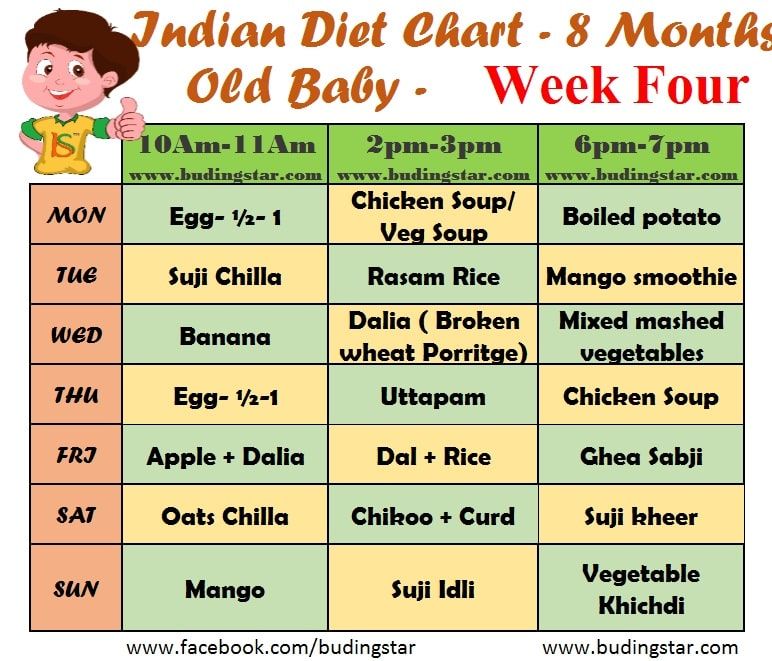
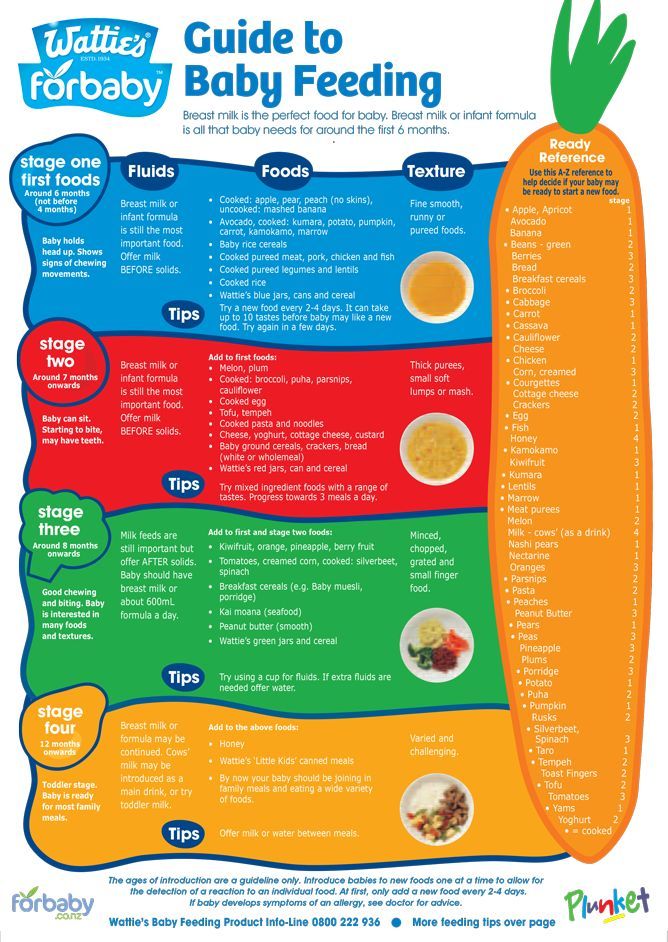
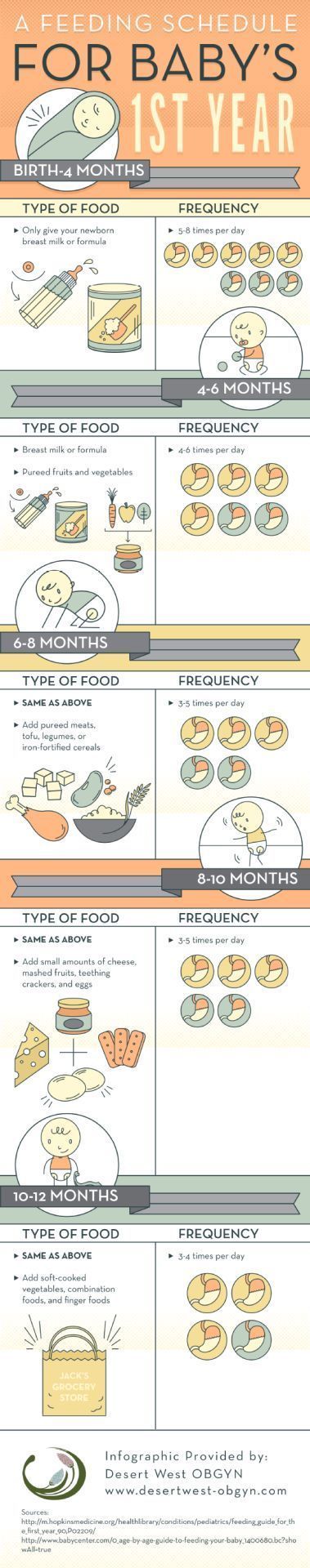
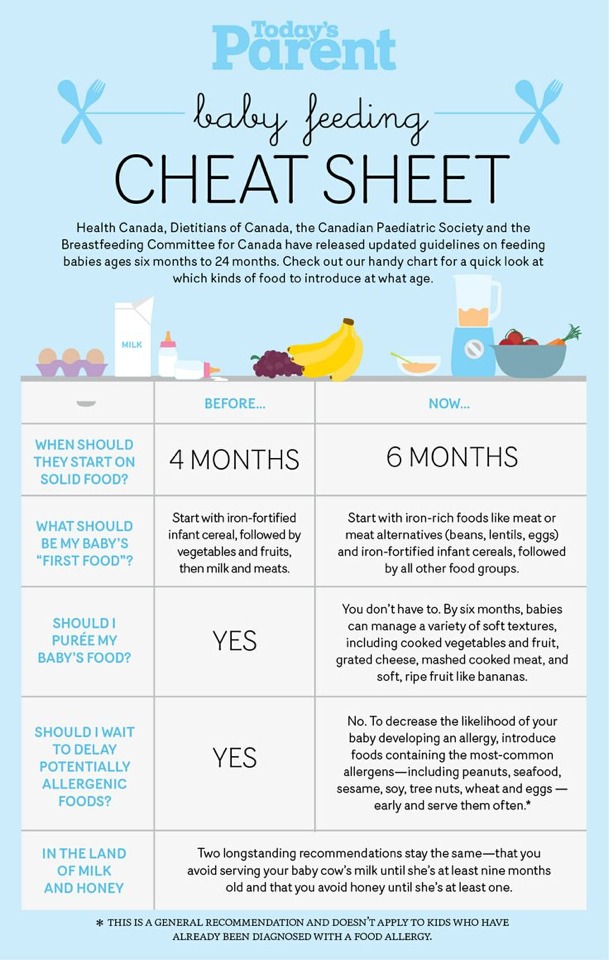
How often do you burp a baby when feeding
Burping Your Baby (for Parents)
Reviewed by: Madhu Desiraju, MD
Primary Care Pediatrics at Nemours Children's Health
en español Hacer eructar a su bebé
An important part of feeding a baby is burping. Burping helps to get rid of some of the air that babies tend to swallow during feeding. Not being burped often and swallowing too much air can make a baby spit up, or seem cranky or gassy.
How to Burp Your Baby
When burping your baby, repeated gentle patting on your baby's back should do the trick. Cup your hand while patting — this is gentler on the baby than a flat palm.
To prevent messy cleanups when your baby spits up or has a "wet burp," you might want to place a towel or bib under your baby's chin or on your shoulder.
Try different positions for burping that are comfortable for you and your baby. Many parents use one of these three methods:
- Sit upright and hold your baby against your chest. Your baby's chin should rest on your shoulder as you support the baby with one hand.
With the other hand, gently pat your baby's back. Sitting in a rocking chair and gently rocking with your baby while you do this may also help.
- Hold your baby sitting up, in your lap or across your knee. Support your baby's chest and head with one hand by cradling your baby's chin in the palm of your hand. Rest the heel of your hand on your baby's chest, but be careful to grip your baby's chin, not the throat. Use the other hand to pat your baby's back.
- Lay your baby on your lap on his or her belly. Support your baby's head and make sure it's higher than their chest. Gently pat your baby's back.
If your baby seems fussy while feeding, stop the session, burp your baby, and then begin feeding again. Try burping your baby every 2 to 3 ounces (60 to 90 milliliters) if you bottle-feed and each time you switch breasts if you breastfeed.
Try burping your baby every ounce during bottle-feeding or every 5 minutes during breastfeeding if your baby:
- tends to be gassy
- spits a lot
- has gastroesophageal reflux (GER)
- seems fussy during feeding
If your baby doesn't burp after a few minutes, change the baby's position and try burping for another few minutes before feeding again. Always burp your baby when feeding time is over.
Always burp your baby when feeding time is over.
To help prevent the milk from coming back up, keep your baby upright after feeding for 10 to 15 minutes, or longer if your baby spits up or has GERD. But don't worry if your baby spits sometimes. It's probably more unpleasant for you than it is for your baby.
Sometimes your baby may awaken because of gas. Picking your little one up to burp might put them back to sleep. As your baby gets older, don't worry if your child doesn't burp during or after every feeding. Usually, it means that your baby has learned to eat without swallowing too much air.
Babies with colic (3 or more hours a day of continued crying) might have gas from swallowing too much air during crying spells, which can make the baby even more uncomfortable. Check with your pediatrician before giving your baby anti-gas drops.
Reviewed by: Madhu Desiraju, MD
Date reviewed: June 2022
How and When to Burp Your Baby
A key part of your baby's feeding routine is burping him. Your baby may swallow lots of air while feeding, and burping can help remove some of that gassiness and ease his fussiness. It may also help prevent him from spitting up.
Your baby may swallow lots of air while feeding, and burping can help remove some of that gassiness and ease his fussiness. It may also help prevent him from spitting up.
Find out how to burp your baby, and pick up some tips on making burping more effective.
How to Burp Your Baby: Positions to Try
Here are three burping techniques that have stood the test of time. After trying each of them out, you’ll probably settle on one that works best for you and your baby:
Hold your baby upright against your chest with his chin on your shoulder, all the while supporting him with one hand as you gently pat his back with your other hand.
Place your baby on your lap with him sitting up, all the while supporting his head and chest with one hand while you softly pat his back with your other hand.
Lay your baby on your lap with his belly faced down, all the while supporting his head so it’s higher than his chest, and pat his back.

Tips for Burping Your Baby
Try these tips the next time you need to burp your baby:
Use repeated, gentle pats on her back.
Cup your hand slightly as you pat her, as this is gentler than using a flattened palm.
Drape a towel or bib over your lap or shoulder to protect your clothing as you burp your baby, in case your baby spits up (sometimes called “wet burps”).
Now that you know how to burp your baby, and these tips help you do so effectively, here’s a helpful visual guide:
How Long Should You Burp Your Baby?
There is no specific length of time needed for burping your baby. The more important factor is how often you burp him. With that in mind, burp your baby frequently throughout feeds, even when it looks like he doesn’t need to be burped.
Waiting until after a feeding to burp your baby may mean your little one has swallowed too much air and may be fussier, so it’s better to stop feeding every so often and try to burp your little one. You could also try paced bottle feeding, which slows the flow of breast milk or formula from the bottle, which could help prevent gas.
You could also try paced bottle feeding, which slows the flow of breast milk or formula from the bottle, which could help prevent gas.
Here are some tips for burping your baby during a feeding:
If you’re bottle feeding (which can include formula feeding or offering expressed breast milk), you’ll want to burp him after every two to three ounces of milk.
If you’re breastfeeding, burp your baby each time he switches breasts. Some breastfed babies may not need to burp as often, as they may not swallow as much air.
If your baby hasn’t burped after some time, go back to feeding. Not every baby burps every time you want him to burp.
If your baby shows any of the following signs, you may want to burp him more regularly — for example, after every ounce of milk during bottle feeding or every five minutes during breastfeeding:
He is gassy
He spits up frequently
He has Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
He seems very fussy.
After a feeding is over, keep your baby in an upright position for 10 to 15 minutes. This can help prevent him from spitting up. You may need to burp him longer if he does spit up or has been diagnosed with GERD.
Other Instances When Burping Your Baby Might Be Beneficial
If your sleeping baby wakes suddenly and you suspect it may be because of gas, burping her might help relieve the pressure and help her fall back asleep.
A colicky baby, who may cry for three or more hours per day, might have gas from all the air she’s swallowed during one of these crying spells. You may consider burping her to see if it helps comfort her.
We hope these tips can help you burp your baby during feeding time to ensure she’s more comfortable.
Don’t forget to stock up on plenty of diapers, which you will surely need after all these feedings and burpings. Get rewarded for your Pampers purchases by using the Pampers Club app to earn rewards like coupons, gifts, and gift cards.
Preventive measures against regurgitation in children
08.03.2017
Regurgitation is the spontaneous reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus and mouth. This condition is not uncommon in infants and is often a cause for concern for parents. The frequency of regurgitation syndrome in children of the first year of life is 18-50%: up to 4 months - 67%, up to 6 months 24%, up to 1 year 5%. In most cases, regurgitation is "benign" and disappears on its own after 12-18 months. At the same time, “benign” or physiological regurgitation characterizes:
-
the age of the child is up to 12 months;
-
spitting up 2 or more times a day for 3 or more weeks;
-
sufficient weight gain;
The child has no signs of metabolic disorders, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or the central nervous system. The child does not experience difficulty in swallowing or feeding, there is no forced position of the body.
Do not confuse regurgitation with vomiting. When a child burps, the abdominal muscles do not tense up. With vomiting, on the contrary, muscle tension occurs and food is ejected by pressure not only through the mouth, but also through the nose. In some cases, there may be general anxiety, pallor, cold extremities. Often with vomiting, the temperature rises, loose stools appear, which is a sign of an infectious disease. Vomit may contain unchanged milk, mucus, blood or bile.
What explains physiological regurgitation
What is the tendency of babies to spit up? This phenomenon is explained by the peculiarity of the structure of the gastrointestinal tract of young children. At the age of one year, the esophagus is shorter and wider, physiological narrowing is weakly expressed. The stomach is located horizontally, its capacity is small, and the muscles that close the entrance to the stomach and prevent the contents from being thrown back into the esophagus are poorly developed. As the child begins to walk, the axis of the stomach becomes more vertical. The capacity of the stomach increases by the year from 30-35 ml to 250-300 ml. The secretory apparatus matures, the work of the closing muscles (sphincters) improves, which leads to a gradual decrease in the frequency and disappearance of regurgitation. These features explain the predisposition of young children to regurgitation and even the inevitability of this condition. However, there are measures to help reduce the frequency of regurgitation.
As the child begins to walk, the axis of the stomach becomes more vertical. The capacity of the stomach increases by the year from 30-35 ml to 250-300 ml. The secretory apparatus matures, the work of the closing muscles (sphincters) improves, which leads to a gradual decrease in the frequency and disappearance of regurgitation. These features explain the predisposition of young children to regurgitation and even the inevitability of this condition. However, there are measures to help reduce the frequency of regurgitation.
Factors contributing to physiological regurgitation include:
-
Overfeeding. As a rule, actively sucking babies begin to suffer from overfeeding, with abundant milk secretion, as well as when switching to artificial or mixed feeding with an incorrect calculation of the required amount of milk formula. Regurgitation appears immediately or some time after feeding in the amount of 5-10 ml. Milk can flow out unchanged or curdled.
-
Swallowing air during feeding (aerophagia).
 A similar situation arises if the child suckles greedily at the breast, and the mother's milk is not very plentiful; due to the retracted, flat nipple of the mother's breast, since the child fails to fully capture the nipple and areola; with artificial feeding, if the hole at the nipple of the bottle is large enough or the nipple is not completely filled with milk. Babies with aerophagia often experience anxiety after feeding, bulging of the abdominal wall (belly inflates). After 10-15 minutes, the swallowed milk flows out unchanged, which is accompanied by a loud sound of air eructation.
A similar situation arises if the child suckles greedily at the breast, and the mother's milk is not very plentiful; due to the retracted, flat nipple of the mother's breast, since the child fails to fully capture the nipple and areola; with artificial feeding, if the hole at the nipple of the bottle is large enough or the nipple is not completely filled with milk. Babies with aerophagia often experience anxiety after feeding, bulging of the abdominal wall (belly inflates). After 10-15 minutes, the swallowed milk flows out unchanged, which is accompanied by a loud sound of air eructation. -
Intestinal colic or constipation. These conditions lead to an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity and a violation of the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract, causing regurgitation.
Until the child is four months old, spitting up up to two teaspoons of milk after feeding, or one spitting up of more than three spoons during the day, is considered the norm.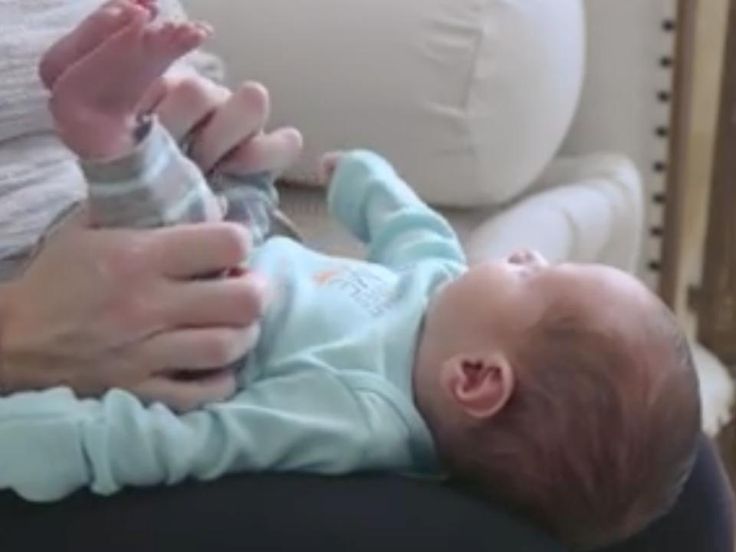 You can check the amount of spitting up in the following way: take a diaper, pour one teaspoon of water on its surface, and then compare this spot with the spot formed after the next spitting up.
You can check the amount of spitting up in the following way: take a diaper, pour one teaspoon of water on its surface, and then compare this spot with the spot formed after the next spitting up.
Pathological regurgitation may be due to:
-
surgical diseases and malformations of the digestive system;
-
diaphragmatic hernia;
-
pathology of the central nervous system, trauma of the cervical spine during childbirth;
-
food intolerance, lactase deficiency;
-
increased intracranial pressure.
Such regurgitation is characterized by intensity, systematicity, the child spits up a large amount of milk. At the same time, there is a violation of the general condition of the baby - the child is whiny, loses or does not gain weight, cannot eat the amount of food necessary for his age. In such a situation, a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, surgeon, allergist, neurologist should be examined. It also requires examination and exclusion of anomalies in the structure of the upper gastrointestinal tract, the preservation of regurgitation for more than 1 year.
It also requires examination and exclusion of anomalies in the structure of the upper gastrointestinal tract, the preservation of regurgitation for more than 1 year.
Scale for assessing the intensity of regurgitation:
-
Less than 5 regurgitations per day with a volume of not more than 3 ml - 1 point.
-
More than 5 regurgitations per day with a volume of more than 3 ml - 2 points.
-
More than 5 regurgitations per day up to half the amount of formula or breast milk, not more often than in half of the feedings - 3 points.
-
Spitting up a small amount of milk for 30 minutes or more after each feeding - 4 points.
-
Regurgitation from half to full volume of formula or breast milk in at least half of the feedings - 5 points.
Regurgitation with an intensity of 3 or more points requires a visit to a doctor.
Preventive measures against regurgitation in children
If regurgitation is physiological in nature, then it is not worth treating or correcting in this case. It is necessary to deal with the elimination of the cause, if possible, and carry out prevention.
It is necessary to deal with the elimination of the cause, if possible, and carry out prevention.
Prevention of regurgitation in children includes the following measures:
-
Postural therapy: when feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby at an angle of 45 °, make sure that he completely grasps the nipple with the areola; after feeding, hold the baby in an upright position ("column") for 20 minutes - to drain the swallowed air. Due to this, the air that has entered the stomach will be able to go out. If nothing happened, then put the baby down and after a minute or two, lift him upright again.
-
Make sure that the opening in the bottle is not too large and that the nipple is filled with milk. Experiment with nipples - perhaps the other will be better. Milk should come out in drops, not a trickle.
-
Before you start feeding your baby, lay him belly down on a solid base.
-
After feeding, try to minimize the baby's physical activity, do not disturb him unnecessarily, and change clothes only if there is an emergency.
-
Avoid squeezing diapers or clothes on the abdomen of the child.
-
If the baby's appetite is good, then it is better to feed him often, but in small portions, otherwise, due to the large amount of food, the stomach may overflow, and this, as a result, leads to regurgitation of excess food.
-
The surface in the bed on which the baby lies should rise 10 cm at the head.
-
In addition, it is possible to use special "thickeners" of milk or anti-reflux mixtures, which the doctor will help you choose.
In the event that regurgitation begins to become more frequent or becomes abundant, or first began after six months of the baby's life, or does not subside by one and a half to two years of life, the child should be consulted by a pediatrician. With a high probability, additional help from a gastroenterologist will be needed.
In our Family Medical Center you can always find highly professional help.
← Back to the list of articles
Why do newborns spit up? | Philips Avent
search support iconSearch Keywords
Home ›› Why is my baby spitting up and how can I help him?
Home ›› Why does my baby spit up and how can I help him?
↑ Top
Whether it's your first baby or your third, you're bound to have questions about feeding. Reflux (spitting up) is a common topic among frequently discussed feeding topics, so you are not alone in finding the answer to the question “Why does my baby spit up so often?”.
So why do babies spit up? And is spitting up normal for babies? You have probably thought about this many times. After reading this article, you will receive important information that will explain the causes of infant spitting up, and you will learn how to act to help the child.
If you have any questions or your child has other symptoms, be sure to contact your doctor.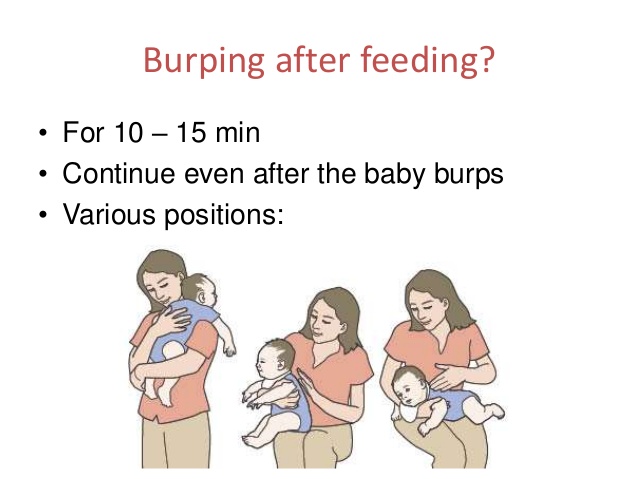
Why do babies spit up and when is it normal?
Let's look at why babies spit up and answer the frequently asked question "Why does my baby spit up so much?". Many newborns spit up after feedings or when burping because their digestive tract is not yet fully developed. However, in some situations, the likelihood of regurgitation in infants increases.
So what causes reflux in babies? The following are some of the main causes of regurgitation in infants:
So is spitting up normal in infants? In simple words: spitting up after some feeds, or even after each, is absolutely normal for a growing baby. However, there are points that need to be noted in order to distinguish ordinary regurgitation from vomiting.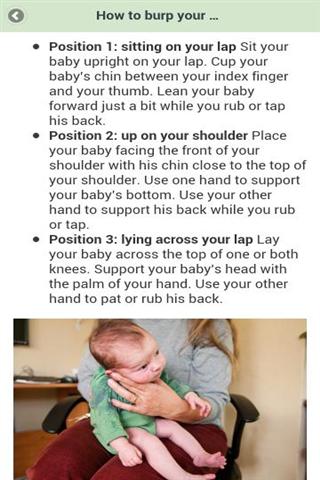 The two processes are very different, so you should check with your doctor if your baby is vomiting heavily after every or most feeds.
The two processes are very different, so you should check with your doctor if your baby is vomiting heavily after every or most feeds.
Also seek medical attention if your child has any of the following symptoms that a doctor can help identify: 2
- The child spit up frequently, does not gain enough height or weight.
- Appears to be in pain, cries a lot, or arches his back.
- Coughing or difficulty breathing, which may be a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Regurgitates even if he hasn't eaten anything.
- There is severe vomiting.
- Fever or diarrhea, which may be a sign of an intestinal infection and lead to dehydration.
If your baby spit up a small amount of milk after a feed and continues to grow and stay healthy, rest assured that this is normal and nothing to worry about. If you have any questions about reflux in infants, check out this article to learn about the symptoms of reflux and how to deal with it!
What to do
Now that you've learned that spitting up is normal and what causes it, you're probably wondering what you can do to help your baby. After you have consulted with your pediatrician and he has determined that spitting up is not a cause for concern, here are a few suggestions to help you when you are unsure: 1
After you have consulted with your pediatrician and he has determined that spitting up is not a cause for concern, here are a few suggestions to help you when you are unsure: 1
1. Regular belching of air.
In addition to burping after feedings, try helping your baby burp when changing breasts. And when feeding from a bottle, try to have the child spit up air every 30-60 ml of the mixture. Consider using an anti-colic bottle with an AirFree valve. The AirFree valve prevents air from entering the nipple even when the bottle is in a horizontal position and the nipple remains completely filled with milk. The use of such a bottle will allow your baby to drink in an upright position, which will reduce the frequency of reflux, improve the digestion process and make the feeding process more comfortable for both you and the baby. Find out more about Philips Avent anti-colic bottles with AirFree valve here.
3. Avoid vigorous movement after feeding.

To avoid spitting up after a feed, it is best to refrain from any bouncing, rocking or active play until the milk has been digested better.
4. Keep your baby's head up while feeding.
When you're trying to find the right feeding position that's comfortable for both your baby and you, try to avoid a position where your baby's head is down. In other words, it is necessary to ensure that in the process of feeding the head of the child is above the level of his legs.
5. Raise the mattress at the head of the bed
It is a good idea to roll up some towels or blankets and place them under the mattress (but not on top of the mattress) in the crib. Make sure that only the headboard is raised and that there are no creases in the middle of the mattress. There should be a very slight slope from which the baby will not slip.
It's a natural process
If you ever ask yourself the question "Why does my baby spit up?" just remember that spitting up is a completely natural, sometimes troublesome process that is part of parenthood. There are various reasons for spitting up in babies, but if your baby looks calm after a feed and is actively developing, you have nothing to worry about. In truth, spitting up is more of a problem for the parents than for the child himself, who may not even notice it.
There are various reasons for spitting up in babies, but if your baby looks calm after a feed and is actively developing, you have nothing to worry about. In truth, spitting up is more of a problem for the parents than for the child himself, who may not even notice it.
Philips Avent Articles & Tips
New Anti-colic Bottle with AirFree Valve
Designed to reduce colic, gas and spit up 1
that the baby is not getting enough milk, do not postpone the visit to the doctor. If the doctor confirms that the baby's spitting up is normal, all you have to do is keep a clean bib ready!
Baby+ app
Download the app and track your child's development and growth with trackers and save those special moments forever.
Download App:
1 kidshealth.org - Breastfeeding FAQs: Some Common Concerns Any links to third party websites that may be included on this site are provided solely as a convenience to you.