Food allergy rash treatment baby
Allergic reaction in baby: Treatment and pictures
A baby can have an allergic reaction for a variety of reasons. An allergic reaction occurs when the body has an adverse response to a usually harmless substance, such as a soap or a specific food.
Babies have sensitive skin, which makes them more likely than adults to develop a rash. Even a slight irritation to a baby’s skin may be enough to trigger a rash.
Identifying the cause of the allergic reaction or sensitivity can help parents and caregivers to prevent and treat any future reactions.
Babies can have several different types of skin rash, which have a range of causes. Some allergic reactions can also lead to additional symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting.
Common types of allergic reactions in infants include the following:
Eczema
Share on PinterestIrritating fabrics, soaps, and heat can lead to eczema outbreaks in babies.Eczema is one of the most common skin conditions in babies. There are different types of eczema, but atopic eczema is one of the most likely to affect babies and small children.
An eczema rash may consist of tiny red bumps, or it may look like scaly, dry skin.
Doctors do not know why some people develop eczema while others do not, but it may be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Common triggers of eczema outbreaks in babies include irritating fabrics, soaps, and heat.
An eczema rash may look slightly different in older infants. According to the National Eczema Association, babies younger than 6 months tend to develop eczema-type rashes on the scalp, face, and forehead.
In babies aged between 6 months and 1 year, the rash often appears on the knees and elbows.
Papular urticaria
Papular urticaria is a localized allergic reaction to a bug bite. Bites from various insects, including mosquitoes, mites, and bedbugs, can cause the reaction.
Although it usually affects children aged 2–6 years, papular urticaria can also occur in infants.
Papular urticaria resembles small clusters of red bumps or bug bites. Some of the bumps may be fluid-filled. Papular urticaria can last for several days or even weeks.
Some of the bumps may be fluid-filled. Papular urticaria can last for several days or even weeks.
Hives
When the body is allergic to a substance, it releases a chemical called histamine that can lead to the development of hives and other allergy symptoms.
Hives are itchy, raised patches on the skin. They can range in size and shape but are usually pink or red with a thin red border.
Hives can develop anywhere on the body and often appear in clusters.
Share on PinterestA baby can develop hives as the result of a food allergy.
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, about 6 percent of children aged 2 and under have food allergies.
Signs of a food allergy can include skin reactions and respiratory or intestinal symptoms, such as:
- hives
- itching
- coughing
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- blood in the stool
Occasionally, it is even possible for babies to have allergic reactions to foods before they start eating them. This is because they can develop allergies to the foods that the person who is breast-feeding them eats.
This is because they can develop allergies to the foods that the person who is breast-feeding them eats.
The foods that children are most likely to be allergic to are:
- milk and dairy products
- peanuts
- shellfish
Once they start eating solid foods, babies may show signs of additional allergies.
Doctors often recommend that parents and caregivers introduce new foods to a baby one at a time. This way, if an allergy does develop, it is easier to determine which food is responsible for the reaction.
Not all reactions in babies require treatment. For example, a mild rash is likely to fade within a few hours and may not trouble the baby in that time.
However, if the symptoms of a reaction are causing visible discomfort, treatment may be necessary.
The treatment can vary according to the type of rash or reaction. In general, the following treatments may help:
- Avoiding triggers: Soaps, detergents, and scented lotions can often irritate a baby’s skin, so it may be best to avoid using chemical cleaners and to choose hypoallergenic products instead.

- Washing with a fragrance-free cleanser: After using a mild, scent-free soap, pat the baby’s skin dry and avoid rubbing too hard, as this can irritate the skin.
- Applying a moisturizer: Using a hypoallergenic moisturizer after a baby’s bath can help to prevent dry skin. Moisturizers also provide a barrier to protect the skin from irritants.
- Using 1-percent hydrocortisone cream: Hydrocortisone cream can treat skin rashes relating to eczema or other allergic reactions. Although it is usually safe to use for infants for short periods, it is essential to speak to a doctor first.
- Considering scratch mitts: Scratch mitts prevent a baby from scratching a rash with their fingernails. Too much scratching can injure the skin and lead to an infection.
It is not possible to prevent all allergic reactions in babies, but there are steps that parents and caregivers can take to reduce the risk. These include:
These include:
- washing the baby’s clothes in hypoallergenic detergent
- using fragrance-free shampoo, lotions, and soap
- washing the baby’s bedding in hot water every week to reduce the chance of dust mites
- vacuuming frequently
- introducing new foods one at a time
If a baby has an allergic reaction after breast-feeding, it might be beneficial to keep a food diary to try to determine the underlying cause. Dairy is a very common culprit, especially before the infant reaches 1 year in age.
After identifying the allergen, it may help to avoid eating this food while breast-feeding. However, it is best to speak to a doctor before making changes to the diet.
Share on PinterestSeek medical advice if a rash worsens over time.
People can often treat allergic reactions in babies at home. However, in some cases, it is best to see a doctor.
If the rash spreads or worsens over time, a person should consult a doctor. It is also essential to seek medical advice if the skin shows signs of an infection, such as blistering, bleeding, or seeping fluid.
In some cases, a rash can signify another illness. If a rash appears alongside the symptoms below, people should consult a doctor:
- fever
- lethargy
- poor feeding
- coughing
- excessive crying
Babies who develop allergic reactions that include wheezing, swelling of the lips or tongue, or trouble breathing will require immediate medical attention. They may be having an anaphylactic reaction, which can be severe.
Allergic reactions and sensitivities are common in babies, in part because they have such sensitive skin.
In most cases, these reactions are mild, and parents or caregivers can treat them at home.
Identifying the allergen can help to prevent future reactions. Many babies will grow out of their allergies, but others will develop new allergies as they get older.
Allergic reaction in baby: Treatment and pictures
A baby can have an allergic reaction for a variety of reasons. An allergic reaction occurs when the body has an adverse response to a usually harmless substance, such as a soap or a specific food.
Babies have sensitive skin, which makes them more likely than adults to develop a rash. Even a slight irritation to a baby’s skin may be enough to trigger a rash.
Identifying the cause of the allergic reaction or sensitivity can help parents and caregivers to prevent and treat any future reactions.
Babies can have several different types of skin rash, which have a range of causes. Some allergic reactions can also lead to additional symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting.
Common types of allergic reactions in infants include the following:
Eczema
Share on PinterestIrritating fabrics, soaps, and heat can lead to eczema outbreaks in babies.Eczema is one of the most common skin conditions in babies. There are different types of eczema, but atopic eczema is one of the most likely to affect babies and small children.
An eczema rash may consist of tiny red bumps, or it may look like scaly, dry skin.
Doctors do not know why some people develop eczema while others do not, but it may be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Common triggers of eczema outbreaks in babies include irritating fabrics, soaps, and heat.
An eczema rash may look slightly different in older infants. According to the National Eczema Association, babies younger than 6 months tend to develop eczema-type rashes on the scalp, face, and forehead.
In babies aged between 6 months and 1 year, the rash often appears on the knees and elbows.
Papular urticaria
Papular urticaria is a localized allergic reaction to a bug bite. Bites from various insects, including mosquitoes, mites, and bedbugs, can cause the reaction.
Although it usually affects children aged 2–6 years, papular urticaria can also occur in infants.
Papular urticaria resembles small clusters of red bumps or bug bites. Some of the bumps may be fluid-filled. Papular urticaria can last for several days or even weeks.
Hives
When the body is allergic to a substance, it releases a chemical called histamine that can lead to the development of hives and other allergy symptoms.
Hives are itchy, raised patches on the skin. They can range in size and shape but are usually pink or red with a thin red border.
Hives can develop anywhere on the body and often appear in clusters.
Share on PinterestA baby can develop hives as the result of a food allergy.
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, about 6 percent of children aged 2 and under have food allergies.
Signs of a food allergy can include skin reactions and respiratory or intestinal symptoms, such as:
- hives
- itching
- coughing
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- blood in the stool
Occasionally, it is even possible for babies to have allergic reactions to foods before they start eating them. This is because they can develop allergies to the foods that the person who is breast-feeding them eats.
The foods that children are most likely to be allergic to are:
- milk and dairy products
- peanuts
- shellfish
Once they start eating solid foods, babies may show signs of additional allergies.
Doctors often recommend that parents and caregivers introduce new foods to a baby one at a time. This way, if an allergy does develop, it is easier to determine which food is responsible for the reaction.
Not all reactions in babies require treatment. For example, a mild rash is likely to fade within a few hours and may not trouble the baby in that time.
However, if the symptoms of a reaction are causing visible discomfort, treatment may be necessary.
The treatment can vary according to the type of rash or reaction. In general, the following treatments may help:
- Avoiding triggers: Soaps, detergents, and scented lotions can often irritate a baby’s skin, so it may be best to avoid using chemical cleaners and to choose hypoallergenic products instead.
- Washing with a fragrance-free cleanser: After using a mild, scent-free soap, pat the baby’s skin dry and avoid rubbing too hard, as this can irritate the skin.
- Applying a moisturizer: Using a hypoallergenic moisturizer after a baby’s bath can help to prevent dry skin.
 Moisturizers also provide a barrier to protect the skin from irritants.
Moisturizers also provide a barrier to protect the skin from irritants. - Using 1-percent hydrocortisone cream: Hydrocortisone cream can treat skin rashes relating to eczema or other allergic reactions. Although it is usually safe to use for infants for short periods, it is essential to speak to a doctor first.
- Considering scratch mitts: Scratch mitts prevent a baby from scratching a rash with their fingernails. Too much scratching can injure the skin and lead to an infection.
It is not possible to prevent all allergic reactions in babies, but there are steps that parents and caregivers can take to reduce the risk. These include:
- washing the baby’s clothes in hypoallergenic detergent
- using fragrance-free shampoo, lotions, and soap
- washing the baby’s bedding in hot water every week to reduce the chance of dust mites
- vacuuming frequently
- introducing new foods one at a time
If a baby has an allergic reaction after breast-feeding, it might be beneficial to keep a food diary to try to determine the underlying cause.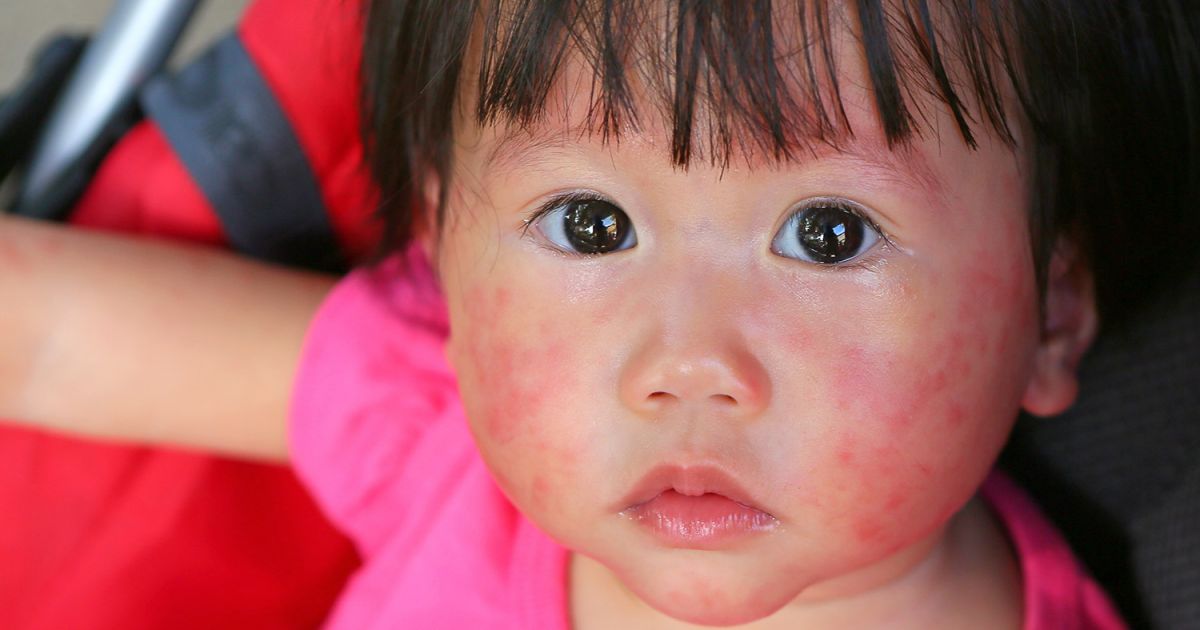 Dairy is a very common culprit, especially before the infant reaches 1 year in age.
Dairy is a very common culprit, especially before the infant reaches 1 year in age.
After identifying the allergen, it may help to avoid eating this food while breast-feeding. However, it is best to speak to a doctor before making changes to the diet.
Share on PinterestSeek medical advice if a rash worsens over time.
People can often treat allergic reactions in babies at home. However, in some cases, it is best to see a doctor.
If the rash spreads or worsens over time, a person should consult a doctor. It is also essential to seek medical advice if the skin shows signs of an infection, such as blistering, bleeding, or seeping fluid.
In some cases, a rash can signify another illness. If a rash appears alongside the symptoms below, people should consult a doctor:
- fever
- lethargy
- poor feeding
- coughing
- excessive crying
Babies who develop allergic reactions that include wheezing, swelling of the lips or tongue, or trouble breathing will require immediate medical attention. They may be having an anaphylactic reaction, which can be severe.
They may be having an anaphylactic reaction, which can be severe.
Allergic reactions and sensitivities are common in babies, in part because they have such sensitive skin.
In most cases, these reactions are mild, and parents or caregivers can treat them at home.
Identifying the allergen can help to prevent future reactions. Many babies will grow out of their allergies, but others will develop new allergies as they get older.
Food allergies in children - symptoms, treatments, diet its individual components. What are its causes, what are the risk factors, and what food to choose in case of an allergic reaction - read in this material.
Food allergy symptoms
The causes of food intolerance are related to the fact that the immune system "incorrectly" recognizes them as potentially dangerous, and produces protective antibodies in excess. Excessively violent reaction leads to the fact that the child develops an allergy to certain types of food. 1. 3
3
Symptoms of food allergy in children are different. But most often, food allergies manifest themselves on the part of the skin - itching, a feeling of tightness and dryness. Local swelling may occur on the skin, a rash (urticaria), redness, blisters may appear. In second place in terms of frequency of manifestation - reactions from the respiratory system. Runny nose, nasal congestion, sore throat, cough of varying intensity. Also, reactions from the organs of the gastrointestinal tract can indicate food allergies. A very young child begins to be disturbed by colic, dyspepsia, stool disorders from diarrhea to constipation. Older children complain of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, a feeling of scratching in the throat, behind the sternum.
Do not forget about the general symptoms of food allergies: the child becomes lethargic, capricious, sleeps poorly, does worse in school (or psycho-emotional development), is prone to daytime sleepiness. 2.3
Causes of food allergies
Newborns and young children, if predisposed, may suffer from allergies due to their physiological characteristics. The fact is that a child is born with an immature gastrointestinal tract, the intestinal walls are permeable to many substances, the enzyme system is still imperfect. Therefore, it is difficult for the body to cope with the digestion of proteins. The body seems to be in a state of constant "combat readiness" and the ingestion of even a small amount of allergens leads to a response from the immune system and the development of a violent allergic reaction. 1.2
The fact is that a child is born with an immature gastrointestinal tract, the intestinal walls are permeable to many substances, the enzyme system is still imperfect. Therefore, it is difficult for the body to cope with the digestion of proteins. The body seems to be in a state of constant "combat readiness" and the ingestion of even a small amount of allergens leads to a response from the immune system and the development of a violent allergic reaction. 1.2
In older children, many internal and external conditions become risk factors. For example, heredity - after all, if one of the child's parents suffered from an allergic disease, then with a high degree of probability the child will also be given a tendency to it. Unfavorable environmental factors influence - polluted atmosphere, car exhausts, lack of green plants in cities. Very often, a violation of the immune system in the form of an allergic reaction occurs in children with a labile, mobile psyche, with sharp transitions from friendliness and calmness to crying and back.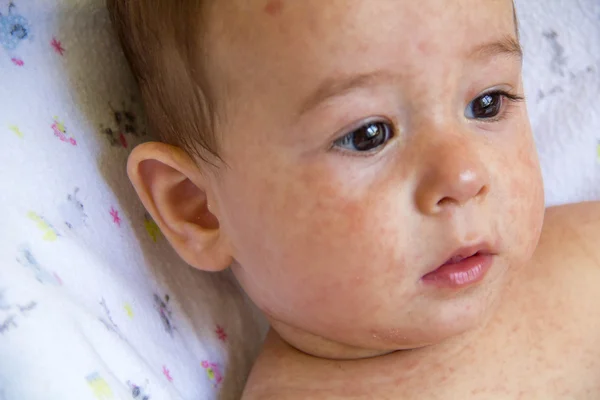 Finally, bad habits, both in children and mothers during pregnancy, become an important factor. This is incorrectly introduced complementary foods and early introduction of potentially allergenic foods into the child's diet: citrus fruits, nuts, chocolate, berries, honey, and, of course, the habit of children to eat only something tasty (usually unhealthy; chocolate, carbonated drinks, fast food ) 2,3,4
Finally, bad habits, both in children and mothers during pregnancy, become an important factor. This is incorrectly introduced complementary foods and early introduction of potentially allergenic foods into the child's diet: citrus fruits, nuts, chocolate, berries, honey, and, of course, the habit of children to eat only something tasty (usually unhealthy; chocolate, carbonated drinks, fast food ) 2,3,4
List of products that provoke allergies
Due to the extreme individuality of the immune system, it is almost impossible to predict its reaction. However, there is a rough list of foods classified into groups depending on their allergenicity - that is, the ability to cause a sharp reaction from the immune system and allergy symptoms. It is important to remember that it is not necessary that any product from the first column will cause a reaction. Like any low allergenic product, in some cases, it can cause an overreaction to it. 2,3,4
Examples of the most typical exoallergens
| Highly allergenic products | Foods of average allergenicity | Low Allergy Products | |
all citrus fruits, strawberries, strawberries, raspberries, blackberries, pineapples. | peaches, cranberries, lingonberries, cherries, blueberries, black currants. | pears, gooseberries, dried apricots, plums, white currants, apples and pears. | |
| carrots, tomatoes, bell peppers, radishes. | potatoes, beets, peppers, peas, corn. | broccoli, green peas, zucchini, squash, white and cauliflower, cucumbers, pumpkin. | |
| eggs, sausages and sausages, chicken, sea fish. | beef, rabbit, pork. | lamb. | |
| whole cow's milk, cheeses, yoghurts with additives. | fermented milk products. | ||
| wheat, rye. | buckwheat, oats, rice, peas, beans. | barley, millet. | |
| coffee, cocoa, chocolate, nuts, honey. | xylitol, fructose | ||
| mushrooms, carbonated drinks, packaged juices. | vegetable oil. |
Diagnosis established
The diagnosis of this allergy, as well as the search for the causes that caused it, requires a careful and serious approach on the part of parents. The younger the child, the easier it is to find foods that cause illness. For this, two conditions must be met.
The first thing is to put a child or mother on a hypoallergenic diet if she is breastfeeding - a detailed nutrition plan will be helped by an allergist together with a pediatrician. Please note that during an exacerbation, the diet will be extremely strict, the so-called elimination diet - aimed at removing the allergen and reaction products to it with the complete elimination of potential and cross allergens. The duration of such a diet is determined by the doctor. When the exacerbation fades, the diet gradually expands due to safe foods. 3.4
And the second is to start keeping a special food diary in which to record everything that was eaten and drunk by the child during the day, as well as what was prepared and how. At the first sign of an allergic reaction, suspicious foods should be eliminated one at a time (or from the mother's diet if the baby is breastfed). After elimination, within a few days, it is worth observing the reaction, if the manifestations of allergies decrease, then the product is really not suitable for the child - it should be avoided. If the child is very small, then the diary is kept according to the opposite principle: all foods that are introduced as complementary foods are recorded in it. The name of the product, the quantity, the time of eating and the reactions of the body are recorded over the next few days (the attending physician will determine the specific timing of observation). Next, the doctor will need to check and confirm the preliminary diagnosis by conducting special tests and analyzes.
At the first sign of an allergic reaction, suspicious foods should be eliminated one at a time (or from the mother's diet if the baby is breastfed). After elimination, within a few days, it is worth observing the reaction, if the manifestations of allergies decrease, then the product is really not suitable for the child - it should be avoided. If the child is very small, then the diary is kept according to the opposite principle: all foods that are introduced as complementary foods are recorded in it. The name of the product, the quantity, the time of eating and the reactions of the body are recorded over the next few days (the attending physician will determine the specific timing of observation). Next, the doctor will need to check and confirm the preliminary diagnosis by conducting special tests and analyzes.
Emergency measures for food allergies
First, you need to assess the severity of the manifestations of food allergies.
For any symptoms, the first step is to avoid contact with a specific familiar allergen or any suspicious food or drink.
If the symptoms of allergy are mild - itching, redness of the skin, then you can give the child an antihistamine, which was previously recommended by the doctor for such cases. In addition, you must also call the local pediatrician and carefully monitor the condition of the child.
In case of obvious or possible signs of deterioration, call an ambulance. Signs that you should pay close attention to and immediately dial 03 include spreading rash and redness, increased itching, fever, drowsiness and lethargy, vomiting and nausea, refusal to drink water, difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness and pallor .
For general symptoms, in which it is difficult to understand whether they are associated with allergies or not, and which may indicate a developing serious condition, an ambulance should be called immediately if the child has any difficulty or changes in breathing, shortness of breath, cough, croup, vote. If pains in the abdomen began, extensive swelling, redness, itchy skin areas appeared. There is dizziness, fainting, as well as changes in the pulse - slowing or increased heart rate. 1,3,4
There is dizziness, fainting, as well as changes in the pulse - slowing or increased heart rate. 1,3,4
How to treat a food allergy in a child
Treatment depends on the stage of the allergic reaction process. With an exacerbation, antihistamines are prescribed that block histamine receptors, hormonal drugs. For skin manifestations of allergies, local preparations are used: creams, powders, etc. Respiratory reactions are treated with inhalation drugs and physiotherapy.
Food allergy in children. How is it manifested and how to treat?
According to WHO, approximately 40% of the world's population has allergies in the 21st century. Mankind suffers from skin allergies, allergies to insect bites, to sunlight and cold. However, the “leader” of the rating is food allergies. And most of all, she worries children - both babies and older kids, and teenagers.
The disease only seems insignificant. She learned to "disguise" herself as other ailments, so not every parent is able to recognize her. How to get rid of allergies, we have already told. Today we will talk about food allergies. Why can one child eat everything without harm to health, while another completely harmless chocolate causes allergies?
How to get rid of allergies, we have already told. Today we will talk about food allergies. Why can one child eat everything without harm to health, while another completely harmless chocolate causes allergies?
What is a food allergy?
A child's food allergy is when the body reacts to one or more foods. During an allergy, the immune system accepts protein or other substances in food not as useful, but as very dangerous and harmful. Against the "enemy" immunity immediately builds protection by producing antibodies.
Each organism and immunity is individual, so it is very difficult to predict the child's reaction to the product. But some foods still cause a reaction more often than others.
From citrus fruits to dried apricots and plums - highly allergenic and low allergenic foods
Foods that cause allergies in a child are divided into highly allergenic, moderately allergenic and low allergenic foods. However, doctors remind: it is not at all necessary that oranges will cause a reaction, but pears will not. Each situation is purely individual.
Each situation is purely individual.
How does food allergy manifest itself in children? 3 main symptoms
Food allergies manifest differently in children of different ages. But parents should know the general symptoms of the disease: the child does not want anything, is naughty, sleeps poorly and anxiously at night, and suffers from lack of sleep during the day.
At the same time, the disease also has its own characteristic alarming "signals". Some appear more frequently, others less frequently. What are the 3 main signs of food allergies in children.
Skin reaction
Food allergies in children are mostly indicated by redness. Pink dots, bubbles and red spots appear. The rash may continue with itching - from this the child sleeps and eats poorly.
Respiratory system
Food allergy in children manifests itself in the respiratory system through a runny nose and nasal congestion, pain and sore throat, cough. With a strong reaction, edema appears. This is a reason to urgently call an ambulance.
This is a reason to urgently call an ambulance.
Gastrointestinal
Allergy disrupts the child's stomach and intestines. The baby is worried about colic, bloating. Older children feel sick and vomit, there is pain in the abdomen.
Food allergy in children. Looking for causes
Why do children develop food allergies? There are several reasons for the appearance of allergic reactions.
1. Immaturity of the child's digestive system
In babies, everything is just starting to work, so it is difficult for the body to cope with digesting proteins. Even small amounts of allergens can lead to a serious reaction.
2. Irrational introduction of complementary foods
Incorrect or early introduction of new foods into the baby's diet can cause allergies. Too much food can also cause an adverse reaction in the body. Therefore, everything new should be given to the baby one at a time, starting with one teaspoon.
An allergy in an infant can manifest itself due to breast milk - if the mother has eaten a new or allergenic product the day before. But here, too, everything is individual.
3. Heredity
Food allergies in children sometimes manifest themselves due to unfavorable heredity. Parents suffer from allergies, and not necessarily food. The risk of developing this disease in a child increases significantly.
4. Ecology
Poor environmental ecology can also affect a child's allergies. These are air and air pollution, climate change, lack of landscaping in cities, the emergence of unnatural food and substitute products.
5. Bad habits
The risk of allergic reactions increases the presence of bad habits. We are talking about smoking, the use of alcohol or drugs, both by the child and the mother during gestation.
We treat food allergies
How to treat food allergies in a child? There are two types of therapy - diet and medication. The treatment program for each child is individual, it will be helped by a pediatrician and narrow specialists - a nutritionist and an allergist.
The treatment program for each child is individual, it will be helped by a pediatrician and narrow specialists - a nutritionist and an allergist.
Diet
Diet is very important in treating a child's food allergy. First, it is necessary, of course, to limit the child from the use of products that cause allergic reactions. Parents should not forget that the diet should be balanced. No need to give up foods rich in vitamins and nutrients.
When it comes to a child who is breastfed, the diet needs to be considered by the mother.
Complementary foods, as we mentioned earlier, should be started gradually. If a child suffers from allergies, then highly allergenic foods - cow's milk, nuts, chicken eggs - doctors advise giving the baby only when he is two years old.
Medications
Doctors usually prescribe antihistamines and adsorbents to relieve food allergy symptoms in children. Creams and ointments will help get rid of redness and skin itching.











