First 100 foods for baby
Baby Led Weaning: 100 of the Best First Foods to Feed Your Baby
Around 6 months old is a good time to start baby led weaning with your baby!
Of course check with your doctor to make sure it’s a good time for you and your child to start.
If you are like me, you did lots of research on the best foods to feed your child, what to feed him first, how to feed him and how much to feed him.
It was important to me, like any mom, that my son get the best and healthiest start to life as possible.
Enter Baby Led Weaning!
(This post contains affiliate links, meaning I make a small commission from any links you click and buy from. I only recommend products I love and appreciate your support! Find the full disclosure policy here.)
I first heard about it before I was even pregnant, but really started researching baby led weaning when my son was born.
Baby led weaning is about letting your child learn to feed themselves from the very beginning.
It’s about keeping the stress out of feeding your child, and allowing them to lead.
D has done so well with solids from the very beginning, and I’ve never been stressed about it. I think that the way we’ve let him eat has helped so much.
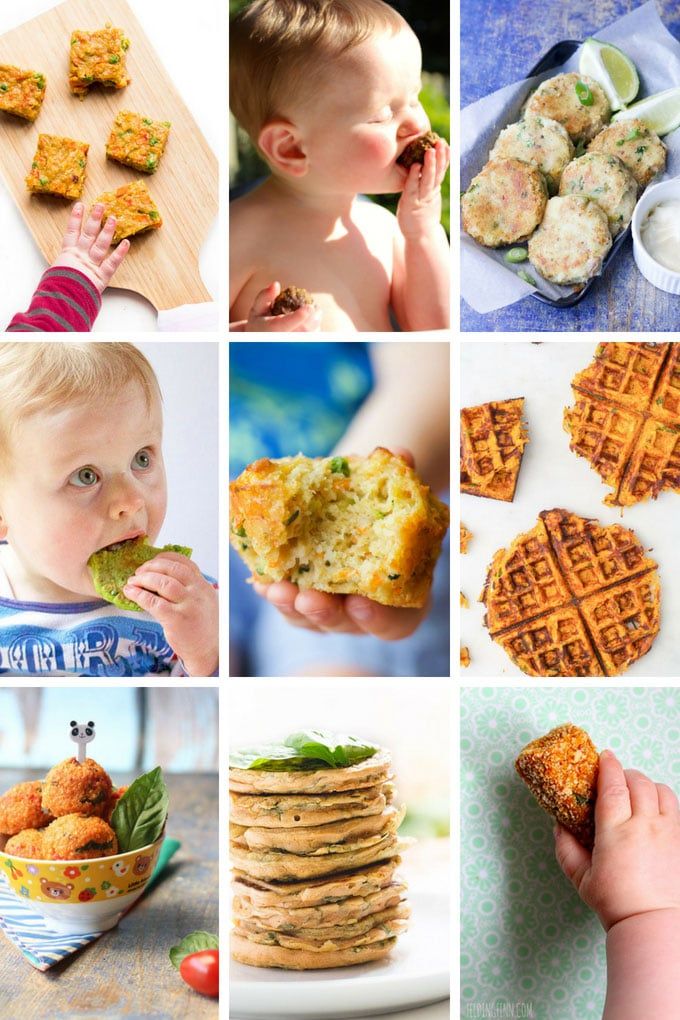
Some people who follow baby led weaning have the goal of feeding their child 100 different foods by the time they are one year old!
The idea with this goal is to make sure you feed your child a wide variety of textures, flavors and colors to get them used to it. They are less likely to be super picky as a toddler!
It can seem daunting, but with D’s birthday right around the corner, I’ve come up with a list of 100 different foods we’ve given him over the last 6 months.
It really wasn’t that hard because once he got the hang of it, we were able to feed him pretty much anything we ate (with some modifications here and there).
D has loved the variety of foods we’ve fed him, and now that he’s reaching toddlerhood, I’m not so worried about him getting picky.
Even when he does decide to pick and choose some things he likes and doesn’t like, I know that there are a whole bunch of things I can fall back on!
HOW TO GET STARTED WITH BABY LED WEANING
RELATED BABY FEEDING POSTS:
How to Start Baby Led Weaning with Your Baby at 6 Months OldI absolutely love this book as a reference guide for all things baby led weaning. It’s full of beautiful pictures with easy and creative recipes, information on how to get started, benefits to the baby led weaning approach and so much more!
EZPZ baby feeding supplies are always my go to. They are made of 100% silicone, super easy to clean and created by a pediatric food specialist. So, you know you’re getting the best with them!
They have an adorable First Foods Set that will easily get you started.
Bloom Baby has the coolest looking highchairs. I absolutely love that you can use them for your newborn as an adorable cradle, right up to a regular kids chair for up to 8 year olds.
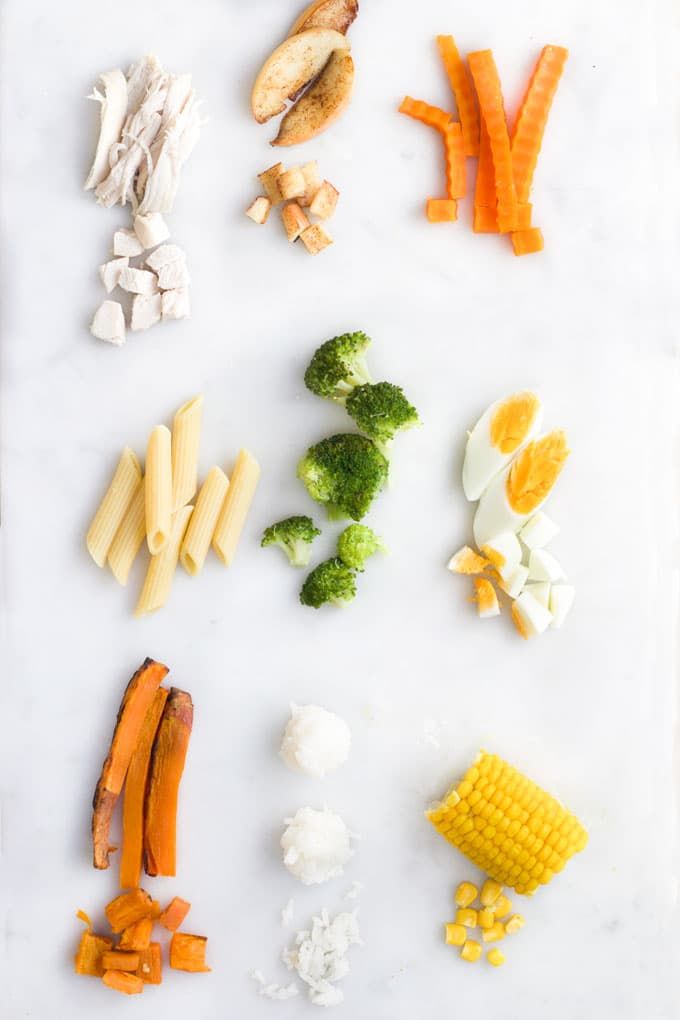
Here is the list of 100 first foods for baby led weaning that we used! If you want the list in printable form, check it out below.
Loading…
100 FIRST FOODS
Fruit
- Apples
- Bananas
- Blackberries
- Raspberries
- Strawberries
- Blueberries
- Peaches
- Mangos
- Avocado
- Grapes
- Tomato
- Melon
- Cantaloupe
- Pineapple
- Pear
- Oranges
- Nectarines
- Apricots
- Kiwi
- Lime
- Lemon
- Watermelon
- Grapefruit
Vegetables
- Carrots
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Zucchini
- Cucumber
- Peppers
- Brussel sprouts
- Kale
- Pickles
- Peas
- Onion
- Green onion
- Parsnips
- Spaghetti squash
- Beets
- Pumpkin
- Spinach
- Corn
- Cabbage
- Green beans
- Lettuce
- Eggplant
- Turnip
- Asparagus
- Garlic
Starch
- Potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Butternut squash
- Gnocchi
- Spaghetti squash
Meat/Protein
- Chicken
- Ground beef
- Ground turkey
- Halibut
- Salmon
- Eggs
- Bacon
- Chicken/Turkey bacon
- Tofu
- Pork
- Shrimp
Grains
- Pasta
- Bread
- Oatmeal
- Rice
- Whole wheat tortilla
- Pita
- Couscous
- Quinoa
Dairy
- Cheddar cheese
- Mozzarella cheese
- Greek yogurt
- Cottage cheese
- Goat cheese
- Cream cheese
- Sour cream
- Parmesan cheese
Legumes
- Black beans
- White beans
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
Other
- Pesto
- Rice cake
- Peanut butter
- Almond butter
- Coconut oil
- Pasta sauce
- Salsa
- Crackers
- Cheerios
Prepped
- Smoothie
- Pancakes
- Muffins
- Hummus
- Soup
- Waffles
- Birthday Cake!
In the last 6 months I’ve made more muffins and pancakes than I’ve ever made in my life.
Of course they are the modified baby versions, but they are amazing for quick breakfasts and snacks.
You can find a ton of recipes on Pinterest from easy blueberry muffins to veggie and fish fritters! I can literally make anything into a muffin and/or a pancake and my son will eat it.
Let me know if your baby has tried any of these and where you are in your baby led weaning journey!
Printable Baby Food Chart: BLW, Purees, Finger Foods
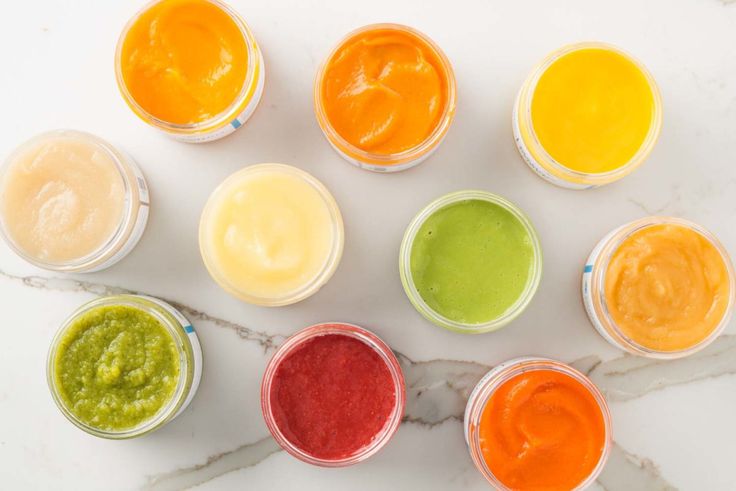
Make feeding your baby easier with this free, downloadable baby food chart. It has straight forward ideas for what to feed baby from when they start solids on up to one year—including purees, baby-led weaning style foods, finger foods, and more.
Baby Food Chart
Starting solids with a baby can be so fun and often a little challenging—but this baby food chart will help. I’ve compiled my best ideas for which foods to serve based on age and development of the baby to make it easy for you to make decisions in the kitchen.
This infant feeding chart is meant to help remind you of options you have at each age. It is not meant to add any pressure or function as a checklist of foods you have to serve (unless you want to do that!).
TIP: Download your free printable baby food chart here.
What baby foods should you start with?
Whether you start with purees or baby led weaning, starting with flavorful and nutrient-dense foods is a simple way to think about introducing foods to a baby. I love simple foods like roasted sweet potato, avocado, banana, and apple puree as first foods for a baby.
Remember that a first food is just that—a first food. It is not going to be the sole thing that determines how your child likes all foods. It can be sweet or savory, or from a variety of food groups. I would do your best to make sure that the food is easy to eat, has some flavor, and that the environment in which you offer it is free from pressure and, maybe even joyful!
What age should baby start eating foods?
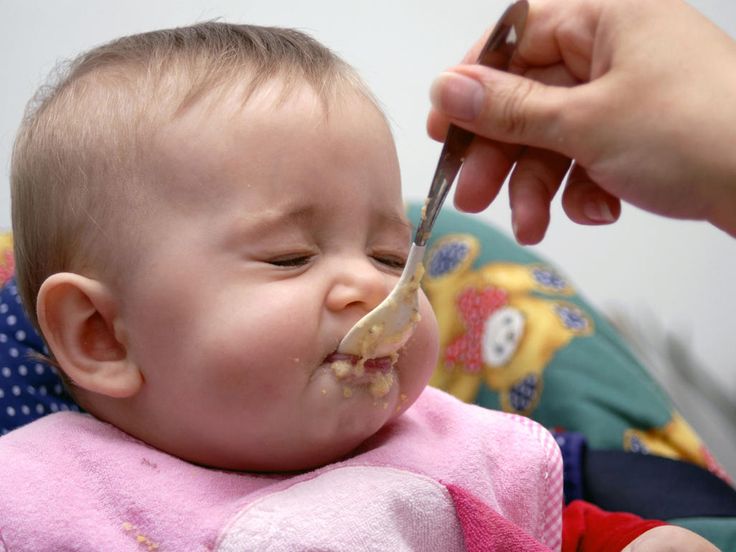
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends waiting to start solids until a baby is 6 months, and to go with wide variety of foods, introduced one at a time. But many pediatricians still say it’s okay to start rice cereal at 4 months.
But many pediatricians still say it’s okay to start rice cereal at 4 months.
If your pediatrician recommends this at the 4 month check up, ask their thoughts on the recommendation from the AAP.
TIP: Learn more about starting solids here.
How much food should I feed my baby?
The best way to know the right amount of food to give to a baby is to follow their lead. It should be very clear when a baby is done eating—they will close their mouth, turn their head, and generally make it very hard to feed them. (They may also play with their food, which is a fine way for them to interact with the foods at this early stage.)
It’s okay if baby eats very little to start. It’s also okay if they surprise you by being very interested in food!
TIP: Download your free printable baby food chart here.
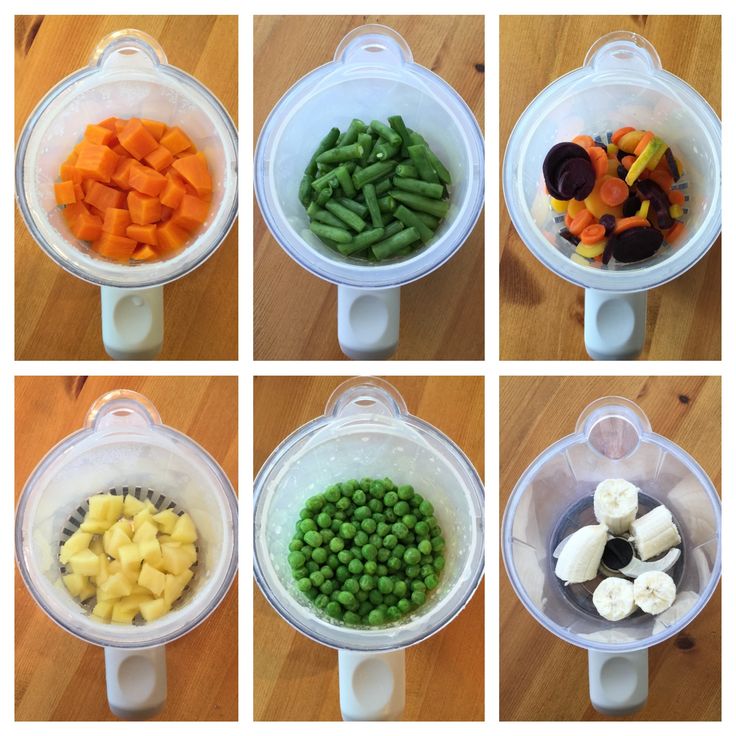
6 Month Baby Food Chart for Purees
If you’re ready to start solids with a baby, here are some foods you may want to start with. This list is perhaps more broad than you expect, but more recent research shows that it’s a good idea to introduce potential allergenic foods earlier and that lots of flavor is a great way to set baby up for eating a range of foods as they grow.
This list is perhaps more broad than you expect, but more recent research shows that it’s a good idea to introduce potential allergenic foods earlier and that lots of flavor is a great way to set baby up for eating a range of foods as they grow.
Don’t feel like you need to serve all of these foods (you 100% don’t!), but it should give you a range of ideas to consider based on season, availability, and your own preference.
- Almond butter puree
- Apple Puree
- Avocado puree
- Banana puree
- Baby oatmeal
- Bean puree
- Butternut squash puree
- Egg yolk, hard cooked mashed with water
- Green bean puree
- Melon puree
- Pea puree
- Peach puree
- Peanut Butter Puree
- Pear puree
- Pumpkin puree
- Sweet potato puree
- Whole milk plain yogurt
- Single ingredient baby food
TIP: Find more in depth details on how to know if your baby is ready to start solids here.
6 Month Baby Food Chart for Baby Led Weaning
If you decide to use the baby led weaning method of feeding, you’ll want to cut these foods into the shape of a finger or larger. The foods should also be soft and easily squishable between two fingers—like the texture of a roasted sweet potato wedge or ripe avocado.
You don’t need to feel like you have to serve all of these foods by any means, but it should give you a range of ideas.
- Apple, roasted wedge
- Avocado spears
- Banana
- Beef, ground (large piece)
- Beef hamburger patty (sliced)
- Beet, steamed or roasted
- Broccoli florets, roasted/steamed
- Cauliflower florets, roasted/steamed
- Chicken, dark meat shredded
- Cucumber
- Green bean
- Egg, hard cooked
- Egg in omelet, sliced
- Figs, halved
- Lamb
- Mango slice
- Meatball
- Melon slices
- Peach, very ripe slice
- Pear, very ripe slice
- Potato, roasted wedges
- Steak slice
- Sweet potato, roasted wedges
- Toast with mashed avocado
- Toast with mashed sweet potato
- Toast with light smear of peanut butter
- Toast with mashed hard cooked egg
- Watermelon slice
- WiId salmon
TIP: Find my Ultimate Guide to Baby Led Weaning here.
7 Month Baby Food Chart
With a 7 month old baby, you can add in a few more foods including those with more acid like citrus. Continue serving the foods on the 6th month list, or introduce ones that you didn’t get to in that first month.
- Baby rice crackers
- Bean puree
- Beet puree
- Brussels Sprouts, pureed (or large piece for BLW)
- Guacamole
- Kiwi puree (or large piece for BLW)
- Hummus
- Mango Puree
- Mixed ingredient baby foods
- Orange segment for BLW
- Pineapple puree (or large piece for BLW)
- Prune puree
- Strawberry puree (or large strawberry for BLW)
- Spinach puree
- Smoothies (simple)
- Tomato sauce
- Tomato sauce with ground meat
TIP: Try my 10 easy No Cook Baby Foods.
9 Month Baby Food Chart
As a baby nears the 9 and 10 month mark, they will begin to be able to pick up small, pea-size pieces of foods with their fingers. This development of the “pincer grasp” means they are ready to start sampling table foods.
This development of the “pincer grasp” means they are ready to start sampling table foods.
A good rule of thumb is to cut foods to about the size of a pea and to serve them very soft and easily squishable between your fingers.
Bread-like textures in foods like pancakes and muffins may be difficult for your child, so you may want to moisten them with water, applesauce, yogurt, breastmilk, or formula.
Remember that babies learn to eat a variety of paces, so follow the lead of your baby and avoid pressuring them to eat foods or amounts of foods that they aren’t ready for. If a baby turns their head away, closes their mouth, shakes their head, or cries, they are done with food and it’s okay to end the meal.
Continue serving foods from the previous months. And try adding:
- Banana, diced and mashed slightly as needed
- Barley, cooked until very soft
- Beans, slightly mashed
- Beef, ground
- Blueberries, diced
- Cheese, shredded
- Chex cereal
- Chia seed in smoothies, yogurt or oatmeal
- Chicken, ground
- Chicken, shredded and chopped into small pieces
- Clementines, diced (you may want to remove the slightly tough membrane)
- Cottage cheese
- Corn
- Flaxseed in smoothies, yogurt or oatmeal
- Goat cheese, soft crumbles
- Grapes, diced (never whole)
- Kefir, plain
- Meatball, diced
- Muffins, diced (moistened if needed)
- Millet
- O cereal
- Oatmeal
- Overnight oats
- Pasta
- Peas
- Potatoes, roasted or mashed
- Puffs
- Raspberries, diced
- Pancake, diced (moistened as needed with applesauce)
- Quinoa
- Rice
- Salmon, small pieces
- Tofu, diced
- Tomatoes, fresh
- Tilapia, small pieces
- Turkey, ground
TIP: Find my best Early Finger Foods, which will cover this stage and early toddlerhood.
Best First Finger Foods for Baby
I put together my go-to first finger foods for babies, which may help you narrow down which foods to start with. Each of these is a nutritious whole food that’s soft and easy for baby to eat. It’s helpful that many of these foods are ones that us grownups like too, so it should make meal planning and prep for the little ones easier on you!
Printable Baby Food Chart
Grab your free copy of my downloadable Baby Food Chart with access to my entire Resource Library of Printable charts by signing up for my newsletter.
You May Also Like
- ABC Baby Muffins
- Master List of Baby Snacks
- Extra-Veggie Baby Soup
- Sweet Potato Teething Biscuits
- Master List of Baby Food Recipes
I’d love to hear your feedback on this chart, so please comment below! I always love to hear from you guys.
This post was first published Jan 2019.
Detailed list of all foods for the first 90 days of introduction of complementary foods for a child.

Download the table of complementary foods in PDF format:
- Zucchini. Zucchini puree contains only 24 kcal per 100 grams of finished product. Proteins -0.6; fat - 0.3; carbohydrates - 4.6. Contains calcium, magnesium, vitamins A, C, B6 and iron. To save vitamins, we will prepare the first puree for a child for a couple. Zucchini cooks quickly, 10 minutes is enough. The first serving is 5 grams (a teaspoon), even less, at the tip of a spoon. We'll give you a taste of the new flavor. Take a small circle of zucchini (we choose the smallest, youngest baby zucchini, the puree will be sweet), wash well (you don’t need to clean and remove the seeds from young zucchini), cook for 10 minutes for a couple and grind through a sieve. Let the child try. The feeding temperature should be around 40 degrees. DEFINITELY try the puree yourself before giving it to a child! Not bitter, not sour, are there any strange aftertastes that may indicate a poor quality vegetable? We offer zucchini for 5-7 days according to the scheme: 5 grams - 10 grams - 20 - 40 - 60 - 60 - 60.
 The zucchini has passed the test! Let's put it aside for now and move on to the next product.
The zucchini has passed the test! Let's put it aside for now and move on to the next product. - Cauliflower. Cauliflower puree contains 33 kcal per 100 grams of finished product. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates, respectively: 1.6 / 0.7 / 5.4. Contains calcium, magnesium, iron, vitamins C and B6. To save vitamins, we cook for a couple. We divide the cabbage into small inflorescences, cook for 15 minutes. Grind the first portion (5 grams) on a sieve, prepare large portions with an immersion blender with the addition of boiled baby water, so that the consistency is the same as that of the zucchini. Cabbage, unlike zucchini, contains less water, so it needs to be added. We give according to the scheme: 5-10-20-40-60-60-60. Recall that it is not necessary to give all 7 days, five days will be enough to test for allergens.
- Broccoli. For 100 grams of finished puree 34 kcal. Proteins 2.8; Fats 0.4; Carbohydrates 6.6. Broccoli contains a lot of vitamin A, as well as calcium, magnesium, iron and vitamin C.
 We prepare mashed potatoes according to the same principle as cauliflower.
We prepare mashed potatoes according to the same principle as cauliflower. - Buckwheat porridge. From vegetables to cereals. It's time to try the cereals. Previously, it was recommended that babies start complementary foods with cereals if they are not gaining weight well, or start complementary foods before six months. But it's all MYTH! Well, the baby will not start gaining better if instead of a portion of fatty milk he receives 60 grams of lean porridge cooked in water. Yes Yes! The first cereals are dairy-free, sugar-free and gluten-free! It is important! For the first test, it is still recommended to introduce special baby cereals, which are sold in stores. Why? Because cereals for children's cereals are not treated with rodenticides, unlike ordinary cereals on store shelves. Yes, and making flour from ordinary buckwheat and cooking 5 grams of such porridge will not be so easy as pouring half a teaspoon of prepared store-bought baby porridge with water, stir and give to the baby.
 Therefore, we suggest buying a pack of special children's dairy-free buckwheat for the first try and cook it according to the cooking method indicated on the package.
Therefore, we suggest buying a pack of special children's dairy-free buckwheat for the first try and cook it according to the cooking method indicated on the package. - Rice porridge. Same as buckwheat: dairy-free, gluten-free, salt-free and sugar-free. We look at the energy value on the packaging.
- Corn porridge. This porridge is the most high-calorie of the three, so it is still better to introduce it as the third one. The scheme is still the same as with vegetables: 5-10-20-40-60-60-60 (the last two days are optional). When the volume of any of the cereals reaches 40 and 60 grams, you can add a little already introduced vegetables to it (also up to 40 grams), so that the porridge is not too viscous and monotonous for the child (“in a dry bag”, as we usually say).
- Pumpkin. Puree and pumpkin will already contain 88 kcal per 100 grams of the finished product. Thus, we gradually raise the calorie content of products.
 Proteins / fats / carbohydrates - 1.7 / 6.2 / 6.3. We clean and cut it into cubes, steam the pumpkin, about 15 minutes. Puree is introduced as before 5-10-20-40-60-60-60. For portions of 40 and 60 grams, you can try to give it together with the already tested porridge and bring the total volume up to 100 grams.
Proteins / fats / carbohydrates - 1.7 / 6.2 / 6.3. We clean and cut it into cubes, steam the pumpkin, about 15 minutes. Puree is introduced as before 5-10-20-40-60-60-60. For portions of 40 and 60 grams, you can try to give it together with the already tested porridge and bring the total volume up to 100 grams. - Apple. It's time to taste fruit. Why weren't they introduced earlier? Because, from birth, a child has a love for sweets, and if you start complementary foods with fruits, then there is a high probability that you will eat vegetables yourself later. We start complementary foods from the most tasteless foods incrementally. The finished puree contains 85 kcal per 100 grams of the finished product. How to cook: wash, peel, cut apples and send to a double boiler or cook in boiling water for 10 minutes (a couple more vitamins will be preserved). Scheme 5-10-20-40-60-60-60. By the way, with regard to fruits, a dose of 60, maximum 80 grams for a child up to a year is quite sufficient.
 If we then increase the portions of vegetables and cereals, then we will leave the fruits. A large amount of sugar is not good for a child. Up to 40 grams we give applesauce as a separate dish, from 40 grams and more we mix with cereals. Now we will gradually increase the volume and replace breakfast with porridge with fruit, seasoned with a small amount of butter (at the rate of 2 grams of butter per 100 grams of porridge).
If we then increase the portions of vegetables and cereals, then we will leave the fruits. A large amount of sugar is not good for a child. Up to 40 grams we give applesauce as a separate dish, from 40 grams and more we mix with cereals. Now we will gradually increase the volume and replace breakfast with porridge with fruit, seasoned with a small amount of butter (at the rate of 2 grams of butter per 100 grams of porridge). - Rabbit. It's time to introduce meat! At this point, the baby should be about 8 months old. It is recommended to start with a rabbit, as this is the most dietary meat. How to cook: we twist the meat in a meat grinder, form small meatballs and weld them a little in boiling water. It’s good if you have a kitchen scale at home and you can immediately prepare meatballs for the required 5-10-20-40 and 50 grams. We throw the boiled meatballs into a colander so that the glass is excess water and they cool, then we freeze. Our semi-finished product is ready! The first 5 and 10 grams are given separately.
 Boil or steam again and grind with a blender. Starting from 20 grams, grind together with the introduced vegetables. Now you can gradually increase the portions and replace lunch with vegetables and meat seasoned with a small amount of vegetable oil (at the rate of 1 teaspoon per 100 grams of vegetables). Meat, unlike all other products that are necessarily introduced in the first half of the day, is introduced at lunchtime.
Boil or steam again and grind with a blender. Starting from 20 grams, grind together with the introduced vegetables. Now you can gradually increase the portions and replace lunch with vegetables and meat seasoned with a small amount of vegetable oil (at the rate of 1 teaspoon per 100 grams of vegetables). Meat, unlike all other products that are necessarily introduced in the first half of the day, is introduced at lunchtime. - Prunes. We prepare mashed potatoes in the same way as from apples, but first, prunes need to be washed, peeled and soaked for a couple of hours in water, then steamed and chopped with a blender. Portions are the same as for an apple: 5-10-20-40-60-60-60. Starting from 40 grams, mix with porridge.
- Turkey. We choose the fillet and give it according to the principle of the rabbit.
- Pear, banana, apricot, peach, plum. We introduce these fruits one by one according to the same principle as we introduced apple and prunes.

So, we have sorted out the safest products for the baby! Selected according to our climate, according to their energy value, composition and vitamin content. To put together a correct balanced diet, you need to know some WHO (World Health Organization) recommendations for complementary foods:
- At 6-8 months, the child should receive 60% kcal from breast milk and 40% kcal per day from complementary foods ;
- At 9-11 months, the baby should receive 45% kcal from breast milk and already 55% kcal per day from complementary foods ;
- The volume of the baby's stomach is approximately equal to 30 ml/kg of the baby's weight;
- At 6-8 months, smoothly go to 2 meals based on complementary foods (breakfast and lunch) and the minimum energy density of the meal should be 0.9 kcal / g for breastfeeding or 1.7 kcal / g for artificial feeding;
- Protein requirements for babies 6-9months 1.
 25 g/kg body weight;
25 g/kg body weight; - Fat should make up 30-40% of the daily calorie intake of the entire diet.
Download the PDF format table:
Ribricapoprome Malyuk
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods for a child 4 - 12 months: first complementary foods, menu, scheme, tables, tables of nutrition of the baby
9009 baby food is a kind of fusion of practical experience and the latest scientific developments. They are based on the recommendations of the European Association of Pediatric Gastroenterologists, Hepatologists, Nutritionists ESPGHAN , American Academy of Pediatrics AAP and national guidelines from relevant ministries and associations.
Modern recommendations are based on the analysis of the results of many studies on the composition, timing of the introduction of complementary foods in Europe for healthy full-term newborns, taking into account various aspects of the introduction of complementary foods, its impact on indicators of physical and mental development. Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods is very important for the growth and development of the child, as well as an outstanding stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to feeding from the general table.
Timely introduction of complementary foods contributes to the optimal development of all systems and organs of the child, physical parameters, psychomotor development, and the activity of the nervous system. The period of introduction of complementary foods is very important for the growth and development of the child, as well as an outstanding stage in the transition of the child from breastfeeding to feeding from the general table.
- It is inappropriate to develop separate recommendations for the introduction of complementary foods for breastfed or artificially fed children, the approaches in these cases are the same
- Breast milk mothers remains the gold standard of exclusive breastfeeding for at least 4 months (17 weeks) of an infant's life, up to 6 months (26 weeks), the standard of exclusive or predominant breastfeeding
- The digestive tract and kidney function are mature enough for a baby to accept complementary foods at 4 months of age, and between 5 and 6 months the baby develops the necessary motor skills to consume solid foods.
 Therefore, at this age, it is important to give food of the right consistency and in the right way
Therefore, at this age, it is important to give food of the right consistency and in the right way - A well-nourished mother can provide all the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals her baby needs through exclusive breastfeeding up to a maximum of 6 months of age
- Some children may need iron supplementation earlier than 6 months
- It is important to continue breastfeeding in parallel with the introduction of complementary foods. This has been proven to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, as well as hospitalizations in a child
- When comparing initiation of complementary foods at 4 or 6 months of age, there were no significant differences in the effect on growth and body weight, development of obesity during the first 3 years of life
- At the same time, a high risk of developing overweight and obesity has been established with the introduction of complementary foods before 4 months of age
- Complementary foods (solid or liquid food other than breast milk or infant formula) should be started no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6 months
- With age, with the introduction of complementary foods, the child should be offered food varied in texture, texture, taste, smell
- Children have an inborn tendency to distinguish and prefer sweet and salty foods, reluctantly eat bitter, which we cannot change.
 But we can shape and adjust the child's taste preferences through training, systematically offering the child foods with different tastes, including sour, bitter green vegetables
But we can shape and adjust the child's taste preferences through training, systematically offering the child foods with different tastes, including sour, bitter green vegetables - Whole cow's milk is not recommended for children under 12 months of age. The use of cow's milk is associated with the intake of an increased amount of energy, protein, fat, and lower - iron. Therefore, children who consumed large amounts of cow's milk at an early age had a higher risk of developing iron deficiency anemia
- Eating more protein when complementary foods increase the risk of overweight and obesity, especially in individuals with a predisposition to this, so protein intake should not exceed 15% of energy intake during the day
- iron requirements are very high during the entire period of complementary feeding, so iron-rich foods must be ensured, especially for breastfed babies
- Allergenic products can be administered from the age of 4 months at any time, since it is during this period that immune tolerance to the allergen is formed.
 For example, children at high risk of developing allergic reactions to peanuts should be administered at 4-12 months of age under specialist supervision. No relationship was found between the timing of the introduction of allergenic complementary foods and the development of allergic or immunological diseases. However, this does not mean the need for early introduction of allergenic products to everyone, but it emphasizes that there is no need to postpone the introduction of allergenic products after 4 months for a longer period;
For example, children at high risk of developing allergic reactions to peanuts should be administered at 4-12 months of age under specialist supervision. No relationship was found between the timing of the introduction of allergenic complementary foods and the development of allergic or immunological diseases. However, this does not mean the need for early introduction of allergenic products to everyone, but it emphasizes that there is no need to postpone the introduction of allergenic products after 4 months for a longer period; - Gluten can be offered to a child aged 4-12 months, but large amounts of gluten should be avoided during the first weeks after initiation of its introduction, thereafter a safe amount has not been established. The type of feeding (breast/artificial) was not identified with the introduction of gluten to reduce the risk of developing celiac disease, type 1 diabetes;
- Sugar or salt should not be added to complementary foods, and sweetened drinks and juices should be avoided.
 Sugary drinks are liked by babies in the first months, but if they are not given, but after 6 months, the children no longer like them very much. Sugar affects future eating behavior. Sugar is an important factor in the development of caries - it contributes to caries, as glucans can be formed, which increase the adhesion of bacteria to tooth enamel, disrupt the diffusion balance of acid and buffer systems, which ultimately contributes to damage to the enamel.
Sugary drinks are liked by babies in the first months, but if they are not given, but after 6 months, the children no longer like them very much. Sugar affects future eating behavior. Sugar is an important factor in the development of caries - it contributes to caries, as glucans can be formed, which increase the adhesion of bacteria to tooth enamel, disrupt the diffusion balance of acid and buffer systems, which ultimately contributes to damage to the enamel. - Vegetarian diets are contraindicated in young children due to the risk of vitamin B12, iron, zinc, folate, long-chain fatty acid, protein and calcium deficiencies, which can lead to irreversible adverse effects and impaired cognitive development;
- Vegetarian diet can only be used under the close supervision of a doctor and nutritionist, with the obligatory additional administration of vitamins B, D, iron, zinc, calcium, proteins, PUFAs, which can ensure the appropriate growth and development of the child.
 It is important that parents should be aware of the risk of irreversible harmful consequences (mental disability, death of the child) that may develop if they do not follow the recommendations of specialists.
It is important that parents should be aware of the risk of irreversible harmful consequences (mental disability, death of the child) that may develop if they do not follow the recommendations of specialists.
The General Rules for the introduction of complementary foods for children of the first year of life:
- enter the first feeding It is better in the morning feeding 9-11 in the morning to trace the reaction of the child to the new product.
- Without added sugar and salt .
- Give the first complementary foods to the child when he is calm and not tired .
- Start with 0.5-2 teaspoons. If the child refuses, do not insist, try to give later or the next day.
- If the reaction is normal - no rash, no skin changes, no stool changes, double the dose the next day.
 Gradually bring the first complementary foods of the child to the age norm 80-200 g
Gradually bring the first complementary foods of the child to the age norm 80-200 g - If there is an allergic reaction or other intolerance reaction - refuse to introduce this complementary food for three days, if the adverse reaction occurs again - do not give this product, contact your pediatrician.
- Each subsequent new complementary food must be one-component only: marrow, cabbage, broccoli, buckwheat, meat, etc.
- Mixed food dish give when the child has already become acquainted with all the products separately.
- It is not advisable to introduce new products three days before and after vaccinations.
If you are thinking about introducing complementary foods, then your child should already have certain signs of readiness for this:
- Holds head
- Able to stand alone, practically without support, sit on a special highchair with side support
- Opens mouth when a spoonful of food is brought
- Turns away from a spoonful of food when not hungry
- Closes mouth with spoon in mouth Holds food in mouth and then swallows rather than pushing or spitting it out
The first complementary foods at 4 months
The age of 4 months as the minimum for the introduction of complementary foods was also chosen because at 4 months the child's gastrointestinal tract becomes more mature: the initially increased permeability of the small intestine mucosa decreases, a series of digestive enzymes, a sufficient level of local immunity is formed, the child acquires the ability to swallow semi-liquid and thicker food, associated with the extinction of the “spoon ejection reflex”.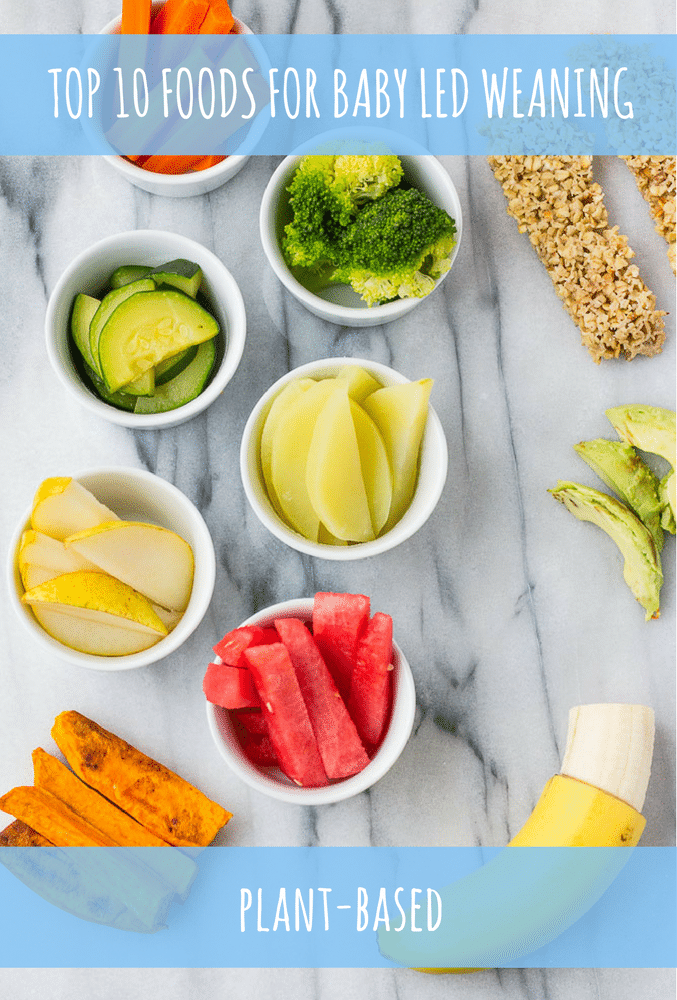
Therefore, to the question whether it is necessary to give complementary foods to a child of 3 months , one can unequivocally answer: no, it's too early!
But 4 months, this is the time when you can think about the introduction of complementary foods. At the same time, it should be remembered that at the age of 4 months, the child has enough mother's milk or a highly adapted milk formula for its full development. In addition, when they talk about complementary foods at 4 months, they usually mean the end of the 4th month of life. It is important to continue breastfeeding in parallel with the introduction of complementary foods.
Video: complementary foods at 4 months
If you introduce complementary foods at the 4th month of the child -this is usually a one-component vegetable or fruit puree 9000 if the child does not gain weight well enough. , then it can be gluten-free porridges: rice and buckwheat . It is better to start with vegetable puree. Kids are smart and if he tries a sweeter fruit puree, he can refuse vegetable puree for quite some time and you may have difficulty introducing this very healthy dish.
, then it can be gluten-free porridges: rice and buckwheat . It is better to start with vegetable puree. Kids are smart and if he tries a sweeter fruit puree, he can refuse vegetable puree for quite some time and you may have difficulty introducing this very healthy dish.
What is useful in vegetable supplements and what is the best way to prepare it?
Vegetable puree - for the first feeding can be prepared from cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, broccoli - these are low-allergenic products, are among the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contain a large amount of healthy proteins, fiber and vitamins, microelements ! Fiber helps move food through the digestive tract and promote beneficial microflora in the gut. Pectins absorb and remove toxins from the baby's body. Vegetables have a positive effect on the acid-base balance of the body, creating conditions for the proper functioning of all organs and systems.
Cauliflower - is a good source of fiber, protein, minerals and vitamins: A, B1, B2, B3 (PP), B6, as well as a small amount of vitamins K, D and tocopherol (vitamin E). In the inflorescences of cabbage there is a lot of magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, iron. It contains twice as much iron as green peas, peppers and lettuce. Cauliflower protein is easily digestible and its content is quite high. Cauliflower protein contains essential vitamin U (methionine). It is one of the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the human body. Other essential amino acids are also present in a small amount: arginine, tryptophan.
Zucchini - rich in vitamins and microelements. It contains potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins C, B1 and B2 and others, folic acid. Which plays an important role in the processes of hematopoiesis. Zucchini is rich in such important trace elements as iron and copper. They are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normalization of metabolism, as well as for the formation of hemoglobin, which is a good prevention of anemia.
They are necessary for the formation of nervous tissue, normalization of metabolism, as well as for the formation of hemoglobin, which is a good prevention of anemia.
Broccoli is a very useful vegetable, which is a kind of cauliflower. Pleasant soft taste and good digestibility of the product, unique composition have a beneficial effect on the health of both adults and children. Eat unopened cabbage inflorescences. This is also a low-allergenic vegetable, rich in protein, fiber, vitamins, calcium, iron, trace elements and even phytoncides. The content of calcium and magnesium is sufficient to balance the functioning of the nervous system, ensure the normal regulation of the child's sleep and wake cycle, and good stress resistance. A child with such nutrition becomes calmer, less excited and naughty.
Broccoli is the leader in choline and methionine content. Only 50 g of broccoli provides the baby with a full set of nutrients for a day.
Pumpkin - the largest vegetable on Earth. It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of useful proteins, fiber and vitamins, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, K, iron, potassium, magnesium, trace elements that are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen immunity and help fight inflammation, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. By the content of carotene, pumpkin exceeds carrots by 5 times.
It is one of the ten most useful vegetables in the diet of children, contains a large amount of useful proteins, fiber and vitamins, including beta-carotene, vitamin C, E, K, iron, potassium, magnesium, trace elements that are indispensable for children's nutrition, as they strengthen immunity and help fight inflammation, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. By the content of carotene, pumpkin exceeds carrots by 5 times.
Vitamins and microelements contained in pumpkin help the child grow, provide healthy sleep, are responsible for the condition of the skin and eyes, improve metabolic processes, and accelerate the removal of harmful substances from the child's body. Due to its beneficial qualities, pumpkin can be one of the first types of complementary foods for an infant.
All vegetable purees have a specific vegetable smell, this is absolutely normal
0094
Introduction of vegetable puree
Vegetables should be introduced into the child's menu gradually. Start giving each new vegetable in the form of a monocomponent puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon, preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of food allergies or intolerance reactions to this product. If all is well, then the next day, offer him a teaspoon. So gradually you need to bring the portion to 50-100 grams. A serving of vegetable puree per day for an 8-month-old baby is approximately 80 grams. In a year, you can increase up to 150 grams. The next product can be administered no earlier than 4-5 days later. If a child has skin rashes, his stool has changed, then you need to remove the product from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
Start giving each new vegetable in the form of a monocomponent puree in the amount of ½ teaspoon, preferably at breakfast, so you can track the manifestations of food allergies or intolerance reactions to this product. If all is well, then the next day, offer him a teaspoon. So gradually you need to bring the portion to 50-100 grams. A serving of vegetable puree per day for an 8-month-old baby is approximately 80 grams. In a year, you can increase up to 150 grams. The next product can be administered no earlier than 4-5 days later. If a child has skin rashes, his stool has changed, then you need to remove the product from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
If the child does not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in small quantities - 1-2 spoons a day, maybe not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help form the right taste habits in the child.
Fruit puree introduction
Fruit puree is a definite alternative and addition to vegetables. It can be made from apples, bananas - by the way, do you know what a berry is?, sweet varieties of pears. These fruits contain substances useful for babies, vitamins and minerals, including iron, which is extremely necessary for children. Prune puree is somewhat separate, it has a good effect on the baby's digestion, especially with a tendency to constipation, and, of course, also contains many useful substances.
Porridge in the diet of a child in the first year of life.
Porridge can be introduced into the baby's diet at the end of 4 months or at the fifth, sixth month of life. As a rule, they go as a second food after vegetable or fruit puree. But if your child is not gaining weight very well, or you have been feeding your child with breast milk or infant formula until almost the end of 6 months, then complementary foods can be started with the introduction of cereals.
It is important to start with one-component, low-allergenic cereals which does not contain gluten : this is buckwheat, rice, corn porridge .
gluten-containing cereals include: wheat, oats, rye, barley, millet .
According to modern data the period of introduction of gluten into the child's diet is not of fundamental importance, but the latest recommendations draw attention to the fact that its amount in the baby's diet should not be large. Therefore, it is better to add semolina and oatmeal to other porridge in a limited amount, and not to give it on its own. No relationship was found between the timing of the start of complementary foods that contain gluten and the development of celiac disease in a child. If your child hasn't tried porridge yet, start with a dairy-free, gluten-free, one-ingredient buckwheat or rice porridge.
Rice - very useful for growing baby. It has a low content of vegetable proteins, therefore it is easily digested and is especially useful for toddlers with unstable stools. Rice has a high nutritional value and, to a certain extent, protects the delicate intestines of the baby due to its enveloping effect. This is a hearty and nutritious dish with a good content of carbohydrates and proteins, potassium and magnesium, calcium and phosphorus, beneficial amino acids and vitamins. It replenishes energy costs, energizes and gives strength. Rice is not recommended for overweight children and those who suffer from severe constipation.
Gluten-free buckwheat porridge - very nutritious and rich in iron, fiber, rich in various vitamins and microelements. This is also a good option for starting a child's acquaintance with adult food. These porridges can be prepared with water, breast milk, milk formula, which your child is used to. No need to add salt and sugar.
No need to add salt and sugar.
Rules for introducing porridge into baby food
If the child already eats porridge from 5 months, then at 6 months you can offer a more complex porridge - for example, rice porridge with apricot or raspberries, rice porridge with banana (this is very successful a combination both in taste and in its properties) or even more complex porridge - corn-rice with banana.
Over time, you can start adding apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries, to the porridge, provided that the child is not allergic to them.
The rules for introducing cereals are the same as for vegetable puree. In order for the child to get used to the new product and its consistency more easily, first prepare 5% porridge (5 g of cereal per 100 g of water), if you make it yourself. Porridge is usually cooked with water, but can be made with breast milk, infant formula. First, give the baby one teaspoon, then, within 7-10 days, bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding (150 g). If all this time the porridge is well tolerated, i.e. there are no skin rashes, the child has stable stools, they switch to a gradual (starting from 20-30 g) introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already at a 10% concentration (10 g of cereal per 100 g of water). In other words, a thicker porridge is administered no earlier than 7-10 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge. The complete introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out in 7-10 days. The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal (in the form of 10% porridge) or the next complementary foods.
First, give the baby one teaspoon, then, within 7-10 days, bring the volume of porridge of the same percentage to the full volume of feeding (150 g). If all this time the porridge is well tolerated, i.e. there are no skin rashes, the child has stable stools, they switch to a gradual (starting from 20-30 g) introduction of porridge of the same cereal, but already at a 10% concentration (10 g of cereal per 100 g of water). In other words, a thicker porridge is administered no earlier than 7-10 days from the beginning of the introduction of porridge. The complete introduction of 10% porridge to the baby is also carried out in 7-10 days. The third week falls on the complete addiction of the child to a new dish. Only after that you can introduce a new cereal (in the form of 10% porridge) or the next complementary foods.
Video: feeding porridge
You need to give porridge with a spoon, it is better in the morning for breakfast. After porridge at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula. With artificial feeding, the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that, together with porridge, it is 200 ml with five meals a day.
After porridge at the stage of its introduction, the child should be offered breast or milk formula. With artificial feeding, the volume of the mixture after a portion of porridge should be such that, together with porridge, it is 200 ml with five meals a day.
Norms for the introduction of cereals
In the future, the volume of the portion of porridge gradually increases, amounting to:
- 7-8 months - 160-170 ml
- 8-9 months - 170-180 ml
- 9-12 months - up to 200 ml (there is a complete replacement of one feeding of the child with complementary foods.)
Cereal schedule
- Day 1 – 1 teaspoon (5 g)
- Day 2 - 2 teaspoons (10 g)
- Day 3 - 3 teaspoons (15 g)
- Day 4 - 4 teaspoons (20 g)
- Day 5 - 50 ml (50 g)
- Day 6 - 100 ml (100 g)
- Day 7 - 150 ml (150 g)
Meat complementary foods - the rules for introducing meat into the child's diet
Meat is usually the third, very important product of complementary foods, after vegetables and cereals. The meat contains amino acids, complete animal protein, B vitamins (B1, B2, B6 and B12), heme iron, potassium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, which are necessary for the growth and development of the child. It is very important to understand that mashed meat contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And the addition of meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them, from vegetables.
Iron deficiency can seriously affect the intellectual development of the child, his immunity, hematopoiesis. Since your task is to raise a healthy and intelligent child, meat complementary foods must be introduced without fail and in a timely manner.
Heme iron - found in meat products and easily digestible (red meat-veal, liver), absorption is about 25%.
Non-heme iron - found in plant foods (beans, beans, lentils, peas, nuts, tomatoes, cauliflower, green leafy vegetables, apples, dried fruits, but it is absorbed much worse from plants - only 3-5% Iron absorption from other animal products (eggs, fish) is 10-15%.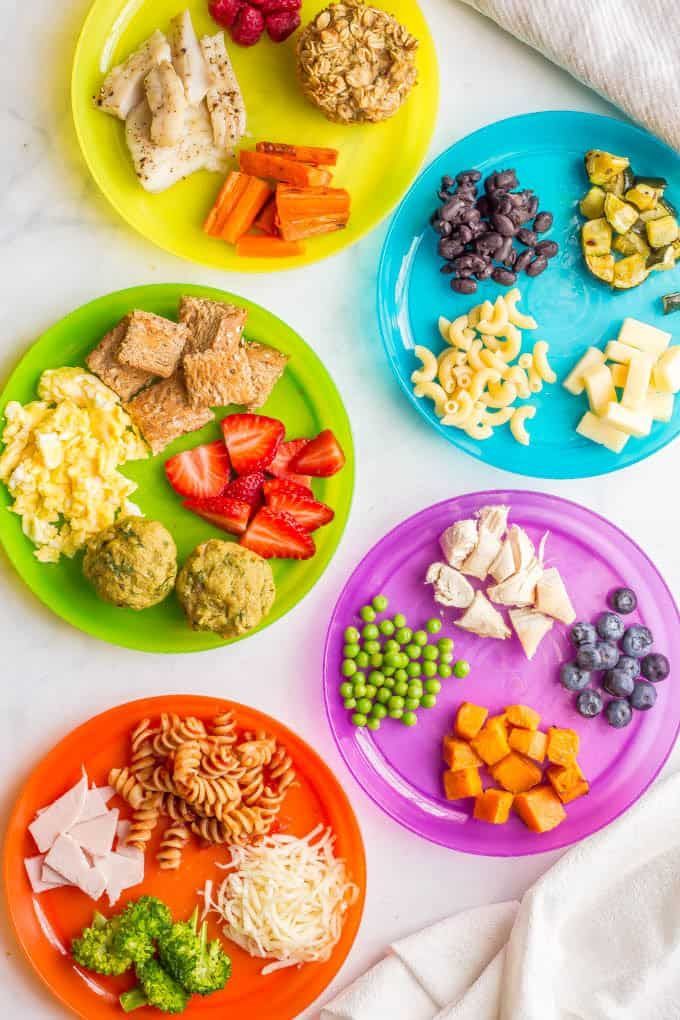 0003
0003
It is important to know that human milk enhances , while cow's milk reduces iron absorption .
Timing of the introduction of meat complementary foods
It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child aged 6-8 months . This, to some extent, depends on when cereals and vegetable/fruit purees were introduced. if your baby has been eating vegetables and cereals since 4 months, meat can be introduced at 6 months. From 7 months it can be administered if the child is not gaining weight. From 8 months to children who started complementary foods at 6 months.
Children at risk of anemia are advised to introduce meat earlier at the age of 5-6 months.
It has been proven that only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can fully meet the needs of children in iron, zinc and other micronutrients.
You can start meat complementary foods with lean beef, veal , but better with less allergenic poultry meat ( turkey, chicken ), or rabbit, these are the most easily digestible meats.
Goose and pork are fatty for the baby, and the meat of duck and other birds of the reservoirs is also not suitable for the first feeding. They are recommended to give only after 3 years;
Horsemeat is perfect for your baby. The product is rich in carbohydrates and proteins, but it is almost impossible to find horse meat for sale.
Meat should be introduced into the child's diet gradually, at lunchtime, at first, a quarter of a teaspoon and, gradually adding, bring it to the daily norm: At 8 months, about 50 g, at 9months-60-70 g.
Video: L food meat
Scheme for the introduction of puree
- 9000
- Day 2 - ½ teaspoon
- Day 3 - 1 teaspoon
- Day 4 - 2 teaspoons
- Day 5 - 3 teaspoons
- Day 6 3-4 teaspoons + vegetables
At first, it is better to give meat with vegetable puree, which the child has already eaten, so that he adapts better to the new product, and iron is better absorbed. Children at the end of the first year of life can already be given 3 varieties of mashed meat.
Children at the end of the first year of life can already be given 3 varieties of mashed meat.
Baby menu at 7-8 months
At 7-8 months you can start giving children 0 baby cottage cheese 9009 Start with 1/2 teaspoon. Within a month, the daily volume of cottage cheese consumption by a baby can be increased to 30-40 g. In addition, a child of 8 months is recommended to give sour-milk infant formula. But ordinary yogurt from the store should not be given. At this age, the child should receive 5 g of butter and 5 g (1 teaspoon) of vegetable oil, ¼- yolk - 2-3 times a week.
Baby's menu at 9 months old
At the age of 9 months old Your baby is already familiar at this age already usually familiar with: , egg yolk . You may have already met meat . Therefore, at this age, they usually give more complex purees and porridges, less homogenized, of various tastes , gradually preparing him for adult nutrition, increasing the variety and quantity of complementary foods. It is desirable to feed the baby at the table with other family members, he must see how his parents eat with pleasure, he learns from them. The amount of food offered should be based on the principles of actively encouraging the baby to eat, it is necessary to continue to gradually change the consistency and increase the variety of complementary foods, adhering to the recommended frequency of introducing complementary foods.
It is desirable to feed the baby at the table with other family members, he must see how his parents eat with pleasure, he learns from them. The amount of food offered should be based on the principles of actively encouraging the baby to eat, it is necessary to continue to gradually change the consistency and increase the variety of complementary foods, adhering to the recommended frequency of introducing complementary foods.
At this age, the child usually gets complementary foods 3 times a day . His diet depends on the age of the start of complementary foods. If the baby began to give new food at 4-5 months, the list of allowed foods will be much wider than if this happened at 6-7 months. Therefore, all this is very individual, there are no absolutely rigid frameworks and recommendations. On the Internet you will find a lot of different advice on baby food, if you are not sure about something, it is better to consult your pediatrician.
From vegetables the baby can be given what he ate before, mixing them: pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots and others, adding 1 tsp. vegetable oil . If the baby does not have skin reactions, then you can give beets . It is also possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups , but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he has not had a reaction to them.
vegetable oil . If the baby does not have skin reactions, then you can give beets . It is also possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups , but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he has not had a reaction to them.
If you have introduced complementary foods, then you need to remember that water is an important part of baby food. You can use purified water or special water for children .
In addition, at 9 months, you can give special baby wheat cookies , which the baby will be happy to eat on his own as an adult, white wheat bread, this improves hand motility, improves eating skills, but at the same time he must be supervised.
At this age, you can start giving fish puree from low-fat varieties: river perch, pollock, hake, haddock, zander, pollack - start with ½ teaspoon, bringing up to 40-50 g , watching the reaction of the child , give at lunchtime instead of mashed meat, 1-2 times a week. But a number of pediatricians do not advise giving it up to a year, it is a useful, but highly allergenic product.
But a number of pediatricians do not advise giving it up to a year, it is a useful, but highly allergenic product.
Baby menu at 10 months
B 10 months usually 2 times a day the child receives the mother's breast or special milk formulas . Various cereals: buckwheat, rice, corn, oatmeal, wheat, semolina . add 5-10 g of butter to cereals. At this age, it is already possible to make complex cereals from 2-3 cereals with which the child is familiar, add various fruits, vegetables: apple, banana, pear, plum and prunes, apricot and dried apricots, broccoli, carrots, berries , provided that the child is not allergic to them, or use ready-made cereals with fruit.
From vegetables the baby can be given what he ate earlier, mixing them: pumpkin, zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli, carrots, beets and others, adding 1 tsp. vegetable oil . It is also already possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups, but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he did not have a reaction to them.
vegetable oil . It is also already possible to give two-, three-component vegetable purees and soups, but only on condition that he is already familiar with these products and he did not have a reaction to them.
At this age, the baby already usually eats about 40-50 g of baby meat puree from chicken, turkey, rabbit , with good tolerance to cow's milk proteins from veal or beef. If he has been eating meat for a month or more, you can start giving him two-component meat purees , such as chicken and turkey.
At this age, fish puree from low-fat varieties is usually started: river perch, pollock, hake, haddock, pike perch, pollock with ½ teaspoon, bringing to 40-50 g, following the reaction of the child, it is better to give at lunch time instead of mashed meat, 1-2 times a week .
At 10 months, children's cottage cheese should be given 2 times a week. Start with 1/2 teaspoon if you have not given it before, the daily amount of cottage cheese at this age 40-50 g .
Start with 1/2 teaspoon if you have not given it before, the daily amount of cottage cheese at this age 40-50 g .
It is recommended to give special sour-milk baby formulas.
At this age, the child can receive 5-10 g of butter and 5 g (1 teaspoon) of vegetable oil, and 2-3 times a week½ - yolk .
Child's menu at 1 year old
The child is one year old. He has already grown up, he already has 6-10 teeth, with which he gnaws everything he sees, he is interested in chewing food, his digestive enzymes already work well and he has already become acquainted with various products: vegetable and fruit purees, various cereal cereals, meat and fish, sour-milk mixtures. In fact, he is already prepared for the transition to a more adult diet. In a year, changing the diet involves turning to new products and gradually changing the way they are prepared and the degree of grinding.
You need to eat 5 times a day with an interval 3.5-4 hours .
semi-liquid dishes should still remain the basis of nutrition, but not only mashed dishes, but also containing small pieces of food . Too dry food should not be given to the baby yet, as he may have difficulty swallowing.
In the year the child already tries to eat with his hands and he should be encouraged to do so. Finely chopped, soft foods can be given eg: small pieces of soft fruit, vegetables, cheese, well-cooked meat, pasta , etc. and foods that dissolve quickly, children's biscuits, children's crispbread - as food with the help of hands.
Must avoid products that can enter the respiratory tract and cause asphyxia - sausages and other hard meat products , nuts (especially peanuts), grapes, raisins, raw carrots, popcorn, round candies . Hold off on this for now.
Hold off on this for now.
In a year, part of the children are without mother's milk. But if your baby is still not weaned - do not rush, if possible, give him a breast before bed at night. You can also breastfeed between meals. At this age, the child receives all the main vitamins and minerals from food, but he can get a number of biologically active components from breast milk.
Dairy products
Dairy products still occupy an important place in the child's diet, it is a source of calcium, B vitamins, protein, milk sugar and fat. It is better to use special baby milk (marked with a triple on the package), baby fermented milk products: kefir, yogurt in total 500-600 ml per day .
Cottage cheese
The child should be given cottage cheese. The daily dose of cottage cheese after 1 year can be increased up to 70 g per day . It can be given pureed or combined with fruit puree, pudding, casserole. This contributes to the development of chewing skills.
It can be given pureed or combined with fruit puree, pudding, casserole. This contributes to the development of chewing skills.
Butter
Butter can be added to cereals or smeared on wheat bread, cookies in a dose of up to 12 g per day.
Low fat sour cream and cream
After 1 year, you can give low-fat sour cream and cream in small quantities.
Vegetables
Every year a child must be given various vegetables , it is good to combine them with protein products, meat . The vegetable diet can now be diversified with green peas, tomatoes, turnips, beets, carrots, spinach in the form of mashed potatoes. Legumes are still better not to give.
Fruits and berries
After 1 year, you can gradually introduce the baby to new fruits and berries: strawberries, cherries, cherries, kiwi, currants, gooseberries, chokeberries, sea buckthorn, raspberries, blackberries, cranberries, blueberries, lingonberries and even citrus fruits . But do it gradually, watching the reaction of the child. Berries with a dense peel (gooseberries) are best mashed, while soft juicy fruits (peaches, strawberries, apricots, kiwi) can be offered to the baby in pieces.
But do it gradually, watching the reaction of the child. Berries with a dense peel (gooseberries) are best mashed, while soft juicy fruits (peaches, strawberries, apricots, kiwi) can be offered to the baby in pieces.
Daily dose of fruits - approx.
Meat products
Meat products can be given in the form of steam cutlets, meatballs, meatballs, meat soufflé and pudding in an amount up to 100 g daily - beef, veal, lean pork, rabbit, turkey, chicken.
Fish
Fish can be given once or twice a week for 30-40 g per meal as a substitute for meat dishes
Eggs
Chicken, quail eggs give boiled or in the form of omelettes in milk, you can try with vegetables.
Kashi
Porridge can be cooked from rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, corn, millet, semolina. At this age, they should still have a uniform consistency, so it will be easier for him to swallow. You can use ready-made industrial, children's instant cereals, for example, various multi-cereal cereals, in which fruits, crackers, cereals have already been added. Give 1 time per day.
At this age, they should still have a uniform consistency, so it will be easier for him to swallow. You can use ready-made industrial, children's instant cereals, for example, various multi-cereal cereals, in which fruits, crackers, cereals have already been added. Give 1 time per day.
Water
Be sure to give the child clean water to drink, better bottled water for children, as much as he wants . In addition to her baby can drink vegetable and fruit juices, dairy products, compotes, weak tea.
No need to give:
confectionery and sweets should not be given to a child 0007 . From sweets at this age, you can sometimes give marmalade, dried fruits and cookies.
Do not give sausages and sausages , they are rarely prepared from high quality meats and are rich in various food additives
Calorie content and volume
0093 1200 ml .