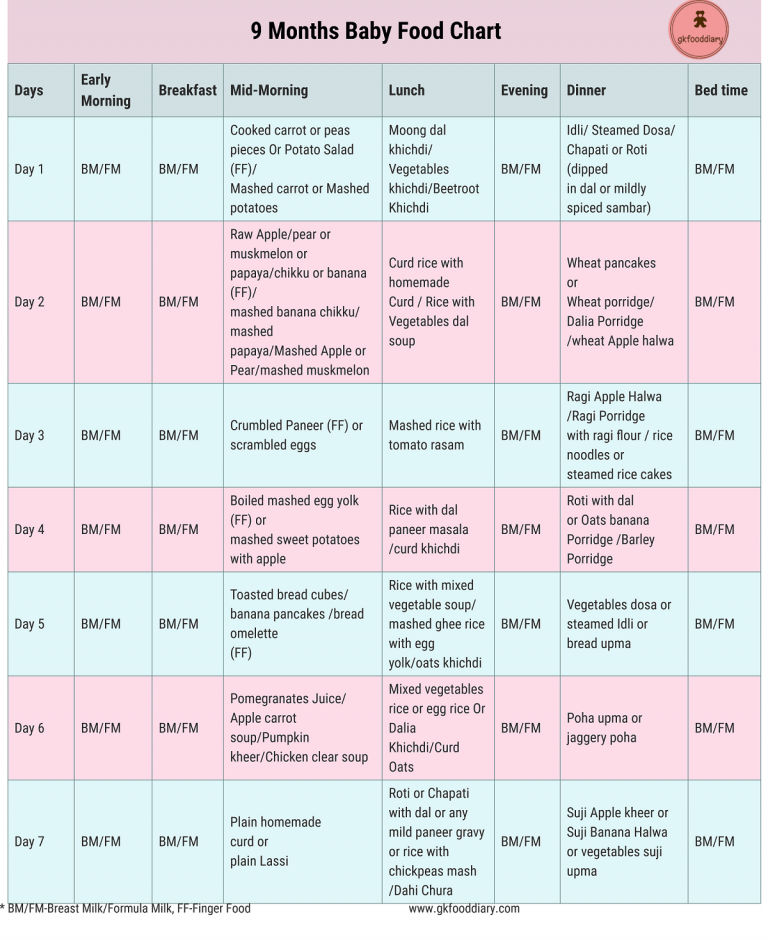
Feeding guidelines for 9 month old baby
What and When Can Babies Eat at 9 Months?
What food is healthy for a nine-month-old?
A nine-month-old baby is growing rapidly, and complex brain development is taking place. A well-balanced, nutritional diet that fills their belly is critical at this time. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, a nine-month-old should be eating a wide variety of foods. If babies are eating cereal, it should be fortified. This will provide the nutrients that they need.
It’s great to include a rainbow of foods in a nine-month-old’s diet. Their food should be colorful, fresh, and tantalizing. Encourage them to try fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and meats. Wait until they have turned one year old before introducing honey, as it may contain the bacteria that can cause botulism. Along the same lines, unpasteurized drinks or foods can contain E. coli and cause severe intestinal problems.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
What solid foods can a baby eat?
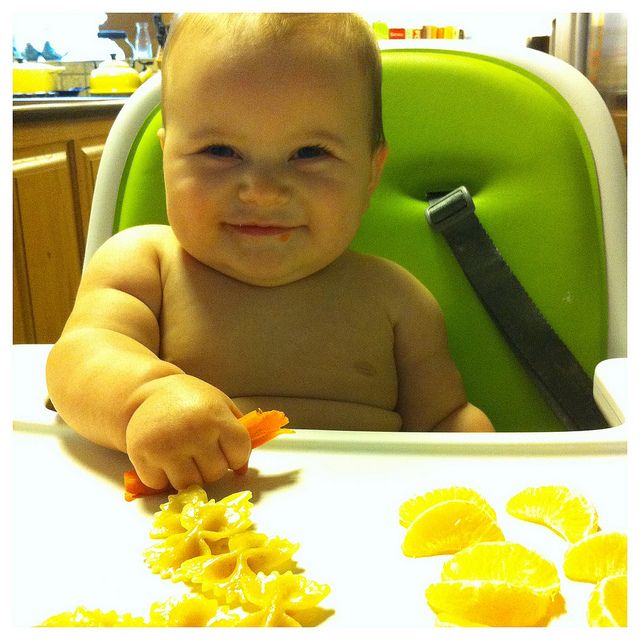
Food for 9-month-olds can be tricky. Many babies at this age are ready to try eating food with their hands. Finger food should be small and soft enough to pick up easily and chew without risk of choking.
At this age, babies’ chewing abilities haven’t yet fully matured. They may not use their teeth yet, instead using their tongue to mash up their food. Some safe options for nine-month-old babies include:
- Soft fruits (e.g., bananas and peaches)
- Bread (without the crust)
- Dry cereal
- Avocado
- Peas
- Green beans and cooked beans
- Tofu
- Meat and fish
- Sweet potato
- Pasta
When offering nine-month-old babies food (especially finger food), size is important. Pieces should be large enough to pick up but small enough that the baby won’t choke. Try to aim for cubes about a third of an inch in size. This is just a little bit bigger than a standard pea.
How much should a 9-month-old eat?
A nine-month-old feeding schedule is not much different than when they were first born. They are still on an on-demand schedule. This basically means that parents should look for signs indicating when the baby is hungry and when they’re full. They might eat a different combination of solid foods, breast milk, and formula every day, depending on their mood.
They are still on an on-demand schedule. This basically means that parents should look for signs indicating when the baby is hungry and when they’re full. They might eat a different combination of solid foods, breast milk, and formula every day, depending on their mood.
How much formula is good for a nine-month-old?
Babies at nine months old still require breast milk and/or formula every day as part of their regular diet. Breast milk and formula contain high levels of nutrients that are necessary for proper growth. Cow milk can be introduced when babies get a bit older.
Babies should eat at least five to six times per day to meet their nutritional requirements. As they begin to eat more solid foods, the amount of formula or breast milk needed will likely decrease in frequency and amount.
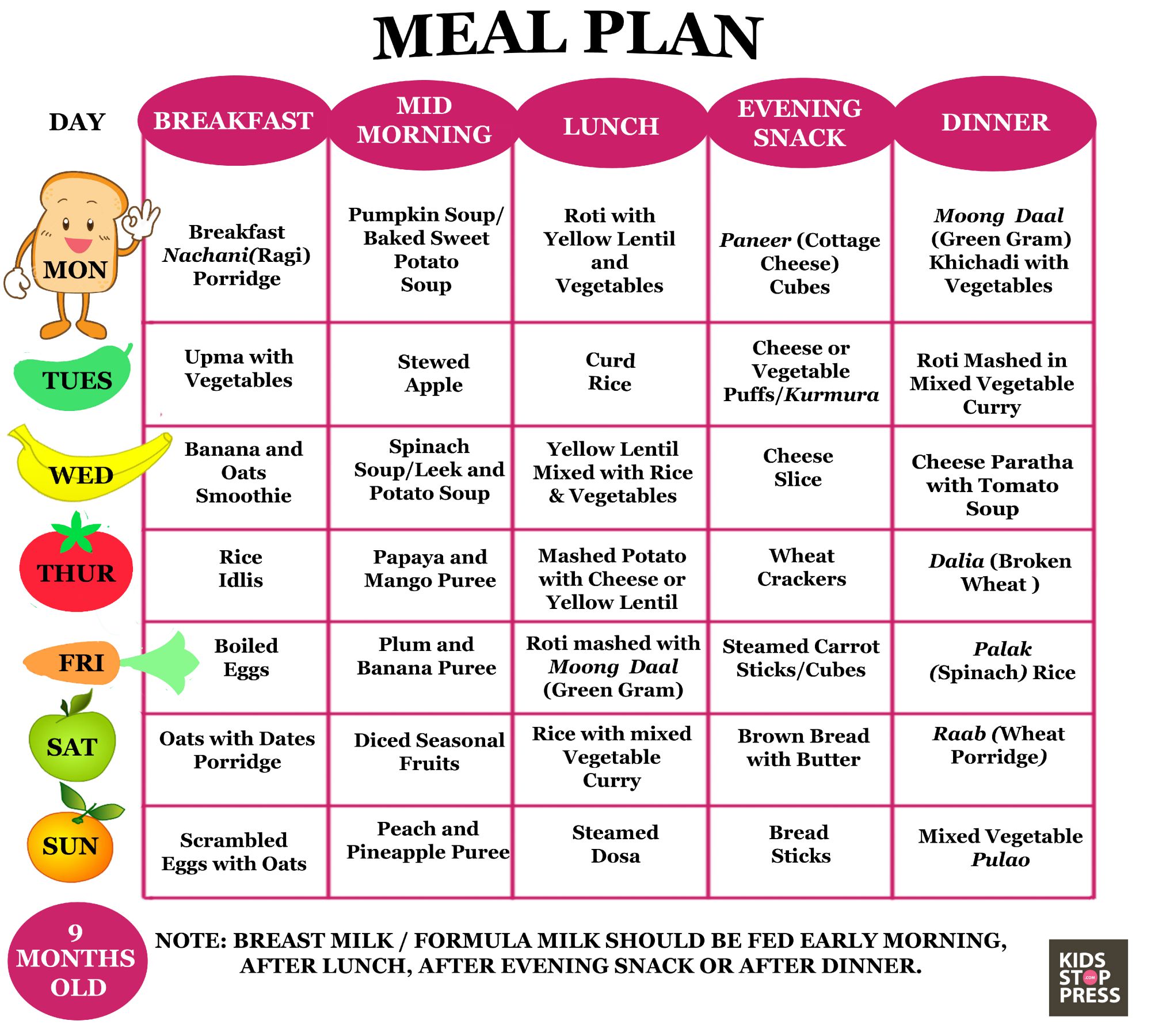
Sample menu for a nine-month-old baby
The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests the following menu and feeding schedule for 9-month-old babies.
Breakfast
¼–½ cup cereal or mashed egg
¼–½ cup fruit, diced (if the child is self-feeding)
4–6 ounces formula or breast milk
Snack
4–6 ounces breast milk, formula, or water
¼ cup diced cheese or cooked vegetables
Lunch
¼–½ cup yogurt, cottage cheese, or meat
¼–½ cup yellow or orange vegetables
4–6 ounces formula or breast milk
Snack
One teething biscuit or cracker
¼ cup yogurt or diced fruit
Water
Dinner
¼ cup diced poultry, meat, or tofu
¼–½ cup green vegetables
¼ cup noodles, pasta, rice, or potatoes
¼ cup fruit
4–6 ounces formula or breast milk
Before bedtime
6–8 ounces formula, breast milk, or water
A nine-month-old baby’s nutritional needs aren’t much different from the nutrients that adults need too.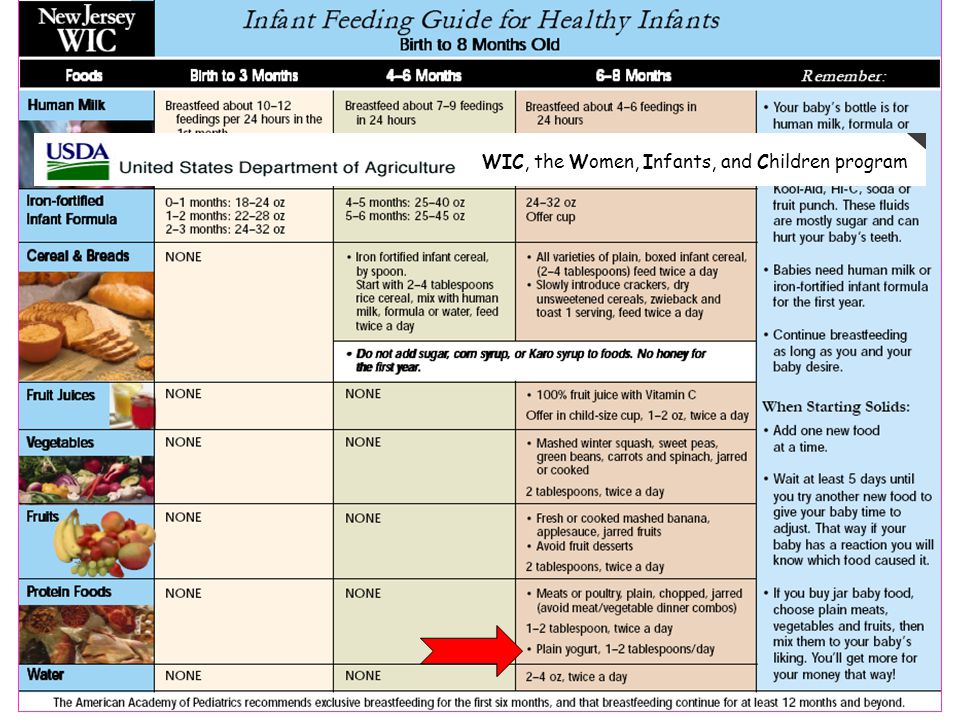 Over the course of a day, offer a 9-month-old foods of different colors. Here are some colorful examples:
Over the course of a day, offer a 9-month-old foods of different colors. Here are some colorful examples:
- Green — green beans, peas, spinach, zucchini, and asparagus
- Orange — cantaloupe and sweet potatoes
- Yellow — peppers, squash, and bananas
- Red, blue, and purple — beans, cooked tomatoes, red peppers, and smashed berries
These different foods can also be a great diet for new parents to follow when breastfeeding and trying to get back in shape after delivery. This is an exciting time for parents and babies. It’s fun to watch babies explore new things, including textures and tastes.
Foods, Tips, and Meal Plan for Feeding Your 9-Month-Old
By the time your baby is 9 months old, they have likely been eating solid foods in addition to either breast milk or formula for a few months.
It can be overwhelming deciding what foods to feed your little one, especially when you’re most likely already busy babyproofing and soaking up all the new and exciting milestones.
This article provides an overview of some of the best foods for your 9-month-old, as well as which foods are best avoided so that you can help your baby get all the nutrients they need.
Even though your 9-month-old is eating food, their main source of nutrition should continue to come from either breast milk or formula. Any additional foods can be considered complementary until your baby turns 1 (1, 2).
Some parents choose to begin with puréed foods when first starting solids, while others may opt for a baby-led weaning approach, which involves offering foods in their solid form with an emphasis on allowing babies to feed themselves (3).
If your baby eats purées, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends beginning to offer foods with varying textures and some more solid foods that help a baby learn how to chew around 8 months of age (2).
Some great foods to offer your 9-month-old baby include:
- Fruits: bananas, soft pears, peaches, watermelon, cantaloupe, strawberries
- Vegetables: soft-cooked broccoli, carrots, green beans, sweet potatoes
- Protein: eggs, soft-cooked or ground meat, tofu, smashed beans, low mercury fish
- Healthy fats: avocado, fish, olive oil, nut butters
- Iron-containing foods: eggs, meats, fish, iron-fortified cereals, whole grain bread or pasta
Key nutrients for baby
Offering a variety of foods will provide your baby with a variety of important nutrients, some of which are especially important for healthy growth and development.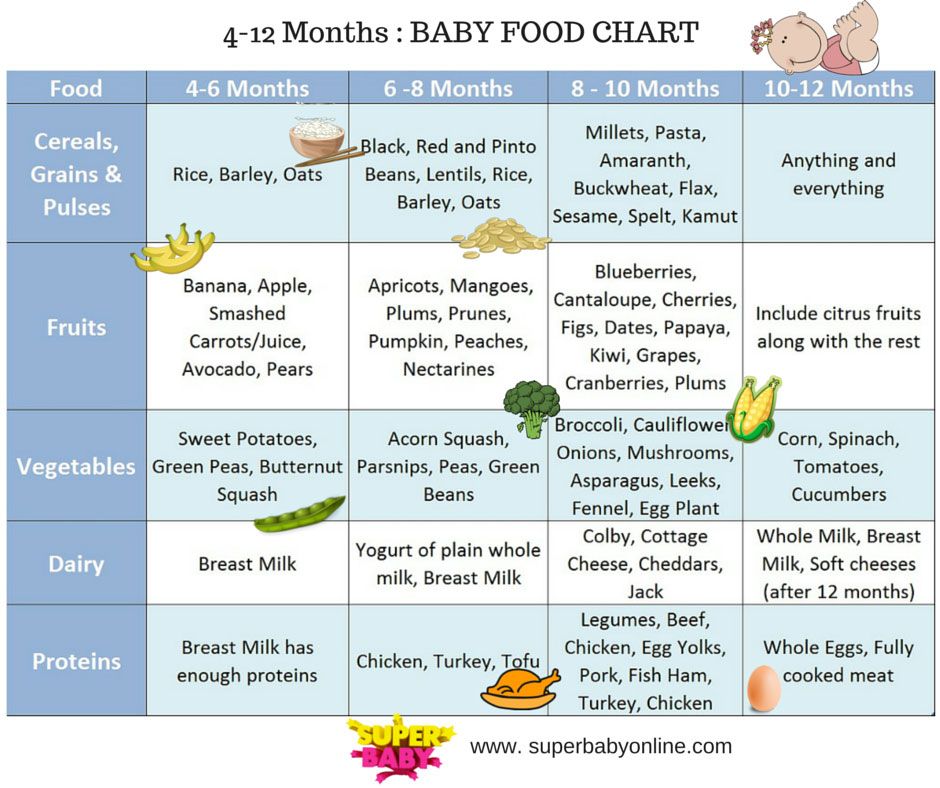
Vitamin D plays an important role in bone health and may help build strong immune systems in babies, though more research is needed on the latter.
Infant formulas are typically fortified with vitamin D, but it’s often recommended that breastfed babies take a supplement of 400 IU of vitamin D per day for their first year of life (4, 5).
Because babies experience such rapid growth in the first year, they’re at a high risk of an iron deficiency, which can lead to serious health outcomes.
Iron supplementation may be needed after the first 6 months, but it may not be necessary if your baby is getting enough iron-rich food sources regularly or drinking formula, which is typically fortified with iron (5, 6).
Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, are also important for babies and young children. They help promote the development and function of brain, eye, and immune health (7, 8, 9).
SummaryOffering your baby a variety of foods will provide them with a variety of important nutrients, but keep in mind, their main source of nutrition should still be breast milk or formula at this age.
While most foods are OK for babies as long as they are prepared and cut appropriately, some foods should be avoided in the first year. Some foods may cause food poisoning in little ones, and others are considered choking hazards.
Here are some important foods to avoid feeding your 9-month-old (10):
- honey
- raw or undercooked meat, fish, or eggs
- fish containing high amounts of mercury, such as shark, swordfish, and marlin
- added sugars
- salt and high sodium foods
- unpasteurized foods
- potential choking hazards like whole grapes, whole nuts, raw fruits and veggies
You may have heard that babies under 1 year shouldn’t drink cow’s milk. That’s because they should still be drinking formula or breast milk to meet their nutritional needs.
They can have milk mixed into foods, such as oatmeal or smoothies, but you could also use breastmilk or formula.
Babies shouldn’t get added sugar, which can replace more nutritious options. Also, too much sodium may be harmful to their developing kidneys, so it’s best to limit their salt intake (10).
Also, too much sodium may be harmful to their developing kidneys, so it’s best to limit their salt intake (10).
SummaryIt’s important to stay away from certain foods in the first year of life because they can cause food poisoning or choking or may not be the best choices for their developing bodies.
A 9-month-old needs 750–900 calories per day and about 400–500 should continue to come from breast milk or formula (2).
You don’t need to track your baby’s calorie intake, but you may wonder how much to offer at each meal and snack.
Babies will eat when they’re hungry and stop when they are full, so you can let them decide how much they would like to eat.
Your baby will likely show cues of feeling full, such as turning his or her head away from you or pushing food away, and also show signs that they’re hungry, such as opening their mouth for food or getting excited (11).
SummaryA 9-month-old baby needs about 750–900 calories per day.
Be sure to keep up with regular formula or breast milk feedings to help them meet their needs, and let your baby decide when they’re full at meals.
It’s normal for your little one’s appetite to vary day to day. Remember, breast milk or formula should continue to be the main source of nutrition for the first year of life, and babies should be getting about 24 ounces (720 mL) of either daily (2, 12).
You can and should also offer water with meals at this age to encourage proper hydration and help wash down solid foods. At this age, it’s recommended babies get about 4–8 ounces (0.5–1 cup) of water per day (13).
As for other beverages, the AAP recommends sticking to just water and breast milk or formula at this age and avoiding sugar-sweetened beverages and other drinks until 2 years of age. Cow’s milk or soy milk can be introduced after 12 months (13).
Here’s a sample menu for a 9-month-old, including 3 meals, snacks, and breast milk or formula:
Breast milk or formula
6 ounces (177. 4 mL)
4 mL)
Breakfast
- 2–4 ounces (59.1–118.3 mL) of prepared iron-fortified cereal
- a banana or other fruit (you can try cutting it up or mashing and mixing it into the cereal, too)
- about 1 teaspoon of nut butter stirred into the cereal
Snack (optional)
One of the following options:
- soft (or cooked) fruit
- plain, whole milk yogurt
- teething biscuits
Breast milk or formula
6 ounces (177.4 mL)
Lunch
- scrambled egg
- soft-cooked broccoli
- whole wheat toast with mashed avocado (try cutting it into strips for easy self-feeding)
Snack (optional)
One of the following options:
- cubed cheese
- whole milk cottage cheese
- soft (or cooked) fruit
Breast milk or formula
6 ounces (177.4 mL)
Dinner
- soft-cooked shredded chicken (the slow cooker is great for this)
- smashed peas
- roasted sweet potato wedges
- soft (or cooked) fruit
Breast milk or formula
6 ounces (177.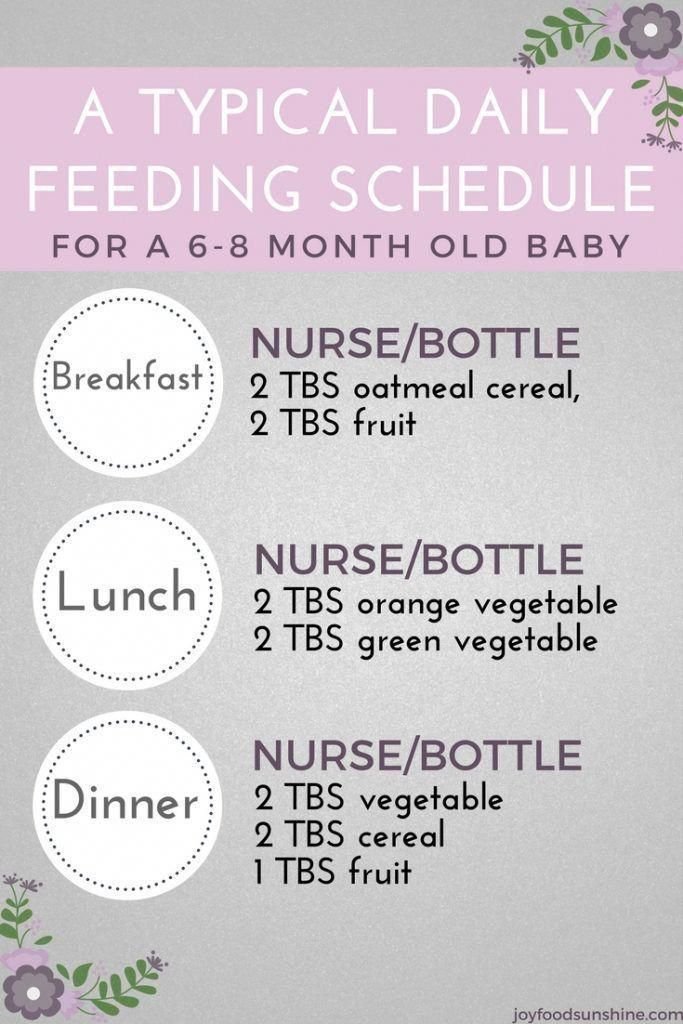 4 mL)
4 mL)
SummaryAbove is a sample menu for a 9-month-old baby. Remember, babies will let you know when they are full, and they may not eat everything offered. It’s important to continue to offer at least 24 ounces (720 mL) of breast milk or formula daily.
Feeding your little one can feel daunting, but there are ways to keep it simple so you don’t have to spend too much time cooking and prepping.
Here are some quick meal and snack ideas for your 9-month-old:
Quick and easy breakfast ideas
- scrambled eggs, or a veggie omelet with soft fruit, and whole wheat toast topped with smashed avocado
- French toast made with 1 egg and a sprinkle of cinnamon, topped with plain whole milk yogurt and no-sugar-added applesauce
- plain, whole milk yogurt or whole milk cottage cheese mixed with soft fruit and Cheerios
- iron-fortified cereals mixed with nut butter and smashed fruit
Quick and easy lunch or dinner ideas
- baby meatballs with mashed potatoes and soft-cooked green beans
- Combine 1 pound (0.
 45 kg) of ground meat with 1 egg and 1/2 cup oat flour (plus any seasoning you’d like, other than salt).
45 kg) of ground meat with 1 egg and 1/2 cup oat flour (plus any seasoning you’d like, other than salt). - Roll the mixture into meatballs and bake or cook them with a little chicken broth in an instant pot or slow cooker.
- Combine 1 pound (0.
- shredded chicken with smashed peas and corn
- whole wheat penne pasta with low sodium marinara sauce
- poached fish with sweet potato wedges and soft-cooked broccoli and carrots
- diced tofu with soft-cooked green beans and smashed chickpeas
Quick and easy snack ideas
- soft-cooked vegetable finger food, such as asparagus, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots, or potatoes
- toast or crackers with smashed avocado
- soft or cooked fruits like banana, ripe peaches, strawberries, or cooked pears
- cubed cheese
- plain whole milk yogurt
- whole milk cottage cheese
- hard-boiled eggs
SummaryFeeding your 9-month-old can be overwhelming and time-consuming.
It’s a good idea to have some go-to ideas in your back pocket for quick and easy meals.
Meal prep
Meal prepping is a great way to save time and set yourself up for an easier week. If you can, try planning some meals ahead of time and doing some cooking in advance so that you can reheat things during the week rather than cooking daily.
By the time your little one is 9 months old, they can eat a lot of what you’re eating. When you prepare a meal for yourself or the rest of the family, see what you can do to make it baby-friendly. Here are some tips:
- Leave the salt out until you portion out your little one’s helping first.
- Cut foods into safe sizes for your baby to consume.
- If you’re using a spicy or high sodium condiment, set aside some food for your baby before adding it in.
- Check the texture of the meal yourself to make sure it’s soft enough for your baby. Pinching a food between your fingers is a great way to see whether they can squish it with their gums.

To reduce their choking risk, cut food small enough for them to grab and bite, but not so small that they can swallow it whole. Some raw fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, are also choking hazards because they’re too hard to bite into.
Food safety
It’s important to prepare your little one’s food using safe cooking practices to reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
Wash your hands and switch cutting boards when handling raw meat to avoid cross contamination. Cook meats, fish, and eggs to safe temperatures — 145–165°F (62.8–73.9°C) — depending on the food (14).
Be sure to refrigerate food soon after finishing it to preserve it. It’s also a good practice to date leftovers so you know when to throw them away. Most food lasts a few days in the refrigerator or 1–2 months in the freezer (15).
Allergens
By the time your child reaches this age, you may have already begun to introduce some common allergens, such as peanut butter, eggs, and fish. If you haven’t yet, now is a great time, as introducing them earlier on may help prevent an allergy (16, 17, 18).
If you haven’t yet, now is a great time, as introducing them earlier on may help prevent an allergy (16, 17, 18).
It’s a good idea to introduce allergens one at a time and wait a few days in between so that you can monitor your baby for any possible reaction (19).
Signs of an allergic reaction include (20):
- wheezing or coughing
- swelling in the lips or throat
- a runny nose
- itchy skin or a rash
- diarrhea, vomiting, or other signs of stomach upset
If you notice any signs of a mild allergic reaction, such as a rash or upset stomach, call your pediatrician. Call 911 if the symptoms are more severe, such as if you suspect anaphylaxis, which usually involves wheezing, hives, drooling, and drowsiness (21).
Packaged foods
Offering packed foods to your baby can be a convenient way to feed them when you’re short on time. We recommend offering a variety of whole foods whenever possible, but having some packaged items in the pantry can come in handy.
When shopping for packaged baby-friendly foods, look for foods that are low in sodium, added sugars, additives, and preservatives. Additionally, be sure they don’t contain any of the foods that should be avoided in the first year, such as honey.
Lastly, remember that mealtimes should be a fun, low pressure experience. Try not to force your baby to eat more if they are showing signs of feeling full. If they refuse a food, you can try offering it again another time.
Repeated exposure to new foods and maintaining a low stress environment has been shown to promote food acceptance among little ones (22).
SummaryProperly handling, preparing, and storing foods for your baby will help prevent choking and possible foodborne illnesses. Do your best to keep mealtimes fun and relaxed, and let your baby take the lead on how much to eat.
With so many exciting changes and challenges that come with parenting, thinking about and preparing healthy meals and snacks for your 9-month-old baby can feel overwhelming.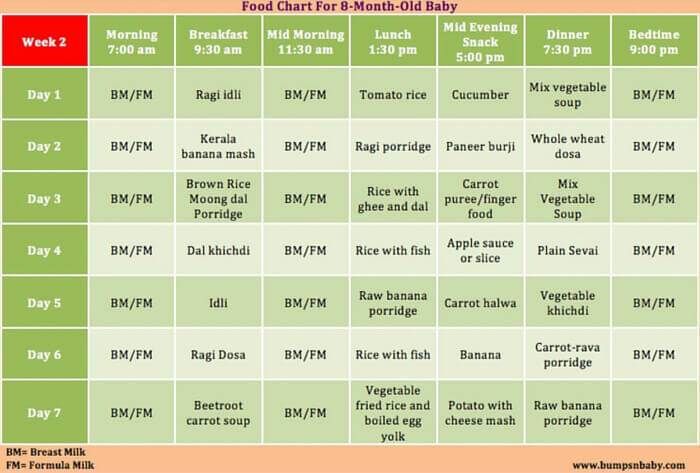
By planning ahead and having some go-to meal ideas, you’ll be able to throw together a healthy, balanced plate for your little one in less time.
Preparing some food ahead of time and making your own meal baby-friendly will help save time and the stress of putting together more than one meal.
While 9-month-olds can eat most of the foods you eat, some foods should be avoided, including honey, salt, added sugars, and undercooked or unpasteurized foods.
Properly handling, cooking, and storing your baby’s food will significantly decrease the risk of them experiencing a foodborne illness. Be sure to cut your little one’s food into safe shapes and offer appropriate textures to reduce their choking risk.
Just one thing
Try this today: Combine 1 pound (0.45 kg) of ground meat (chicken, turkey, beef, or pork), 1/2 cup (45 grams) of oat flour, 1 egg, and 2 teaspoons of dried oregano.
Roll the mixture into meatballs and place them on a greased baking sheet in the oven at 400°F (204°C) for 20–25 minutes, or until they’re fully cooked.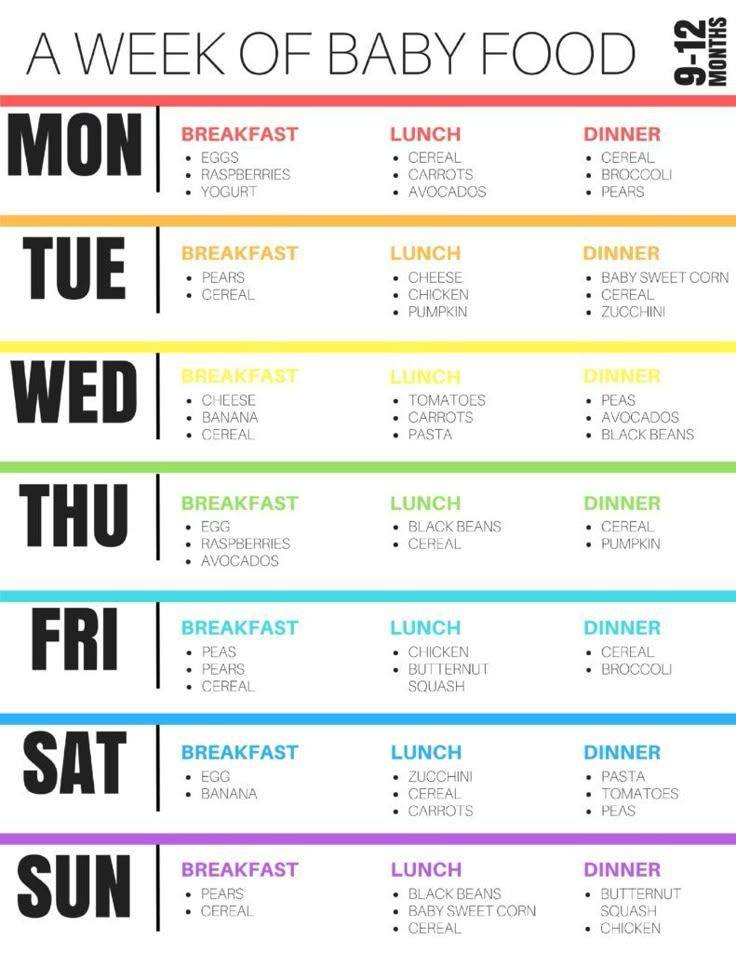
Freeze them and defrost 1 or 2 at a time when you need a quick protein source for your little one.
Baby menu at 9 months
6-12 months
Article
5/5 1 reviews
Although breast milk or formula remains the mainstay of infant nutrition at this age, a 9-month-old baby's menu becomes more varied with new complementary foods. The correct diet of the child is the basis of his harmonious development, good health and good mood. But how to organize a diet, what can be given at this age and how much should a child eat at one meal?
8 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
The correct diet for a nine-month-old baby includes 5 meals: a day the baby receives liquid food twice and thick food three times.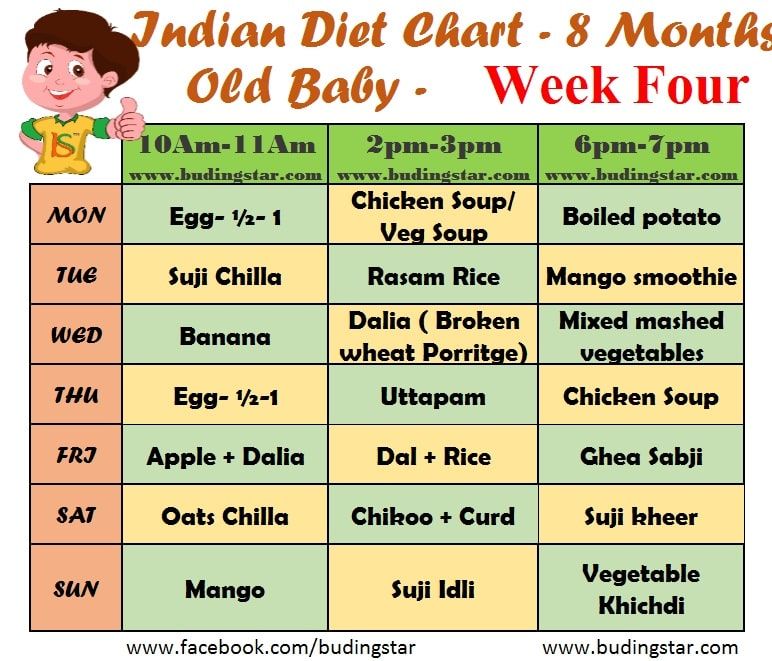 This is due to the fact that mashed potatoes and cereals take longer to digest than milk, so they give the baby a longer energy supply. Feeding is usually carried out at intervals of 4 hours. If the baby asks to eat 2-3 hours after liquid food, offer her a baby snack, fruit or vegetable (in small pieces or in the form of a puree).
This is due to the fact that mashed potatoes and cereals take longer to digest than milk, so they give the baby a longer energy supply. Feeding is usually carried out at intervals of 4 hours. If the baby asks to eat 2-3 hours after liquid food, offer her a baby snack, fruit or vegetable (in small pieces or in the form of a puree).
A 9-month-old baby's daily diet includes many healthy foods and drinks that provide essential nutrients such as vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals. In addition to milk and infant formula, the following foods can be given to a child:
- Fruits and vegetables in the form of puree (apple, pear, cauliflower, etc.)
- Fruit juices and compotes without sugar.
- Meat in various forms.
- Fish.
- Kashi from various cereals.
- Chicken or quail egg yolk.
- Children's fresh cottage cheese.
- Children's low-fat kefir.
- Children's cookies, croutons, bread.
Read also: The baby refuses new products
According to WHO recommendations, by the 9th month, all of the above products should already be on the menu. If something from the food is still unfamiliar to your child, it is recommended to gradually add it to the diet.
If something from the food is still unfamiliar to your child, it is recommended to gradually add it to the diet.
Start with smaller portions and see how your child reacts to the new food. If there is no allergic reaction to the product, you can increase the volume and add it to new dishes. New complementary foods are recommended to be introduced at intervals of 5-7 days. An indicative table for one day will help to create an optimal diet for health. It also shows how much formula or milk the baby should eat per day.
* infant formula.
**Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or infant formula given to the baby. Milk porridge is diluted with water.
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge* | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil < | about 1 tsp | |
| Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 70 g | |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree or pureed soup | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Meat puree (rabbit, turkey) | 50 g | |
| Fruit juice | 70 g | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree | 50 g |
| Vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge | 180 g | |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Meat puree | 50 g | |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
*dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or it is safe for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins.
** you can eat porridge or vegetables, so you can eat grass - porridge with vegetables.
1st day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Buckwheat porridge with pumpkin, juice |
| Lunch | Pumpkin steam cutlets, veal puree |
| Snack | Rusks or baby biscuits, yoghurt |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
2nd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal, berry juice |
| Lunch | Steamed fish, rice, fruit compote |
| Snack | Vegetable puree |
| Dinner | Vegetable puree |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
3rd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Semolina porridge, quail egg yolk |
| Lunch | Steamed zucchini, boiled veal, apple compote |
| Snack | Pumpkin and apple puree |
| Dinner | Curd casserole with carrots |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Fourth day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, fruit puree |
| Lunch | Mashed potatoes or turkey meatball soup |
| Snack | Carrot Apple Juice |
| Dinner | Kefir |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
5th day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal and apple puree |
| Lunch | Cream soup with chicken and vegetables |
| Snack | Carrot juice |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree, crackers or bread |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
6.
 Sixth day
Sixth day | First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, half yolk (chicken egg) |
| Lunch | Vegetable soup with chicken breast, juice |
| Snack | Baked apple |
| Dinner | Spinach mashed potatoes |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Seventh day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Millet porridge, croutons |
| Lunch | Steamed chicken cutlets, vegetable puree |
| Snack | Apple juice |
| Dinner | Curd with fruits |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Parents need to gradually accustom the child to eating solid foods, because now he is moving to a new level of development: more teeth appear, so the baby can now chew food. If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
No need to grind fish and potatoes in a blender - just put the food on a plate and mash well with a fork. Meat can be offered in the form of meatballs to develop chewing skills. It can be turkey, rabbit, veal, beef, chicken. The norm of meat for one meal is 60-70 g.
It is quite normal if at first large pieces in a dish cause discontent in a child or even a gag reflex - he will soon get used to it. Sometimes it happens the other way around - the baby willingly tries the pieces, but refuses pureed food. Treat your baby with apple slices, bread, crackers or baby snacks. But the meat is still better to grind thoroughly.
At this age, consumption of mother's milk or adapted formula decreases. There are only two feedings per day - in the morning and in the evening. Everything else is "adult" food. Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Please note that uneaten food (already cooked) must not be stored and reheated. It is also not recommended to add sugar and salt to the dish.
If you give your child ready-made baby puree, we recommend that you do not feed him immediately from a jar, but pour the right amount onto a plate. In this case, the rest can be stored in the refrigerator for another 24 hours.
Find out more: Baby Portion
Pay attention to the quality of food you cook: appearance, smell and expiration date. It is better to use seasonal vegetables and fruits, and shop in trusted places.
Wash food thoroughly under running water before cooking. You can also use special children's products for washing fruits and vegetables.
All products must be brought to full readiness, and then thoroughly crushed to the desired consistency, so that the baby can comfortably chew small pieces. After eating, wash the dishes with a special detergent.
How to properly feed a 9-month-old baby if he refuses food and does not eat the foods you suggest?
Poor appetite is one of the indicators of a baby's health. The problem may concern the digestive tract, glucose levels, central nervous system. The feeling of hunger appears when the level of sugar in the blood decreases. But for this you need to take breaks between meals. Also, the smell of food affects the appetite - it causes the release of gastric juice.
How to regain your appetite:
- observe the diet;
- develop a delicious menu for a baby at 9 months;
- Serve dishes beautifully and set the table;
- ventilate the room before eating;
- let your baby use cutlery.
See also: The baby does not eat well, how to feed?
In order for the baby to eat willingly, he must be in a good mood. Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere.
Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere.
If the baby refuses to eat or eats very slowly, do not rush or force him to eat. Also, do not force the little one to eat foods that he refuses. Otherwise, in the future, he will have a negative attitude towards the feeding process, refuse to eat any food at all. He can even feel sick and vomit only with one kind of food.
Important
Games and cartoons during meals do not really improve appetite. On the contrary, in this way you only teach the baby to eat without noticing the dishes.
With the help of our tips, you can create a menu for a child at 9 months for every day, which will meet the requirements of a healthy diet and preferences of the baby
1. What should not be given to a child at 9 months?
It is not recommended to give cow's milk until the age of one. It contains too much calcium, which overloads the kidneys, and protein, which is poorly digested. Also be careful with foods that can cause allergies or contain a lot of sugar
Also be careful with foods that can cause allergies or contain a lot of sugar
2. Should oil be included in a baby's diet?
A 9-month-old baby's menu should include animal and vegetable oil, as it contains many vitamins, proteins and fatty acids necessary for the proper development of the baby. Among the useful products of plant origin, it is worth noting olive, corn, sesame or linseed oil.
3. Can a 9-month-old baby be given fish?
Low-fat white fish can be a healthy addition to your baby's menu. It is recommended to give fish 1-2 times a week instead of a meat dinner - flounder, cod, hake or pike perch are suitable. If the baby responds well to the product, try making fish cakes or meatballs.
Related Articles:
Cooking or using baby food?
At what age can a child be given kefir
Last reviews
Average customer rating
1 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- 5 one
- four 0
- 3 0
- 2 0
- one 0
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods for a child 4 - 12 months: the first complementary foods, menus, charts, tables, baby nutrition principles
Modern principles of complementary feeding of children is a kind of fusion of practical experience and the latest scientific developments. They are based on the recommendations of the European Association of Pediatric Gastroenterologists, Hepatologists, Nutritionists ESPGHAN , American Academy of Pediatrics AAP and national recommendations of relevant ministries and associations. Complementary foods for a child: online course mental development. Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods is very important for the growth and development of the child, as well as an outstanding stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to feeding from the general table.
They are based on the recommendations of the European Association of Pediatric Gastroenterologists, Hepatologists, Nutritionists ESPGHAN , American Academy of Pediatrics AAP and national recommendations of relevant ministries and associations. Complementary foods for a child: online course mental development. Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods is very important for the growth and development of the child, as well as an outstanding stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to feeding from the general table.
- It is inappropriate to develop separate recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for breastfed or artificially fed children, the approaches in these cases are the same
- Breastmilk mother remains the gold standard of exclusive breastfeeding for at least 4 months (17 weeks) of an infant's life, up to 6 months (26 weeks), the standard of exclusive or predominant breastfeeding
- The digestive tract and kidney function are mature enough for a baby to accept complementary foods at 4 months of age, and between 5 and 6 months the baby develops the necessary motor skills to consume solid foods.
 Therefore, at this age, it is important to give food of the right consistency and in the right way
Therefore, at this age, it is important to give food of the right consistency and in the right way - A well-nourished mother can provide all the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals her baby needs through exclusive breastfeeding up to a maximum of 6 months of age
- Some children may need iron supplementation earlier than 6 months
- It is important to continue breastfeeding in parallel with the introduction of complementary foods. This has been shown to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, as well as hospitalizations in a child
- When comparing initiation of complementary foods at 4 or 6 months of age, no significant differences were found in the effect on infant growth and body weight, development of obesity during the first 3 years of life
- At the same time, a high risk of developing overweight and obesity has been established with the introduction of complementary foods before 4 months of age
- Complementary foods (solid or liquid food other than breast milk or infant formula) should be started not earlier than 4 months and not later than 6 months
- With age, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child should be offered food varied in texture, texture, taste, smell
- Children have an innate tendency to distinguish and prefer sweet and salty foods, reluctantly eat bitter, which we cannot change.
 But we can shape and adjust the child's taste preferences through training, systematically offering the child foods with different tastes, including sour, bitter green vegetables
But we can shape and adjust the child's taste preferences through training, systematically offering the child foods with different tastes, including sour, bitter green vegetables - Whole cow's milk Not recommended for infants under 12 months of age. The use of cow's milk is associated with the intake of an increased amount of energy, protein, fat, and lower - iron. Therefore, children who consumed large amounts of cow's milk at an early age had a higher risk of developing iron deficiency anemia
- Eating more protein when complementary foods increase the risk of overweight and obesity, especially in individuals with a predisposition to this, so protein intake should not exceed 15% of energy intake during the day
- The baby's need for iron is very high during the entire period of complementary feeding, therefore it is necessary to ensure the provision of iron-rich foods, especially for breast-fed children
- Allergenic products can be administered from the age of 4 months at any time, since it is during this period that the formation of immune tolerance to the allergen occurs.
 For example, children at high risk of developing allergic reactions to peanuts should be administered at 4-12 months of age under specialist supervision. No relationship was found between the timing of the introduction of allergenic complementary foods and the development of allergic or immunological diseases. However, this does not mean the need for early introduction of allergenic products to everyone, but it emphasizes that there is no need to postpone the introduction of allergenic products after 4 months for a longer period;
For example, children at high risk of developing allergic reactions to peanuts should be administered at 4-12 months of age under specialist supervision. No relationship was found between the timing of the introduction of allergenic complementary foods and the development of allergic or immunological diseases. However, this does not mean the need for early introduction of allergenic products to everyone, but it emphasizes that there is no need to postpone the introduction of allergenic products after 4 months for a longer period; - Gluten may be offered to a child aged 4-12 months, however large amounts of gluten should be avoided during the first weeks after initiation of its introduction, thereafter a safe amount has not been established. The type of feeding (breast/artificial) was not identified with the introduction of gluten to reduce the risk of developing celiac disease, type 1 diabetes;
- Sugar or salt should not be added to complementary foods, and sweetened drinks and juices should be avoided.
 Sugary drinks are liked by babies in the first months, but if they are not given, but after 6 months, the children no longer like them very much. Sugar affects future eating behavior. Sugar is an important factor in the development of caries - it contributes to caries, as glucans can be formed, which increase the adhesion of bacteria to tooth enamel, disrupt the diffusion balance of acid and buffer systems, which ultimately contributes to damage to the enamel.
Sugary drinks are liked by babies in the first months, but if they are not given, but after 6 months, the children no longer like them very much. Sugar affects future eating behavior. Sugar is an important factor in the development of caries - it contributes to caries, as glucans can be formed, which increase the adhesion of bacteria to tooth enamel, disrupt the diffusion balance of acid and buffer systems, which ultimately contributes to damage to the enamel. - Vegetarian diets are contraindicated in young children due to the risk of vitamin B12, iron, zinc, folate, long chain fatty acid, protein and calcium deficiencies, which can lead to irreversible adverse effects and impaired cognitive development;
- Vegetarian diet can only be used under the close supervision of a doctor and nutritionist, with the obligatory additional administration of vitamins B, D, iron, zinc, calcium, proteins, PUFAs, which can ensure the appropriate growth and development of the child.
 It is important that parents should be aware of the risk of irreversible harmful consequences (mental disability, death of the child) that may develop if they do not follow the recommendations of specialists.
It is important that parents should be aware of the risk of irreversible harmful consequences (mental disability, death of the child) that may develop if they do not follow the recommendations of specialists.
General rules for the introduction of complementary foods for children of the first year of life:
- Introduce the first complementary foods Better feeding 9-11 in the morning , to trace the reaction of the child to the new product.
- Sugar and salt free .
- Give the first complementary foods to the child when he is calm and not tired .
- Start with 0.5-2 teaspoons. If the child refuses, do not insist, try to give later or the next day.
- If the reaction is normal - no rash, no skin changes, no stool changes, double the dose the next day.
 Gradually bring the baby's first complementary foods to the age norm 80-200 g
Gradually bring the baby's first complementary foods to the age norm 80-200 g - If there is an allergic reaction or other intolerance reaction - refuse to introduce this complementary food for three days, if the adverse reaction occurs again - do not give this product, contact your pediatrician.
- Each subsequent new complementary food product must be one-component only: marrow, cabbage, broccoli, buckwheat, meat, etc.
- Mixed food dish give when the child has already become acquainted with all the products separately.
- It is not advisable to introduce new products three days before and after vaccinations.
If you are thinking about introducing complementary foods, then your child should already have certain signs of readiness for this:
- Holds head
- Able to stand alone, practically without support, sit on a special highchair with side support
- Opens mouth when a spoonful of food is offered
- Turns away from a spoonful of food when not hungry
- Closes mouth with spoon in mouth , holds food in mouth and then swallows rather than pushing or spitting it out
First complementary foods at 4 months
The age of 4 months as the minimum for the introduction of complementary foods was also chosen because at 4 months the child's gastrointestinal tract becomes more mature: the initially increased permeability of the small intestine mucosa decreases, a series of digestive enzymes, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, associated with the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”.
Therefore, to the question whether it is necessary to give complementary foods to a 3-month-old baby , we can unequivocally answer: no, it's too early!
But 4 months, this is the time when you can think about the introduction of complementary foods. At the same time, it should be remembered that at the age of 4 months, the child has enough mother's milk or a highly adapted milk formula for its full development. In addition, when they talk about complementary foods at 4 months, they usually mean the end of the 4th month of life. It is important to continue breastfeeding in parallel with the introduction of complementary foods.
Video: Lifts at 4 months
If you enter complementary foods at the 4th month of life of the child -this is usually a one-component Puree , if the child does not suffer well enough well. , then it can be gluten-free porridges: rice and buckwheat . It is better to start with vegetable puree. Kids are smart and if he tries a sweeter fruit puree, he can refuse vegetable puree for quite some time and you may have difficulty introducing this very healthy dish.
, then it can be gluten-free porridges: rice and buckwheat . It is better to start with vegetable puree. Kids are smart and if he tries a sweeter fruit puree, he can refuse vegetable puree for quite some time and you may have difficulty introducing this very healthy dish.
What is useful in vegetable supplements and what is the best way to prepare it?
Vegetable puree - for the first feeding can be prepared from cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli - these are low-allergenic products, are among the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contain a large amount of healthy proteins, fiber and vitamins, microelements ! Fiber helps move food through the digestive tract and promote beneficial microflora in the gut. Pectins absorb and remove toxins from the baby's body. Vegetables have a positive effect on the acid-base balance of the body, creating conditions for the proper functioning of all organs and systems.
Cauliflower - is a good source of fiber, protein, minerals and vitamins: A, B1, B2, B3 (PP), B6, as well as a small amount of vitamins K, D and tocopherol (vitamin E). In the inflorescences of cabbage there is a lot of magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, iron. It contains twice as much iron as green peas, peppers and lettuce. Cauliflower protein is easily digestible and its content is quite high. Cauliflower protein contains essential vitamin U (methionine). It is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Other essential amino acids are also present in a small amount: arginine, tryptophan.
Zucchini - rich in vitamins and microelements. It contains potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins C, B1 and B2 and others, folic acid. Which plays an important role in the processes of hematopoiesis. Zucchini is rich in such important trace elements as iron and copper. They are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normalization of metabolism, as well as for the formation of hemoglobin, which is a good prevention of anemia.
They are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normalization of metabolism, as well as for the formation of hemoglobin, which is a good prevention of anemia.
Broccoli is a very useful vegetable, which is a kind of cauliflower. Pleasant soft taste and good digestibility of the product, unique composition have a beneficial effect on the health of both adults and children. Eat unopened cabbage inflorescences. This is also a low-allergenic vegetable, rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, calcium, iron, trace elements and even phytoncides. The content of calcium and magnesium is sufficient to balance the functioning of the nervous system, ensure the normal regulation of the child's sleep and wake cycle, and good stress resistance. A child with such nutrition becomes calmer, less excited and naughty.
Broccoli is the leader in choline and methionine content. Only 50 g of broccoli provides the baby with a full set of nutrients for a day.
Pumpkin - the largest vegetable on Earth. It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of useful proteins, fiber and vitamins, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, K, iron, potassium, magnesium, trace elements that are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen immunity and help fight inflammation, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. By the content of carotene, pumpkin exceeds carrots by 5 times.
It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of useful proteins, fiber and vitamins, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, K, iron, potassium, magnesium, trace elements that are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen immunity and help fight inflammation, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. By the content of carotene, pumpkin exceeds carrots by 5 times.
Vitamins and microelements contained in pumpkin help the child grow, provide healthy sleep, are responsible for the condition of the skin and eyes, improve metabolic processes, and accelerate the removal of harmful substances from the child's body. Due to its beneficial qualities, pumpkin can be one of the first types of complementary foods for an infant.
All vegetable purees have a specific vegetable smell, this is absolutely normal
0039
Introduction of vegetable puree
Vegetables should be introduced into the child's menu gradually. Start giving each new vegetable in the form of a monocomponent puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon, preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of food allergies or intolerance reactions to this product. If all is well, then the next day, offer him a teaspoon. So gradually you need to bring the portion to 50-100 grams. A serving of vegetable puree per day for an 8-month-old baby is approximately 80 grams. In a year, you can increase up to 150 grams. The next product can be administered no earlier than 4-5 days later. If a child has skin rashes, his stool has changed, then you need to remove the product from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
Start giving each new vegetable in the form of a monocomponent puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon, preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of food allergies or intolerance reactions to this product. If all is well, then the next day, offer him a teaspoon. So gradually you need to bring the portion to 50-100 grams. A serving of vegetable puree per day for an 8-month-old baby is approximately 80 grams. In a year, you can increase up to 150 grams. The next product can be administered no earlier than 4-5 days later. If a child has skin rashes, his stool has changed, then you need to remove the product from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
If the child does not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in small quantities - 1-2 spoons a day, maybe not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help form the right taste habits in the child.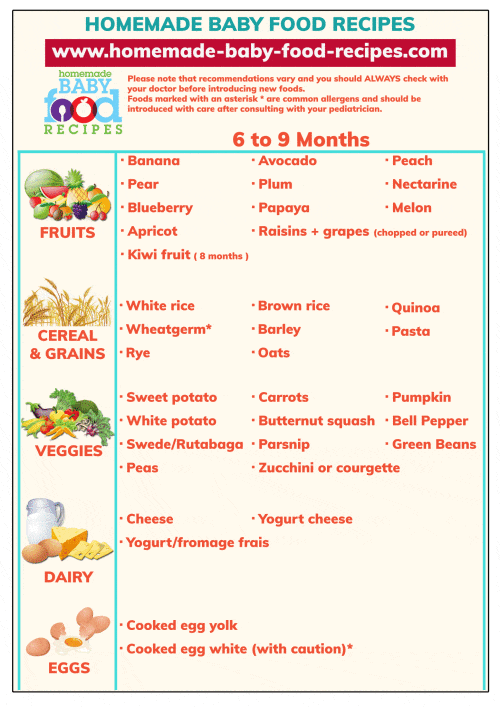
Fruit puree introduction
Fruit puree is a definite alternative and addition to vegetables. It can be made from apples, bananas - by the way, do you know what a berry is?, sweet varieties of pears. These fruits contain substances useful for babies, vitamins and minerals, including iron, which is extremely necessary for children. Prune puree is somewhat separate, it has a good effect on the baby's digestion, especially with a tendency to constipation, and, of course, also contains many useful substances.
Porridge in the diet of a child in the first year of life.
Porridge can be introduced into the baby's diet at the end of 4 months or at the fifth, sixth month of life. As a rule, they go as a second food after vegetable or fruit puree. But if your child is not gaining weight very well, or you have been feeding your child with breast milk or infant formula until almost the end of 6 months, then complementary foods can be started with the introduction of cereals.
It is important to start with one-component, low-allergenic cereals which does not contain gluten : this is buckwheat, rice, corn porridge .
gluten-containing cereals include: wheat, oats, rye, barley, millet .
According to modern data , the period of introduction of gluten into the child's diet is not of fundamental importance, but the latest recommendations draw attention to the fact that its amount in the baby's diet should not be large. Therefore, it is better to add semolina and oatmeal to other porridge in a limited amount, and not to give it on its own. No relationship was found between the timing of the start of complementary foods that contain gluten and the development of celiac disease in a child. If your child hasn't tried porridge yet, start with a dairy-free, gluten-free, one-ingredient buckwheat or rice porridge.
Rice - very useful for growing baby. It has a low content of vegetable proteins, therefore it is easily digested and is especially useful for toddlers with unstable stools. Rice has a high nutritional value and, to a certain extent, protects the delicate intestines of the baby due to its enveloping effect. This is a hearty and nutritious dish with a good content of carbohydrates and proteins, potassium and magnesium, calcium and phosphorus, beneficial amino acids and vitamins. It replenishes energy costs, energizes and gives strength. Rice is not recommended for overweight children and those who suffer from severe constipation.
Gluten-free buckwheat porridge - very nutritious and rich in iron, fiber, rich in various vitamins and microelements. This is also a good option for starting a child's acquaintance with adult food. These porridges can be prepared with water, breast milk, milk formula, which your child is used to. No need to add salt and sugar.
No need to add salt and sugar.
Rules for introducing porridge into baby food
If the child already eats porridge from 5 months, then at 6 months you can offer a more complex porridge - for example, rice porridge with apricot or raspberries, rice porridge with banana (this is very successful a combination both in taste and in its properties) or even more complex porridge - corn-rice with banana.
Over time, you can start adding apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries, to the porridge, provided that the child is not allergic to them.
The rules for introducing cereals are the same as for vegetable puree. In order for the child to get used to the new product and its consistency more easily, first prepare 5% porridge (5 g of cereal per 100 g of water), if you make it yourself. Porridge is usually cooked with water, but can be made with breast milk, infant formula. First, give the baby one teaspoon, then, within 7-10 days, bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding (150 g). If all this time the porridge is well tolerated, i.e. there are no skin rashes, the child has stable stools, they switch to a gradual (starting from 20-30 g) introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already at a 10% concentration (10 g of cereal per 100 g of water). In other words, a thicker porridge is administered no earlier than 7-10 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge. The complete introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out in 7-10 days. The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal (in the form of 10% porridge) or the next complementary foods.
First, give the baby one teaspoon, then, within 7-10 days, bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding (150 g). If all this time the porridge is well tolerated, i.e. there are no skin rashes, the child has stable stools, they switch to a gradual (starting from 20-30 g) introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already at a 10% concentration (10 g of cereal per 100 g of water). In other words, a thicker porridge is administered no earlier than 7-10 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge. The complete introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out in 7-10 days. The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal (in the form of 10% porridge) or the next complementary foods.
Video: feeding porridge
You need to give porridge with a spoon, it is better in the morning for breakfast. After porridge at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula. With artificial feeding, the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that, together with porridge, it is 200 ml with five meals a day.
After porridge at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula. With artificial feeding, the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that, together with porridge, it is 200 ml with five meals a day.
Norms for the introduction of cereals
In the future, the volume of the portion of porridge gradually increases, amounting to:
- 7-8 months - 160-170 ml
- 8-9 months - 170-180 ml
- 9-12 months - up to 200 ml (there is a complete replacement of one feeding of the child with complementary foods.)
Cereal schedule
- Day 1 – 1 teaspoon (5 g)
- Day 2 - 2 teaspoons (10 g)
- Day 3 - 3 teaspoons (15 g)
- Day 4 - 4 teaspoons (20 g)
- Day 5 - 50 ml (50 g)
- Day 6 - 100 ml (100 g)
- Day 7 - 150 ml (150 g)
Meat complementary foods - the rules for introducing meat into the child's diet
Meat is usually the third, very important product of complementary foods, after vegetables and cereals. The meat contains amino acids, complete animal protein, B vitamins (B1, B2, B6 and B12), heme iron, potassium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, which are necessary for the growth and development of the child. It is very important to understand that mashed meat contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And the addition of meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them, from vegetables.
The meat contains amino acids, complete animal protein, B vitamins (B1, B2, B6 and B12), heme iron, potassium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, which are necessary for the growth and development of the child. It is very important to understand that mashed meat contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And the addition of meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them, from vegetables.
Iron deficiency can seriously affect the intellectual development of the child, his immunity, hematopoiesis. Since your task is to raise a healthy and intelligent child, meat complementary foods must be introduced without fail and in a timely manner.
Heme iron - found in meat products and easily digestible (red meat-veal, liver), absorption is about 25%.
Non-heme iron - found in plant foods (beans, beans, lentils, peas, nuts, tomatoes, cauliflower, green leafy vegetables, apples, dried fruits, but it is absorbed much worse from plants - only 3-5% Iron absorption from other animal products (eggs, fish) is 10-15%. 0003
0003
It is important to know that human milk enhances and cow's milk reduces iron absorption .
Timing of the introduction of meat complementary foods
It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child aged 6-8 months old . This, to some extent, depends on when cereals and vegetable/fruit purees were introduced. if your baby has been eating vegetables and cereals since 4 months, meat can be introduced at 6 months. From 7 months it can be administered if the child is not gaining weight. From 8 months to children who started complementary foods at 6 months.
Children at risk for anemia are advised to introduce meat earlier at 5-6 months of age.
It has been proven that only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can fully meet the needs of children in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
You can start meat complementary foods with lean beef, veal , but better with less allergenic poultry meat ( turkey, chicken ), or rabbit, these are the most easily digestible meats.
Goose and pork are fatty for the baby, and the meat of duck and other birds of the reservoirs is also not suitable for the first feeding. They are recommended to give only after 3 years;
Horsemeat is perfect for your little one. The product is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, but it is almost impossible to find horse meat for sale.
Meat should be introduced into the child's diet gradually, at lunchtime, at first, a quarter of a teaspoon and, gradually adding, bring it to the daily norm: At 8 months, about 50 g, at 9months-60-70 g.
Video: Power feeding meat
Meat Puree Board 9000
- 1 day ¼ of the vegetables
- Day 2 - ½ teaspoon
- Day 3 - 1 teaspoon
- Day 4 - 2 teaspoons
- Day 5 - 3 teaspoons
- Day 6 3-4 teaspoons + vegetables
At first, it is better to give meat with vegetable puree, which the child has already eaten, so he will better adapt to the new product, and iron is better absorbed. Children at the end of the first year of life can already be given 3 varieties of mashed meat.
Children at the end of the first year of life can already be given 3 varieties of mashed meat.
Baby menu at 7-8 months
At 7-8 months you can start giving children 0 baby cottage cheese 905 Start with 1/2 teaspoon. Within a month, the daily volume of cottage cheese consumption by a baby can be increased to 30-40 g. In addition, a child of 8 months is recommended to give sour-milk infant formula. But ordinary yogurt from the store should not be given. At this age, the child should receive 5 g of butter and 5 g (1 teaspoon) of vegetable oil, ¼- yolk - 2-3 times a week.
Baby's menu at 9 months
At the age of 9 months Your baby is already familiar at this age already usually familiar: , egg yolk . You may have already met meat . Therefore, at this age, they usually give more complex purees and porridges, less homogenized, of various tastes , gradually preparing him for adult nutrition, increasing the variety and quantity of complementary foods.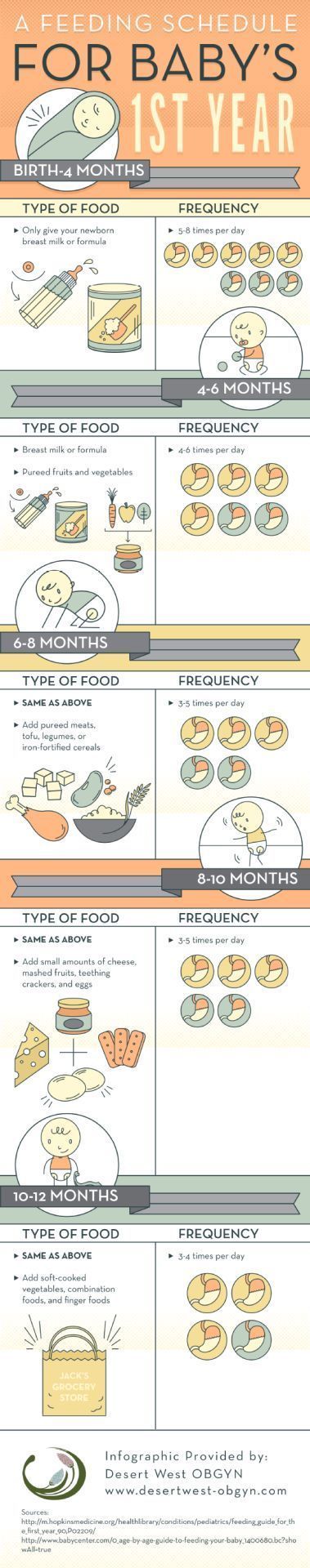 It is desirable to feed the baby at the table with other family members, he must see how his parents eat with pleasure, he learns from them. The amount of food offered should be based on the principles of actively encouraging the baby to eat, it is necessary to continue to gradually change the consistency and increase the variety of complementary foods, adhering to the recommended frequency of introducing complementary foods.
It is desirable to feed the baby at the table with other family members, he must see how his parents eat with pleasure, he learns from them. The amount of food offered should be based on the principles of actively encouraging the baby to eat, it is necessary to continue to gradually change the consistency and increase the variety of complementary foods, adhering to the recommended frequency of introducing complementary foods.
At this age, the child usually gets complementary foods 3 times a day . His diet depends on the age of the start of complementary foods. If the baby began to give new food at 4-5 months, the list of allowed foods will be much wider than if this happened at 6-7 months. Therefore, all this is very individual, there are no absolutely rigid frameworks and recommendations. On the Internet you will find a lot of different advice on baby food, if you are not sure about something, it is better to consult your pediatrician.
From vegetables the baby can be given what he ate before, mixing them: pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots and others, adding 1 tsp. vegetable oil . If the baby does not have skin reactions, then you can give beets . It is also possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups , but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and has not had a reaction to them.
vegetable oil . If the baby does not have skin reactions, then you can give beets . It is also possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups , but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and has not had a reaction to them.
If you have introduced complementary foods, then you need to remember that water is an important part of baby food. You can use purified water or special water for children .
In addition, at 9 months you can give special baby wheat cookies , which the baby will be happy to eat on his own as an adult, white wheat bread, this improves hand motility, improves eating skills, but at the same time he must be supervised.
At this age, you can start giving fish puree from low-fat varieties: river perch, pollock, hake, haddock, zander, saithe - start with ½ teaspoon, bringing up to 40-50 g , watching the reaction of the child , give at lunchtime instead of mashed meat, 1-2 times a week. But a number of pediatricians do not advise giving it up to a year, it is a useful, but highly allergenic product.
But a number of pediatricians do not advise giving it up to a year, it is a useful, but highly allergenic product.
10 month old baby menu
B 10 months usually 2 times a day the child receives mother's breast or special milk formulas . Various porridges : buckwheat, rice, corn, oatmeal, wheat, semolina porridge . 5-10 g of butter should be added to cereals . At this age, it is already possible to make complex cereals from 2-3 cereals with which the child is familiar, add various fruits, vegetables: apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries , provided that the child is not allergic to them, or use ready-made cereals with fruit.
From vegetables the baby can be given what he ate earlier, mixing them: pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots, beets and others, adding 1 tsp. vegetable oil . It is also already possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups, but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he did not have a reaction to them.
vegetable oil . It is also already possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups, but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he did not have a reaction to them.
At this age, the baby already usually eats about 40-50 g of baby meat puree from chicken, turkey, rabbit , with good tolerance to cow's milk proteins from veal or beef. If he has been eating meat for a month or more, you can start giving him two-component meat purees , eg chicken and turkey.
At this age, fish puree from low-fat varieties is usually started: river perch, pollock, hake, haddock, pike perch, pollack with ½ teaspoon, bringing to 40-50 g, following the reaction of the child, it is better to give at lunch time instead of meat puree, 1-2 times a week .
At 10 months, children's cottage cheese should be given twice a week. Start with 1/2 teaspoon if you have not given it before, the daily amount of cottage cheese at this age 40-50 g .
Start with 1/2 teaspoon if you have not given it before, the daily amount of cottage cheese at this age 40-50 g .
It is recommended to give special sour-milk baby formulas.
At this age, the child can receive 5-10 g of butter and 5 g (1 teaspoon) of vegetable oil, and 2-3 times a week½ - yolk .
1 year old child's menu
The child is one year old. He has already grown up, he already has 6-10 teeth, with which he gnaws everything he sees, he is interested in chewing food, his digestive enzymes already work well and he has already become acquainted with various products: vegetable and fruit purees, various cereal cereals, meat and fish, sour-milk mixtures. In fact, he is already prepared for the transition to a more adult diet. In a year, changing the diet involves turning to new products and gradually changing the way they are prepared and the degree of grinding.
You need to eat 5 times a day with an interval 3.5-4 hours .
semi-liquid dishes should still remain the basis of nutrition, but not only mashed, but also containing small pieces of food . Too dry food should not be given to the baby yet, as he may have difficulty swallowing.
In the year the child already tries to eat with his hands and should be encouraged to do so. Finely chopped, soft foods can be given, for example: small pieces of soft fruit, vegetables, cheese, well-cooked meat, pasta , etc. and foods that dissolve quickly, children's cookies, children's bread - as food with the help of hands.
Must avoid products that can enter the respiratory tract and cause asphyxiation - sausages and other hard meat products , nuts (especially peanuts), grapes, raisins, raw carrots, popcorn, round candies .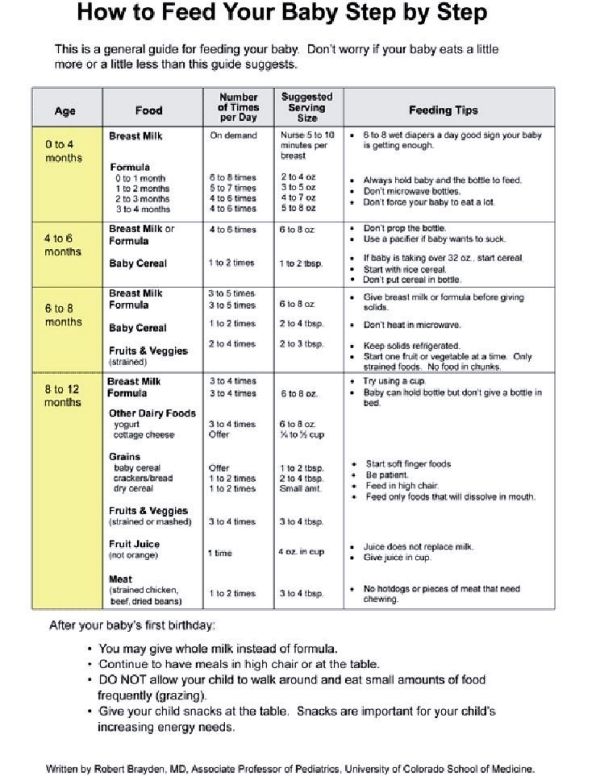 Hold off on this for now.
Hold off on this for now.
In a year, part of the children are without mother's milk. But if your baby is still not weaned - do not rush, if possible, give him a breast before bed at night. You can also breastfeed between main meals. At this age, the child receives all the main vitamins and minerals from food, but he can get a number of biologically active components from breast milk.
Dairy products
Dairy products still occupy an important place in the child's diet, it is a source of calcium, B vitamins, protein, milk sugar and fat. It is better to use special baby milk (marked with a triple on the packaging), baby fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt in total 500-600 ml per day .
Cottage cheese
The child should be given cottage cheese. The daily dose of cottage cheese after 1 year can be increased up to 70 g per day .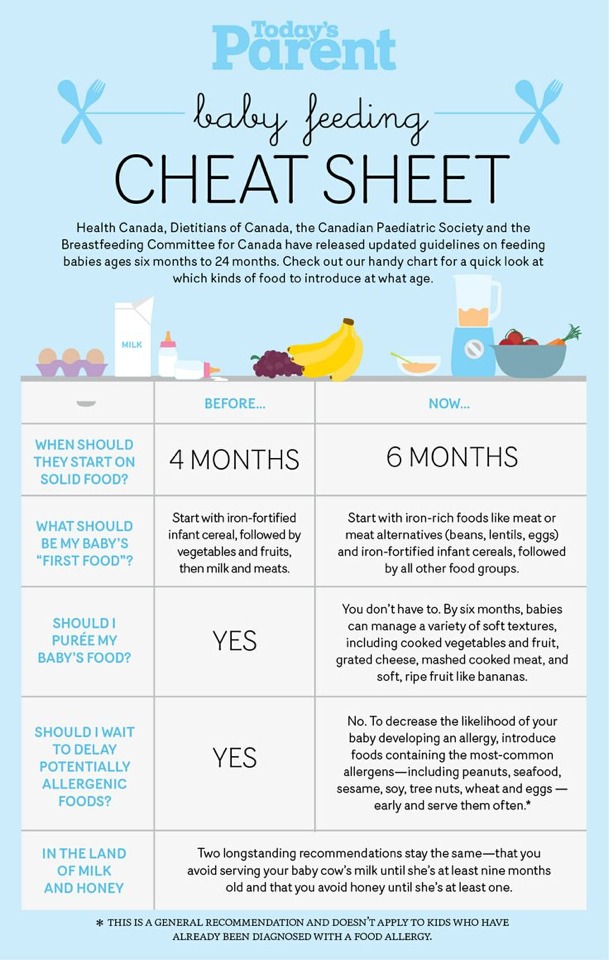 It can be given pureed or combined with fruit puree, pudding, casserole. This contributes to the development of chewing skills.
It can be given pureed or combined with fruit puree, pudding, casserole. This contributes to the development of chewing skills.
Butter
Butter can be added to cereals or smeared on wheat bread, cookies in a dose of up to 12 g per day.
Low fat sour cream and cream
After 1 year, low-fat sour cream and cream can be given in small quantities to .
Vegetables
Every year a child must be given various vegetables , it is good to combine them with protein products, meat . The vegetable diet can now be diversified with green peas, tomatoes, turnips, beets, carrots, spinach in the form of mashed potatoes. Legumes are still better not to give.
Fruits and berries
After 1 year, you can gradually introduce the baby to new fruits and berries: strawberries, cherries, cherries, kiwi, currants, gooseberries, chokeberries, sea buckthorn, raspberries, blackberries, cranberries, blueberries, lingonberries and even citrus fruits . But do it gradually, watching the reaction of the child. Berries with a dense peel (gooseberries) are best mashed, while soft juicy fruits (peaches, strawberries, apricots, kiwi) can be offered to the baby in pieces.
But do it gradually, watching the reaction of the child. Berries with a dense peel (gooseberries) are best mashed, while soft juicy fruits (peaches, strawberries, apricots, kiwi) can be offered to the baby in pieces.
Daily dose of fruits - approx.
Meat products
Meat products can be given in the form of steam cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, meat souffle and pudding in an amount up to 100 g daily - beef, veal, lean pork, rabbit, turkey, chicken.
Fish
Fish can be given once or twice a week for 30-40 g per meal as a substitute for meat dishes
Eggs
Chicken, quail eggs give boiled or in the form of omelettes in milk, you can try with vegetables.
Kashi
Porridge can be cooked from rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, corn, millet, semolina.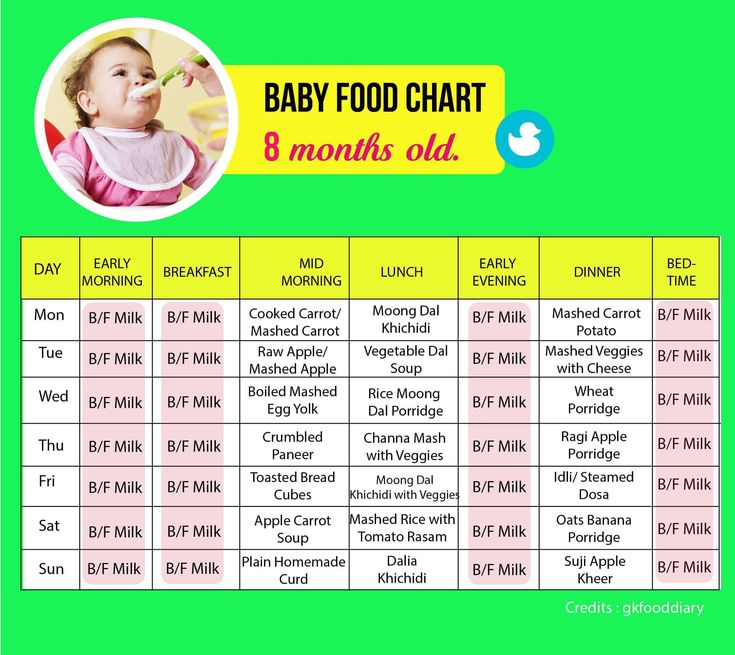 At this age, they should still have a uniform consistency, so it will be easier for him to swallow. You can use ready-made industrial, children's instant cereals, for example, various multi-cereal cereals, in which fruits, crackers, cereals have already been added. Give 1 time per day.
At this age, they should still have a uniform consistency, so it will be easier for him to swallow. You can use ready-made industrial, children's instant cereals, for example, various multi-cereal cereals, in which fruits, crackers, cereals have already been added. Give 1 time per day.
Water
Be sure to give the child to drink clean water, better than bottled water for children, as much as he wants . In addition to her baby can drink vegetable and fruit juices, dairy products, compotes, weak tea.
Do not give:
do not give confectionery and sweets . From sweets at this age, you can sometimes give marmalade, dried fruits and cookies.
Do not give sausages and sausages , they are rarely prepared from high quality meats and are rich in various food additives
Calories and volume
0038 1200 ml .