Feeding your baby cereal for the first time
How to Get Started – The Baby's Brew
I will always remember feeding each of my babies their first foods. After months of only breastfeeding and bottles, my husband and I couldn’t wait to introduce the next milestone to each of our babies. But with the first baby at least, there was also apprehension. Our pediatrician had recommended we start with a single-grain baby cereal such as rice cereal, but I didn’t know which one to get and I wanted to make sure I fed my baby the right way!
So to get you started off on the right food with baby feeding 101, I’ve put together this guide to giving your baby cereal for the first time. And it will only get more exciting as you introduce other foods to your little one.
Choosing a First Baby CerealBefore you actually feed your baby, you have to choose what you want to give them from the array of cereals and other options available.
Most parents reach for the rice cereal to give their baby as their first food. I know I did as a new mom! It’s an easy choice and one that doctors suggest due to its benefits. It's easy to such as its digest, won’t trigger an allergic reaction and is tolerated well by babies who’ve only been fed breastmilk or formula. It’s also iron-fortified, which babies need as their iron stores start to deplete around 6 months of age.
Though rice cereal has traditionally been suggested as the best first food for your baby, even many doctors may still give this recommendation, it has gotten a bit of a bad rap in recent years due to the arsenic that’s found in rice - causing parents to look at other options. (This article from Healthy Children explains how you can ensure rice cereal can be used in a healthy diet for your baby.)
If you do choose rice cereal, you’ll want to start introducing other solids to your baby shortly so that’s not all that they are getting, as recommended by the FDA.
Fortunately, if you want to skip the rice cereal completely, you can! There is no need to feel like this is the only first food for your baby. Many experts share that any iron-fortified single-grain baby cereal is a great choice, such as baby oatmeal or barley. You can even start with other pureed foods which we discuss later on in this article.
When to Start Feeding Your Baby CerealSeveral years ago the recommendation was that parents could feed their babies at four months if they showed readiness signs. But medical advice evolves and this is a guideline that medical experts have changed to give babies the healthiest start possible.
It’s now suggested that it’s best to wait til closer to your baby’s ½ birthday to introduce solids, especially if he is breastfed. There’s really no reason to rush it!
But it’s not just age you want to pay attention to as we know that all babies develop at different rates.
Here are signs to look for that will let you know your baby is ready for solid foods:
- able to sit up supported in a high chair
- has proper head control
- no more tongue thrust
- eager to take a spoon
- are interested in the food that you are eating
If your baby isn’t yet showing these signs, you’ll want to wait a bit longer before starting baby cereal or other solid foods. No need to worry - all babies are ready in their own time! Your baby will continue to get the nutrition they need from their breastmilk or formula so you don’t need to be concerned that they are missing out on important nutrients. If you do have concerns, it’s always best to talk to your pediatrician.
Can you give your baby cereal in a bottle?Even though your well-meaning grandma may suggest that you mix cereal into your baby’s bottle to help fill them up so they can sleep better, this practice is actually not safe according to the CDC. In fact, they share that it won’t help your baby sleep better anyway. This practice puts your baby at risk for choking or overfeeding and also may encourage parents to start solid foods long before they are ready.
In fact, they share that it won’t help your baby sleep better anyway. This practice puts your baby at risk for choking or overfeeding and also may encourage parents to start solid foods long before they are ready.
Instead, follow the guideline to not feed your baby solid foods until he or she is at least 5-6 months in age and watch for the other readiness signs mentioned above. At this point you can feed your baby with a spoon and introduce finger foods as they are ready.
RELATED: Starting Solid Foods With Your Baby
How to Introduce Cereal to Your BabyBreastmilk and formula will continue to be your baby’s primary source of nutrition until the age of one, but cereal is a great way to get them started with supplemental nutrition and transition them to solid foods. So how do you go about it?
Here are the steps to follow to give your baby her first single-grain cereal:
- Make sure they meet the recommended readiness signs. This will not only make for a safe feeding experience for your little guy or gal, but it will also be a lot more enjoyable for you.
- Plan to feed your little one after they’ve had a full feeding of breastmilk or formula. This way their tummy will mostly be full which means they’ll likely be happy to try a little cereal. (If you try to introduce solids to a hungry baby they will most likely be uncooperative!) Initially you’ll only feed your baby once per day, and it’s up to you when you want that time to be. We recommend choosing a time that your baby is usually in good spirits!
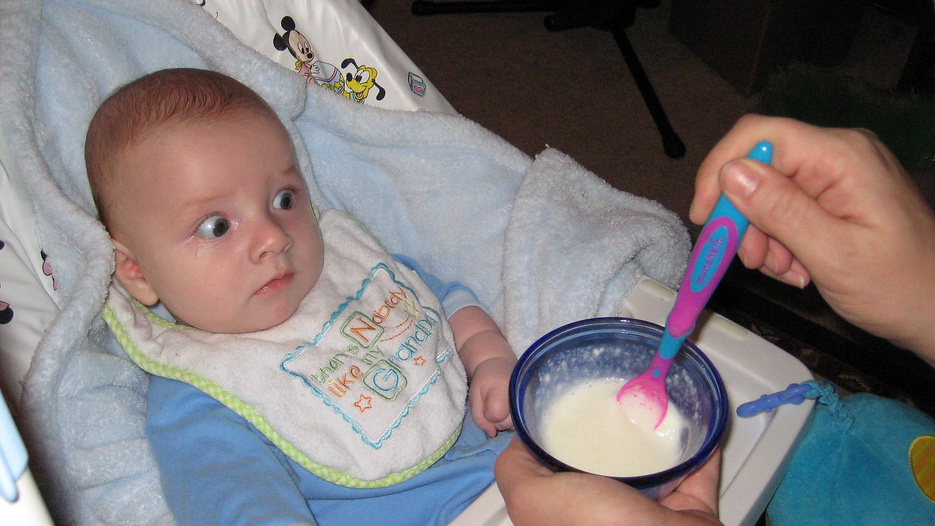
- Follow the directions on the label of your chosen baby cereal. You don’t need much to start! 1 tablespoon of cereal mixed with breastmilk or formula until it’s a runny consistency will be plenty for those first couple of feedings. If your baby is used to drinking warm milk or formula, you’ll want to use that same temperature of milk to mix with your baby’s food. (This is why we love the Baby’s Brew portable bottle warmer...you can choose your baby’s milk temperature with the push of a button!)
- Be sure your baby is sitting upright.
 Ideally this would be in a highchair, but they could also be sitting on your lap. You’ll want them to be wearing a bib as a lot your little one’s food won’t make it into their mouth initially.
Ideally this would be in a highchair, but they could also be sitting on your lap. You’ll want them to be wearing a bib as a lot your little one’s food won’t make it into their mouth initially. - Use an infant spoon to feed your baby. Do your best to get the spoon into their open mouth, but just know it’s going to be a bit messy at first as they get the hang of what’s going on. It won’t be long before they are opening wide at mealtime!
- Watch for cues from your baby that show that they are full (or are just are no longer interested). If your baby turns their head, is fussy or won’t open their mouth to eat, it’s time to be “all done!”
And that’s it! You can do another feeding the next day (or you can just do every other day) with the same type of cereal. Be sure to wait three - five days before introducing another food so you can keep an eye out for any allergic reactions. This is the recommendation given by the CDC.
After a couple weeks to a month of successfully feeding your baby once per day you can move to twice per day.
Some parents choose to start with a different food or may take baby cereal out of their little one’s diet altogether. Starting with other pureed foods instead is totally fine and may even work better for some babies. WebMD shares that both pureed vegetables or fruits are good starter foods and that there’s no rule saying that baby cereals must be first.
Some great first foods, if you want to skip the cereal route, include:
- Avocados
- Bananas
- Blended Red Meat (great source of iron)
- Squash
- Sweet Potatoes
- Pears
Just remember that these all need to be pureed and made into a runny consistency that’s easy for your baby to eat. Mixing with your baby’s warmed breastmilk or formula will help to bring this to a consistency that your baby can manage. You’ll also want to avoid giving your baby any of the top allergen foods such as the ones listed here unless you’ve been given different advice from your doctor.![]() These are best introduced when your baby gets a little older.
These are best introduced when your baby gets a little older.
Still not sure which food to start with? It can be a bit overwhelming! This is a great conversation to have with your doctor before your baby turns 6 months and they can help guide you on what would be the best option. Whatever you choose, it is sure to be an exciting time for your family as your little guy or gal begins his journey of eating "real" food!
When, What, and How to Introduce Solid Foods | Nutrition
For more information about how to know if your baby is ready to starting eating foods, what first foods to offer, and what to expect, watch these videos from 1,000 Days.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend children be introduced to foods other than breast milk or infant formula when they are about 6 months old. Introducing foods before 4 months old is not recommended. Every child is different. How do you know if your child is ready for foods other than breast milk or infant formula? You can look for these signs that your child is developmentally ready.
Your child:
- Sits up alone or with support.
- Is able to control head and neck.
- Opens the mouth when food is offered.
- Swallows food rather than pushes it back out onto the chin.
- Brings objects to the mouth.
- Tries to grasp small objects, such as toys or food.
- Transfers food from the front to the back of the tongue to swallow.
What Foods Should I Introduce to My Child First?
The American Academy of Pediatrics says that for most children, you do not need to give foods in a certain order. Your child can begin eating solid foods at about 6 months old. By the time he or she is 7 or 8 months old, your child can eat a variety of foods from different food groups. These foods include infant cereals, meat or other proteins, fruits, vegetables, grains, yogurts and cheeses, and more.
If your child is eating infant cereals, it is important to offer a variety of fortifiedalert icon infant cereals such as oat, barley, and multi-grain instead of only rice cereal. Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
Only providing infant rice cereal is not recommended by the Food and Drug Administration because there is a risk for children to be exposed to arsenic. Visit the U.S. Food & Drug Administrationexternal icon to learn more.
How Should I Introduce My Child to Foods?
Your child needs certain vitamins and minerals to grow healthy and strong.
Now that your child is starting to eat food, be sure to choose foods that give your child all the vitamins and minerals they need.
Click here to learn more about some of these vitamins & minerals.
Let your child try one single-ingredient food at a time at first. This helps you see if your child has any problems with that food, such as food allergies. Wait 3 to 5 days between each new food. Before you know it, your child will be on his or her way to eating and enjoying lots of new foods.
Introduce potentially allergenic foods when other foods are introduced.
Potentially allergenic foods include cow’s milk products, eggs, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soy, and sesame. Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
Drinking cow’s milk or fortified soy beverages is not recommended until your child is older than 12 months, but other cow’s milk products, such as yogurt, can be introduced before 12 months. If your child has severe eczema and/or egg allergy, talk with your child’s doctor or nurse about when and how to safely introduce foods with peanuts.
How Should I Prepare Food for My Child to Eat?
At first, it’s easier for your child to eat foods that are mashed, pureed, or strained and very smooth in texture. It can take time for your child to adjust to new food textures. Your child might cough, gag, or spit up. As your baby’s oral skills develop, thicker and lumpier foods can be introduced.
Some foods are potential choking hazards, so it is important to feed your child foods that are the right texture for his or her development. To help prevent choking, prepare foods that can be easily dissolved with saliva and do not require chewing. Feed small portions and encourage your baby to eat slowly. Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Always watch your child while he or she is eating.
Here are some tips for preparing foods:
- Mix cereals and mashed cooked grains with breast milk, formula, or water to make it smooth and easy for your baby to swallow.
- Mash or puree vegetables, fruits and other foods until they are smooth.
- Hard fruits and vegetables, like apples and carrots, usually need to be cooked so they can be easily mashed or pureed.
- Cook food until it is soft enough to easily mash with a fork.
- Remove all fat, skin, and bones from poultry, meat, and fish, before cooking.
- Remove seeds and hard pits from fruit, and then cut the fruit into small pieces.
- Cut soft food into small pieces or thin slices.
- Cut cylindrical foods like hot dogs, sausage and string cheese into short thin strips instead of round pieces that could get stuck in the airway.
- Cut small spherical foods like grapes, cherries, berries and tomatoes into small pieces.

- Cook and finely grind or mash whole-grain kernels of wheat, barley, rice, and other grains.
Learn more about potential choking hazards and how to prevent your child from choking.
Top of Page
Nursing nipple care | Breast Care
Breastfeeding is good for you and your baby, but it can be a real challenge for the nipples. Check out our tips and tricks to help reduce the pain.
Share this information
Sioned Hilton, health visitor, neonatal nurse and lactation consultant:
A mother of three, Sioned Hilton has been supporting families with newborns and young children for over 30 years. She provides advice on breastfeeding and pumping, both in clinics and at home. In addition, Schoned writes articles for parenting magazines, attends conferences, and conducts seminars for attending physicians.
New mothers often hear: "Breastfeeding doesn't have to be painful." However, in the early days, many are faced with the opposite.
In most women during pregnancy, the nipples enlarge and become more sensitive. When a newborn baby begins to suckle, it creates a certain pressure, and this is a completely new and unfamiliar sensation for a woman (at least for a first-time mother).
Feedings can be prolonged for a long time, sometimes up to an hour, and the child may ask to be breastfed up to 13 times a day. 1 This sucking, pressure and saliva of the baby can cause sore nipples.
Remember how your lips crack in the wind and sun. The more often you lick them, the more they will dry and become inflamed. Therefore, lips require good hydration to soften, protect and speed up the healing of cracks. The same thing happens with nipples.
However, sore nipples usually don't last more than a couple of weeks and go away as your baby and your breasts get used to breastfeeding. It is important to start nipple care as early as possible to prevent the situation from worsening. Therefore, if your nipples become very inflamed, crack or bleed, contact your doctor as soon as possible.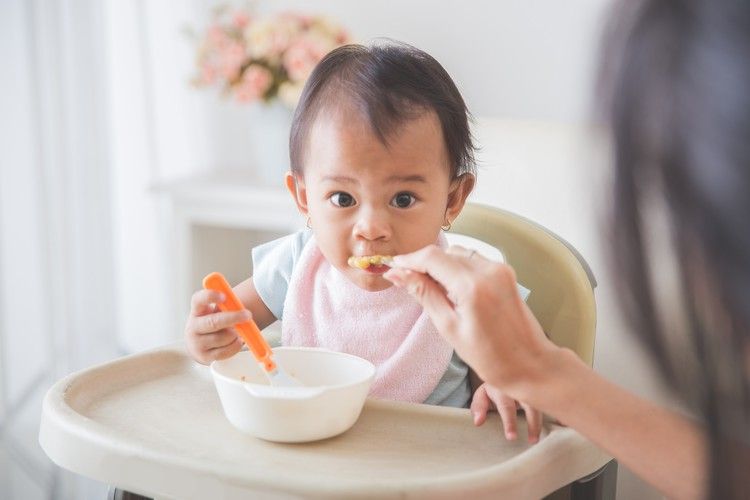 2
2
Prevention is better than cure, so check out our tips.
Check your baby's latch-on
Correct latch is the key to pain-free breastfeeding. When putting the baby to the breast, point the nipple towards his palate. This will allow him to grab the nipple and the part of the areola (the darker skin around the nipple) underneath. When the nipple and part of the breast is in the baby's mouth, feeding is taking place correctly. 3
For the first few days, see a lactation consultant or specialist to check for proper latch. He will be able to give you advice on how to solve problems and recommend other feeding positions that will make it less painful for you to feed your baby.
Check tongue tie
Tongue tie (ankyloglossia) occurs in 4-11% of
newborns. 4 At the same time, the strip of skin that attaches the tongue to the bottom of the mouth - the so-called frenulum - is too short. A child with a shortened frenulum will not be able to open his mouth wide enough to latch onto the breast well, and his tongue will not cover the lower gum when sucking. As a result, the baby will be nervous, and your nipples may become inflamed.
As a result, the baby will be nervous, and your nipples may become inflamed.
The doctor or lactation consultant must examine the baby to make this diagnosis. The problem of a shortened bridle is solved by a simple undercutting procedure. It is performed by a doctor, and is usually done without blood and does not require anesthesia. Cutting the bridle allows you to restore the normal feeding mechanism almost instantly. 5
Less common in children is a short frenulum of the upper lip. In this case, it is necessary to dissect the skin that connects the upper lip to the gum. A shortened frenum of the tongue or upper lip in a newborn is not always detected during the examination conducted immediately after birth, so if you think that this is what is causing your nipples pain, seek medical advice as soon as possible. 4
Breastfeeding Tips
- Wash your breasts with water only when you shower or bathe. Small bumps on the areola (Montgomery's glands) secrete oil that moisturizes and protects your nipples.
 Soaps and shower gels can strip away this natural defense, causing dryness and irritation. 6
Soaps and shower gels can strip away this natural defense, causing dryness and irritation. 6 - Pat the nipples gently with a soft towel or simply let them air dry. In the past, women were often advised to rub their nipples to make them stiffer, but thankfully, such advice is a thing of the past!
- Do not wash breasts or nipples before feeding. The bacteria found on the surface of the breast actually help the baby's intestinal microflora to develop. 7
- Fresh breast milk helps to heal cracked nipples, 8 so rub a few drops of milk into them before and after feeding.
- Change your bra pads often if they get wet. This will reduce the risk of bacterial and fungal infections, including thrush. 6
- It is not necessary to increase the intervals between feedings to give the nipples a "rest". For a baby to be healthy and grow well, it needs to be fed on demand. Remember, frequent feeding stimulates and maintains milk production, so keep feeding despite the pain.
 9
9
Healthy teat care products
- Pure lanolin teat cleaner, a natural product derived from sheep's wool. It moisturizes and promotes healing of the nipples. This cream is safe for the baby, so it does not need to be washed off before feeding.
- Hydrogel Pads* can be applied to sore nipples to relieve pain while feeding and help promote healing. They can even be stored in the refrigerator to enhance the soothing cooling effect.
- Breast pads* fit inside the bra. They help prevent nipple irritation from clothing and have air holes to help nipples heal.
- Nursing Bras** are made from breathable material such as cotton or a special fabric that dries quickly and wicks moisture away from sore nipples.
- Nursing pads* are special silicone pads that fit over the nipples. They have small holes through which milk flows when you are breastfeeding. The pads help to protect the skin underneath and help the baby to better latch on to the nipple by making the nipple stiffer.
Do not use nursing pads for a long time. If you have problems or pain, contact your healthcare professional or lactation consultant.
When to Seek Medical Care
The soreness should go away as your nipples and baby get used to breastfeeding. It is worth repeating that the main cause of sore nipples is improper grip. If your lactation consultant has not been able to resolve your pain while feeding, see another specialist and a third if necessary.
If nipple pain persists or if you notice unusual symptoms, talk to your doctor. The appearance of white spots or flakes on the nipples may be a sign of thrush, whitish or bluish nipples may indicate a circulation disorder such as Raynaud's disease (vasospasm), and pus and redness indicate an infection. 2
Literature
1 Kent JC et al. Volume and frequency of breastfeedings and fat content of breast milk throughout the day. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3): e 387-395.![]() - Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
- Kent J.S. et al., "Amount and frequency of breastfeeding and fat content of breast milk during the day." Pediatrix (Pediatrics). 2006;117(3):e387-95.
2 Berens P et al. Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine. ABM Clinical Protocol#26: Persistent pain with breastfeeding. Breastfeeding Medicine. 2016;11(2):46-53. - Behrens P. et al., Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine, "AVM Clinical Protocol #26: Persistence of Pain During Breastfeeding." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine). 2016;11(2):46-53.
3 Cadwell K. Latching - On and Suckling of the Healthy Term Neonate: Breastfeeding Assessment. J Midwifery & Women's Health. 2007;52(6):638-42. — Cadwell, K., "Latching and sucking in healthy newborns: evaluation of breastfeeding." F Midwifery Women Health. 2007;52(6):638-642.
4 Segal LM et al. Prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment of ankyloglossia: methodological review. Canadian Family Physician. 2007;53(6):1027-1033. - Segal L.M. et al., Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Ankyloglossia: A Methodological Review. Canadian Family Physic. 2007;53(6):1027-1033.
Canadian Family Physician. 2007;53(6):1027-1033. - Segal L.M. et al., Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Ankyloglossia: A Methodological Review. Canadian Family Physic. 2007;53(6):1027-1033.
5 O'Shea JE et al. Frenotomy for tongue - tie in newborn infants. The Cochrane Library. 2017. - O'Shea J.I. et al., "Dissection of the frenulum in the newborn", The Cochrane Labrery (Cochrane Library), 2017.
6 Jacobs A et al. S3-guidelines for the treatment of inflammatory breast disease during the lactation period. Geburtshilfe und Frauenheilkunde. 2013;73(12):1202-1208. - Jacobs A. et al., "Recommendations S -3 for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the breast during breastfeeding. Geburtskhilfe und Frauenheilkünde. milk bacterial communities and establishment and development of the infant gut microbiome JAMA pediatrics 2017;171(7):647-654 - P. S. Pannaraj et al. development of the neonatal gut microbiome." JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
S. Pannaraj et al. development of the neonatal gut microbiome." JAMA pediatric. 2017;171(7):647-654.
8 Mohammadzadeh A et al. The effect of breast milk and lanolin on sore nipples. Saudi medical journal. 2005;26(8):1231-1234. — Mohammedzade A. et al., "Effects of breast milk and lanolin on sore nipples." Saudi Medical Journal. 2005;26(8):1231-1234.
9 Kent JC et al. Principles for maintaining or increasing breast milk production. J Obstet , Gynecol , & Neonatal Nurs . 2012;41(1):114-121. - Kent J.S. et al., "Principles for Maintaining and Increasing Milk Production". J Obstet Ginecol Neoneutal Nurs. 2012;41(1):114-121.
Read instructions before use. Consult a specialist about possible contraindications.
* RC № № ФСЗ 2010/07352 dated 19.07.2010
** RU No. ФСЗ 2009/05592 dated 11.25.2009
ФСЗ 2009/05592 dated 11.25.2009
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods for a child 4-12 months old: first complementary foods, menus, charts, tables, principles of feeding a baby
is a kind of fusion of practical experience and the latest scientific developments. They are based on the recommendations of the European Association of Pediatric Gastroenterologists, Hepatologists, Nutritionists ESPGHAN , American Academy of Pediatrics ААР and national recommendations of relevant ministries and associations.
Complementary foods: online course
Modern recommendations are based on the analysis of the results of many studies on the composition, timing of the introduction of complementary foods in Europe for healthy full-term newborns, taking into account various aspects of the introduction of complementary foods, its impact on physical and mental development.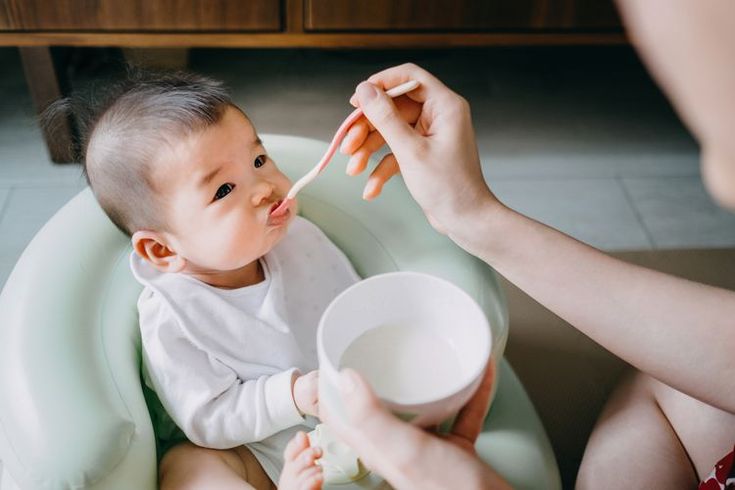 Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods is very important for the growth and development of the child, as well as an outstanding stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to feeding from the general table.
Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods is very important for the growth and development of the child, as well as an outstanding stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to feeding from the general table.
- It is inappropriate to develop separate recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for breastfed or artificially fed children, the approaches in these cases are the same
- mother's breast milk remains the gold standard of exclusive breastfeeding for at least 4 months (17 weeks) of an infant's life, up to 6 months (26 weeks) of exclusive or predominant breastfeeding
- The digestive tract and kidney function are mature enough for a baby to accept complementary foods at 4 months of age, and between 5 and 6 months the baby develops the necessary motor skills to consume solid foods.
 Therefore, at this age, it is important to give food of the right consistency and in the right way
Therefore, at this age, it is important to give food of the right consistency and in the right way - A well-nourished mother can provide all the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals her baby needs through exclusive breastfeeding up to a maximum of 6 months of age
- Some children may need iron supplementation earlier than 6 months
- It is important to continue breastfeeding in parallel with the introduction of complementary foods. This has been shown to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, as well as hospitalizations in a child
- When comparing initiation of complementary foods at 4 or 6 months of age, no significant differences were found in the effect on growth and body weight, development of obesity during the first 3 years of life
- At the same time, a high risk of developing overweight and obesity was established with the introduction of complementary foods before 4 months of age
- Complementary foods (solid or liquid food other than breast milk or infant formula) should be started not earlier than 4 months and not later than 6 months
- With age, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child should be offered food varied in texture, texture, taste, smell
- Children have an innate tendency to distinguish and prefer sweet and salty foods, reluctantly eat bitter, which we cannot change.
 But we can shape and adjust the child's taste preferences through training, systematically offering the child foods with different tastes, including sour, bitter green vegetables
But we can shape and adjust the child's taste preferences through training, systematically offering the child foods with different tastes, including sour, bitter green vegetables - Whole cow's milk Not recommended for infants under 12 months of age. The use of cow's milk is associated with the intake of an increased amount of energy, protein, fat, and lower - iron. Therefore, children who consumed large amounts of cow's milk at an early age had a higher risk of developing iron deficiency anemia
- Eating more protein when complementary foods increase the risk of overweight and obesity, especially in individuals with a predisposition to this, so protein intake should not exceed 15% of energy intake during the day
- The baby's requirement for iron is very high during the entire period of complementary feeding, therefore it is necessary to ensure the provision of iron-rich foods, especially for breastfed children
- Allergenic products can be administered from 4 months of age at any time, since it is during this period that immune tolerance to the allergen is formed.
 For example, children at high risk of developing allergic reactions to peanuts should be administered at 4-12 months of age under specialist supervision. No relationship was found between the timing of the introduction of allergenic complementary foods and the development of allergic or immunological diseases. However, this does not mean the need for early introduction of allergenic products to everyone, but it emphasizes that there is no need to postpone the introduction of allergenic products after 4 months for a longer period;
For example, children at high risk of developing allergic reactions to peanuts should be administered at 4-12 months of age under specialist supervision. No relationship was found between the timing of the introduction of allergenic complementary foods and the development of allergic or immunological diseases. However, this does not mean the need for early introduction of allergenic products to everyone, but it emphasizes that there is no need to postpone the introduction of allergenic products after 4 months for a longer period; - Gluten may be offered to a child aged 4-12 months, however large amounts of gluten should be avoided during the first weeks after initiation of its introduction, thereafter a safe amount has not been established. The type of feeding (breast/artificial) was not identified with the introduction of gluten to reduce the risk of developing celiac disease, type 1 diabetes;
- Sugar or salt should not be added to complementary foods, and sweetened drinks and juices should be avoided.
 Sugary drinks are liked by babies in the first months, but if they are not given, but after 6 months, the children no longer like them very much. Sugar affects future eating behavior. Sugar is an important factor in the development of caries - it contributes to caries, as glucans can be formed, which increase the adhesion of bacteria to tooth enamel, disrupt the diffusion balance of acid and buffer systems, which ultimately contributes to damage to the enamel.
Sugary drinks are liked by babies in the first months, but if they are not given, but after 6 months, the children no longer like them very much. Sugar affects future eating behavior. Sugar is an important factor in the development of caries - it contributes to caries, as glucans can be formed, which increase the adhesion of bacteria to tooth enamel, disrupt the diffusion balance of acid and buffer systems, which ultimately contributes to damage to the enamel. - Vegetarian diets are contraindicated in young children due to the risk of vitamin B12, iron, zinc, folate, long-chain fatty acid, protein and calcium deficiencies, which can lead to irreversible adverse effects and impaired cognitive development;
- Vegetarian diet can be used only under the close supervision of a doctor and nutritionist, with the obligatory additional administration of vitamins B, D, iron, zinc, calcium, proteins, PUFAs, which can ensure the appropriate growth and development of the child.
 It is important that parents should be aware of the risk of irreversible harmful consequences (mental disability, death of the child) that may develop if they do not follow the recommendations of specialists.
It is important that parents should be aware of the risk of irreversible harmful consequences (mental disability, death of the child) that may develop if they do not follow the recommendations of specialists.
General rules for the introduction of complementary to children of the first year of life:
- Introduce the first feeding Better feeding 9-11 in the morning to trace the reaction of the child to a new product.
- Without added sugar and salt .
- Give the first complementary foods to the child when he is calm and not tired .
- Start with 0.5-2 teaspoons. If the child refuses, do not insist, try to give later or the next day.
- If the reaction is normal - no rash, no skin changes, no stool changes, double the dose the next day. Gradually bring the baby's first complementary foods to the age norm 80-200 g
- If there is an allergic reaction or other reaction of intolerance - refuse to introduce this complementary food for three days, if there is a repeated adverse reaction - do not give this product, contact your pediatrician.

- Each subsequent new complementary food must be one-component only: marrow, cabbage, broccoli, buckwheat, meat, etc.
- Mixed food dish give when the child has already become acquainted with all the products separately.
- It is not advisable to introduce new products three days before and after vaccinations.
If you are thinking about introducing complementary foods, then your child should already have certain signs of readiness for this:
- Holds head
- Able to stand alone, practically without support, sit on a special high chair with side support
- Opens mouth when a spoonful of food is brought
- Turns away from a spoonful of food when not hungry
- Closes mouth with spoon in mouth holds food in mouth and then swallows rather than pushing or spitting it out
The first complementary foods at 4 months
The age of 4 months as the minimum for the introduction of complementary foods was also chosen because at 4 months the child's gastrointestinal tract becomes more mature: the initially increased permeability of the small intestine mucosa decreases, a series of digestive enzymes, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, associated with the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”.
Therefore, to the question whether it is necessary to give complementary foods to a 3-month-old baby , we can unequivocally answer: no, it's too early!
But 4 months, this is the time when you can think about the introduction of complementary foods. At the same time, it should be remembered that at the age of 4 months, the child has enough mother's milk or a highly adapted milk formula for its full development. In addition, when they talk about complementary foods at 4 months, they usually mean the end of the 4th month of life. It is important to continue breastfeeding in parallel with the introduction of complementary foods.
Video: Bedary of 4 months
If you introduce complementary foods at the 4th month of life of the child -this is usually a single-component Puree , if the child does not sufficiently well gains weight. , then it can be gluten-free cereals: rice and buckwheat . It is better to start with vegetable puree. Kids are smart and if he tries a sweeter fruit puree, he can refuse vegetable puree for quite some time and you may have difficulty introducing this very healthy dish.
, then it can be gluten-free cereals: rice and buckwheat . It is better to start with vegetable puree. Kids are smart and if he tries a sweeter fruit puree, he can refuse vegetable puree for quite some time and you may have difficulty introducing this very healthy dish.
What is useful in vegetable supplements and what is the best way to prepare it?
Vegetable puree - for the first feeding can be prepared from cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli - these are low-allergenic foods, are among the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contain a large amount of healthy proteins, fiber and vitamins, microelements ! Fiber helps move food through the digestive tract and promote beneficial microflora in the gut. Pectins absorb and remove toxins from the baby's body. Vegetables have a positive effect on the acid-base balance of the body, creating conditions for the proper functioning of all organs and systems.
Cauliflower - is a good source of fiber, protein, minerals and vitamins: A, B1, B2, B3 (PP), B6, as well as a small amount of vitamins K, D and tocopherol (vitamin E). In the inflorescences of cabbage there is a lot of magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, iron. It contains twice as much iron as green peas, peppers and lettuce. Cauliflower protein is easily digestible and its content is quite high. Cauliflower protein contains essential vitamin U (methionine). It is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Other essential amino acids are also present in a small amount: arginine, tryptophan.
Zucchini - rich in vitamins and microelements. It contains potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins C, B1 and B2 and others, folic acid. Which plays an important role in the processes of hematopoiesis. Zucchini is rich in such important trace elements as iron and copper. They are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normalization of metabolism, as well as for the formation of hemoglobin, which is a good prevention of anemia.
They are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normalization of metabolism, as well as for the formation of hemoglobin, which is a good prevention of anemia.
Broccoli is a very healthy vegetable that is a type of cauliflower. Pleasant mild taste and good digestibility of the product, unique composition have a beneficial effect on the health of both adults and children. Eat unopened cabbage inflorescences. This is also a low-allergenic vegetable, rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, calcium, iron, trace elements and even phytoncides. The content of calcium and magnesium is sufficient to balance the functioning of the nervous system, ensure the normal regulation of the child's sleep and wake cycle, and good stress resistance. A child with such nutrition becomes calmer, less excited and naughty.
Broccoli is the leader in choline and methionine content. Only 50 g of broccoli provides the baby with a full set of nutrients for a day.
Pumpkin is the largest vegetable on Earth. It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of useful proteins, fiber and vitamins, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, K, iron, potassium, magnesium, trace elements that are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen immunity and help fight inflammation, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. By the content of carotene, pumpkin exceeds carrots by 5 times.
It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of useful proteins, fiber and vitamins, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, K, iron, potassium, magnesium, trace elements that are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen immunity and help fight inflammation, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. By the content of carotene, pumpkin exceeds carrots by 5 times.
Vitamins and microelements contained in pumpkin help the child grow, provide healthy sleep, are responsible for the condition of the skin and eyes, improve metabolic processes, and accelerate the removal of harmful substances from the child's body. Due to its beneficial qualities, pumpkin can be one of the first types of complementary foods for an infant.
All vegetable purees have a specific vegetable smell, this is absolutely normal
0102
Introduction of vegetable puree
Vegetables should be introduced into the child's menu gradually. Start giving each new vegetable in the form of a monocomponent puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon, preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of food allergies or intolerance reactions to this product. If all is well, then the next day, offer him a teaspoon. So gradually you need to bring the portion to 50-100 grams. A serving of vegetable puree per day for an 8-month-old baby is approximately 80 grams. In a year, you can increase up to 150 grams. The next product can be administered no earlier than 4-5 days later. If a child has skin rashes, his stool has changed, then you need to remove the product from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
Start giving each new vegetable in the form of a monocomponent puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon, preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of food allergies or intolerance reactions to this product. If all is well, then the next day, offer him a teaspoon. So gradually you need to bring the portion to 50-100 grams. A serving of vegetable puree per day for an 8-month-old baby is approximately 80 grams. In a year, you can increase up to 150 grams. The next product can be administered no earlier than 4-5 days later. If a child has skin rashes, his stool has changed, then you need to remove the product from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
If the child does not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in small quantities - 1-2 spoons a day, maybe not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help form the right taste habits in the child.
Fruit puree introduction
Fruit puree is a definite alternative and addition to vegetables. It can be made from apples, bananas - by the way, do you know what a berry is?, sweet varieties of pears. These fruits contain substances useful for babies, vitamins and minerals, including iron, which is extremely necessary for children. Prune puree is somewhat separate, it has a good effect on the baby's digestion, especially with a tendency to constipation, and, of course, also contains many useful substances.
Porridges in the nutrition of a child in the first year of life.
Porridge can be introduced into the baby's diet at the end of 4 months or at the fifth, sixth month of life. As a rule, they go as a second food after vegetable or fruit puree. But if your child is not gaining weight very well, or you have been feeding your child with breast milk or infant formula until almost the end of 6 months, then complementary foods can be started with the introduction of cereals.
It is important to start with one-component, low-allergenic cereals which does not contain gluten : this is buckwheat, rice, corn porridge .
gluten-containing cereals include: wheat, oats, rye, barley, millet .
According to modern data the period of introduction of gluten into the child's diet is not of fundamental importance, but the latest recommendations draw attention to the fact that its amount in the baby's diet should not be large. Therefore, it is better to add semolina and oatmeal to other porridge in a limited amount, and not to give it on its own. No relationship was found between the timing of the start of complementary foods that contain gluten and the development of celiac disease in a child. If your child hasn't tried porridge yet, start with a dairy-free, gluten-free, one-ingredient buckwheat or rice porridge.
Rice - very useful for growing baby. It has a low content of vegetable proteins, therefore it is easily digested and is especially useful for toddlers with unstable stools. Rice has a high nutritional value and, to a certain extent, protects the delicate intestines of the baby due to its enveloping effect. This is a hearty and nutritious dish with a good content of carbohydrates and proteins, potassium and magnesium, calcium and phosphorus, beneficial amino acids and vitamins. It replenishes energy costs, energizes and gives strength. Rice is not recommended for overweight children and those who suffer from severe constipation.
Gluten-free buckwheat porridge - very nutritious and rich in iron, fiber, rich in various vitamins and microelements. This is also a good option for starting a child's acquaintance with adult food. These porridges can be prepared with water, breast milk, milk formula, which your child is used to. No need to add salt and sugar.
No need to add salt and sugar.
Rules for the introduction of porridge into baby food
If the child already eats porridge from 5 months, then at 6 months you can offer a more complex porridge - for example, rice porridge with apricot or raspberries, rice porridge with banana (this is very successful a combination both in taste and in its properties) or even more complex porridge - corn-rice with banana.
Over time, you can start adding apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries to porridge, , provided that the child is not allergic to them.
The rules for introducing cereals are the same as for vegetable puree. In order for the child to get used to the new product and its consistency more easily, first prepare 5% porridge (5 g of cereal per 100 g of water), if you make it yourself. Porridge is usually cooked with water, but can be made with breast milk, infant formula. First, give the baby one teaspoon, then, within 7-10 days, bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding (150 g). If all this time the porridge is well tolerated, i.e. there are no skin rashes, the child has stable stools, they switch to a gradual (starting from 20-30 g) introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already at a 10% concentration (10 g of cereal per 100 g of water). In other words, a thicker porridge is administered no earlier than 7-10 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge. The complete introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out in 7-10 days. The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal (in the form of 10% porridge) or the next complementary foods.
First, give the baby one teaspoon, then, within 7-10 days, bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding (150 g). If all this time the porridge is well tolerated, i.e. there are no skin rashes, the child has stable stools, they switch to a gradual (starting from 20-30 g) introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already at a 10% concentration (10 g of cereal per 100 g of water). In other words, a thicker porridge is administered no earlier than 7-10 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge. The complete introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out in 7-10 days. The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal (in the form of 10% porridge) or the next complementary foods.
Video: feeding porridge
You need to give porridge from a spoon, it is better in the morning for breakfast. After porridge at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula. With artificial feeding, the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that, together with porridge, it is 200 ml with five meals a day.
After porridge at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula. With artificial feeding, the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that, together with porridge, it is 200 ml with five meals a day.
Norms for the introduction of cereals
In the future, the volume of the portion of porridge gradually increases, amounting to:
- 7-8 months - 160-170 ml
- 8-9 months - 170-180 ml
- 9-12 months - up to 200 ml (there is a complete replacement of one feeding of the child with complementary foods.)
Cereal schedule
- Day 1 – 1 teaspoon (5 g)
- Day 2 - 2 teaspoons (10 g)
- Day 3 - 3 teaspoons (15 g)
- Day 4 - 4 teaspoons (20 g)
- Day 5 - 50 ml (50 g)
- Day 6 - 100 ml (100 g)
- Day 7 - 150 ml (150 g)
Meat complementary foods - the rules for introducing meat into the child's diet
Meat is usually the third, very important product of complementary foods, after vegetables and cereals. Meat contains amino acids, complete animal protein, B vitamins (B1, B2, B6 and B12), heme iron, potassium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, which are necessary for the growth and development of the child. It is very important to understand that mashed meat contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And the addition of meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them, from vegetables.
Meat contains amino acids, complete animal protein, B vitamins (B1, B2, B6 and B12), heme iron, potassium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, which are necessary for the growth and development of the child. It is very important to understand that mashed meat contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And the addition of meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them, from vegetables.
Iron deficiency can seriously affect the intellectual development of the child, his immunity, hematopoiesis. Since your task is to raise a healthy and intelligent child, meat complementary foods must be introduced without fail and in a timely manner.
Heme iron - found in meat products and easily digestible (red meat-veal, liver), absorption is about 25%.
Non-heme iron - found in plant foods (beans, beans, lentils, peas, nuts, tomatoes, cauliflower, green leafy vegetables, apples, dried fruits, but it is absorbed from plants much worse - only 3-5% Iron absorption from other animal products (eggs, fish) is 10-15%. 0003
0003
It is important to know that human milk enhances , while cow's milk reduces iron absorption .
Timing of the introduction of meat complementary foods
It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child aged 6-8 months . This, to some extent, depends on when cereals and vegetable/fruit purees were introduced. if your baby has been eating vegetables and cereals since 4 months, meat can be introduced at 6 months. From 7 months it can be administered if the child is not gaining weight. From 8 months to children who started complementary foods at 6 months.
Children at risk for anemia are advised to introduce meat earlier at 5-6 months of age.
It has been proven that only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can fully meet the needs of children in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
You can start meat complementary foods with lean beef, veal , but better with less allergenic poultry meat ( turkey, chicken ), or rabbit, these are the most easily digestible meats.
Goose and pork are fatty for the baby, and the meat of duck and other birds of the reservoirs is also not suitable for the first feeding. They are recommended to give only after 3 years;
Horsemeat is perfect for your little one. The product is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, but it is almost impossible to find horse meat for sale.
Meat should be introduced into the child's diet gradually, at lunchtime, at first, a quarter of a teaspoon and, gradually adding, bring it to the daily norm: At 8 months, about 50 g, at 9months-60-70 g.
Video: Lift meat
Scheme of meat puree
- 1 day ¼ of vegetables
- Day 2 - ½ teaspoon
- Day 3 - 1 teaspoon
- Day 4 - 2 teaspoons
- Day 5 - 3 teaspoons
- Day 6 3-4 teaspoons + vegetables
At first, it is better to give meat with vegetable puree that the child has already eaten, so that he adapts better to the new product, and iron is better absorbed. Children at the end of the first year of life can already be given 3 varieties of mashed meat.
Baby menu at 7-8 months
At 7-8 months you can start giving babies baby cottage cheese . Start with 1/2 teaspoon. Within a month, the daily volume of cottage cheese consumption by a baby can be increased to 30-40 g. In addition, a child of 8 months is recommended to give sour-milk infant formula. But ordinary yogurt from the store should not be given. At this age, the child should receive 5 g of butter and 5 g (1 teaspoon) of vegetable oil, ¼- yolk - 2-3 times a week.
Baby's menu at 9 months
At the age of 9 months Your baby is already familiar at this age already usually familiar: , egg yolk . You may have already met meat . Therefore, at this age, they usually give already more complex purees and porridges, less homogenized, of various tastes , gradually preparing him for adult nutrition, increasing the variety and quantity of complementary foods. It is desirable to feed the baby at the table with other family members, he must see how his parents eat with pleasure, he learns from them. The amount of food offered should be based on the principles of actively encouraging the baby to eat, it is necessary to continue to gradually change the consistency and increase the variety of complementary foods, adhering to the recommended frequency of introducing complementary foods.
It is desirable to feed the baby at the table with other family members, he must see how his parents eat with pleasure, he learns from them. The amount of food offered should be based on the principles of actively encouraging the baby to eat, it is necessary to continue to gradually change the consistency and increase the variety of complementary foods, adhering to the recommended frequency of introducing complementary foods.
At this age, the child usually gets complementary foods 3 times a day . His diet depends on the age of the start of complementary foods. If the baby began to give new food at 4-5 months, the list of allowed foods will be much wider than if this happened at 6-7 months. Therefore, all this is very individual, there are no absolutely rigid frameworks and recommendations. On the Internet you will find a lot of different advice on baby food, if you are not sure about something, it is better to consult your pediatrician.
From vegetables the baby can be given what he ate before, mixing them: pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots and others, adding 1 tsp. vegetable oil . If the baby does not have skin reactions, then you can give beets . It is also possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups , but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and has not had a reaction to them.
vegetable oil . If the baby does not have skin reactions, then you can give beets . It is also possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups , but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and has not had a reaction to them.
If you have introduced complementary foods, then you need to remember that water is an important part of baby food. You can use purified water or special water for children .
In addition, at 9 months you can give special baby wheat cookies , which the baby will be happy to eat on his own as an adult, white wheat bread, this improves hand motility, improves eating skills, but at the same time he must be supervised.
At this age, you can start giving fish puree from low-fat varieties: river perch, pollock, hake, haddock, zander, saithe - start with ½ teaspoon, bringing up to 40-50 g , watching the reaction of the child , give at lunchtime instead of mashed meat, 1-2 times a week. But a number of pediatricians do not advise giving it up to a year, it is a useful, but highly allergenic product.
But a number of pediatricians do not advise giving it up to a year, it is a useful, but highly allergenic product.
10 month old baby menu
B 10 months usually 2 times a day the child receives mother's breast or special milk formulas . Various cereals: buckwheat, rice, corn, oatmeal, wheat, semolina porridge . Add 5-10 g of butter to cereals . At this age, it is already possible to make complex cereals from 2-3 cereals with which the child is familiar, add various fruits, vegetables: apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries , provided that the child is not allergic to them, or use ready-made cereals with fruit.
From vegetables the baby can be given what he ate earlier, mixing them: pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots, beets and others, adding 1 tsp. vegetable oil . It is also already possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups, but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he did not have a reaction to them.
vegetable oil . It is also already possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups, but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he did not have a reaction to them.
At this age, the baby already usually eats about 40-50 g of baby meat puree from chicken, turkey, rabbit , with good tolerance to cow's milk proteins from veal or beef. If he has been eating meat for a month or more, you can start giving him two-component meat purees , such as chicken and turkey.
At this age, fish puree from low-fat varieties is usually started: river perch, pollock, hake, haddock, zander, pollack with ½ teaspoon, bringing to 40-50 g, monitoring the reaction of the child, it is better to give at lunchtime instead of mashed meat, 1-2 times a week .
At 10 months, children's cottage cheese should be given 2 times a week. Start with 1/2 teaspoon if you have not given it before, the daily amount of cottage cheese at this age 40-50 g .
Start with 1/2 teaspoon if you have not given it before, the daily amount of cottage cheese at this age 40-50 g .
It is recommended to give special sour-milk baby formulas.
At this age, the child can receive 5-10 g of butter and 5 g (1 teaspoon) of vegetable oil, and 2-3 times a week½ - yolk .
Child's menu at 1 year old
The child is one year old. He has already grown up, he already has 6-10 teeth, with which he gnaws everything he sees, he is interested in chewing food, his digestive enzymes already work well and he has already become acquainted with various products: vegetable and fruit purees, various cereal cereals, meat and fish, sour-milk mixtures. In fact, he is already prepared for the transition to a more adult diet. In a year, changing the diet involves turning to new products and gradually changing the way they are prepared and the degree of grinding.
You need to eat 5 times a day with an interval 3.5-4 hours .
semi-liquid dishes should still remain the basis of nutrition, but not only mashed, but also containing small pieces of food . Too dry food should not be given to the baby yet, as he may have difficulty swallowing.
In the year the child already tries to eat with his hands and he should be encouraged to do so. Finely chopped, soft foods can be given eg: small pieces of soft fruit, vegetables, cheese, well-cooked meat, pasta , etc. and foods that dissolve quickly, children's cookies, children's bread - as food with the help of hands.
Must avoid products that can enter the respiratory tract and cause asphyxia - sausages and other hard meat products , nuts (especially peanuts), grapes, raisins, raw carrots, popcorn, round candies . Hold off on this for now.
Hold off on this for now.
In a year, part of the children are without mother's milk. But if your baby is still not weaned - do not rush, if possible, give him a breast before bed at night. You can also breastfeed between main meals. At this age, the child receives all the main vitamins and minerals from food, but he can get a number of biologically active components from breast milk.
Dairy products
Dairy products still occupy an important place in the child's diet, it is a source of calcium, B vitamins, protein, milk sugar and fat. It is better to use special baby milk (marked with a triple on the package), baby fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt in total 500-600 ml per day .
Cottage cheese
The child should be given cottage cheese. The daily dose of cottage cheese after 1 year can be increased up to 70 g per day . It can be given pureed or combined with fruit puree, pudding, casserole. This contributes to the development of chewing skills.
It can be given pureed or combined with fruit puree, pudding, casserole. This contributes to the development of chewing skills.
Butter
Butter can be added to cereals or smeared on wheat bread, biscuits at a dose of up to 12 g per day.
Low fat sour cream and cream
After 1 year, you can give low-fat sour cream and cream in small quantities.
Vegetables
Every year a child must be given various vegetables, it is good to combine them with protein products, meat . The vegetable diet can now be diversified with green peas, tomatoes, turnips, beets, carrots, spinach in the form of mashed potatoes. Legumes are still better not to give.
Fruits and berries
After 1 year, you can gradually introduce the baby to new fruits and berries: strawberries, cherries, cherries, kiwi, currants, gooseberries, chokeberries, sea buckthorn, raspberries, blackberries, cranberries, blueberries, lingonberries and even citrus fruits . But do it gradually, watching the reaction of the child. Berries with a dense peel (gooseberries) are best mashed, while soft juicy fruits (peaches, strawberries, apricots, kiwi) can be offered to the baby in pieces.
But do it gradually, watching the reaction of the child. Berries with a dense peel (gooseberries) are best mashed, while soft juicy fruits (peaches, strawberries, apricots, kiwi) can be offered to the baby in pieces.
Daily dose of fruits - approx.
Meat products
Meat products can be given in the form of steam cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, meat souffle and pudding in an amount up to 100 g daily - beef, veal, lean pork, rabbit, turkey, chicken.
Fish
Fish can be given once or twice a week for 30-40 g per meal as a substitute for meat dishes
Eggs
Chicken, quail eggs give boiled or in the form of omelettes in milk, you can try with vegetables.
Kashi
Porridge can be cooked from rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, corn, millet, semolina. At this age, they should still have a uniform consistency, so it will be easier for him to swallow. You can use ready-made industrial, children's instant cereals, for example, various multi-cereal cereals, in which fruits, crackers, cereals have already been added. Give 1 time per day.
At this age, they should still have a uniform consistency, so it will be easier for him to swallow. You can use ready-made industrial, children's instant cereals, for example, various multi-cereal cereals, in which fruits, crackers, cereals have already been added. Give 1 time per day.
Water
Be sure to give the child to drink clean water, better for children in bottles, as much as he wants . In addition to her baby can drink vegetable and fruit juices, dairy products, compotes, weak tea.
No need to give:
no need to give confectionery and sweets to a child 0008 . From sweets at this age, you can sometimes give marmalade, dried fruits and cookies.
Do not give sausages and sausages , they are rarely prepared from high quality meats and are rich in various food additives
Calorie content and volume
0101 1200 ml .