How often should i feed my 1 month old baby formula
Formula Feeding FAQs: How Much and How Often (for Parents)
Whether you plan to formula feed your baby from the start, want to supplement your breast milk with formula, or are switching from breast milk to formula, you probably have questions.
Here are answers to some common questions about formula feeding.
How Often Should I Feed My Baby?
Newborns and young babies should be fed whenever they seem hungry. This is called on-demand feeding.
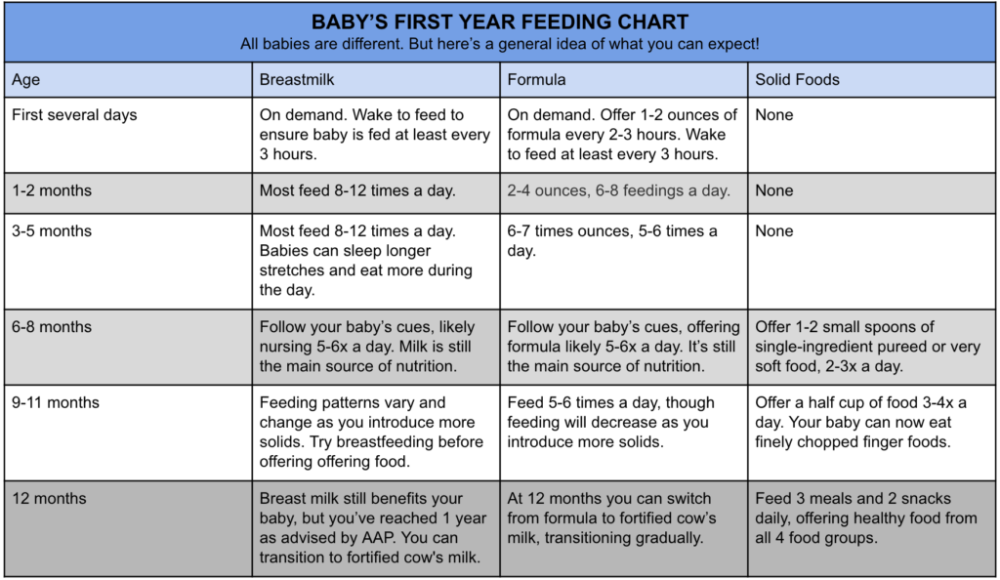
After the first few days of life, most healthy formula-fed newborns feed about every 2–3 hours. As they get bigger and their tummies can hold more milk, they usually eat about every 3–4 hours. As babies get older, they’ll settle into a more predictable feeding routine and go longer stretches at night without needing a bottle.
Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about feeding your baby, especially if your baby is very small, is not gaining weight, or was born early (prematurely).
How Can I Tell When My Baby Is Hungry?
Signs that babies are hungry include:
- moving their heads from side to side
- opening their mouths
- sticking out their tongues
- placing their hands, fingers, and fists to their mouths
- puckering their lips as if to suck
- nuzzling again their mothers' breasts
- showing the rooting reflex (when a baby moves its mouth in the direction of something that's stroking or touching its cheek)
Babies should be fed before they get upset and cry. Crying is a late sign of hunger. But every time your baby cries is not because of hunger. Sometimes babies just need to be cuddled or changed. Or they could be sick, tired, too hot or too cold, in pain, or have colic.
How Much Should My Baby Drink?
In the first few weeks, give 2- to 3-ounce (60- to 90-milliliter) bottles to your newborn. Give more or less depending on your baby’s hunger cues.
Here's a general look at how much your baby may be eating at different ages:
- On average, a newborn drinks about 1.5–3 ounces (45–90 milliliters) every 2–3 hours. This amount increases as your baby grows and can take more at each feeding.
- At about 2 months, your baby may drink about 4–5 ounces (120–150 milliliters) every 3–4 hours.
- At 4 months, your baby may drink about 4–6 ounces (120-180 milliliters) at each feeding, depending on how often they eat.
- By 6 months, your baby may drink 6–8 ounces (180–230 milliliters) about 4–5 times a day.

Watch for signs that your baby is hungry or full. Respond to these cues and let your baby stop when full. A baby who is full may suck with less enthusiasm, stop, or turn away from the bottle.
Why Does My Baby Seem Hungrier Than Usual?
As babies grow, they begin to eat more at each feeding and can go longer between feedings. Still, there may be times when your little one seems hungrier than usual.
Your baby may be going through a period of rapid growth (called a growth spurt). These can happen at any time, but in the early months are common at around:
- 7–14 days old
- between 3–6 weeks
- 4 months
- 6 months
During these times and whenever your baby seems especially hungry, follow their hunger cues and continue to feed on demand, increasing the amount of formula you give as needed.
Is My Baby Eating Enough?
At times, you may wonder whether your baby is getting enough nutrients for healthy growth and development. Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
Babies who get enough to eat seem satisfied after eating and are regularly peeing and pooping.
At your baby’s checkups, the doctor will review your baby’s growth chart, track your little one’s development, and answer any questions. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your baby’s feeding and nutrition.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Feeding Your 1- to 3-Month-Old (for Parents)
During your baby's first 3 months, breast milk or formula will provide all the nutrition needed. Doctors recommend waiting until your baby is about 6 months old to start solid foods. Some babies may be ready for solids sooner than 6 months, but wait until your baby is at least 4 months old.
What Changes Should I Expect?
As your infant grows, feeding will change. Babies will start drinking more milk during each feeding, so they won't need to feed as often and will sleep longer at night.
Your baby's appetite will increase during growth spurts. Continue to feed on demand and increase the number of feedings as needed.
Continue to feed on demand and increase the number of feedings as needed.
Your infant also will become more alert as the weeks go by, cooing and smiling. So there will be more interaction between you and your baby during feedings.
The following are general guidelines, and your baby may be hungrier more or less often than this. That's why it's important to pay attention to your baby's signals of being hungry or full. A baby who is getting enough might slow down, stop, or turn away from the breast or bottle.
Breastfeeding: How Much and How Often?
As babies get older, they will start to breastfeed less often and sleep for longer periods at night. Your infant probably is eating enough if he or she:
- seems alert, content, and active
- is steadily gaining weight and growing
- feeds six to eight times per day
- is wetting and soiling diapers on a regular basis
Babies might not be eating enough if they:
- don't appear satisfied
- cry constantly
- are irritable, even after feeding
- are not making wet diapers
Call your doctor if you're concerned your baby isn't eating enough.
A few weeks after birth, breastfed babies tend to have fewer bowel movements (BMs, or poop) than they did before. At around 2 months of age, your baby may not poop after each feeding, or even every day. During growth spurts, you may notice that your little one wants to feed more often. This frequent nursing sends a signal to make more milk. Within a couple of days, supply and demand will get into balance.
Babies who get breast milk only should get vitamin D supplements within the first few days of life. Other supplements, water, juice, and solid foods aren't usually needed.
Formula Feeding: How Much and How Often?
Babies digest formula more slowly than breast milk, so if you're bottle-feeding, your baby may have fewer feedings than a breastfed infant.
As babies grow, they can eat more at each feeding and may go for longer stretches between feedings. You'll also notice that your baby is starting to sleep longer at night.
During the second month, infants may take about 4 or 5 ounces at each feeding. By the end of 3 months, your baby may need an additional ounce at each feeding.
By the end of 3 months, your baby may need an additional ounce at each feeding.
It's easy to overfeed a baby when using a bottle because it easier to drink from a bottle than from a breast. Make sure that the hole on the bottle's nipple is the right size. The liquid should drip slowly from the hole and not pour out. Also, resist the urge to finish the bottle when your baby shows signs of being full.
Never prop a bottle. Propping a bottle might cause choking and it increases the chances of getting ear infections and tooth decay.
Should I Worry About Spitting Up?
It's normal for infants to "spit up" after eating or during burping. Spitting up a small amount — usually less than 1 ounce (30 ml) — shouldn't be a concern as long as it happens within an hour of feeding and doesn't bother your baby.
You can reduce spitting up in these early months by:
- feeding before your baby gets very hungry
- keeping your baby in a semi-upright position during the feeding and for an hour after
- burping your baby regularly
- avoiding overfeeding
- not jostling or playing vigorously with your baby right after a feeding
If your baby seems to be spitting up large amounts, is spitting up forcefully, is irritable during or after feedings, or seems to be losing weight or is not gaining weight as expected, call your doctor. And if your child has a fever or shows any signs of dehydration (such as not wetting diapers), call the doctor right away.
And if your child has a fever or shows any signs of dehydration (such as not wetting diapers), call the doctor right away.
Call your doctor if you have any questions or concerns about feeding your infant.
Reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD
Date reviewed: November 2021
Feeding baby formula
All parents dream that their child grows and develops correctly and harmoniously. However, the formation of a child's body largely depends on balanced nutrition that the baby receives from the first days of life.
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
Of course, the best food for a baby is mother's milk, because it gives the child a lot of useful and necessary substances for growth and development. The quality of a child's nutrition in early childhood largely determines the state of his health in adulthood. In addition, nutrition is important in the development of the child's central nervous system and affects his intelligence and abilities.
In addition, nutrition is important in the development of the child's central nervous system and affects his intelligence and abilities.
If the child is artificially fed, it is all the more important to consciously approach the issue of his nutrition, carefully choosing the right mixture. Carefully monitor the feeding regime and introduce complementary foods in a timely manner. It is in the power of parents to provide the baby with health for many years.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
It is important to follow a few rules, always remembering that when choosing a diet, consultation with a doctor is required!
1. Give preference only to adapted mixtures, since in their composition they are as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
2. Take into account the individual characteristics of the body and the state of health of the baby.
3. Take into account the age of the child and select mixtures of the appropriate stage - initial and subsequent. To make it easier for parents to navigate, the formulas are labeled with numbers: 1 (0–6 months), 2 (6–12 months), 3 (from 12 months). The initial (starter) mixture is indicated by the number 1 and is intended for children in the first six months of life. Subsequent formulas have the numbers 2 and 3 on the packaging. They are intended for older babies from 6 months. It is important to remember that in mixtures for each stage, the composition formula changes, taking into account the age-related characteristics of development and the needs of children.
To make it easier for parents to navigate, the formulas are labeled with numbers: 1 (0–6 months), 2 (6–12 months), 3 (from 12 months). The initial (starter) mixture is indicated by the number 1 and is intended for children in the first six months of life. Subsequent formulas have the numbers 2 and 3 on the packaging. They are intended for older babies from 6 months. It is important to remember that in mixtures for each stage, the composition formula changes, taking into account the age-related characteristics of development and the needs of children.
4. Observe the dosage in accordance with the instructions on the packaging. Deviation from these norms can adversely affect the well-being and health of the child. If you take too much dry matter, the mixture will come out with an increased content of nutrients, which can lead to more frequent regurgitation, unstable stools and excessive stress on the kidneys and intestines. If you take the powder less than the specified norm, then the mixture will turn out to be low-calorie and insufficiently nutritious - the baby will remain hungry.
5. Use specially prepared water to dilute the mixture. Only clean and boiled water should be used.
With artificial feeding, it is impossible to abruptly transfer the baby to a qualitatively new food and without the need to change the mixture. It is very important to properly control the amount of feeding. For each age, the daily volume is calculated, which is divided by the number of doses. This is done so that the actual volumes eaten by the baby do not exceed the calculated recommended norms. To calculate the amount of feeding for the baby yourself, you should rely on the following data.
- For a child in the first days of life, the volume of feedings (day and night) per day should be 1/5 of the child's body weight. Approximately 600-900
- In the first 2 months, the volume of feeding per day should not exceed 1/5-1/6 of the child's body weight. For example, if a child weighs 4 kilograms, then he should eat no more than 800 g of the mixture per day.

- For a 2-4 month old baby, the daily formula is 1/6 of body weight (800-1000 g)
- For a 4-6 month old baby, the maximum daily amount of formula should be 1/7 of body weight (900-1000 g).
- After six months and up to 9 months, the baby should eat within the daily volume of the mixture not exceeding 1/8 of his body weight (1000-1100 g).
- At the age of 9–12 months, the daily volume of milk formula is already 1/9 of the child's body weight (1100–1200 g).
To calculate the volume of each feeding, it is necessary to divide the calculated daily volume of milk formula by the optimal number of feedings. With artificial feeding of children in the first months of life, as a rule, 6-7 meals a day are recommended after 3 or 3.5 hours with a 6.5 or 6-hour break.
0-2 months - 7-10 feedings per day
2-4 months - 6-7 feedings per day
4-6 months - 5-6 feedings per day
6-12 months - 4-5 feedings per day
If a child has at least some deviations in development, a lag in weight gain, then you should definitely consult with a pediatrician to draw up a baby nutrition plan!
Most doctors and infant nutritionists agree that “free” (on demand) feeding is optimal for a baby. To meet the needs of the child, it is important for parents to listen to the child. However, when a child is bottle-fed, you should pay attention to some nuances. Already in the first days of life, babies show their individual character - one eats in moderation, the other can overeat. Therefore, when feeding with milk formulas, it is recommended to stick to the golden mean and choose a partially limited "free mode", when there are no restrictions on the time and frequency of feeding, but the volume of the mixture eaten is controlled.
To meet the needs of the child, it is important for parents to listen to the child. However, when a child is bottle-fed, you should pay attention to some nuances. Already in the first days of life, babies show their individual character - one eats in moderation, the other can overeat. Therefore, when feeding with milk formulas, it is recommended to stick to the golden mean and choose a partially limited "free mode", when there are no restrictions on the time and frequency of feeding, but the volume of the mixture eaten is controlled.
From the first days of the transition to artificial feeding, it is important to carefully monitor the reactions of the baby and record them. The best option is to keep a child's food diary, where you need to write down all the nuances associated with feeding: time, amount of food, baby's reactions after feeding. If necessary, such a diary will help you and your baby's pediatrician adjust the schedule and volume of feedings, as well as understand the possible causes of problems with nutrition and growth.
After a year, the time comes to transfer the child to a diet that is closest to what is eaten in the family. And then the question arises of when to give up formula milk. If up to a year a child is breastfed or artificially fed and does not particularly need regular milk, then after a year it becomes an important source of nutrients: calcium, phosphorus, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But even the best cow's milk in its original form is not suitable for feeding young children. Why?
It's all about the large amount of casein - a protein that is difficult to digest and thereby increases the load on the child's digestive systems, which do not produce enough hydrochloric acid and enzymes to digest casein.
The ideal option for children from one year old is special baby milk or a milk drink that will provide the child's body with all the necessary nutrients, helping to occur a natural transition and adaptation to the next, adult, stage of nutrition. Valio specialists have developed a special baby milk Valio Baby 3, which can be used with mixed and artificial feeding. It is ideal for children from one year old, who become more mobile and active every day. You can also learn more about the correct complementary foods menu in our blog.
Valio specialists have developed a special baby milk Valio Baby 3, which can be used with mixed and artificial feeding. It is ideal for children from one year old, who become more mobile and active every day. You can also learn more about the correct complementary foods menu in our blog.
5 1
FoodShare:
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
Formula-fed regime - Articles about baby food from pediatricians and MAMAKO experts
— Polina Aleksandrovna could fully grow and develop. How significant is the difference between breast milk and its substitute?
— Mom's milk is a living substance that, in addition to nutrients, microelements and other useful components, contains biologically active substances responsible for immunity and components that cannot be synthesized. An adapted milk formula is as close to the composition of human milk as possible, but it is not a 100% substitute. Therefore, breastfeeding is preferable. However, if it is not possible to breastfeed, this is not a disaster. The most valuable nutrients a child can get from infant formula.
An adapted milk formula is as close to the composition of human milk as possible, but it is not a 100% substitute. Therefore, breastfeeding is preferable. However, if it is not possible to breastfeed, this is not a disaster. The most valuable nutrients a child can get from infant formula.
— What could be the reasons for transferring a child to artificial feeding?
— The most common reason why pediatricians recommend artificial feeding is because of the health of the child. In addition, artificial feeding can help a mother who is unable to feed her child on her own, for example, in cases where:
- lactation is difficult;
- there are contraindications for women's health;
- child and mother are not together;
- the nursing mother has obvious psychological discomfort.
— What products can be used for artificial feeding?
- Adapted infant formula or special therapeutic formulas, which may be dairy or, more rarely, dairy-free. You do not need to feed the baby with other products: whole cow's or whole goat's milk is not adapted for a small child. When the time comes for complementary foods, formula-fed babies, as well as breastfed babies, will gradually begin to try solid food in the same mode.
You do not need to feed the baby with other products: whole cow's or whole goat's milk is not adapted for a small child. When the time comes for complementary foods, formula-fed babies, as well as breastfed babies, will gradually begin to try solid food in the same mode.
— How common are colic, bloating, bottle-feeding disorders?
- When compared with breastfeeding, there is no particular prerequisite for colic, bloating or other disorders to occur more often from bottle feeding. In "artificial" stools become a little denser, which does not mean constipation. Changes in its consistency are caused by a certain composition of the milk substitute. This is completely normal. And colic, bloating and other problems may arise due to intolerance to some components of the mixture. A specialized therapeutic mixture will help to solve a specific problem and save the baby from these unpleasant sensations.
— Is it necessary to follow the feeding schedule for artificial feeding of a baby, or is it better to feed a child when he wants to?
- Formula-fed baby must be given a bottle on schedule, free feeding is not allowed. Surely many have heard that a newborn and a young child needs to be fed on demand, but on artificial feeding, the intervals between feedings should be at least 3 hours, even for a very small child.
Surely many have heard that a newborn and a young child needs to be fed on demand, but on artificial feeding, the intervals between feedings should be at least 3 hours, even for a very small child.
— Do I need to consult a specialist and take tests before formulating a formula diet?
— Before switching to an artificial formula, most often a mother consults with a pediatrician. The feeding mode (not the amount of food) is standard and does not depend on any features. Breaks equal to three hours should be stably maintained by the baby at one month and at six months. Skipping night feedings is possible, and breaks longer than three hours are acceptable, but still not less.
— What should be taken into account before drawing up a regimen?
— The most important thing is that the feeding regimen and the child's sleep and wakefulness regimens overlap with each other. When a mother builds a day regimen for artificial feeding, it is worth paying attention to what time she plans to put the baby to bed and wake her up so that feeding does not have to be in the middle of daytime sleep. Both mother and baby should be as comfortable as possible - so that they do not have to wake the baby for a meal or so that he does not wake up early from hunger.
Both mother and baby should be as comfortable as possible - so that they do not have to wake the baby for a meal or so that he does not wake up early from hunger.
— What are the key and general rules for establishing a feeding schedule for a formula-fed baby?
- Feeding regimen with artificial feeding should overlap with the sleep regimen. It is important to separate the nutrition and sleep of the baby. With artificial nutrition, this is easier to do than with natural. However, formula-fed infants often form a negative association with sleep when a bottle of nutrition is needed to fall asleep or eat immediately after waking up. Therefore, between feeding and sleep should be a small period of time - 10-15 minutes before and after sleep. With a newborn, it is usually not possible to reach this gap, because the wakefulness of the child is too short and only accommodates feeding. This is normal, but you need to strive to ensure that breaks appear and increase. Then by the end of the first month, most likely, everything will work out.
— How to distribute meals throughout the day? Can parents calculate the number of feedings and portion sizes themselves?
— Composing the feeding regime and calculating the amount of food, you need to focus on the age and weight of the child. Based on these indicators, the pediatrician determines the daily volume of the baby's food. Taking into account children's age, the daily amount of food is distributed over a certain number of feedings - the younger the baby, the more often he eats and the smaller his portion.
Over time, the intervals between meals increase due to the skipping of night feedings. The portion that the child missed is distributed between daily feedings. Consequently, the portion increases, and the frequency of feeding decreases.
How often to give the baby a mixture per day, including how many times to feed the baby at night on the IV, is calculated by the doctor for each specific baby, taking into account his age and weight parameters.
Read also
- about what determines the amount of formula a baby eats and how to calculate how much formula a baby needs
— Polina Aleksandrovna, the schedule has been drawn up, but the child eats little or rarely — should I be worried?
— If the weight gain is within normal limits, then the baby is getting enough nutrition. It happens that children eat less than the norm, but at the same time they fulfill their needs, do not lag behind in physical and psycho-emotional development, which means that for these children the norm is less than average.
The child eats little or rarely, the weight is added poorly - it must be shown to the doctor.
— Is it worth it to force a baby to live according to the regimen at night if he does not wake up and does not ask for food, but has not eaten the daily allowance?
— You need to watch how the child is gaining weight and growing, and monitor his condition, because situations are different.
- The baby eats normally, maintains the usual intervals and just starts to skip night feedings - it means that he has enough food during the day and it is not worth waking him up.
- The baby sleeps soundly until the morning, and during the day he gets off the routine and starts asking for food more often - therefore, he is malnourished, and you need to increase the size of the daily portion in order to maintain the daily norm, or wake the child up to feed at night. The first option is preferable, but, of course, within the age norm. It is most physiological when children eat less and less at night, and by one year they either sleep until morning or wake up once.
- Can children's health problems arise if the artificial feeding regimen has changed?
- You may run into problems if the diet has shifted very much. But you need to consider the reason for what is happening. When a sick child's appetite decreases, this is an adequate response to poor health, and it is not necessary to force-feed him.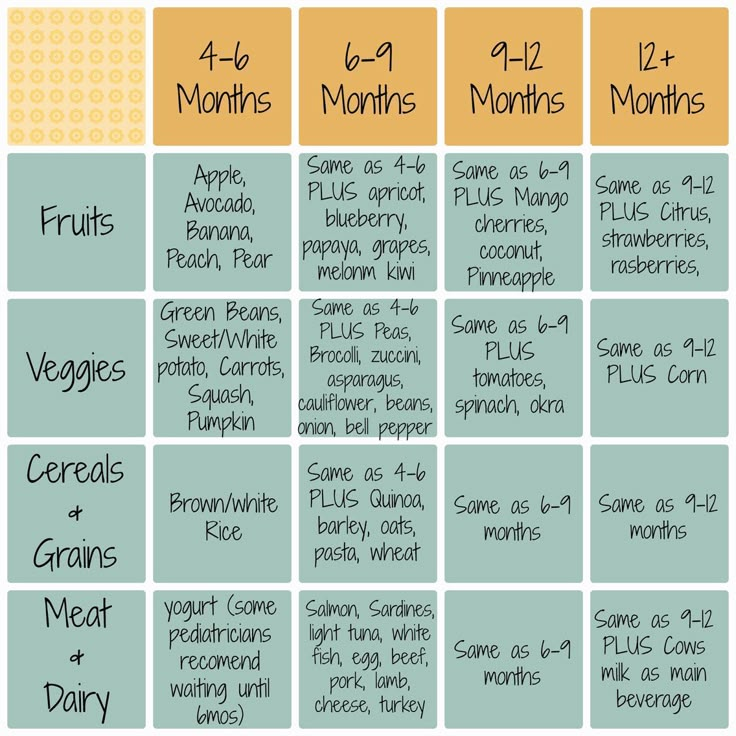 After recovery, he will try to compensate for the lack of food in the previous days and begin to eat more actively.
After recovery, he will try to compensate for the lack of food in the previous days and begin to eat more actively.
With the new regime, for example, due to the change in time zones, it may be difficult for the child to adapt, but this does not mean at all that he will be worried for a whole month. After one or two days, the regime returns to normal. And, of course, without the need to change the mode is impractical.
— Polina Aleksandrovna, tell us about the main advantages of MAMAKO ® baby food.
- The manufacturer has a fairly wide range of products. Parents can choose food according to the age and needs of their baby. With age-adapted milk formulas, it is easy to maintain an artificial feeding regimen from birth to three years. Porridges, mashed potatoes and cream soups are optimal for complementary foods. What is especially valuable, all these products are made on the basis of goat's milk, which children digest more easily and better than cow's milk and which is considered more suitable for children's nutrition. A child who initially tried the "goat" formula, and then switched to complementary foods with the addition of goat's milk, will have an easier time accepting them.
A child who initially tried the "goat" formula, and then switched to complementary foods with the addition of goat's milk, will have an easier time accepting them.
The composition of the milk formula is maximally adapted to children's needs, but still it is not saturated with absolutely all the components and biologically active substances that are found in women's breast milk. Technology does not yet allow this. Accordingly, breastfeeding is preferable for babies, but when it is not possible, ready-made products come to the rescue. When feeding with infant formula, it is recommended to adhere to a diet so that the baby does not overeat, easily digests and digests food comfortably. If the order of feeding has gone astray, try to return the usual diet for the child as soon as possible, and then everything will be fine.
* Breast milk is the best food for babies. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of a child's life and continued breastfeeding after complementary foods are introduced until the age of 2 years.