Foods that affect breastfeeding babies
Breastfeeding FAQs: Your Eating and Drinking Habits (for Parents)
Breastfeeding is a natural thing to do, but it still comes with its fair share of questions. Here's what you need to know about your eating and drinking habits — and how they may affect your baby — during breastfeeding.
What Should I Eat?
As you did when you were pregnant, eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, protein, and calcium-rich foods. You’ll need about 450 to 500 extra calories per day while breastfeeding. Follow the recommendations in the MyPlate food guide and you'll be well on your way to giving both you and your baby a nutritious diet.
Breastfeeding can make you thirsty, so keep a water bottle nearby so it's there when you need it.
Do I Need to Take Vitamins?
Your doctor may ask you to continue taking a prenatal vitamin or women’s supplement.
It’s important to get enough iodine, an important mineral, while breastfeeding. To get enough:
- Take a supplement with 150 micrograms of iodine per day.
- Use iodized salt in your cooking.
- Eat foods that are high in iodine, like seafood and dairy products.
If you are vegan or don't eat fish or dairy, talk to your doctor about getting checked for iodine deficiency.
Can My Baby Have a Reaction to Something I Eat?
It’s possible for your breastfed baby to have an allergic reaction or sensitivity to something you eat or drink.
Foods like beans, broccoli, cauliflower, or some dairy products can cause fussiness, gassiness, or colicky behavior in some babies. Foods like cow's milk, soy, wheat, corn, oats, eggs, nuts and peanuts, and fish or shellfish are common allergy-causing foods.
If you think your baby had a reaction to a food, call your doctor and avoid eating or drinking anything your little one can't seem to tolerate. Keep a journal of exactly what you eat and drink, along with any reactions your baby had. This can help both you and your doctor pinpoint what the problem food, or foods, might be.
Although such a reaction is extremely rare, if your child has trouble breathing or has swelling of the face, call 911 right away.
Is Alcohol Still a "No-No"?
Drinking in moderation — one or two drinks within a 24-hour period — is fine, as long as you wait to feed your baby.
When you drink alcohol, a small amount gets into your breast milk. The amount of alcohol in breast milk depends on the amount of alcohol in the blood. It takes about 2 hours after having one drink for the alcohol to no longer be a concern for your baby. So do not give your baby fresh breast milk for at least 2 hours if you've had one drink, 4 hours if you've had two drinks, and so on.
If you plan to drink more than a few, do so after breastfeeding's been established for about a month and then "pump and dump." This is when you pump your milk and throw it away.
But drinking to excess when you're nursing is not a good idea. Even if you "pump and dump," there are other risks to your baby. Drinking too much changes your ability to be alert and think clearly. It affects how you care for your baby and may prevent you from responding to your baby's needs. It's also a risk factor for SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome).
Drinking too much changes your ability to be alert and think clearly. It affects how you care for your baby and may prevent you from responding to your baby's needs. It's also a risk factor for SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome).
Should I Still Avoid Some Types of Fish?
As during pregnancy, nursing moms should avoid or limit eating fish that is high in mercury. High mercury levels can damage a baby’s developing nervous system.
Can I Have Caffeine?
As with alcohol, it's best to limit caffeine while breastfeeding. One or two cups of coffee a day are fine, but more than one or two servings per day may affect your baby's mood and/or sleep.
Reviewed by: Jamila H. Richardson, BSN, RN, IBCLC
Date reviewed: January 2021
Foods to Eat or Avoid When Breastfeeding
Reviewed by Poonam Sachdev on June 26, 2022
It’s a good source of protein. Some, like salmon and tuna, also give you omega-3s, which your body needs. But what about mercury and other contaminants? You can have cooked seafood twice per week. Each serving can be up to 6 ounces, which is the size of two decks of cards. Choose types that are lower in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, and trout. Avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, which have high levels of mercury.
Each serving can be up to 6 ounces, which is the size of two decks of cards. Choose types that are lower in mercury, such as salmon, tilapia, and trout. Avoid shark, swordfish, king mackerel, and tilefish, which have high levels of mercury.
Love hot sauce? Most babies can handle it and other fiery foods in your diet. But if your little one is gassy or colicky and gets diarrhea every time you sprinkle red pepper flakes over your pizza, cut back on the heat for a few weeks to see if that helps.
They’re full of flavor. But some herbs may affect how much milk your body makes. For instance, eating a lot of parsley could curb lactation. And too much sage and peppermint may cut your milk supply. For some nursing moms, even peppermint-flavored toothpaste and candies are a problem.
It’s rarely a problem. But see how your baby does. Tell your pediatrician if your tot gets skin problems, has trouble breathing after breastfeeding, or has other symptoms.
As refreshing as your cup of chai or Earl Grey may be, it has some downsides. It’s got caffeine, which can affect your sleep – and your baby’s. It may also make it harder for your body to absorb iron, which you need for energy. If you drink hot or iced tea, try not to sip it when you eat foods that are rich in iron, such as lean meat; dark, leafy greens; and fortified breakfast cereals.
It’s got caffeine, which can affect your sleep – and your baby’s. It may also make it harder for your body to absorb iron, which you need for energy. If you drink hot or iced tea, try not to sip it when you eat foods that are rich in iron, such as lean meat; dark, leafy greens; and fortified breakfast cereals.
What if you aren’t allergic, and you want to prevent your baby from developing an allergy? Sorry, but there’s no proof that you can do that by skipping specific foods. Cutting certain foods out of your diet may make the skin condition eczema less likely for your little one. Ask your doctor or pediatrician for advice.
Breastfeeding can make you thirstier than you usually are. If that’s the case, drink a glass of water every time you breastfeed. But no matter how parched you feel, don’t go for regular sodas or fruit drinks, which give you calories without nutrition.
It's best for your baby if you don't have any booze at all. But if you do choose to drink, don’t breastfeed until the alcohol has completely cleared your milk. For 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of liquor, wait at least 3 hours. Pumping doesn’t speed that up.
For 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of liquor, wait at least 3 hours. Pumping doesn’t speed that up.
Common culprits include beans, broccoli, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts. Bloating, burping, and passing gas are normal. But if your baby is gassy or has colic, avoid these foods for a few weeks to see whether they relieve the symptoms.
Both have caffeine. You’ll also find it in energy drinks and cola. If you’re lost without your latte, limit yourself to 2-3 cups per day of the brewed kind. Or you could switch to decaf.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Getty
2) Getty
3) Getty
4) Getty
5) Getty
6) Getty, iStock
7) Getty
8) Getty
9) Getty
10) Getty
SOURCES:
Mayo Clinic.
The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
La Leche League.
The American Academy of Pediatrics.
U.S. Department of Agriculture.
© 2022 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
What to eat while breastfeeding | Breastfeeding Diet
You know that breast milk is the best food for your baby.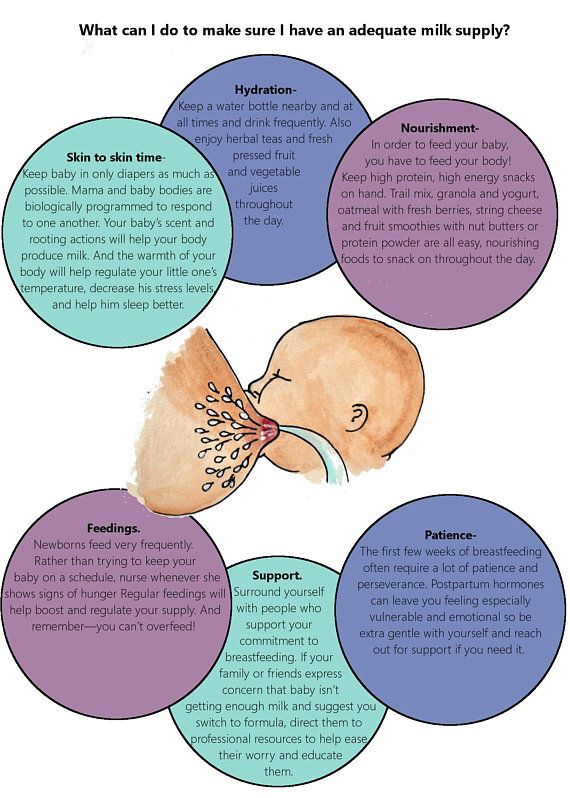 What about your own nutrition while breastfeeding? We asked the nutritionist a few questions about the nutrition of a nursing mother.
What about your own nutrition while breastfeeding? We asked the nutritionist a few questions about the nutrition of a nursing mother.
Share this information
Priya Tew, UK-based registered dietitian :
Priya is a nutritionist, M.D., multi-award winning member of the British Dietetic Association and the Health Professions Council. She has three children, and she breastfed each of them for up to 18 months.
During breastfeeding, there is no need to follow a special diet, the main thing is that your diet is balanced. It should include plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains such as oats, brown rice, various cereals, and breads labeled "whole grain", "wholemeal" or "wholemeal". These foods, along with potatoes, pasta, and couscous, are high in starch, an important source of energy.
In addition, you need lean proteins found in chicken, eggs, legumes, lentils, fish, and lean beef, as well as healthy fats found in olive oil, nuts, seeds, avocados, and fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel. Oily fish is very good for your health and development of your baby, but you should not eat more than two servings per week (about 140 g), as it may contain harmful impurities. 1
Oily fish is very good for your health and development of your baby, but you should not eat more than two servings per week (about 140 g), as it may contain harmful impurities. 1
Should I take vitamins while breastfeeding?
The most important is vitamin D. It is essential for healthy bones, you and your baby. We get most of this vitamin from the sun. If you live in a region with insufficient solar activity, especially in winter, your body may lack it. In this case, the doctor may advise taking vitamin D supplements. 2
You also need to get enough calcium, as it is excreted from the body during breastfeeding. 3 Try to eat four servings of foods rich in this mineral a day. These can be dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, or non-dairy products such as nuts, tofu, sesame seeds, and leafy vegetables. One serving may consist of, for example, half a cup of green vegetables or a small piece of cheese (50 g).
What foods should I avoid while breastfeeding?
The good news is that you can eat almost anything while breastfeeding. Only the consumption of oily fish should be limited. In small quantities, even caffeine is acceptable - more on this below.
Only the consumption of oily fish should be limited. In small quantities, even caffeine is acceptable - more on this below.
If you are not allergic to peanuts, there is no reason to deny yourself products that contain peanuts. Recent studies show that if you eat peanuts while breastfeeding and gradually introduce them into your baby's diet during the first year, your baby will be less likely to become allergic to them in the future. 4
Are extra calories needed while breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding mothers need about 500 more calories per day. 5 But every mother is unique and your energy needs will change throughout your breastfeeding period. The number of calories you need depends on your baby's age, appetite, height, and weight, as well as your body mass index (BMI), your activity, and factors such as whether you are exclusively breastfeeding or not, and whether you are breastfeeding twins or multiple babies.
Can I go on a diet while breastfeeding?
Trying to lose weight while breastfeeding is not a good idea because you need to get enough nutrients for you and your baby.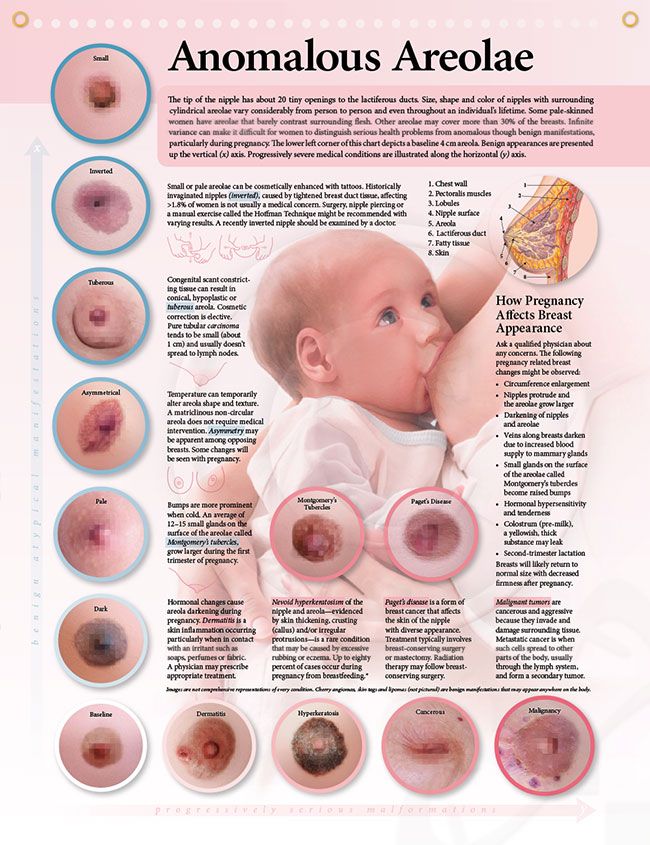 The fat accumulated during pregnancy is used to produce milk, so breastfeeding in itself will help you shed those extra pounds.
The fat accumulated during pregnancy is used to produce milk, so breastfeeding in itself will help you shed those extra pounds.
If your weight changes by more than 1 kg per week, check if you are eating a healthy and balanced diet and adjust if necessary. You can also ask your doctor for advice.
How can I find time to prepare healthy meals?
Having devoted yourself to feeding a child, you can forget about your own nutrition. However, it is important to ensure that your diet does not consist only of sweets and cookies. Of course, sweet snacks are easy and quick, but they do not bring any benefit to your body.
Opt for quick yet nutritious meals like scrambled eggs with spinach or fried chicken with brown rice. Oatmeal is great for breakfast, as it provides a slow release of energy from grains and soluble dietary fiber, which is what you need to restore strength in the morning after a night of breastfeeding.
Store pre-cut fruits and vegetables in the refrigerator for light snacks, or carry unsalted nuts in your bag. It's much easier than peeling tangerines with one hand while holding a baby with the other.
It's much easier than peeling tangerines with one hand while holding a baby with the other.
Should I drink more water while breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding can make you thirsty, so it's important to drink enough water. A person needs six to eight glasses of fluid a day, and even more if breastfeeding. 6 Make it a habit to drink a glass of water, milk or fruit juice without sugar every time you feed your baby.
I love coffee. Do I need to quit caffeine?
Coffee, like everything you eat or drink, passes into your breast milk, so it is advisable to limit your intake while breastfeeding. Legal coffee limits vary by country, but the average recommendation is not to exceed 200-300 mg of caffeine per day (300 mg is equivalent to two cups of filtered coffee or four cups of tea). Talk to your doctor about the acceptable amount of coffee consumption for you. Also, don't forget that caffeine is found in cola and energy drinks, and a small bar of dark chocolate can contain up to 50 mg. 7
7
If I eat a varied diet, will my baby be less picky?
Breast milk has the flavor of everything you eat. 8 Therefore, if you eat a variety of foods during breastfeeding, giving your baby different tastes to try, he may like them in the future.
If you like spicy and spicy foods, there is no reason to refuse them while breastfeeding. When my first child was born, I ate a lot of spicy food. When my daughter was two years old, we went to Sri Lanka, coincidence or not, but she ate absolutely everything.
Can something in my diet not be suitable for a child?
At an early age, babies often suffer from colic or are picky eaters, so mothers naturally wonder if their diet is causing this. Most likely no. Studies show that the proportion of children who are allergic to any component of breast milk is only slightly more than 1%. 9 Cow's milk, eggs, corn, and soy proteins in moms' diets are much more likely to cause allergic reactions than spicy foods, hot sauces, or cruciferous vegetables, which moms usually worry about.
If your baby is allergic to substances in your milk, it can cause profuse vomiting, rash, bloody stools, or prolonged constipation. If your baby has an intolerance to any food, you will notice symptoms such as moodiness and crying after feeding, burping, diarrhea, or the baby will press his knees to his chest. Contact your doctor if something is bothering you. He may suggest eliminating certain foods for a couple of weeks, and then see if the child's behavior changes after eating them again.
You can also keep a food diary: write down everything you eat and drink, as well as your child's symptoms, and you may notice some patterns. However, before cutting out any foods, such as dairy, always check with your doctor, as it's important to know that you're getting the nutrients you need from other sources. Depending on where you live, you will be referred to a nutritionist or other specialist.
Does a vegetarian diet affect breast milk?
If you are getting enough calories and all the nutrients your body needs (carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals), then you have nothing to worry about. A vegetarian or vegan diet requires plenty of vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids while breastfeeding, so opt for foods and supplements that provide you with these essential nutrients.
A vegetarian or vegan diet requires plenty of vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids while breastfeeding, so opt for foods and supplements that provide you with these essential nutrients.
If you are on a vegetarian, vegan, macrobiotic, or other special diet, you may need additional medical advice to make sure you are getting all the nutrients your baby needs.
Literature
1 National Health Service (NHS) [Internet]. Burnley, UK: Department of Health; 2018. Should pregnant and breastfeeding women avoid some types of fish?; 2015 Jul 06 [cited 2018 Apr 12]; Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/should-pregnant-and-breastfeeding-women-avoid-some-types-of-fish.aspx - National Health Service (NHS) [Internet]. Burnley, UK: Department of Health; 2018. "Should a pregnant and lactating woman refrain from eating certain types of fish?"; July 6, 2015 [cited April 12, 2018]; See article on site https://www.nhs.uk/chq/Pages/should-pregnant-and-breastfeeding-women-avoid-some-types-of-fish. aspx
aspx
2 Oberhelman SS et al. Maternal vitamin D supplementation to improve the vitamin D status of breast-fed infants: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013;88(12):1378–1387. - Oberhelman S.S. et al., Introduction of Vitamin D to the Diet of Nursing Mothers to Increase Vitamin D in children: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Klin Prok. 2013;88(12):1378–1387. : effects on the mother and the fetus. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194(4):937-945. - Thomas M., Weisman S. M., "Calcium supplementation during pregnancy and lactation: effects on the mother and on the fetus". Am J Obstet Ginekol (American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology). 2006;194(4):937-945.
4 Pitt et al Reduced risk of peanut sensitization following exposure through breast-feeding and early peanut introduction. J Allergy Clinic Immunol. 2018;141(2):620-625. e 1 - Pitt et al., "Reducing the Risk of Peanut Allergy by Introducing Peanuts into the Breastfeeding Mother's Diet and as a Baby's First Food." G Allergy Clean Immunol. 2018;141(2):620-625.e1
J Allergy Clinic Immunol. 2018;141(2):620-625. e 1 - Pitt et al., "Reducing the Risk of Peanut Allergy by Introducing Peanuts into the Breastfeeding Mother's Diet and as a Baby's First Food." G Allergy Clean Immunol. 2018;141(2):620-625.e1
5 Dewey KG. Energy and protein requirements during lactation. Annu Rev Nutr. 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36. - Dewey K. J., "Energy and Protein Requirements During Lactation". Anna Rev Nutr . 1997 Jul;17(1):19-36.
6 Food Standards Agency (FSA) [Internet]. London, UK: Crown copyright 2002. Eating for breastfeeding; [cited 2018 Apr 13]; Available from: https://www.food.gov.uk - Food Standards Agency (FSA) [Internet]. London, UK: State Copyright 2002. "Eat to feed" [cited April 13, 2018]. See article on https://www.food.gov.uk
7 National Health Service (NHS) [Internet].