How much food should i feed my baby at 8 months
Feeding your baby: 6–12 months
At 6 months of age, breastmilk continues to be a vital source of nutrition; but it’s not enough by itself. You need to now introduce your baby to solid food, in addition to breastmilk, to keep up with her growing needs.
Be sure you give your baby her first foods after she has breastfed, or between nursing sessions, so that your baby continues to breastfeed as much as possible.
When you start to feed your baby solid food, take extra care that she doesn’t become sick. As she crawls about and explores, germs can spread from her hands to her mouth. Protect your baby from getting sick by washing your and her hands with soap before preparing food and before every feeding.
Your baby's first foods
When your baby is 6 months old, she is just learning to chew. Her first foods need to be soft so they’re very easy to swallow, such as porridge or well mashed fruits and vegetables. Did you know that when porridge is too watery, it doesn't have as many nutrients? To make it more nutritious, cook it until it’s thick enough not to run off the spoon.
Feed your baby when you see her give signs that she's hungry – such as putting her hands to her mouth. After washing hands, start by giving your baby just two to three spoonfuls of soft food, twice a day. At this age, her stomach is small so she can only eat small amounts at each meal.
The taste of a new food may surprise your baby. Give her time to get used to these new foods and flavours. Be patient and don’t force your baby to eat. Watch for signs that she is full and stop feeding her then.
As your baby grows, her stomach also grows and she can eat more food with each meal.
Feeding your baby: 6–8 months old
From 6–8 months old, feed your baby half a cup of soft food two to three times a day. Your baby can eat anything except honey, which she shouldn't eat until she is a year old. You can start to add a healthy snack, like mashed fruit, between meals. As your baby gets increasing amounts of solid foods, she should continue to get the same amount of breastmilk.
Feeding your baby: 9–11 months old
From 9–11 months old, your baby can take half a cup of food three to four times a day, plus a healthy snack. Now you can start to chop up soft food into small pieces instead of mashing it. Your baby may even start to eat food herself with her fingers. Continue to breastfeed whenever your baby is hungry.
Each meal needs to be both easy for your baby to eat and packed with nutrition. Make every bite count.
Foods need to be rich in energy and nutrients. In addition to grains and potatoes, be sure your baby has vegetables and fruits, legumes and seeds, a little energy-rich oil or fat, and – especially – animal foods (dairy, eggs, meat, fish and poultry) every day. Eating a variety of foods every day gives your baby the best chance of getting all the nutrients he needs.
If your baby refuses a new food or spits it out, don’t force it. Try again a few days later. You can also try mixing it with another food that your baby likes or squeezing a little breastmilk on top.
Feeding non-breastfed babies
If you're not breastfeeding your baby, she’ll need to eat more often. She'll also need to rely on other foods, including milk products, to get all the nutrition her body needs.
- Start to give your baby solid foods at 6 months of age, just as a breastfed baby would need. Begin with two to three spoonfuls of soft and mashed food four times a day, which will give her the nutrients she needs without breastmilk.
- From 6–8 months old, she’ll need half a cup of soft food four times a day, plus a healthy snack.
- From 9–11 months old, she’ll need half a cup of food four to five times a day, plus two healthy snacks.
Sample Menu for a Baby 8 to 12 Months Old
Log in | Register
Ages & Stages
Ages & Stages
Now that your baby is eating solid foods, planning meals can be more challenging. At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At this age, your baby needs between 750 and 900 calories each day, of which about 400 to 500 should come from
breast milk or formula (if you are not breastfeeding)—roughly 24 ounces (720 mL) a day. Breast milk and formula contain vitamins, minerals, and other important components for brain growth.
At about eight months, you may want to introduce foods that are slightly coarser than strained pureed foods. They require more chewing than baby foods. You can expand your baby's diet to include soft foods such as yogurt, oatmeal, mashed banana, mashed potatoes, or even thicker or lumpy pureed vegetables. Eggs (including scrambled) are an excellent source of protein, as are cottage cheese, Greek yogurt, and avocado.
Sample menu ideas for an 8- to 12-month-old baby:
1 cup = 8 ounces = 240 ml
¾ cup = 6 ounces = 180 ml
½ cup = 4 ounces = 120 ml
¼ cup = 2 ounces = 60 ml
Breakfast
2 to 4 ounces cereal, or 1 mashed or scrambled egg
2 to 4 ounces mashed or diced fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Lunch
2 to 4 ounces yogurt or cottage cheese, or pureed or diced beans or meat
2 to 4 ounces cooked pureed or diced yellow or orange vegetables
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Snack
Dinner
2 to 4 ounces diced diced poultry, meat, or tofu
2 to 4 ounces cooked green vegetables
2 to 4 ounces cooked soft-whole grain pasta or potato
2 to 4 ounces diced or mashed fruit
Breastmilk or 4 to 6 ounces formula
Before bedtime
Breastmilk or 6 to 8 ounces formula, or water. (If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
(If breastmilk or formula, follow with water or
brush teeth afterward).
More information
- Sample Menu for a One-Year-Old
- Starting Solid Foods
- Breastfeeding Mealtime Milestones
- Ask the Pediatrician: Is it OK to make my own baby food?
- Last Updated
- 8/12/2022
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Ration: making a menu for a child at 8 months
6-12 months
Article
5/5 4 reviews
The first year of a baby's life is full of discoveries.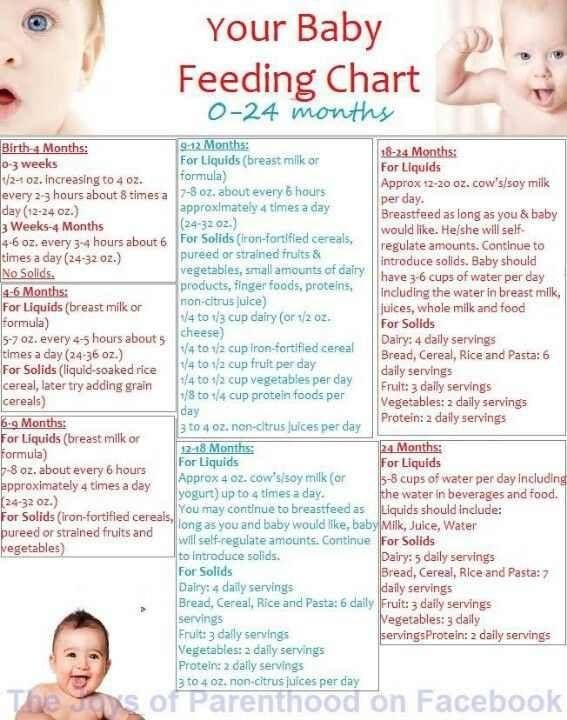 He almost daily learns something new about the world, in particular, gets acquainted with new products. At 6 months, the baby masters gruel, vegetable and fruit purees. The menu of a child at 8 months becomes more diverse. Sour-milk products, meat, lean fish and egg yolks appear in the diet. How to introduce new food into the baby's complementary foods? And how to make a tasty and healthy menu? nine0003
He almost daily learns something new about the world, in particular, gets acquainted with new products. At 6 months, the baby masters gruel, vegetable and fruit purees. The menu of a child at 8 months becomes more diverse. Sour-milk products, meat, lean fish and egg yolks appear in the diet. How to introduce new food into the baby's complementary foods? And how to make a tasty and healthy menu? nine0003
7 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
What can I give my baby at 8 months? What foods to add to the diet to ensure a balanced diet? Here is a rough list that you can take into account.
1. Egg yolks.
The polyunsaturated fatty acids and healthy cholesterol they contain are essential for the development of the nervous system. The yolk can be given to children from 7–8 months of age, starting with half a chicken or one quail. By this time, enzymes appear in the body to break down this product. nine0017 Important!
nine0017 Important!
Some people think that quail yolks are better digested and can therefore be given to allergic babies. But quail yolk can also cause a negative reaction. Therefore, eggs must be introduced into the diet with caution, starting with 1 teaspoon and monitoring the reaction.
2. Porridge.
At the age of 8 months, a child can already eat all kinds of cereals: buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, corn and wheat. By consistency, they should be quite liquid and homogeneous. To cook baby porridge correctly, see the instructions on the product packaging and follow all the recommendations. nine0003
Learn more: Gerber® Cereals
3. Meat.
Introduce solid foods gradually, giving your baby dietary varieties: chicken, veal, turkey and rabbit. The meat is rich in proteins, which are necessary for growth and development, and iron, and is also very useful for the circulatory system. The norm of meat is about 50-70 g per day.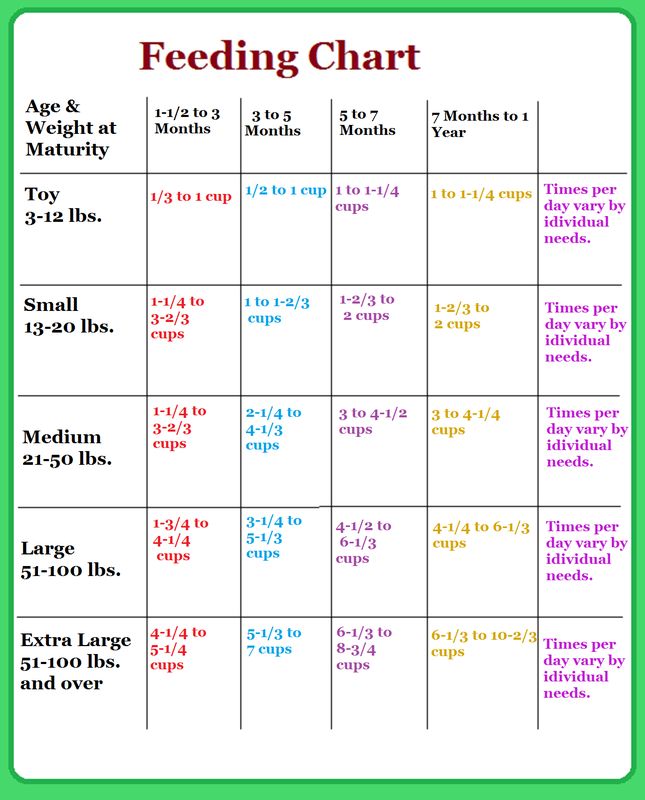
Learn more: Gerber® Meat Purees
4. Lean white fish.
If the baby does not have a tendency to allergic reactions and your pediatrician sees no contraindications, let him try the fish. Due to the smaller amount of connective tissue, fish is an excellent source of easily digestible protein. It contains many minerals, amino acids, arachidonic acid, fluorine and iodine. The latter are minerals needed to strengthen bones and improve thyroid hormone production. In addition, there are a lot of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in fish, which are needed for the cells of the brain, vision, cardiovascular system and immunity of the child to develop normally. Start introducing fish into the child's menu at 8 months with a teaspoon and carefully monitor that there are no adverse events. If all is well, then give it no more than twice a week. nine0003
5. Fruit and vegetable purees.
Your little one has already become familiar with these products, but you can diversify the taste a bit by combining vegetables with meat or different types of fruits.
Learn more: Gerber® Vegetable and Meat Puree
6. Dairy products.
Kefir and cottage cheese are good for the intestines, but can cause bloating, colic or allergies. Therefore, first consult with your doctor and introduce dairy products very carefully. nine0003
See also: Why is cow's milk not good for babies?
7. Vegetable decoctions and light soups.
Start with vegetable broths made from potatoes and carrots, lightly seasoned with onions. For the first time, give 20-30 grams, and if the baby perceives the dish well, gradually increase the amount of soup and the variety of its ingredients.
8. Flour.
You can dilute the menu with baby biscuits, crackers and bread. But enter them carefully. In flour products there is a special protein of plant origin - gluten, to which the baby's fragile body can react with allergies and diarrhea. nine0003
Diet: when and how much to eat at 8 months
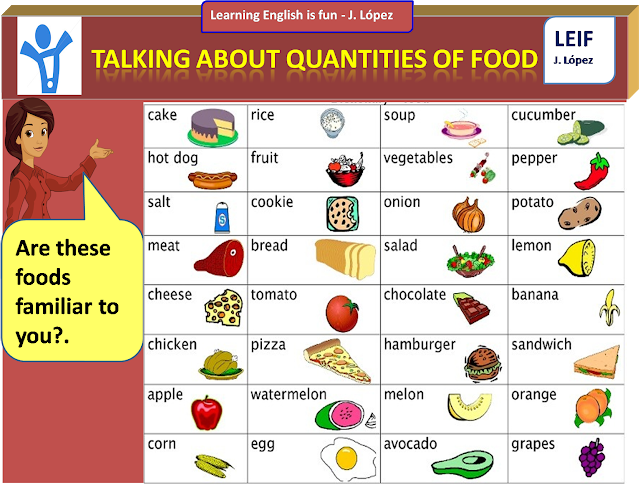
- If the baby is breastfed, feed him about once every 3-4 hours.
- If the baby is fed expressed breast milk, give him approximately 700 grams per day. With 5-6 meals a day, this is about 120 to 200 grams of milk per meal.
- Formula-fed (IV) babies are given 170 to 230 grams of formula 4-6 times a day. To find out exactly how much mixture you need, be guided by the instructions on the package, the recommendations of the pediatrician. nine0086
- Complementary foods are best included in the menu of a child at 8 months three times a day: it can be one teaspoon per sample or 50-180 grams of already familiar food.
Important!
The calculation of servings and the number of feedings depends on the individual characteristics of the development and needs of the child. Therefore, first of all, be guided by the recommendations of your pediatrician and the needs of the baby.
We form the basis of the diet for every day
At 8 months old, a baby needs a variety of foods with enough calories to ensure that the actively growing body receives sufficient nutrients. Divide the daily food intake, which is approximately 1000–1200 ml, into 5–6 doses at intervals of 3.5–4 hours: early breakfast, breakfast, lunch, dinner and feeding before bedtime. If the baby is not full on complementary foods, supplement with breast milk or formula if the baby is formula-fed.
Divide the daily food intake, which is approximately 1000–1200 ml, into 5–6 doses at intervals of 3.5–4 hours: early breakfast, breakfast, lunch, dinner and feeding before bedtime. If the baby is not full on complementary foods, supplement with breast milk or formula if the baby is formula-fed.
Tip!
Do not salt or sweeten food. Introduce the baby to sugar and salt not earlier than 12 months, but better later.
The list of allowed foods at 8 months of age is quite extensive, which gives you room for culinary experiments. Use this table to create a menu for the week, changing types of cereals, alternating purees and juices from different vegetables and fruits, adding new foods or additional ingredients to dishes already familiar to your baby. For example, if the crumbs are already fed up with some kind of porridge or mashed potatoes, improve the recipe a little - add a spoonful of vegetable or butter, or pieces of fruit.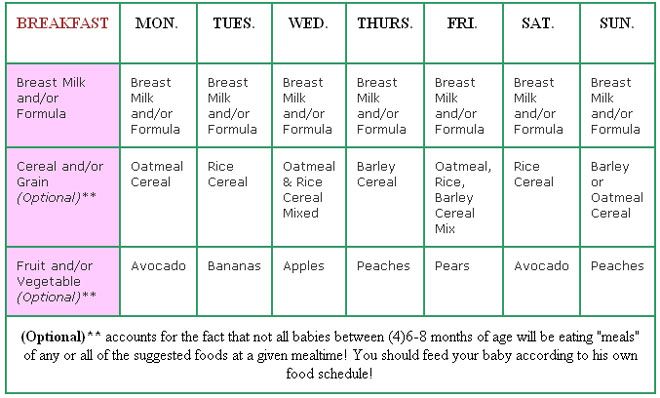 And the child will eat again with pleasure. nine0003
And the child will eat again with pleasure. nine0003
Read also: Breastfeeding: first steps after childbirth
Important!
If the child is allergic, add something new to the diet with extra care. Especially food rich in animal proteins - cottage cheese, kefir, yolks, milk porridge, fish. Before offering them to your baby, consult a pediatrician.
Sample menu for a child at 8 months per day: table
| Feeding time | Products | Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Gerber® Milk Oatmeal with Banana and Mango | 170 g |
| Butter | about ½ tsp | |
| Boiled egg yolk | ½ pcs. | |
| Supplementing with breast milk or infant formula | 50 ml | |
| III feeding 10 hours | Gerber® Meat and Vegetable Puree "Tender Vegetables with Veal" | 170 g |
| Vegetable oil | about ½ tsp.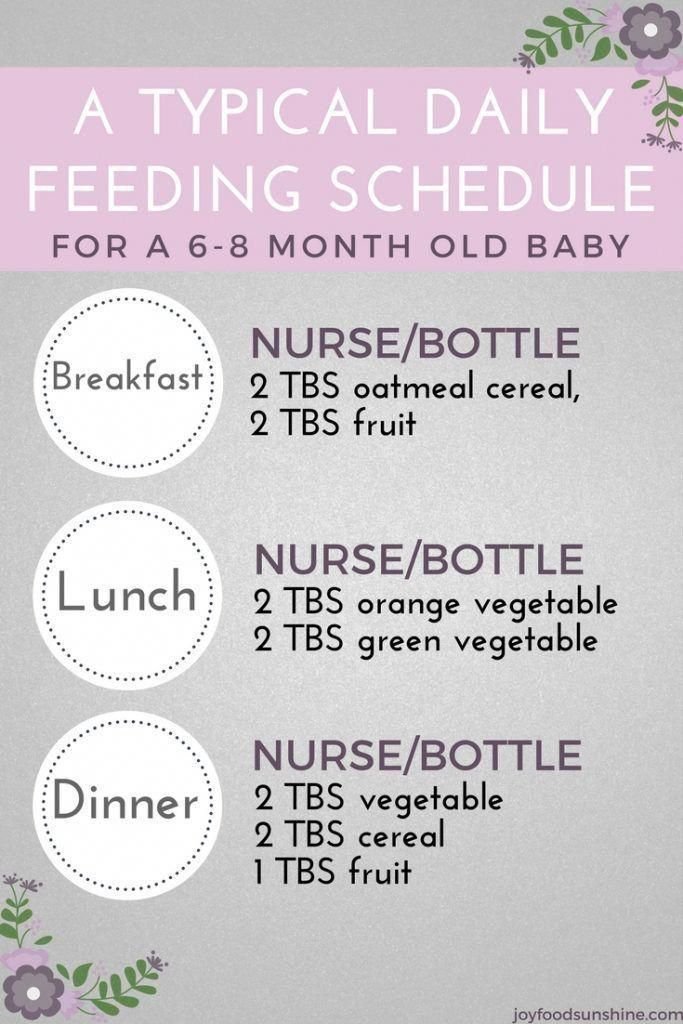 | |
| Gerber® Clarified Apple-Pear Juice | ½ pcs. | |
| Supplementing with breast milk or infant formula | 50 ml | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Gerber® Apple & Wild Berries Fruit Puree | 70 g |
| Baby biscuits | 1-2 pcs. | |
| Kefir | 40 ml | |
| Supplementing with breast milk or infant formula | 100 ml | |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
Sample diet for an 8 month old baby with cow's milk protein intolerance: table
| Feeding time | Products | Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | nine0151 Dairy-free Gerber® oatmeal with wheat130 g | |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp.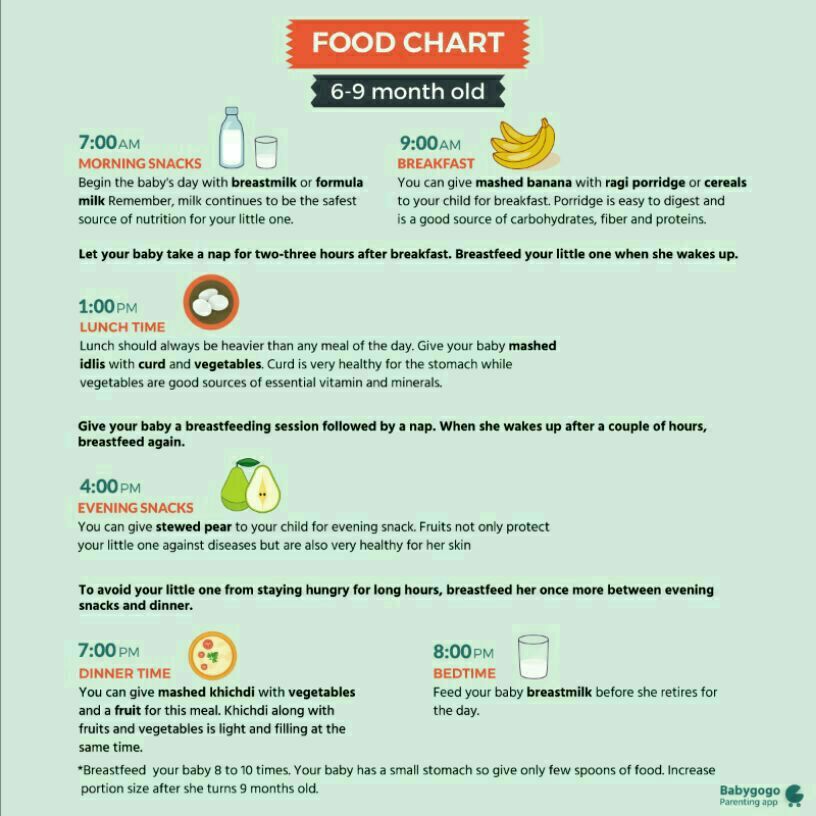 | |
| Gerber® Apple & Peach Fruit Puree | 70 g | |
| Gerber® Clarified Apple Juice | 30 ml | |
| III feeding 10 hours | Gerber® Cauliflower & Potato Puree | 170 g |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. | |
| Gerber® Gentle Rabbit Meat Puree | 50 g | |
| Gerber® Broccoli Vegetable Puree | 70 g | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp. |
| Gerber® Tender Turkey Meat Puree | 30 g | |
| Supplementation with breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 100 ml | |
| Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
Important!
To create a menu for a child, calculate the size of portions and the number of feedings, first of all, be guided by the recommendations of your pediatrician, the individual needs and characteristics of your baby's body.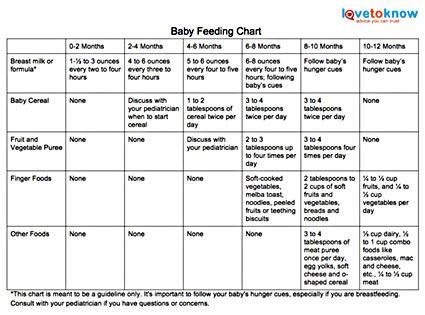
FAQ:
1. How much should a baby eat at 8 months?
An 8-month-old baby needs a portion of food per day, which is equal to about ⅛ of body weight. This is 1000-1300 ml of food, excluding water, juices, children's tea. Divide this amount by about 5 feedings and you will get a single serving of 200-210 ml.
2. When can cow's and goat's milk be added to complementary foods?
Whole cow's and goat's milk should not be given to children until at least 9 years of age according to WHO recommendations.months, and possibly up to 12 months. In order not to deprive the baby of the benefits of dairy products, replace with milk-baby kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese. But before introducing dairy into the menu, consult with your pediatrician.
3. If the baby has allergies, what should I do?
Atopic dermatitis, redness, itching are all signs of intolerance to a substance or food. If, after introducing a new food, you notice any of these symptoms, you need to eliminate the allergen from the diet. If you experience severe symptoms: swelling, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, consult a doctor immediately. The pediatrician will select the therapy for the baby: it can be a special diet or medication. nine0003
If you experience severe symptoms: swelling, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, consult a doctor immediately. The pediatrician will select the therapy for the baby: it can be a special diet or medication. nine0003
Articles on the topic:
Baby refuses new foods
Eat right and without mistakes
Products containing iron
Last reviews
Average customer rating
4 customer ratings
Snapshot of community ratings
- five 4
- 4 0
- 3 0
- 2 0 nine0086
- one 0
Diet for an 8-month-old baby
Fish can be introduced into the diet of babies at the ninth month. Along with animal meat, fish is a source of complete protein with a well-balanced composition of amino acids, fat, vitamins B2, B12 and minerals.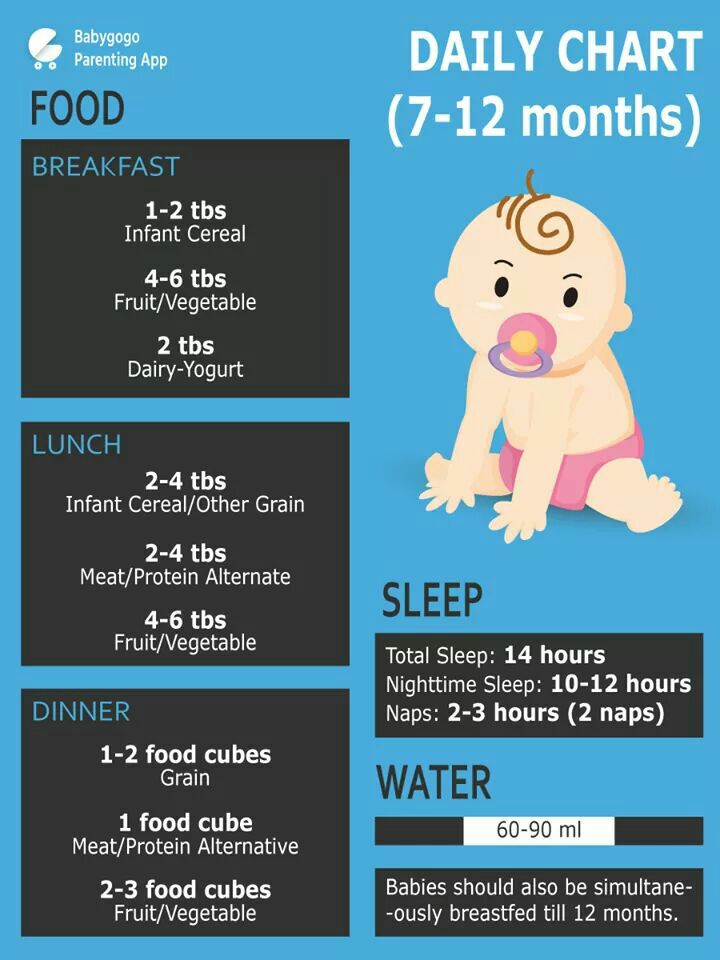 Compared to meat, fish contains 5 times less connective tissue, due to which it is quickly boiled soft, has a delicate texture after heat treatment and is easier to digest. Fish oil is characterized by a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the ω-3 class. These substances are necessary for the child to mature the brain, retina, strengthen the cardiovascular and immune systems. Sea fish contains such important trace elements for the child's body as iodine and fluorine. The child should be given 1-2 times a week instead of meat, be sure to monitor how the child tolerates fish in general and its individual varieties. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock), red salmon can be recommended, river pike perch, carp. nine0003
Compared to meat, fish contains 5 times less connective tissue, due to which it is quickly boiled soft, has a delicate texture after heat treatment and is easier to digest. Fish oil is characterized by a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, including the ω-3 class. These substances are necessary for the child to mature the brain, retina, strengthen the cardiovascular and immune systems. Sea fish contains such important trace elements for the child's body as iodine and fluorine. The child should be given 1-2 times a week instead of meat, be sure to monitor how the child tolerates fish in general and its individual varieties. Preference should be given to oceanic fish, preferably white (cod, hake, pollock), red salmon can be recommended, river pike perch, carp. nine0003
Self-cooked fish is given to a child with boiled and mashed vegetables. You can also offer your baby fish and vegetable canned food, but they contain only 10 - 20% of fish.
At this age, when all the main food groups have already been introduced, special attention should be paid to the diversity of the composition of dishes. New, possibly combined products are introduced, for example, not only purees from various fruits and berries, but also their combinations with cottage cheese, cream, cereals, etc.
New, possibly combined products are introduced, for example, not only purees from various fruits and berries, but also their combinations with cottage cheese, cream, cereals, etc.
From the age of 8 months, the child's diet can be expanded to include fermented milk products (baby kefir, biokefir, bifidokefir, yogurt, bioyogurt, biolact). Fermented milk products are prepared using a special starter culture that breaks down milk protein, so that the baby can get an indispensable set of amino acids in a well-available form. Fermented milk products improve the composition of the intestinal microflora of the child, are rich in B vitamins and calcium. Their regular use favorably affects the functioning of the intestines, stimulates appetite, and increases the absorption of micronutrients. Children's dairy products are introduced into the baby's diet gradually, starting with 1 tsp. and with good tolerance increase their volume to 150-200 ml per day. nine0003
Sample menu for a healthy baby 8 months old
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or infant formula | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free* or milk porridge Butter Boiled egg yolk Fruit puree Fruit juice | 180 g |