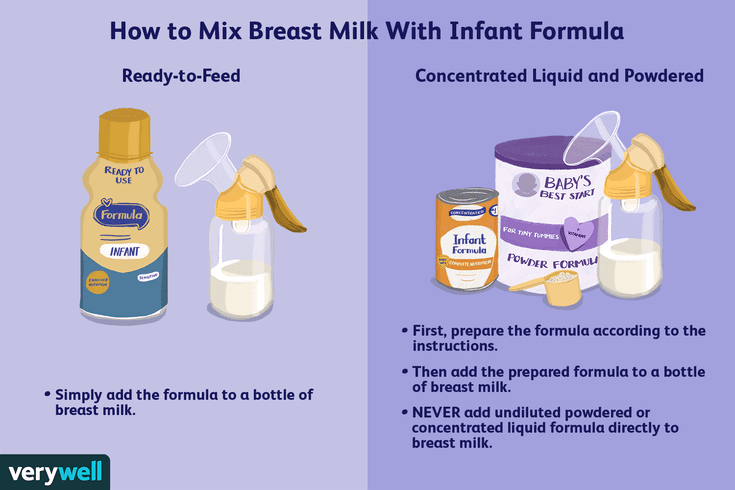
Good iron food for babies
Iron | Nutrition | CDC
What Does Iron Do?
Iron is a mineral that has many functions. Iron helps red blood cells carry oxygen through the body and supports a child’s ability to learn. Having enough iron in the body can help prevent iron deficiencyalert icon and iron deficiency anemia.alert icon
What Happens If My Child Does Not Get Enough Iron?
If your child does not get enough iron, your child may develop anemia.alert icon Anemia is when there are not enough red blood cells in the body or your child’s ability to carry oxygen throughout the body is lowered. There are many causes of anemia. In young children, one common cause is not enough iron. Children who do not receive enough iron either from iron-rich foods or supplements are at greater risk for developing anemia.
When Does My Child Need Iron? And How Much?
All children need iron. It is important at all stages of your child’s development. Babies fed only breast milk, only formula, or a mix of breast milk and formula have different needs when it comes to iron.
Talk to your child’s doctor or nurse about your child’s iron needs at his or her next check-up.
Preterm babies often need more iron than full-term babies.
In addition, preterm babies may need extra iron beyond what they get from breast milk or infant formula. Talk to your child’s doctor or nurse about your child’s iron needs at his or her next check-up.
Breast Milk
- Talk with your child’s nurse or doctor about if your child needs iron supplements before 6 months old.
- Once your child starts to eat foods, it is important to give foods with iron to meet nutritional needs.
Formula
- Your child’s iron needs can be met by standard infant formulas for the first 12 months of life.
- Choose a formula that is fortified with iron. Most commercial infant formulas sold in the U.S. contain iron.
- Standard iron-fortified infant formulas contain enough iron (12mg/dL) to support your growing child’s needs.

- Once your child starts to eat foods, introduce your child to foods that contain iron.
Mix of Breast Milk and Formula
- Once your child starts to eat foods, it is important to give foods with iron to meet nutritional needs pdf icon[PDF-30.6MB]external icon.
Top of Page
Once My Child Starts to Eat Solid Foods, How Can I Make Sure My Child Gets Enough Iron?
When your child is about 6 months old, you can start giving solid foods to your child. Make sure to choose foods that contain iron. Iron found in foods comes in two forms: heme and non-heme iron.
Heme iron is commonly found in animal products and is more easily absorbed by the body. Sources of heme iron include:
- Red meat (for example, beef, pork, lamb, goat, or venison)
- Seafood (for example, fatty fishexternal icon)
- Poultry (for example, chicken or turkey)
- Eggs
Your child needs to be screened for anemia.
At around 12 months, your child’s doctor or nurse will likely test to see if your baby has anemia. Anemia can occur among children who do not get enough iron. Talk to your child’s doctor or nurse about anemia and iron at your baby’s next check-up.
Non-heme iron can be found in plants and iron-fortified alert icon products. This type of iron is less easily absorbed by the body and will require careful planning to get enough iron for your baby. Sources of non-heme iron include:
- Iron-fortified infant cereals
- Tofu
- Beans and lentils
- Dark green leafy vegetables
Pairing non-heme iron sources with foods high in vitamin C can help your baby absorb the iron he or she needs to support development. Vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetablesexternal icon include:
- Citrus fruits like oranges
- Berries
- Papaya
- Tomatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Dark green leafy vegetables
Making sure your child is getting enough iron is important. Some children may need more iron than others. Talk to your child’s doctor or nurse about iron at your child’s next check-up.
Some children may need more iron than others. Talk to your child’s doctor or nurse about iron at your child’s next check-up.
Top of Page
Best Iron-Rich Foods for Babies, Toddlers, & Kids (+50 Recipes!)
Ensuring that our kids eat a well balanced diet, including iron-rich foods, can be hard when they’re eating unpredictably. I hope this info on iron-rich foods for kids (and the recipe ideas at the bottom) helps to set your mind at ease!
Iron-Rich Foods
Ensuring that your kids are getting enough iron can seem hard when they’re in a phase of picky eating—or just not eating a ton. But since iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia are still common issues with kids and it can impact their development and behavior, it’s important to try to include iron-rich foods in their daily meals.
For some context, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics, “Among children ages 1 to 3 years, iron deficiency occurs in 6.6 percent to 15.2 percent of toddlers, depending on ethnicity and socioeconomic status. ” Which is much higher than I would have expected. They say that preterm infants, exclusively breastfed infants, and infants at risk of developmental disabilities are at higher risk for deficiencies.
” Which is much higher than I would have expected. They say that preterm infants, exclusively breastfed infants, and infants at risk of developmental disabilities are at higher risk for deficiencies.
I never want any parents to worry excessively about their child’s nutritional intake and thankfully, adding iron to a diet is actually quite easy.
(My favorite iron-rich recipes include Spinach Muffins, Extra-Veggie Baby Pasta, Oatmeal Bars, Meatballs, Chicken Puree, Butter Chicken, Chicken Tacos and Spinach Eggs. For more, scroll down.)
How much iron does my child need?
Toddlers ages 1 to 3 years need 7 mg/day of iron. Kids aged 4-8 need 10 mg/day. For context:
- ¾ cup of Cheerios: 6 mg
- 1 serving fortified infant oatmeal: 5 mg
- 4 ounce hamburger: 5 mg
- 2 ounces Banza chickpea pasta: 4 mg
- ½ cup dried peaches: 3.2 mg
- 2 ounces Barilla red lentil pasta: 3 mg
- ½ cup of lentils: 3 mg
- 1 cup prune juice: 3 mg
- Spinach Quesadilla: 2.
 1 mg
1 mg - ½ cup dried apricots: 1.7 mg
- ½ cup oatmeal: 1.7 mg
- Simple Green Smoothie: 1.7 mg
- Spinach Banana Muffin: 1.4 mg
- 1 egg: 1.4 mg iron
- ½ cup raisins: 1.5 mg
- 1 slice whole wheat bread: 0.7 mg
- ½ cup fortified baby puffs: 0.7 mg
- 1 ounce hummus: 0.7 mg
- 2 tbsp peanut butter: 0.6 mg
- ½ cup edamame beans: 0.5 mg
- 1 cup watermelon: 0.4 mg
TIP: It’s possible that your kiddo is already getting enough just by eating normal toddler-size servings.
Does my child need an iron supplement?
This question will vary a lot by child so it’s best to check in with your doctor. Kids are routinely screened for iron deficiency when they’re babies and toddlers, so definitely discuss this with your pediatrician if you don’t remember what those results were, if your child is older, or if you’re just curious about supplementing.
It can be hard to find a multivitamin with iron, so check your label, or consider a separate iron supplement in consultation with your doctor.
What are the best sources of iron for kids?
The AAP recommends that iron comes from iron-rich foods first and foremost. The type of iron in meat, fish, and poultry is easier for our bodies to absorb, but adding a range of iron-rich foods is your best bet. Here are some examples of foods with a good dose of iron.
- Red meats like beef and lamb
- Dark meat poultry
- Fish including shrimp and oysters
- Iron-rich vegetables including dark leafy greens (think Popeye!), baked potatoes, and pumpkin
- Beans and legumes like kidney beans, lentils, and tofu
- Fortified cereals like Cheerios and some hot cereals including baby oatmeal
- Whole grains and whole grain products (including some of the newer bean pastas like Banza)
TIP: A toddler-size serving of meat is 2 tablespoons to ¼ cup. A toddler-size serving of produce is 2 tbsp to ¼ cup. A serving of beans and legumes is 1-2 tablespoons for younger kids and ¼ cup for older kids. (Find more specifics in my Daily Toddler Nutrition Guide.)
(Find more specifics in my Daily Toddler Nutrition Guide.)
Top 10 Best Iron-Rich Foods for Babies
Here are my go-to foods with a lot of iron that you can feed to a baby who’s eating purees or baby led weaning style foods.
- Beef, ground
- Bean puree
- Beans, very soft and lightly mashed
- Bean pasta, cooked very soft (like Banza)
- Chicken, finely shredded or ground or Chicken Puree
- Eggs, scrambled or Egg Yolk Puree
- Green bean puree
- Infant cereal like baby oatmeal, fortified
- Oatmeal
- O cereal
- Smoothies with spinach or kale (serve on a spoon or in a reusable pouch)
- Sweet potatoes, mashed
- Pea puree
- Peanut butter puree
- Strawberry puree
TIP: Iron stores in babies start to run out starting around 6 months, so you’ll want to incorporate these foods into your baby’s diet from an early age.
Top 15 Best Iron-Rich Foods for Toddlers and Big Kids
These foods are easy to prepare and packed with iron for kids.
- Apricots, dried
- Beans
- Bean pasta (like Banza with marinara sauce)
- Beef burgers
- Broccoli
- Eggs
- Green beans
- Oatmeal
- Peanut butter
- Raisins
- Smoothies with spinach or kale
- Spinach Pesto
- Strawberries
- Watermelon
- Wheat bread
TIP: Aim to serve 2-3 of these foods (from either the baby or toddler list) most days and you should easily provide enough opportunities for your child to eat enough iron.
Add Vitamin C for Increased Iron Absorption
If you pair iron-rich foods with produce with plenty of Vitamin C—think citrus, strawberries, kiwi, tomatoes, dark greens, and bell peppers—the iron will be more readily absorbed by the body. Some ideas to consider:
- Pasta with Meatballs (Vitamin C from tomatoes, iron from beef)
- Bean Burritos with salsa (iron in beans, Vitamin C from salsa)
- Bean Quesadillas with chopped tomatoes on the side (iron in beans and whole grain tortilla, Vitamin C from tomatoes)
- Simple Green Smoothie (iron from greens, Vitamin C from fruit)
- Spinach Banana Muffins with Banana with kiwi (iron in spinach, Vitamin C from kiwi)
Limit Milk to No More than 24 Ounces Each Day to Avoid Limiting Iron Absorption
Experts at the Mayo Clinic also advise against letting the kids have more than 24 ounces of milk in a day (or three 8 ounce servings) which could negatively impact iron absorption. That much milk could also make them less hungry for other foods, which could also limit how much iron they’re able to eat through foods.
That much milk could also make them less hungry for other foods, which could also limit how much iron they’re able to eat through foods.
50 Best Iron-Rich Recipes for Babies, Toddlers, and Kids
Here are some of my favorite recipes for kids of all ages that are rich in iron. (The list is organized alphabetically for easy reference, not in order of preference!)
- Bean Puree
- Bean Pasta with Marinara Sauce
- Beef Burritos with Veggies
- Black Bean Quesadillas
- Black Bean Soup with Citrus
- Broccoli Pesto
- Broccoli Cheddar Soup
- BBQ Shredded Chicken
- Cheesy Meat Buns
- Chicken Meatballs with Sweet Potato
- Chocolate Smoothie with Hidden Veggies
- Green Smoothie
- Kale Bites
- Lentils and Rice with Dried Fruit
- Lentils with Tomatoes and Italian Spices
- Lentil Soup with Veggies
- Lentil Falafel
- Meatballs with Hidden Veggies
- Mini Egg Muffins
- Mexican Egg Muffins with Spinach
- Moroccan Lamb Meatballs
- No-Bake Energy Bites
- Nut-Free Hummus
- Oatmeal with Apple and Raisins
- Oatmeal Bars
- Oatmeal with Pumpkin
- Pesto Chicken and Brown Rice
- Potato Nachos
- Pumpkin Oatmeal Bars
- Pumpkin Oatmeal Muffins
- Slow Cooker Chicken and Bean Tacos
- Slow Cooker Black Bean Soup
- Slow Cooker Chicken Tacos
- Spinach Banana Muffins with Banana
- Spinach Pancakes
- Spinach Eggs
- Spinach Pesto
- Spinach Quesadillas
- Strawberry Puree
- Strawberry Smoothie
- Strawberry Muffins
- Sweet Potato Quesadillas
- Sweet Potato Baby Food
- Tofu Nuggets
- Tofu, Baked
- Tofu with Sesame
- Whole Wheat Bread
- Veggie Chili
- Veggie Chili Mac
- Zucchini Burgers
Printable Iron-Rich Foods List
For easy reference, you can print this list of iron-rich foods for kids keep in your kitchen, or save the image on your phone. Simply sign up for my newsletter and gain access to my entire FREE Resource Library of printables.
Simply sign up for my newsletter and gain access to my entire FREE Resource Library of printables.
Related Recipes
I’d love to hear if iron has been an issue for you with your kids. Chime in below in the comments!
Anemia in a child. Prevention and treatment
In modern conditions, it is quite difficult to find high-quality products that contain in their composition all the substances necessary for a growing organism. In addition to this, most pregnant and lactating mothers do not eat properly, whole cow's milk is introduced too early into the baby's diet. All this leads to the fact that the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is made in almost every pregnant woman and many children at an early age. How to solve this problem? After all, drugs for anemia can cause various stool disorders, allergic reactions, and so on, and the disease itself negatively affects the well-being and development of the child. nine0003
Prevention of iron deficiency anemia
Since the problem of iron deficiency in the body is more of a nutritional problem, the main measure for the prevention of pathology is to ensure a balanced diet (regardless of the age of the person). Adults need 1-2 mg of iron per day, children from 0.5 to 1.2. It should be noted that only a part of the iron consumed with food is absorbed in the intestine - approximately 10-15%.
Adults need 1-2 mg of iron per day, children from 0.5 to 1.2. It should be noted that only a part of the iron consumed with food is absorbed in the intestine - approximately 10-15%.
The main source of iron from food is animal products. The most valuable in this regard are beef and lamb. In fish, chicken and cottage cheese, the iron content is much less. It is important not only the amount of the substance in the product, but also its bioavailability (that is, absorption). Unlike animal products, plant foods have a lower level of iron absorption. Certain factors are necessary for good absorption. So, for example, vitamin C improves the absorption of iron, and tinic acid (found in tea) or phytates significantly reduce the degree of absorption of the trace element. nine0003
Consider the main recommendations for the prevention of iron deficiency published by the American Academy of Pediatrics:
1. A healthy full-term baby has an adequate supply of iron in the first 4 months of life, and there is no need to take iron-containing drugs. The breastfed child then needs supplemental iron until complementary foods are introduced. The dosage of the drug at this age should be 1 mg per 1 kg of weight per day. nine0003
The breastfed child then needs supplemental iron until complementary foods are introduced. The dosage of the drug at this age should be 1 mg per 1 kg of weight per day. nine0003
2. If a healthy full-term baby is on a mixed type of feeding (mother's milk is about 50%), he needs an additional intake of iron at a dosage of 1 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day. Duration of admission - before the introduction of complementary foods.
3. With artificial feeding, it is recommended to give the child a mixture enriched with iron. In this case, the need for additional medication is not required. At the same time, whole cow's milk is not recommended for children under the age of one year! nine0003
4. Children from 6 months to a year need to consume about 11 mg of iron per day. To ensure the normal functioning of the body, red meat and vegetables containing a large amount of iron should be introduced into early complementary foods. With insufficient consumption of such products, the child is prescribed iron-containing drops or syrups.
5. From a year to 3 years, the daily norm of iron is 7 mg. At the same time, it is recommended to get it from those foods that contain both iron and vitamin C. nine0003
6. Children born prematurely must receive at least 2 mg of iron per 1 kg of body weight per day until the onset of 12 months.
Note that the content of meat in the diet is only the prevention of anemia, if the child has already been diagnosed with a pathology, it can only be dealt with with iron preparations! However, if anemia has not been detected at the moment, then drinking iron as a prophylaxis is not advisable.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia
The most important task in the treatment of anemia is to eliminate the cause of its occurrence (diet, detection and elimination of sources of blood loss, etc.), as well as the fight against iron deficiency in the body.
The main provisions of the treatment of the disease include:
1. The use of medicinal iron-containing preparations. Other ways to restore the normal level of the trace element have not yet been invented. Do not mistakenly believe that only one diet will be able to raise the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Iron reserves must be replenished purposefully. nine0003
Other ways to restore the normal level of the trace element have not yet been invented. Do not mistakenly believe that only one diet will be able to raise the level of hemoglobin in the blood. Iron reserves must be replenished purposefully. nine0003
2. Taking oral medications. Treatment with intramuscular or intravenous injections is recommended only if there are contraindications to taking oral medications or if they have proven ineffective.
3. Preliminary calculation of the dosage of the drug in accordance with the body weight of the child and the chosen tactics for the treatment of anemia.
4. Calculation of the duration of iron intake depending on the severity of the disease. Mild degree - 3 months, medium - 4.5, severe - six months. In the course of treatment, a general clinical blood test is monitored. nine0003
5. Replenishment of microelement reserves in the so-called "iron depot".
6. Regular monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment by taking blood tests.
In our country, the tactics of treating anemia are determined by the Protocol for the management of patients diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia, which was published in 2004. There are also relevant WHO recommendations based on the principles of evidence-based medicine.
At present, there are only two preparations of iron: nine0003
1. Based on saline solutions. The drug is toxic, often causes side effects. However, there are cases when only he helps.
2. Based on a polymaltose hydroxide complex. Most useful in the treatment of anemia.
Modern studies show that drugs of the first and second groups have the same degree of effectiveness. In pediatrics, the children's dosage of the second type is 5 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day (regardless of the age of the child). nine0003
Criteria for the effectiveness of therapy for anemia
1. On the 7-10th day from the start of therapy, the level of reticulocytes begins to rise.
2. The concentration of hemoglobin increases by the end of the 4th week by 10 g/l. Hematocrit increases by 3% compared to the original data.
3. After 1-1.5 months of taking the drugs, the clinical manifestations of iron deficiency disappear.
4. "Depot of iron" is restored after 3-6 months (depending on the degree of the disease). It is necessary to evaluate the level in terms of serum ferritin (more than 30 ng / ml). nine0003
In the event that after 4 weeks the results of the blood test do not change, it is necessary to stop treatment and reconsider the diagnosis. In some cases, these patients have non-iron deficiency anemia.
If resistance to treatment with iron-containing drugs occurs, the adequacy of the prescribed therapy should be checked. Maybe anemia is not related to iron deficiency. This requires an additional consultation of a pediatric hematologist.
Proper nutrition of a child with iron deficiency anemia
— Valeria Maksimovna, what happens in the body of a baby with iron deficiency anemia?
- Iron deficiency anemia in young children is a pathological condition characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells or hemoglobin concentration in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron. It is a transport protein and participates in gas exchange: it takes oxygen from the lungs, transfers it to organs and tissues and vice versa, takes carbon dioxide from organs and tissues and delivers it to the lungs. This protein needs iron to function. nine0003
Hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron. It is a transport protein and participates in gas exchange: it takes oxygen from the lungs, transfers it to organs and tissues and vice versa, takes carbon dioxide from organs and tissues and delivers it to the lungs. This protein needs iron to function. nine0003
Causes of iron deficiency in infants
— What are the clinical symptoms of iron deficiency anemia in a child?
— The diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is based on clinical symptoms and laboratory confirmation. In this case, the signs of iron deficiency anemia in infants depend on the severity of the disease.
Mild anemia
Asthenovegetative syndrome
— Occurs as a result of hypoxia of organs and tissues, because the cells do not receive enough oxygen, and therefore energy. Cells, including cells in the brain and nervous system, cannot function normally. nine0003
Cells, including cells in the brain and nervous system, cannot function normally. nine0003
- The child is lethargic. The kid does not need anything, he is not interested in anything.
- Games are monotonous, inactive.
- The child does not want to do anything.
- Sleeps constantly or for a long time, wakes up with difficulty.
- Tearful, irritable.
- Gets tired quickly when walking and running.
- Dizziness may occur.
Children should be active, but with asthenovegetative syndrome, on the contrary, the baby is not interested in anything. He lags behind in physical development, he seems to be supposed to sit and get up by age, but for some reason he does not want or cannot do this. And such a condition may not be associated with neurological problems, but with a lack of energy in the body. nine0003
The syndrome is non-specific and may occur in other diseases, often in respiratory infections and chronic conditions. Therefore, correct differential diagnosis is important.
Therefore, correct differential diagnosis is important.
Epithelial syndrome
— Consists of changes in the skin.
- Dry skin.
- Hyperkeratosis (scales, increased keratinization of the skin, which is especially noticeable on the elbows, knees).
- Non-healing cracks in the corners of the mouth (also a marker of immunodeficiency). nine0098
- Damage to the oral mucosa (aphthous stomatitis - sores).
Dyspeptic symptoms
— Conditions associated with bowel dysfunction. You can observe diametrically opposite symptoms: in each child, iron deficiency manifests itself in different ways.
- Loss of appetite.
- Constipation or diarrhoea.
- Flatulence.
- Aching pain in the abdomen.
If iron deficiency anemia is a consequence of a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, then the symptoms of the underlying disease that the child has are added. These can be, for example, signs of metabolic disorders and dysbacteriosis, which further worsens the baby's condition and iron absorption. nine0003
nine0003
Severe anemia
Changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular system
— Consists of changes in the skin.
- Tachycardia.
- Shortness of breath.
- Various heart murmurs (specific dull murmur in anemia).
Immunodeficiency states
— The body tries to somehow compensate for the current situation and spends all its energy on maintaining normal work — therefore, it no longer has the resources to ensure normal immunity. nine0003
— What tests confirm iron deficiency anemia in infants?
— Clinical and biochemical blood tests are carried out. The doctor analyzes the content of red blood cells, hemoglobin, the degree of saturation with hemoglobin, the level of ferritin (displays the depot of iron in the body). After evaluating these and other indicators, conclusions are drawn. However, the diagnosis of anemia based on the results of a single examination is not made.
It must be understood that in children under six months of age there may be a physiological decrease in hemoglobin. A breastfed baby will not get the required amount of iron. But taking into account the introduction of complementary foods from six months, the condition is leveling off. nine0003
A breastfed baby will not get the required amount of iron. But taking into account the introduction of complementary foods from six months, the condition is leveling off. nine0003
If the doctor first sees deviations in ferritin in the baby, that is, iron stores are reduced in the body with normal levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin, he is in no hurry to make a diagnosis and prescribe drugs. First, the pediatrician will observe the child in dynamics, correct nutrition and search for a possible cause of iron loss.
— Is it possible to predict the development of iron deficiency anemia in a child at the prenatal stage?
— Antenatal factors are taken into account. In women with anemia, a history of acute and chronic diseases, blood loss, children are at risk for the development of iron deficiency anemia. But this does not mean that the child will necessarily be born with the disease - it is simply that the risk of developing anemia is higher than that of a child born with a favorable pregnancy. nine0003
nine0003
— How to treat iron deficiency anemia in a child?
- They act on the cause of the disease. If these are antenatal factors that cannot be influenced, or some kind of congenital disease associated with metabolic disorders and other conditions that are difficult to model, symptomatic treatment is prescribed, including iron preparations.
If the reason is that the child is not getting enough iron, then the severity of the anemia needs to be looked at. Very often it is enough to prescribe a special diet. But if the diet does not help, then iron preparations are also introduced. nine0003
— What to feed a child if he does not have enough iron?
— Iron deficiency anemia in infants can be prevented and treated. A diet for babies should consist of foods rich in heme iron.
— There is a difference in oxidation state between heme and non-heme iron. In the stomach, special mechanisms help convert one iron into another. Absorbed in the body and participates in the formation of hemoglobin only Fe2+. Therefore, of course, for the prevention and treatment of anemia, you need to eat more foods that contain heme iron, since it is absorbed faster and easier, and additional energy costs are not required to get from one form to another. nine0003
Therefore, of course, for the prevention and treatment of anemia, you need to eat more foods that contain heme iron, since it is absorbed faster and easier, and additional energy costs are not required to get from one form to another. nine0003
Breast milk, milk formula and sour-milk complementary foods should be consumed separately from iron-containing products. There is a lot of calcium in milk nutrition, which inhibits the reaction of converting non-heme iron into heme, slows down its absorption. Phosphates, which are found in eggs, cheeses and milk, and tannins contained in tea, cocoa, also act.
— What complementary foods should I give to a baby? If the child is not yet on meat supplements or is not ready to introduce complementary foods, the doctor first assesses the seriousness of the situation and the possibility of waiting for complementary foods, since the priority is to manage the child without specific supplements. If this does not work, then mashed potatoes and cereals enriched with iron are introduced, and iron-containing preparations are prescribed in addition. nine0003
nine0003
Read also
- about what substances are necessary for the proper development of the body of a newborn.
- Are children allergic to foods that contain a lot of iron?
- Food allergies can be to any food. For better absorption of iron, vitamin C is needed. It is found in large quantities in fruits, and there may be an allergy to them.
— Valeria Maksimovna, in addition to proper nutrition, what will help to avoid iron deficiency? nine0072
— Without a doctor's prescription, the child does not need to be given any iron supplements. A mother can, without a doctor's recommendation, offer her baby only children's products enriched with iron.
The mother herself should not have anemia: it is necessary to treat the disease during pregnancy, and this will be the prevention of iron deficiency in the unborn child. When breastfeeding, there should also not be an anemic state, since iron will first of all begin to be spent on the needs of the mother's body and will practically not be transmitted with breast milk to the child. But if the mother’s health is all right, then additional iron intake will not lead to an improvement in the baby’s condition. nine0003
But if the mother’s health is all right, then additional iron intake will not lead to an improvement in the baby’s condition. nine0003
Iron poisoning or excess iron buildup is rare because the body will take in as much as it needs. But with increased iron intake, the baby may experience problems with the gastrointestinal tract: flatulence, bloating, constipation, colic and other side effects.
- Are the complementary foods that are sold in the store already fortified with iron and substances that help it to be absorbed?
— Among the baby foods you can find ready-made complementary foods enriched with iron. Manufacturers declare this on the packaging. But you need to look at what kind of iron the product contains, with what components it is presented. nine0003
Iron fortification of baby food is desirable but not required by manufacturers. Iron has been added to MAMAKO ® cereals with goat milk. As we have already said, the intake of dairy food should be spaced apart in time with the nutrition of iron-containing foods, but this does not apply to milk porridges. Ready-made goat milk cereals have a balanced composition, their components are selected taking into account bioavailability. This food contains auxiliary elements - vitamins, minerals, amino acids. They help the body convert non-heme iron Fe3+ from cereals into heme Fe2+ and promote its absorption and better absorption. nine0003
Ready-made goat milk cereals have a balanced composition, their components are selected taking into account bioavailability. This food contains auxiliary elements - vitamins, minerals, amino acids. They help the body convert non-heme iron Fe3+ from cereals into heme Fe2+ and promote its absorption and better absorption. nine0003
In addition, goat's milk is rich in vitamin A. Although it does not participate in the process of iron absorption itself, it is important for the mobilization of iron from the depot. If health problems arise, then vitamin A will support immunity and help mobilize iron stores in the body, which also helps in the treatment and prevention of anemia.
The best treatment for iron deficiency anemia is early prevention. Mothers should pay attention to antenatal prevention: monitor their health during pregnancy, protect themselves from respiratory diseases, and if anemia develops, then undergo treatment so that there are resources and strength for breastfeeding. The primary prevention of anemia in a child is a balanced diet for a nursing mother, breastfeeding, an adapted infant formula with iron, and adequate complementary foods. You can use cereals and mashed potatoes enriched with iron, and also start giving meat at six months. It has been proven that the delayed introduction of meat is directly proportional to the development of iron deficiency anemia. By following these simple requirements, many can prevent this disease. But if a child has developed iron deficiency anemia, you should not come up with ways to treat the baby yourself - in this case, regular examination of the child and strict adherence to the doctor's prescriptions are necessary. nine0003
The primary prevention of anemia in a child is a balanced diet for a nursing mother, breastfeeding, an adapted infant formula with iron, and adequate complementary foods. You can use cereals and mashed potatoes enriched with iron, and also start giving meat at six months. It has been proven that the delayed introduction of meat is directly proportional to the development of iron deficiency anemia. By following these simple requirements, many can prevent this disease. But if a child has developed iron deficiency anemia, you should not come up with ways to treat the baby yourself - in this case, regular examination of the child and strict adherence to the doctor's prescriptions are necessary. nine0003
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist.