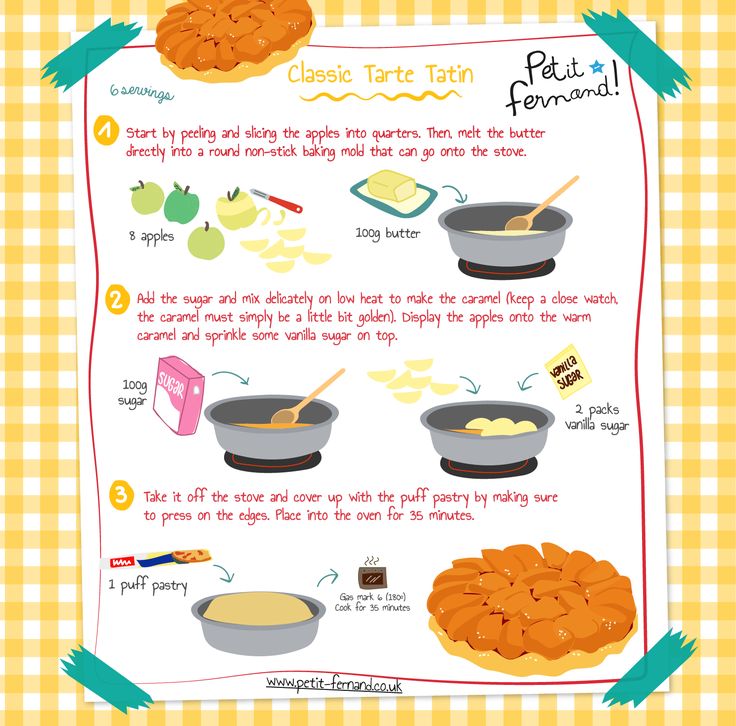
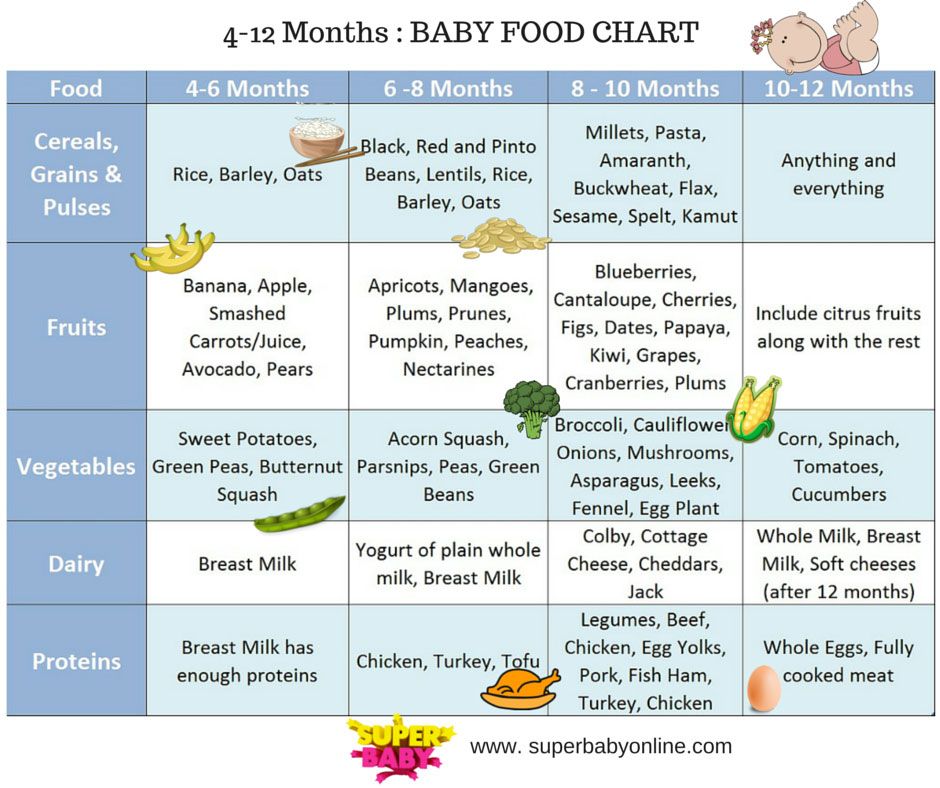
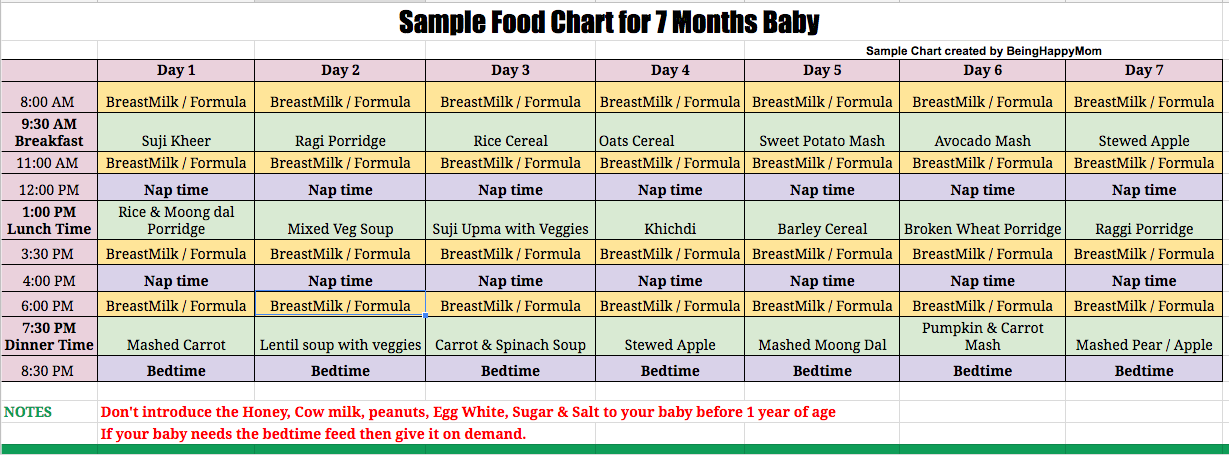
How much pellets to feed baby rabbit
A Healthy Diet For Young Rabbits
Many people bring home a rabbit when they are still just a young bunny. But most of the information you find about rabbit care and health is directed toward adult rabbits. You may find very helpful information about how to keep an adult rabbit on a healthy diet, but what about your new baby bunny?
Young rabbits are growing bunnies! They have special dietary needs that differ from their adult counterparts. The amount that you feed your rabbit and even the type of food that they need is different for a young bunny. Then, of course, there is a transition period. As your rabbit grows up, they’ll need to be safely transitioned from a young rabbit diet to an adult rabbit diet.
Important: This page may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate and an associate to other companies I earn a small commission from qualifying purchases.
Baby bunnies (under 8 weeks old)
Baby rabbits should not be separated from their mother until they are older than 2 months. This helps to ensure that the baby rabbits have developed a fully functioning immune system by digesting their mother’s milk and cecal droppings. There are many states in the U.S. that even ban the sale of rabbits under 2 months because of the danger it poses to the newborn rabbit.
Baby rabbit diet
Baby bunnies, also called kittens, should not be weaned off of their mother’s milk until they are about 8 weeks, or 2 months, of age. These tiny bunnies need the high concentration of fat and protein that is found in rabbit milk so that they can grow up big and strong. The babies also depend on the antibodies they receive from their mother’s milk to protect them from infection and disease since they don’t have a fully functioning immune system of their own yet.
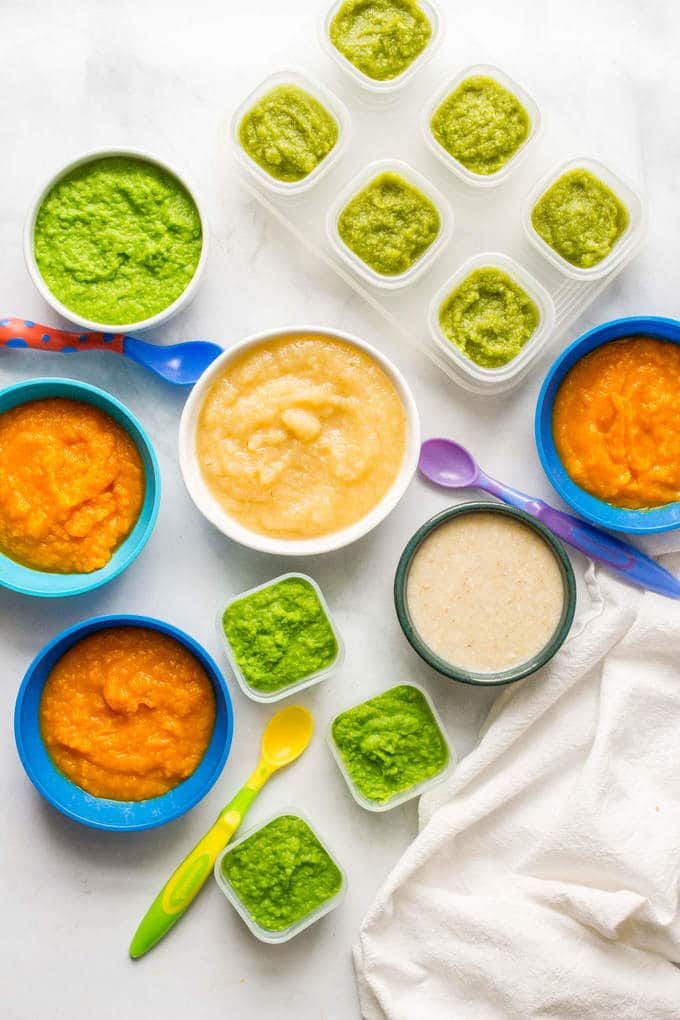
When they are babies, rabbits need to have access to their mother’s milk. They should not be fully weaned until they are 8 weeks old.Once the kittens are about 3 or 4 weeks old, they will start exploring a little bit around the nest area. At this point, it will be okay to start introducing solid foods into their diet. You can provide some alfalfa hay and alfalfa pellets for the babies to munch on, but their main food source will still be the milk from their mother.
At this point, it will be okay to start introducing solid foods into their diet. You can provide some alfalfa hay and alfalfa pellets for the babies to munch on, but their main food source will still be the milk from their mother.
As the babies reach 7-8 weeks old, the amount of dry pellets and hay should be increased so they have some to munch on all the time. However, they should still have access to their mother during this time so they can drink milk. They’ll also be able to eat some of her cecal droppings to improve their immunity and digestion. The baby rabbits will also start to produce their own cecotropes as their digestive systems begin working properly. You should also make sure your rabbits have access to fresh water as they are weaned off of their mother’s milk.
| Age | Diet |
| 0-3 Weeks | Mother’s milk |
| 3-7 Weeks | Mother’s milk and some access to alfalfa hay and alfalfa pellets |
| 7-8 Weeks | Mother’s milk and constant access to alfalfa hay and alfalfa pellets |
Abandoned or orphaned baby bunnies
If you have orphaned or abandoned rabbits that cannot drink their mother’s milk, do not replace it with cow’s milk. There are no direct replacements you can buy for rabbit milk, so the best alternatives you can use are kitten formula or goat’s milk. A milk replacer for puppies is also an option if you can’t find one of the former.
There are no direct replacements you can buy for rabbit milk, so the best alternatives you can use are kitten formula or goat’s milk. A milk replacer for puppies is also an option if you can’t find one of the former.
In these cases, you will have to attempt to syringe feed the baby bunnies until they are able to drink for themselves. You will need to syringe feed your babies 2 times per day.
Sadly, if a rabbit is orphaned there are high chances that they will not survive. Baby rabbits have very delicate digestion, and it’s just too easy for something to go wrong. The House Rabbit Society offers some advice to care for orphaned or abandoned domestic rabbits:
| Age | Amount to Feed |
| Newborn | 2.5 mL twice a day |
| 1 Week Old | 6-7 mL twice a day |
| 2 Weeks Old | 12-13 mL twice a day |
| 3-6 Weeks Old | 15 mL twice a day |
 They should also be introduced to leafy greens and have a small amount on a daily basis.
They should also be introduced to leafy greens and have a small amount on a daily basis.Young rabbits (2-6 months)
Once a young rabbit reaches 2 months old, they should be separated from their mother and have a diet of all solid food. However, they will still have a diet that differs from adult rabbits. These bunnies are still growing a lot! They need more protein and calcium in their diets to make sure they grow up to be healthy rabbits.
Hay
Unlike adult rabbits, who should receive mostly timothy hay, young rabbits should have a supply of alfalfa hay. Alfalfa hay has a much higher amount of protein and calcium, which makes it ideal for a growing bunny. You’ll want to make sure your rabbit has an unlimited amount of alfalfa hay, so they’ll always have something to munch on.
Hay should be a large portion of your rabbit’s diet because it promotes good digestion and healthy teeth. It’s not going to make up as large a percentage of the diet as it does for adult rabbits, but you still want to make sure your young bunny is munching on hay every day.
Luckily, alfalfa hay tends to be yummier for rabbits, making it more likely they will munch on it. Alfalfa hay is slightly sweeter and softer than adult rabbit timothy hay, so usually, young rabbits will be happy to nibble on it.
Some rabbits prefer to eat hay from higher levels. Try purchasing or creating a hanging hay rack or a raised hay trough that can be attached to the side of the rabbit enclosure.Pellets
Pellets are very important to a young rabbit’s diet. This rabbit food has higher levels of proteins, nutrients, and calcium than hay, and it’s made to help rabbits put on weight. Young rabbits should be given an alfalfa-based pellet blend because it will promote healthy growth for young rabbits.
You want to make sure to give your young rabbit a healthy brand of pellets. Stay away from any blend that has lots of colorful pieces, or dried pieces of fruits, vegetables or seeds. These have added sugar, and usually include pieces that are bad for a rabbit’s digestive system.
Instead, opt for a bag of just plain, brown pellets. Check the ingredients to make sure that Alfalfa hay (or alfalfa grass) is the number one ingredient on the list.
I recommend Oxbow’s pellets for young rabbits. Oxbow is a well-known and respected brand in the rabbit community. They have fortified pellets made with a healthy list of ingredients and all the necessary vitamins and nutrients to help your rabbit grow up healthy.
How much dry food should you give your young rabbit?
Most guides for a young rabbit diet will encourage you to give your rabbit an unlimited supply of pellets. However, I offer this advice with some caution because you want to make sure your rabbit is also eating their hay.
Most rabbits will prefer pellets to hay. Therefore, when they have unlimited pellets available, they may end up completely ignoring their pile of hay. Watch your rabbit to see what their behavior is. If giving them unlimited pellets means they don’t touch their hay at all, then you will need to limit their pellets a little bit.
If your young rabbit is ignoring their hay and eating only pellets, then limit the pellets to about ¼ cup per day for every 2 pounds that a rabbit weighs. This is not an exact measurement, and you may need to adjust the amount for your rabbit. Watch your rabbit to make sure they are still energetic and happy, and be sure they are maintaining healthy body weight as they grow.
Leafy greens
When a rabbit is about 3 months old, you can start to introduce some leafy greens into their diet.
Take it slow and only introduce one type of leafy green vegetable at a time. This will help to ensure that nothing is causing an imbalance in your rabbit’s digestion.
The first time you give your rabbit a new leafy green you want to give them only a small amount to introduce the new food. Only give them 2-3 sprigs of parsley, for example. Over the next couple of days, you can increase the amount that you give your rabbit as their digestion gets used to the new food.
After you’ve given one type of green for a week, you can introduce another kind. Even as your rabbit grows to be an adult, you’ll want to introduce new foods slowly.
Try to give your rabbit their food at the same time every day to get them used to a daily routine.How much leafy greens should you give your young rabbit?
You don’t want to give your young bunny too many leafy greens at this stage in their life. Their digestion is more sensitive right now and can more easily become unbalanced. Therefore, you want to very gradually increase the amount of green you give your rabbit until you give them about 1 cup per day for a 5-pound rabbit.
You can start to diversify the leafy greens that your rabbit eats. Giving your rabbit three varieties of greens per day is an ideal goal to have. But you still want your rabbit’s main foods to be their pellets and hay.
Treats
It’s best to avoid giving young rabbits any sweet treats for the time being. Their digestion is still developing at this time and can easily be unbalanced by the introduction of highly sugary foods.
Their digestion is still developing at this time and can easily be unbalanced by the introduction of highly sugary foods.
These sweet foods that you should avoid giving young rabbits are foods that are typically considered healthy for humans. Fruits like berries, bananas, and apples have a high sugar content for rabbits, and vegetables like carrots, tomatoes, and bell peppers do too. This means you should not give your rabbit too many fruits and vegetables during this stage in their lives. Sweet human foods, like candy and cookies, should never be given to rabbits.
Water bowls are usually the better option for a pet rabbit. Sometimes a rabbit will be a sloppy drinker or try to flip over the bowl. In those cases a water bottle is a good option.Water
By this time, your young rabbit should be weaned off of their mother’s milk and should be fully independent. This means they should have constant access to fresh water so they can stay healthy and hydrated.
It’s best if you can give your rabbit their water in a dish instead of a bottle since this is a more natural way to drink. However, there are some occasions where you will want to provide them with a bottle instead.
However, there are some occasions where you will want to provide them with a bottle instead.
- If your rabbit is a messy drinker. If having a bowl means your rabbit ends up getting soaked with water because they are a sloppy drinker, then you’ll want to give them a bottle for the time being. Try to reintroduce a bowl after a couple of months and see if they’re a little bit neater.
- If your rabbit flips over their bowls. You don’t want your rabbit to flip over their water bowl and have no more water until you notice the mess. You can try giving your rabbit a heavier, ceramic bowl, but you also may have to give them a water bottle instead.
Transitioning to an adult diet (6 months – 1 year)
After rabbits reach 6 months old, they will need to be slowly transitioned to a healthy adult diet. During this time, the young rabbits are still growing, so they’ll need more food than adult rabbits, however, adjustments should be made to the diet over time and not all at once.
During this time, the young rabbits are still growing, so they’ll need more food than adult rabbits, however, adjustments should be made to the diet over time and not all at once.
As with a young rabbit diet, you don’t want to make any drastic changes to a rabbit’s transitional diet in a short period of time. You want to make sure that you give your rabbit’s digestion time to adjust to their healthy adult diet.
You can get fun toys for your rabbit where you can hide treats in a pile of hay. This will encourage your rabbit to munch on hay until they can get to the yummy treat.Hay
Timothy is much healthier for an adult rabbit diet than alfalfa hay. When your rabbit reaches 6 months old, you’ll want to start to transition them to a timothy-based diet and slowly phase out the alfalfa hay.
To do this, you’ll first want to add in small handfuls of the timothy hay to the alfalfa hay your rabbit already gets. Over the next number of months, you’ll want to increase the percentage of timothy hay you give your rabbit and decrease the amount of alfalfa hay they get.
Unfortunately, this transition can be difficult for many rabbits. Alfalfa hay is usually much tastier and easier to eat than timothy hay. Many young rabbits will protest the change. What can you do to encourage your picky rabbit to eat their hay?
- Mix in other types of hay. Timothy hay is best for rabbits, but there are other kinds that are also good for a rabbit’s digestion. Add in handfuls of other grass-based hays, such as orchard hay, oat hay, or meadow hay to make the transition more appetizing to your young rabbit.
- Look for fresh brands of hay. Fresh hay tastes better than old, browned hay. I like to get my hay from an online store called Small Pet Select. They have impressed me with the quality of their hay and I never hesitate to recommend them. Check out their timothy hay for your growing bunny (and get 15% off your first order by using the code BUNNYLADY at checkout)
- Place the hay near the litter box.
 Rabbits like to munch and poop at the same time, so placing the new timothy hay near the litter box can encourage them to nibble on it.
Rabbits like to munch and poop at the same time, so placing the new timothy hay near the litter box can encourage them to nibble on it. - Hide treats in hay. You can hide dried herbs or pieces of dried fruit in the hay pile. You could even make toys with toilet paper tubes where you hide a treat in the middle and cover it with hay.
Pellets
Just like with hay, you’ll want to transition your rabbit from alfalfa-based rabbit food pellets to timothy-based rabbit food pellets. Your rabbit is still growing during this time, but not as rapidly as they do during the first 6 months. They won’t require as much excess protein and calcium that the alfalfa pellets give them.
As with the alfalfa pellets, you’ll want to make sure the timothy mixture you give your rabbit does not have any extra colorful pieces in it. Excess sugar is bad for a rabbit’s health and digestion, so sweet fruits, and vegetables should only be given as treats.
I again recommend the Oxbow brand. They have Garden Select Pellets for adult rabbits, making it easy to transition from the young rabbit pellets.
They have Garden Select Pellets for adult rabbits, making it easy to transition from the young rabbit pellets.
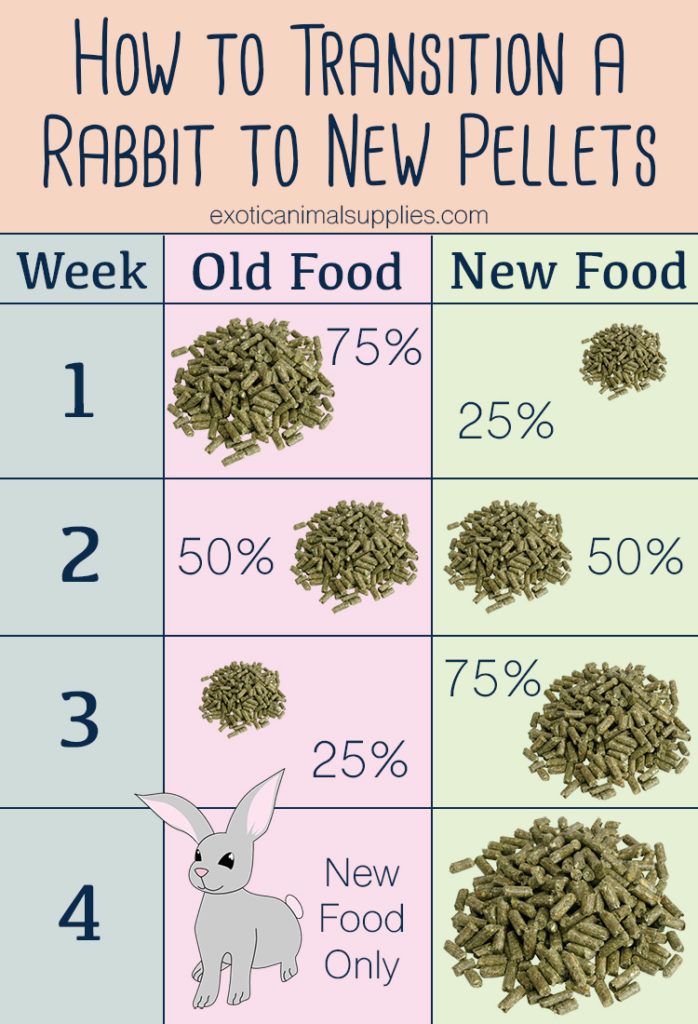
When transitioning your rabbit to a new food, you want to take it slow. Don’t replace all of your rabbit alfalfa pellets with timothy pellets all at once, since this could be a shock to their digestion. Instead over the course of 3-4 months, you’ll want to slowly decrease the percentage of the alfalfa pellets you give your rabbit and increase the amount of timothy pellets.
- Month 1: 75% alfalfa pellets + 25% timothy pellets
- Month 2: 50% alfalfa pellets + 50% timothy pellets
- Month 3: 25% alfalfa pellets + 75% timothy pellets
- Month 4: All timothy pellets
You will also need to decrease the amount of pellets you give your rabbit during this period of time. They are still growing bunnies, so you’ll want to give them more pellets than an adult rabbit, but you’ll want to limit the amount you give them.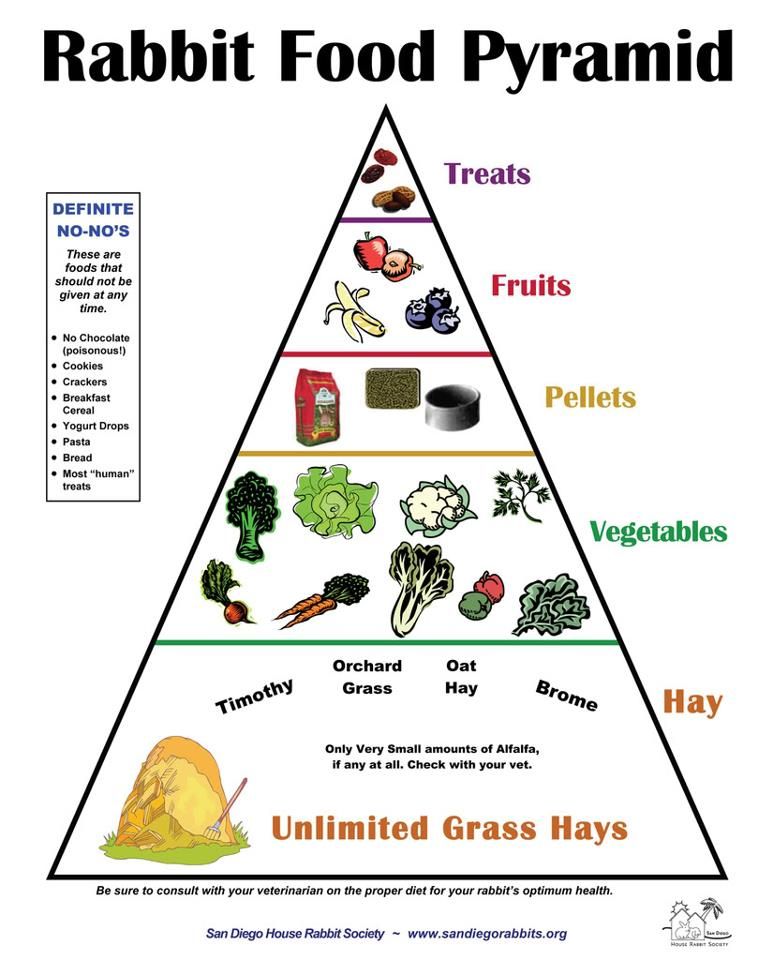
During this transitional stage of your rabbit’s life, you’ll want to give them about ¼ cup of pellets for every 3 pounds that they weigh. Once your rabbit reaches their adult weight, you’ll want to reduce the amount even further to about ¼ cup for every 5 pounds that your rabbit weighs.
Leafy Greens
You can also start to increase the amount of fresh leafy greens you give your rabbit on a daily basis. As their digestion is able to handle more variety, you can double the amount that you give your rabbit.
How much leafy green vegetables should a rabbit have daily?
| Weight of the rabbit | Maximum amount of leafy greens |
| 2 lbs | 1 cup |
| 3 lbs | 1.5 cups |
| 4 lbs | 2 cups |
| 5 lbs | 2.5 cups |
| 6 lbs | 3 cups |
| 7 lbs | 3.5 cups |
| 8 lbs | 4 cups |
| 9 lbs | 4. 5 cups 5 cups |
| 10 lbs | 5 cups |
You still want to be sure to introduce new leafy greens gradually, but your rabbit can have a lot of different varieties. Try to give them a lot of choices to find out what they like best. For some ideas try these:
- Arugula
- Basil
- Bok choy
- Broccoli leaves
- Butter lettuce
- Cabbage
- Carrot Tops
- Cilantro
- Collard greens
- Dandelion greens
- Dill
- Frisee lettuce
- Leafy lettuce
- Kale
- Lemongrass
- Mint
- Oregano
- Parsley
- Peppermint
- Radicchio
- Romaine lettuce
- Rosemary
- Sage
- Spinach
- Spring greens
- Thyme
- Turnip greens
- Watercress
- Wheatgrass
- Yu choy
Treats
Once your rabbit reaches 6 months old, you can start to introduce some yummy treats for them. You do not want to give your rabbit too many treats. That can mess with their balanced diet and cause problems with their digestion. Keep the treats you give your young rabbit to 1 tablespoon or less per day.
You do not want to give your rabbit too many treats. That can mess with their balanced diet and cause problems with their digestion. Keep the treats you give your young rabbit to 1 tablespoon or less per day.
As with all other foods, you want to introduce treats to your rabbit slowly. The first time you give a new type of fruit or vegetable to your rabbit, only give them a very small piece to make sure their digestion can handle it. Over the next couple of days, you can increase the amount of that treat you give your rabbit a little bit, but continue to limit the total amount of sweet foods you give your rabbit.
What kinds of treats are safe for rabbits?
Bags of mixed treats marketed toward rabbits in pet stores are often not good for rabbits. They usually contain a lot of added sugars or seeds and nuts that rabbits shouldn’t be eating. So you want to be careful about the types of treats you give your rabbit.
Some treats that are safe for rabbits:
- Fresh or dried fruits and vegetables (make sure there is no added sugar)
- Baked hay treats.
 Oxbow has a variety of flavors of baked hay treats. These are especially good because they are hay-based, making them healthy for your rabbit.
Oxbow has a variety of flavors of baked hay treats. These are especially good because they are hay-based, making them healthy for your rabbit. - Dried herbs. The only place where I’ve seen herb blends being sold is Small Pet Select. They have a number of herbal blends that also have mild medicinal properties to keep your rabbit healthy. (don’t forget to take 15% off your order with the code BUNNYLADY)
- DIY treats. You can try making your own treats using your rabbit’s pellets and some fresh fruit and vegetables.
How to tell if your young rabbit has a healthy diet
All rabbits grow at different rates, so the specific guidelines given are not always accurate for your specific rabbit’s situation. During this growing phase, you will need to keep an eye on your rabbit to make sure they are healthy and no adjustments need to be made to their diet.
How to know your rabbit is healthy:
- Energy levels.
 Most young rabbits are energetic little balls of fluff. They’ll be zooming around, and they’ll be very curious about the world around them.
Most young rabbits are energetic little balls of fluff. They’ll be zooming around, and they’ll be very curious about the world around them. - Healthy appetite. Young growing rabbits with lots of energy should also be eating quite a bit. Make sure they are eating both their pellets and their hay for a balanced diet.
- Healthy pooping. Young rabbit poop should be round ‘cocoa puff’ looking droppings. They should not be squishy or deformed. Rabbits also poop little, soft clusters called cecotropes that rabbits should reingest. If you notice a lot of these around uneaten, it may mean your rabbit is not eating enough hay.
- Bodyweight. While you are petting your rabbit, check to make sure they have a healthy amount of fat as they grow. You should be able to feel their spine, ribs, and hips, but these bones should not feel sharp to the touch.
Sources:
- “Rabbit Food.” House Rabbit Society, https://rabbit.
 org/faq-diet.
org/faq-diet.
Tips and Tricks Newsletter
If you are new to caring for rabbits, check out the Bunny Lady bimonthly newsletter. Right after you sign up, you’ll receive a FREE pdf rabbit care guidebook. I put together a guide that goes over all the basics of rabbit care so you have it all in one place. Then you will receive tips and tricks about rabbit care straight to your inbox so that you know you’ll be taking excellent care of your new rabbit.
Related Posts
Rabbit Diet 101: What to Feed Your Rabbit
How to Care For Your Rabbit Through All Their Life Stages
Feeding Your Rabbit | VCA Animal Hospital
Rabbits are herbivores (plant eaters) and are considered grazers, in that they eat continuously. They have complex digestive systems and are very efficient at processing food. They also have very specific dietary needs. If you introduce new foods too quickly, or feed inappropriate food choices, the rabbit's normal digestive flora (normal bacteria) will be disturbed, gas- and toxin-producing bacteria can overgrow, and the rabbit may become very sick and possibly die.
What do rabbits eat?
Rabbits should have a daily diet of mostly hay, a smaller amount of fresh vegetables, and a limited number of pellets. Hay is the most important part of a rabbit's daily intake. Unlimited, high-quality grass hay, such as Timothy, orchard or brome, should make up the bulk of a rabbit's diet. Grass hay is high in fiber, which is critical to maintaining a rabbit’s healthy digestive tract. While young, growing rabbits can eat any type of grass hay, alfalfa hay is not recommended for adult rabbits, as it is too rich in protein and too high in calcium.
Timothy pellets can be offered at approximately 1/8-1/4 cup per 5 lbs (2.25 kg) of bodyweight. Over-feeding pellets to adult rabbits is a common cause of obesity and soft stool (caused by an overgrowth of abnormal bacteria in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract), as pellets are generally low in fiber and high in carbohydrates. In addition to hay, wild rabbits eat a lot of other fresh vegetation.
A pet rabbit's diet should be supplemented with a variety of leafy green vegetables every day. Rabbits can consume as many vegetables as they want to each day as long as they do not get diarrhea and as long as the vegetables are not high in carbohydrates, as carrots and potatoes are. Variety is important. Introduce new vegetables slowly and in small quantities, and monitor for soft feces, diarrhea, or signs of gas pain.
"Carrots should be fed sparingly, as they are very high in carbohydrate and may upset GI bacterial flora."
Particularly good vegetables include the dark leafy greens like romaine lettuce, bok choy, mustard greens, carrot tops, cilantro, watercress, basil, kohlrabi, beet greens, broccoli greens, and cilantro.
Some leafy greens, such as collard and dandelion greens, parsley, kale, Swiss chard, and escarole, should be fed in limited quantities, as they are high in calcium and may contribute to the development of calcium-based bladder stones if fed in excess. Other acceptable vegetables include broccoli, green peppers, Brussel sprouts, endive, wheat grass, radicchio, and squash. Iceberg or head lettuce should not be fed, as it is mainly water and contains few nutrients.
Other acceptable vegetables include broccoli, green peppers, Brussel sprouts, endive, wheat grass, radicchio, and squash. Iceberg or head lettuce should not be fed, as it is mainly water and contains few nutrients.
Carrots should be fed sparingly, as they are very high in carbohydrate and may upset GI bacterial flora. A small amount of many different vegetables is much better than a large amount of one food item.
Young rabbits, under approximately 7-8 months old, should be fed alfalfa pellets and alfalfa hay free-choice; they need the extra protein and calcium as they grow. They, too, can have a variety of vegetables. At approximately 7 months, they must be weaned onto an adult diet, as described above, since their growth slows down.
How often should I feed my rabbit?
Rabbits should be fed and provided with fresh water daily; hay should always be available. As nibblers, they should have food available at all times.
Do I need to give my rabbit vitamins?
No, rabbits do not require extra vitamins. They just need a varied, high-fiber diet.
Can I offer my rabbit treats?
Yes, but first be sure to check with your veterinarian about the types of treats that are recommended. Rabbits certainly can become overweight if fed an abundance of high-calorie treats. Cookies, nuts, seeds, grains, and bread should not be fed to rabbits.
"Cookies, nuts, seeds, grains, and bread should not be fed to rabbits."
Fruits can be fed in very limited quantities – no more than 1-2 tablespoons of high-fiber fresh fruit (such as apple, pear, or berries) every 1-2 days. The high sugar content in fruits (and even carrots) may upset the normal GI tract bacteria if given in excess.
What are the water requirements of rabbits?
Fresh water should be available 24 hours a day. Some rabbits prefer water bowls, and others prefer sipper bottles. If you offer water in a sipper bottle, be sure to inspect it for clogs and fill it with clean water daily. If you offer your rabbit water in a bowl, make sure the rabbit does not spill it in its cage or soil it with feces.
If you offer your rabbit water in a bowl, make sure the rabbit does not spill it in its cage or soil it with feces.
Is there anything else I should know?
Rabbits need to chew to maintain the health of their continuously growing teeth. Chew toys should always be available; hard wooden chew toys (blocks and sticks) and cardboard are best.
"Rabbits engage in coprophagy, which means they eat their own feces."
Rabbits engage in coprophagy, which means they eat their own feces. This occurs at night, and these fecal pellets are different from the ones normally excreted and seen by the owners. They are called cecotropes, cecal droppings, nocturnal droppings, or night droppings. They are usually small, soft or pasty, darker, and have a strong fermented or sweet smell. These pellets serve as a rich source of nutrients for the rabbit, specifically protein and vitamins B and K. Most owners never observe this behavior, as it happens in the early hours of the morning. If you do, remember that it is normal and necessary for the health of your rabbit.
How many times a day to feed the rabbits?
Do you breed rabbits and want them to grow up active and healthy? Then they should be properly fed.
Animals can eat a lot, often and approach the feeders 30 times a day, so you need to follow the feeding regimen. To provide pets with the necessary useful elements, add feed & life from the Ukrainian manufacturer Feed & Life to the menu.
Types of feed
Greens: legumes, vegetable tops (except tomato) and grass. To improve digestion, animals should be fed with wormwood, dill, chicory and yarrow. It is necessary to give rabbits plantain and nettle. nine0003
Succulent foods: beets, carrots, potatoes, marrows, pumpkins, cabbages, watermelons and apples.
Concentrated feed: grain (oats, wheat, corn), peas, beans, bran, meal, compound feed.
In summer and winter, the diet is different, but regardless of the season, food should be varied. Pets should be fed at the same time each day. Also, rabbits need to provide constant access to water.
Daily feed intake for rabbits
In order for rabbits to intensively gain weight and develop properly, they must be provided with a complex of useful substances. And for this, you should adhere to the diet and the daily norm of feeding.
The amount of feed that an animal must eat per day is formed depending on the season, sex and age of the individual. So, pregnant and lactating rabbits need more food than when they are at rest. The daily feed intake also increases in the winter months and during the growth of young animals. nine0003
If you feed rabbits with compound feed, then one individual per day is necessary:
- young animals - 50-250 g;
- rabbits in mating - 230 g;
- pregnant females (first period) - 230 g;
- pregnant females (after 10 days of pregnancy) - 180 g;
- lactating rabbits - 280-640 g.

With a mixed ration in the morning the animals are given half the daily allowance of compound feed, in the afternoon - hay or greens, and in the evening - the second half of the compound feed. nine0003
For the entire fattening period, one animal must eat 10 kg of compound feed (if it is young), 1.8-4.6 kg (female females) and 16 kg (lactating rabbits).
Qualitative indicators of TM "Feed&Life" compound feeds and feeding schemes can be seen in the tables in the "Products" section, in the "For rabbits" subsection.
How to feed rabbits?
Lactating rabbits and young rabbits up to 2.5 months of age should be fed 4 times a day, and young and adult rabbits - 2-3 times. nine0003
Feeding in summer
In summer the menu is based on herbs and succulent foods. Rabbits eat well the branches of trees such as birch, linden, pear, apple, maple, willow, acacia, etc. But beets should be given in small portions, as the product causes bloating.
Adult rabbits eat 600 g of grass per day, and rabbits - more than 150 g. Lactating rabbits can eat 2 times more than normal.
Feeding rates
| Rabbits | Greens and succulents (g/day) | Concentrates (g/day) |
| Fattening rabbits | 700 | 70 |
| Males in mating | 800 | nine0073 |
| Pregnant rabbits | 800-900 | 50-70 |
| Lactating rabbits | 1200 | 70 |
| Young growth 1-2 months | 300 | 20 |
| Young growth 3-4 months | 500 | 45 |
| Young growth 5-7 months | 600 | 55 |
| Resting rabbits | nine0073 30 |
Young animals 1-2 months old should also be given 0. 5 g of salt per day.
5 g of salt per day.
Available
PC 92-1. Grass meal grower, for rabbits 5-14 weeks
Winter feeding
In winter, rabbits are given dry grass, dried vegetables and fruits, roots and twigs. 50% of the diet is grain feed.
Feeding rates
| Rabbits | Dry grass and branches (g/day) | Root crops (g/day) | Concentrates (g/day) |
| Fattening rabbits | 150 | 500 | 80 nine0076 |
| Males in mating | 150 | 200 | 55 |
| Pregnant rabbits | 180-250 | 200-300 | 70-90 |
| Lactating rabbits | 200 | 400 | 90 |
| Young growth 1-2 months | 50 | 150 | 35 |
| Young growth 3-4 months | 100 nine0076 | 300 | 55 |
| Young growth 5-7 months | 200 | 400 | 90 |
| Resting rabbits | 150 | 150 nine0076 | 40 |
Available
PC 90-2.
 For lactating female rabbits
For lactating female rabbits Compound feed for rabbits
As a rule, in summer, greens and succulent feed are enough for animals to get enough vitamins and microelements. The rest of the time, as well as in cases where it is not possible to diversify the diet, mineral supplements should be added to the diet.
Rabbits need nutrients for rapid growth, strengthening immunity and energy. nine0003
Compound feeds produced by Feed&Life contain fiber, amino acids and a complex of vitamins and minerals. You can order the product in the online store or by phone, and see the rabbit feeding scheme on the website in the "Products" section.
Types of feed for rabbits
Balanced and easily digestible feed for rabbits TM "Feed&Life" consists exclusively of natural ingredients and provides complete nutrition of animals, supplying their body with nutrients. nine0003
The online store offers the following types of compound feed:
- PK 92-1 – grower for individuals 5-14 weeks old.
 Designed for fattening animals and can be fed up to slaughter. The product contains barley, grass flour, oats, wheat, meal, bran, chalk, salt, etc. The compound feed provides a rapid increase in mass and a good coat.
Designed for fattening animals and can be fed up to slaughter. The product contains barley, grass flour, oats, wheat, meal, bran, chalk, salt, etc. The compound feed provides a rapid increase in mass and a good coat. - PK 90-2 - for rabbits during lactation. This dietary feed helps to improve metabolism, increase milk production and increase the nutritional value of milk. The composition contains: barley, grass flour, wheat, oats, meal, bran and other substances. nine0037
- PK 90-1 - food for female rabbits. The product helps to maintain the weight of the rabbits, increase the number of litters and get viable and well developed young. Compound feed consists of barley, grass flour, oats, wheat, sunflower meal, bran and vitamin and mineral top dressing.
Rabbit pellets
Rabbit pellets are often used on farms. What does he represent? These are compressed granules, which consist of grain, hay, mineral and vitamin supplements. They are used as concentrated feed, especially often in winter. They perfectly replace usual grain and cake. nine0003
They perfectly replace usual grain and cake. nine0003
[content]
Granular rabbit food
Feeding rabbits with this food is very beneficial, especially since the composition of the food can be well regulated. Animals eat almost all the food, without any leftovers. Its composition is balanced, because the rabbits grow well and do not get sick. Granules are bought or made independently. Purchased food is quite expensive, so many rabbit breeders prefer to make it themselves. To do this, you need to have special equipment, a granulator or an extruder. If there are a lot of rabbits on the farm, the equipment quickly pays off. nine0003
Contents of the article:
- 1 How to calculate the amount of pellets
- 2 How to choose pellets
- 3 How to make your own pellets
How to calculate the amount of pellets
needs. If the granules include grass, then they can become the only food for rabbits out of mating, and for rabbits who do not bear and do not feed the young. With a content of hay in a granule in the amount of 40%, the nutritional value is 80-90 feed units. There are granules completely herbal, their nutritional value is lower, about 40 units.
With a content of hay in a granule in the amount of 40%, the nutritional value is 80-90 feed units. There are granules completely herbal, their nutritional value is lower, about 40 units.
Outside of mating rabbits need to eat about 180 grams of pelleted food. During the mating period, the portion is increased to 230 grams. A pregnant rabbit needs 170-180 grams of granular food, but be sure to add hay to the diet, about 70 grams. A lactating female in the first ten days after birth should receive 330 grams of granules and 110 grams of hay. From the eleventh to the twentieth day, the portion is increased to 440 and 190 grams respectively. From the twenty-first to the thirtieth day, the ratio of granules and hay should be 560/200, and from the thirtieth to forty-fifth - 700/230.
To calculate a year's supply, multiply the daily rate by the number of days. The mating period lasts approximately two weeks or fifteen days. For the rest of the days, food for the male is calculated in the amount of 180 grams per day. The rabbit's pregnancy is 150 days. The female feeds milk for about 200 days a year. Thirty head of young animals, which should theoretically appear next year, will eat approximately 420 kg of pellets. It is not worth buying a lot of feed for future use, they quickly deteriorate, which negatively affects the health of rabbits. nine0003
The rabbit's pregnancy is 150 days. The female feeds milk for about 200 days a year. Thirty head of young animals, which should theoretically appear next year, will eat approximately 420 kg of pellets. It is not worth buying a lot of feed for future use, they quickly deteriorate, which negatively affects the health of rabbits. nine0003
How to choose kibble
The composition of kibble should be as follows:
- Plant fibers - 20-25%
- Proteins - 13-15%
- Fats - up to 2%
corn, barley, legumes, alfalfa, meadow grass hay. Sunflower cake, vegetables, minerals (chalk, salt, bone meal, etc.) can also be added to the feed. Sometimes vitamins can be added to ready-made pelleted rabbit food, their amount should not exceed one percent. By the color of the granule, you can determine its composition. If it is light, yellow, gray or beige, then cereals predominate in the composition. Grass pellets have a bright green color. A richer and darker shade of green indicates that there are vegetables in the composition. nine0003
nine0003
The granules of the finished feed must be all the same color, so you can be sure of the stability of their composition. If there are different granules in the bag, it is more likely that they were made in separate batches and then mixed.
This food is considered to be of poor quality. According to their structure, the granules should be dense and not disintegrate in the hands. When transporting large batches, some of them still crumble and grains form in the bag, which rabbits eat with reluctance. The smaller the grains, the better the kibble. Also, the composition of the feed should not include dyes or growth stimulants. The exact vitamin composition should be indicated on the package. nine0003
How to make your own granulated food
It is more profitable to make your own granulated food, in addition, you can be absolutely sure of its composition. To do this, you need to have special equipment - an extruder or a granulator. The machine is powered by electricity. During processing, grain and hay are heated to ninety degrees and pressed. The output is sausages of different diameters (depending on the size of the nozzle) that are easily divided into granules. It also does not hurt to have a grain crusher on the farm and a special grinder for hay, since only crushed components can be loaded into the granulator. nine0003
During processing, grain and hay are heated to ninety degrees and pressed. The output is sausages of different diameters (depending on the size of the nozzle) that are easily divided into granules. It also does not hurt to have a grain crusher on the farm and a special grinder for hay, since only crushed components can be loaded into the granulator. nine0003
Food composition may vary. Suitable granulated alfalfa for rabbits, grain mixtures, mixers with the addition of cake and hay from meadow grasses. Fresh grass is not used as it contains too much water. For small rabbits, acidophilus is added to the feed. This component regulates digestion well and the mortality of young animals is minimized. Below are a few recipes for mixes for making pellets.
Grass mix
- Chopped hay or grass meal - 35%
- oats or barley grains - 25%
- Sunflower Circle - 20%
- corn grains or polka dots - 15%
- bran, 5%
Grain mixture:
- Yamen - about 30 - about 30 %
- Wheat grains - 20%
- Sunflower Cake - 10%
- corn - about 10%
- oats - approximately 15%
- GOOKS - 15%
A mixture with mineral and vitamin additives:
- 9
- Oat grains - approx.