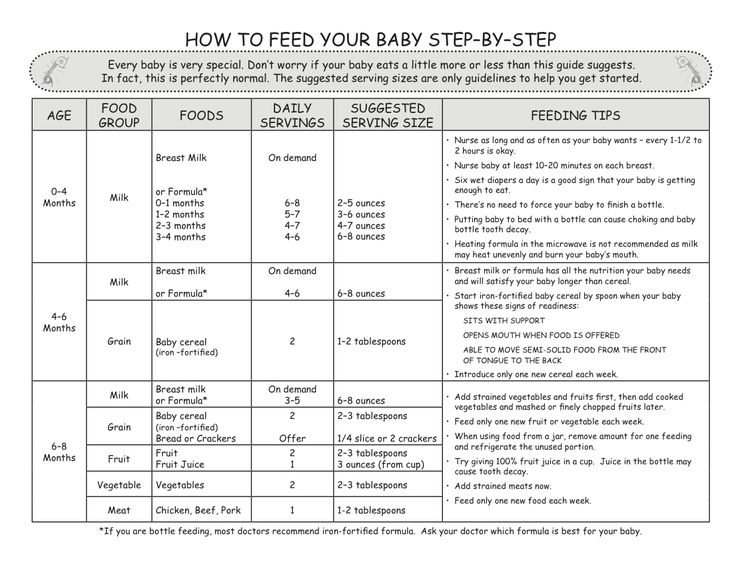
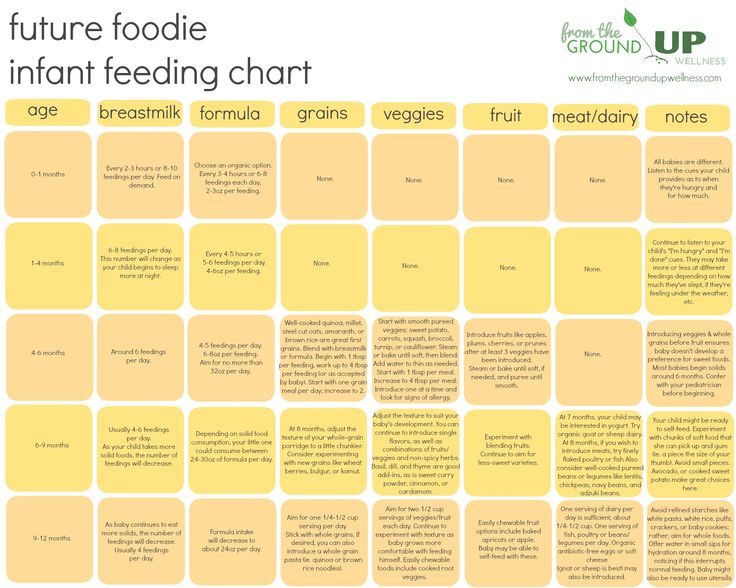
How often do you feed a six month old baby
Feeding your baby: 6–12 months
At 6 months of age, breastmilk continues to be a vital source of nutrition; but it’s not enough by itself. You need to now introduce your baby to solid food, in addition to breastmilk, to keep up with her growing needs.
Be sure you give your baby her first foods after she has breastfed, or between nursing sessions, so that your baby continues to breastfeed as much as possible.
When you start to feed your baby solid food, take extra care that she doesn’t become sick. As she crawls about and explores, germs can spread from her hands to her mouth. Protect your baby from getting sick by washing your and her hands with soap before preparing food and before every feeding.
Your baby's first foods
When your baby is 6 months old, she is just learning to chew. Her first foods need to be soft so they’re very easy to swallow, such as porridge or well mashed fruits and vegetables. Did you know that when porridge is too watery, it doesn't have as many nutrients? To make it more nutritious, cook it until it’s thick enough not to run off the spoon.
Feed your baby when you see her give signs that she's hungry – such as putting her hands to her mouth. After washing hands, start by giving your baby just two to three spoonfuls of soft food, twice a day. At this age, her stomach is small so she can only eat small amounts at each meal.
The taste of a new food may surprise your baby. Give her time to get used to these new foods and flavours. Be patient and don’t force your baby to eat. Watch for signs that she is full and stop feeding her then.
As your baby grows, her stomach also grows and she can eat more food with each meal.
Feeding your baby: 6–8 months old
From 6–8 months old, feed your baby half a cup of soft food two to three times a day. Your baby can eat anything except honey, which she shouldn't eat until she is a year old. You can start to add a healthy snack, like mashed fruit, between meals. As your baby gets increasing amounts of solid foods, she should continue to get the same amount of breastmilk.
Feeding your baby: 9–11 months old
From 9–11 months old, your baby can take half a cup of food three to four times a day, plus a healthy snack. Now you can start to chop up soft food into small pieces instead of mashing it. Your baby may even start to eat food herself with her fingers. Continue to breastfeed whenever your baby is hungry.
Each meal needs to be both easy for your baby to eat and packed with nutrition. Make every bite count.
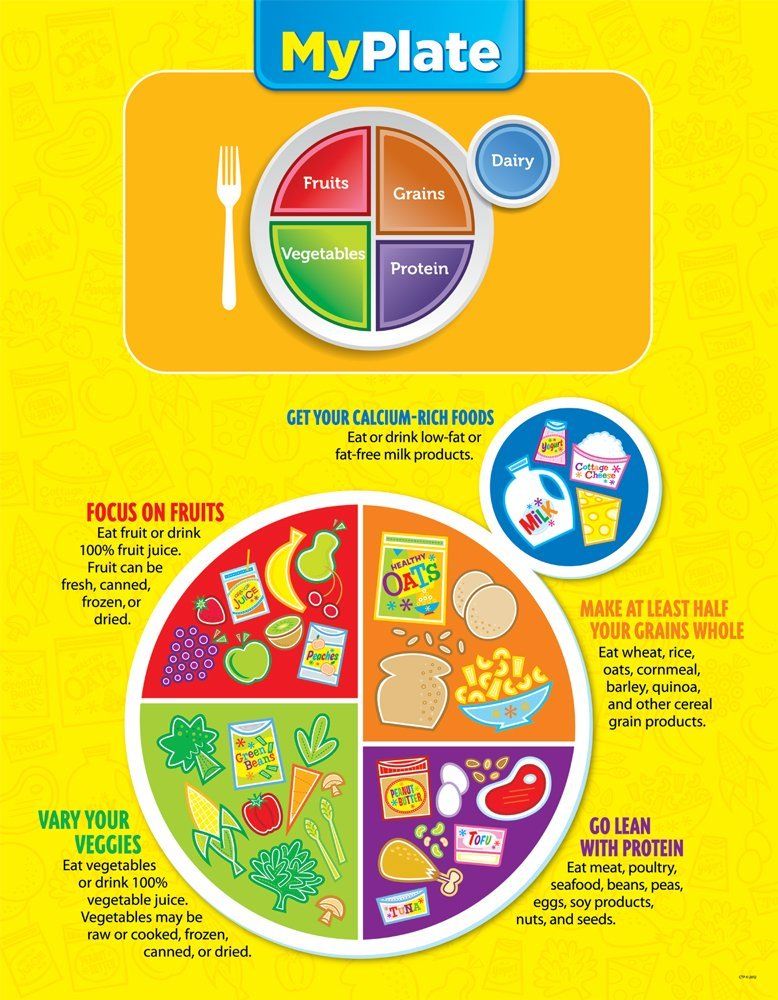
Foods need to be rich in energy and nutrients. In addition to grains and potatoes, be sure your baby has vegetables and fruits, legumes and seeds, a little energy-rich oil or fat, and – especially – animal foods (dairy, eggs, meat, fish and poultry) every day. Eating a variety of foods every day gives your baby the best chance of getting all the nutrients he needs.
If your baby refuses a new food or spits it out, don’t force it. Try again a few days later. You can also try mixing it with another food that your baby likes or squeezing a little breastmilk on top.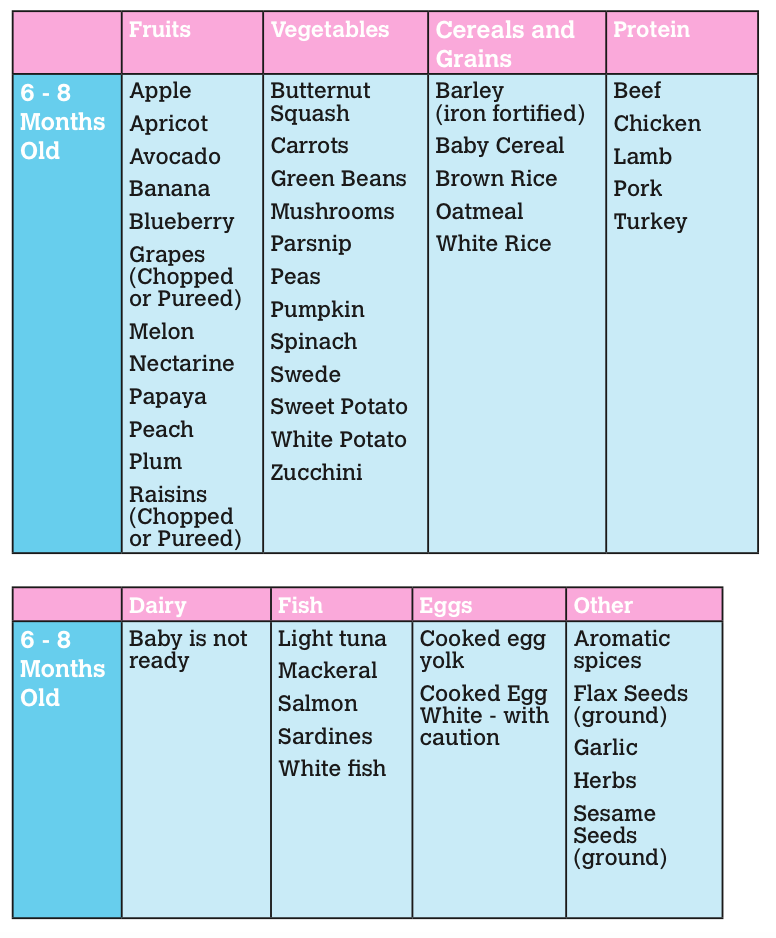
Feeding non-breastfed babies
If you're not breastfeeding your baby, she’ll need to eat more often. She'll also need to rely on other foods, including milk products, to get all the nutrition her body needs.
- Start to give your baby solid foods at 6 months of age, just as a breastfed baby would need. Begin with two to three spoonfuls of soft and mashed food four times a day, which will give her the nutrients she needs without breastmilk.
- From 6–8 months old, she’ll need half a cup of soft food four times a day, plus a healthy snack.
- From 9–11 months old, she’ll need half a cup of food four to five times a day, plus two healthy snacks.
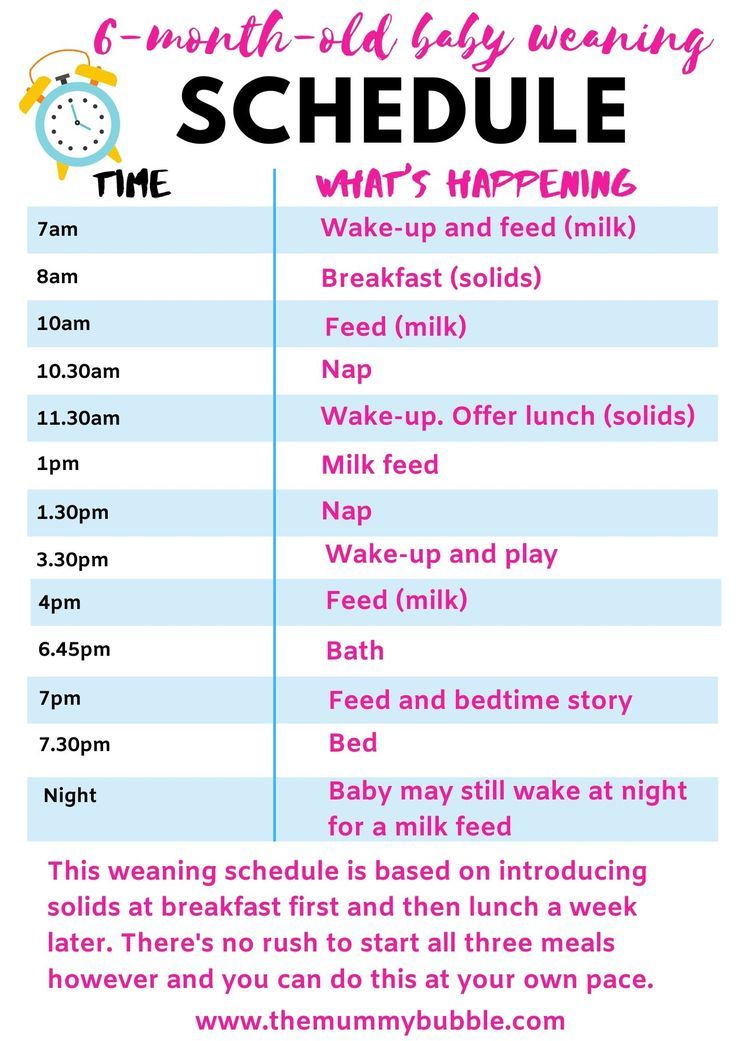
6-month-old feeding schedule: Timetable
A baby’s 6-month birthday marks an important transition as many infants are ready to start trying solids at this point.
While breast milk or formula should still form the core of a 6-month-old’s diet, some caregivers find that a child’s feeding schedule shifts as they begin eating purees and other solids.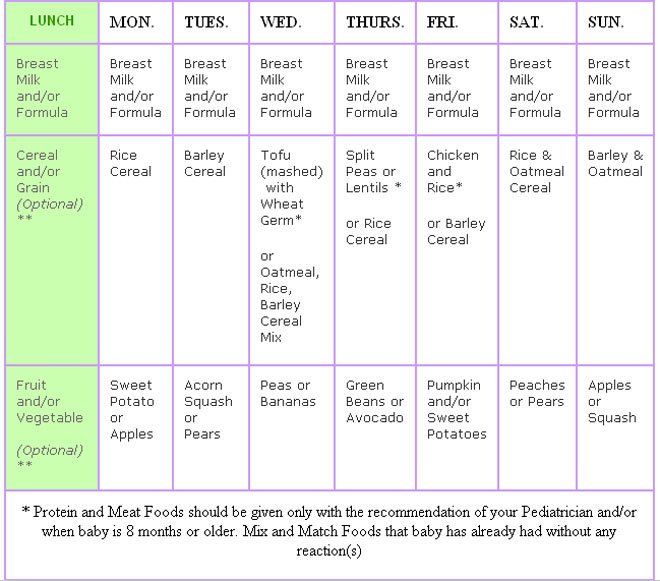
Babies typically need to eat every 2–3 hours, five to six times during the day.
It is normal for a baby’s schedule to change from day to day, or for babies to eat different amounts of food each day.
Caregivers can follow a baby’s cues, even if they have established a schedule already. A parent or caregiver does not need to deny food to a baby just because it has already eaten.
Introducing solids
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) advise that parents exclusively breastfeed infants for about 6 months if possible. By the time a baby hits their half birthday, they may be ready to try solids.
A baby may be ready for solids at 6 months if:
- they have good head control
- they can hold their head up for extended periods
- they can sit up with no or very little assistance
- they no longer have the tongue thrust reflect to push food out of the mouth with the tongue
- they show interest at mealtime and lean toward food if a caregiver offers it
At this age, breast milk or formula is still a baby’s most important form of nutrition and solids are an addition.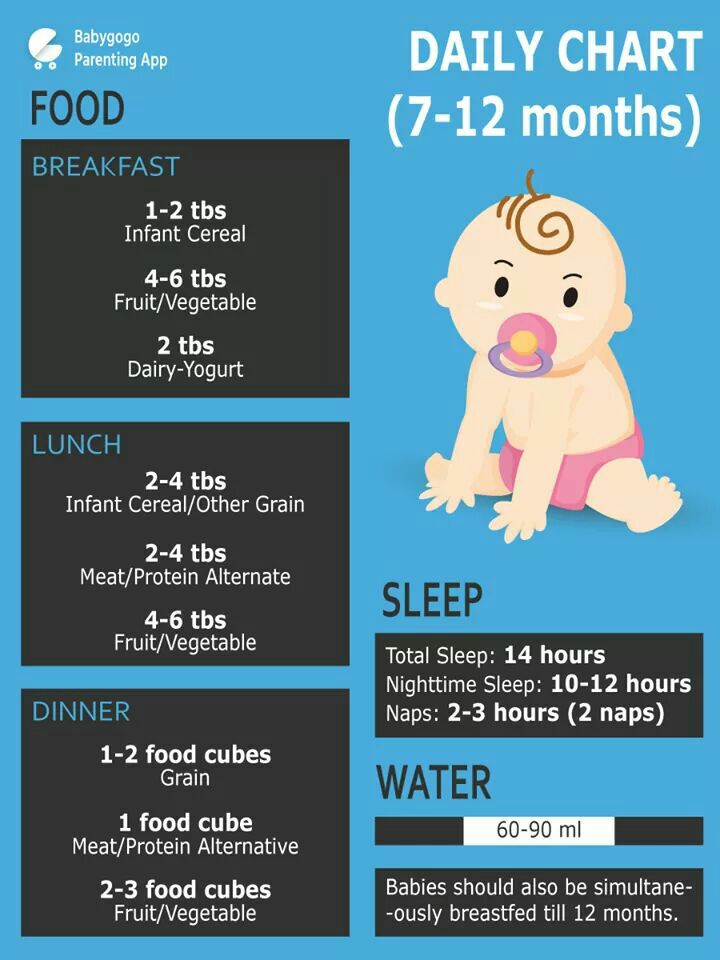
Not all 6-month-olds are ready for solids. If a baby shows no interest, a caregiver can wait a few weeks and try again.
Giving a baby 1–2 tablespoons of iron fortified cereal or fruit or vegetable purees per feeding can be a good place to start.
Gradually increasing this as the baby’s interest and appetite increase can follow.
To ensure a baby eats sufficient food, the adult can breastfeed or give a bottle before offering solids.
Caregivers can give solid food as a supplement each time they nurse the baby or give a bottle. Or, they can include the baby in family meals by giving solids at mealtime.
At 6 months of age, when an infant may begin to want solids, a caregiver can offer these just once per day.
Choosing a time of day when the caregiver is relaxed and not pressed for time, and the baby is not overly hungry, fussy, or tired often works best.
Once a baby is enjoying their once-a-day solids, the frequency can increase to two and then three times a day.
There is no “right” schedule, but caregivers should plan to increase the number of solids babies get gradually.
At 6 months, the goal is not to introduce new foods and eating habits. Similarly, there is no need to force a baby to eat solids or restrict new food if a baby indicates they want more.
Regardless of their size and eating habits, babies need access to an expanding variety of solid foods.
Most babies will need to try new foods several times before they feel comfortable eating them. It is fine to let a child eat at their own pace, in the way that feels right to them.
It is acceptable at this age for a baby to play with their food since this is a way of exploring new things.
Breast milk and formula
Breast milk or formula remains the most important food at 6 months of age. The easiest way to ensure a baby eats enough is to nurse or formula feed them on demand when they show signs of hunger.
Research supports the value of feeding on demand.
A longitudinal study of 10,419 children found better academic achievement and a four-point Intelligent Quotient (IQ) advantage at 8 years old among children whose caregivers fed them on demand.
However, the caregivers of these children got less sleep and had lower overall well-being.
These results may point to adults finding a happy medium, such as steadily shaping the baby’s preferred schedule into one that works for them.
In general, caregivers should plan to breastfeed babies 3 to 5 times per day, and sometimes more. However, babies vary greatly and every 3–4 hours is common, which can amount to up to eight times in 24 hours.
Some babies prefer cluster feedings, during which they nurse several times in a short period. Growing or sick babies may also nurse more frequently.
If a baby has formula, giving 24–32 ounces of iron fortified formula spread over five or six feeds per day is typical. While some babies sleep through the night at 6 months, others will still wake or want to feed.
A nighttime “dream feed” around the time caregivers retire for the evening may help babies sleep longer.
Other liquids
Babies do not need juice at 6 months. The extra calories can decrease a baby’s appetite, and the sugar may damage a child’s developing teeth. Soda and other drinks are not healthful for babies.
Babies can have water beginning at 6 months, or when caregivers introduce solids, whichever is later. Introducing a cup of water along with solid meals may be helpful.
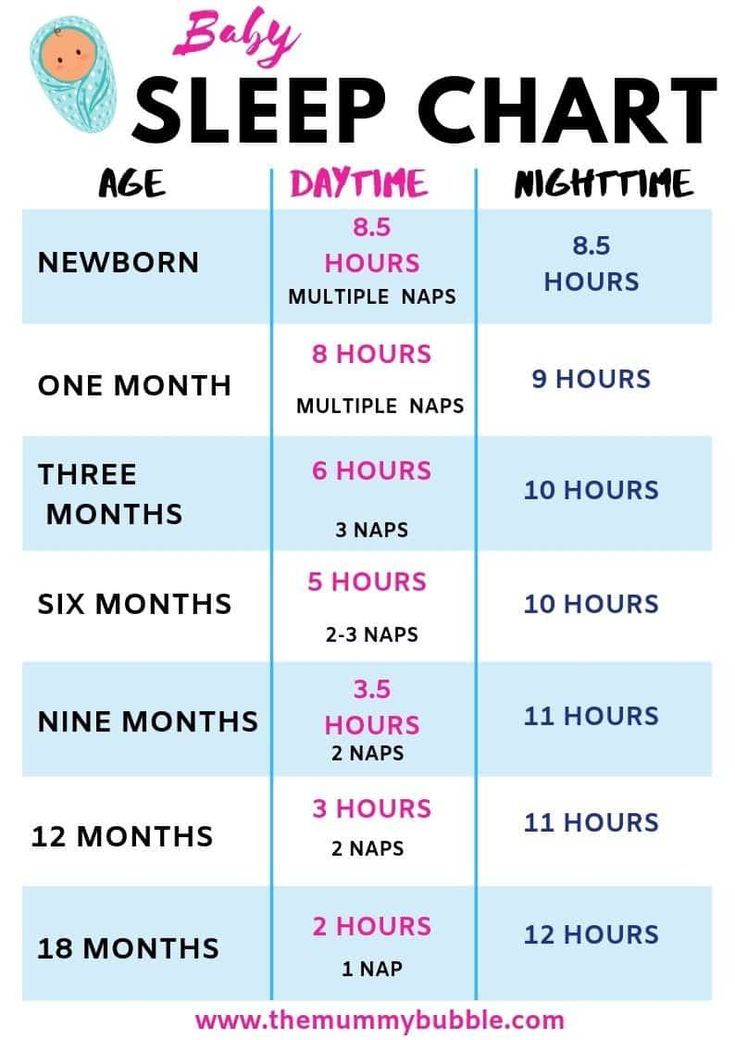
Around 6 months old, some babies begin transitioning from three or four daily naps to two. The baby might take a midmorning nap and a midafternoon nap. At this age, most babies need 12–15 hours of sleep per day, and naps usually last 1–3 hours.
Caregivers are best finding a schedule that works for them and the child. Some children are used to falling asleep by nursing or with a bottle. Others happily doze off on their own.
A caregiver can follow the baby’s cues and work to adapt their needs to the family’s schedule slowly.
These feeding tips may help:
- Babies may be hungrier after waking from a long nap. This can be a good time to try solids after offering formula or breast milk to ease their initial hunger.
- There is no evidence that adding cereal to a bottle helps babies sleep longer. Doing so can increase their risk of choking.
- Babies must never have food without close supervision. nor have solids, even very thin purees, in bed.
Deciding what, when, and how to feed a baby can be challenging, especially during the transition to solids. As long as babies get regular breast milk or formula, caregivers do not need to rush the transition to solids or worry that babies are not eating enough.
Some babies take longer than others to embrace solids, while some will eagerly eat anything. The right schedule is one that works for the baby and family. This schedule may change over time which is also fine.
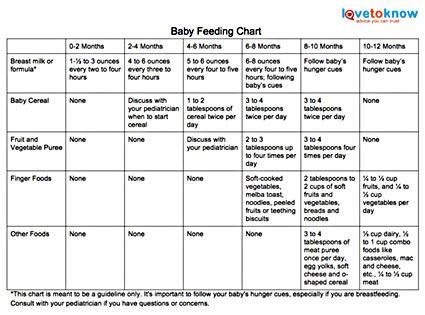
Diet for a 4-6 month old baby
Your baby is already 4 months old. He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
He has noticeably grown up, become more active, is interested in objects that fall into his field of vision, carefully examines and reaches for them. The emotional reactions of the child have become much richer: he joyfully smiles at all the people whom he often sees more and more often, makes various sounds.
You are still breastfeeding your baby or have had to switch to mixed or formula feeding. The child is actively growing, and only with breast milk or infant formula, he can no longer always get all the necessary nutrients. And that means it's time to think about complementary foods. nine0003
The optimal time to start its introduction is between 4 and 6 months, regardless of whether the baby is receiving breast milk or formula. This is the time when children respond best to new foods. Up to 4 months, the child is not yet ready to perceive and digest any other food. And with the late introduction of complementary foods - after 6 months, children already have significant deficiencies of individual nutrients and, first of all, micronutrients (minerals, vitamins, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, etc. ). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them. nine0003
). In addition, toddlers at this age often refuse new foods, they have delayed development of chewing skills for thick foods, and inadequate eating habits are formed. It is important to know that, no matter how strange it may seem at first glance, with a delayed appointment of complementary foods, allergic reactions more often occur on them. nine0003
When is it advisable to introduce complementary foods as early as 4 months, and when can you wait until 5.5 or even 6 months? To resolve this issue, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
As a rule, at an earlier age (4 - 4.5 months), complementary foods are introduced to children at risk of developing iron deficiency anemia, as well as children with insufficient weight gain and with functional digestive disorders.
The optimal time to start complementary foods for a healthy baby is between 5 and 5.5 months of age. nine0003
The World Health Organization recommends that breastfed babies should be introduced to complementary foods from 6 months of age. From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well. nine0003
From the point of view of domestic pediatricians, which is based on extensive practical experience and scientific research, this is possible only in cases where the child was born on time, without malnutrition (since in these cases the mineral reserves are very small), he is healthy, grows well and develops. In addition, the mother should also be healthy, eat well and use either specialized enriched foods for pregnant and lactating women, or vitamin and mineral complexes in courses. Such restrictions are associated with the depletion of iron stores even in a completely healthy child by 5-5.5 months of age and a significant increase in the risk of anemia in the absence of complementary foods rich or fortified with iron. There are other deficits as well. nine0003
The first complementary food can be vegetable puree or porridge, fruit puree is better to give the baby later - after tasty sweet fruits, children usually eat vegetable puree and cereals worse, often refuse them altogether.
Where is the best place to start? In cases where the child has a tendency to constipation or he puts on weight too quickly, preference should be given to vegetables. With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa. nine0003
With a high probability of developing anemia, unstable stools and small weight gains - from baby cereals enriched with micronutrients. And if you started introducing complementary foods with cereals, then the second product will be vegetables and vice versa. nine0003
If the first complementary food is introduced at 6 months, it must be baby porridge enriched with iron and other minerals and vitamins, the intake of which with breast milk is no longer enough.
Another important complementary food product is mashed meat. It contains iron, which is easily absorbed. And adding meat to vegetables improves the absorption of iron from them. It is advisable to introduce meat puree to a child at the age of 6 months. Only the daily use of children's enriched porridge and meat puree can satisfy the needs of babies in iron, zinc and other micronutrients. nine0003
But it is better to introduce juices later, when the child already receives the main complementary foods - vegetables, cereals, meat and fruits. After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
After all, complementary foods are needed so that the baby receives all the substances necessary for growth and development, and there are very few in their juices, including vitamins and minerals.
Juices should not be given between feedings, but after the child has eaten porridge or vegetables with meat puree, as well as for an afternoon snack. The habit of drinking juice between meals leads to frequent snacking in the future, a love of sweets is instilled, children have more tooth decay and an increased risk of obesity. nine0003
With the start of the introduction of complementary foods, the child is gradually transferred to a 5-time feeding regimen.
Rules for the introduction of complementary foods:
- preference should be given to baby products of industrial production, they are made from environmentally friendly raw materials, have a guaranteed composition and degree of grinding
- Complementary foods should be offered to the baby by spoon at the start of feeding, before breastfeeding (formula feeding)
- the volume of the product increases gradually, starting with ½ - 1 spoon, and in 7 - 10 days we bring it to the age norm, subsequent products within the same group (cereals from other cereals or new vegetables)
- can be entered faster, in 5 - 7 days
- start introduction with monocomponent products
- it is undesirable to give a new product in the afternoon, it is important to follow how the child reacts to it
- do not introduce new products in the event of acute illnesses, as well as before and immediately after prophylactic vaccination (should be abstained for several days)
When introducing a new type of complementary food, first try one product, gradually increasing its amount, and then gradually “dilute” this product with a new one.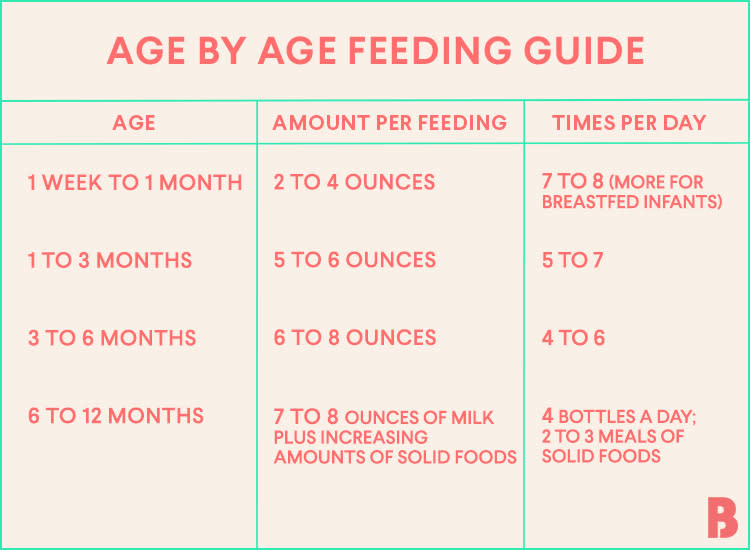 For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster. nine0003
For example, vegetable complementary foods can be started with a teaspoon of zucchini puree. During the week, give the baby only this product, gradually increasing its volume. After a week, add a teaspoon of mashed broccoli or cauliflower to the zucchini puree and continue to increase the total volume every day. Vegetable puree from three types of vegetables will be optimal. The portion should correspond to the age norm. Over time, you can replace the introduced vegetables with others faster. nine0003
After the introduction of one vegetable (bringing its volume to the required amount), you can proceed to the intake of porridge, and diversify the vegetable diet later.
If the child did not like the dish, for example, broccoli, do not give up and continue to offer this vegetable in a small amount - 1-2 spoons daily, you can not even once, but 2-3 times before meals, and after 7 - 10, and sometimes 15 days, the baby will get used to the new taste. This diversifies the diet, will help to form the right taste habits in the baby. nine0003
nine0003
Spoon-feeding should be done with patience and care. Forced feeding is unacceptable!
In the diet of healthy children, porridge is usually introduced after vegetables (with the exception of healthy breastfed children, when complementary foods are introduced from 6 months). It is better to start with dairy-free gluten-free cereals - buckwheat, corn, rice. At the same time, it is important to use porridge for baby food of industrial production, which contains a complex of vitamins and minerals. In addition, it is already ready for use, you just need to dilute it with breast milk or the mixture that the baby receives. nine0003
Children suffering from food allergies are introduced complementary foods at 5-5.5 months. The rules for the introduction of products are the same as for healthy children, in all cases it is introduced slowly and begins with hypoallergenic products. Be sure to take into account individual tolerance. The difference is only in the correction of the diet, taking into account the identified allergens.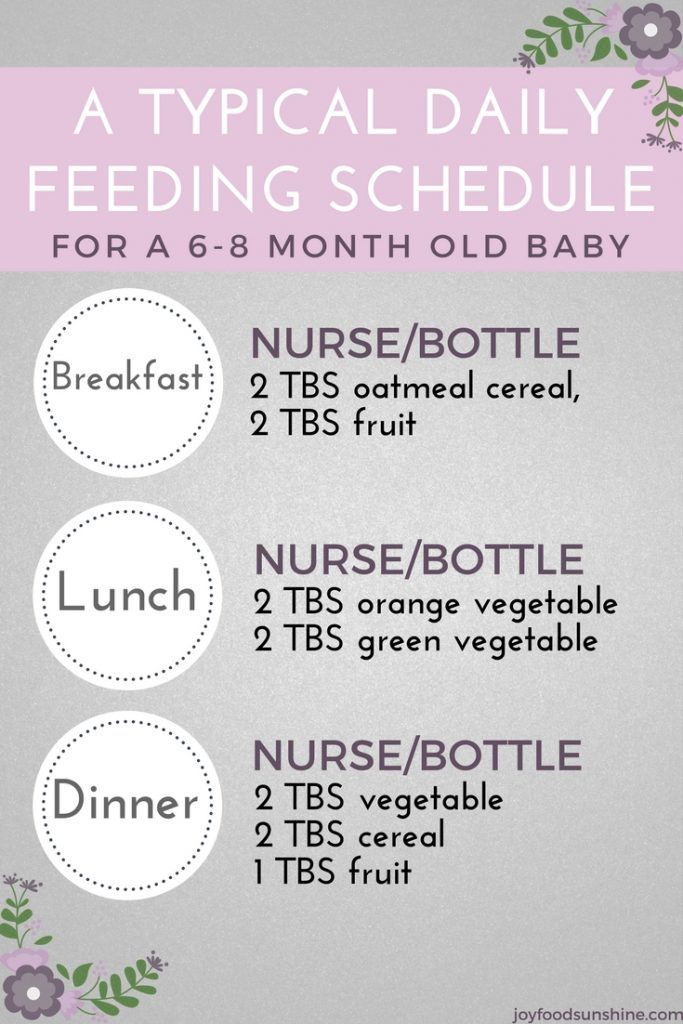 From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
From meat products, preference should first be given to mashed turkey and rabbit.
Diets for different age periods
Explain how you can make a diet, it is better to use a few examples that will help you navigate in compiling a menu specifically for your child.
From 5 months, the volume of one feeding is on average 200 ml.
Option 1.
If your baby started receiving complementary foods from 4-5 months, then at 6 months his diet should look like this:
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge** Supplementation with breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 50 ml |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree Meat puree Vegetable oil Supplemental breast milk or VHI* | 150 g 5 - 30 g 1 tsp 30 ml |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree Breast milk or VHI* | 60 g 140 ml |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or VHI* | 200 ml |
* - infant formula
** - diluted with breast milk or VHI
Option 2.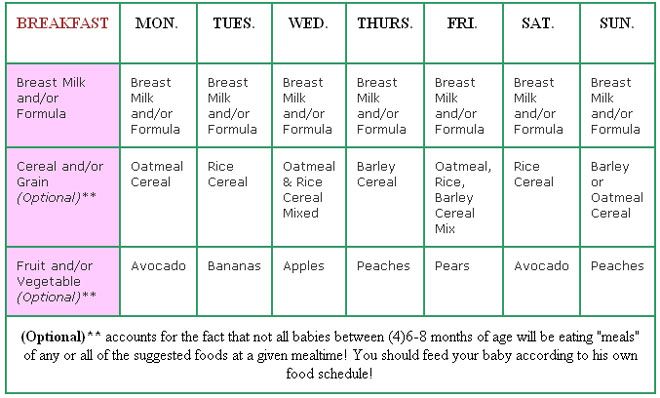
* - infant formula Option 3. : ** - diluted with breast milk Up to 7 months, increase the volume of porridge and vegetable puree to 150 g and introduce fruit puree. The materials were prepared by the staff of the Healthy and Sick Child Nutrition Laboratory of the National Research Center for Children's Health of the Ministry of Health of Russia and are based on the recommendations given in the National Program for Optimizing the Feeding of Children in the First Year of Life in the Russian Federation, approved at the XV Congress of Pediatricians of Russia (02.2009d.) Published: 02/10/2021 Reading time: 4 min. Number of reads: 197663 Author of the article: Ponomareva Yuliya Vladimirovna Pediatrician, candidate of medical sciences, allergist-immunologist Changes in a child in the first year of life are very rapid, and each month is not like another. The 6-month milestone is very important, it is largely evaluative and transitional. Content: Hide 22 If the baby is healthy and breastfed, and his mother eats a full and varied diet, exclusive breastfeeding is possible until this age. Cereal complementary foods in this case are preferable to start. However, the rate of expansion of the child's diet in this situation will be accelerated. Before the 8th month of life, it is necessary to introduce all basic food groups into the baby’s menu, since in the second half of the year the need for additional intake of nutrients and micronutrients is very high. Another reason explaining the importance of the rapid introduction of complementary foods is the formation of immunity of the immune cells of the intestine to ordinary food. If a child is introduced to these foods at the age of 4-8 months, the risk of developing food allergies has been proven to be reduced. nine0003 In modern life, the nutrition of a nursing mother, unfortunately, is not always complete. Therefore, for most breastfed babies, complementary foods already need to be introduced from 5 months in order to prevent deficient conditions. If a child is bottle-fed, then by the 4th month of life, the baby will not have enough adapted formula alone, and in this group of children, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods usually shifts a month earlier than in breast-fed babies. Accordingly, by 6 months, children will have vegetable puree and gluten-free porridge (buckwheat, corn and rice) in their diet. In the first half of life, monocomponent meals are used (that is, from one type of grain and vegetables), prepared on the basis of water, breast milk or an adapted mixture. nine0003 Fruit puree and juice can be another possible complementary food for children under 6 months of age without allergy symptoms. In a child with a risk of developing or manifesting allergies, the timing of the introduction of fruit complementary foods is shifted to the 8th month. Children over 6 months of age can supplement their diet with cereals containing gluten. From the age of 6 months, the baby's diet is expanded with such important products as meat and cottage cheese. These products are a source of high-quality protein, fats, and are also rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and phosphorus. Pediatricians and nutritionists recommend introducing meat and cottage cheese as part of combined dishes based on a fruit and vegetable and / or grain component in a ratio of 1 (cottage cheese / meat): 4–5 (fruits / vegetables / cereals). To enrich the diet with polyunsaturated fatty acids in the second half of the year, the menu includes vegetable oil in the amount of 3–5 grams per day, which can be added to the complementary food dish. I feeding
6 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Fruit puree 150 g
20 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Fruit juice 150 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp
60 ml IV feeding
18 hours Fruit puree
Breast milk or VHI* 40 g
140 ml V feeding
22 hours Breast milk or VHI* 200 ml
** - diluted with breast milk or VMS 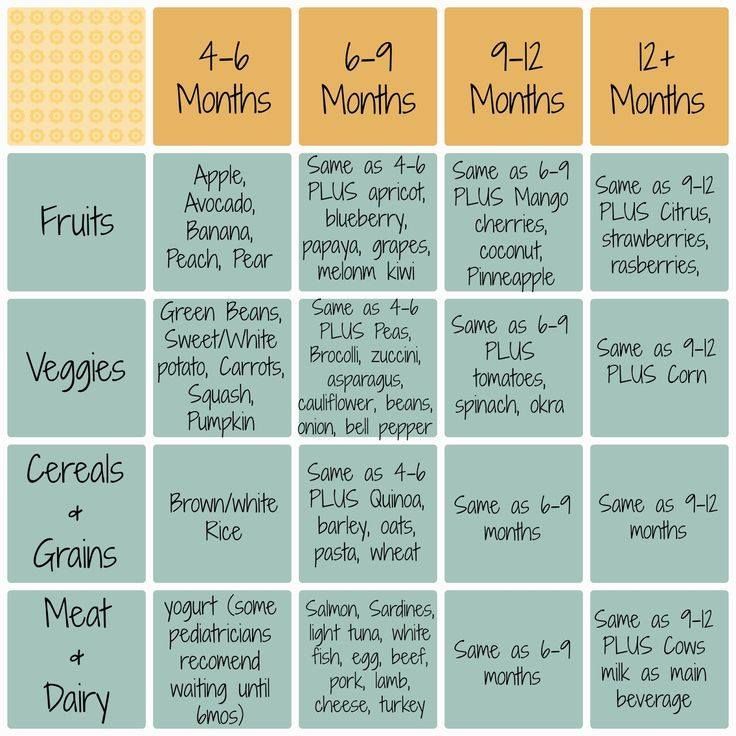
I feeding
6 hours Breast milk II feeding
10 hours Dairy-free porridge**
Breast milk supplement 100 g III feeding
14 hours Vegetable puree
Meat puree Vegetable oil
Breast milk supplement 100 g
5 - 30 g
1 tsp IV feeding
18 hours Breast milk V feeding nine0079 Breast milk
22 hours 
diet for a 6-month-old baby with breast and artificial feeding, sample menu for a week in the table, diet for a day
 By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different. nine0003
By this age, most babies have doubled their birth weight, are about 15 cm tall, and some babies have already erupted their teeth. The age of 6 months is also transitional in terms of nutrition. Breast milk or an adapted formula is still the basis of the diet, but with the beginning of the second half of life, all children, without exception, should begin to receive complementary foods. Despite the general graph of growth and weight gain and indicators of psychomotor development, the status and diet of children at 6 months can be very different. nine0003
The first feeding of 6 months
 This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods. nine0003
This is due to the high energy and nutritional value of cereals, the ability to significantly enrich the baby's diet with a delayed start of the introduction of complementary foods. nine0003
Complementary feeding starts at 4-5 months
Second six months of life
 First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life. nine0003
First of all, these are oatmeal and wheat porridge, and then multi-cereal dishes with the addition of other cereals (millet, barley, rye). If the child does not have any manifestations of allergies, milk porridge can be included in the menu at this age. Bebi Premium industrial baby food products include specially prepared milk that is safe to use in healthy babies in the first year of life. nine0003