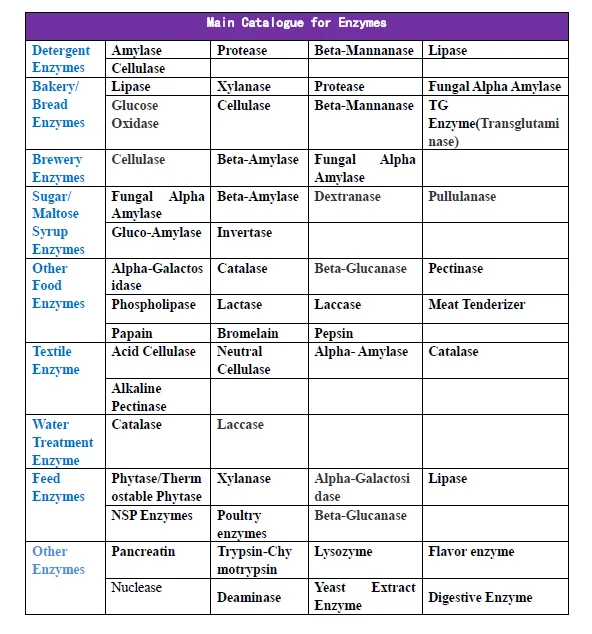
How are enzymes used in baby food
Enzymes Essay; Enzymes used in the Baby Food industry - GCSE Science
- Search
- Join over 1.2 million students every month
- Accelerate your learning by 29%
- Unlimited access from just £6.99 per month
Extracts from this document...
Enzymes used in the 'Baby Food' industry Enzymes allow chemical reactions to be carried out under milder conditions (lower temperature and pressure), thus saving costs. Since most supplements are not substrates for enzymes, the enzymes usually do not interact with them. You should be able to mix most supplements and medicines with enzymes. Enzymes may affect the properties of time-released medications increasing the rate at which they are broken-down, and thus, released. The enzymes which are used in baby food are there because they allow the food to be pre-digested in the baby's stomach. ...read more.
The main two enzymes used in the baby food industry are 'protease' and 'lipases'. A protease enzyme is usually used to break down protein it does this when it breaks peptide bonds by a process called hydrolosis. These bonds are linked together to create an amino acid. The best condition for use of protease is in acidic areas. Finally the proteases occur naturally in all organisms. A lipase is a water-soluble enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ester bonds in water-insoluble, lipid substrates. ...read more.
A protease in another industry is not used as it creates a higher mortality rate in the medicine industry for HIV/Aids. This enzyme has therefore been made into an alternate structure but with the same properties but not with the same processes. This in turn creates a social factor to be seen when treating the disease so the scientists have made a new type of ingredient called NNRTI to serve the same purpose as the protease enzyme. ?? ?? ?? ?? ...read more.
The above preview is unformatted text
This student written piece of work is one of many that can be found in our GCSE Humans as Organisms section.
Found what you're looking for?
Here's what a teacher thought of this essay
3 star(s)
***
A few good points but this is otherwise a rather superficial overview of the topic. The author should double check finished work to make sure it reads well and makes sense.
Marked by teacher Adam Roberts 30/07/2013
Not the one? Search for your essay title...
- Join over 1.2 million students every month
- Accelerate your learning by 29%
- Unlimited access from just £6.99 per month
See related essays
-
5 star(s)
protein to boost their immune system * When someone is pregnant they need proteins so that they get passed through to the child. In lactation (breast-feeding) there needs to be extra so that there is enough for the child and you Kwashiorkor Many protein rich foods are expensive.
-
5 star(s)
who fail to develop measles immunity after the first dose. [13] The second dose is given to everyone because it is impossible to distinguish which children have and which have not been immunised by the first vaccination without putting them at risk.
-
4 star(s)
Ventricular pressure continues to rise until eventually the pulmonary and aortic valves are forced open and blood is ejected into the pulmonary artery and aorta'. When the heart rate is increased the amount of time the diastole and systole take place is shortened, so that more blood is pumped out in one minute.
-
3 star(s)
This type of pace maker works on a requirement only bases. These may be used when patients whose sino-arterial node sends out signals too slowly, or the electrical pathway is partly or completely blocked, or the timing of atrial and ventricular contractions is uncoordinated (asynchronous), in this case a double chamber pace maker is used.
-
3 star(s)
doing surgery, that doctor would pass on to the next visited patient a potentially life threatening disease. He insisted that those doctors who worked for him wash their hands in calcium chloride after an operation and before visiting a new patient.
-
Water * Acts a solvent * Absorbs heat (temperature regulation) * Provides a medium for chemical reactions Salt * Maintains the osmotic balance in the body Change in Diet Obesity Kwashiorkor Pregnancy Puberty (Girls) Is excess growth Diet high in fat Leads sudden gain of weight Blockage of blood vessels
-
Respiration may completely stop due to the denaturation of all the enzymes associated with breaking down respiratory substrate. I have used a higher proportion of respiratory substrate in comparison to yeast because in order for the yeast to respire at an optimum rate throughout the experiment there must be excess substrate present.
-
The stronger heart moves more blood with each beat and therefore can do the same amount of work with fewer beats. This means that in my experiment, someone with a higher BMI (of 30, for example) may have a lower resting heart rate than those with a lower BMI.
- Over 160,000 pieces
of student written work - Annotated by
experienced teachers - Ideas and feedback to
improve your own work
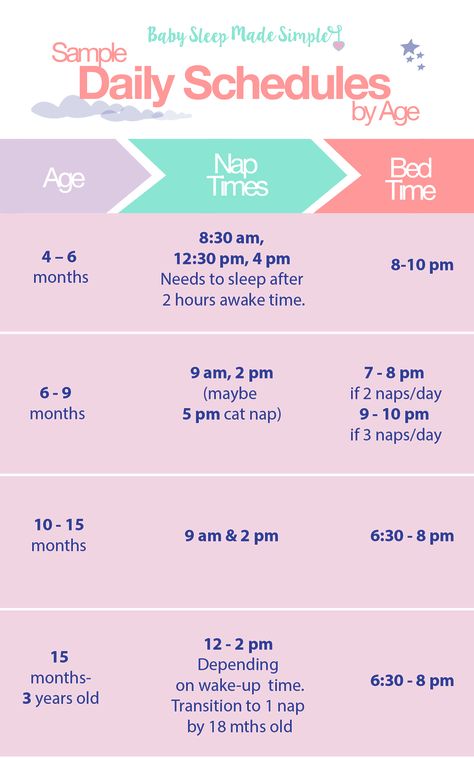
Baby Food Schedule Based on a Baby's Enzyme Development
I may receive commissions from purchases made through links in this article.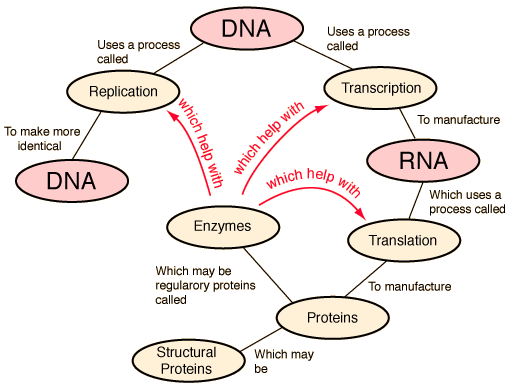 Full Disclosure
Full Disclosure
For being such a seemingly simple thing, introducing solids to babies actually involves a lot of consideration. Parents need to know when their baby is ready for solids, whether to do purees or baby-led weaning, and even being aware of food allergies and how to recognize if your baby has a reaction.
But there’s one more thing to consider and that’s the order we introduce solids to a baby.
Now before we dig in, I’m going to say (like I do in most of my posts concerning raising kids): even if you don’t follow all the rules, even if you are feeding your baby junk food… they are still going to turn out fine.
So if you haven’t been feeding your baby this way or after reading this you decide it’s not for you, then no worries.
Did you know that there is an order to which foods we should introduce our babies to? I’m not talking about how easy the food is to chew either, I’m talking about when to introduce meat, when to add dairy into their diet, when to give babies grains.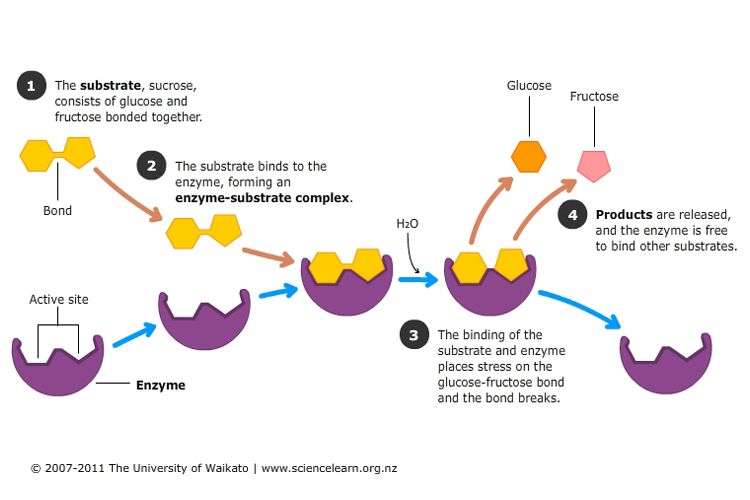
Now we are going to get a bit scientific here. As I’m sure you are aware of, babies continue developing even after they are born. This is true of their digestion as well. That’s why I’m writing this baby food schedule based on a baby’s enzyme development.
Enzymes are needed to digest our food, without them digestive problems and allergies can occur. In the beginning, babies only have the enzyme: lactase, which handily enough is what is needed to digest breastmilk. Other enzymes, which help digest proteins, fats, starches, and carbohydrates, develop as baby grows.
Produce – 6-9 months.
Around 6-9 months babies produce the enzymes, which help digest fruits and vegetables. Notice I didn’t say rice cereal?
Egg yolk – 6-9 months.
Some families with egg allergies avoid eggs altogether. However, all babies should not have egg whites until 12 months due to the high allergy possibility.Egg yolks however are fine. You can boil an egg and feed the baby just the yolk or you can separate the egg before cooking and cook just the yolk for your baby.
Meats – 6-9 months.
This is pretty much any meat with of course the exception of fish (after 1 year) and shellfish (after 2 years) due to the allergy possibility.Babies may not enjoy the texture of real meat so many parents puree it a bit. I add meat to my daughter’s veggie purees.
Broth – 6-9 months.
Homemade broth from chicken or even beef is a wonderful thing to add to your baby’s meals. Cook vegetables in broth, puree meats or veggies with broth, or just offer it by itself!
Healthy Fats – 6-9 months.
Babies need fat to develop properly. Adding healthy fats such as butter or coconut oil to your baby’s food is a great thing. In fact, when fat is added to vegetables, the nutrients are better absorbed! One more reason to add fats to baby’s and your food!
Dairy – 9-12 months.
Around this time you can introduce dairy. Cheese, yogurt, cottage cheese, etc are all great. However, leave cows milk out until after 12 months.
Grains – Sometime later, between 12-18 months
When a baby’s 1 year molar teeth are fully developed, babies are ready to start properly digesting grains. This is shocking news to most people.
All we ever hear is to start them on rice cereal and that cheerios make a great baby snack.However, this is quite far from the truth! The enzyme to digest grains is one of the last to develop!
When you are finally ready to introduce grains to your baby, non-gluten grains (rice, quinoa, millet) should be introduced first. Gluten grains (wheat, barley, oats) can be introduced last, I personally wait until my baby is 2 years old before adding in gluten.
Foods to avoid until after baby turns 1:
Honey
Cows milk
Citrus fruits
Nuts
Egg Whites
Choking Hazards such as raisins, grapes, popcorn
Grains
Fish
You can read more about what to feed a baby at the Weston A Price Foundation.
Enzyme deficiency in infants - Articles about baby food from pediatricians and MAMAKO experts
Enzymes (or enzymes) are protein catalysts that take part in a chemical reaction and change its rate.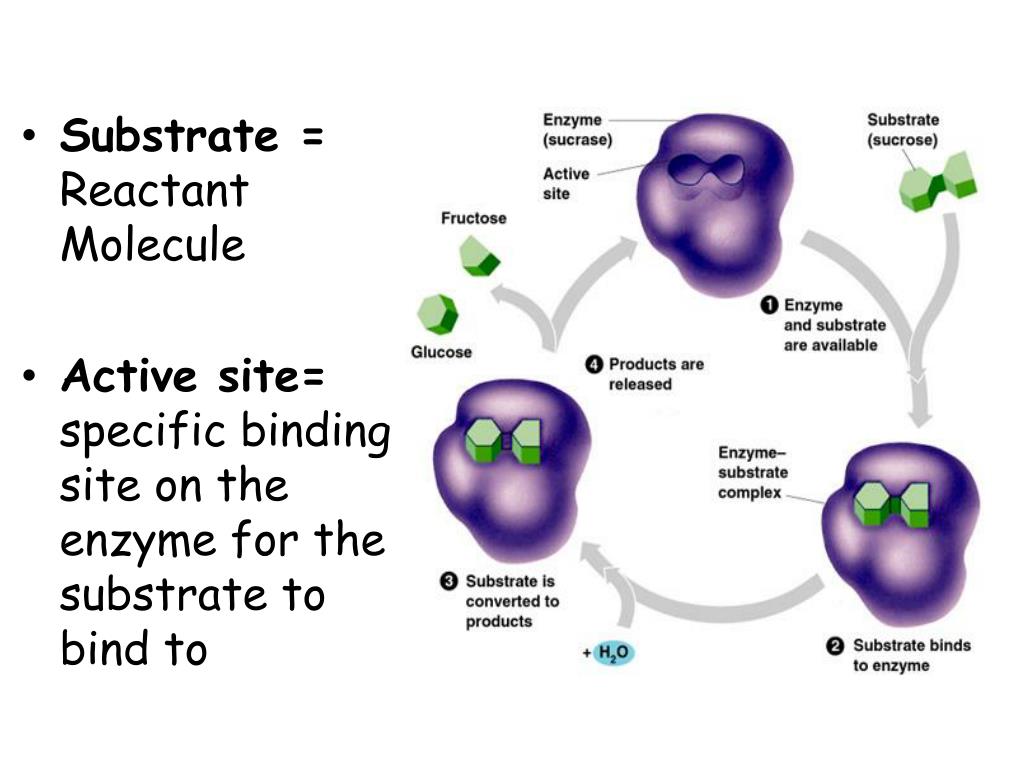
— Alla Anatolyevna, what is the importance of digestive enzymes for newborns?
— Enzymes are produced by the pancreas. They are involved in the breakdown of nutrients - proteins, fats, carbohydrates. Enzymes have different structures and functions depending on the reaction in which they are involved. The breakdown of nutrients to the necessary components allows them to be absorbed into the intestines and further participate in the growth and development of a small child.
— What is enzyme deficiency in children?
— Enzyme deficiency, or enzyme deficiency, is a lack of enzymes, which can manifest itself, among other things, in violation of the digestive process. In young children, this is lactase deficiency - a lack of the enzyme lactase, which breaks down the milk sugar (lactose) contained in breast milk, powdered and liquid milk mixtures.
Most infants experience transient (temporary) lactase deficiency in the first three months.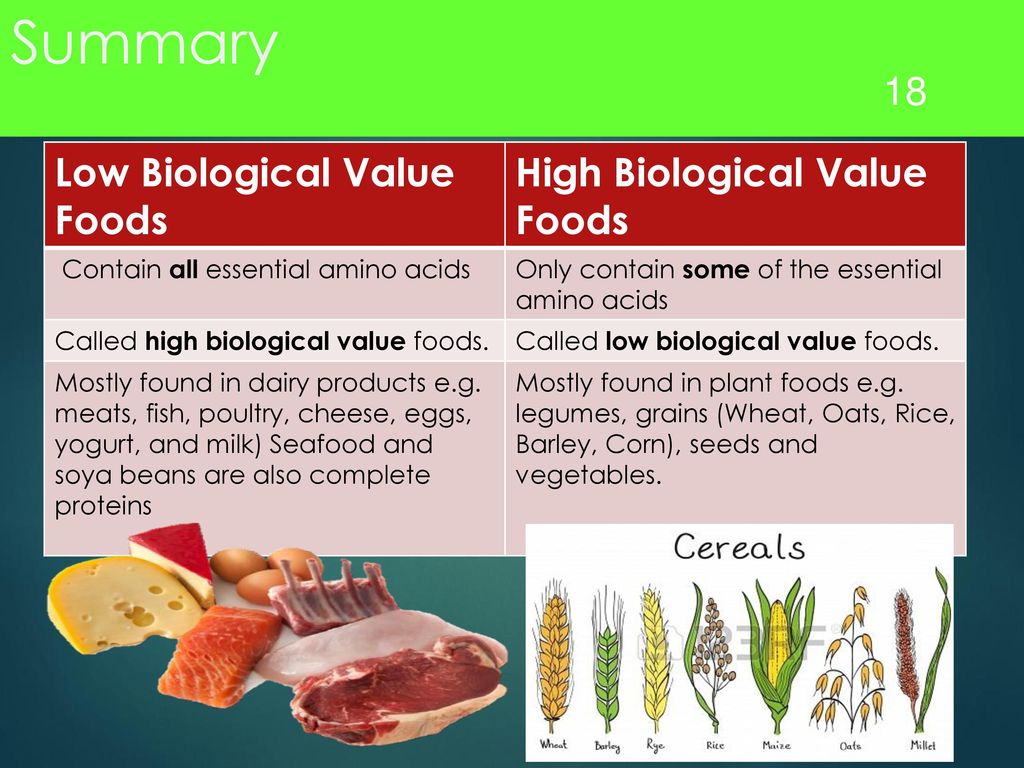 At this age, this is the norm, because the pancreas is still immature and its function is reduced, there is a little lack of lactase. The child’s stool is more liquid: we can say that this is how transient lactase deficiency helps to empty the intestines and fights constipation.
At this age, this is the norm, because the pancreas is still immature and its function is reduced, there is a little lack of lactase. The child’s stool is more liquid: we can say that this is how transient lactase deficiency helps to empty the intestines and fights constipation.
If the baby worries moderately, there is no catastrophe, the problem itself will go away with time. This is a difficult period in the life of a child that needs to be experienced.
— Are the causes of enzyme deficiency in a baby explainable?
— Nature invented it so that the body of a newborn is able to absorb not all milk sugar, but only part of it. Milk sugar residues serve as a nutrient substrate for the emerging gut microbiota and contribute to looser stools.
— What types of enzyme deficiency occur?
- Enzyme deficiency in the gastrointestinal tract can be divided into types depending on the lack of certain enzymes:
- protease - lack of enzymes for the breakdown of proteins;
- lipase - lack of enzymes for the breakdown of fats;
- amylase - lack of enzymes for the breakdown of carbohydrates.
- Despite the fact that reduced enzymatic activity in children is quite physiological, many parents do not calm down until they pass the tests. How to identify enzyme deficiency in infants?
— A typical medical test for lactose intolerance in an infant is a fecal carbohydrate test that measures the amount of lactose in the stool. In my practice, I do not prescribe such a study, because even lactose found in the feces is the norm for an infant at the age when the pancreas is being trained, its tolerance. And if a child gains weight well, eats well, observes the daily routine, maintains intervals between feedings, he is healthy.
— Alla Anatolyevna, how to treat enzyme deficiency in a newborn in order to alleviate its manifestations?
— Some doctors prescribe enzymes and multienzymes despite the fact that in children of the first months of life, enzyme (lactase) deficiency is not treated. It goes away with time, when the pancreas grows.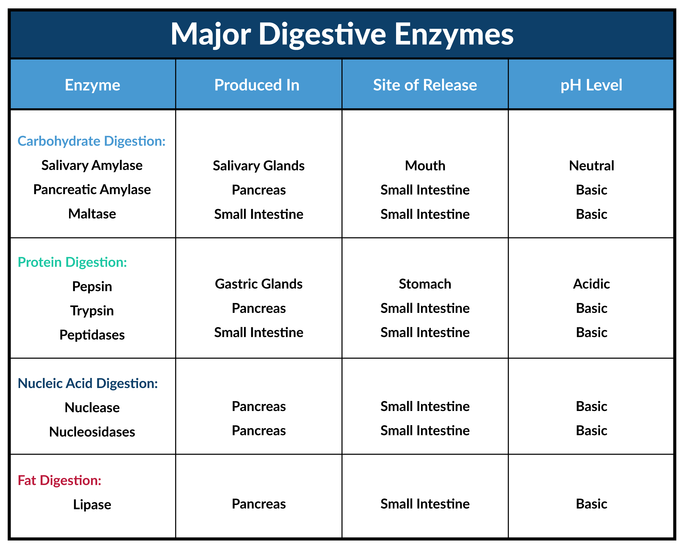 And adding the enzyme lactase to baby food does not affect the baby's digestion too much. With the baby's expressed anxiety, it is more correct to prescribe an additional examination, look for and treat another cause of problems with the tummy.
And adding the enzyme lactase to baby food does not affect the baby's digestion too much. With the baby's expressed anxiety, it is more correct to prescribe an additional examination, look for and treat another cause of problems with the tummy.
When the child grows up, the pancreas will begin to produce enough enzymes, milk sugar will be completely digested and transient lactase deficiency will go away.
— When are lactose-free milk formulas used that are consonant with the problem?
- The introduction of any mixture is best discussed with your doctor. Lactose is involved in the formation of galactocerebrosides in the brain. This is a necessary component for the growth and full development of the baby. Therefore, lactose-free formula should not be fed for a long time.
Such mixtures can be used in the acute period of intestinal infection, when the functions of the pancreas suffer, for example, after a viral gastroenteritis. During the recovery period, digestion must be supported - therefore, the appointment of a lactose-free nutritional formula is allowed. But only for a few days. When the acute period of intestinal infection passes, the mixture is canceled.
But only for a few days. When the acute period of intestinal infection passes, the mixture is canceled.
MAMAKO ® Premium formula based on goat's milk is suitable for feeding healthy children up to one year old, including babies with transient lactase deficiency.
— How to introduce complementary foods to a child with an enzyme deficiency?
- The time for the introduction of the first complementary foods is 5.5-6 months. At this age, the pancreas is already growing and begins to produce a sufficient amount of enzymes. Therefore, complaints associated with lactase deficiency are already disappearing, and complementary foods are given to such babies as healthy children. With a gradual introduction, these are the same vegetables, cereals, fruit purees, curds.
Enzyme deficiency is a deficiency of enzymes, including those produced by the pancreas and responsible for digestion. They break down nutrients into components that are easily digested in the intestines.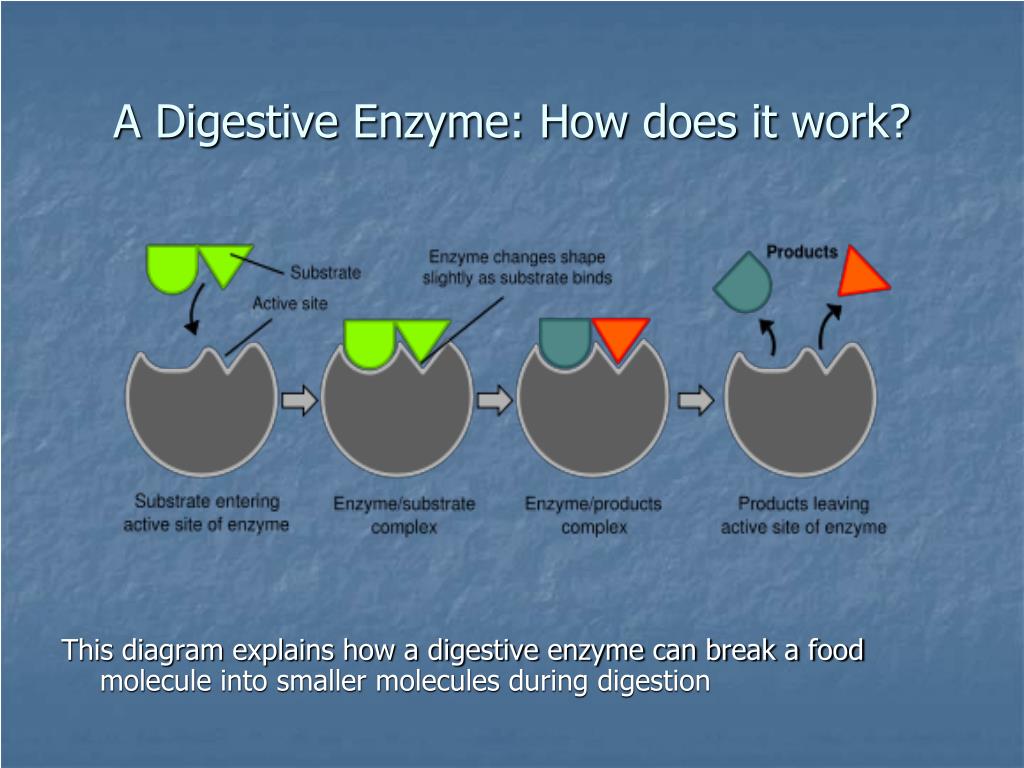 In children of the first months of life, there is often a deficiency of the lactase enzyme, which is able to digest the milk sugar of breast milk and milk formulas. Hence the problems with the tummy and stool. As a rule, lactase deficiency is caused by physiological immaturity. It will pass at about three months of age without a change in diet and the use of any medication.
In children of the first months of life, there is often a deficiency of the lactase enzyme, which is able to digest the milk sugar of breast milk and milk formulas. Hence the problems with the tummy and stool. As a rule, lactase deficiency is caused by physiological immaturity. It will pass at about three months of age without a change in diet and the use of any medication.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years. Before introducing new products into the baby's diet, you should consult with a specialist. The material is for informational purposes and cannot replace the advice of a healthcare professional. For feeding children from birth. The product is certified.
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates in baby food
Proteins are important for a young child, being the main building material for cells and tissues of the body.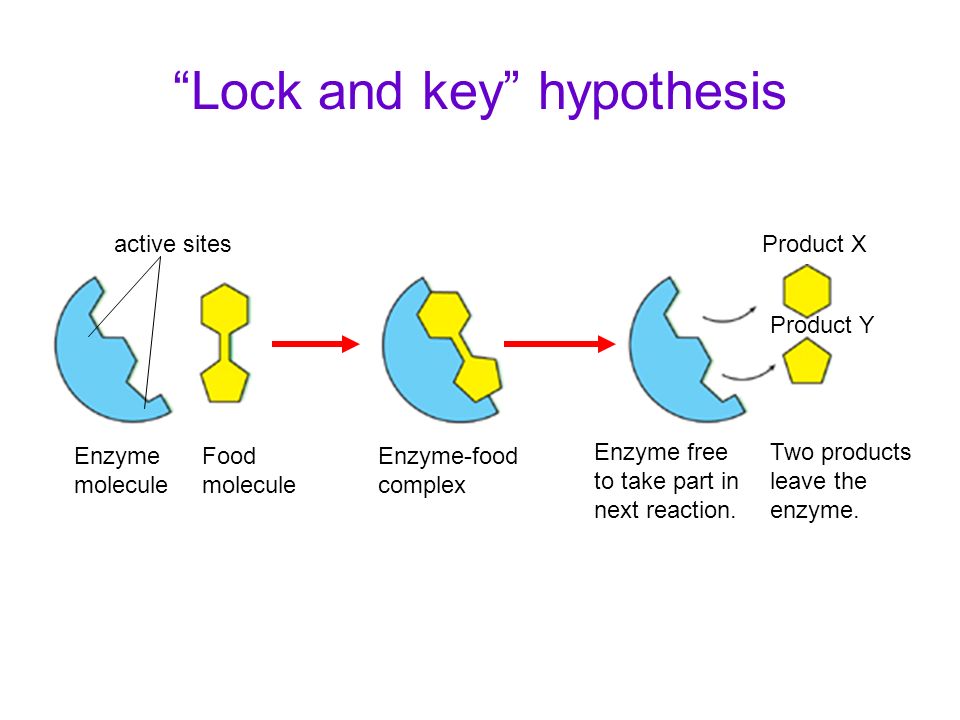 They are part of all vital compounds - enzymes, hormones, antibodies, etc.
They are part of all vital compounds - enzymes, hormones, antibodies, etc.
Inadequate intake of protein from food can lead to a slowdown in growth and weight gain, reduced immunity, impaired neuropsychic development, hematopoiesis and other disorders. For young children, not only the amount of protein in the diet is important, but also its quality, which is determined by the composition of its amino acids.
Of particular value are essential amino acids, which are not synthesized in the child's body, but come only with food. The main sources of essential amino acids are animal proteins (milk and dairy products, meat, eggs, fish). For children aged 1 to 3 years, the percentage of animal protein required is 70%
However, not only an insufficient amount of protein, but also its excess in nutrition can lead to serious shifts, increasing the risk of developing obesity, diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension in the future . So, an excess of protein in the diet is associated with accelerated growth and the risk of developing obesity, creates an increased burden on the child's kidneys, and increases the risk of developing allergic diseases.
An interesting fact is that the consumption of meat protein is not associated with an increase in the accumulation of adipose tissue. It is the increased consumption of milk protein that is associated with the accumulation of adipose tissue. How can excess protein in baby food affect the development of obesity in the future? If a child receives more protein than required, then “unused” amino acids accumulate in the blood. Among them are the so-called "insulinogenic". It is the excess of these amino acids that contributes to an increase in the level of insulin in the blood and, as a result, to the formation of more fat cells.
Breast milk contains the ideal protein for the baby, both in quantity (9-12 g/l) and in quality. Therefore, continued breastfeeding is critical to long-term health.
Important!
Protein requirement is 36 g/day for children aged 1 to 2 years, 42 g/day for children aged 2 to 3 years.
There is no need to rush to introduce cow's milk into the child's diet, since the protein content in it is 3 times higher than the needs of his body.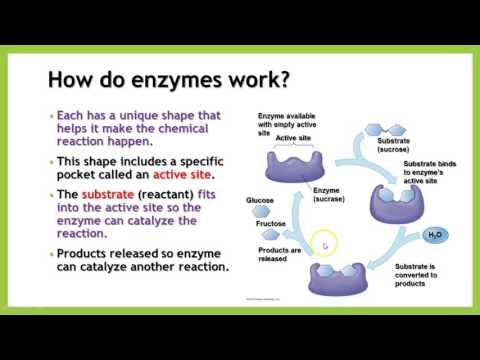 For children under 3 years old, special adapted products should be preferred.
For children under 3 years old, special adapted products should be preferred.
Choose a healthy milk for a baby over a year old
Fats, like proteins, are of great importance for the child's body, being a building material for the cell framework, serve as the main source of energy and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), take part in immune reactions.
Milk and vegetable fats are used in the nutrition of young children. Milk fat is easily digestible, contains vitamins (A, D), carotene, choline, cholesterol. Vegetable fats are a source of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), which are not synthesized in the body and come only with food, as well as vitamin E. PUFAs are involved in the formation of the nervous system, the organ of vision, and have an immunomodulatory effect.
Important!
The proportion of vegetable fats in the diet should be at least 25-30% of the total amount of fat. The fat requirement is 40 g/day for children aged 1 to 2 years, 47 g/day for children aged 2 to 3 years.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, like proteins and fats, are the main components of food. One of the main functions of carbohydrates is to provide the body with energy. The contribution of carbohydrates to the energy value of the diet is 55-58%.
There are three types of carbohydrates: sugars, starches and dietary fiber. Carbohydrates can only be absorbed in the form of monosaccharides; for this, the body has special enzymes that break down carbohydrates to such a state. If there is no enzyme, or it is not active enough, carbohydrates are not absorbed. A manifestation of this condition may be excessive gas formation, loose stools or constipation, etc. In children of the first year of life, the main carbohydrate is lactose (milk sugar) contained in breast milk.
Physiological immaturity of the child, diseases associated with dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, may be manifested by lactase deficiency (if the child's lactase enzyme, which should break down lactose, is not active enough). In such cases, the pediatrician should prescribe an enzyme or select an adequate diet in which lactose is absent or its amount is reduced. With the introduction of complementary foods, the child begins to receive starches that are part of cereal cereals.
In such cases, the pediatrician should prescribe an enzyme or select an adequate diet in which lactose is absent or its amount is reduced. With the introduction of complementary foods, the child begins to receive starches that are part of cereal cereals.
In a small child, the enzymes that break down starches do not yet work at full capacity. Therefore, manufacturers of industrial cereals use a special technology for splitting cereals. This contributes to a more complete digestion and absorption of carbohydrates by the child's body, reduces the viscosity of porridge. And, importantly, it reduces the addition of sugar to porridge, since after splitting carbohydrates become sweeter, the natural sweetness of cereals appears.
Dietary fiber is an indigestible carbohydrate. They are not broken down by enzymes in the upper parts of the digestive tract, they enter the large intestine unchanged, where they become a nutrient medium for the intestinal microflora. The addition of dietary fiber (prebiotics) to baby food has a positive effect on intestinal motility, promotes the formation of regular stools in a child.